Utilization of Epidural Electrodes as a Diagnostic Tool in Intractable Epilepsy—A Technical Note
Abstract
:1. Introduction
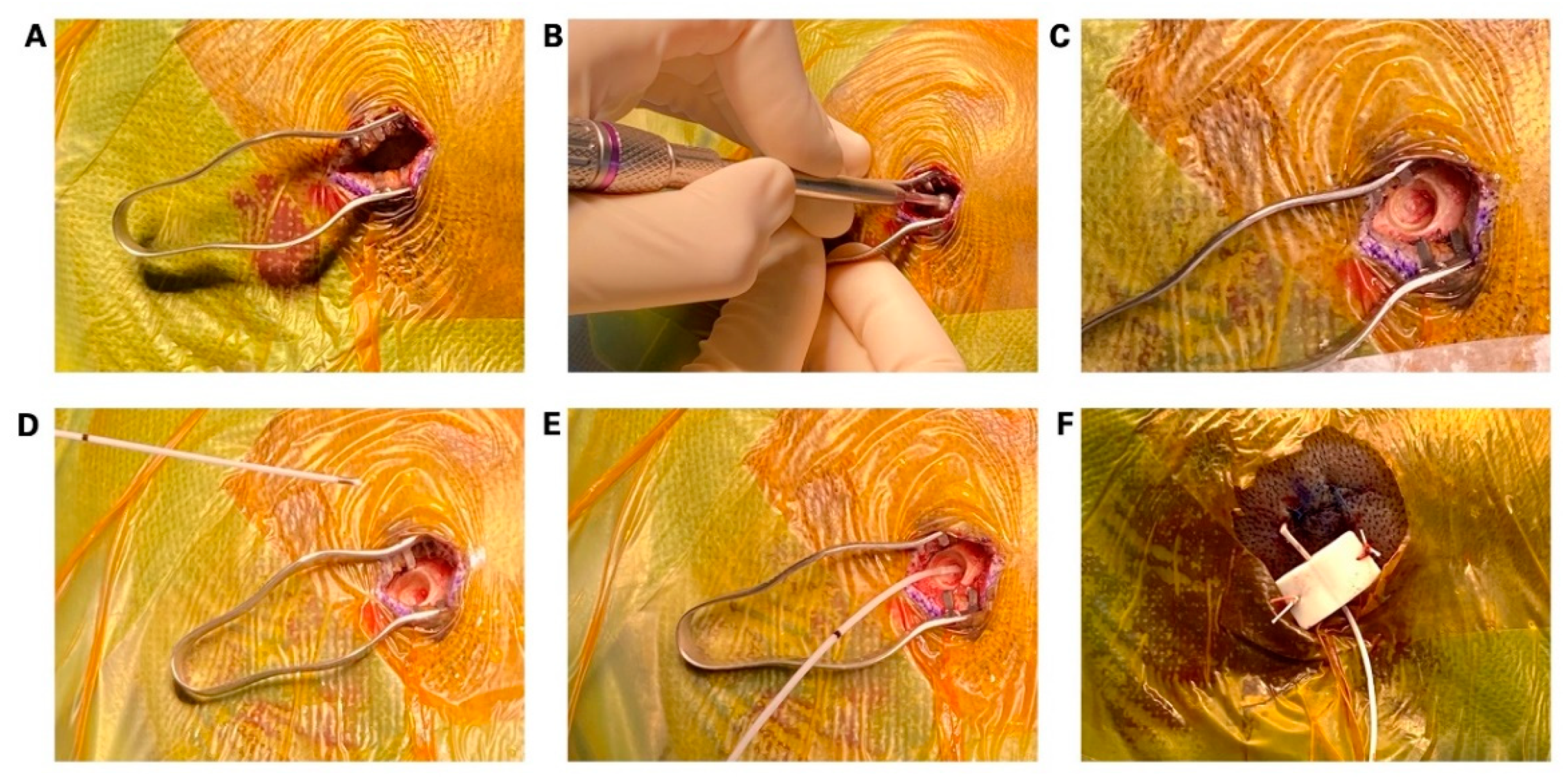
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
3.1. Patient Characteristics
3.2. Complications
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kwan, P.; Brodie, M.J. Early Identification of Refractory Epilepsy. N. Engl. J. Med. 2000, 342, 314–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dwivedi, R.; Ramanujam, B.; Chandra, P.S.; Sapra, S.; Gulati, S.; Kalaivani, M.; Garg, A.; Bal, C.S.; Tripathi, M.; Dwivedi, S.N.; et al. Surgery for Drug-Resistant Epilepsy in Children. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 377, 1639–1647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Picot, M.-C.; Jaussent, A.; Neveu, D.; Kahane, P.; Crespel, A.; Gelisse, P.; Hirsch, E.; Derambure, P.; Dupont, S.; Landré, E.; et al. Cost-effectiveness analysis of epilepsy surgery in a controlled cohort of adult patients with intractable partial epilepsy: A 5-year follow-up study. Epilepsia 2016, 57, 1669–1679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jayakar, P.; Gotman, J.; Harvey, A.S.; Palmini, A.; Tassi, L.; Schomer, D.; Dubeau, F.; Bartolomei, F.; Yu, A.; Kršek, P.; et al. Diagnostic utility of invasive EEG for epilepsy surgery: Indications, modalities, and techniques. Epilepsia 2016, 57, 1735–1747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Almeida, A.N.; Martínez, V.; Feindel, W. The First Case of Invasive EEG Monitoring for the Surgical Treatment of Epilepsy: Historical Significance and Context. Epilepsia 2005, 46, 1082–1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Awad, I.A.; Assirat, J.A.; Burgess, R.; Barnett, G.H.; Luders, H. A new class of electrodes of ‘Intermediate Invasiveness’: Preliminary experience with epidural pegs and foramen ovale electrodes in the mapping of seizure foci. Neurol. Res. 1991, 13, 177–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barnett, G.H.; Burgess, R.C.; Awad, I.A.; Skipper, G.J.; Edwards, C.R.; Luders, H. Epidural peg electrodes for the presurgical evaluation of intractable epilepsy. Neurosurgery 1990, 27, 113–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldring, S.; Gregorie, E.M. Surgical management of epilepsy using epidural recordings to localize the seizure focus. J. Neurosurg. 1984, 60, 457–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kuzniecky, R.; Faught, E.; Morawetz, R. Surgical Treatment of Epilepsy: Initial Results Based Upon Epidural Electroencephalographic Recordings. South. Med. J. 1990, 83, 637–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hedegärd, E.; Bjellvi, J.; Edelvik, A.; Rydenhag, B.; Flink, R.; Malmgren, K. Complications to invasive epilepsy surgery workup with subdural and depth electrodes: A prospective population-based observational study. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2013, 85, 716–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Schmidt, R.F.; Wu, C.; Lang, M.J.; Soni, P.; Williams, K.A.; Boorman, D.; Evans, J.J.; Sperling, M.R.; Sharan, A.D. Complications of subdural and depth electrodes in 269 patients undergoing 317 procedures for invasive monitoring in epilepsy. Epilepsia 2016, 57, 1697–1708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wellmer, J.; von der Groeben, F.; Klarmann, U.; Weber, C.; Elger, C.E.; Urbach, H.; Clusmann, H.; von Lehe, M. Risks and benefits of invasive epilepsy surgery workup with implanted subdural and depth electrodes. Epilepsia 2012, 53, 1322–1332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Byrne, R.W.; Jobe, K.W.; Smith, M.C.; Kanner, A.; Bergen, D.C.; Palac, S.M.; Balabanov, A.J.; Ajiboye, N.A.; Takagi, I.; Whisler, W.W. Epidural cylinder electrodes for presurgical evaluation of intractable epilepsy: Technical note. Surg. Neurol. 2008, 70, 160–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arya, R.; Mangano, F.T.; Horn, P.S.; Holland, K.D.; Rose, D.F.; Glauser, T.A. Adverse events related to extraoperative invasive EEG monitoring with subdural grid electrodes: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Epilepsia 2013, 54, 828–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lee, W.-S.; Lee, J.-K.; Lee, S.-A.; Kang, J.-K.; Ko, T.-S. Complications and results of subdural grid electrode implantation in epilepsy surgery. Surg. Neurol. 2000, 54, 346–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| 1-Contact Electrodes (1-CE) | Peg Electrodes | ||
|---|---|---|---|
 | platinum contact cylindrical-shaped removable stylet contact length: 2.41 mm diameter: 1.12 mm total length: 330 mm |  | platinum contact mushroom-shaped (material: polyurethane [shaft] and silicone [cap]) length of shaft: 3–19 mm diameter: 3.5 mm total length: 200 mm |
| Age | |
|---|---|
| median (range) | 36.3 (17–57) |
| Gender | |
| female | 30 |
| male | 26 |
| diverse | 0 |
| Implanted electrodes | 507 |
| Epidural electrodes | 381 |
| Peg (old) | 222 |
| 3 mm | 3 |
| 4 mm | 34 |
| 5 mm | 29 |
| 6 mm | 46 |
| 7 mm | 30 |
| 8 mm | 29 |
| 9 mm | 15 |
| 10 mm | 24 |
| 11 mm | 2 |
| 12 mm | 10 |
| 1-CE (new) | 159 |
| Fo electrodes | 93 |
| Depth electrodes | 33 |
| Surgical time | |
| total (mean ± SD) | 100.5 ± 38 min |
| time/electrode (mean ± SD) | 11.8 ± 5 min |
| Complications | Revision Surgery | Electrode | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Complication Rate | |||
| Fo dislocation | 8 | 7 | 8/93 (8.6%) |
| Dura laceration | 6 | 0 | 6/381 (1.6%) |
| Epidural electrodes | 6 | 1 | 6/381 (1.6%) |
| Peg dislocation | 3 | 3/222 (1.4%) | |
| 1-CE | 2 | 2/159 (1.3%) | |
| 1-CE malfunction | 1 | 1/159 (0.6%) | |
| wound infection | 3 | 3 | |
| hemorrhage | 2 | 2/33 (6.1%) | |
| from depth electrodes | |||
| total | 24 | 11 | 14/507 (3.2%) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xu, R.; Achberger, J.; Wedel, D.v.; Vajkoczy, P.; Onken, J.; Schneider, U.C. Utilization of Epidural Electrodes as a Diagnostic Tool in Intractable Epilepsy—A Technical Note. Micromachines 2022, 13, 397. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi13030397
Xu R, Achberger J, Wedel Dv, Vajkoczy P, Onken J, Schneider UC. Utilization of Epidural Electrodes as a Diagnostic Tool in Intractable Epilepsy—A Technical Note. Micromachines. 2022; 13(3):397. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi13030397
Chicago/Turabian StyleXu, Ran, Johannes Achberger, Dario von Wedel, Peter Vajkoczy, Julia Onken, and Ulf C. Schneider. 2022. "Utilization of Epidural Electrodes as a Diagnostic Tool in Intractable Epilepsy—A Technical Note" Micromachines 13, no. 3: 397. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi13030397
APA StyleXu, R., Achberger, J., Wedel, D. v., Vajkoczy, P., Onken, J., & Schneider, U. C. (2022). Utilization of Epidural Electrodes as a Diagnostic Tool in Intractable Epilepsy—A Technical Note. Micromachines, 13(3), 397. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi13030397







