Dynamic Adaptive Display System for Electrowetting Displays Based on Alternating Current and Direct Current
Abstract
:1. Introduction
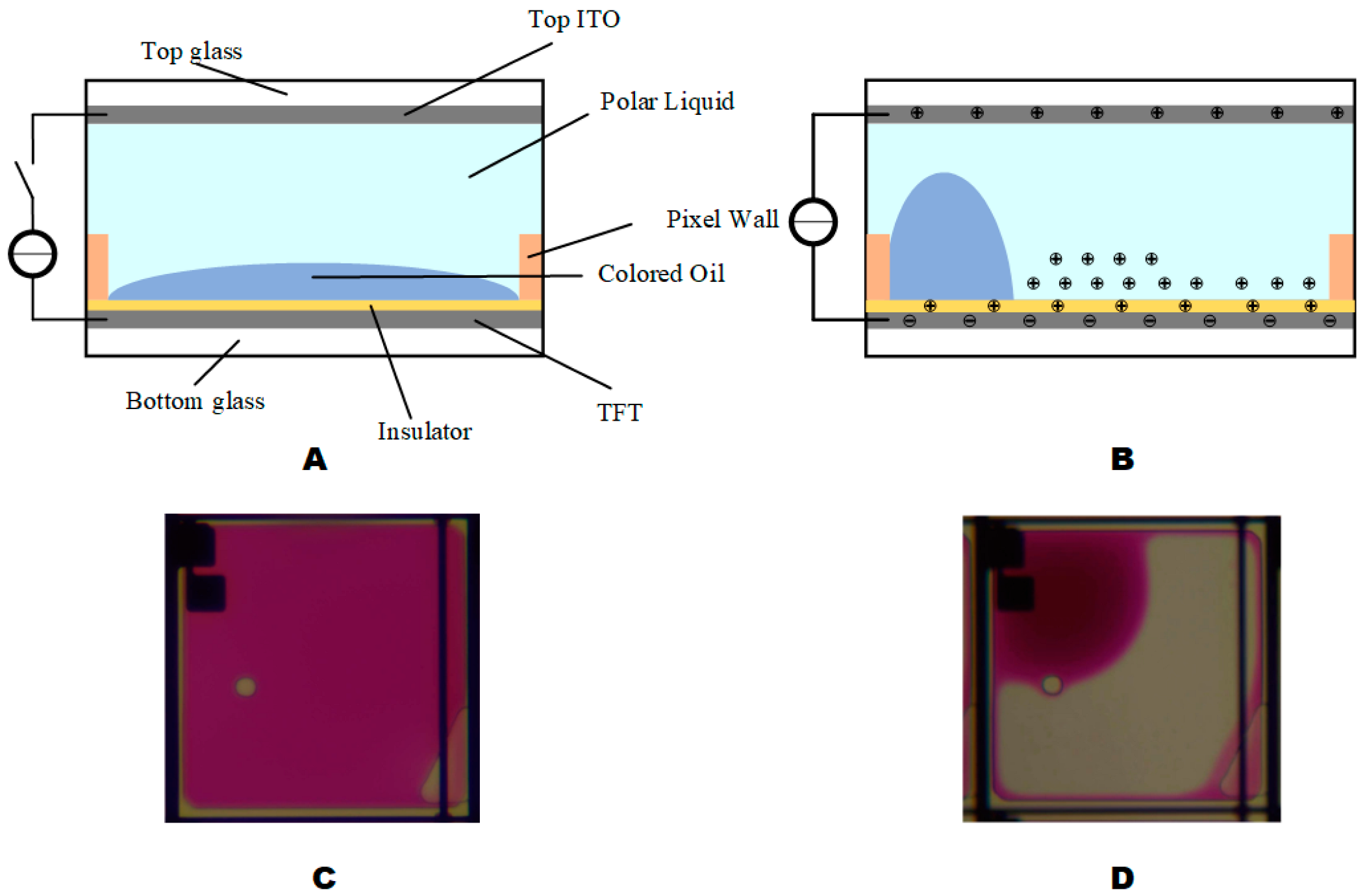
2. Principle of EWDs
3. Dynamic Adaptive Display System
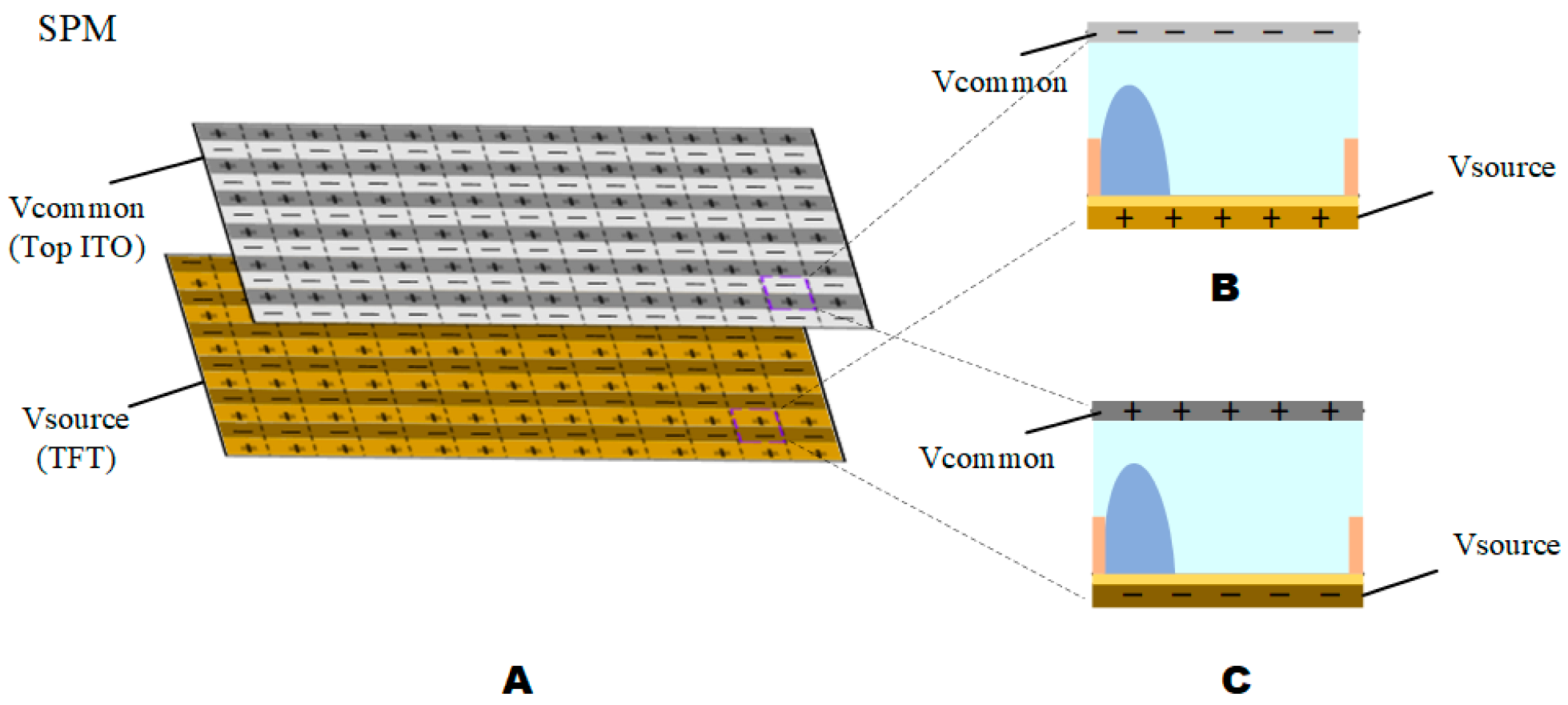
3.1. Dynamic Adaptive Display Model
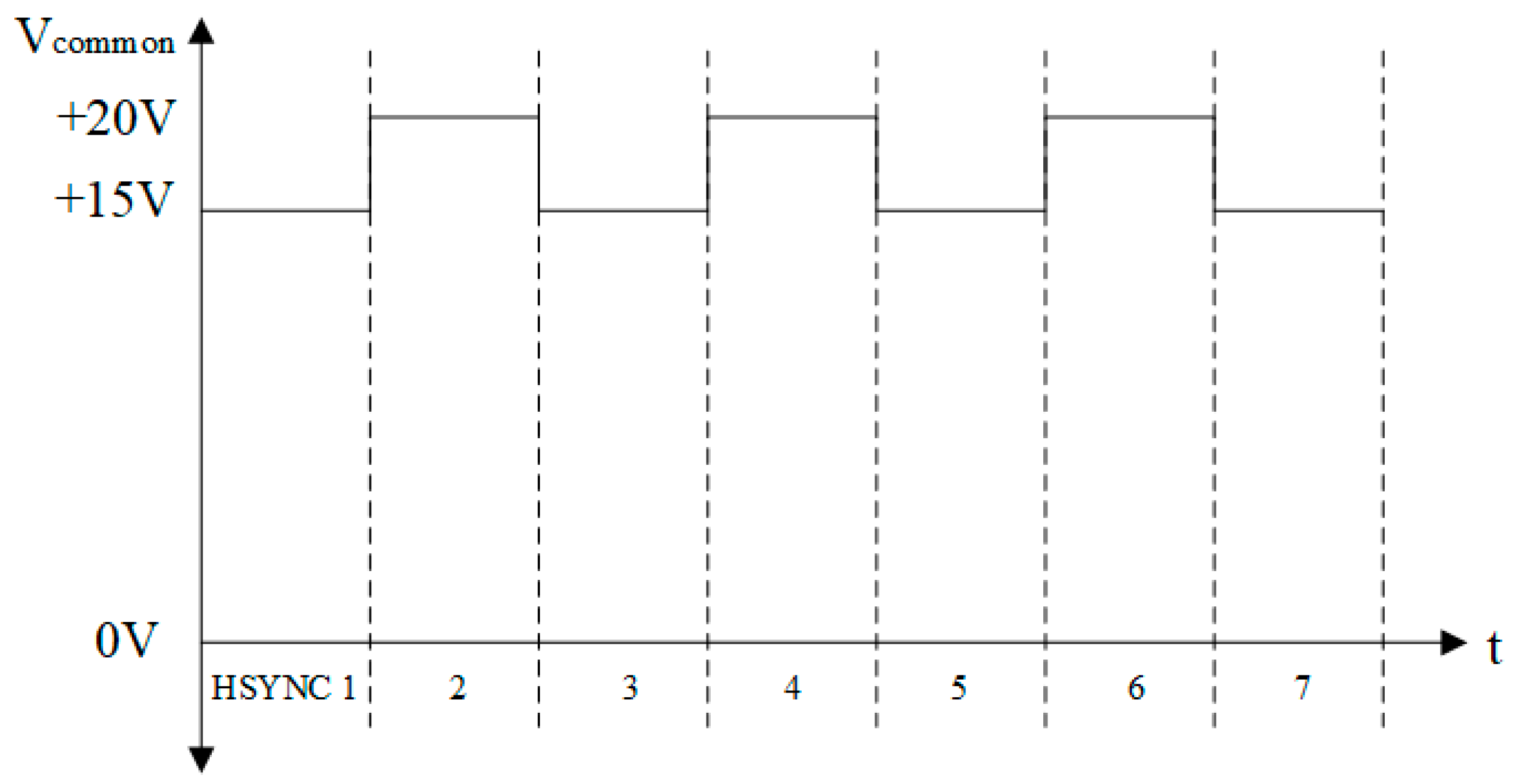
3.2. DC Driving Model for Static Play
3.3. AC Driving Models for Dynamic Displays
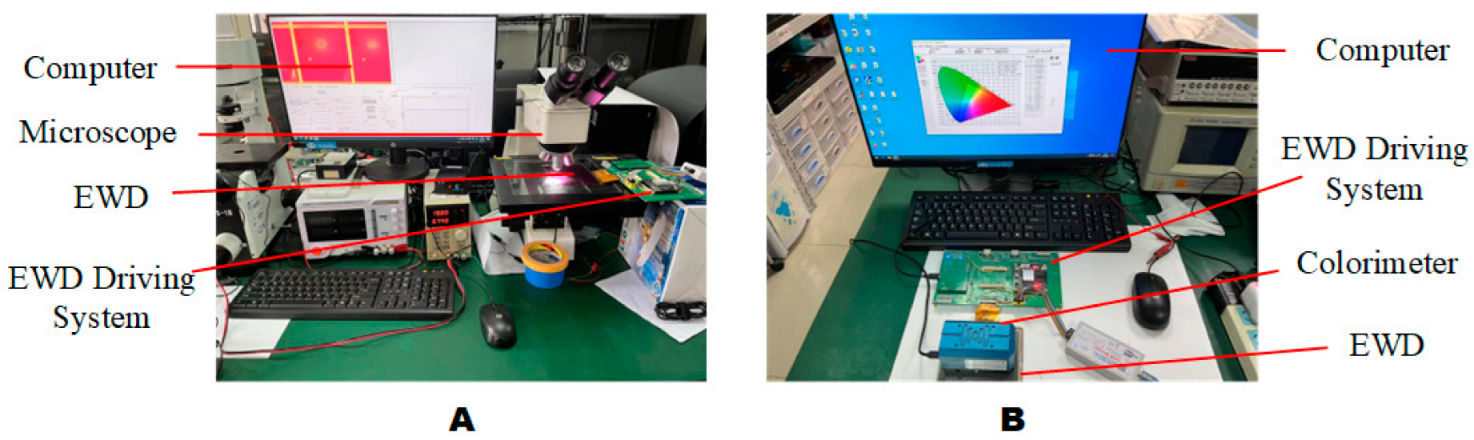
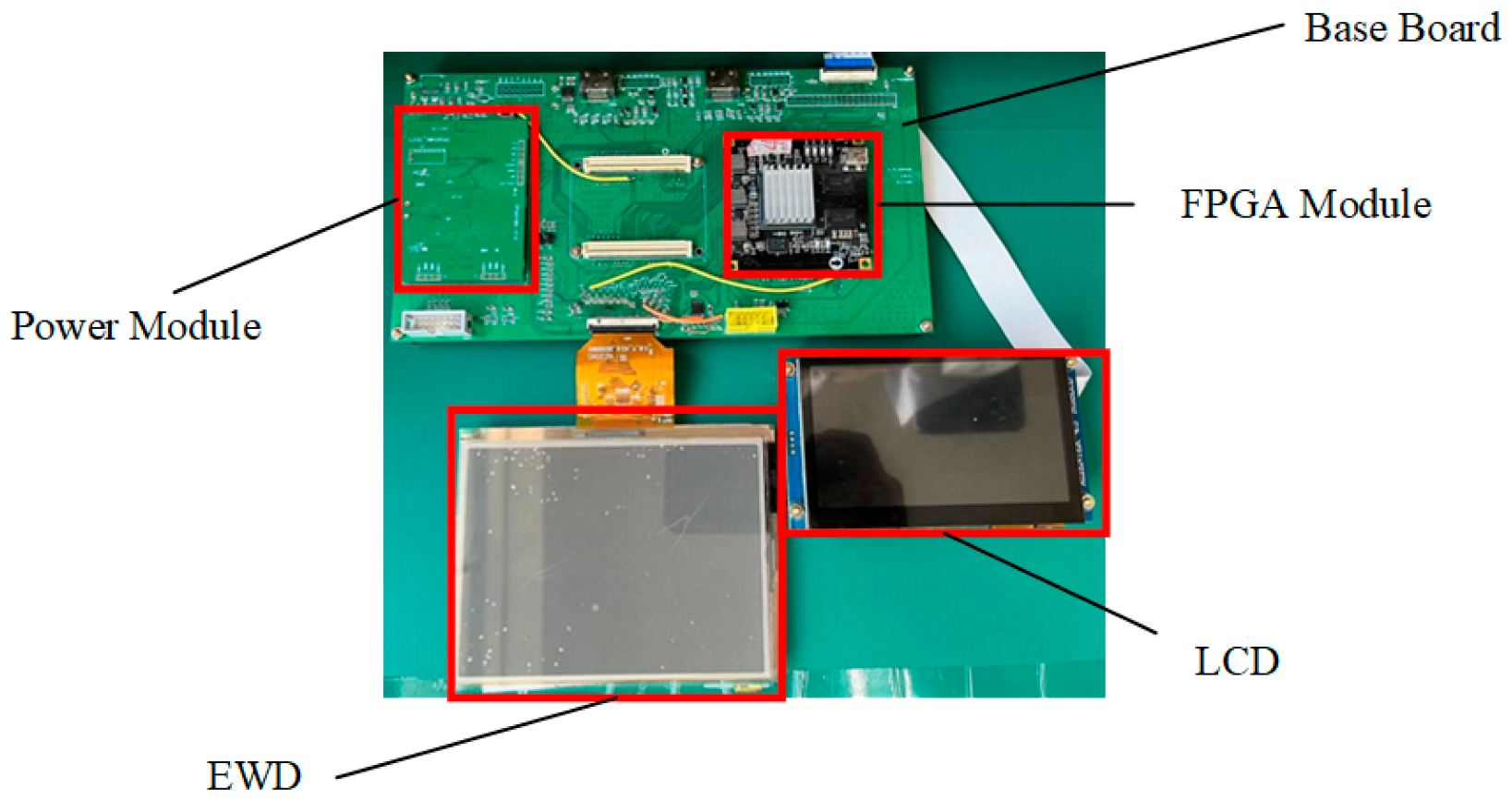
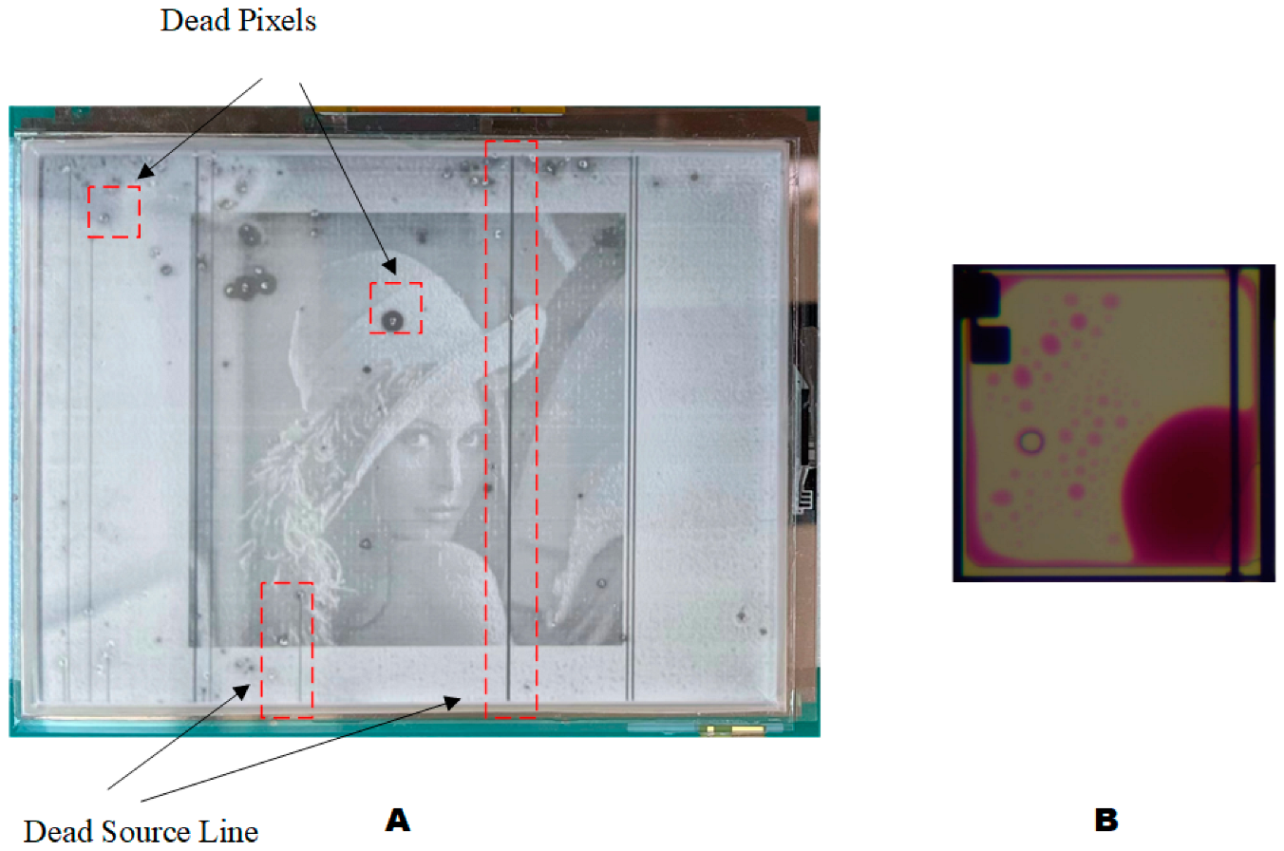
3.4. Dynamic Adaptive Display Testing System
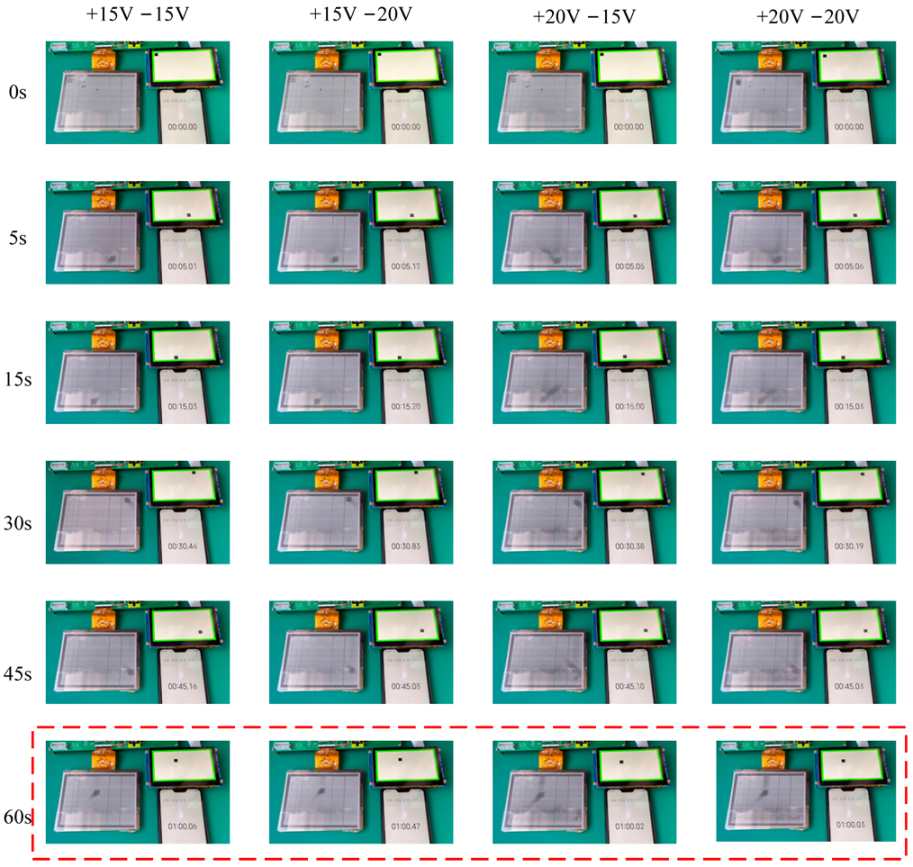
4. Results and Discussion
4.1. DC Driving Waveform Test
4.2. AC Driving Waveform Test
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A

Appendix B

References
- Li, W.; Wang, L.; Henzen, A. A Multi Waveform Adaptive Driving Scheme for Reducing Hysteresis Effect of Electrowetting Displays. Front. Phys. 2020, 8, 618811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, S.; Zeng, S.; Qian, M.; Lin, Z.; Guo, T.; Tang, B. Improvement of display performance of electrowetting displays by optimized waveforms and error diffusion. J. Soc. Inf. Disp. 2019, 27, 619–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayes, R.A.; Feenstra, B.J. Video-speed electronic paper based on electrowetting. Nature 2003, 425, 383–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, E.; Lin, J.; Yang, T.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, X.; Ye, Y.; Sun, J.; Yan, Q.; Guo, T. Asymmetric Quantum-Dot Pixelation for Color-Converted White Balance. ACS Photonics 2021, 8, 2158–2165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Cai, J.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, M.; Chen, E.; Sun, J.; Yan, Q.; Guo, T. Design of inclined omni-directional reflector for sidewall-emission-free micro-scale light-emitting diodes. Opt. Laser Technol. 2022, 154, 108335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, G.; Liu, L.; Zheng, Z.; Henzen, A.; Xi, K.; Bai, P.; Zhou, G. A portable driving system for high-resolution active matrix electrowetting display based on FPGA. J. Soc. Inf. Disp. 2019, 28, 287–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, C.; Tang, B.; Xu, B.; Groenewold, J.; Zhou, G. Oil Conductivity, Electric-Field-Induced Interfacial Charge Effects, and Their Influence on the Electro-Optical Response of Electrowetting Display Devices. Micromachines 2020, 11, 702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Tang, B.; Yuan, D.; Bai, P.; Li, H.; Yi, Z.; Deng, Y.; Zhou, R.; Zhong, B.; Jang, H.; et al. 3.1: Invited Paper: Electrowetting display: Towards full-color video reflective display. SID Symp. Dig. Tech. Pap. 2021, 52, 59–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Wang, L.; Zhang, T.; Lai, S.; Liu, L.; He, W.; Zhou, G.; Yi, Z. Driving Waveform Design with Rising Gradient and Sawtooth Wave of Electrowetting Displays for Ultra-Low Power Consumption. Micromachines 2020, 11, 145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yi, Z.; Liu, L.; Wang, L.; Li, W.; Shui, L.; Zhou, G. A Driving System for Fast and Precise Gray-Scale Response Based on Amplitude–Frequency Mixed Modulation in TFT Electrowetting Displays. Micromachines 2019, 10, 732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, Z.; Huang, Z.; Lai, S.; He, W.; Wang, L.; Chi, F.; Zhang, C.; Shui, L.; Zhou, G. Driving Waveform Design of Electrowetting Displays Based on an Exponential Function for a Stable Grayscale and a Short Driving Time. Micromachines 2020, 11, 313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yi, Z.; Zhang, H.; Zeng, W.; Feng, H.; Long, Z.; Liu, L.; Hu, Y.; Zhou, X.; Zhang, C. Review of Driving Waveform for Electrowetting Displays. Front. Phys. 2021, 9, 728804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, Z.; Yi, Z.; Zhang, H.; Lv, J.; Liu, L.; Chi, F.; Shui, L.; Zhang, C. Toward Suppressing Oil Backflow Based on a Combined Driving Waveform for Electrowetting Displays. Micromachines 2022, 13, 948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, L.; Zhang, H.; Yi, Z.; Zhang, B.; Zhou, R.; Zhou, G.; Gong, J. Inhibiting Oil Splitting and Backflow in Electrowetting Displays by Designing a Power Function Driving Waveform. Electronics 2022, 11, 2081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Deng, Y. Driving Waveform Design of Electrowetting Displays Based on a Reset Signal for Suppressing Charge Trapping Effect. Front. Phys. 2021, 9, 672541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Zhang, H.; Li, W.; Li, J.; Yi, Z.; Wan, Q.; Zhang, J.; Ma, P. Driving Scheme Optimization for Electrowetting Displays Based on Contact Angle Hysteresis to Achieve Precise Gray-Scales. Front. Phys. 2021, 9, 655547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Bai, P.; Yi, Z.; Zhou, G. A Separated Reset Waveform Design for Suppressing Oil Backflow in Active Matrix Electrowetting Displays. Micromachines 2021, 12, 491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feenstra, J. Video-Speed Electrowetting Display Technology. In Handbook of Visual Display Technology; Chen, J., Cranton, W., Fihn, M., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2012; pp. 1731–1745. [Google Scholar]
- Roques-Carmes, T.; Hayes, R.A.; Feenstra, B.J.; Schlangen, L.J.M. Liquid behavior inside a reflective display pixel based on electrowetting. J. Appl. Phys. 2004, 95, 4389–4396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verheijen, H.J.J.; Prins, M.W.J. Reversible Electrowetting and Trapping of Charge: Model and Experiments. Langmuir 1999, 15, 6616–6620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liang, C.C.; Chen, Y.C.; Chiu, Y.H.; Chen, H.Y.; Cheng, W.Y.; Lee, W.Y. A Decoupling Driving Scheme for Low Voltage Stress in Driving a Large-area High-resolution Electrowetting Display. In SID Symposium Digest of Technical Papers; Blackwell Publishing Ltd.: Oxford, UK, 2009; Volume 40, Books I–III; pp. 375–378. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, S.W. Universal Overdrive Technology for LCD Systems and High-Refresh Rate LC TVs. In Proceedings of the IDW’10: Proceedings of the 17th International Display Workshops, Fukuoka, Japan, 1–3 December 2010; Volumes 1–3, pp. 2177–2180. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, B.; Zhang, P. Algorithm of Dispersed PWM and Dynamic Refresh Mode for LED Display. In Proceedings of the 2011 International Conference on Control, Automation and Systems Engineering (CASE), Singapore, 30–31 July 2011; pp. 1–3. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.; Tong, Z.; Ji, B.; Wu, G. TDN: Temporal Difference Networks for Efficient Action Recognition. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Virtual, 20–25 June 2021; pp. 1895–1904. [Google Scholar]
- Li, S.; Bai, P.; Qin, Y. Dynamic Adjustment and Distinguishing Method for Vehicle Headlight Based on Data Access of a Thermal Camera. Front. Phys. 2020, 8, 354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, W.; Yi, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Zeng, W.; Ma, S.; Zhou, X.; Feng, H.; Liu, L.; Shui, L.; Zhang, C.; et al. Design of Driving Waveform Based on Overdriving Voltage for Shortening Response Time in Electrowetting Displays. Front. Phys. 2021, 9, 642682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, V.K.P.; Sagar, T. Numerical evaluation of the influence of AC and DC electric field on the response of the droplet. In Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Condensed Matter and Applied Physics (Icc-2019), Bikaner, India, 14–15 October 2019; Volume 2220, p. 130006. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, C.; Su, Q.; Miao, Y.; Chen, D.; Liao, Y.; Lee, S.; Shao, X. P-12.3: The Research on the Influence of Pixel Polarity Arrangement on Display Quality. SID Symp. Dig. Tech. Pap. 2021, 52, 970–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





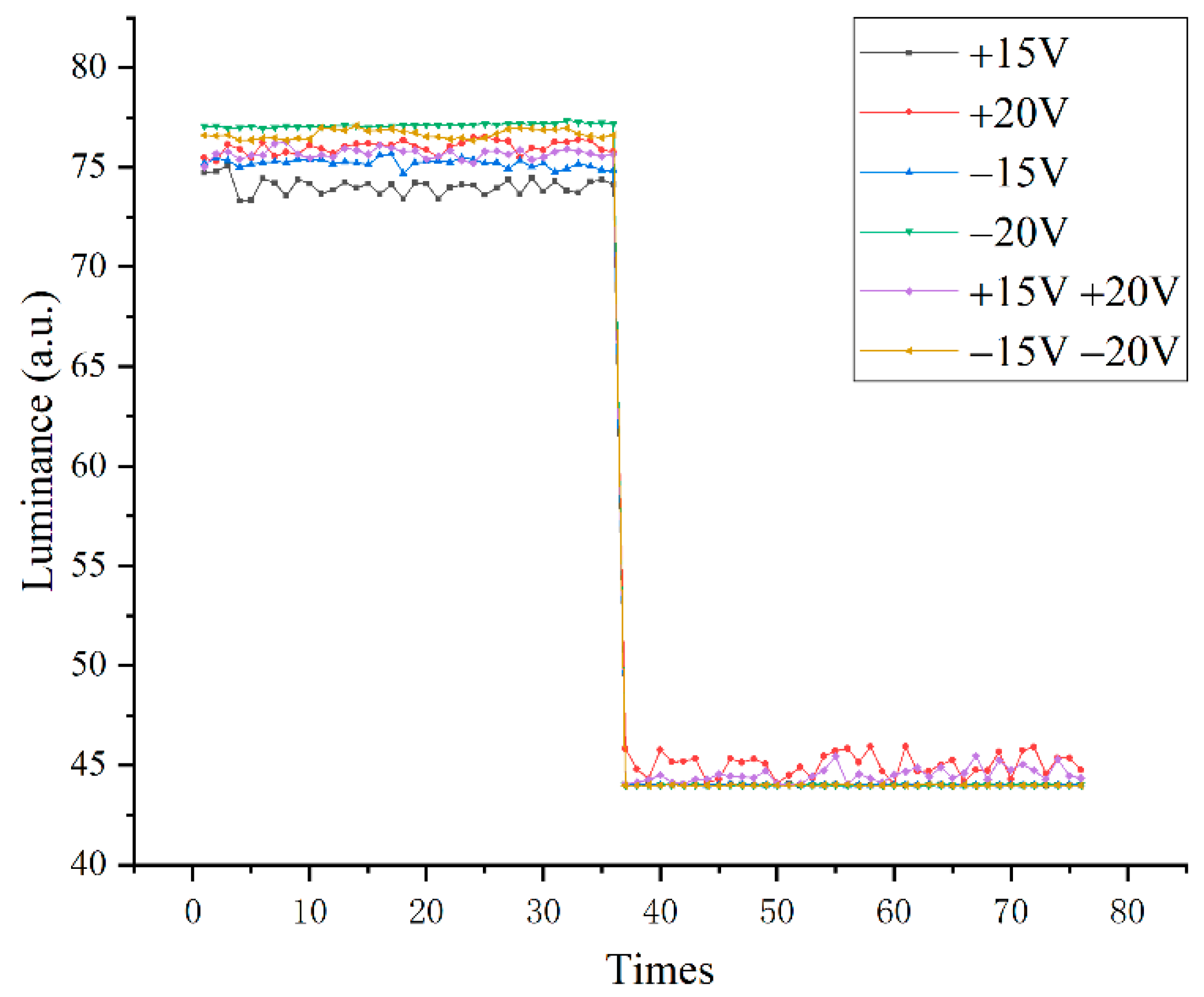
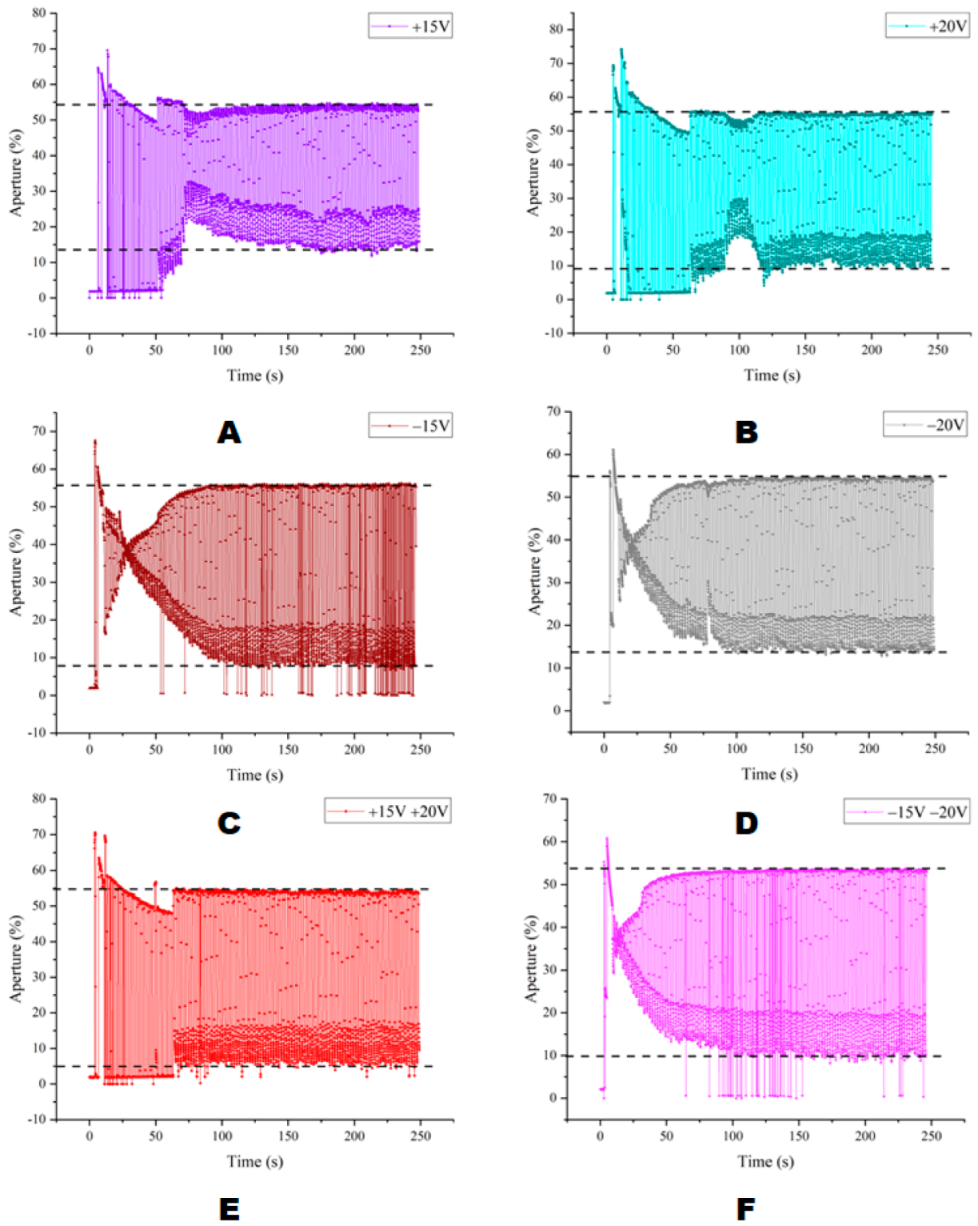


| Waveforms | “On” State Maximum (%) | “Off” State Minimum (%) | “On” State Average (%) | “Off” State Average (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| +15 V | 69.5 | 1.82 | 52.76 | 16.14 |
| +20 V | 74.18 | 0 | 54.48 | 12.07 |
| −15 V | 67.61 | 0 | 51.54 | 14.66 |
| −20 V | 61.16 | 1.91 | 51.93 | 19.96 |
| +15 V +20 V | 70.55 | 0 | 53.36 | 8.38 |
| −15 V −20 V | 60.79 | 0 | 50.77 | 16.19 |
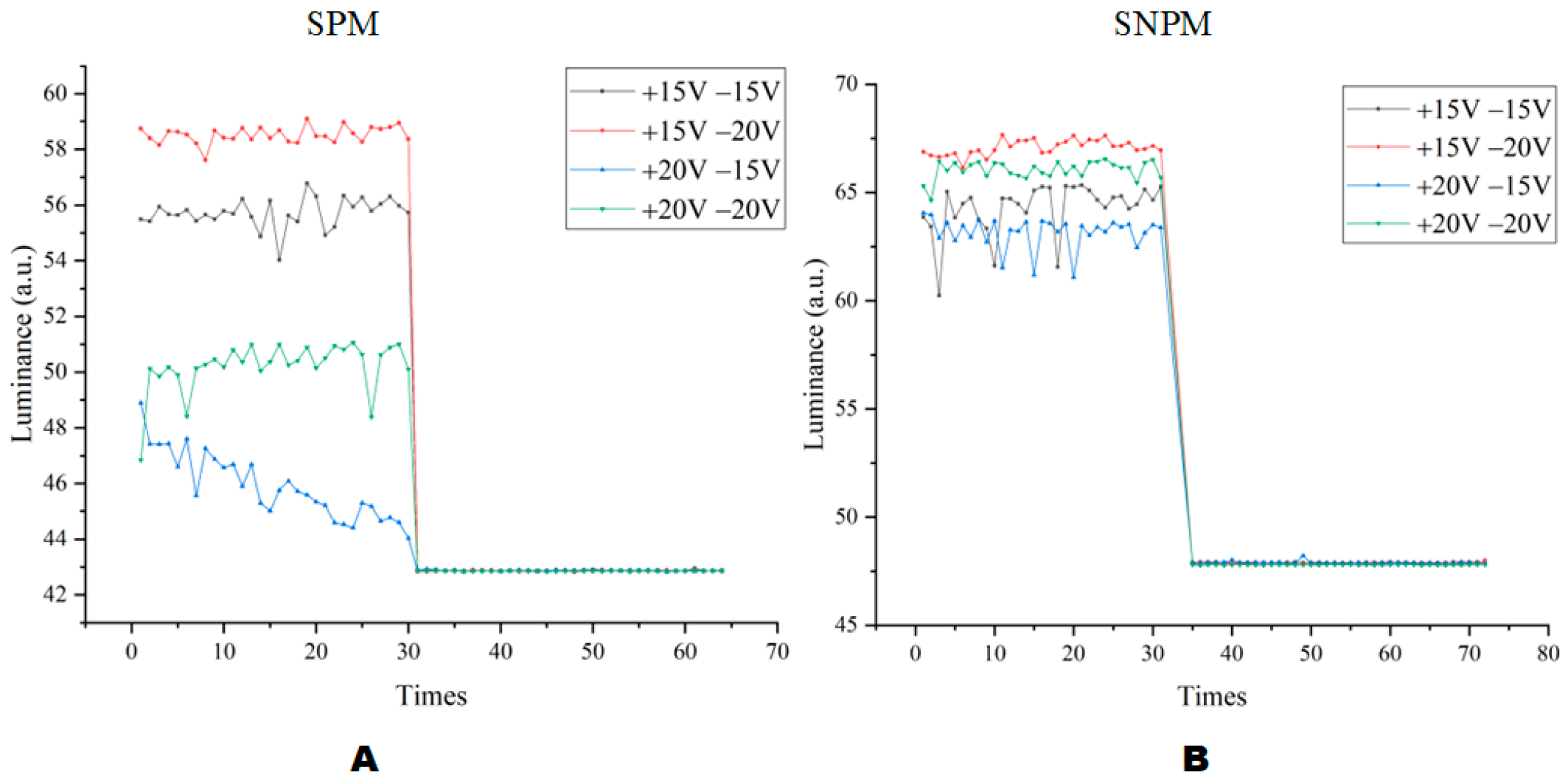
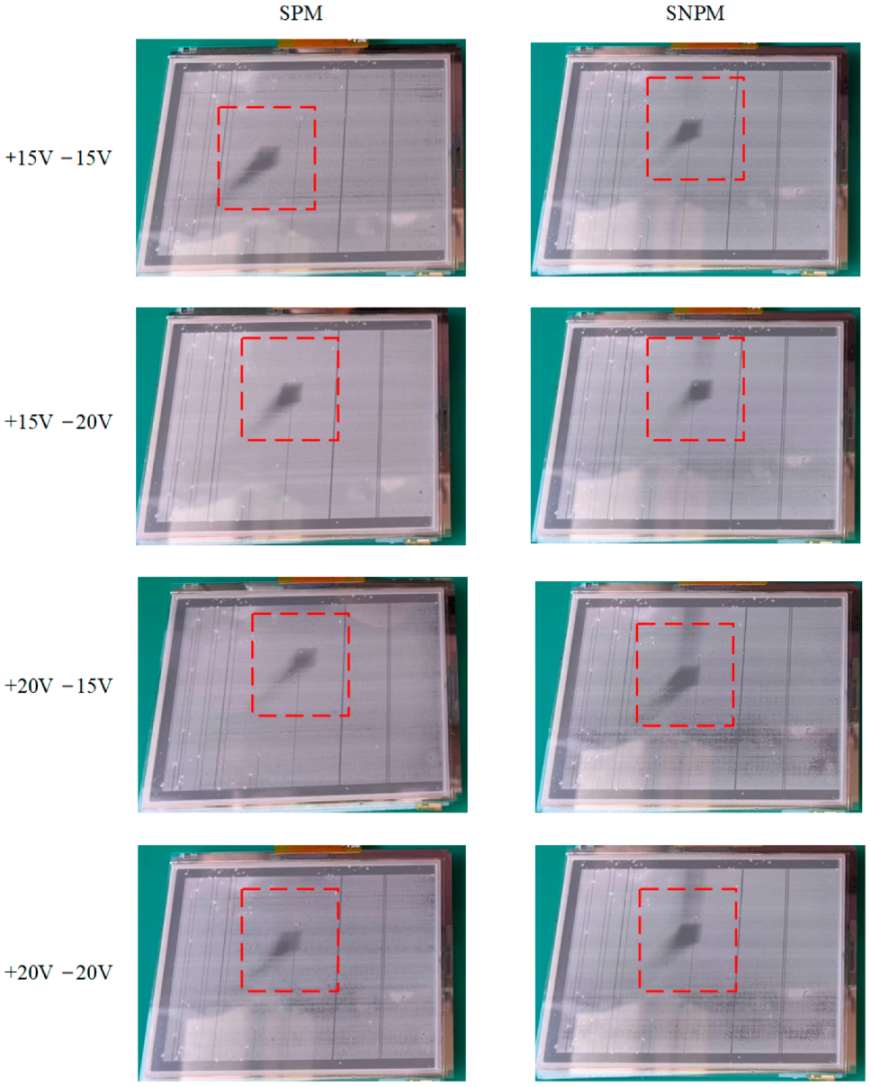
| Methods | Waveforms | “On” State Maximum (%) | “Off” State Minimum (%) | “On” State Average (%) | “Off” State Average (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SPM | +15 V −15 V | 59.23 | 0.56 | 28.69 | 12.78 |
| +15 V −20 V | 70.97 | 0.84 | 26.19 | 16.47 | |
| +20 V −15 V | 71.58 | 0 | 29.94 | 14.68 | |
| +20 V −20 V | 66.02 | 12.64 | 24.37 | 15.71 | |
| SNPM | +15 V −15 V | 72.51 | 11.43 | 52.06 | 13.19 |
| +15V −20 V | 73.87 | 15.69 | 51.42 | 16.33 | |
| +20 V −15 V | 74.51 | 0 | 52.10 | 14.11 | |
| +20 V −20 V | 73.91 | 0 | 51.49 | 16.19 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, S.; Xu, Y.; Zhan, Z.; Du, P.; Liu, L.; Li, Z.; Wang, H.; Bai, P. Dynamic Adaptive Display System for Electrowetting Displays Based on Alternating Current and Direct Current. Micromachines 2022, 13, 1791. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi13101791
Li S, Xu Y, Zhan Z, Du P, Liu L, Li Z, Wang H, Bai P. Dynamic Adaptive Display System for Electrowetting Displays Based on Alternating Current and Direct Current. Micromachines. 2022; 13(10):1791. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi13101791
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Shixiao, Yijian Xu, Zhiyu Zhan, Pengyuan Du, Linwei Liu, Zikai Li, Huawei Wang, and Pengfei Bai. 2022. "Dynamic Adaptive Display System for Electrowetting Displays Based on Alternating Current and Direct Current" Micromachines 13, no. 10: 1791. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi13101791
APA StyleLi, S., Xu, Y., Zhan, Z., Du, P., Liu, L., Li, Z., Wang, H., & Bai, P. (2022). Dynamic Adaptive Display System for Electrowetting Displays Based on Alternating Current and Direct Current. Micromachines, 13(10), 1791. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi13101791






