Development of a Simple Fabrication Method for Magnetic Micro Stir Bars and Induction of Rotational Motion in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
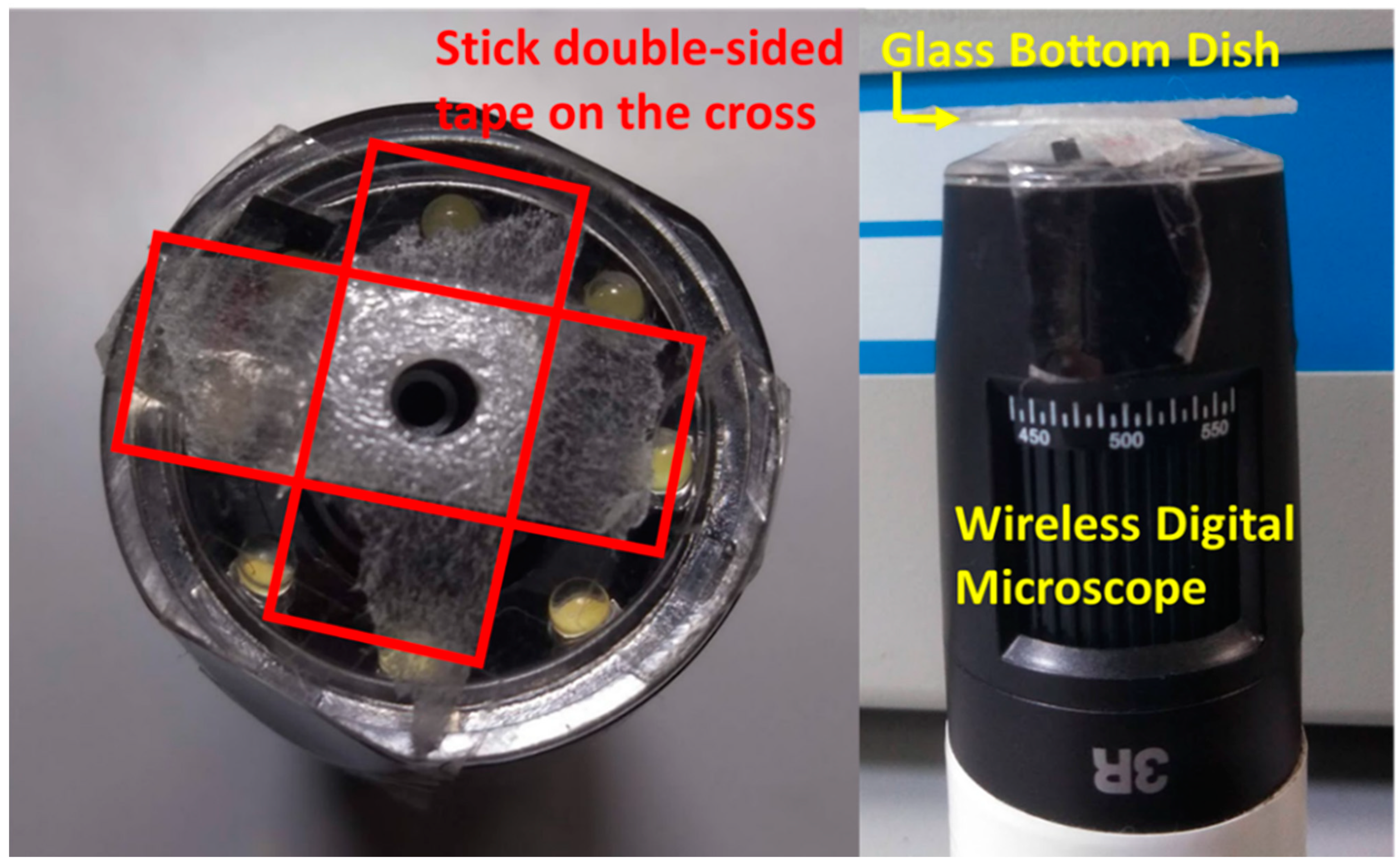
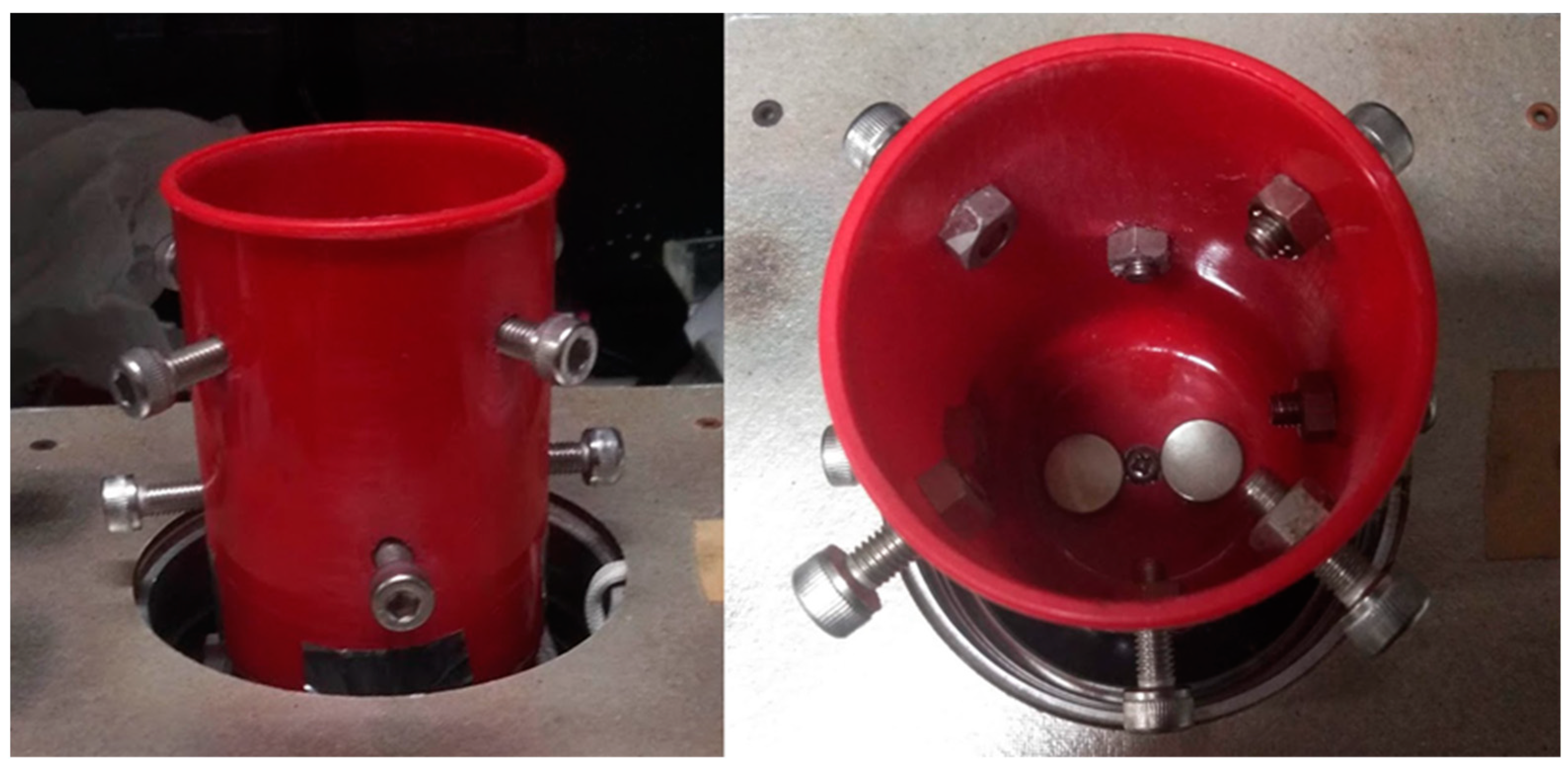
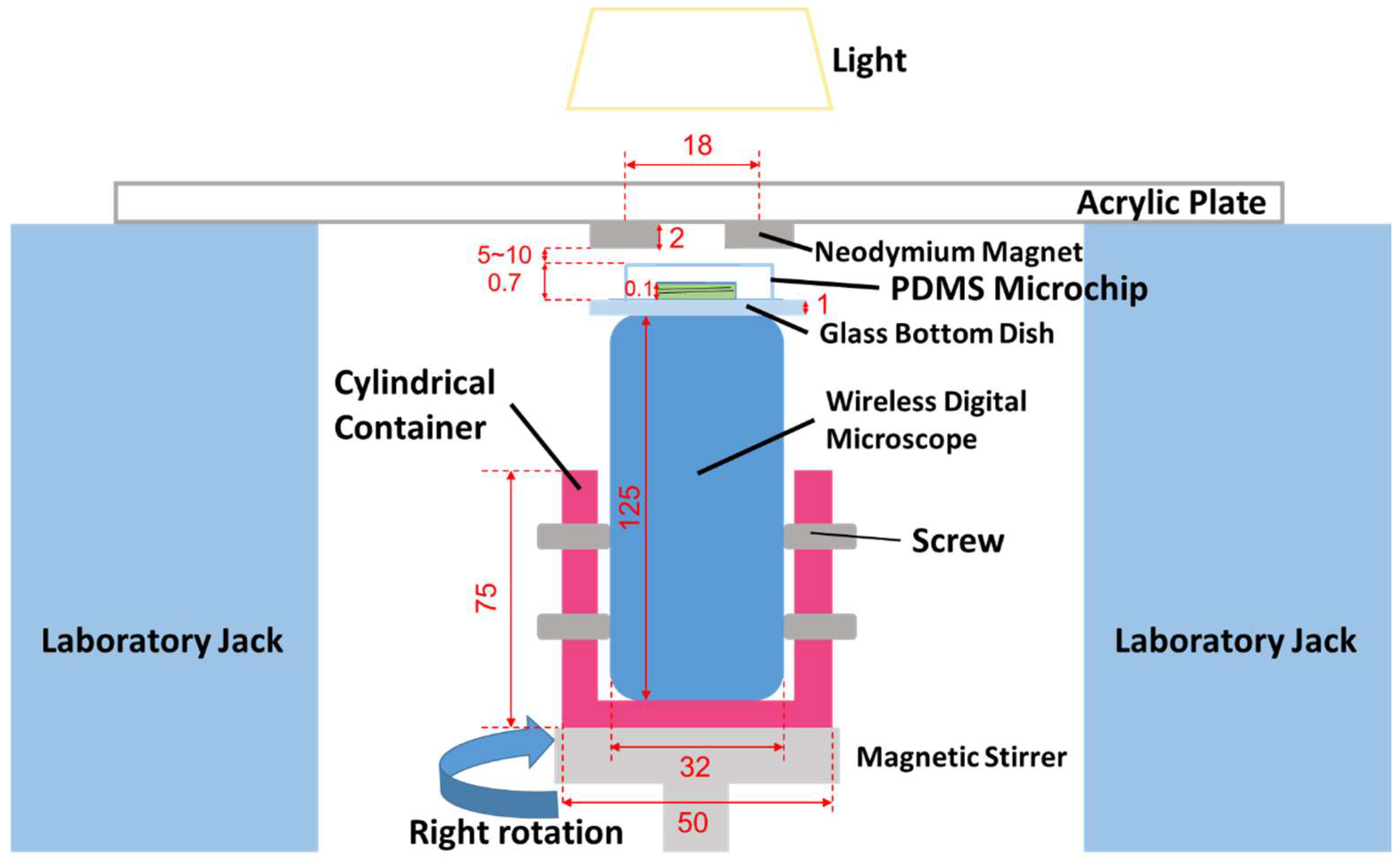
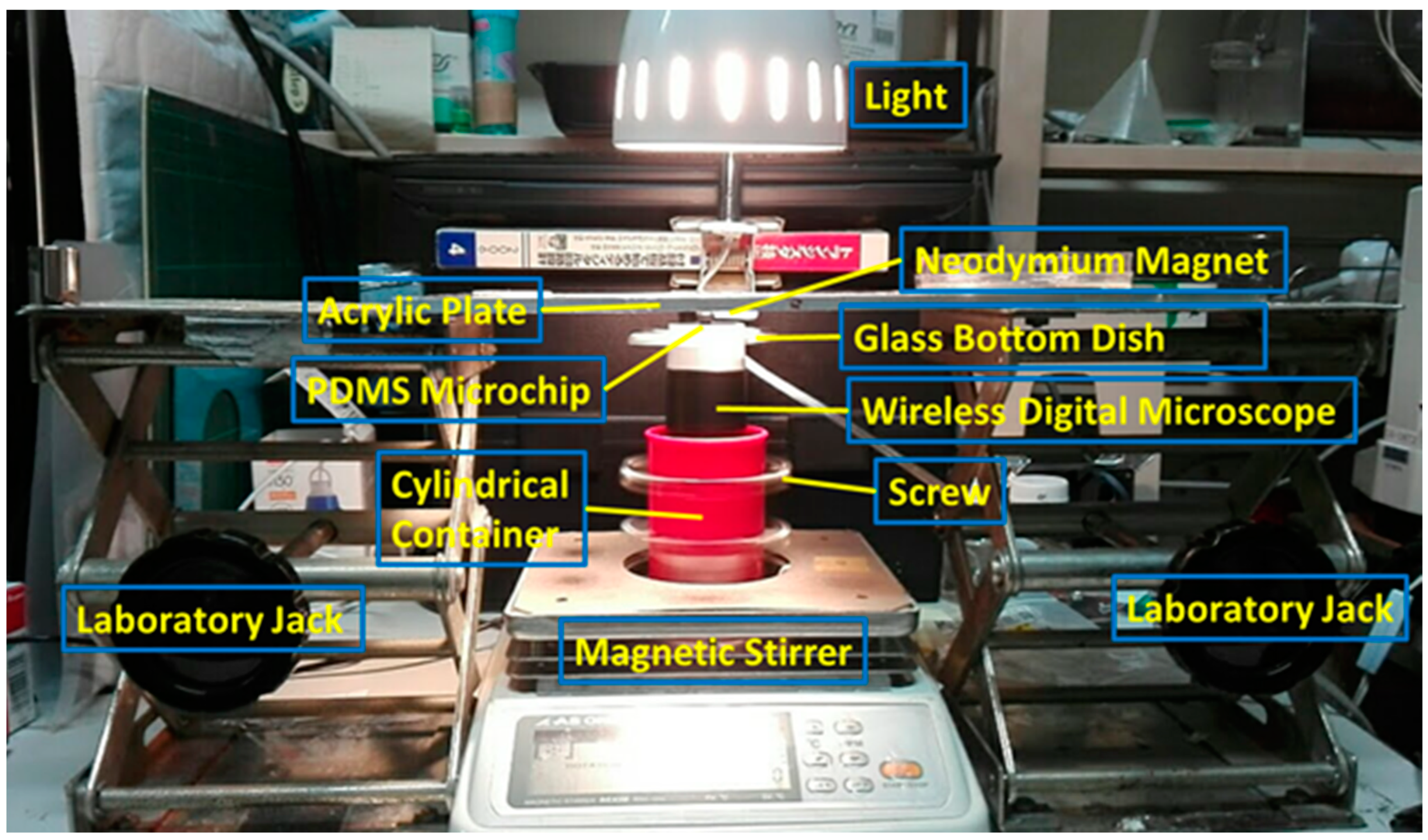
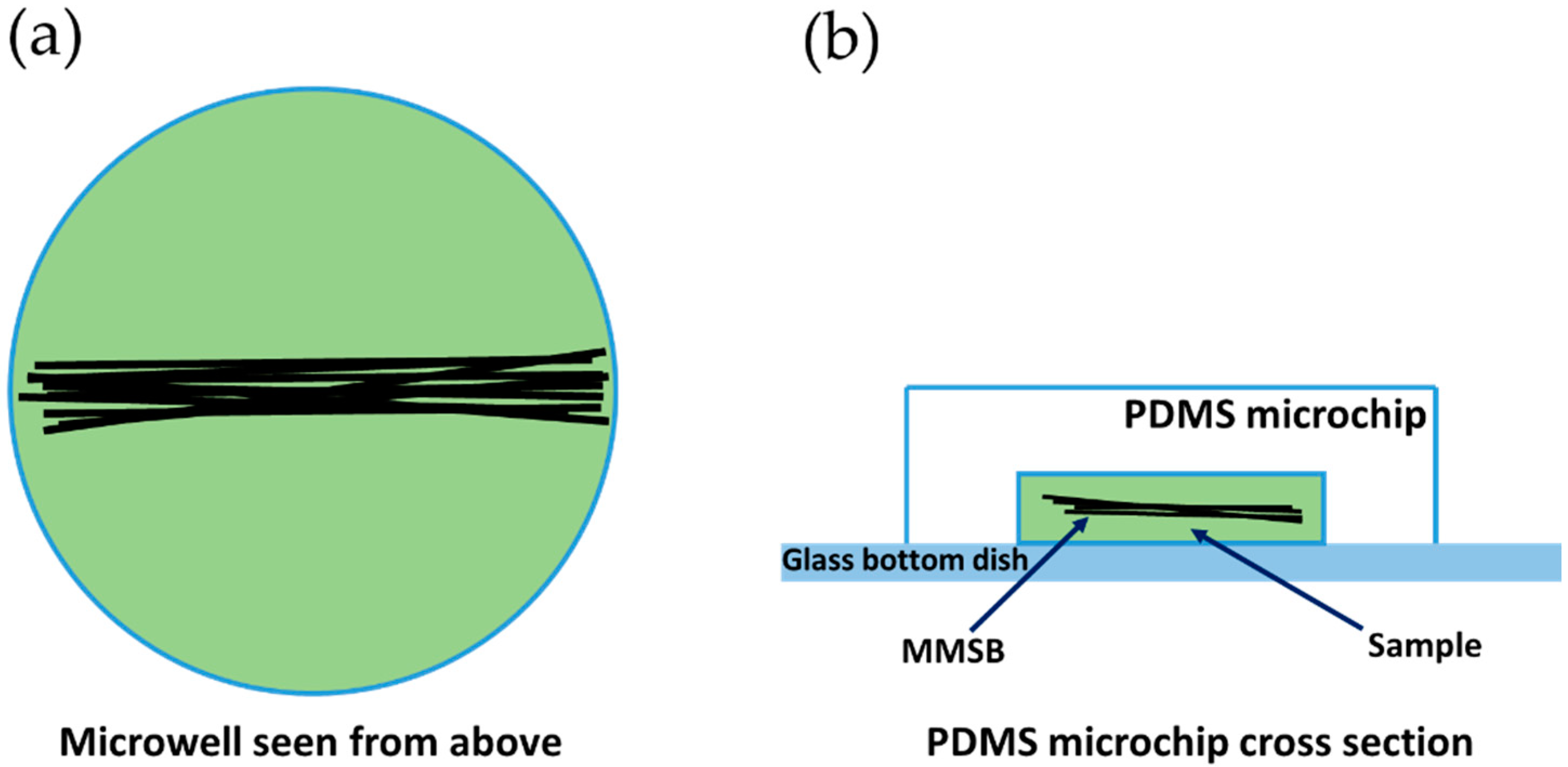
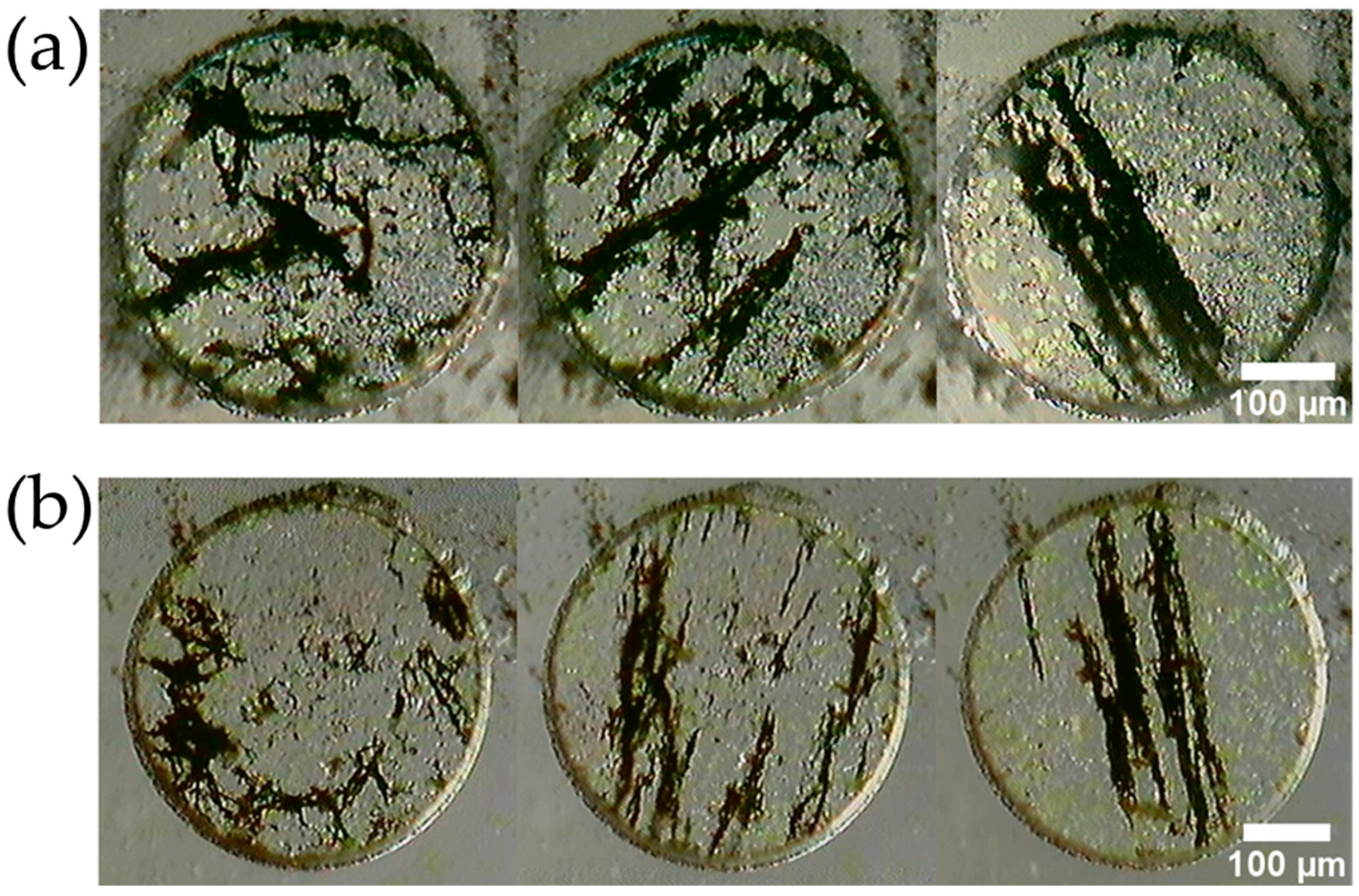
2.1. Fabrication Method for MMSB
2.2. Observation Method for MMSB
2.3. Sample Preparation
2.4. Effects of MMSB on C. reinhardtii
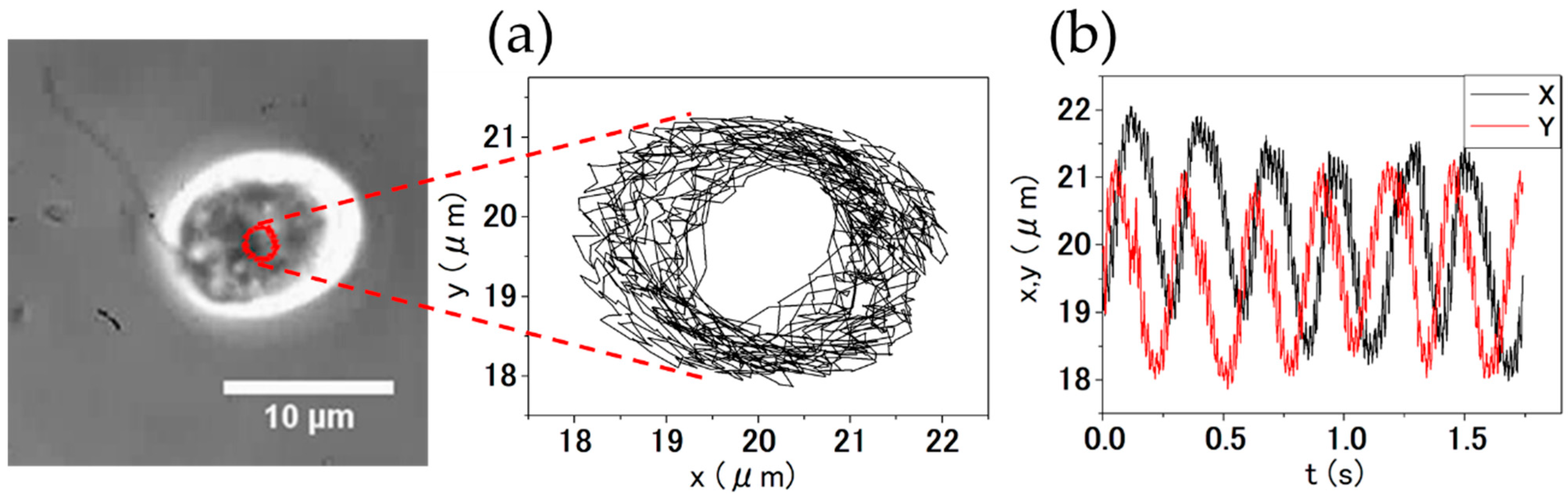
2.5. Observation of the Rotational Movement of C. reinhardtii
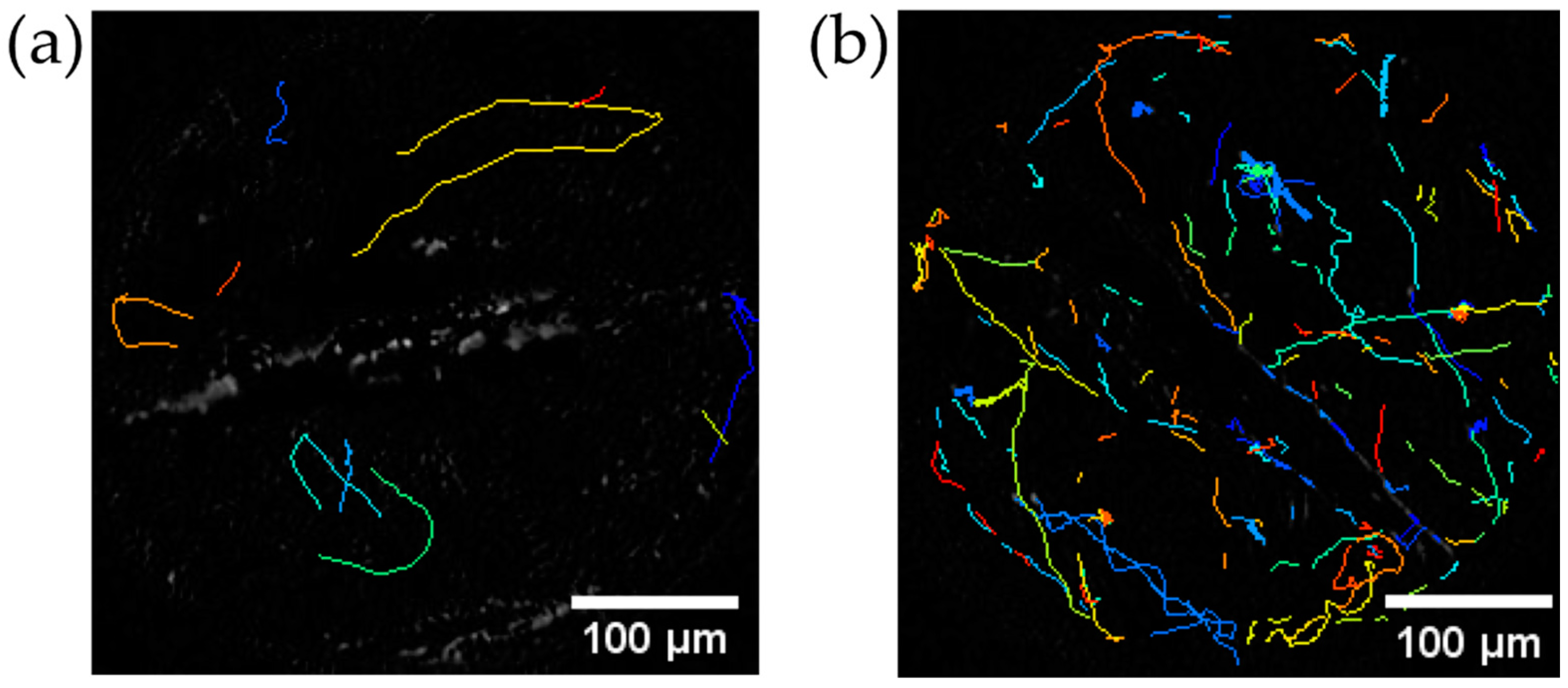
2.6. Trajectory Analysis of C. reinhardtii after Stirring
3. Results
4. Discussion
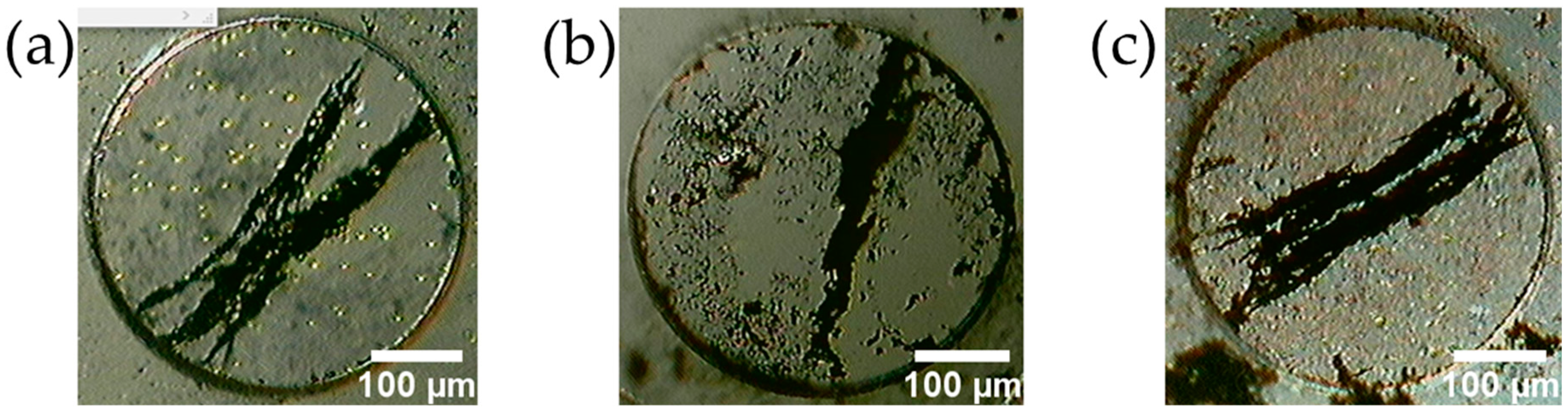
4.1. Characteristics of the Fabricated MMSB
4.2. Effects of MMSB on C. reinhardtii
4.3. Orbital Motion of C. reinhardtii
4.4. Trajectory of C. reinhardtii before and after Stirring
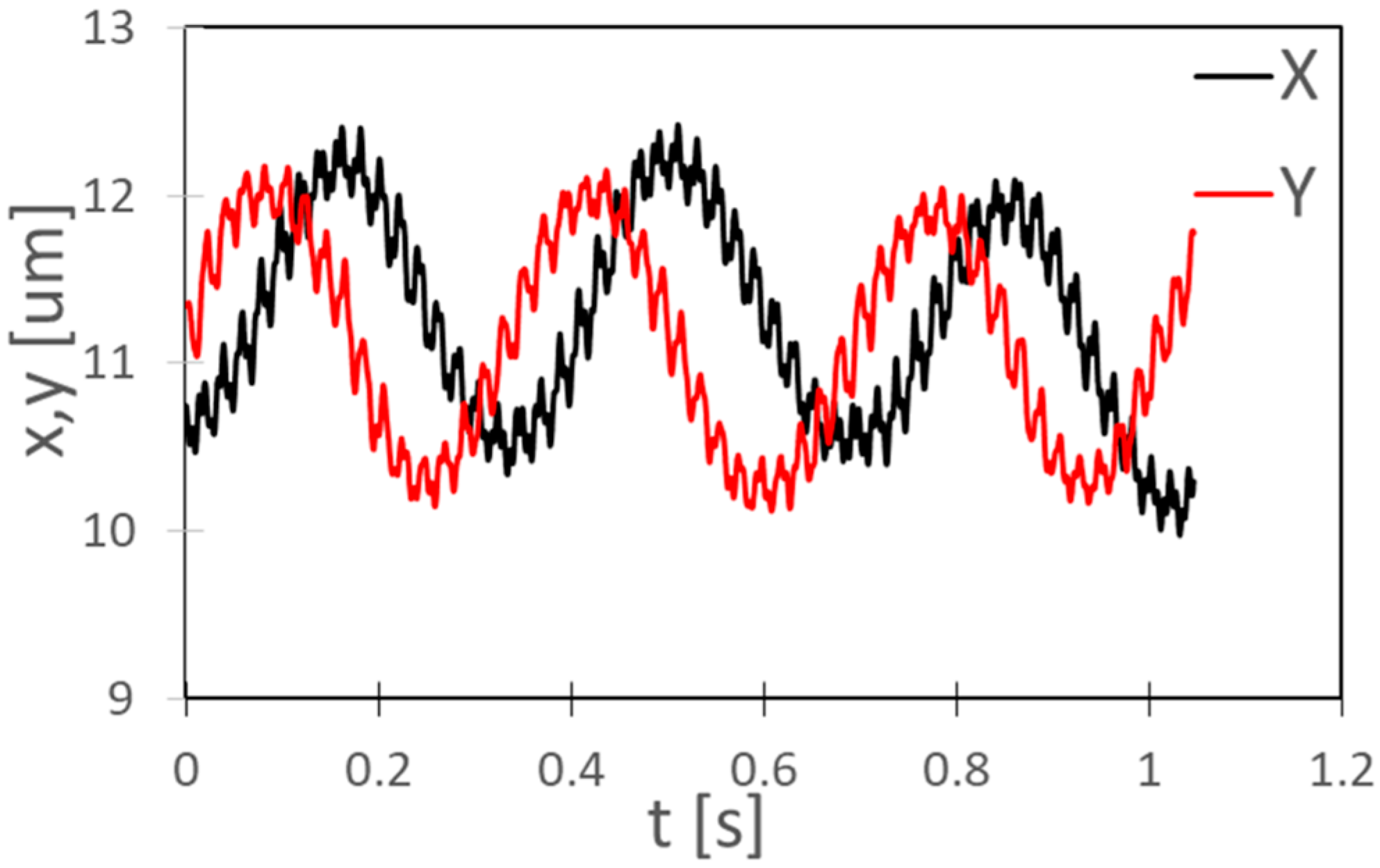
4.5. Kinematic Analysis of the Rotational Motion of C. reinhardtii
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Xiong, Q.; Lim, C.Y.; Ren, J.; Zhou, J.; Pu, K.; Chan-Park, M.B.; Mao, H.; Lam, Y.C.; Duan, H. Magnetic Nanochain Integrated Microfluidic Biochips. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 1743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Reenen, A.; de Jong, A.M.; den Toonder, J.M.J.; Prins, M.W.J. Integrated Lab-on-Chip Biosensing Systems Based on Magnetic Particle Actuation—A Comprehensive Review. Lab Chip 2014, 14, 1966–1986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, T.-H. Micro Magnetic Gyromixer for Speeding up Reactions in Droplets. Microfluid. Nanofluid. 2012, 12, 787–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Bruyker, D.D.; Recht, M.I.; Bhagat, A.A.S.; Torres, F.E.; Bell, A.G.; Bruce, R.H. Rapid Mixing of Sub-Microlitre Drops by Magnetic Micro-Stirring. Lab Chip 2011, 11, 3313–3319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Kang, T.G.; Hulsen, M.A.; Anderson, P.D.; den Toonder, J.M.J.; Meijer, H.E.H. Chaotic Mixing Induced by a Magnetic Chain in a Rotating Magnetic Field. Phys. Rev. E 2007, 76, 066303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vázquez-Quesada, A.; Franke, T.; Ellero, M. Theory and Simulation of the Dynamics, Deformation, and Breakup of a Chain of Superparamagnetic Beads under a Rotating Magnetic Field. Phys. Fluids 2017, 29, 032006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franke, T.; Schmid, L.; Weitz, D.A.; Wixforth, A. Magneto-Mechanical Mixing and Manipulation of Picoliter Volumes in Vesicles. Lab Chip 2009, 9, 2831–2835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Hulsen, M.A.; Kang, T.G.; den Toonder, J.M.J. Numerical and Experimental Study of a Rotating Magnetic Particle Chain in a Viscous Fluid. Phys. Rev. E 2012, 86, 041503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vuppu, A.K.; Garcia, A.A.; Hayes, M.A. Video Microscopy of Dynamically Aggregated Paramagnetic Particle Chains in an Applied Rotating Magnetic Field. Langmuir 2003, 19, 8646–8653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, T.; Sinha, A.; Chakraborty, S.; Ganguly, R.; Puri, I.K. Magnetic Microsphere-Based Mixers for Microdroplets. Phys. Fluids 2009, 21, 027101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, M.; Gabayno, J.L.F.; Ye, R.; Huang, K.-W.; Chang, Y.-J. Mixing Efficiency Enhancing in Micromixer by Controlled Magnetic Stirring of Fe3O4 Nanomaterial. Microsyst. Technol. 2017, 23, 457–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chong, W.H.; Chin, L.K.; Tan, R.L.S.; Wang, H.; Liu, A.Q.; Chen, H. Stirring in Suspension: Nanometer-Sized Magnetic Stir Bars. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2013, 52, 8570–8573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruffert, C.; Ruffert, C. Magnetic Bead—Magic Bullet. Micromachines 2016, 7, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Y.; He, L.; Yin, Y. Magnetically Responsive Photonic Nanochains. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2011, 50, 3747–3750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pankhurst, Q.A.; Connolly, J.; Jones, S.K.; Dobson, J. Applications of Magnetic Nanoparticles in Biomedicine. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2003, 36, R167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gijs, M.A.M. Magnetic Bead Handling on-Chip: New Opportunities for Analytical Applications. Microfluid. Nanofluid 2004, 1, 22–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peyer, K.E.; Zhang, L.; Nelson, B.J. Bio-Inspired Magnetic Swimming Microrobots for Biomedical Applications. Nanoscale 2013, 5, 1259–1272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilfan, M.; Potočnik, A.; Kavčič, B.; Osterman, N.; Poberaj, I.; Vilfan, A.; Babič, D. Self-Assembled Artificial Cilia. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 1844–1847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, L.; Zhu, Y.-Z.; Wang, H.-F. Nickel-Decorated Fe3O4 Nanoparticles as Recyclable Magnetic Self-Stirring Nanocatalysts for Microreactions. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2017, 5, 1864–1870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Fu, J.; Wang, K.; Gao, M.; Wang, X.; Wang, Z.; Chen, J.; Xu, Q. Facile Synthesis of Pd Nanoparticles on Polydopamine-Coated Fe-Fe2O3 Magnetic Nanochains as Recyclable High-Performance Nanocatalysts. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2018, 459, 208–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Kim, J.; Kim, H.; Kim, J.; Kwon, S. Colour-Barcoded Magnetic Microparticles for Multiplexed Bioassays. Nat. Mater. 2010, 9, 745–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kavaldzhiev, M.; Perez, J.E.; Ivanov, Y.; Bertoncini, A.; Liberale, C.; Kosel, J. Biocompatible 3D Printed Magnetic Micro Needles. Biomed. Phys. Eng. Express 2017, 3, 025005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, E.H. The Chlamydomonas Sourcebook, 2nd ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Yagi, T.; Yamashita, K.; Okada, N.; Isono, T.; Momose, D.; Mineki, S.; Tokunaga, E. Hydrogen Photoproduction in Green Algae Chlamydomonas reinhardtii Sustainable over 2 Weeks with the Original Cell Culture without Supply of Fresh Cells nor Exchange of the whole Culture Medium. J. Plant Res. 2016, 129, 771–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Isono, T.; Yamashita, K.; Momose, D.; Kobayashi, H.; Kitamura, M.; Nishiyama, Y.; Hosoya, T.; Kanda, H.; Kudo, A.; Okada, N.; et al. Scan-Free Absorbance Spectral Imaging A(x, y, λ) of Single Live Algal Cells for Quantifying Absorbance of Cell Suspensions. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0128002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Barber, C.F.; Heuser, T.; Carbajal-González, B.I.; Botchkarev, V.V.; Nicastro, D. Three-Dimensional Structure of the Radial Spokes Reveals Heterogeneity and Interactions with Dyneins in Chlamydomonas Flagella. MBoC 2012, 23, 111–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayly, P.V.; Lewis, B.L.; Ranz, E.C.; Okamoto, R.J.; Pless, R.B.; Dutcher, S.K. Propulsive Forces on the Flagellum during Locomotion of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Biophys. J. 2011, 100, 2716–2725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lefebvre, P.A. Cilia and Flagella Chapter 1 Flagellar Amputation and Regeneration in Chlamydomonas. In Methods in Cell Biology; Dentler, W., Witman, G., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1995; Volume 47, pp. 3–7. [Google Scholar]
- Guasto, J.S.; Johnson, K.A.; Gollub, J.P. Oscillatory Flows Induced by Microorganisms Swimming in Two Dimensions. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2010, 105, 168102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Böddeker, T.J.; Karpitschka, S.; Kreis, C.T.; Magdelaine, Q.; Bäumchen, O. Dynamic Force Measurements on Swimming Chlamydomonas Cells Using Micropipette Force Sensors. J. R. Soc. Interface 2020, 17, 20190580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, Y.J.; Zhu, L.; Teo, W.S.; Tan, Y.W.; Yang, Y.; Wang, C.; Chen, H. Revisiting the Stöber Method: Inhomogeneity in Silica Shells. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2011, 133, 11422–11425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, J.; Yin, Y. Magnetically Tunable Colloidal Photonic Structures in Alkanol Solutions. Adv. Mater. 2008, 20, 3485–3491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biswal, S.L.; Gast, A.P. Micromixing with Linked Chains of Paramagnetic Particles. Anal. Chem. 2004, 76, 6448–6455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, S.; Wu, L.; Tong, Z.; Chen, H.-E.; Chen, Z.; Uchimoto, T.; Takagi, T. Influence of Plastic Deformation and Fatigue Damage on Electromagnetic Properties of 304 Austenitic Stainless Steel. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2018, 54, 6201710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, J.C.; Merchant, S.S. Photo-Oxidative Stress Impacts the Expression of Genes Encoding Iron Metabolism Components in Chlamydomonas. Photochem. Photobiol. 2008, 84, 1395–1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glaesener, A.G.; Merchant, S.S.; Blaby-Haas, C.E. Iron Economy in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Front. Plant Sci. 2013, 4, 337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eckhardt, U.; Buckhout, T.J. Iron Assimilation in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii Involves Ferric Reduction and Is Similar to Strategy I Higher Plants. J. Exp. Bot. 1998, 49, 1219–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Beerens, J.; van Reenen, A.; Hulsen, M.A.; de Jong, A.M.; Prins, M.W.J.; den Toonder, J.M.J. Strong Vortical Flows Generated by the Collective Motion of Magnetic Particle Chains Rotating in a Fluid Cell. Lab Chip 2015, 15, 351–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamb, H. Hydrodynamics; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1895. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Q.; Prosperetti, A. Wall Effects on a Rotating Sphere. J. Fluid Mech. 2010, 657, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yagi, T.; Minoura, I.; Fujiwara, A.; Saito, R.; Yasunaga, T.; Hirono, M.; Kamiya, R. An Axonemal Dynein Particularly Important for Flagellar Movement at High Viscosity: Implications from a New Chlamydomonas Mutant Deficient in the Dynein Heavy Chain Gene DHC9. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 41412–41420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minoura, I.; Kamiya, R. Strikingly Different Propulsive Forces Generated by Different Dynein-Deficient Mutants in Viscous Media. Cell Motil. Cytoskelet. 1995, 31, 130–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCord, R.P.; Yukich, J.N.; Bernd, K.K. Analysis of Force Generation during Flagellar Assembly through Optical Trapping of Free-Swimming Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Cell Motil. Cytoskelet. 2005, 61, 137–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Material of MMSB | Stability of Bar Shape | Magnetism | Cytotoxicity |
|---|---|---|---|
| Neodymium magnet | Stable | Very strong | High |
| SUS304 | Unstable | Very weak | Medium |
| Magnet sheet | Stable | Strong | Low |
| Material of MMSB | Effects on the Cells |
|---|---|
| Neodymium magnet | Under weak light with a PFD of 5 μmol m−2 s−1, cells stopped moving in 10 min. |
| SUS304 | Under weak light with a PFD of 5 μmol m−2 s−1, cells weakened over time (over 10 min). Under a lower PFD, motility recovered. |
| Magnet sheet | Under medium light with a PFD of 100 μmol m−2 s−1, the cells survived actively for several days. |
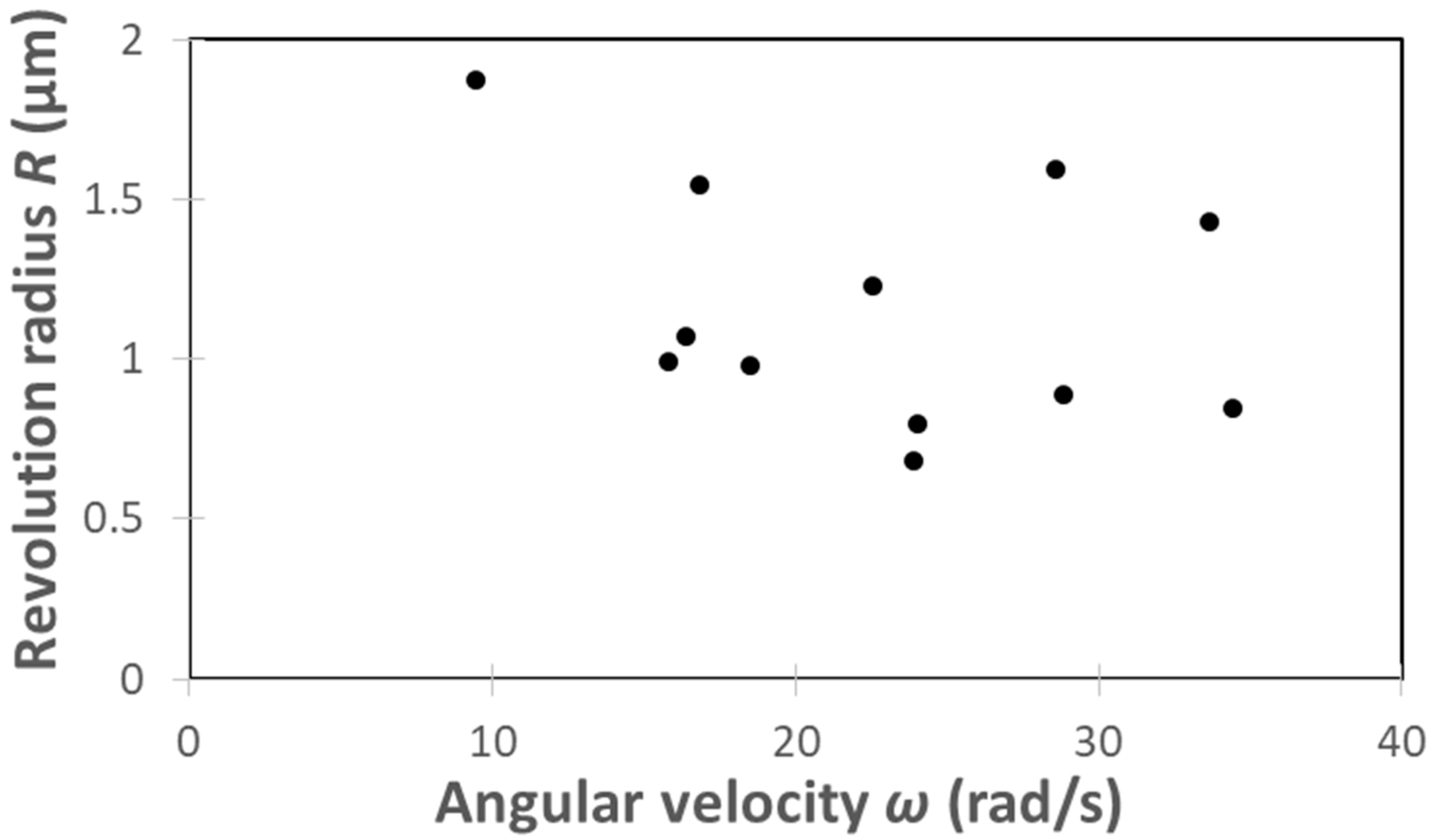
| C. reinhardtii | Angular Velocity ω (rad/s) | Revolution Radius R (μm) |
|---|---|---|
| ① | 28.81 | 0.89 |
| ② | 34.42 | 0.84 |
| ③ | 24.05 | 0.80 |
| ④ | 33.66 | 1.43 |
| ⑤ | 23.91 | 0.68 |
| ⑥ | 18.52 | 0.98 |
| ⑦ | 28.57 | 1.59 |
| ⑧ | 16.87 | 1.55 |
| ⑨ | 9.48 | 1.87 |
| ⑩ | 16.36 | 1.07 |
| ⑪ | 15.81 | 0.99 |
| ⑫ | 22.54 | 1.23 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shimizu, I.; Yamashita, K.; Tokunaga, E. Development of a Simple Fabrication Method for Magnetic Micro Stir Bars and Induction of Rotational Motion in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Micromachines 2022, 13, 1842. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi13111842
Shimizu I, Yamashita K, Tokunaga E. Development of a Simple Fabrication Method for Magnetic Micro Stir Bars and Induction of Rotational Motion in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Micromachines. 2022; 13(11):1842. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi13111842
Chicago/Turabian StyleShimizu, Ichiro, Kyohei Yamashita, and Eiji Tokunaga. 2022. "Development of a Simple Fabrication Method for Magnetic Micro Stir Bars and Induction of Rotational Motion in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii" Micromachines 13, no. 11: 1842. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi13111842
APA StyleShimizu, I., Yamashita, K., & Tokunaga, E. (2022). Development of a Simple Fabrication Method for Magnetic Micro Stir Bars and Induction of Rotational Motion in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Micromachines, 13(11), 1842. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi13111842





