Double-Sided Sapphire Optrodes with Conductive Shielding Layers to Reduce Optogenetic Stimulation Artifacts
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experiments and Methods
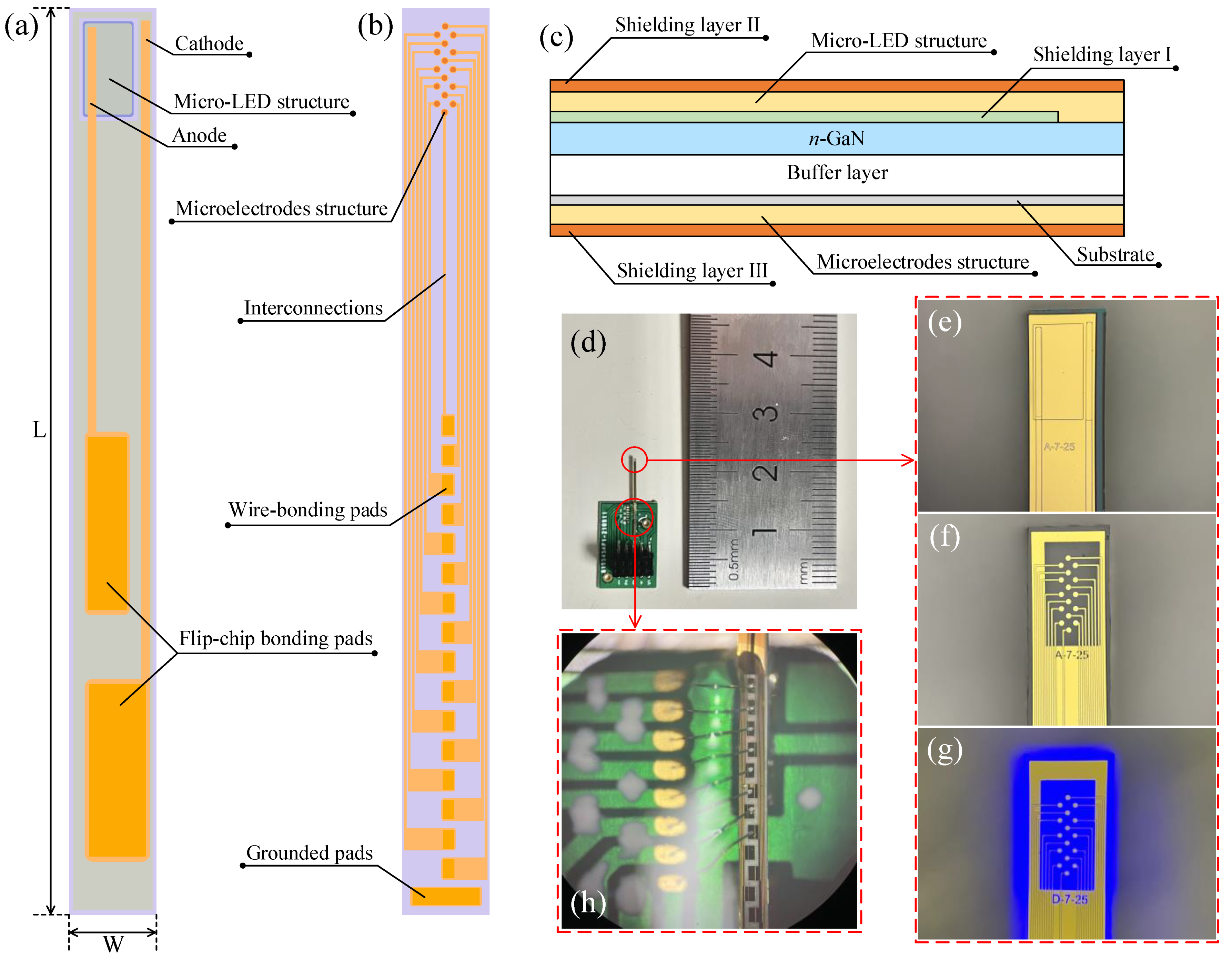
2.1. Device Design
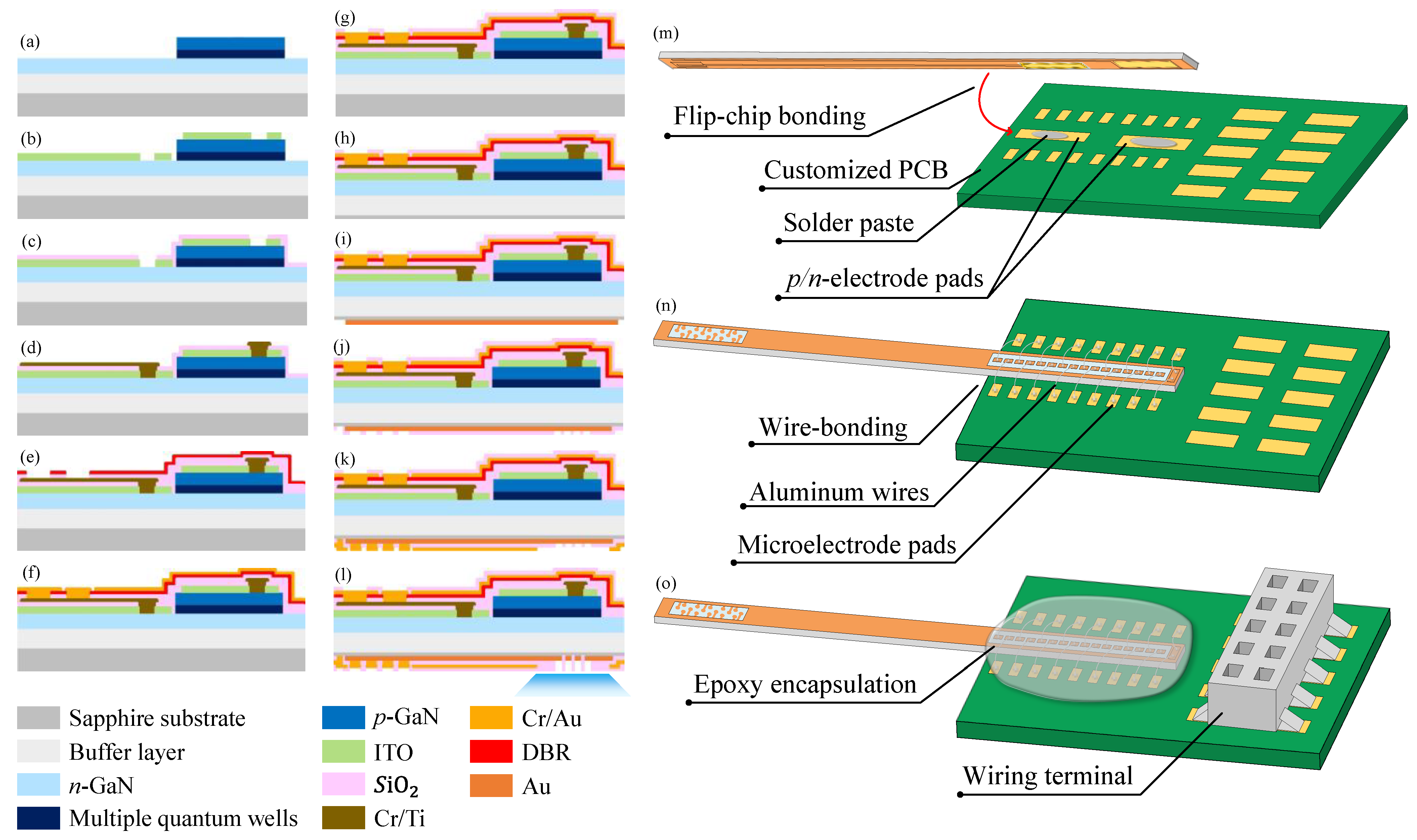
2.2. Fabrication and Encapsulation
3. Results and Discussions
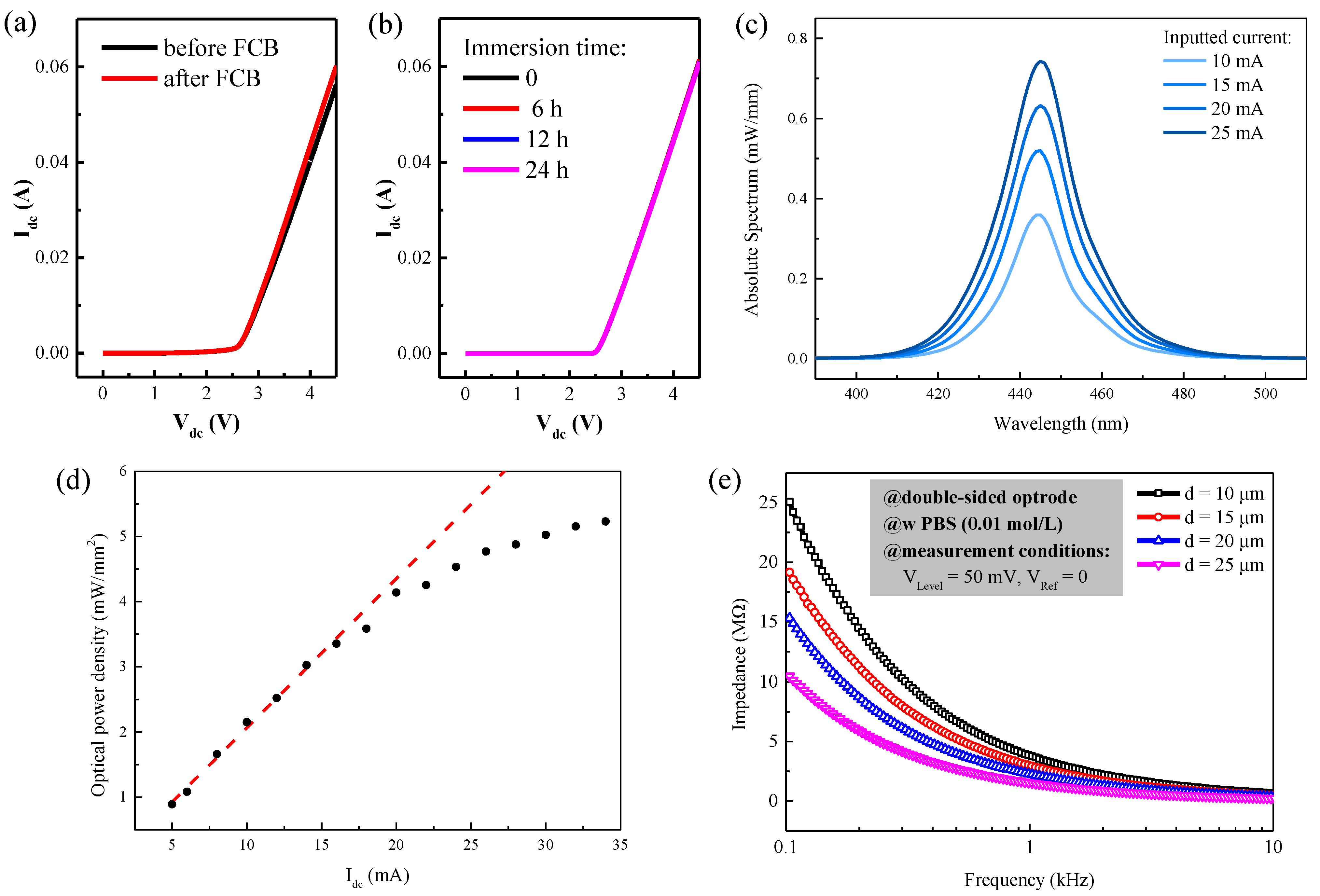
3.1. Electrical and Optical Performance
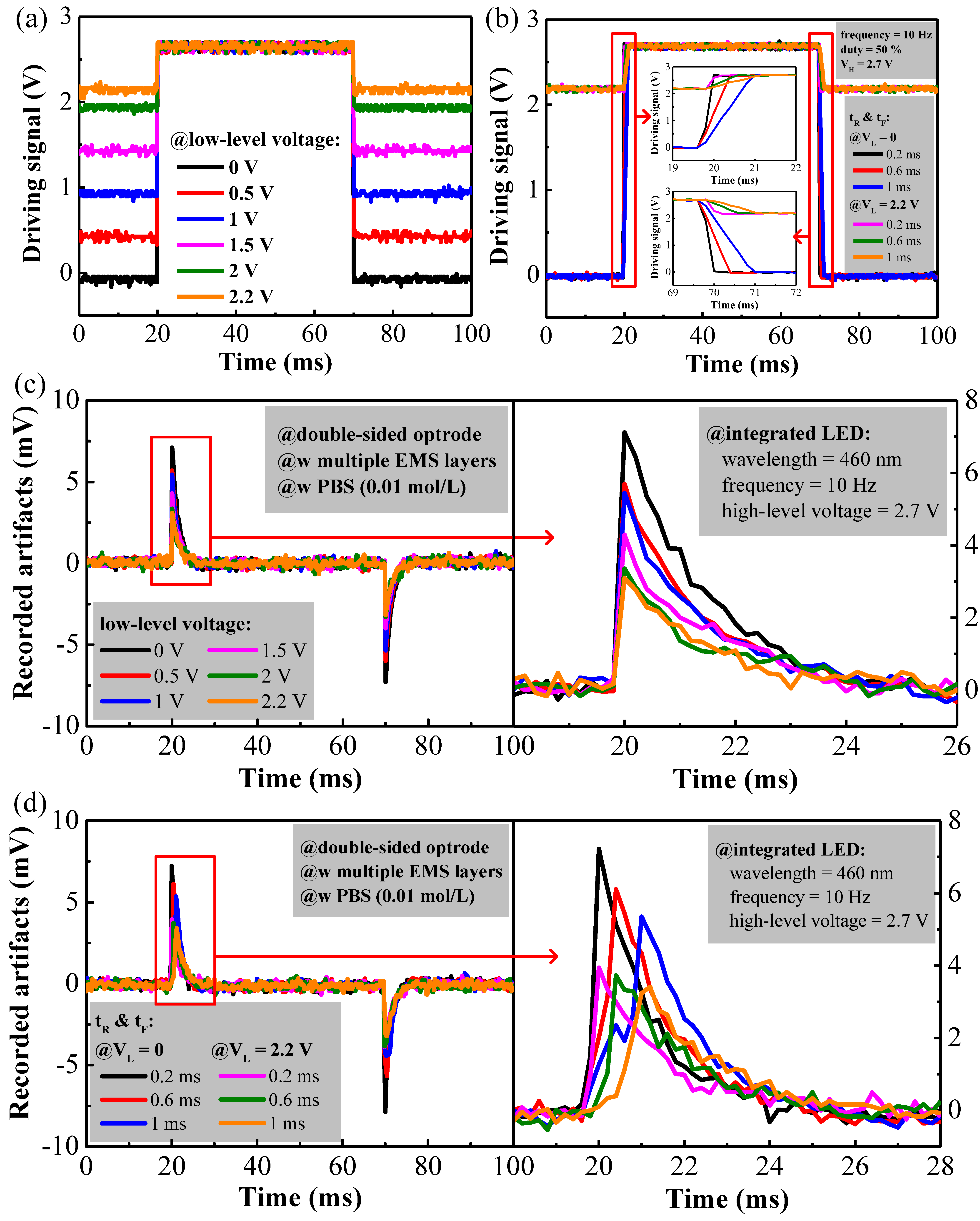
3.2. Reduction of Optogenetic Stimulation Artifacts
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yizhar, O.; Fenno, L.E.; Davidson, T.J.; Mogri, M.; Deisseroth, K. Optogenetics in neural systems. Neuron 2011, 71, 9–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mickle, A.D.; Gereau, R.W. A bright future? Optogenetics in the periphery for pain research and therapy. Pain 2018, 159 (Suppl. 1), S65–S73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Aravanis, A.M.; Adamantidis, A.; Lecea, L.D.; Deisseroth, K. Circuit-breakers: Optical technologies for probing neural signals and systems. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2007, 8, 577–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, K.; Jackel, Z.; Schneider, A.; Paul, O.; Diester, I.; Ruther, P. Multifunctional optrode for opsin delivery, optical stimulation, and electrophysiological recordings in freely moving rats. J. Neural Eng. 2021, 18, 066013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seymour, J.P.; Wu, F.; Wise, K.D.; Yoon, E. State-of-the-art MEMS and microsystem tools for brain research. Microsyst. Nanoeng. 2017, 3, 16066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Juboori, S.I.; Dondzillo, A.; Stubblefield, E.A.; Felsen, G.; Lei, T.C.; Klug, A. Light scattering properties vary across different regions of the adult mouse brain. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e67626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.H.; Mccullagh, E.A.; Pun, S.H.; Mak, P.U.; Vai, M.I.; Mak, P.I.; Klug, A.; Lei, T.C. An Integrated Circuit for Simultaneous Extracellular Electrophysiology Recording and Optogenetic Neural Manipulation. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2017, 64, 557–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.; English, D.; Mckenzie, S.; Wu, F.; Stark, E.; Seymour, J.; Ku, P.C.; Wise, K.; Buzsaki, G.; Yoon, E. GaN-on-Si μLED optoelectrodes for high-spatiotemporal-accuracy optogenetics in freely behaving animals. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE International Electron Devices Meeting (IEDM), San Francisco, CA, USA, 3–7 December 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Buzsaki, G.; Stark, E.; Berenyi, A.; Khodagholy, D.; Kipke, D.R.; Yoon, E.; Wise, K.D. Tools for probing local circuits: High-density silicon probes combined with optogenetics. Neuron 2015, 86, 92–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Royer, S.; Zemelman, B.V.; Barbic, M.; Losonczy, A.; Buzsaki, G.; Magee, J.C. Multi-array silicon probes with integrated optical fibers: Light-assisted perturbation and recording of local neural circuits in the behaving animal. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2010, 31, 2279–2291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, K.; Voroslakos, M.; Seymour, J.P.; Wise, K.D.; Buzsaki, G.; Yoon, E. Artifact-free and high-temporal-resolution in vivo opto-electrophysiology with microLED optoelectrodes. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 2063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, F.; Stark, E.; Ku, P.C.; Wise, K.D.; Buzsaki, G.; Yoon, E. Monolithically Integrated muLEDs on Silicon Neural Probes for High-Resolution Optogenetic Studies in Behaving Animals. Neuron 2015, 88, 1136–1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, H.; Gu, L.; Mohanty, S.K.; Chiao, J.C. An integrated muLED optrode for optogenetic stimulation and electrical recording. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2013, 60, 225–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendrela, A.E.; Kanghwan, K.; Daniel, E.; Sam, M.; John, P.S.; György, B.; Euisik, Y. A High-Resolution Opto-Electrophysiology System with a Miniature Integrated Headstage. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Circuits Syst. 2018, 12, 1065–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kampasi, K.; English, D.F.; Seymour, J.; Stark, E.; McKenzie, S.; Voroslakos, M.; Buzsaki, G.; Wise, K.D.; Yoon, E. Dual color optogenetic control of neural populations using low-noise, multishank optoelectrodes. Microsyst. Nanoeng. 2018, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kozai, T.D.; Vazquez, A.L. Photoelectric artefact from optogenetics and imaging on microelectrodes and bioelectronics: New Challenges and Opportunities. J. Mater. Chem. B 2015, 3, 4965–4978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Lu, Y.; Iseri, E.; Shi, Y.; Kuzum, D. A Compact Closed-Loop Optogenetics System Based on Artifact-Free Transparent Graphene Electrodes. Front. Neurosci. 2018, 12, 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khurram, A.; Seymour, J.P. Investigation of the photoelectrochemical effect in optoelectrodes and potential uses for implantable electrode characterization. In Proceedings of the 2013 35th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBC), Osaka, Japan, 3–7 July 2013; pp. 3032–3035. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, J.; Xu, Y.; Xiao, Z.; Liu, Y.; Liu, H.; Wang, F.; Yao, W.; Yan, Z.; Zhang, M.; Wu, Z.; et al. Influence of the Surface Material and Illumination upon the Performance of a Microelectrode/Electrolyte Interface in Optogenetics. Micromachines 2021, 12, 1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Ge, C.; Wang, M.; Ji, B.; Guo, Z.; Wang, X.; Yang, B.; Li, C.; Liu, J. An artefact-resist optrode with internal shielding structure for low-noise neural modulation. J. Neural Eng. 2020, 17, 046024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.; Ji, B.; Wang, M.; Ge, C.; Wang, L.; Gu, X.; Yang, B.; Wang, X.; Li, C.; Liu, J. A Polyimide-Based Flexible Optoelectrodes for Low-Noise Neural Recording. IEEE Electron Device Lett. 2019, 40, 1190–1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, B.W.; Ge, C.F.; Guo, Z.J.; Wang, L.C.; Wang, M.H.; Xie, Z.Q.; Xu, Y.S.; Li, H.B.; Yang, B.; Wang, X.L.; et al. Flexible and stretchable opto-electric neural interface for low-noise electrocorticogram recordings and neuromodulation in vivo. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2020, 153, 112009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rui, Y.F.; Liu, J.Q.; Yang, B.; Li, K.Y.; Yang, C.S. Parylene-based implantable platinum-black coated wire microelectrode for orbicularis oculi muscle electrical stimulation. Biomed. Microdevices 2012, 14, 367–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.C.; Wang, M.H.; Ge, C.F.; Ji, B.W.; Guo, Z.J.; Wang, X.L.; Yang, B.; Li, C.Y.; Liu, J.Q. The use of a double-layer platinum black-conducting polymer coating for improvement of neural recording and mitigation of photoelectric artifact. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2019, 145, 111661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, M.; Guo, B.; Ji, B.; Fan, Y.; Wang, L.; Ye, L.; Chen, Y.; Cheng, Y.; Dong, L.; Wang, G. Controlled Electrodeposition of Graphene Oxide doped Conductive polymer on Microelectrodes for Low-Noise Optogenetics. IEEE Electron Device Lett. 2021, 42, 418–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Ozden, I.; Song, Y.K.; Nurmikko, A.V. Transparent intracortical microprobe array for simultaneous spatiotemporal optical stimulation and multichannel electrical recording. Nat. Methods 2015, 12, 1157–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Pei, W.; Yang, X.; Guo, X.; Xing, X.; Liu, R.; Liu, Y.; Gui, Q.; Chen, H. A sapphire based monolithic integrated optrode. In Proceedings of the 38th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, Orlando, FL, USA, 16–20 August 2016; pp. 6186–6189. [Google Scholar]
- Kirby, J.F.; Swain, C.J. Improving the spatial resolution of effective elastic thickness estimation with the fan wavelet transform. Comput. Geosci. 2021, 37, 1345–1354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, C.; Ke, D.; Wang, L.; Lu, Y.; Wang, L. Bioactive interpenetrating polymer networks for improving the electrode/neural-tissue interface. Electrochem. Commun. 2017, 79, 59–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.H.; Pun, S.H.; Mak, P.U.; Vai, M.I.; Klug, A.; Lei, T.C. Circuit Models and Experimental Noise Measurements of Micropipette Amplifiers for Extracellular Neural Recordings from Live Animals. BioMed Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 135026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shen, J.; Xu, Y.; Xiao, Z.; Liu, Y.; Liu, H.; Wang, F.; Yan, C.; Wang, L.; Chen, C.; Wu, Z.; et al. Double-Sided Sapphire Optrodes with Conductive Shielding Layers to Reduce Optogenetic Stimulation Artifacts. Micromachines 2022, 13, 1836. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi13111836
Shen J, Xu Y, Xiao Z, Liu Y, Liu H, Wang F, Yan C, Wang L, Chen C, Wu Z, et al. Double-Sided Sapphire Optrodes with Conductive Shielding Layers to Reduce Optogenetic Stimulation Artifacts. Micromachines. 2022; 13(11):1836. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi13111836
Chicago/Turabian StyleShen, Junyu, Yanyan Xu, Zhengwen Xiao, Yuebo Liu, Honghui Liu, Fengge Wang, Chaokun Yan, Liyang Wang, Changhao Chen, Zhisheng Wu, and et al. 2022. "Double-Sided Sapphire Optrodes with Conductive Shielding Layers to Reduce Optogenetic Stimulation Artifacts" Micromachines 13, no. 11: 1836. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi13111836
APA StyleShen, J., Xu, Y., Xiao, Z., Liu, Y., Liu, H., Wang, F., Yan, C., Wang, L., Chen, C., Wu, Z., Liu, Y., Mak, P. U., Vai, M. I., Pun, S. H., Lei, T. C., & Zhang, B. (2022). Double-Sided Sapphire Optrodes with Conductive Shielding Layers to Reduce Optogenetic Stimulation Artifacts. Micromachines, 13(11), 1836. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi13111836






