Electrically Tunable Lenses for Imaging and Light Manipulation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Electrowetting Liquid Lens
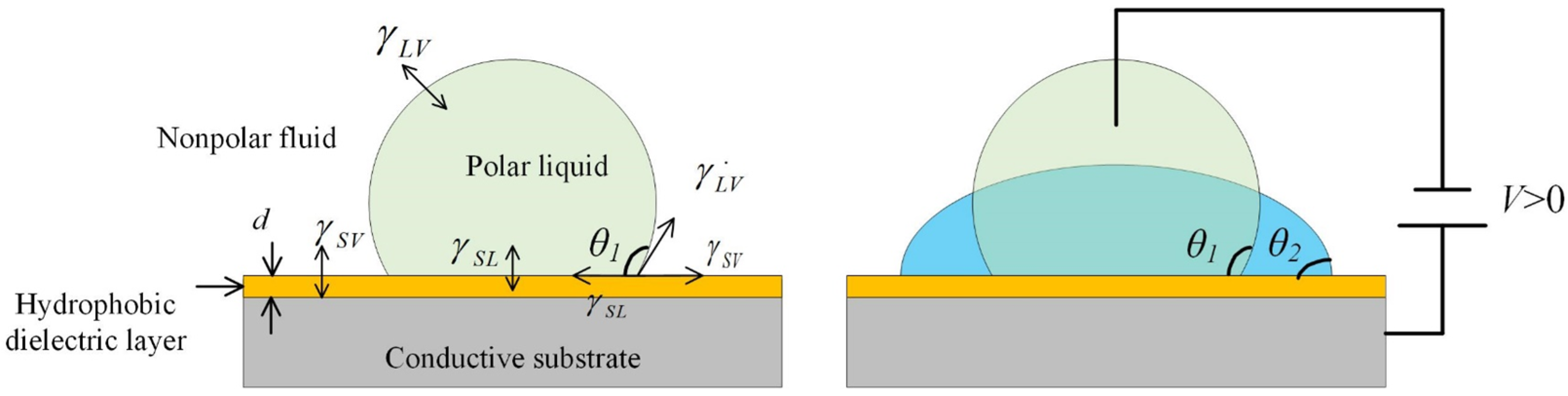
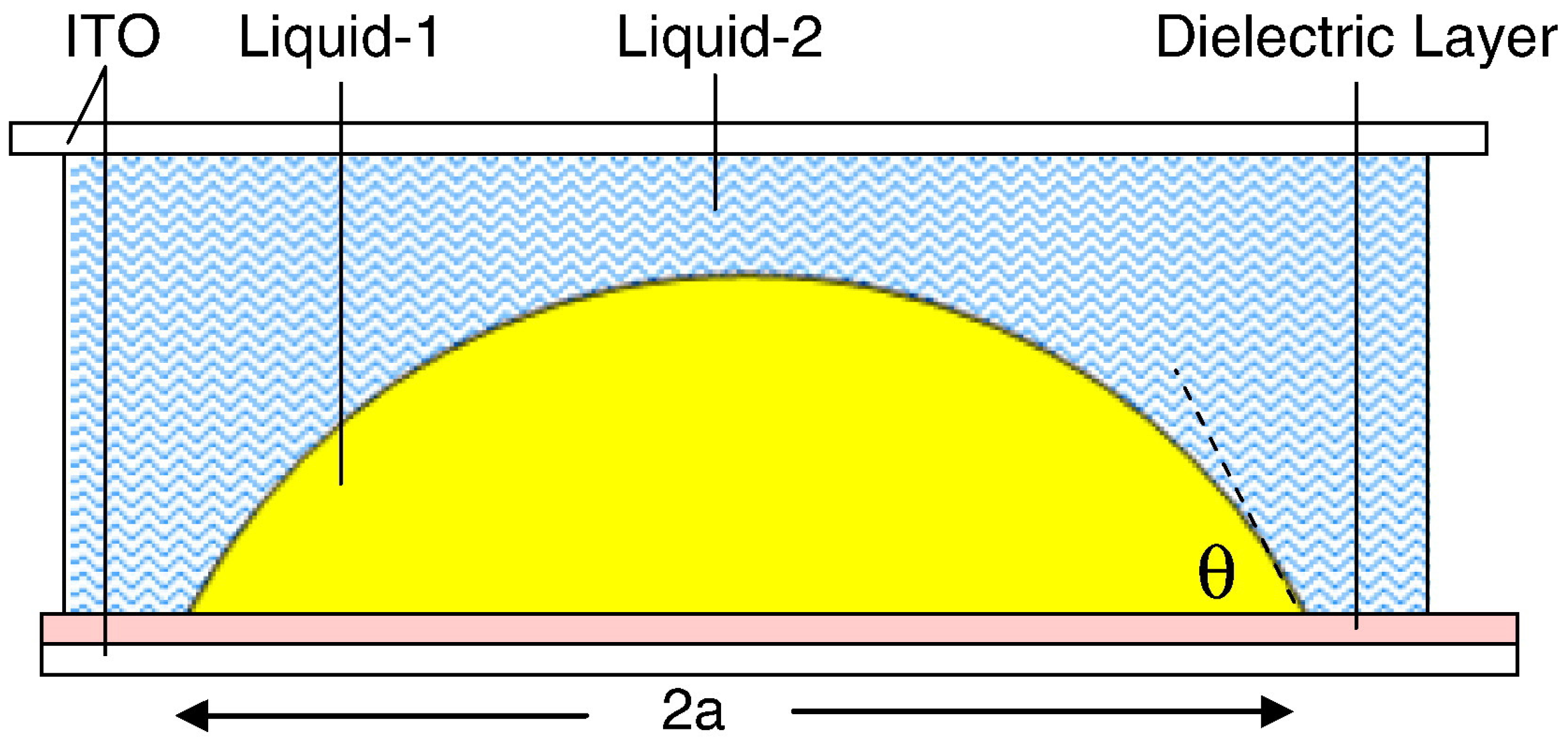
2.1. The principle of Electrowetting
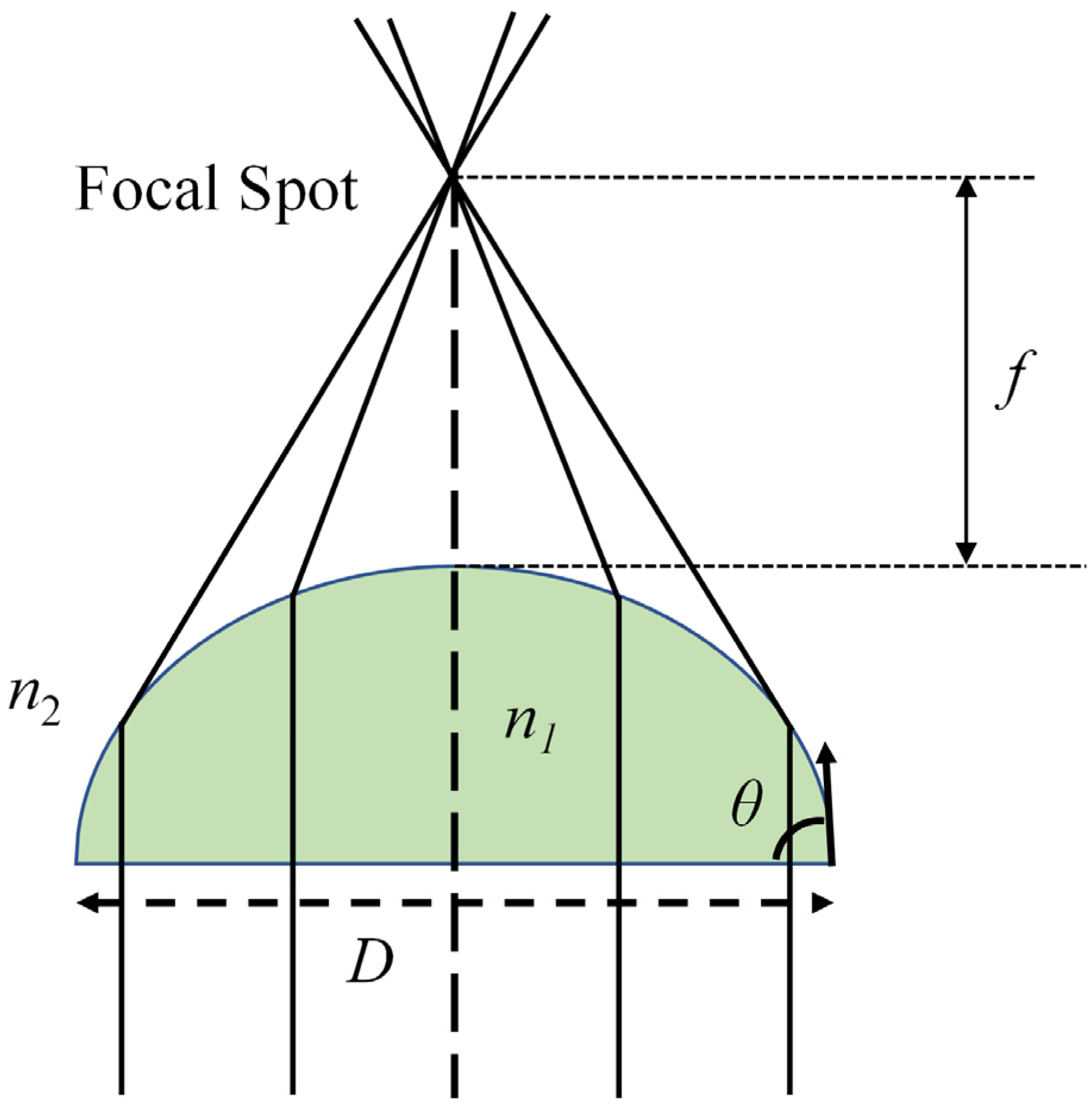
2.2. Electrowetting Lens and Its Focal Length Tunablity
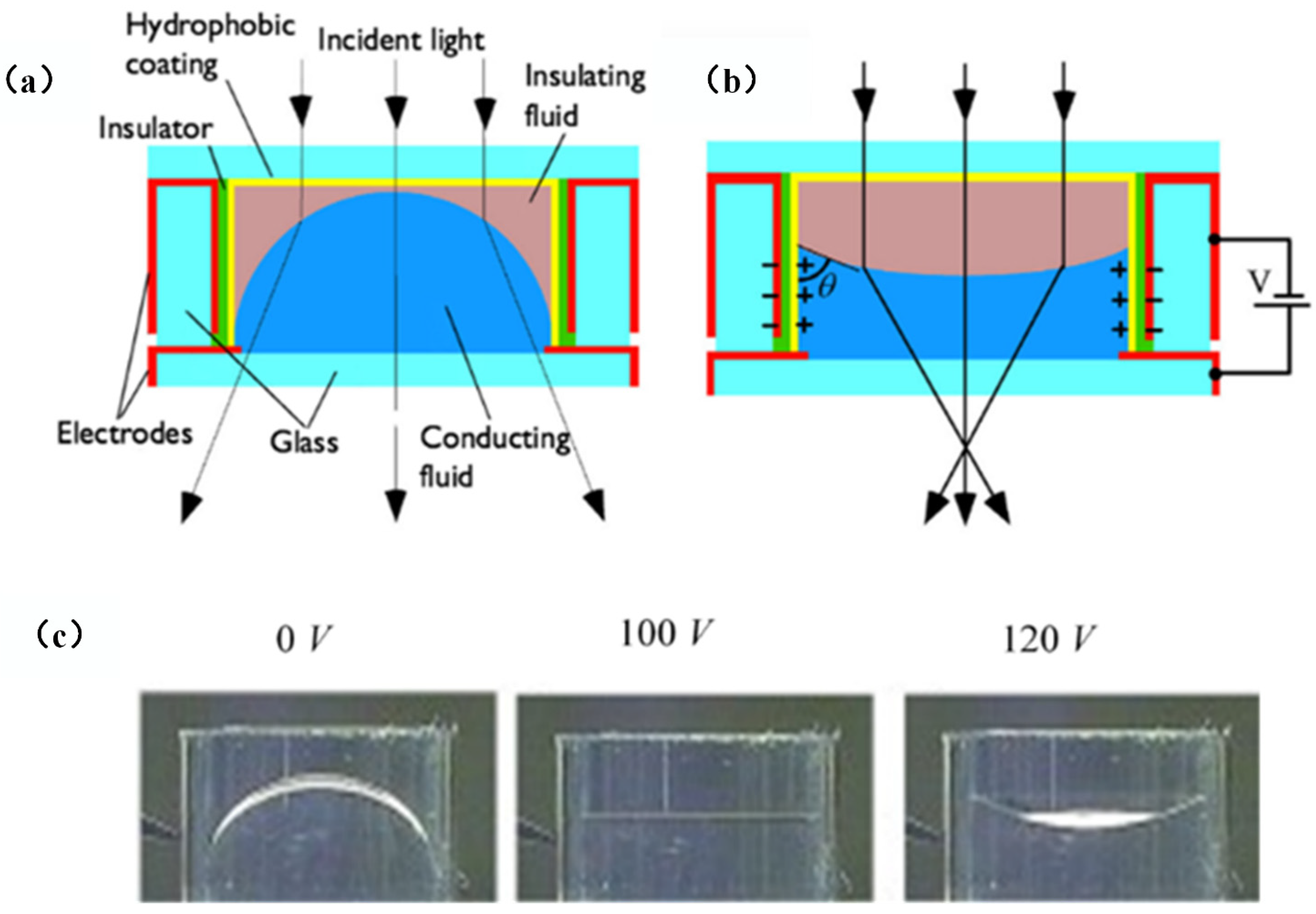
2.3. Imaging Application of Electrowetting Lens
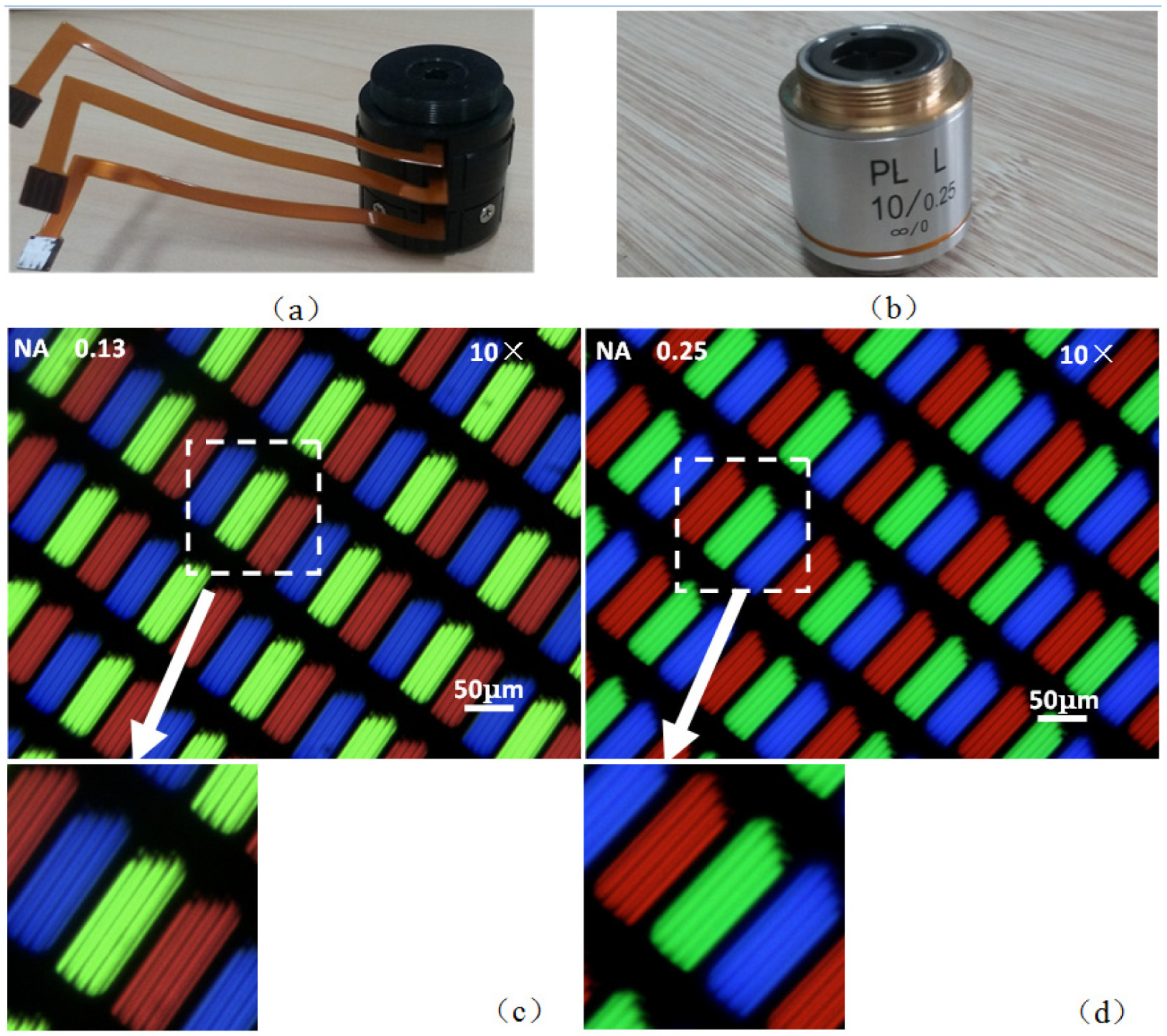
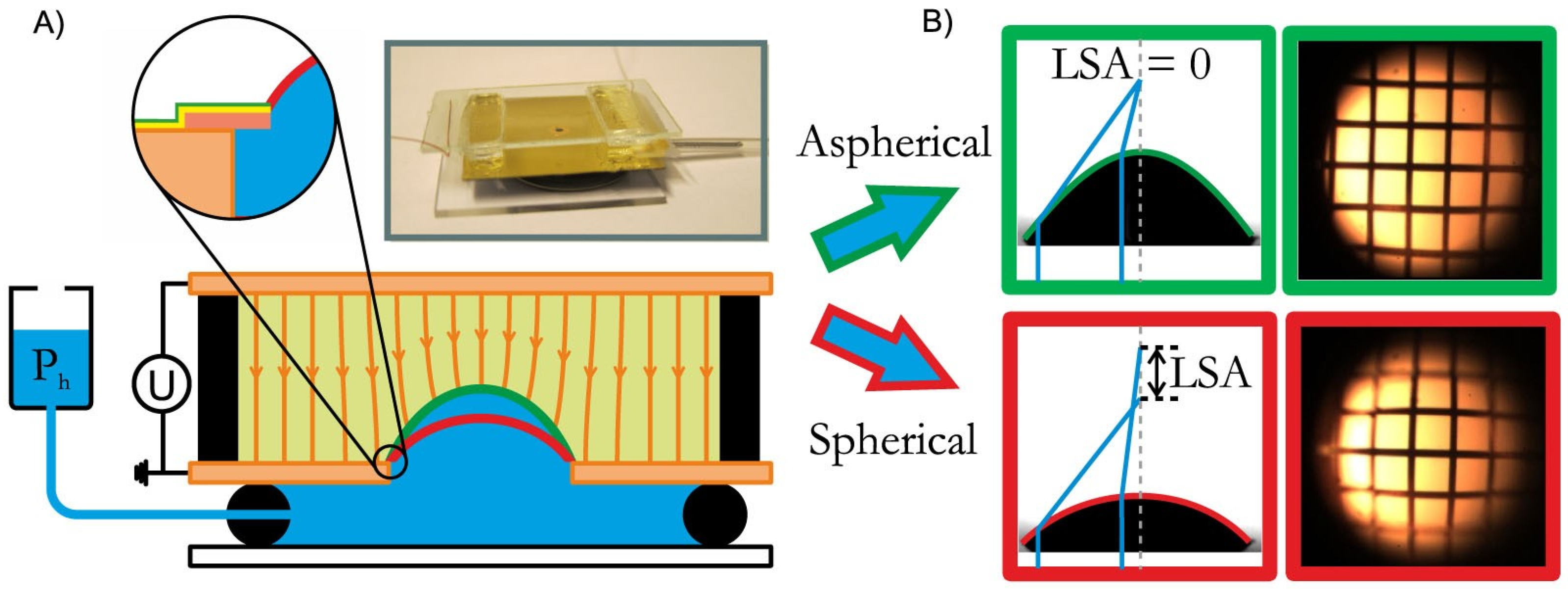
2.4. Methods to Enhance the Electrowetting Lens’ Performance
3. Dielectrophoresis-Actuated Lenses and Applications
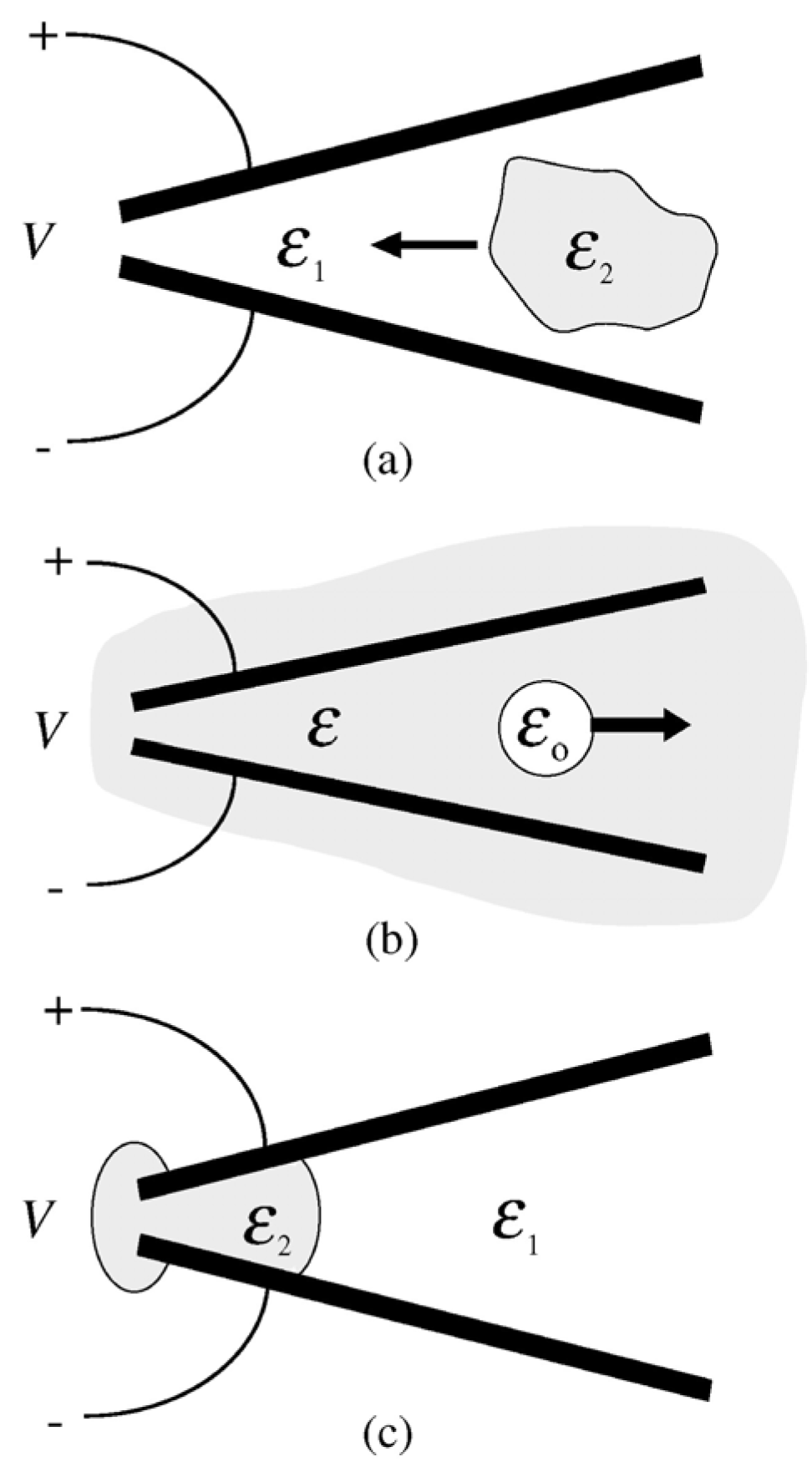
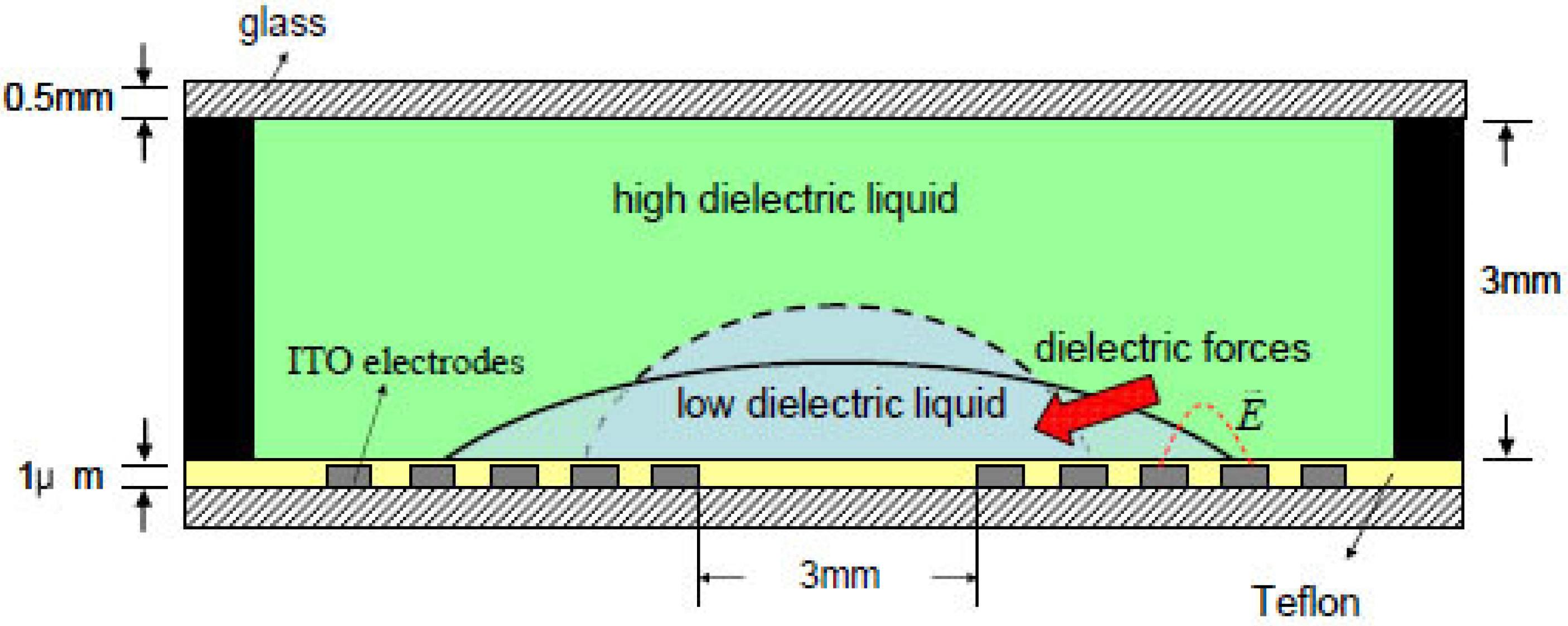
3.1. Working Principle of Dielectrophoresis
3.2. Dielectrophoresis-Actuated Out-Of-Plane Lens
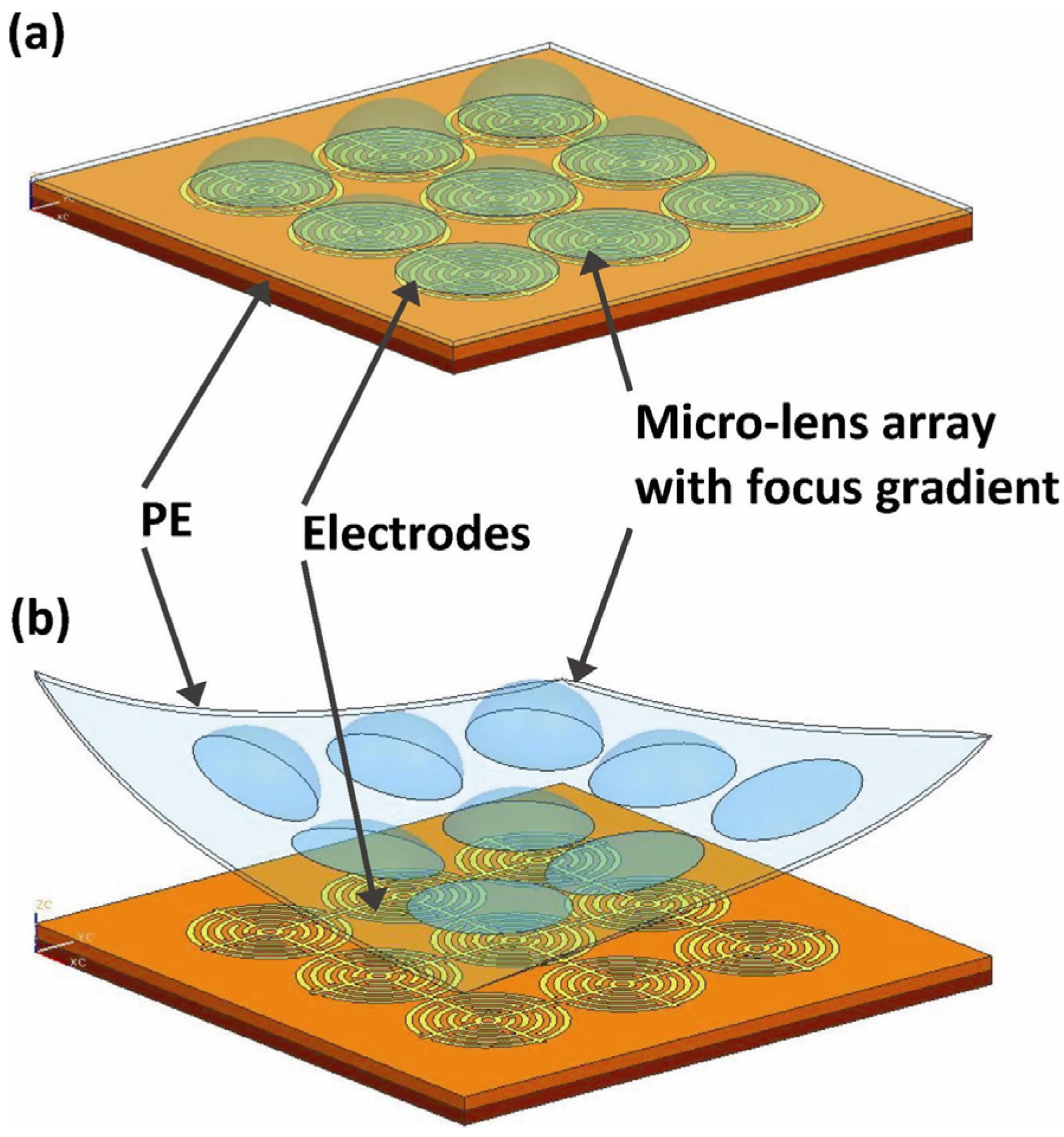
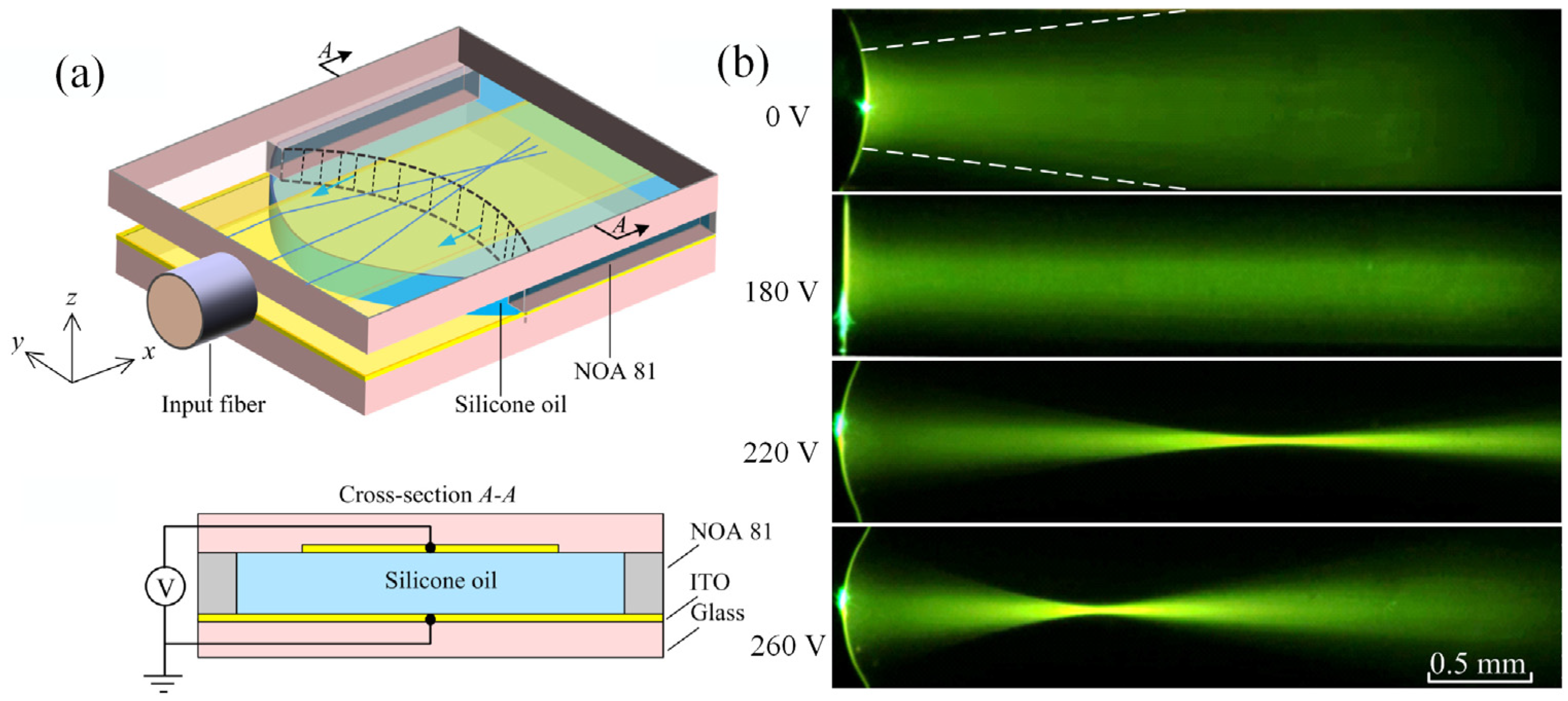
3.3. Dielectrophoresis Actuated Devices for in-Plane Applications
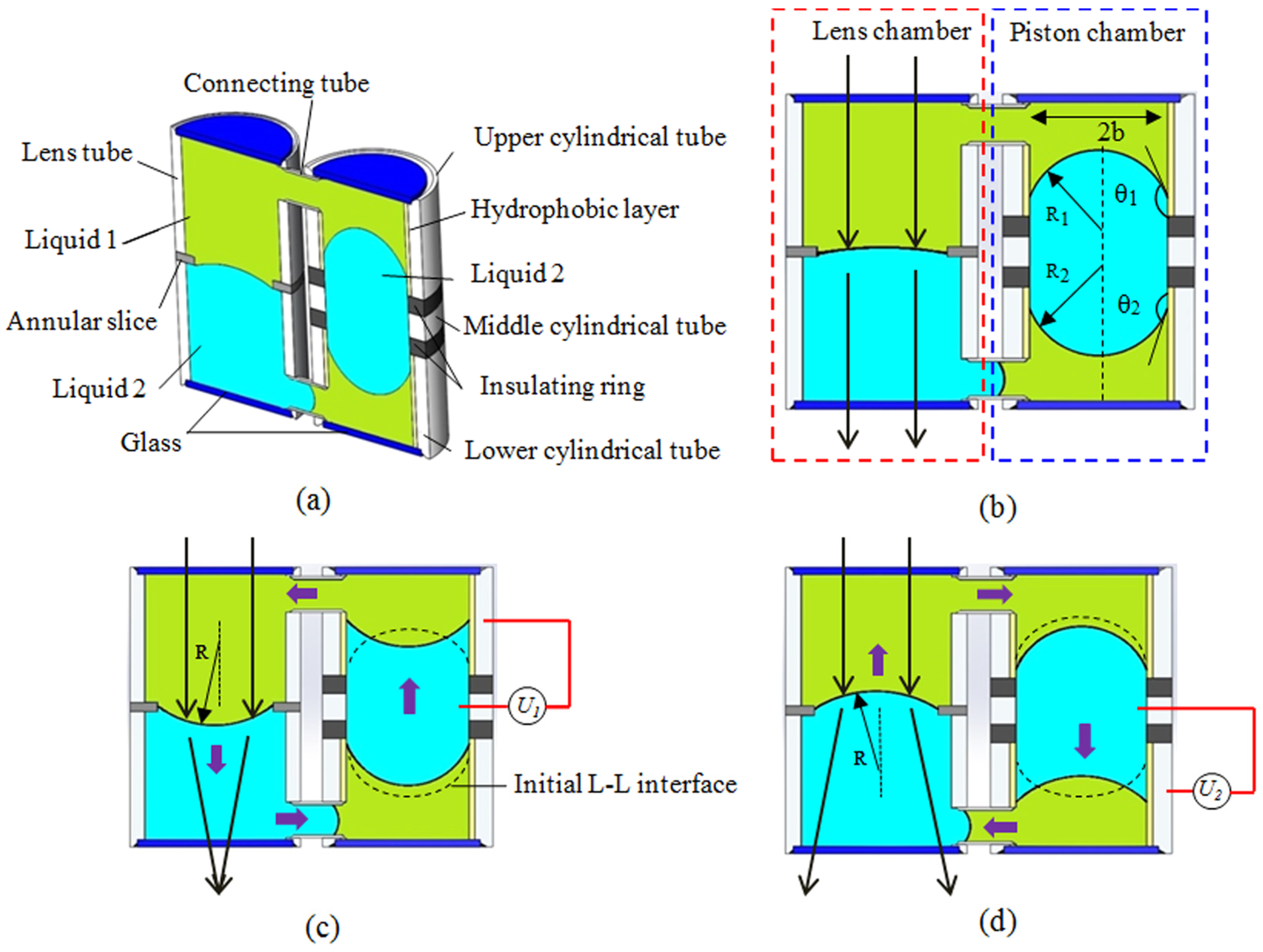
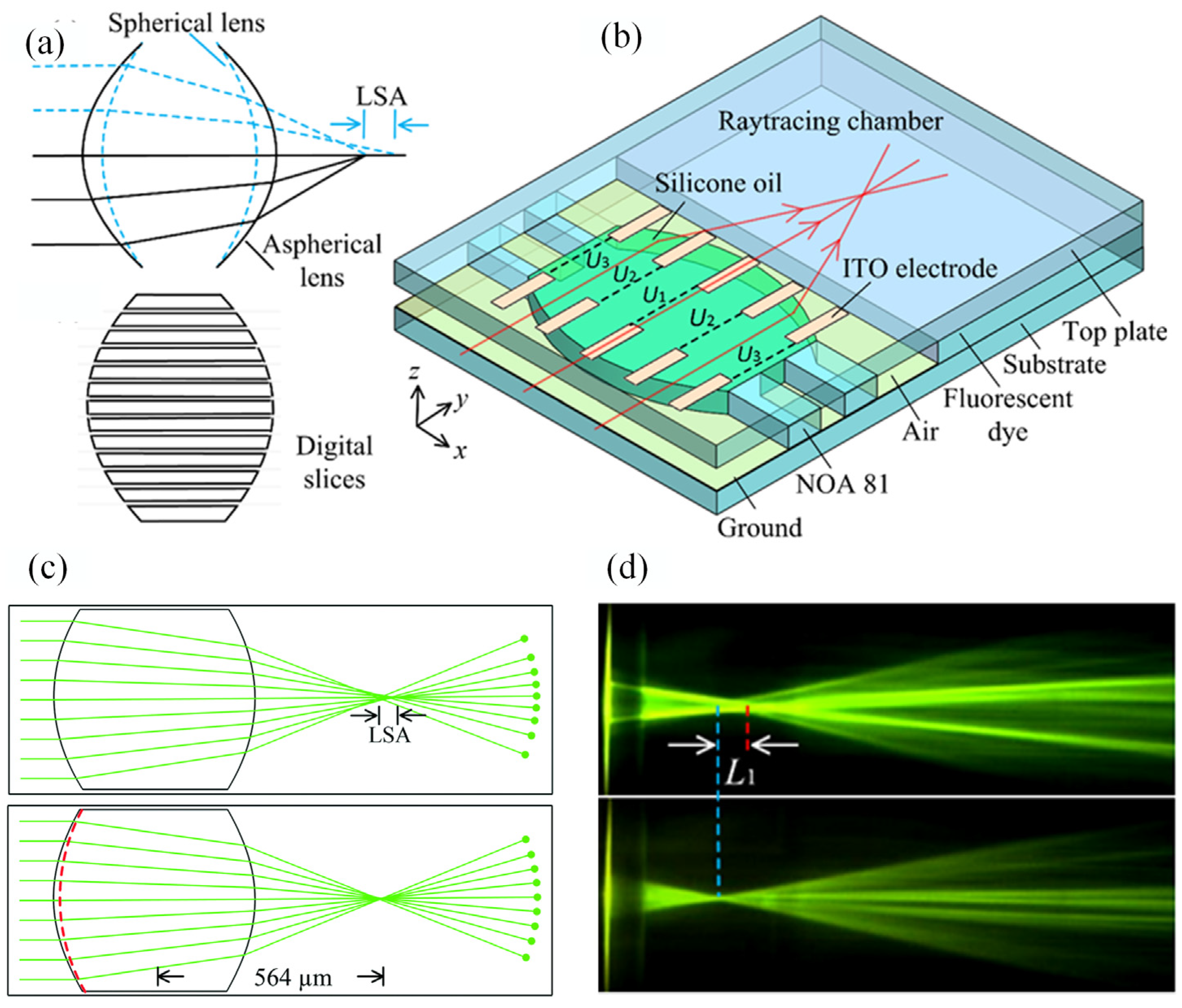
4. Novel Designs for Electrical Liquid Lens
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Psaltis, D.; Quake, S.R.; Yang, C.H. Developing optofluidic technology through the fusion of 360 microfluidics and optics. Nature 2006, 442, 381–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhao, Y.; Stratton, Z.S.; Guo, F.; Lapsley, M.I.; Chan, C.Y.; Lin, S.-C.S.; Huang, T.J. Optofluidic imaging: Now and beyond. Lab Chip 2013, 13, 17–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Monat, C.; Domachuk, P.; Eggleton, B.J. Integrated optofluidics: A new river of light. Nat. Photon. 2007, 1, 106–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fan, X.; White, I.M. Optofluidic Microsystems for Chemical and Biological Analysis. Nat. Photon. 2011, 5, 591–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pang, L.; Chen, H.M.; Freeman, L.M.; Fainman, Y. Optofluidic devices and applications in photonics, sensing and imaging. Lab chip 2012, 12, 3543–3551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.F.; Jiang, L.; Mancuso, M.; Jain, A.; Oncescu, V.; Erickson, D. Optofluidic opportunities in global health, food, water and energy. Nanoscale 2012, 4, 4839–4857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Erickson, D.; Sinton, D.; Psaltis, D. Optofluidics for energy applications. Nat. Photon. 2011, 5, 583–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levy, U.; Shamai, R. Tunable optofluidic devices. Microfluid Nanofluidics 2007, 4, 97–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monat, C.; Domachuk, P.; Grillet, C.; Collins, M.; Eggleton, B.J.; Cronin-Golomb, M.; Mutzenich, S.; Mahmud, T.; Rosengarten, G.; Mitchell, A. Optofluidics: A novel generation of reconfigurable and adaptive compact architectures. Microfluid Nanofluidics 2007, 4, 81–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandal, S.; Erickson, D. Nanoscale optofluidic sensor arrays. Opt. Express 2008, 16, 1623–1631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunt, H.C.; Wilkinson, J.S. Optofluidic integration for microanalysis. Microfluid Nanofluidics 2008, 4, 53–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, X.; Yun, S.H. The potential of optofluidic biolasers. Nat. Methods 2014, 11, 141–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, S.K.Y.; Mayers, B.T.; Vezenov, D.V.; Whitesides, G.M. Optical waveguiding using thermal gradients across homogeneous liquids in microfluidic channels. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2006, 88, 061112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Liu, A.Q.; Chin, L.K.; Zhang, X.M.; Tsai, D.P.; Lin, C.L.; Lu, C.; Wang, G.P.; Zheludev, N.I. Optofluidic waveguide as a transformation optics device for lightwave bending and manipulation. Nat. Commun. 2012, 3, 651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nguyen, N.T. Micro-optofluidic Lenses: A review. Biomicrofluidics 2010, 4, 031501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hayes, R.A.; Feenstra, B.J. Video-speed electronic paper based on electrowetting. Nature 2003, 425, 383–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J.; Stratton, Z.; Lin, S.C.S.; Huang, H.; Huang, T.J. Tunable optofluidic microlens through active pressure control of an air–liquid interface. Microfluidics Nanofluidics 2010, 9, 313–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, H.; Fox, D.; Anderson, P.A.; Wu, B.; Wu, S.T. Tunable-focus liquid lens controlled using a servo motor. Opt. Express 2006, 14, 8031–8036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuiper, S.; Hendriks, B.H.W. Variable-focus liquid lens for miniature cameras. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2004, 85, 1128–1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, S.; Ren, H.; Wu, S. Dielectrophoretically tunable optofluidic devices. J. Phys. D 2013, 46, 483001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, S.; Wang, F. Multiphase optofluidics on an electro-microfluidic platform powered by electrowetting and dielectrophoresis. Lab Chip 2014, 14, 2728–2738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.; Ghilardi, M.; Busfield, J.J.C.; Carpi, F. Electrically Tunable Lenses: A Review. Front. Robot. AI 2021, 8, 678046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mugele, F.; Baret, J.-C. Electrowetting: From basics to applications. J. Phys. 2005, 17, 705–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krogmann, F.; Mönch, W.; Zappe, H. A MEMS-Based Variable Microlens System. J. Opt. 2006, 8, 330–336. [Google Scholar]
- Li, L.-Y.; Yuan, R.-Y.; Wang, J.-H.; Li, L.; Wang, Q.-H. Optofluidic lens based on electrowetting liquid piston. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 13062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, C.; Jiang, H. Electrowetting-driven variable-focus microlens on flexible surfaces. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2012, 100, 231105–2311054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cheng, Y.; Cao, J.; Tang, X.; Hao, Q. Optical zoom imaging systems using adaptive liquid lenses. Bioinspir. Biomim. 2021, 16, 041002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Wang, D.; Liu, C.; Wang, Q.-H. Zoom microscope objective using electrowetting lenses. Opt. Express 2016, 24, 2931–2940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Wang, J.-H.; Wang, Q.-H.; Wu, S.-T. Displaceable and focus-tunable electrowetting optofluidic lens. Opt. Express 2018, 26, 25839–25848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Xiao, L.; Wang, J.H.; Wang, Q.H. Movable electrowetting optofluidic lens for optical axial scanning in microscopy. Opto-electron. Adv. 2019, 2, 18002501–18002505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Park, Y.; Chung, S.-K. Multifunctional liquid lens for variable focus and aperture. Sens. Actuator A Phys. 2019, 287, 177–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mo, Z.; Wei, Y.L.; Bright, V.M.; Gopinath, J.T. High extinction ratio, low insertion loss, optical switch based on an electrowetting prism. Opt. Express 2020, 28, 5991–6001. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, C.; Shin, D.; Koo, G.; Yong, H.W. Fabrication of electrowetting liquid microlens array for focus tunable integral imaging system. Opt. Lett. 2020, 45, 511–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watson, A.M.; Dease, K.; Terrab, S.; Roath, C.; Gopinath, J.T.; Bright, V.M. Focus-tunable low-power electrowetting lenses with thin parylene films. Appl. Opt. 2015, 54, 6224–6229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kornyshev, A.A.; Kucernak, A.R.; Marinescu, M.; Monroe, C.W.; Sleightholme, A.E.S.; Urbakh, M. Ultra-Low-Voltage Electrowetting. J. Phys. Chem. C 2010, 114, 14885–14890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kopp, D.; Zappe, H. Tubular astigmatism-tunable fluidic lens. Opt. Lett. 2016, 41, 2735–2738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, X.; Zhang, H.; Li, D.; Jia, D.; Liu, T. Electrowetting lens with large aperture and focal length tunability. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 16318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Supekar, O.D.; Zohrabi, M.; Gopinath, J.T.; Bright, V.M. Enhanced Response Time of Electrowetting Lenses with Shaped Input Voltage Functions. Langmuir 2017, 33, 4863–4869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, P.; Li, Y.; Zappe, H. Accelerated electrowetting-based tunable fluidic lenses. Opt. Express 2021, 29, 15733–15746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, T.B. Liquid dielectrophoresis on the microscale. J. Electrostat 2001, 51–52, 290–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Barman, J.; Shao, W.; Tang, B.; Yuan, D.; Groenewold, J.; Zhou, G. Wettability Manipulation by Interface-Localized Liquid Dielectrophoresis: Fundamentals and Applications. Micromachines 2019, 10, 329. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, H.; Xianyu, H.; Xu, S.; Wu, S.T. Adaptive dielectric liquid lens. Opt. Express 2008, 16, 14954–14960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, S.K.; Lee, H.P.; Chien, C.C.; Lu, Y.W.; Chiu, Y.; Lin, F.Y. Reconfigurable liquid-core/liquid-cladding optical waveguides with dielectrophoresis-driven virtual microchannels on an electromicrofluidic platform. Lab Chip 2016, 16, 847–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, Y.J.; Chen, K.M.; Wu, S.T. Broadband and polarization-independent beam steering using dielectrophoresis-tilted prism. Opt. Express 2009, 17, 8651–8656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, C.V.; Wells, G.G.; Newton, M.I.; McHale, G. Voltage-programmable liquid optical interface. Nat. Photonics 2009, 3, 403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ren, H.; Xu, S.; Liu, Y.; Wu, S.T. Electro-optical properties of dielectric liquid microlens. Opt. Commun. 2011, 284.8, 2122–2125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, C.C.; Yeh, J.A. Dielectrically actuated liquid lens. Opt. Express 2007, 15, 7140–7145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, C.C.; Chang, C.A.; Yeh, J.A. Variable focus dielectric liquid droplet lens. Opt. Express 2006, 14, 4101–4106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.C.; Tsai, Y.C.; Shin, W.P. Flexible pdms micro-lens array with programmable focus gradient fabricated by dielectrophoresis force. Microelectron Eng. 2011, 88, 2748–2750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Li, T.; Li, Z.; Long, J.; Zhang, X. Optofluidic Tunable Lenses for In-Plane Light Manipulation. Micromachines 2018, 9, 97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, Q.; Li, T.; Zhu, Y.; Yu, W.; Zhang, X. Dielectrophoresis-actuated in-plane optofluidic lens with tunability of focal length from negative to positive. Opt. Express 2018, 26, 6532–6541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Q.; Li, T.; Li, Z.; Lu, C.; Zhang, X. Dielectrophoresis-actuated liquid lenses with dual air/liquid interfaces tuned from biconcave to biconvex. Lab Chip 2018, 24, 3849–3854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Tong, X.; Zhu, Y.; Tsoi, C.C.; Jia, Y.; Li, Z.; Zhang, X. Aberration-free aspherical in-plane tunable liquid lenses by regulating local curvatures. Lab Chip 2020, 5, 995–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, K.; Murade, C.; Carreel, B.; Roghair, I.; Oh, J.M.; Manukyan, G.; van den Ende, D.; Mugele, F. Optofluidic lens with tunable focal length and asphericity. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 6378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cang, C.; Cao, Y.; Jiang, D.; Tian, J.; Zhang, C. Triboelectric effect-modulated varifocal liquid lens. Microsyst. Nanoeng. 2020, 6, 61. [Google Scholar]






Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, L.; Liang, S.; Chen, Z.; Liang, X.; Chen, Q. Electrically Tunable Lenses for Imaging and Light Manipulation. Micromachines 2023, 14, 319. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi14020319
Chen L, Liang S, Chen Z, Liang X, Chen Q. Electrically Tunable Lenses for Imaging and Light Manipulation. Micromachines. 2023; 14(2):319. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi14020319
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Lijun, Shijie Liang, Zhenshi Chen, Xifa Liang, and Qingming Chen. 2023. "Electrically Tunable Lenses for Imaging and Light Manipulation" Micromachines 14, no. 2: 319. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi14020319
APA StyleChen, L., Liang, S., Chen, Z., Liang, X., & Chen, Q. (2023). Electrically Tunable Lenses for Imaging and Light Manipulation. Micromachines, 14(2), 319. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi14020319





