1. Introduction
The tactile sensor can provide useful contact information for robot feedback and control to better complete manipulation tasks in a complex environment. Existing research on tactile sensors has achieved monitoring of static contact information, such as temperature, curvature, and contact force [
1,
2,
3], but the research on the acquisition of dynamic contact information is not thorough enough. Surface texture information, that is, the height, width, spatial period, and other texture shape information of the contacted object, is an important part of the dynamic contact information. It has been proved that the tactile sensing detection of the surface texture information of the object is helpful for dexterous manipulation [
4,
5] and minimally invasive surgery [
6,
7]. Vision is also an effective method to obtain surface texture information [
8], but due to the uncertainty of the viewing angle during operation, the visual perception is often limited. In addition, it is noteworthy that the sensing process of the tactile sensor is the exploratory movement of the sensor sliding on the surface to obtain texture information, such as vibration information [
9]. In other words, as long as the sensor has sufficient performance and can touch well the object, the surface texture information of the object can be obtained even under complex manipulation conditions.
Some existing researches use multi-array tactile sensors and fast Fourier transform (FFT, hereafter) technology to obtain characteristic signals and estimate the surface texture information of objects, which had certain limitations. In 2011, C.M. Oddo et al. [
10,
11] developed a 2 × 2 MEMS piezoresistive tactile sensor array with high spatial resolution and sensitivity and integrated it on the fingertips of humanoid robot fingers with bionic fingerprints. When actively touching, it could quantitatively evaluate the ridge texture with a spatial period difference as low as 40 μm (400, 440, 480 μm spatial periods, 1 mm ridge height). H.B. Muhammad et al. [
12] proposed a capacitive tactile sensor array based on silicon MEMS, which resolved forces in the sub-mN range and successfully distinguished fine ridge textures with ridge heights of 200 μm and spatial periods as low as 200 μm. However, the research mentioned above on object surface information detection mainly focused on the estimation of the spatial period of ridge textures in the micron range and did not reach the capability to detect fine textures with ridge heights of several microns, such as human fingers [
13,
14]. In order to eliminate the influence of the difference between the mechanical properties of structural materials such as friction and frequency characteristics and human fingers on the sliding tactile signal, in 2019, Yasutoshi Takekawa et al. [
15,
16,
17] developed a wearable skin vibration sensor to detect the skin-propagated vibration caused by finger rubbing an object surface, and successfully identified the spatial period and ridge height information of the fine ridge texture by calculating the power spectral density of the sensor output signal. The minimum ridge height of the fine texture exceeded the limitation to 25 μm, but in this situation, the characteristic of the signal was already very weak, and the detectable performance of the signal was limited.
Another commonly used method is using the tactile signal obtained by the designed tactile sensor for machine learning to classify and identify the surface texture of the object. In 2012, in order to achieve the ability of human fingertips to detect texture, Jeremy A. Fishel et al. [
18,
19] proposed Bio-Tac, a tactile finger with a solid–liquid composite structure, which could transmit the vibration of the skin through an incompressible liquid. The tactile finger could detect continuous vibrations as small as a few nanometers at 330 Hz and very small transient events that occurred when small particles fell on the finger, which was beyond human fingers’ capabilities. The Bayesian exploration method was used to classify 16 natural textures with an accuracy of 99.6%. In 2017, Udaya B. Rongala et al. [
20,
21] imported the output signal of the 2 × 2 piezoresistive tactile sensor array into the lzhikevich neuron model to enable neuromorphic artificial touch and simulate the firing pattern of mechanoreceptors in the skin. The generated neural spike pattern was used to perform neural network learning and classification of 10 natural textures, including glass materials with a grain size of less than 90 nm. In 2019, Sriramana Sankar et al. [
5,
22] designed a flexible bionic finger integrated with a 3 × 3 tactile sensor array. When the finger touched seven different texture samples (flat, ridges, bumps), the corresponding tactile response also transformed into a neural spike pattern with different characteristics that simulated the firing pattern of mechanoreceptors, and the support vector machine classifier was used to learn and classify with an accuracy of 99.21%. The above research revealed the capability of simulating human tactile behavior and accurately classifying different texture information, including fine textures, but the detailed texture information is still insufficient, and the complex structure encapsulation and machine learning algorithms limit their applications.
To sum up, research on texture detection needs more extensive and systematic investigations. FFT processing directly on the tactile signals can quickly and easily obtain texture feature information, such as the spatial period and ridge height of the ridge texture. However, due to the limited performance of most simple-structured tactile sensors to discern the tiny structural variation, FFT processing does not perform well in situations of fine texture detection. Thus, a tactile sensor with a higher sensitivity is needed. However, the capability of the existing simple tactile sensor to detect weak force changes is still far behind that of humans [
23]. Another common processing method is the machine learning method. The tactile signals are used to train the models to accurately classify different textures, but that needs to go through a complicated learning process, and detailed feature information of the surface textures cannot be detected. Therefore, a universal, real-time method based on a tactile sensor with a simple structure for fine texture detection is extremely needed.
In the process of detecting fine textures, the signals generated by the tactile sensor are weak and may even be submerged in system noise, such as touch action noise, circuit noise, etc., resulting in its characteristics being difficult to detect. The stochastic resonance algorithm (SR, hereafter) is a commonly used weak signal detecting method, which adds random noise to the weak signal to improve the detectability of the target signal or enhance the accuracy of information interpretation [
24]. Through a series of psychophysical experiments, Kadir Beceren et al. [
25,
26] proved that SR could affect the difference threshold of human tactile sensation, and appropriate noise can enhance the accuracy of tactile sensing. Yuichi Kurita et al. [
27] used the SR to develop surgical forceps with sensorimotor-enhancing capabilities and verified its texture detection capability, which was of great help to surgeons in laparoscopic surgery. To this end, we have introduced the SR into our tactile sensor system to enhance the capability of our tactile sensor for fine textures detection.
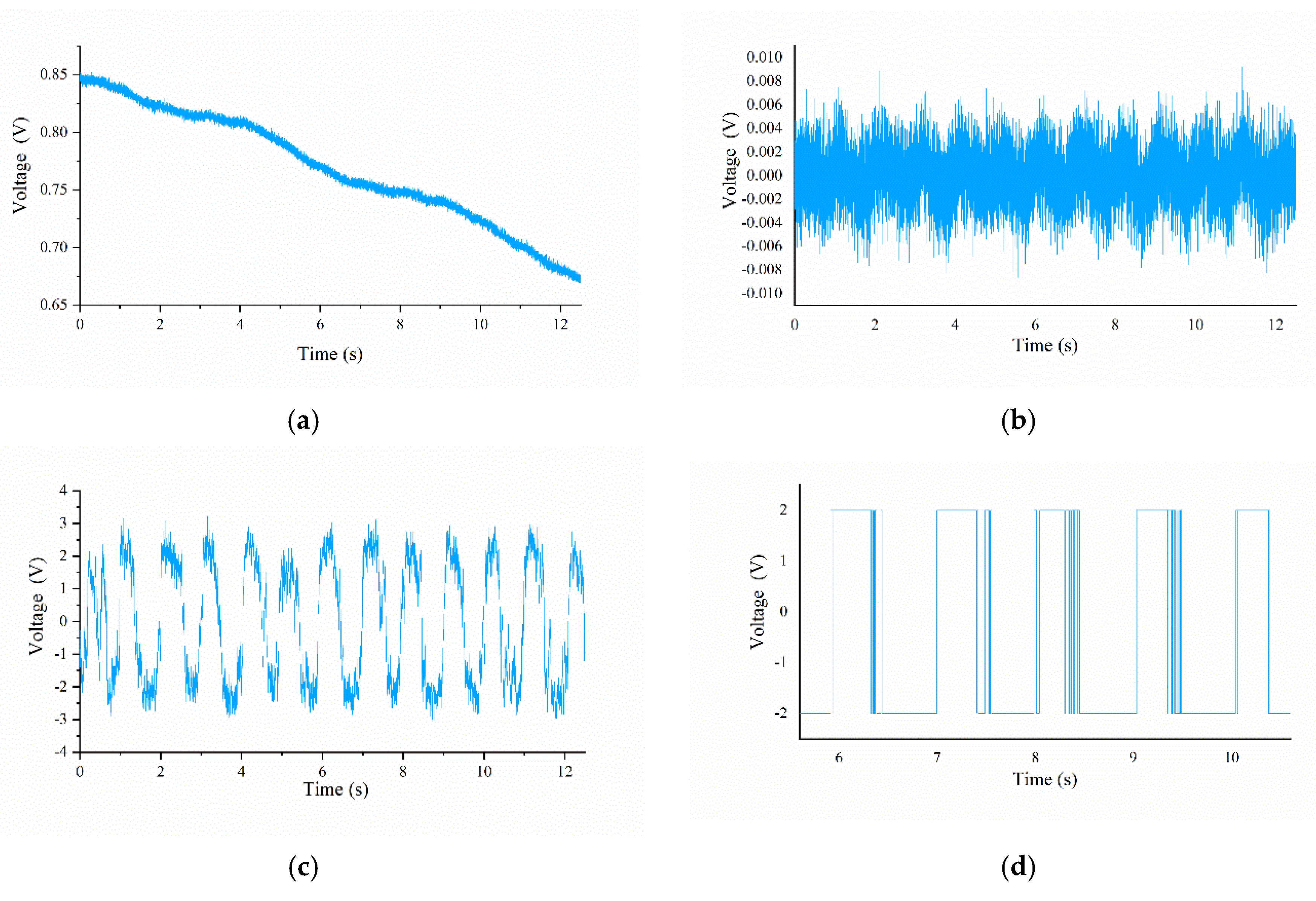
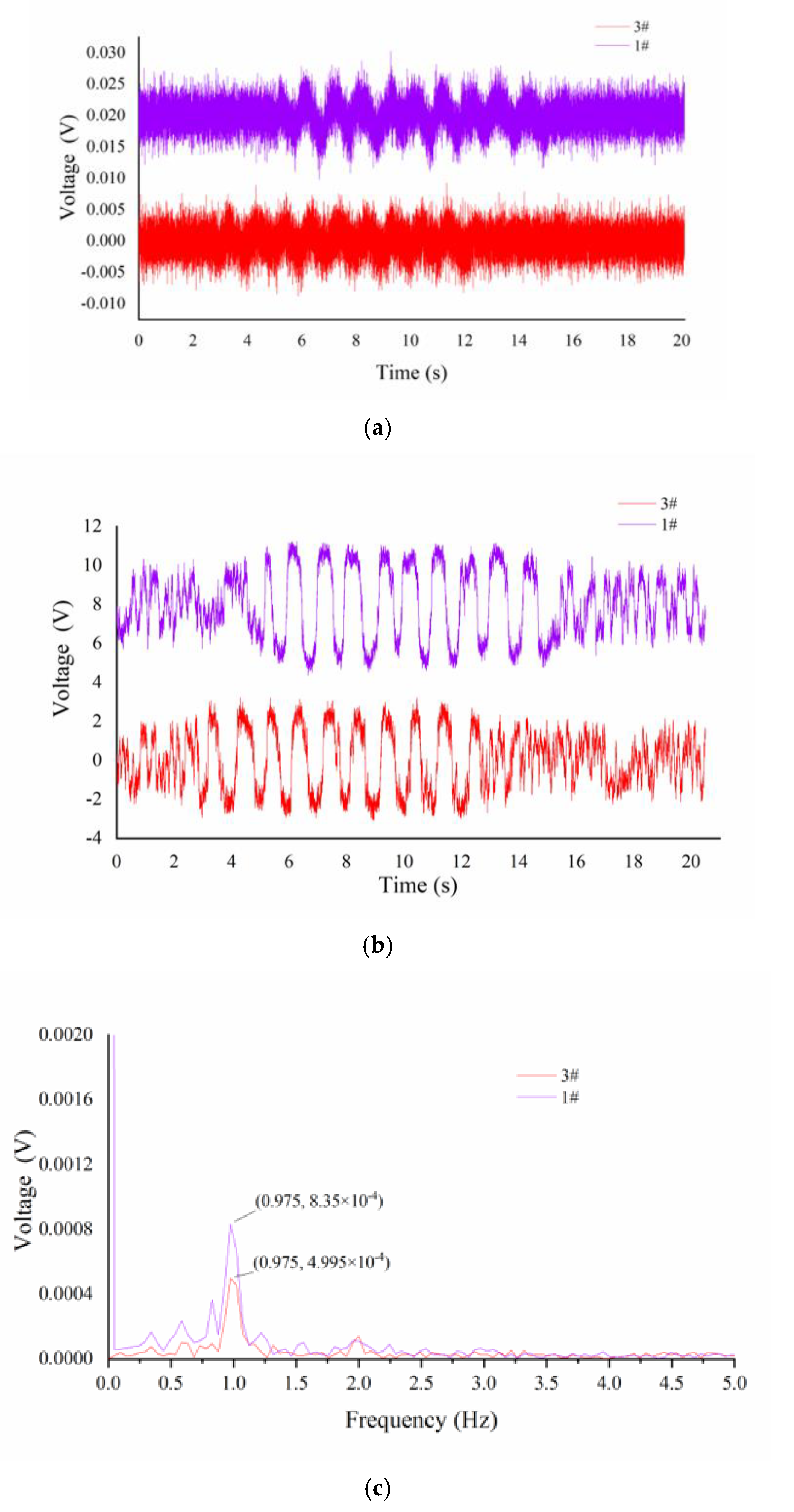
In this article, we use a 2 × 2 solid–liquid composite flexible tactile sensor array to obtain tactile information. A method of fine texture detection based on SR is put forward. By adding random noise to the output signal of the tactile sensor and inputting the mixed signal to a bistable SR model, we obtain tactile signals with strong signal characteristics and figure out the corresponding texture information through numerical analysis. The presence of the flexible layer will lead to a decrease in the transmission efficiency of the contact force, and the thicker the flexible layer, the greater the attenuation of the contact force [
28,
29]. It is meaningful to use a solid–liquid composite conduction structure to reduce the attenuation of the contact force through a flexible layer. Most of the existing tactile texture detection methods are aimed at the detection of micron-level fine texture or can only classify a limited number of textures. The method proposed in this article has the potential to detect sub-micron fine ridge texture. In addition, the authors estimate the texture features of the fine ridge texture, such as the spatial period, ridge height, and ridge width. At last, the authors present the signal characteristic change of the output tactile signal and the error of the texture characteristic value.
The rest of this article is organized as follows. The tactile sensor device is presented in
Section 2, followed by the introduction of the tactile signal processing methodology based on SR in
Section 3. Detailed experiments and experimental results are presented in
Section 4. Subsequently, the results are commented on in
Section 5. Finally, the conclusion and prospect are discussed in
Section 6.
2. Tactile Senor Device
In this article, we propose a 2 × 2 piezoresistive solid–liquid composite flexible sensor array to detect fine texture based on previous research in the laboratory [
30]. Piezoresistive sensors are small in size, have a good frequency response, and are especially sensitive to small pressure differences, which are easier to meet our requirements for tactile sensor arrays. The structure of the sensor is a thin flexible layer encapsulating the fluid and the silicon-sensing elements inside. We replaced some parts of the traditional single flexible layer with incompressible liquids to utilize the characteristics of high hydraulic transmission efficiency to reduce the attenuation of the contact force. Different from traditional hydraulic devices, the fluid chamber of this sensor cell is made of soft material, and there is a coupling effect between its deformation and the encapsulated liquid compression. Therefore, when the flexible layer is deformed by external pressure and compresses the liquid inside, the encapsulated liquid will generate pressure to act on the sensing elements, causing it to produce a corresponding output. After the output signal is conditioned by the NSA2860 chip, the encapsulated sensing cell has good sensing performances, with a sensitivity of 3.46 mV/mN, linearity of 0.996, repeatability error of 1.2%, and hysteresis error of 1.5%. The force sensing range is from 1 mN to 1.5 N.
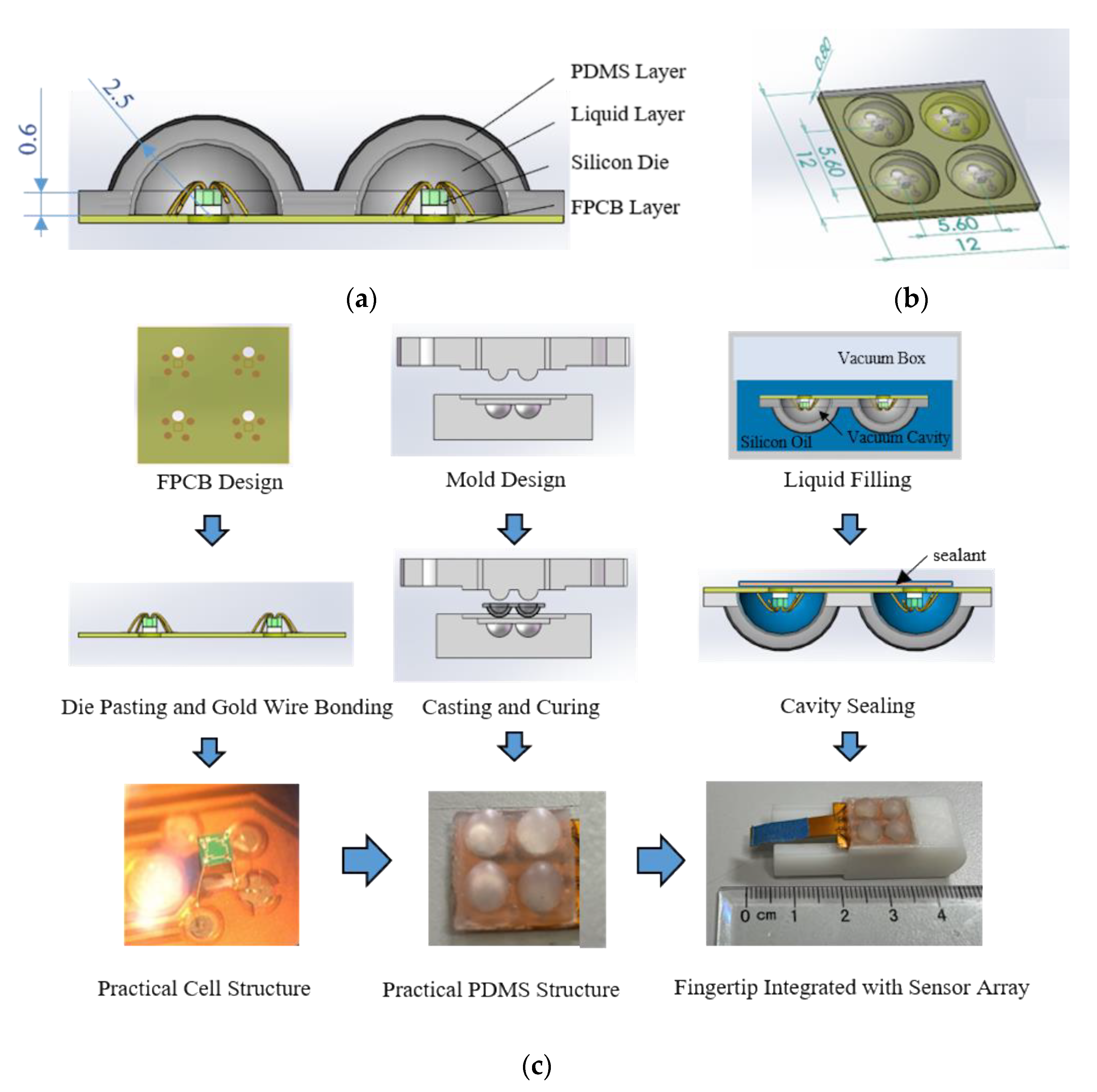
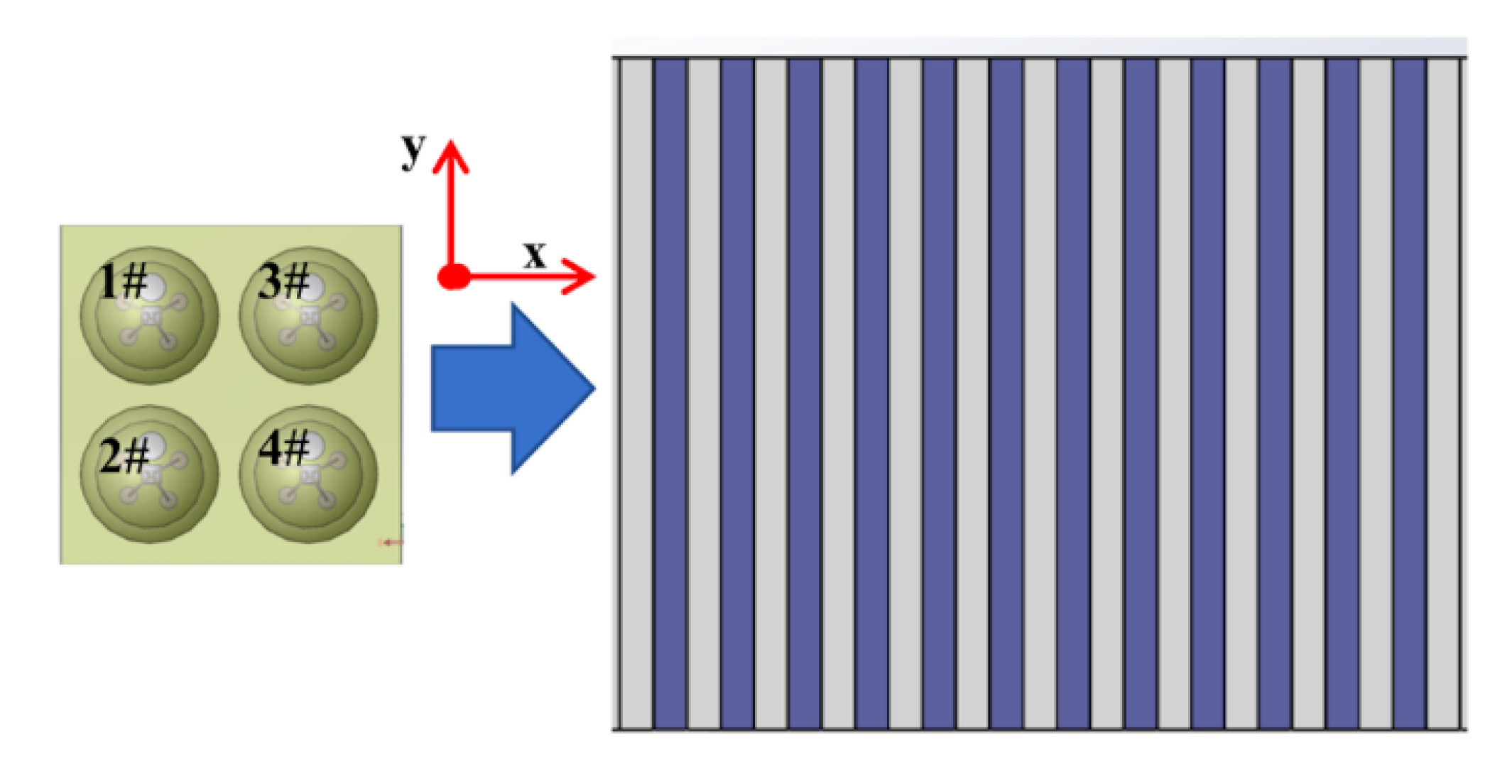
The structure of the sensing cell is shown in
Figure 1a. The sensor array mainly consists of four parts: flexible printed circuit board (FPCB, hereafter) base, silicon pressure sensing die, silicone oil liquid layer, and polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS, hereafter) layer. The overall size is 12 mm × 12 mm × 2.5 mm, including four sensor cells in a 2 × 2 layout, with the spacing of sensor cells of 5.6 mm. The thickness of the PDMS flexible layer is 0.6 mm. The selected piezoresistive sensor element was a cubic silicon pressure sensor die (Silicon Microstructures, Inc., SM5108C-060, Milpitas, CA, USA). The silicone oil liquid layer was filled with 50cSt silicone oil (Dow Corning Inc. pmx-200, Midland, MI, USA). The silicone oil liquid not only acts as a transferring medium of pressure conduction but also effectively protects the silicon-based sensing element. The schematic diagram of the sensor array is shown in
Figure 1b. To sum up, the whole sensor has a size similar to a human fingertip and is made of flexible material, which is easy to integrate on the prosthetic fingertip with various curves on its surface.
The sensor fabrication process is shown in
Figure 1c. Firstly, paste the sensing element on the FPCB base and connect the four pads on the sensing element and the corresponding pads on the FPCB base with gold wires, respectively; secondly, design the mold and obtain the shaped PDMS layer through casting and curing, then paste it on the FPCB base to form the liquid cavity; thirdly, evacuate the air in the liquid cavity and fill it with silicone oil in the vacuum box; fourthly, take the sensor out and seal the structure with sealant; finally, integrate the prepared sensor array on the fingertip of the prosthesis.
5. Discussion
In the existing research on fine texture detection using tactile technology, HB Muhammad et al. [
12] successfully distinguished ridge texture samples with a ridge height of 200 μm and a spatial period as low as 200 μm. Yasutoshi Takekawa et al. [
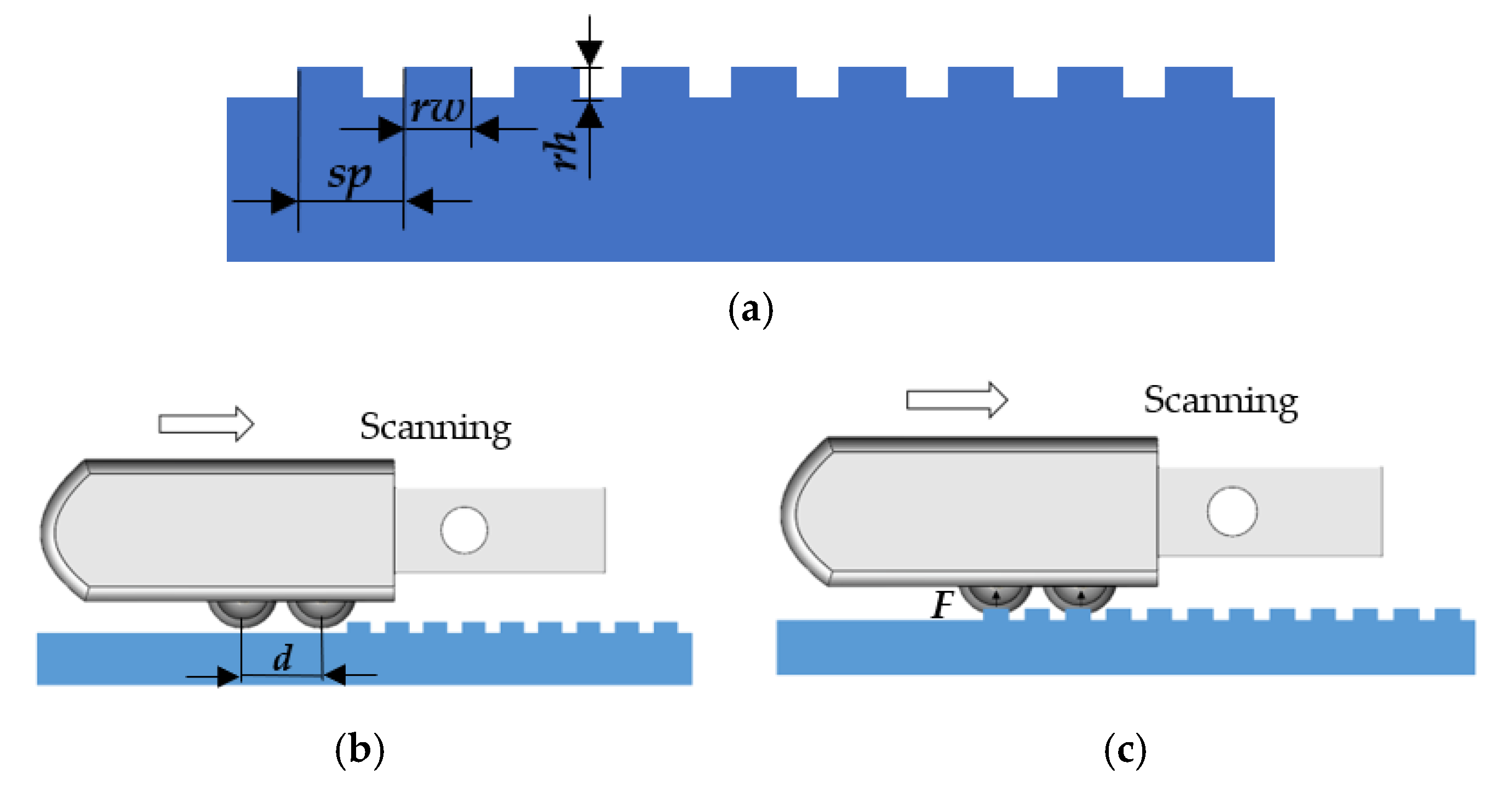
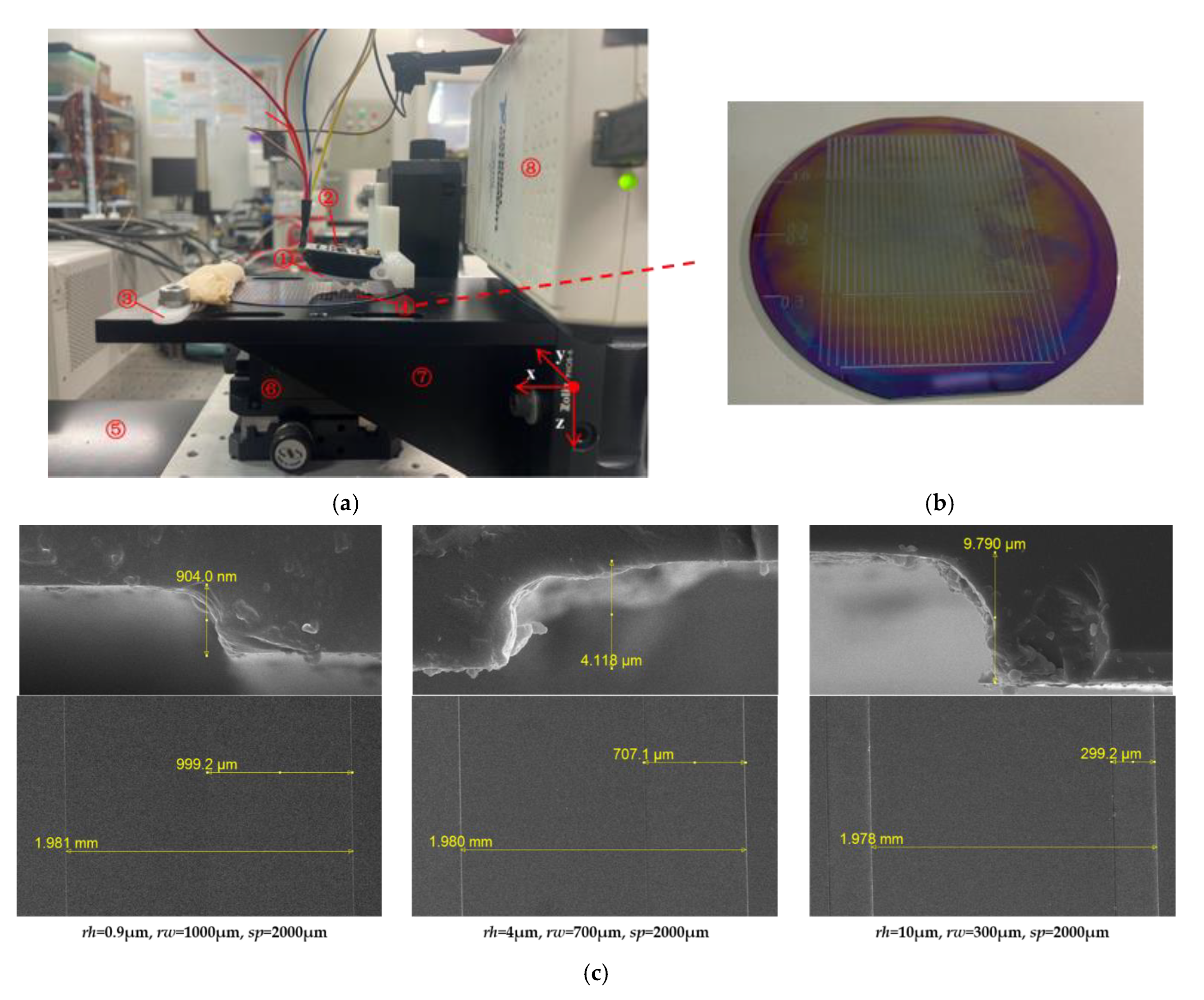
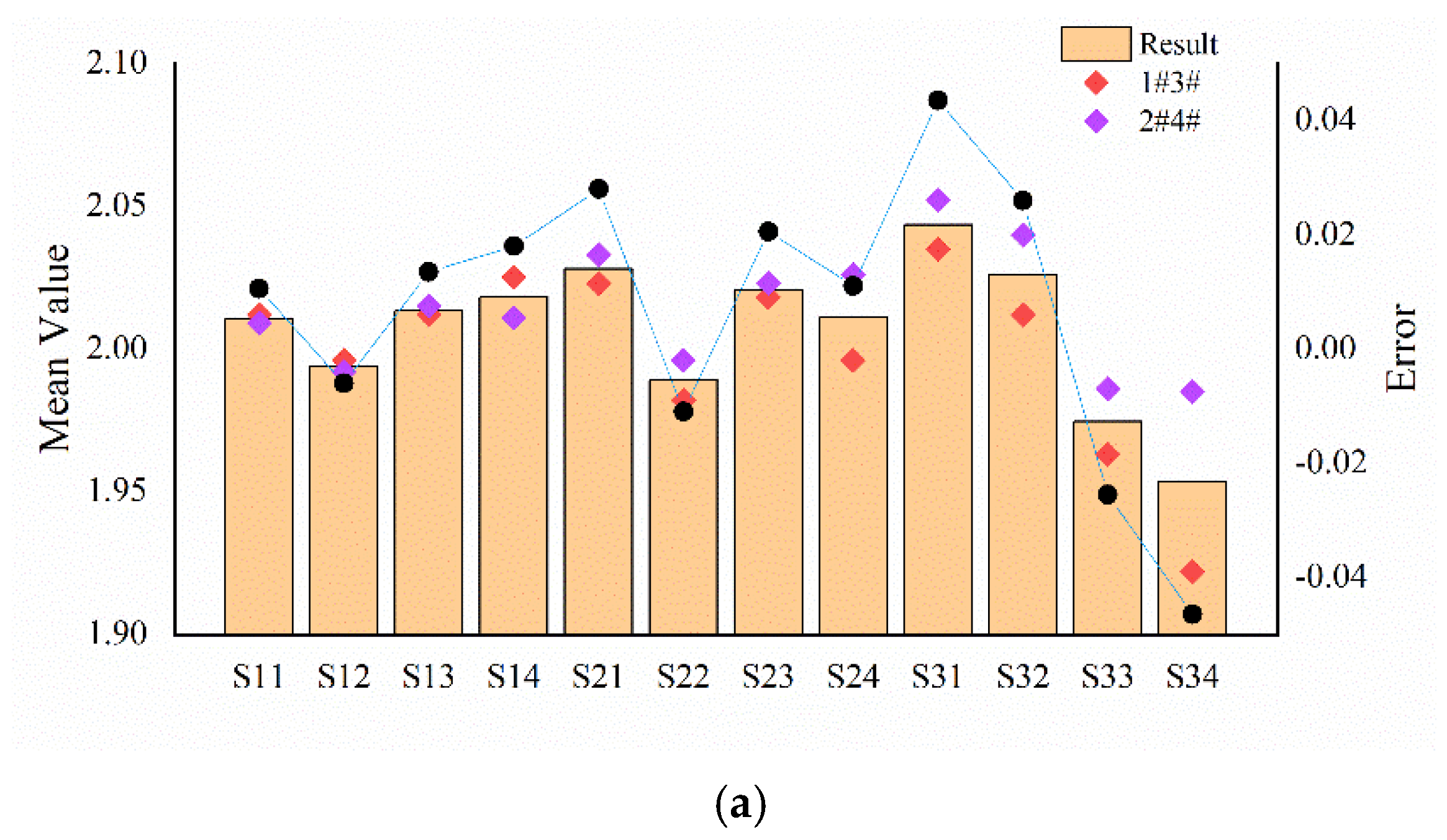
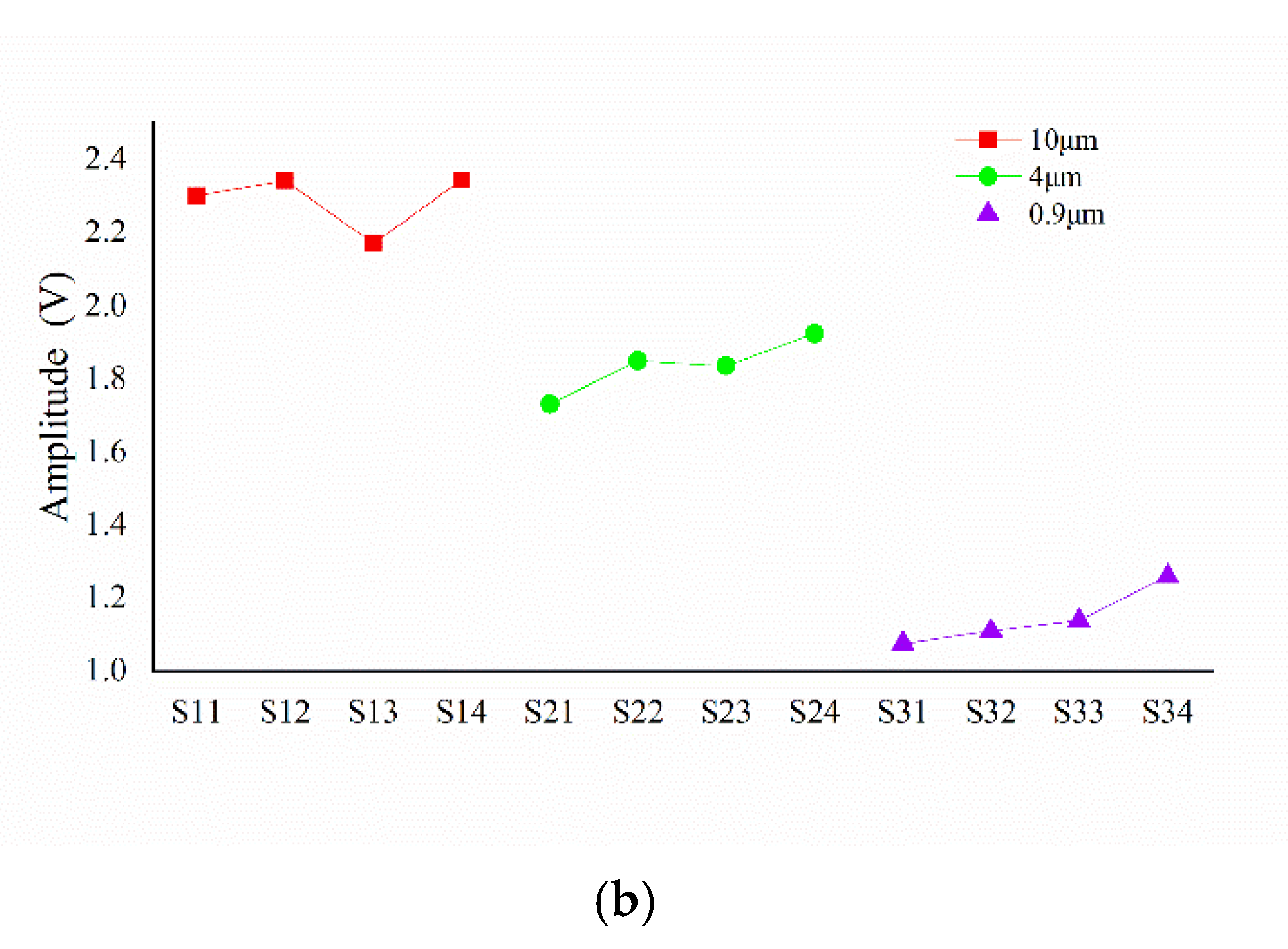
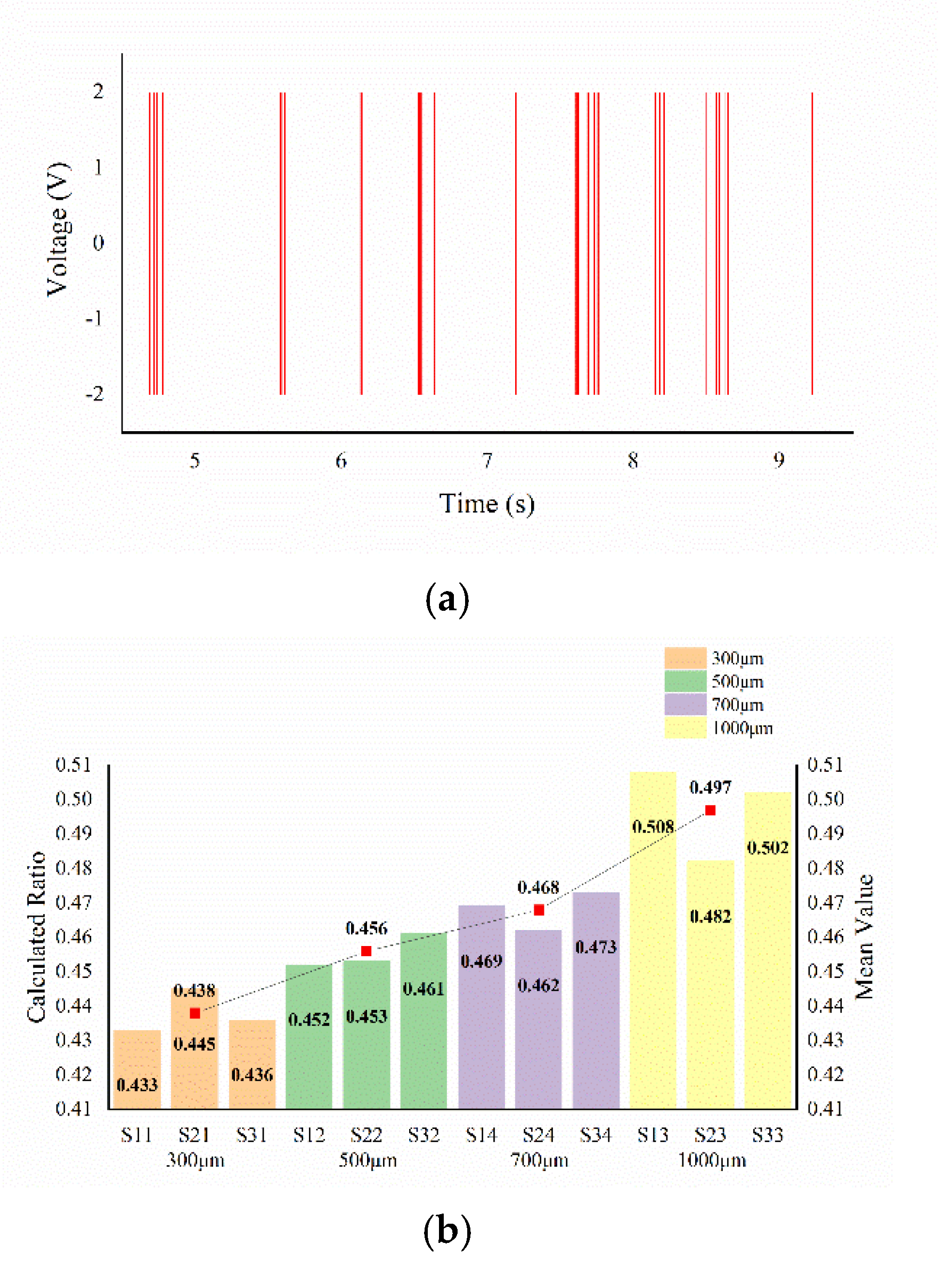
17] succeeded in obtaining the spatial period and ridge height information of ridge texture samples with ridge heights as low as 25 μm. In this article, we tested fine ridge texture samples with different ridge heights (0.9, 4, 10 μm) and different ridge widths (0.3, 0.5, 0.7, 1 mm) but with the same spatial period (2 mm). The mean relative error of the estimation of the space period was 1.085%. The ridge width and ridge height had a mapping relationship with their corresponding parameters, respectively, and the error tolerances are acceptable. Under more systematic experiments, the feature information of the fine texture with a ridge height as low as 0.9 μm can be detected, which indicated that our tactile sensor coupled with the SR method has the potential to achieve the detection of texture with a sub-micron or lower ridge height.
More strikingly, we have completed the detection task of fine textures with fewer data sets based on a sensor array with a simple structure and a simple method. In 2012, Jeremy A. Fishel et al. [
19] achieved the classification of 16 natural textures through simple tactile fingers supplemented by Bayesian exploration methods, with an accuracy of 99.6%. In 2017, Udaya B. Rongala et al. [
21] used neural network methods to identify 10 natural textures, including glass materials with a grain size of less than 90 nm. The aforementioned methods all require a large number of data sets and a complex learning and training process and neglect the detailed information of the texture, but just judge the texture category of a given sample. The SR method we chose can detect weak periodic signals under the condition of a shorter data set, and the output results have obvious signal characteristics for subsequent calculations. This method generally has an effect on low-frequency signals, but the frequency of periodic signals for texture detection may be as high as 300 Hz. Thus, when the frequency of the periodic signal to be detected is high, the frequency detection range can be increased by performing a normalized scale transformation on the bistable system.
In more detail, the noticeable difference in mind caused by external stimulus difference in human finger touches can be used to evaluate the fine texture detection capability of the sensor. In 2012, Kadir Beceren et al. [
25] validated the enhancement effect of SR on human dynamic tactile through a series of psychophysical experiments. The smallest noticeable difference is 1.6 μm under the condition of no noise input but reached 0.93 μm after adding the appropriate noise, which is similar to the detection capability of our tactile sensor after SR enhancement.
6. Conclusions and Outlook
In this article, a flexible solid–liquid composite tactile sensor array developed by our laboratory was used to systematically investigate the performance of tactile sensors in fine ridge texture detection through a bistable system stochastic resonance model, including estimation of the spatial period and recognition of ridge height and ridge width. Our experiment used several fine ridge texture samples to provide a weak periodic stimulus to validate the detection capability of the tactile sensor array. The results show that this method can significantly improve the signal characteristic of the output signal. Regarding the detection of texture information, the results show that the mean relative error of the estimation for the spatial period is 1.085%, and the ridge width and ridge height, respectively, have a monotonic mapping relationship with the corresponding model output parameters. Compared with the human finger experiment, the tactile sensor has a similar capability to sensing fine textures, which shows that the sensor designed in the laboratory has a very promising application prospect.
In future work, the following aspect can be improved and expanded on the work of this article: explore the accurate estimation method of ridge width and ridge height, consider the self-adaptability of the model parameters of the stochastic resonance bistable system, and extend the fine texture detection method to non-periodic ridge texture.