Effects of Electrical Parameters on Micro-Arc Oxidation Coatings on Pure Titanium
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Methods and Procedure
2.1. Sample Preparation
2.2. Micro-Arc Oxidation Film Formation
2.3. Microstructural Observation and Surface Roughness
2.4. Pin-on-Disc Wear Test
2.5. Corrosion Resistance Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
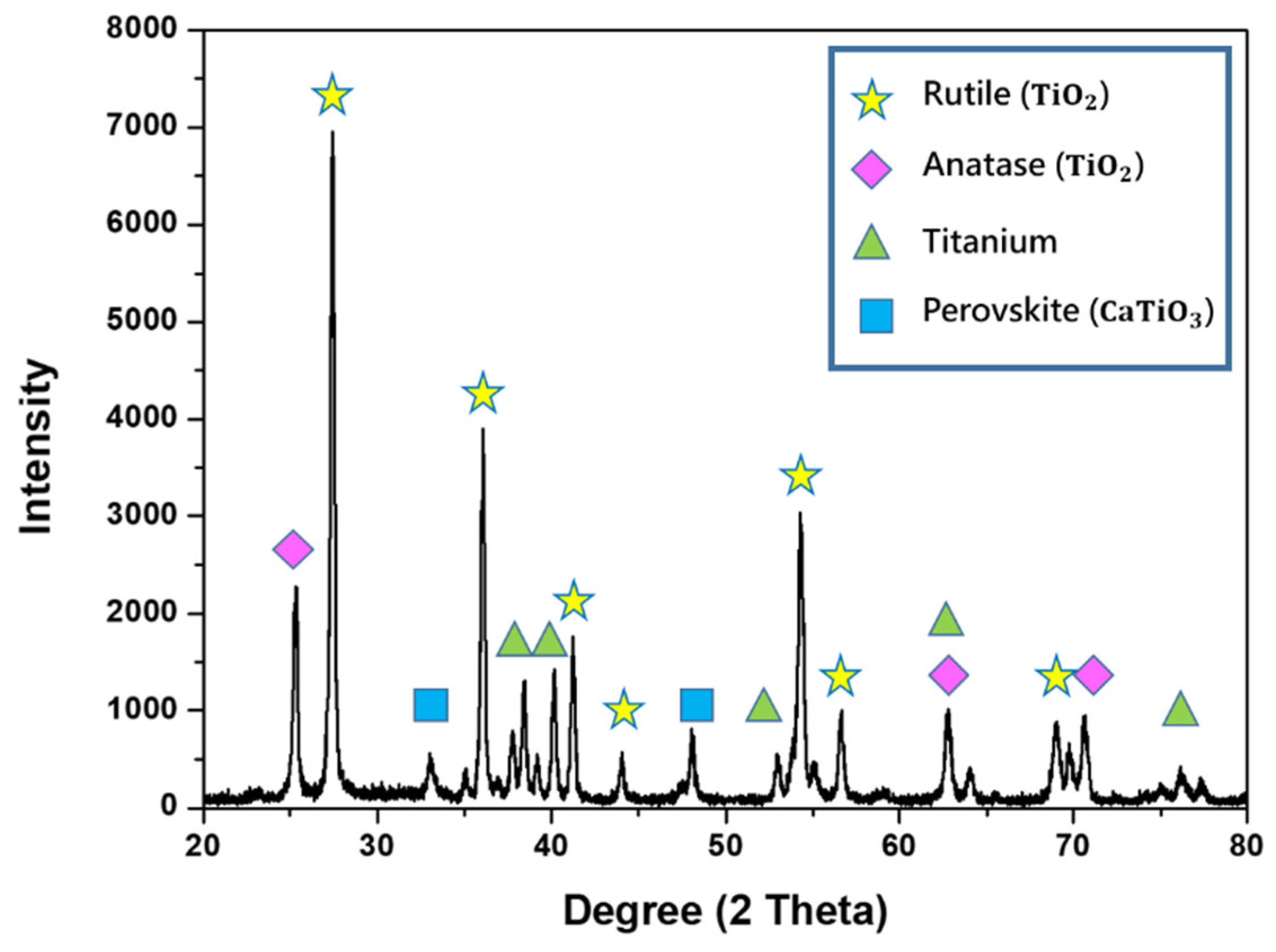
3.1. Process Characterization
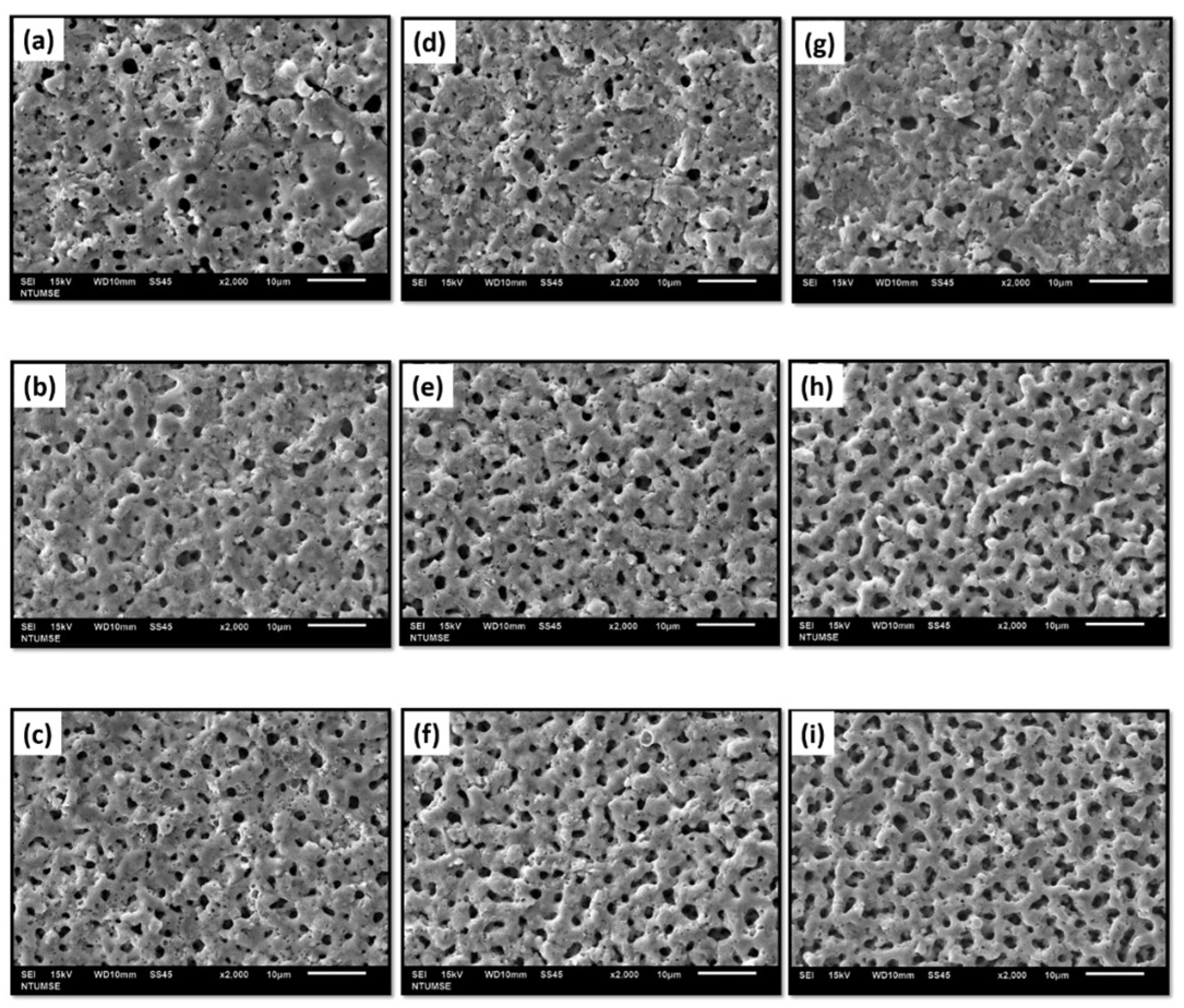
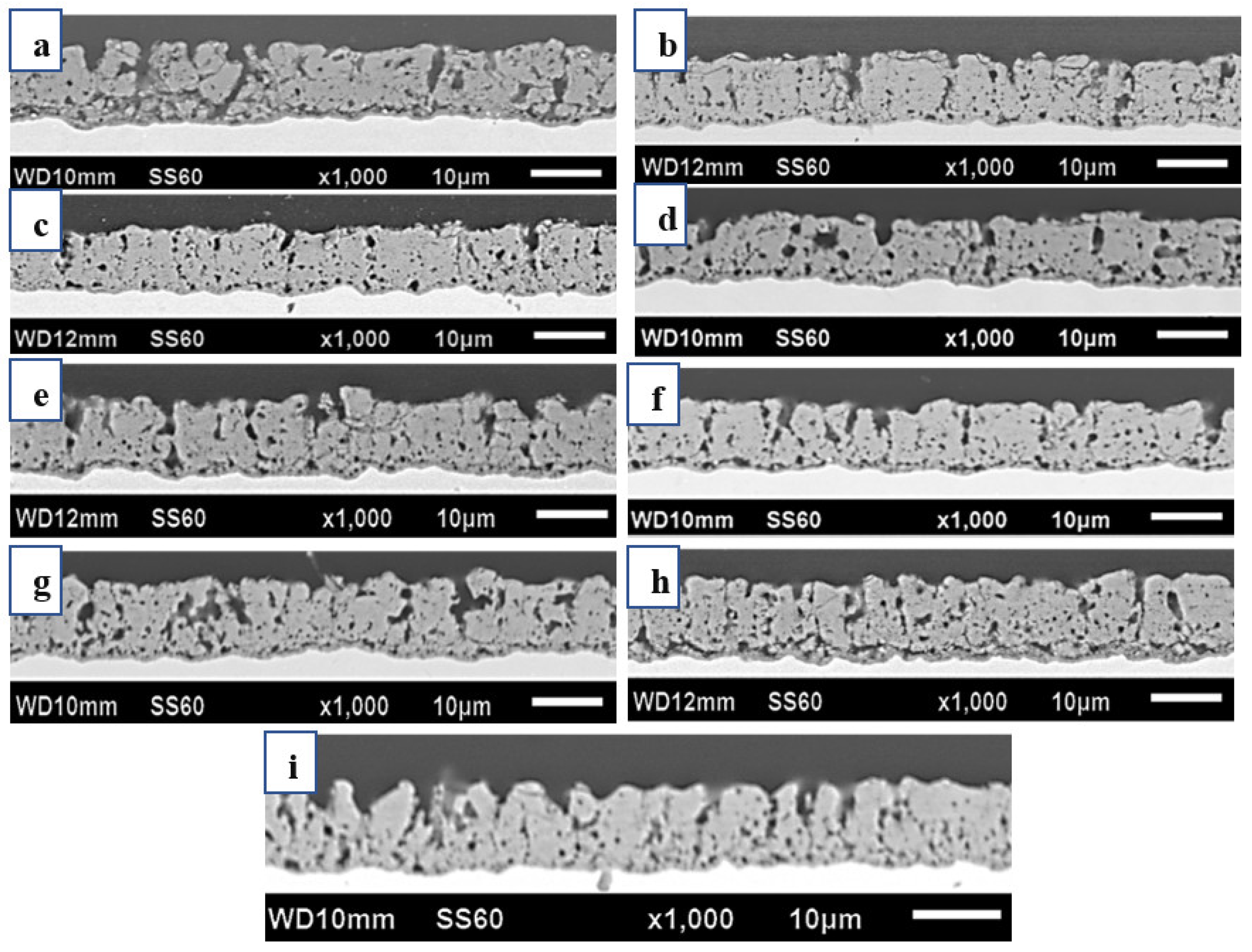
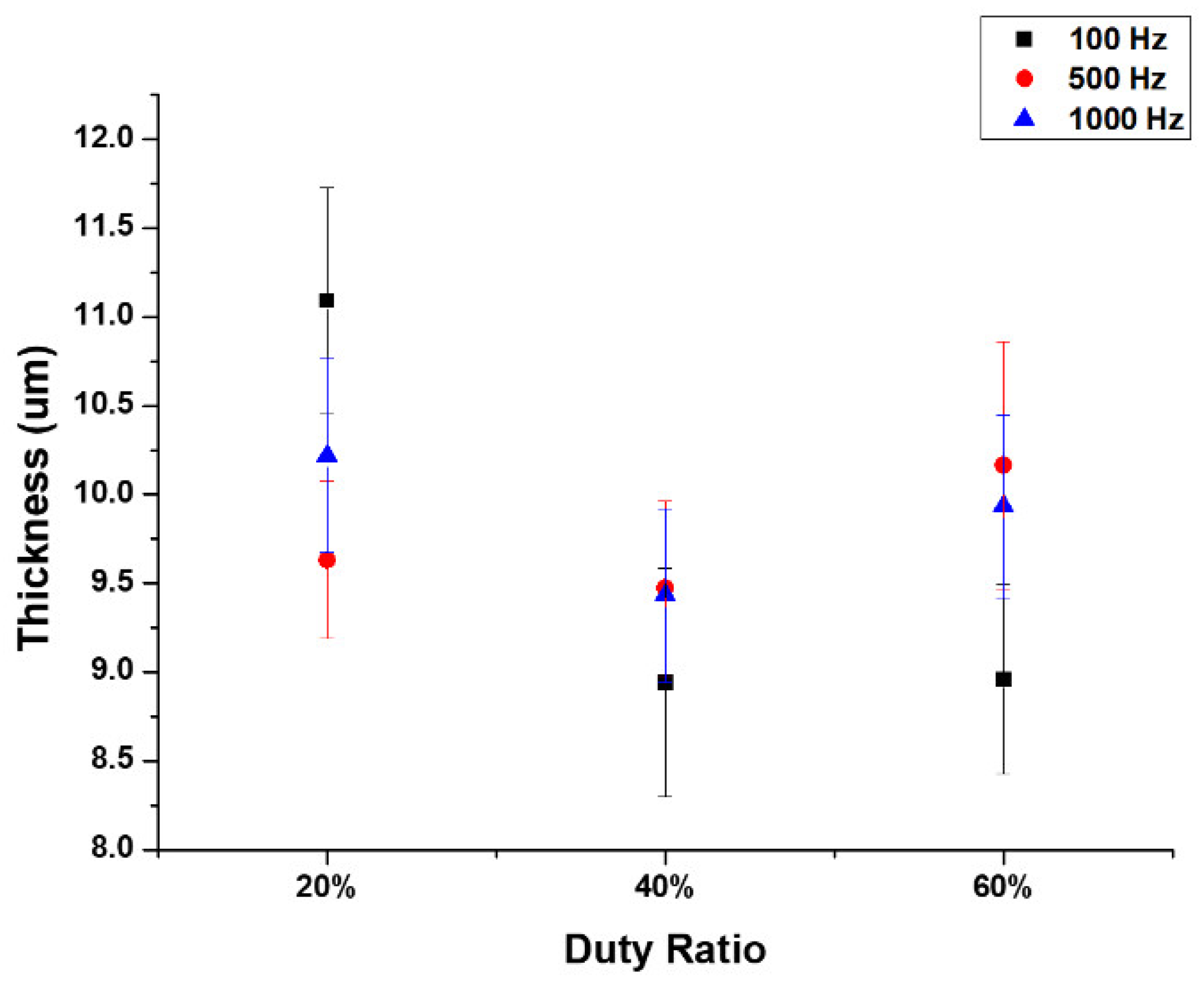
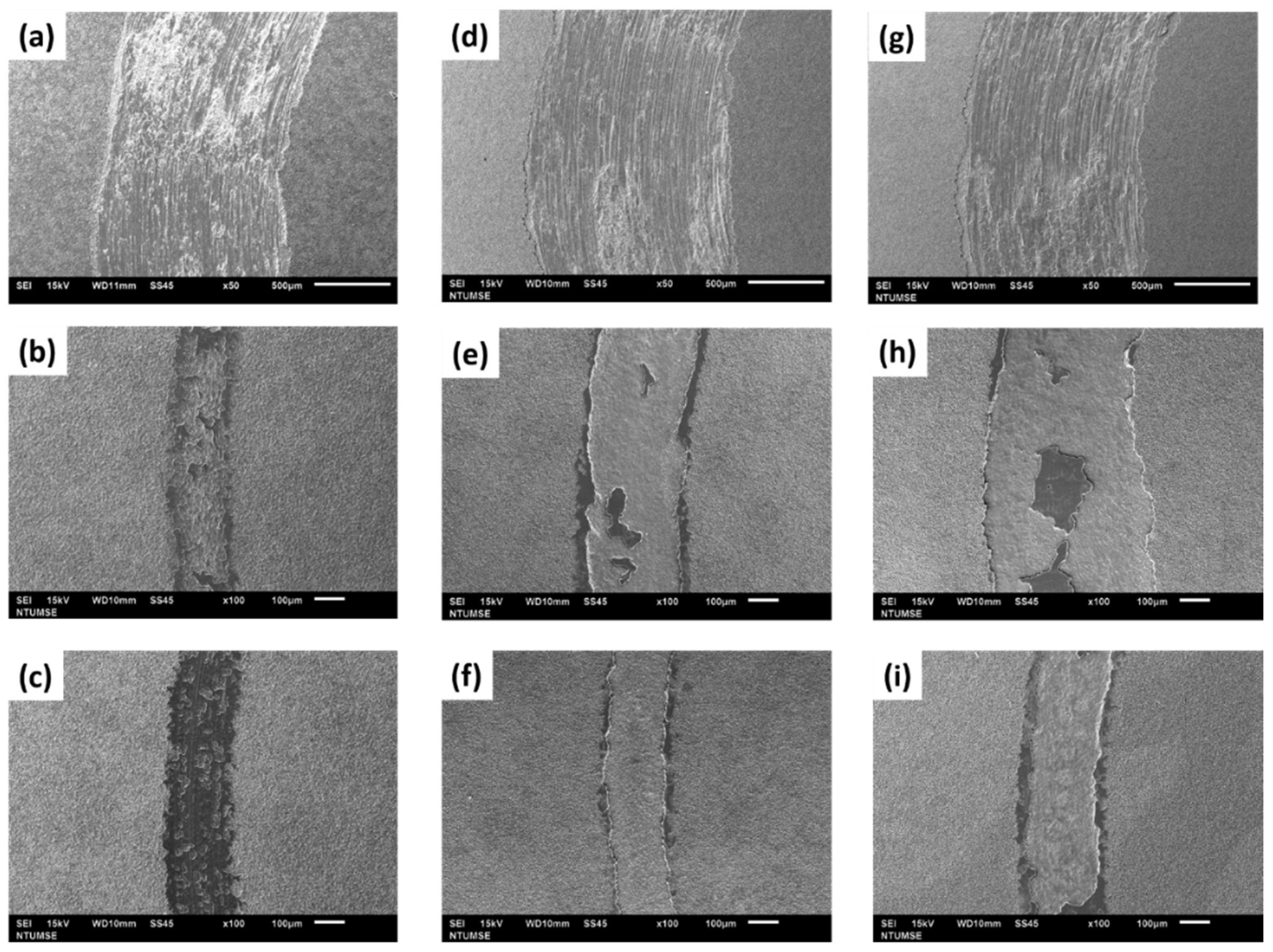
3.2. Surface Characterization
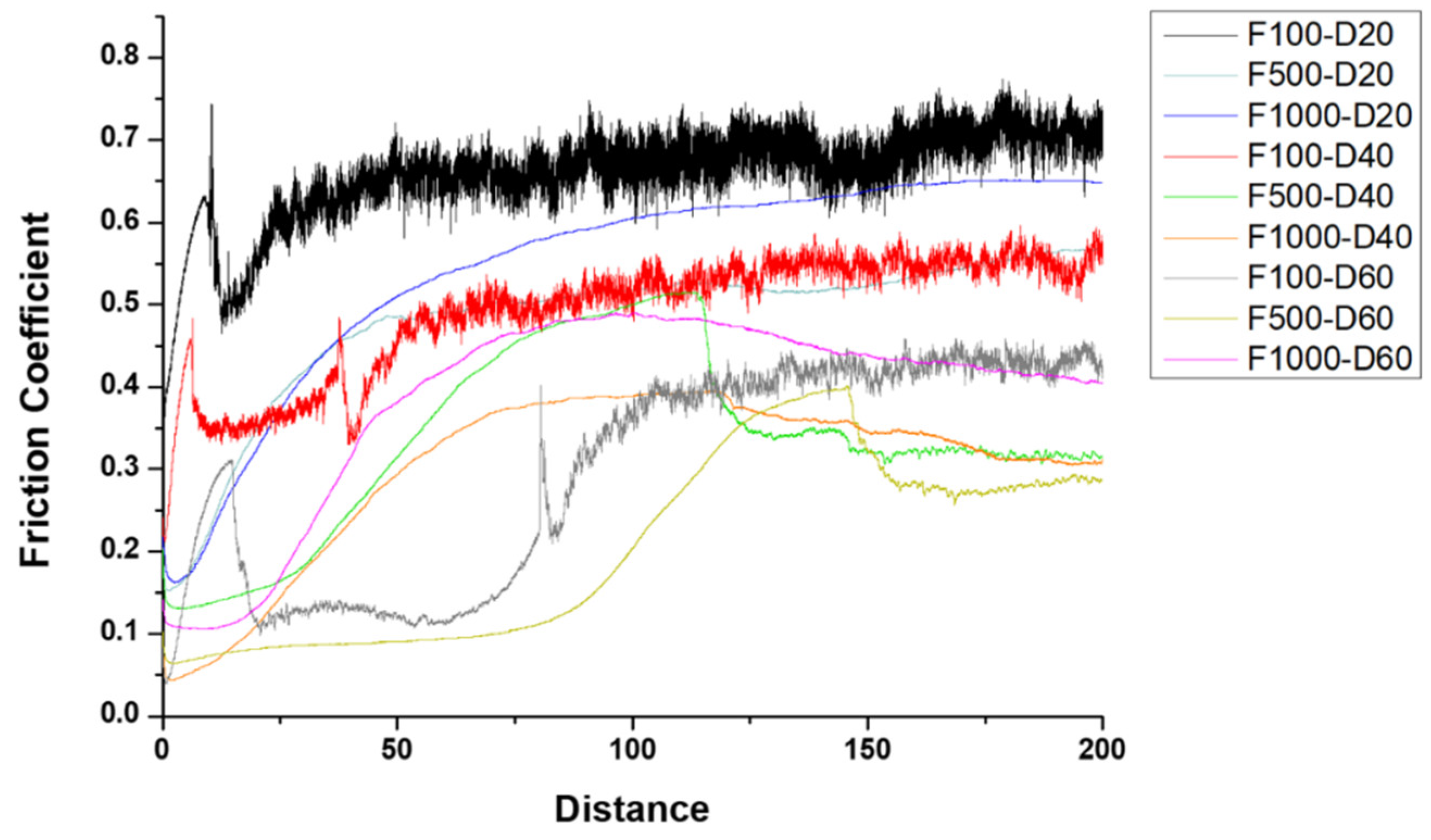
3.3. Wear Resistance Performance
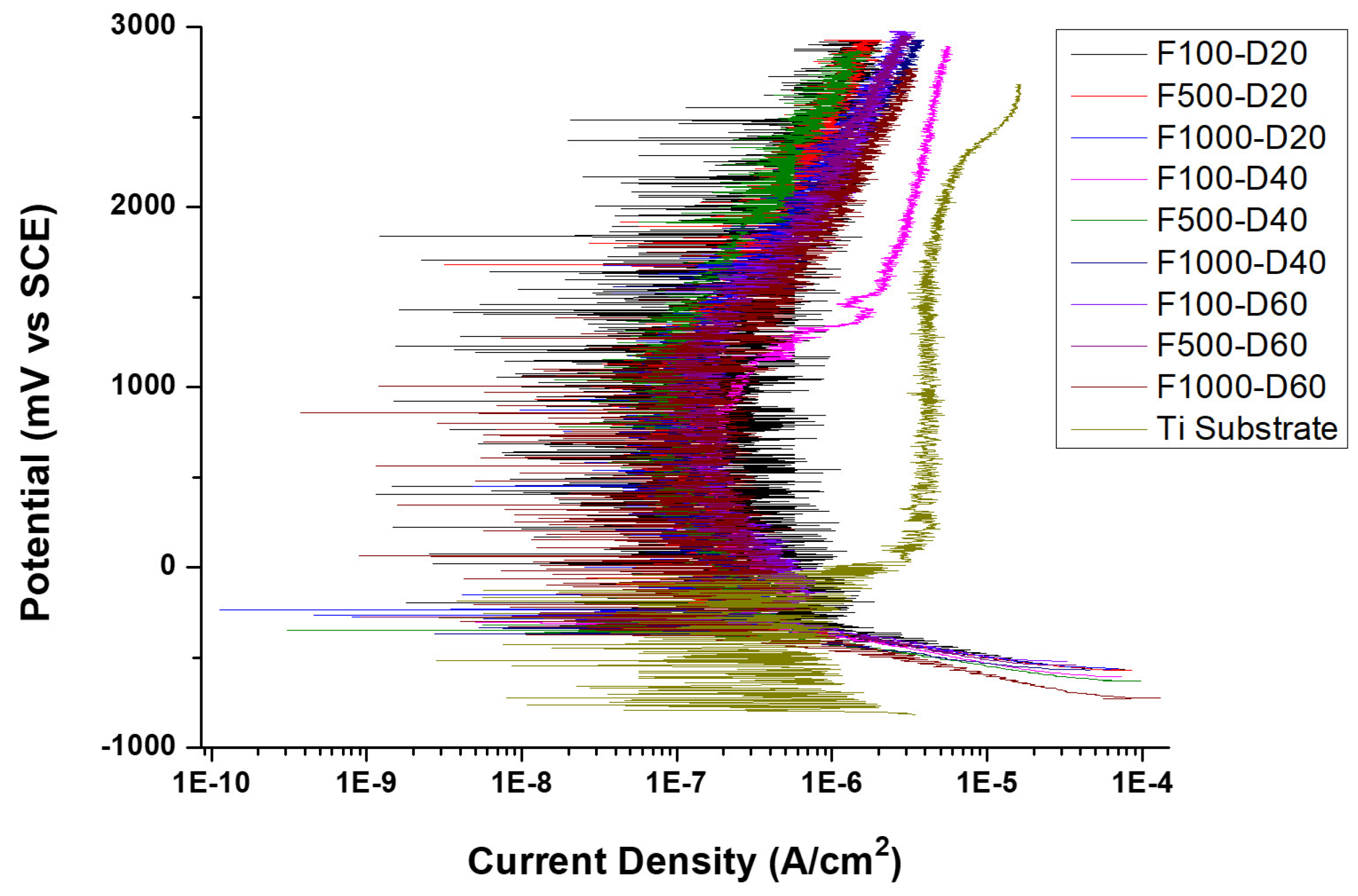
3.4. Corrosion Resistance
4. Conclusions
- The micro-arc oxidation film surface exhibited a porous microstructure. By fixing the frequency at 500 Hz and 1000 Hz, and adjusting the duty cycle from 20% to 60%, the surface porosity became more pronounced.
- At a fixed frequency of 100 Hz and a duty ratio of 60%, the micro-arc oxide film’s structure was denser. The protracted discharge arc promoted the molten substrate’s eruption to the surface while also sintering the oxide film layer.
- Implementing medium and high-frequency parameters enhanced the film’s wear resistance, as demonstrated by the cross-sectional microstructure of the micro-arc oxidation film. A lower porosity in the film resulted in higher resistance to abrasion.
- The polarization curve of the micro-arc oxide film under all conditions showed a consistent pattern. By fixing the duty cycle, the utilization of medium and high-frequency parameters enhanced the resistance of the film against corrosion. Corrosion resistance was improved with fewer holes in the cross-sectional structure of the film. When set at a fixed frequency of 500 and 1000 Hz with a duty cycle of 20%, the micro-arc oxide film exhibited the lowest corrosion current density.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liu, X.; Chu, P.K.; Ding, C. Surface modification of titanium, titanium alloys, and related materials for biomedical applications. Mater. Sci. Eng. R Rep. 2004, 47, 49–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Li, J.; Lv, K.; Zhang, W.; Ding, X.; Yang, G.; Liu, X.; Jiang, X. Surface thermal oxidation on titanium implants to enhance osteogenic activity and in vivo osseointegration. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 31769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, Y.; Wu, X.-Q.; Xue, Z.; Matykina, E.; Skeldon, P.; Thompson, G.E. Microstructure, corrosion and wear performance of plasma electrolytic oxidation coatings formed on Ti–6Al–4V alloy in silicate-hexametaphosphate electrolyte. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2013, 217, 129–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, W.; Wang, C.; Chen, R.; Deng, Z. Structure and properties characterization of ceramic coatings produced on Ti–6Al–4V alloy by microarc oxidation in aluminate solution. Mater. Lett. 2002, 52, 435–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yerokhin, A.L.; Nie, X.; Leyland, A.; Matthews, A. Characterisation of oxide films produced by plasma electrolytic oxidation of a Ti–6Al–4V alloy. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2000, 130, 195–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussein, R.O.; Nie, X.; Northwood, D.O. An investigation of ceramic coating growth mechanisms in plasma electrolytic oxidation (PEO) processing. Electrochim Acta 2013, 112, 111–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Jiang, Z.; Xin, S.; Yao, Z. Composition and mechanical properties of hard ceramic coating containing α-Al2O3 produced by microarc oxidation on Ti–6Al–4V alloy. Thin Solid Films 2005, 471, 194–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, H.; Bell, T. Enhanced wear resistance of titanium surfaces by a new thermal oxidation treatment. Wear 2000, 238, 131–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aliasghari, S.; Skeldon, P.; Thompson, G.E. Plasma electrolytic oxidation of titanium in a phosphate/silicate electrolyte and tribological performance of the coatings. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2014, 316, 463–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stankiewicz, A.; Szczygieł, I.; Szczygieł, B. Self-healing coatings in anti-corrosion applications. J. Mater. Sci. 2013, 48, 8041–8051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Xie, F.; Hu, Z.; Wang, L. Effects of additives on corrosion and wear resistance of micro-arc oxidation coatings on TiAl alloy. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 2010, 20, 1032–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shokouhfar, M.; Dehghanian, C.; Montazeri, M.; Baradaran, A. Preparation of ceramic coating on Ti substrate by plasma electrolytic oxidation in different electrolytes and evaluation of its corrosion resistance: Part II. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2012, 258, 2416–2423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarbishei, S.; Sani, M.A.F.; Mohammadi, M.R. Effects of alumina nanoparticles concentration on microstructure and corrosion behavior of coatings formed on titanium substrate via PEO process. Ceram. Int. 2016, 42, 8789–8797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobolev, A.; Kossenko, A.; Borodianskiy, K. Study of the Effect of Current Pulse Frequency on Ti-6Al-4V Alloy Coating Formation by Micro Arc Oxidation. Materials 2019, 12, 3983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, J.; Wang, S.; Zhou, Y.; Dong, H. Effects of the Power Supply Mode and Loading Parameters on the Characteristics of Micro-Arc Oxidation Coatings on Magnesium Alloy. Metals 2020, 10, 1452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rapheal, G.; Kumar, S.; Scharnagl, N.; Blawert, C. Effect of current density on the microstructure and corrosion properties of plasma electrolytic oxidation (PEO) coatings on AM50 Mg alloy produced in an electrolyte containing clay additives. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2016, 289, 150–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Wu, T.; Xiao, Y.T.; Zhang, L.; Pu, J.; Cao, W.J.; Zhong, X.M. Characterization of micro-arc oxidation coatings on aluminum drillpipes at different current density. Vacuum 2017, 142, 21–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beltrán, A.; Gracia, L.; Andrés, J. Density Functional Theory Study of the Brookite Surfaces and Phase Transitions between Natural Titania Polymorphs. J. Phys. Chem. B 2006, 110, 23417–23423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haggerty, J.E.S.; Schelhas, L.T.; Kitchaev, D.A.; Mangum, J.S.; Garten, L.M.; Sun, W.; Stone, K.H.; Perkins, J.D.; Toney, M.F.; Ceder, G.; et al. High-fraction brookite films from amorphous precursors. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 15232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanaor, D.A.H.; Sorrell, C.C. Review of the anatase to rutile phase transformation. J. Mater. Sci. 2011, 46, 855–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gen-Yu, C.; Han-Hua, W.; Yue, L.; Hong, C.; Yuan-Guang, T. Effect of electrical parameters on characteristics of microarc oxidation coatings of commercially pure titanium in colloid. Acta Phys. Sin. 2010, 59, 1958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dziaduszewska, M.; Shimabukuro, M.; Seramak, T.; Zielinski, A.; Hanawa, T. Effects of Micro-Arc Oxidation Process Parameters on Characteristics of Calcium-Phosphate Containing Oxide Layers on the Selective Laser Melted Ti13Zr13Nb Alloy. Coatings 2020, 10, 745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, Y.-F.; Lee, H.; Lin, H.-C. A Study of Dark TiO2 Coating on Pure Titanium By Micro Arc Oxidation. ECS Meet. Abstr. 2019, MA2019-01, 1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, Y.; Yan, J.; Wang, C.; Mei, L. Effect of electrical parameters on the growth and properties of 7075 aluminum alloy film based on scanning micro-arc oxidation with mesh electrode. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2023, 25, 988–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASTM G99-17; Standard Test Method for Wear Testing with a Pin-on-Disk Apparatus. ASTM: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2017.
- Dehnavi, V.; Luan, B.L.; Shoesmith, D.W.; Liu, X.Y.; Rohani, S. Effect of duty cycle and applied current frequency on plasma electrolytic oxidation (PEO) coating growth behavior. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2013, 226, 100–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yerokhin, A.L.; Snizhko, L.O.; Gurevina, N.L.; Leyland, A.; Pilkington, A.; Matthews, A. Spatial characteristics of discharge phenomena in plasma electrolytic oxidation of aluminium alloy. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2004, 177–178, 779–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walsh, F.C.; Low, C.T.J.; Wood, R.J.K.; Stevens, K.T.; Archer, J.; Poeton, A.R.; Ryder, A. Plasma electrolytic oxidation (PEO) for production of anodised coatings on lightweight metal (Al, Mg, Ti) alloys. Trans. IMF 2009, 87, 122–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.F.; An, M.Z. Growth of ceramic coatings on AZ91D magnesium alloys by micro-arc oxidation in aluminate–fluoride solutions and evaluation of corrosion resistance. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2005, 246, 229–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; Xue, Z.; Wang, Q.; Wu, X.-Q.; Matykina, E.; Skeldon, P.; Thompson, G.E. New findings on properties of plasma electrolytic oxidation coatings from study of an Al–Cu–Li alloy. Electrochim Acta 2013, 107, 358–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Zhang, X.; Wang, X.; Qin, L. Review of Antibacterial Activity of Titanium-Based Implants’ Surfaces Fabricated by Micro-Arc Oxidation. Coatings 2017, 7, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sundararajan, G.; Rama Krishna, L. Mechanisms underlying the formation of thick alumina coatings through the MAO coating technology. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2003, 167, 269–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussein, R.O.; Nie, X.; Northwood, D.O. Production of High Quality Coatings on Light Alloys Using Plasma Electrolytic Oxidation (PEO); WIT Press: Ashurst, UK, 2016; pp. 439–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, S.; Song, L.; Zhao, R.; Hu, X. Influence of cathodic current on composition, structure and properties of Al2O3 coatings on aluminum alloy prepared by micro-arc oxidation process. Thin Solid Films 2006, 515, 326–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, P.; Wu, X.; Guo, Y.; Jiang, Z. Effects of cathode current density on structure and corrosion resistance of plasma electrolytic oxidation coatings formed on ZK60 Mg alloy. J. Alloys Compd. 2009, 475, 773–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussein, R.O.; Nie, X.; Northwood, D.O. Influence of process parameters on electrolytic plasma discharging behaviour and aluminum oxide coating microstructure. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2010, 205, 1659–1667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortega, F.; Sova, A.; Monzón, M.D.; Marrero, M.D.; Benítez, A.N.; Bertrand, P. Combination of electroforming and cold gas dynamic spray for fabrication of rotational moulds: Feasibility study. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2015, 76, 1243–1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, J.J.; Song, R.G.; Xiang, N.; Xiong, Y.; Hu, Q. Effect of current density on microstructure and properties of PEO ceramic coatings on magnesium alloy. Surf. Eng. 2017, 33, 744–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
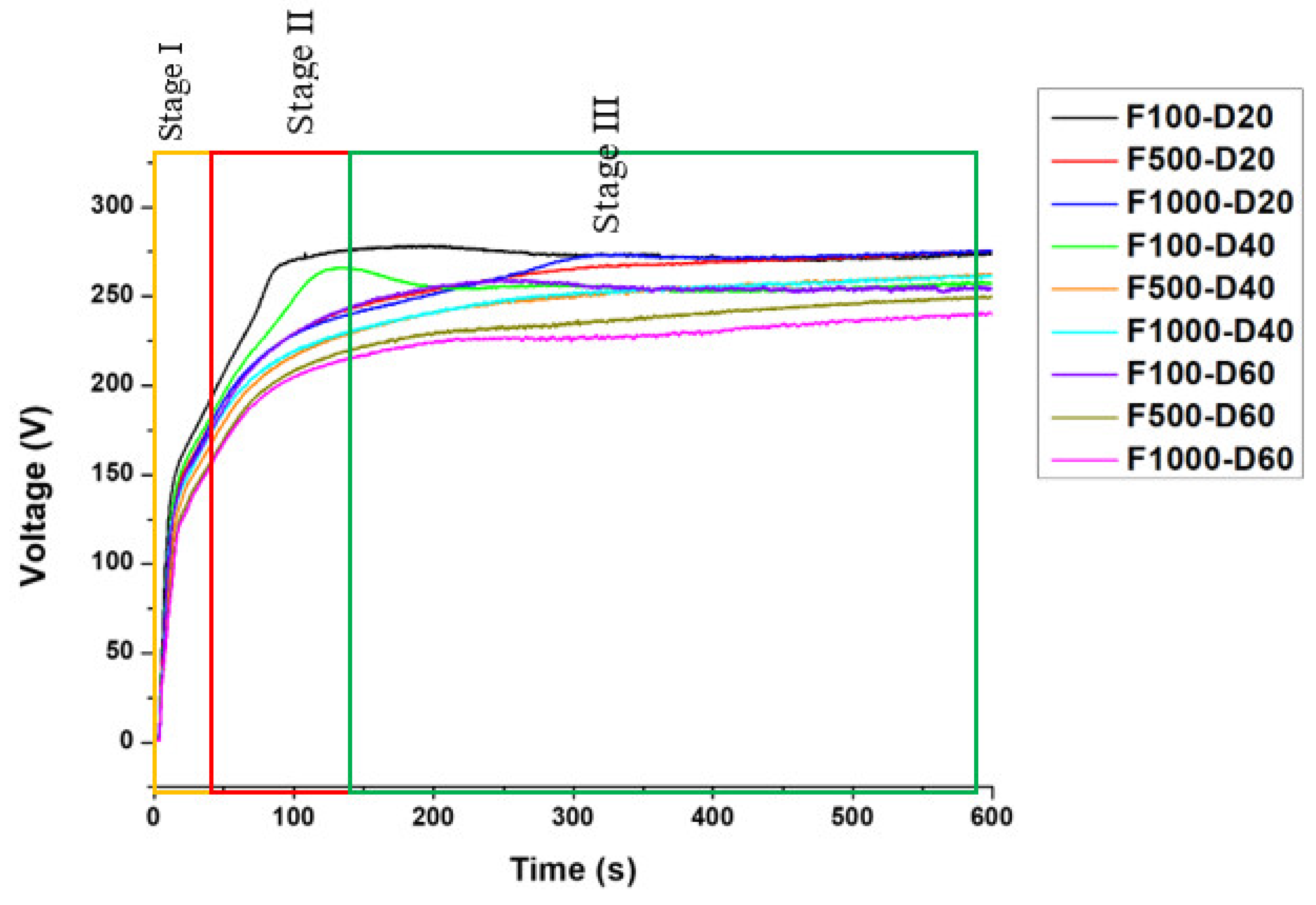

| Duty Ratio | 20% | 40% | 60% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Frequency | ||||
| 100 Hz | F100-D20 | F100-D40 | F100-D60 | |
| 500 Hz | F500-D20 | F500-D40 | F500-D60 | |
| 1000 Hz | F1000-D20 | F1000-D40 | F1000-D60 | |
| Time | (μs) | (μs) | (μs) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sample | |||||
| F100-D20 | 2000 | 2500 | 3000 | 2500 | |
| F100-D40 | 4000 | 2500 | 1000 | 2500 | |
| F100-D60 | 6000 | 1500 | 1000 | 1500 | |
| F500-D20 | 400 | 500 | 600 | 500 | |
| F500-D40 | 800 | 500 | 200 | 500 | |
| F500-D60 | 1200 | 300 | 200 | 300 | |
| F1000-D20 | 200 | 250 | 300 | 250 | |
| F1000-D40 | 400 | 250 | 100 | 250 | |
| F1000-D60 | 600 | 150 | 100 | 150 | |
| Frequency | 20% | 40% | 60% | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Width (μm) | Depth (μm) | Rate mm3/(m.N) | Width (μm) | Depth (μm) | Rate mm3/(m.N) | Width (μm) | Depth (μm) | Rate mm3/(m∙N) | |
| 500 Hz | 214.028 | 2.646 | 1.179 × 10−5 | 366.415 | 8.813 | 1.014 × 10−4 | 447.608 | 9.146 | 1.286 × 10−4 |
| 1000 Hz | 207.310 | 0.805 | 5.243 × 10−6 | 250.911 | 1.783 | 1.405 × 10−5 | 251.906 | 4.304 | 3.406 × 10−5 |
| Sample | Corrosion Potential (mV) | Current Density (A/cm2) |
|---|---|---|
| F100-D20 | −264.740 | 1.320 × 10−5 |
| F500-D20 | −266.876 | 4.588 × 10−6 |
| F1000-D20 | −266.571 | 2.618 × 10−6 |
| F100-D40 | −306.702 | 7.272 × 10−6 |
| F500-D40 | −348.053 | 6.114 × 10−6 |
| F1000-D40 | −367.126 | 4.795 × 10−6 |
| F100-D60 | −276.337 | 6.304 × 10−6 |
| F500-D60 | −274.658 | 6.314 × 10−6 |
| F1000-D60 | −272.980 | 6.195 × 10−6 |
| Ti Substrate | −514.984 | 9.500 × 10−5 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Abbas, A.; Kung, H.-P.; Lin, H.-C. Effects of Electrical Parameters on Micro-Arc Oxidation Coatings on Pure Titanium. Micromachines 2023, 14, 1950. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi14101950
Abbas A, Kung H-P, Lin H-C. Effects of Electrical Parameters on Micro-Arc Oxidation Coatings on Pure Titanium. Micromachines. 2023; 14(10):1950. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi14101950
Chicago/Turabian StyleAbbas, Aqeel, Hsuan-Ping Kung, and Hsin-Chih Lin. 2023. "Effects of Electrical Parameters on Micro-Arc Oxidation Coatings on Pure Titanium" Micromachines 14, no. 10: 1950. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi14101950
APA StyleAbbas, A., Kung, H.-P., & Lin, H.-C. (2023). Effects of Electrical Parameters on Micro-Arc Oxidation Coatings on Pure Titanium. Micromachines, 14(10), 1950. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi14101950






