Fundamental Understanding of Multicellular Triboelectric Nanogenerator with Different Electrical Configurations
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experiment and Finite Element Simulation
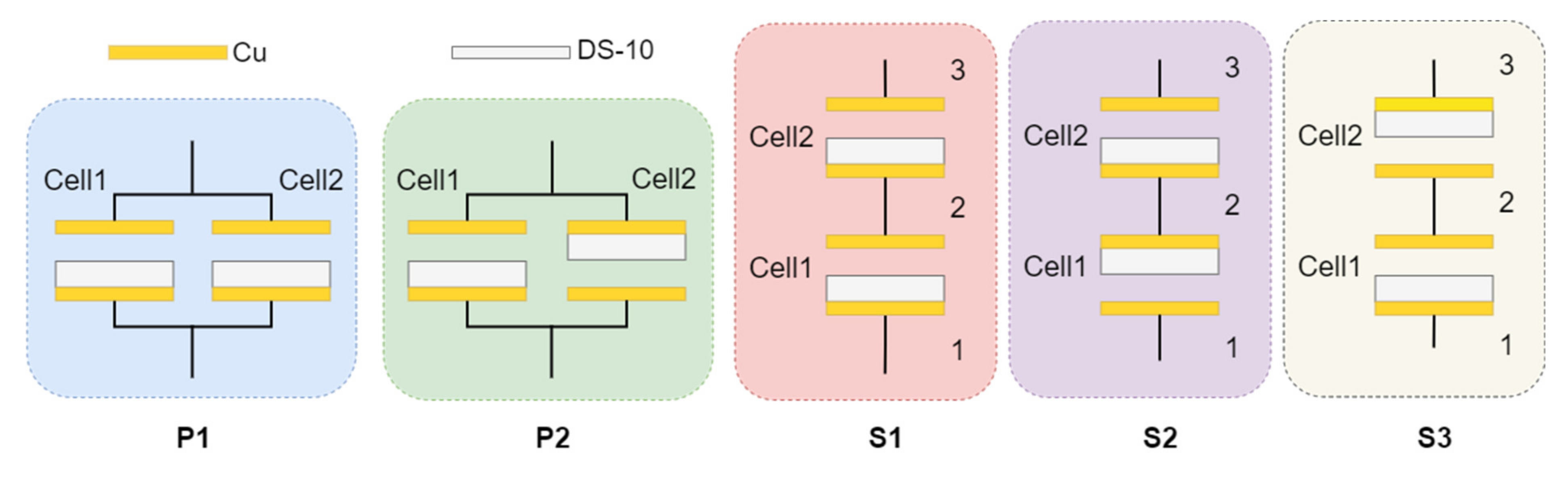
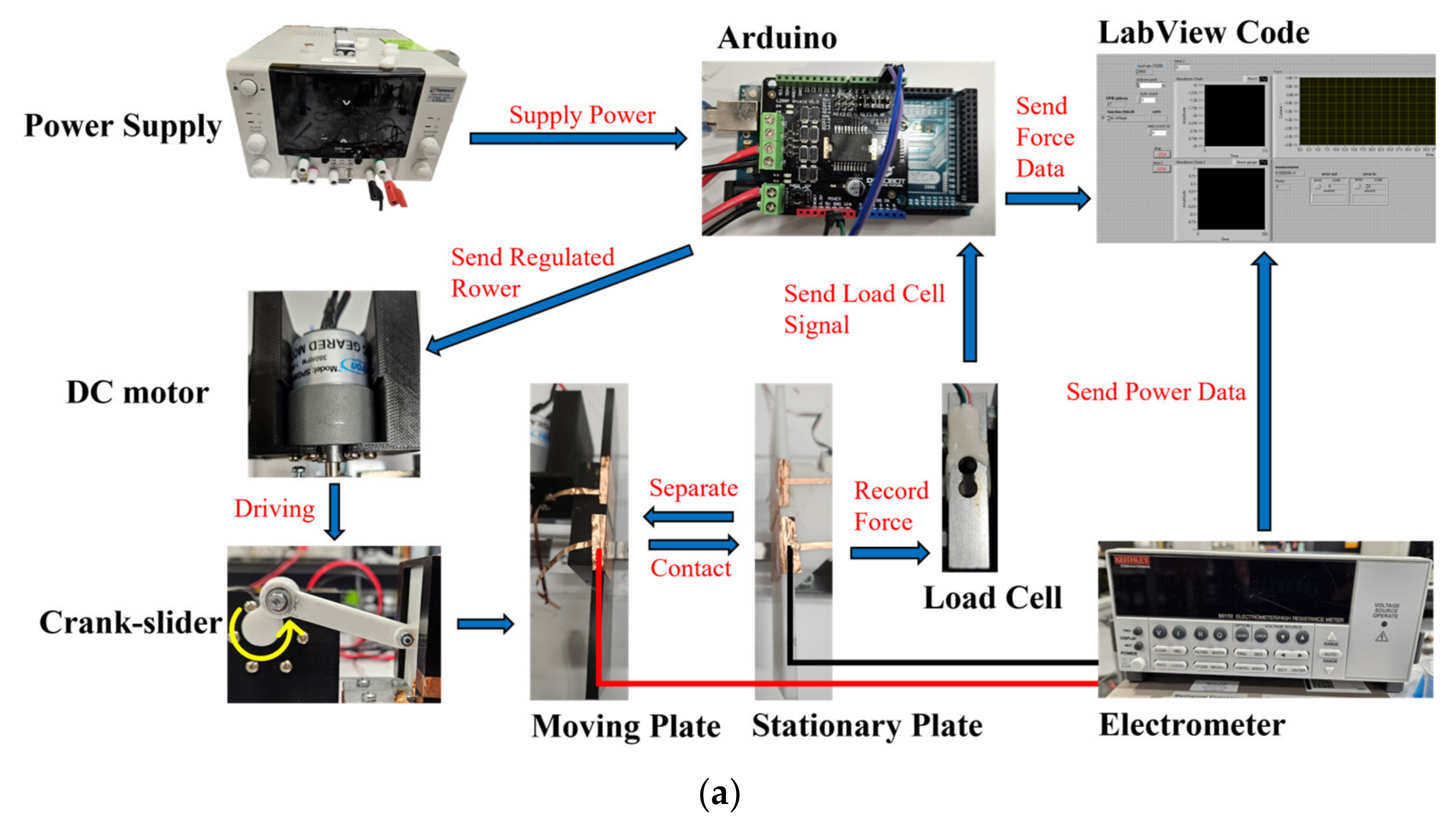
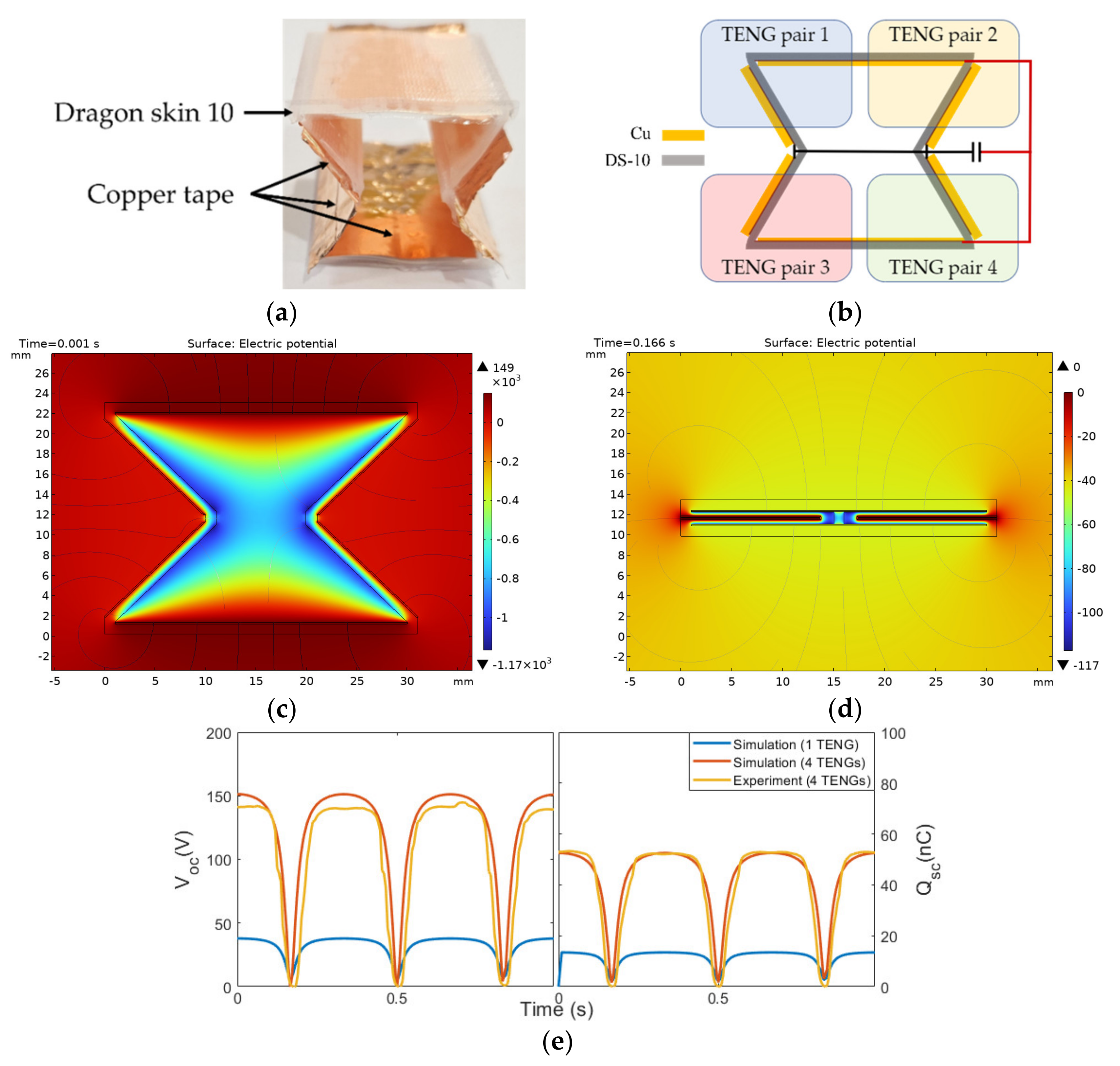
2.1. TENG Configuration and Experimental Setup
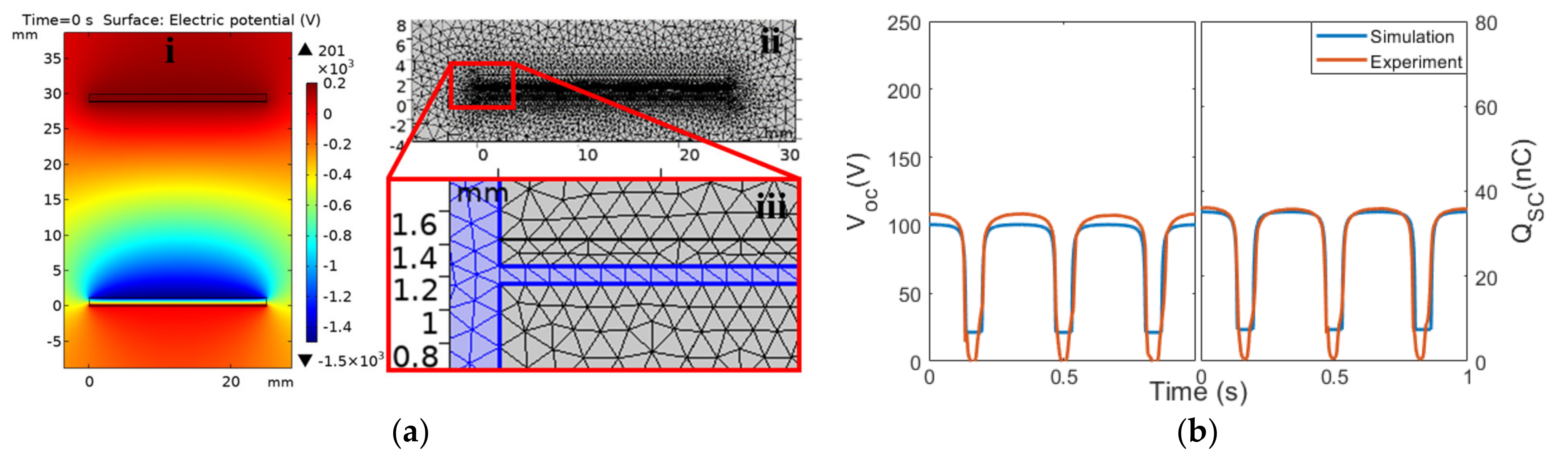
2.2. Finite Element Simulation
3. Results and Discussion
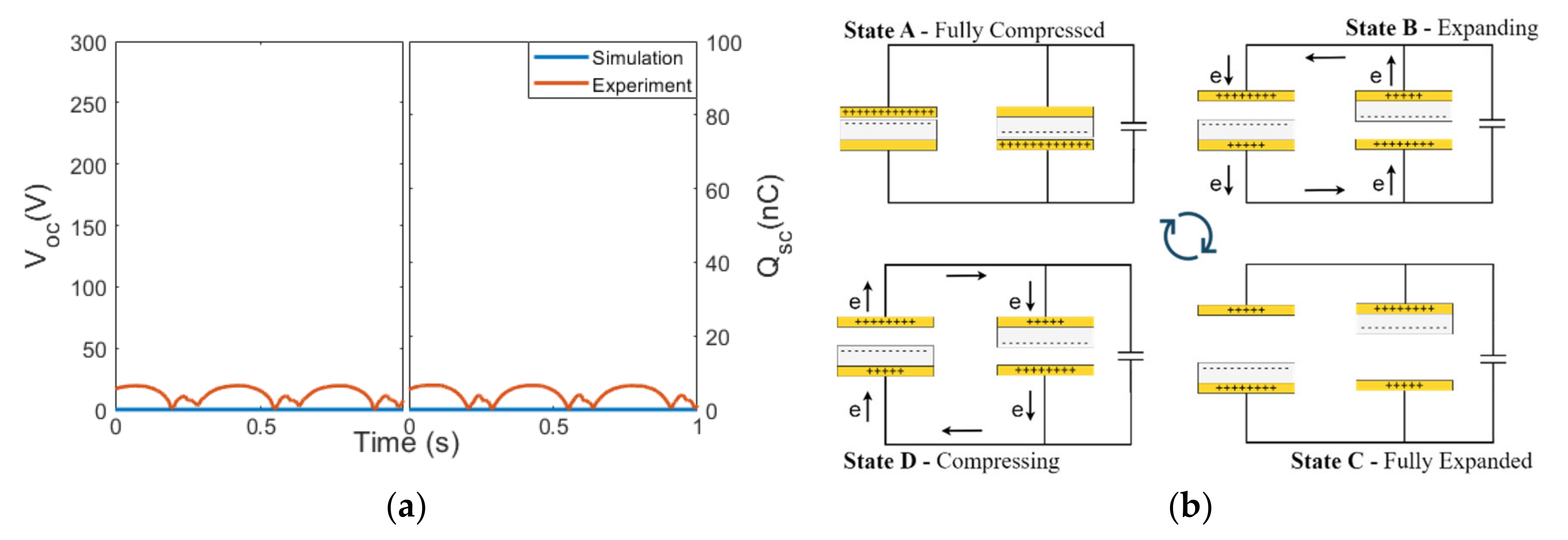
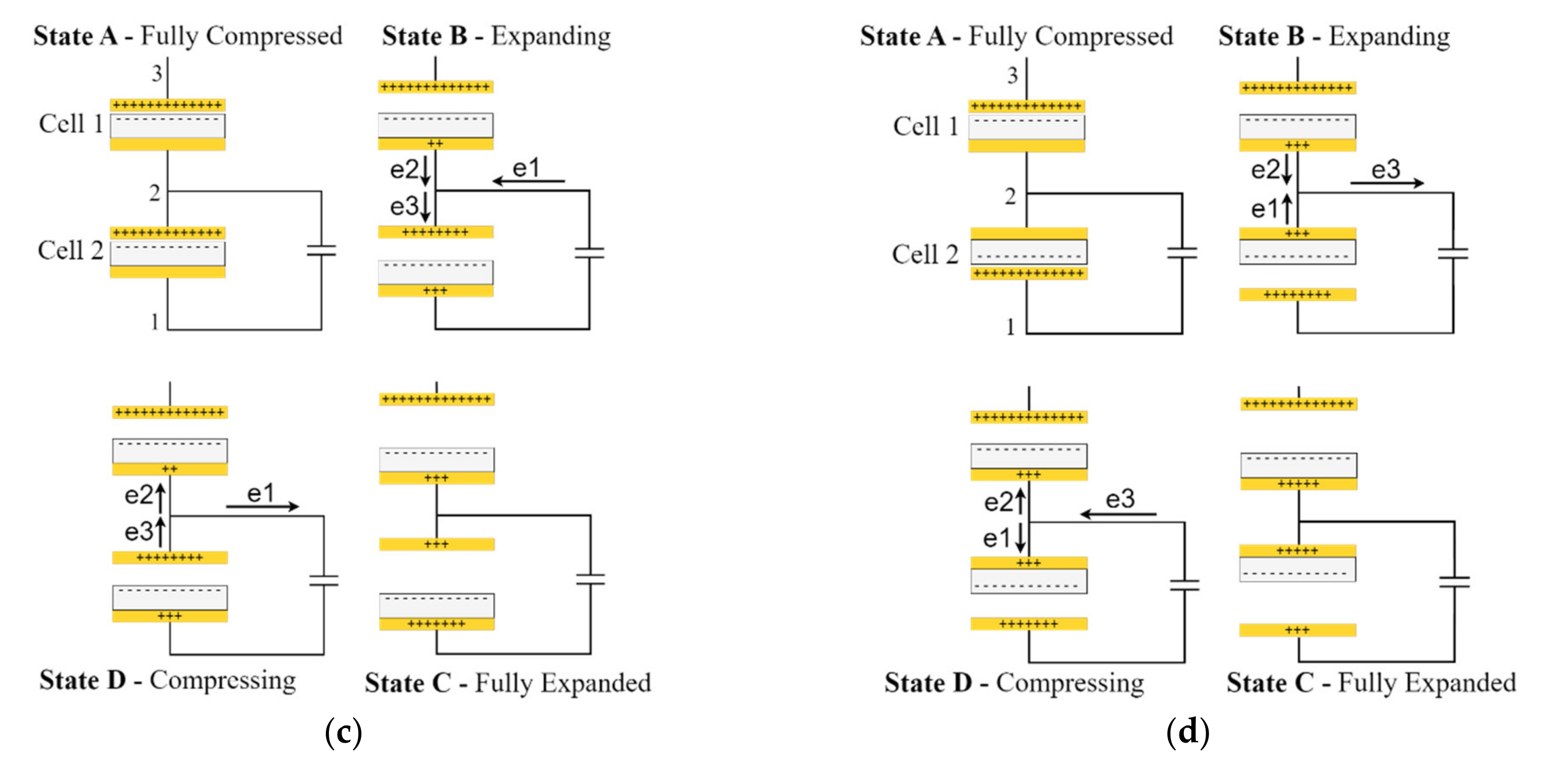
3.1. Configuration P1
3.2. Configuration P2
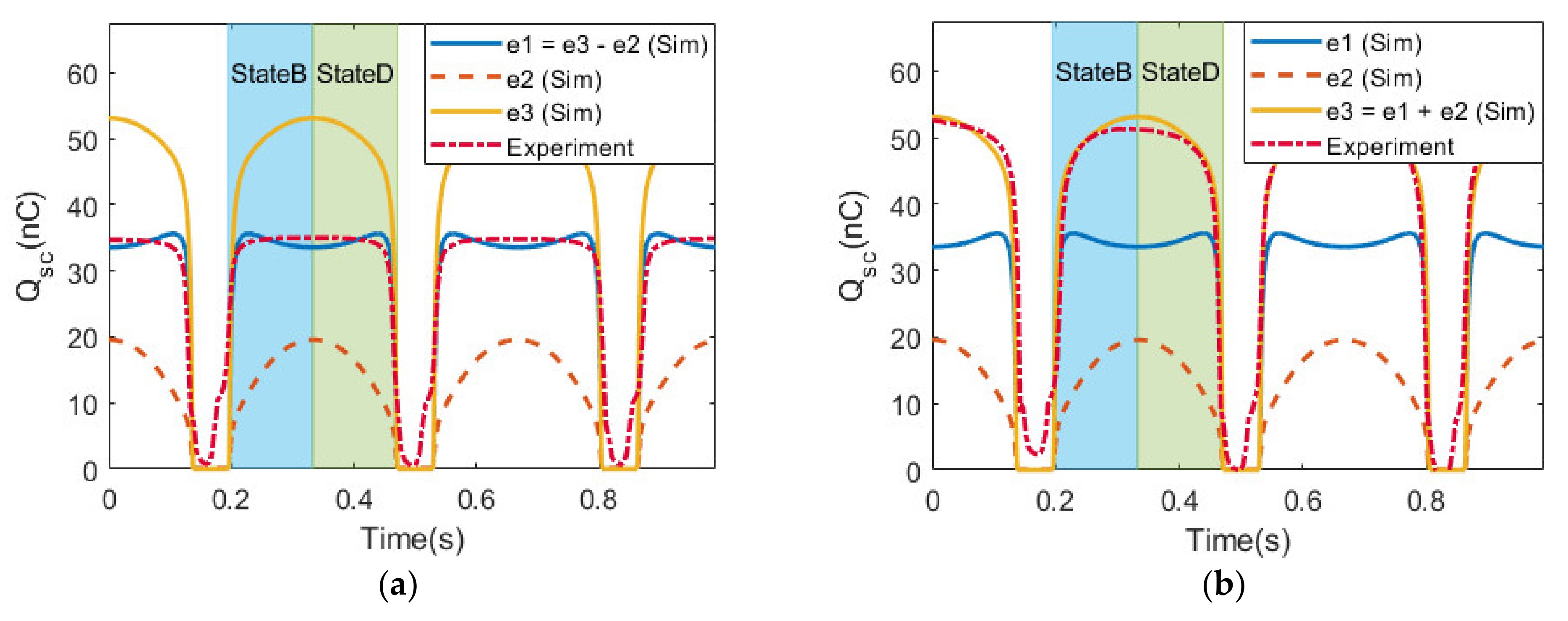
3.3. Configuration S1
3.4. Configurations S2 and S3
3.5. Special Cases
3.6. Comparison and Discussion
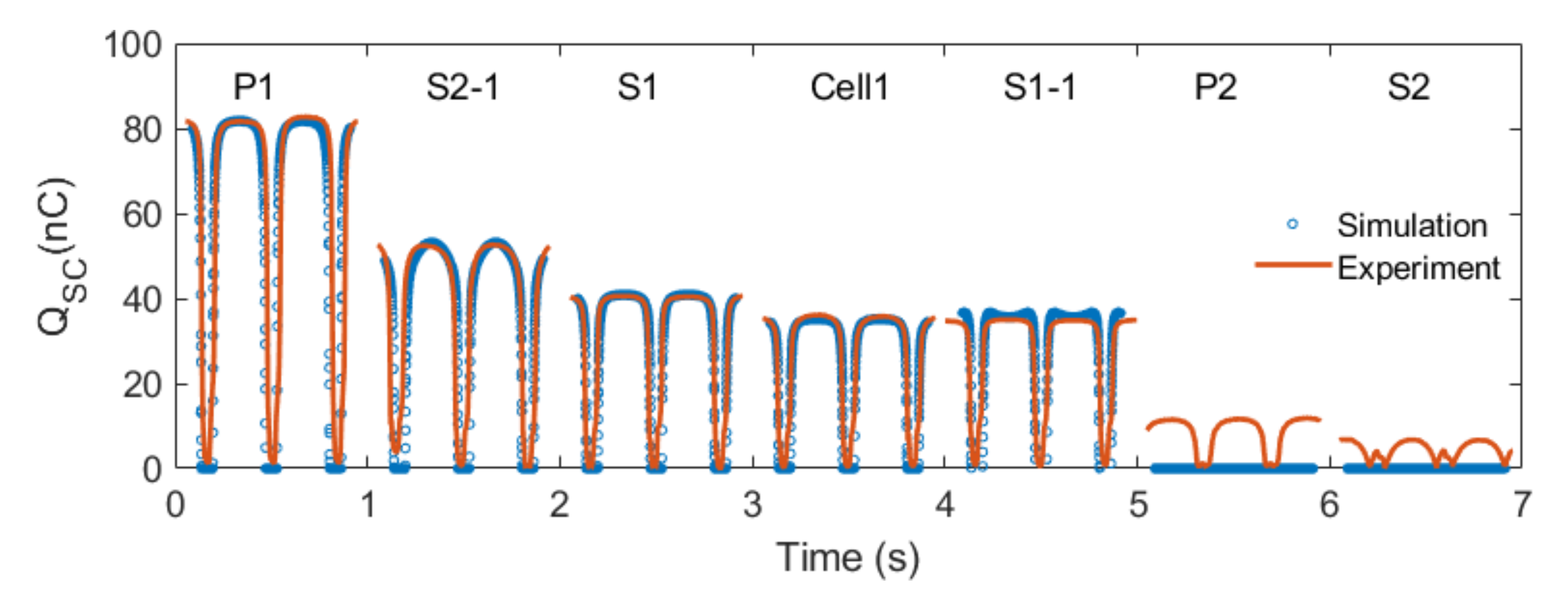
4. Further Case Study
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, Z.L. Nanogenerators, Self-Powered Systems, Blue Energy, Piezotronics and Piezo-Phototronics–A Recall on the Original Thoughts for Coining These Fields. Nano Energy 2018, 54, 477–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.-S.; Han, M.; Kim, B.; Bao, J.-F.; Brugger, J.; Zhang, H. All-in-One Self-Powered Flexible Microsystems Based on Triboelectric Nanogenerators. Nano Energy 2018, 47, 410–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haight, R.; Haensch, W.; Friedman, D. Solar-Powering the Internet of Things. Science 2016, 353, 124–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Fuqaha, A.; Guizani, M.; Mohammadi, M.; Aledhari, M.; Ayyash, M. Internet of Things: A Survey on Enabling Technologies, Protocols, and Applications. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor. 2015, 17, 2347–2376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Okonkwo, E.G.; Huang, G.; Xu, S.; Sun, W.; He, Y. On the Sustainability of Lithium Ion Battery Industry–A Review and Perspective. Energy Storage Mater. 2021, 36, 186–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Min, J.; Yu, Y.; Wang, H.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Gao, W. Wireless Battery-Free Wearable Sweat Sensor Powered by Human Motion. Sci. Adv. 2020, 6, eaay9842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larcher, D.; Tarascon, J.-M. Towards Greener and More Sustainable Batteries for Electrical Energy Storage. Nat. Chem. 2015, 7, 19–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Li, S.; Yi, F.; Zi, Y.; Lin, J.; Wang, X.; Xu, Y.; Wang, Z.L. Sustainably Powering Wearable Electronics Solely by Biomechanical Energy. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 12744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Thostenson, J.O.; Li, Z.; Kim, C.H.J.; Ajnsztajn, A.; Parker, C.B.; Liu, J.; Peterchev, A.V.; Glass, J.T.; Goetz, S.M. Integrated Flexible Conversion Circuit between a Flexible Photovoltaic and Supercapacitors for Powering Wearable Sensors. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2018, 165, B3122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Fukuda, K.; Karki, A.; Park, S.; Kimura, H.; Jinno, H.; Watanabe, N.; Yamamoto, S.; Shimomura, S.; Kitazawa, D.; et al. Thermally Stable, Highly Efficient, Ultraflexible Organic Photovoltaics. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, 4589–4594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kanan, R.; Elhassan, O.; Bensalem, R. An IoT-Based Autonomous System for Workers’ Safety in Construction Sites with Real-Time Alarming, Monitoring, and Positioning Strategies. Autom. Constr. 2018, 88, 73–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaziri, N.; Boughamoura, A.; Müller, J.; Mezghani, B.; Tounsi, F.; Ismail, M. A Comprehensive Review of Thermoelectric Generators: Technologies and Common Applications. Energy Rep. 2020, 6, 264–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nozariasbmarz, A.; Collins, H.; Dsouza, K.; Polash, M.H.; Hosseini, M.; Hyland, M.; Liu, J.; Malhotra, A.; Ortiz, F.M.; Mohaddes, F.; et al. Review of Wearable Thermoelectric Energy Harvesting: From Body Temperature to Electronic Systems. Appl. Energy 2020, 258, 114069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chorsi, M.T.; Curry, E.J.; Chorsi, H.T.; Das, R.; Baroody, J.; Purohit, P.K.; Ilies, H.; Nguyen, T.D. Piezoelectric Biomaterials for Sensors and Actuators. Adv. Mater. 2019, 31, 1802084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, Y.; Ma, Y.; Zheng, H.; Ramakrishna, S. Piezoelectric Materials for Flexible and Wearable Electronics: A Review. Mater. Des. 2021, 211, 110164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; You, Z. A Shoe-Embedded Piezoelectric Energy Harvester for Wearable Sensors. Sensors 2014, 14, 12497–12510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashyap, A.Y.I.; Dahlan, S.H.B.; Zainal Abidin, Z.; Abbasi, M.I.; Kamarudin, M.R.; Majid, H.A.; Dahri, M.H.; Jamaluddin, M.H.; Alomainy, A. An Overview of Electromagnetic Band-Gap Integrated Wearable Antennas. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 7641–7658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.-W.; Ke, Y.-W.; Huang, P.-C.; Hsieh, P.-H. Electromagnetic Energy Harvester Interface Design for Wearable Applications. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. II Express Briefs 2018, 65, 667–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamid, R.; Yuce, M.R. A Wearable Energy Harvester Unit Using Piezoelectric–Electromagnetic Hybrid Technique. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2017, 257, 198–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J.; Wang, Z.L. Recent Progress of Triboelectric Nanogenerators: From Fundamental Theory to Practical Applications. EcoMat 2020, 2, e12059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, M.; Kang, Z.; Liao, Q.; Zhang, Q.; Gao, F.; Zhao, X.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, Y. Development, Applications, and Future Directions of Triboelectric Nanogenerators. Nano Res. 2018, 11, 2951–2969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, A.; Hassan, I.; Helal, A.S.; Sencadas, V.; Radhi, A.; Jeong, C.K.; El-Kady, M.F. Triboelectric Nanogenerator versus Piezoelectric Generator at Low Frequency (<4 Hz): A Quantitative Comparison. iScience 2020, 23, 101286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, X.; Song, Y.; Han, M.; Meng, B.; Su, Z.; Miao, L.; Zhang, H. A Flexible Large-Area Triboelectric Generator by Low-Cost Roll-to-Roll Process for Location-Based Monitoring. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2016, 247, 206–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.W.; Lee, J.H.; Kim, J.K.; Jeong, U. Material Aspects of Triboelectric Energy Generation and Sensors. NPG Asia Mater. 2020, 12, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Li, Y.; Zou, Y.; Rao, W.; Gai, Y.; Xue, J.; Wu, L.; Qu, X.; Liu, Y.; Xu, G.; et al. A Multi-Mode Triboelectric Nanogenerator for Energy Harvesting and Biomedical Monitoring. Nano Energy 2022, 92, 106715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dharmasena, R.D.I.G.; Jayawardena, K.D.G.I.; Mills, C.A.; Dorey, R.A.; Silva, S.R.P. A Unified Theoretical Model for Triboelectric Nanogenerators. Nano Energy 2018, 48, 391–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dharmasena, R.D.I.G.; Jayawardena, K.D.G.I.; Mills, C.A.; Deane, J.H.B.; Anguita, J.V.; Dorey, R.A.; Silva, S.R.P. Triboelectric Nanogenerators: Providing a Fundamental Framework. Energy Environ. Sci. 2017, 10, 1801–1811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, S.; Wang, S.; Lin, L.; Liu, Y.; Zhou, Y.S.; Hu, Y.; Wang, Z.L. Theoretical Study of Contact-Mode Triboelectric Nanogenerators as an Effective Power Source. Energy Environ. Sci. 2013, 6, 3576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, P.; Aw, K.C.; Jiang, X.; Xin, C.; Guo, H.; Tang, L.; Peng, Y.; Li, Z. Fish Gills Inspired Parallel-Cell Triboelectric Nanogenerator. Nano Energy 2022, 95, 106976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.Y.; Chun, J.; Lee, J.-H.; Kim, K.N.; Kang, N.-R.; Kim, J.-Y.; Kim, M.H.; Shin, K.-S.; Gupta, M.K.; Baik, J.M.; et al. Hydrophobic Sponge Structure-Based Triboelectric Nanogenerator. Adv. Mater. 2014, 26, 5037–5042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, W.-G.; Kim, D.-W.; Tcho, I.-W.; Kim, J.-K.; Kim, M.-S.; Choi, Y.-K. Triboelectric Nanogenerator: Structure, Mechanism, and Applications. ACS Nano 2021, 15, 258–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, S.; Zhang, Z. Fundamental Theories and Basic Principles of Triboelectric Effect: A Review. Friction 2019, 7, 2–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Cheng, L.; Zheng, Y.; Qin, Y.; Wang, Z.L. Enhancing the Performance of Triboelectric Nanogenerator through Prior-Charge Injection and Its Application on Self-Powered Anticorrosion. Nano Energy 2014, 10, 37–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, Y.; Xu, J.; Chen, K.; Chen, J. Advances in Nanostructures for High-Performance Triboelectric Nanogenerators. Adv. Mater. Technol. 2021, 6, 2000916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.T.; Rana, S.S.; Zahed, M.A.; Lee, S.; Yoon, E.-S.; Park, J.Y. Metal-Organic Framework-Derived Nanoporous Carbon Incorporated Nanofibers for High-Performance Triboelectric Nanogenerators and Self-Powered Sensors. Nano Energy 2022, 94, 106921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rana, S.M.S.; Rahman, M.T.; Salauddin, M.; Sharma, S.; Maharjan, P.; Bhatta, T.; Cho, H.; Park, C.; Park, J.Y. Electrospun PVDF-TrFE/MXene Nanofiber Mat-Based Triboelectric Nanogenerator for Smart Home Appliances. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 4955–4967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, S.; Yu, B.; Huang, T.; Yu, H.; Wang, H.; Zhang, Q.; Zhu, M. Gas-Enhanced Triboelectric Nanogenerator Based on Fully-Enclosed Structure for Energy Harvesting and Sensing. Nano Energy 2019, 55, 463–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Bu, T.Z.; Yang, X.D.; Zhang, C.; Wang, Z.L. Ultrahigh Charge Density Realized by Charge Pumping at Ambient Conditions for Triboelectric Nanogenerators. Nano Energy 2018, 49, 625–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walden, R.; Kumar, C.; Mulvihill, D.M.; Pillai, S.C. Opportunities and Challenges in Triboelectric Nanogenerator (TENG) Based Sustainable Energy Generation Technologies: A Mini-Review. Chem. Eng. J. Adv. 2022, 9, 100237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Zhu, C.; Wang, W.; Xu, R.; Chen, P.; Du, T.; Xue, T.; Wang, Z.; Xu, M. A Stackable Triboelectric Nanogenerator for Wave-Driven Marine Buoys. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, P.; Zhu, G.; Lin, Z.-H.; Jing, Q.; Chen, J.; Zhang, G.; Ma, J.; Wang, Z.L. Integrated Multilayered Triboelectric Nanogenerator for Harvesting Biomechanical Energy from Human Motions. ACS Nano 2013, 7, 3713–3719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tao, K.; Chen, Z.; Yi, H.; Zhang, R.; Shen, Q.; Wu, J.; Tang, L.; Fan, K.; Fu, Y.; Miao, J.; et al. Hierarchical Honeycomb-Structured Electret/Triboelectric Nanogenerator for Biomechanical and Morphing Wing Energy Harvesting. Nano-Micro Lett. 2021, 13, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chandrarathna, S.C.; Graham, S.A.; Ali, M.; Yu, J.S.; Lee, J.-W. An Efficient Power Management System Using Dynamically Configured Multiple Triboelectric Nanogenerators and Dual-Parameter Maximum Power Point Tracking. Adv. Energy Mater. 2022, 12, 2103249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Liu, G.; Zeng, J.; Dai, Y.; Zhou, W.; Xiao, C.; Dang, T.; Yu, W.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, C. Recent Progress of Switching Power Management for Triboelectric Nanogenerators. Sensors 2022, 22, 1668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, J.; Chen, P.; Li, C.; Li, F.; Jiang, T.; Wang, Z.L. Methods for Correctly Characterizing the Output Performance of Nanogenerators. Nano Energy 2022, 93, 106884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Zhang, H.; Jiang, J.; Liu, X. Output Characteristics of Series-Parallel Triboelectric Nanogenerators. Nanotechnology 2023, 34, 155403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, P.; Tang, L.; Li, Z.; Guo, H.; Aw, K.C. Circuit Representation, Experiment and Analysis of Parallel-Cell Triboelectric Nanogenerator. Energy Convers. Manag. 2023, 278, 116741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, K.; Zhu, Z.; Zhang, H.; Du, C.; Xu, Z.; Wang, R. Painting a High-Output Triboelectric Nanogenerator on Paper for Harvesting Energy from Human Body Motion. Nano Energy 2018, 50, 571–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, D.; Liu, T.; Meng, X.; Luo, B.; Yuan, J.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, S.; Cai, C.; Gao, C.; Wang, J.; et al. Wearable Triboelectric Visual Sensors for Tactile Perception. Adv. Mater. 2023, 35, 2209117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Property | Value |
|---|---|
| Positive triboelectric material | Cu |
| Thickness of positive triboelectric layer | d1 = 0.16 mm |
| Negative triboelectric material | Silicone |
| Thickness of negative triboelectric layer | d2 = 1 mm |
| Permittivity of negative triboelectric layer | ϵr = 3.53 |
| Triboelectric surface area | A = 7.5 cm2 |
| Initial surface charge density | 4.8 nC/cm2 |
| Maximum separation gap | Xmax = 2.77 cm |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, Z.; Gan, W.C.; Tang, L.; Aw, K.C. Fundamental Understanding of Multicellular Triboelectric Nanogenerator with Different Electrical Configurations. Micromachines 2023, 14, 1333. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi14071333
Li Z, Gan WC, Tang L, Aw KC. Fundamental Understanding of Multicellular Triboelectric Nanogenerator with Different Electrical Configurations. Micromachines. 2023; 14(7):1333. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi14071333
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Zifan, Wee Chen Gan, Lihua Tang, and Kean Chin Aw. 2023. "Fundamental Understanding of Multicellular Triboelectric Nanogenerator with Different Electrical Configurations" Micromachines 14, no. 7: 1333. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi14071333
APA StyleLi, Z., Gan, W. C., Tang, L., & Aw, K. C. (2023). Fundamental Understanding of Multicellular Triboelectric Nanogenerator with Different Electrical Configurations. Micromachines, 14(7), 1333. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi14071333








