Design of a High-Speed Rotary Ultrasonic Machining Machine Tool for Machining Microstructure of Brittle Materials
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. The Design of the HRUM Machine Tool
2.1. The Overall Structure of the Machine Tool
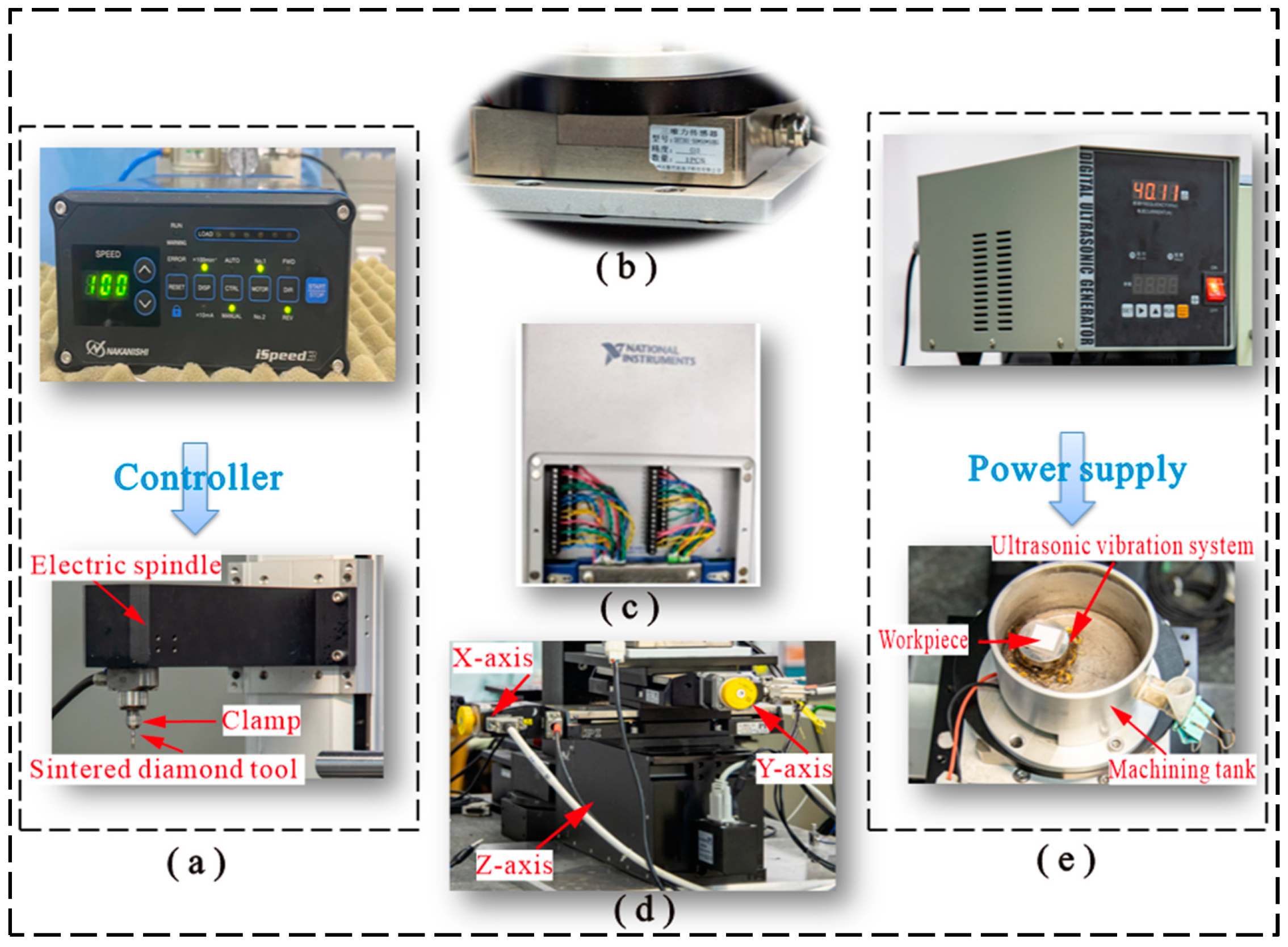
2.2. Design for Major Machine Components
Ultrasonic Vibration System Design
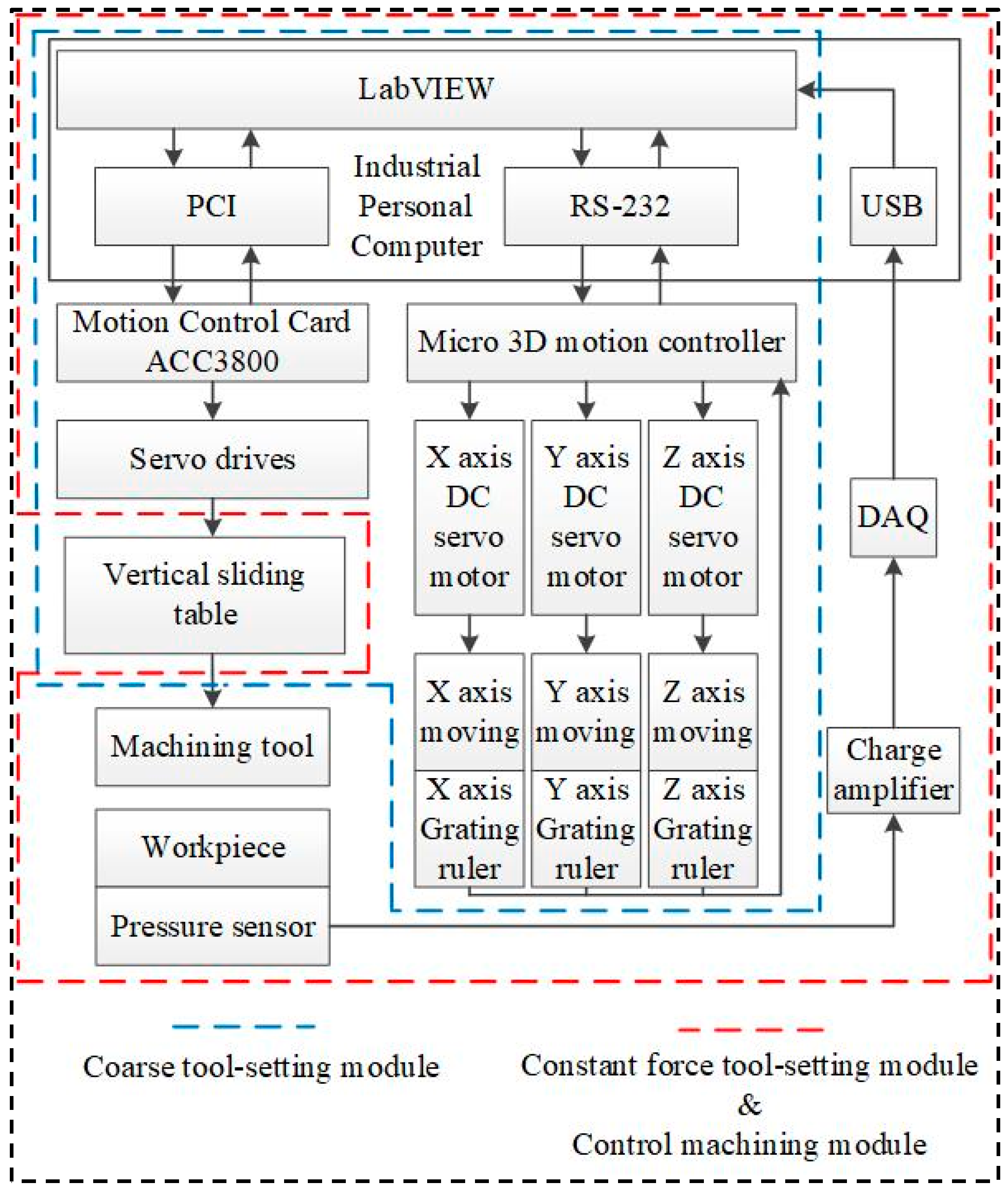
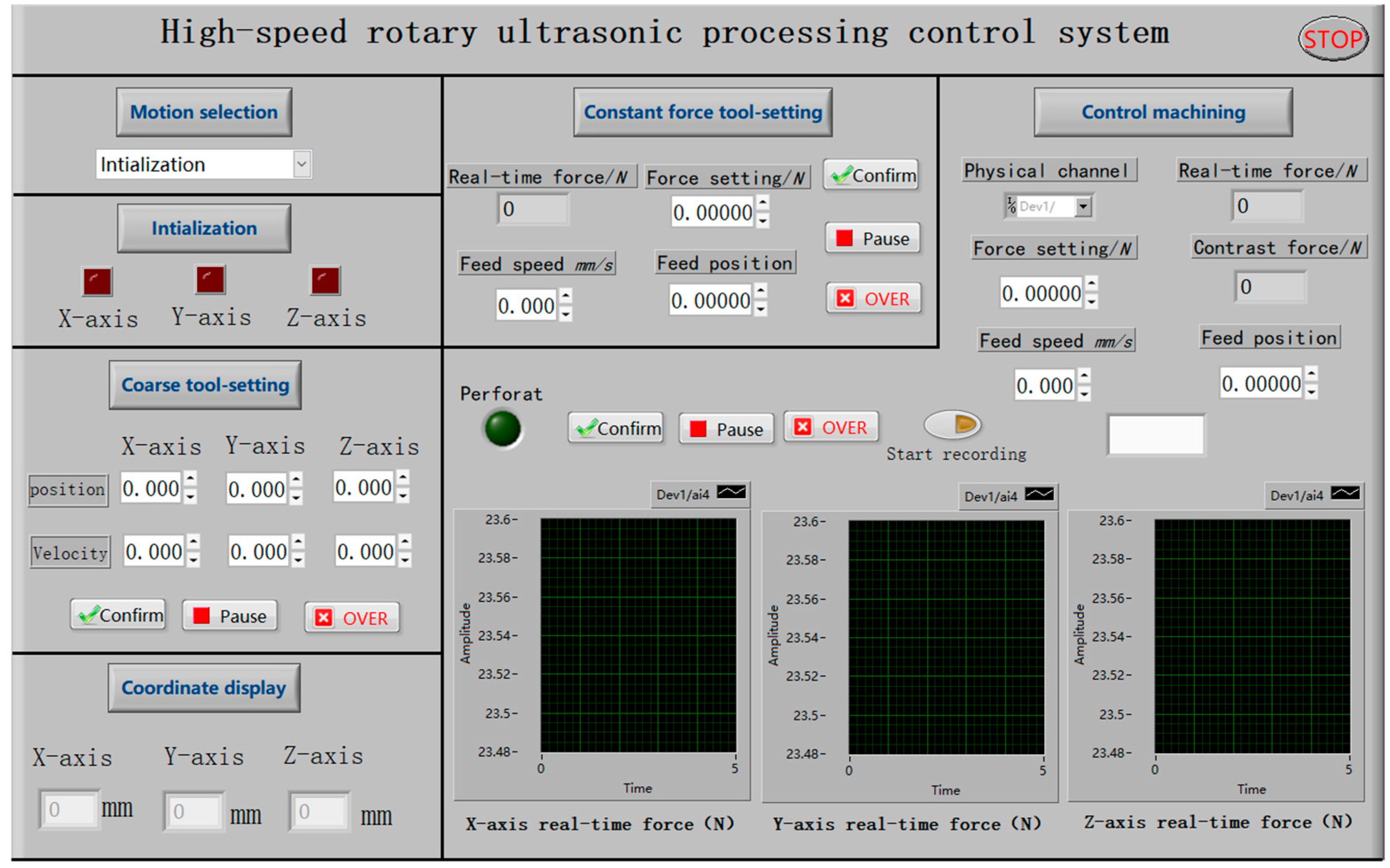
3. Machine Tool Control System Design
3.1. Constant Force Tool-Setting Module
3.2. Control Machining Module
4. Experimental Research
4.1. Experimental Setup
4.2. Results and Discussion
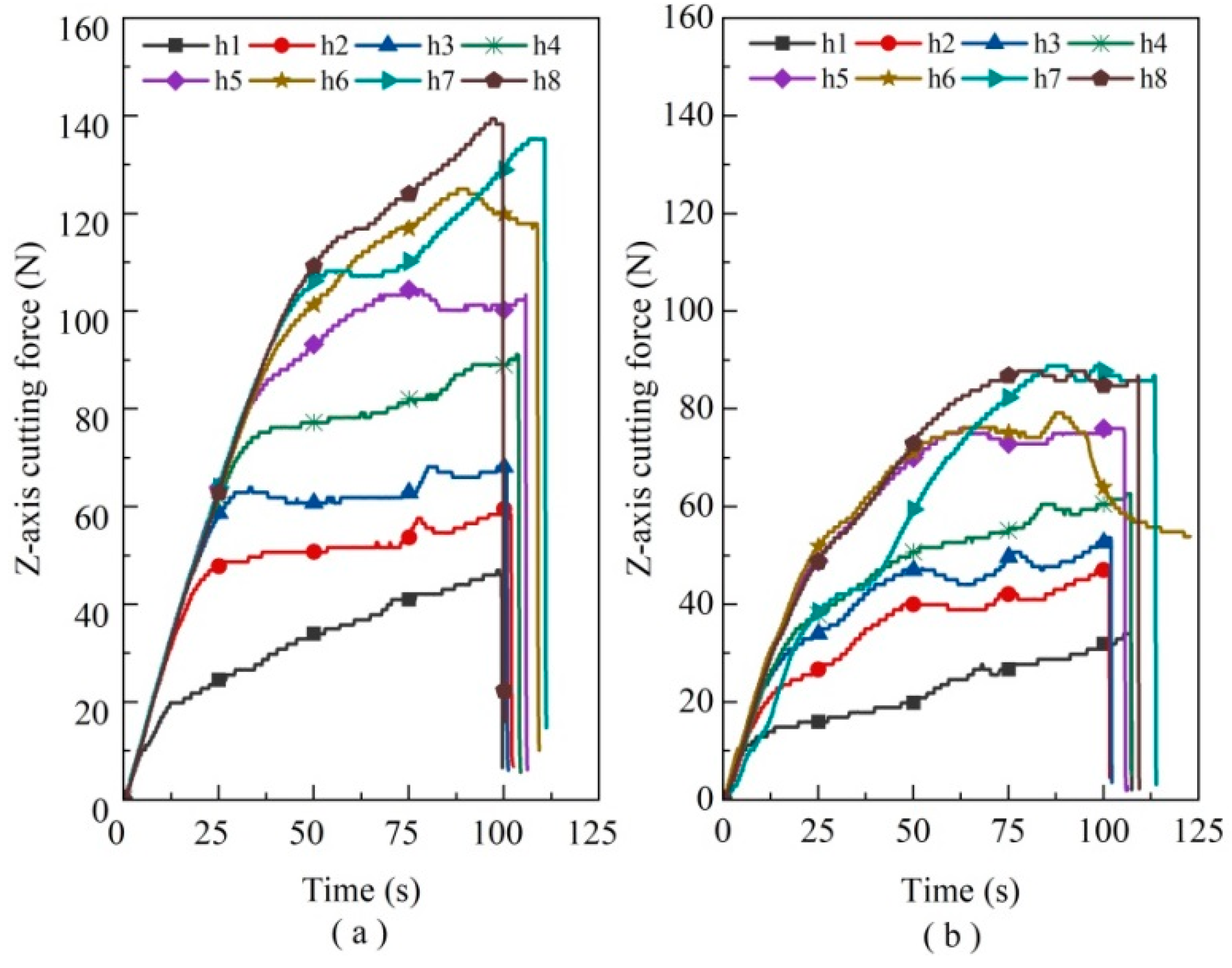
4.2.1. Effect of Tool Wear on Cutting Force and the Number of Holes Made
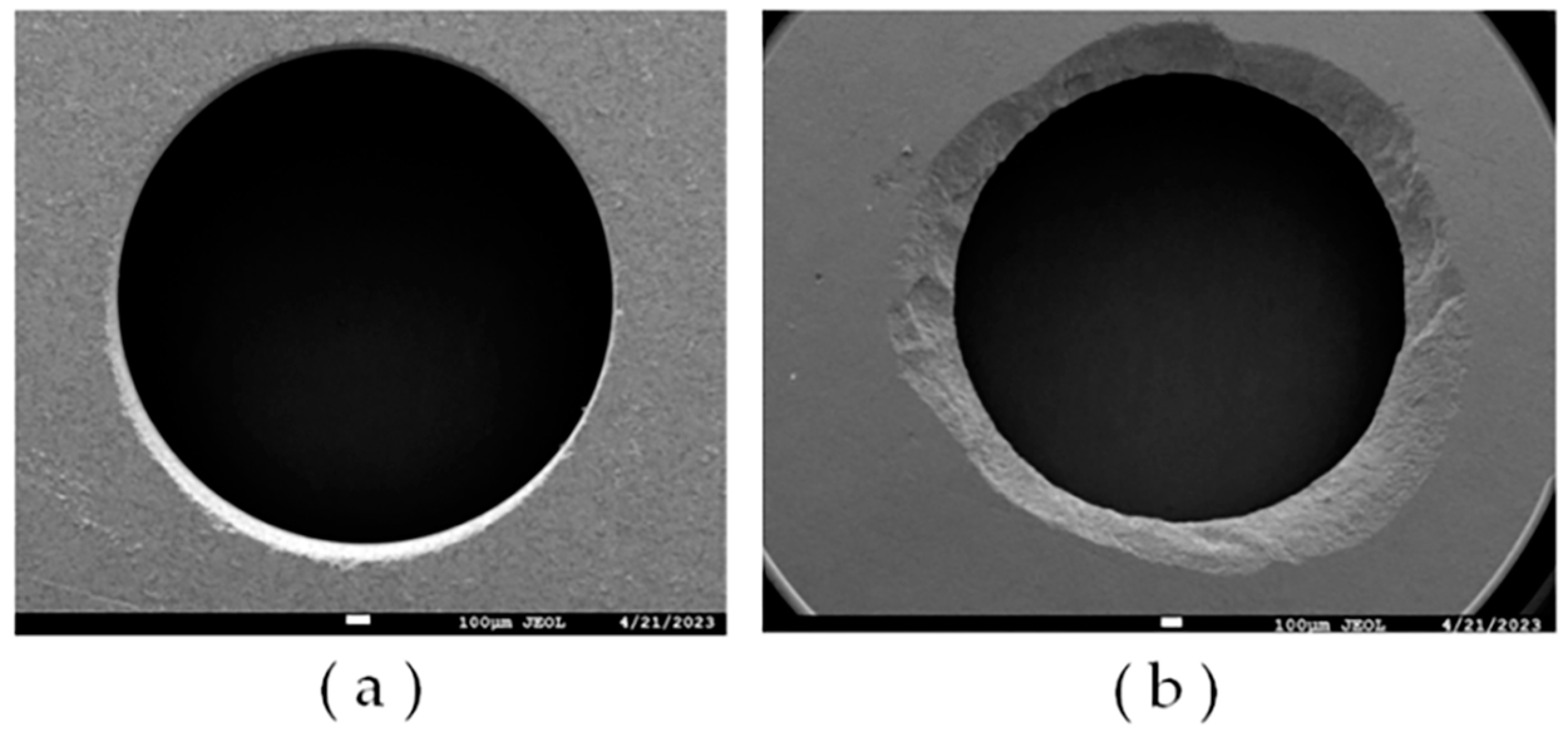
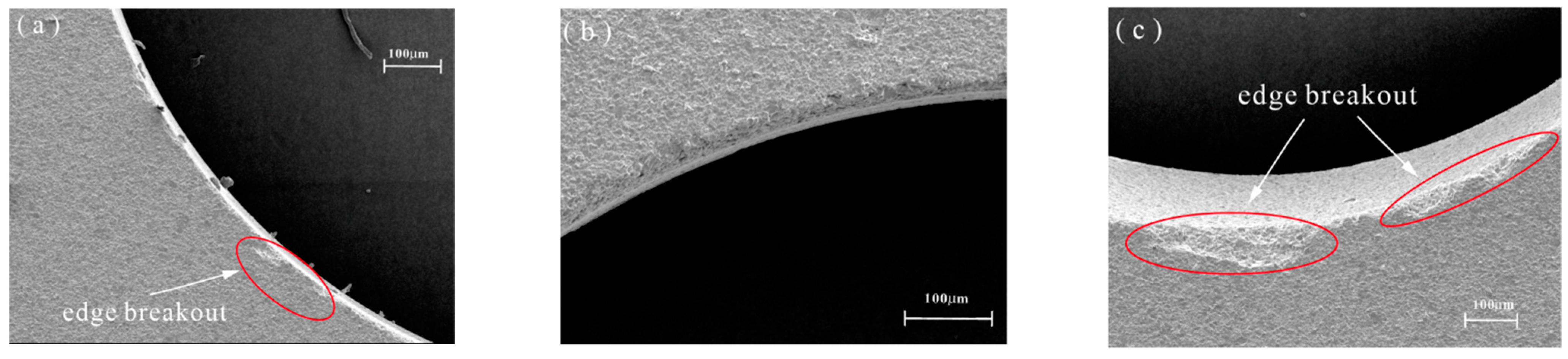
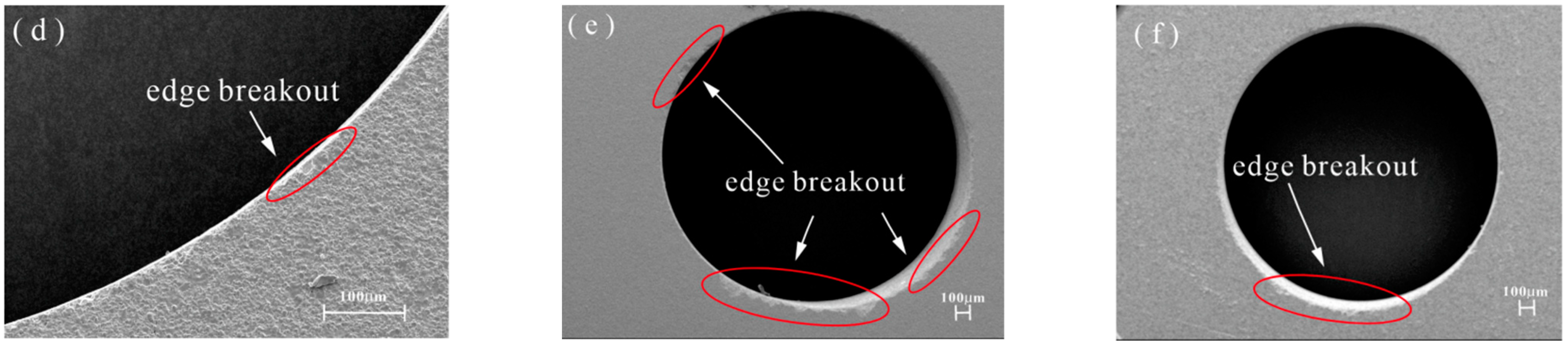
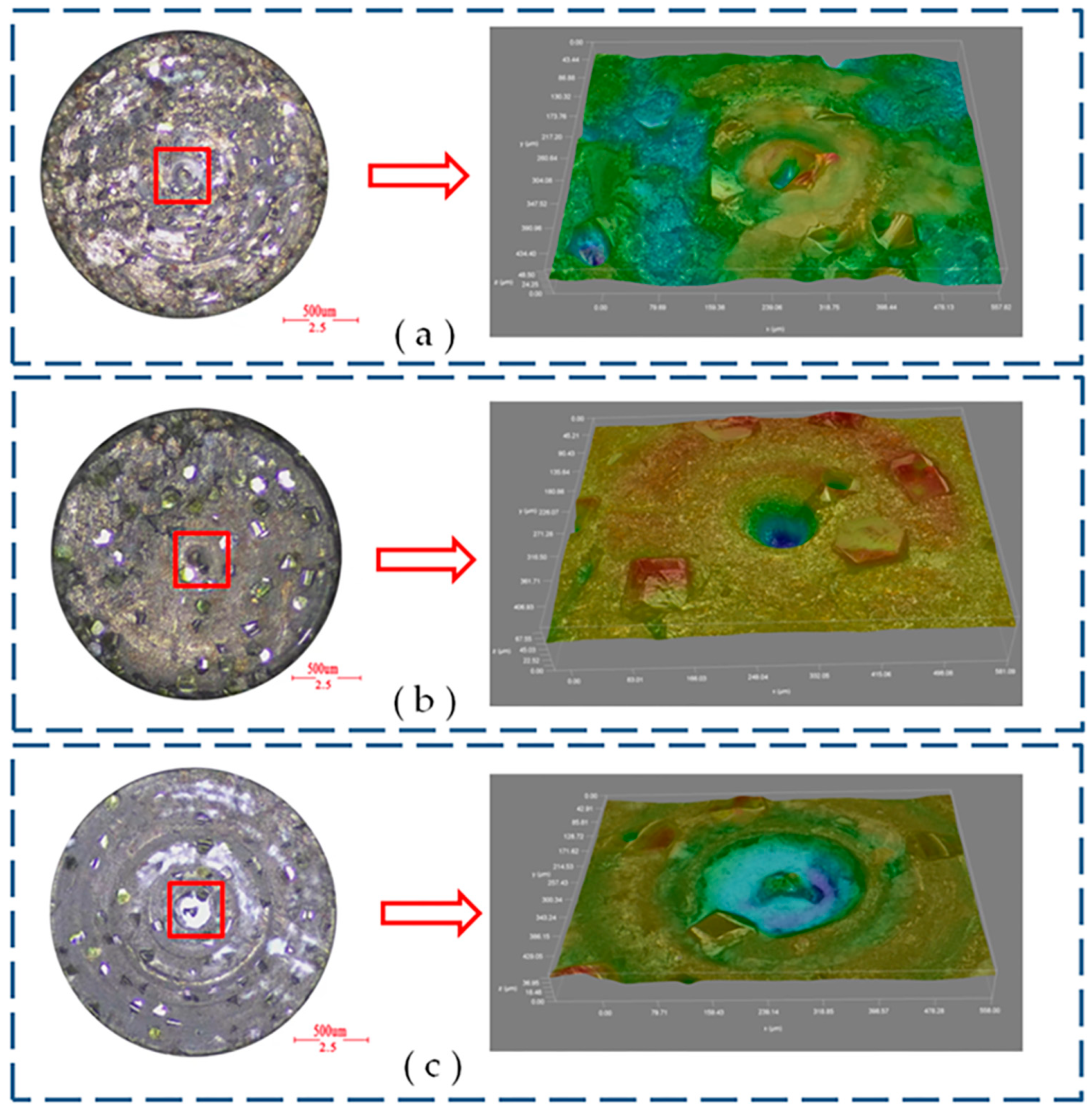
4.2.2. Effect of Tool Wear on the Surface Quality of the Hole
4.2.3. Sintered Diamond Tool End-Face Wear
5. Conclusions
- (1)
- The hardware part of the machine tool mainly includes the spindle module, micro-motion system module, ultrasonic machining tank module, and DAQ system module.
- (2)
- A LabView-based controlled machining control system is developed, which includes modules such as motion selection, initialization, coarse tool setting, constant force tool setting, control machining, and the coordinate display module.
- (3)
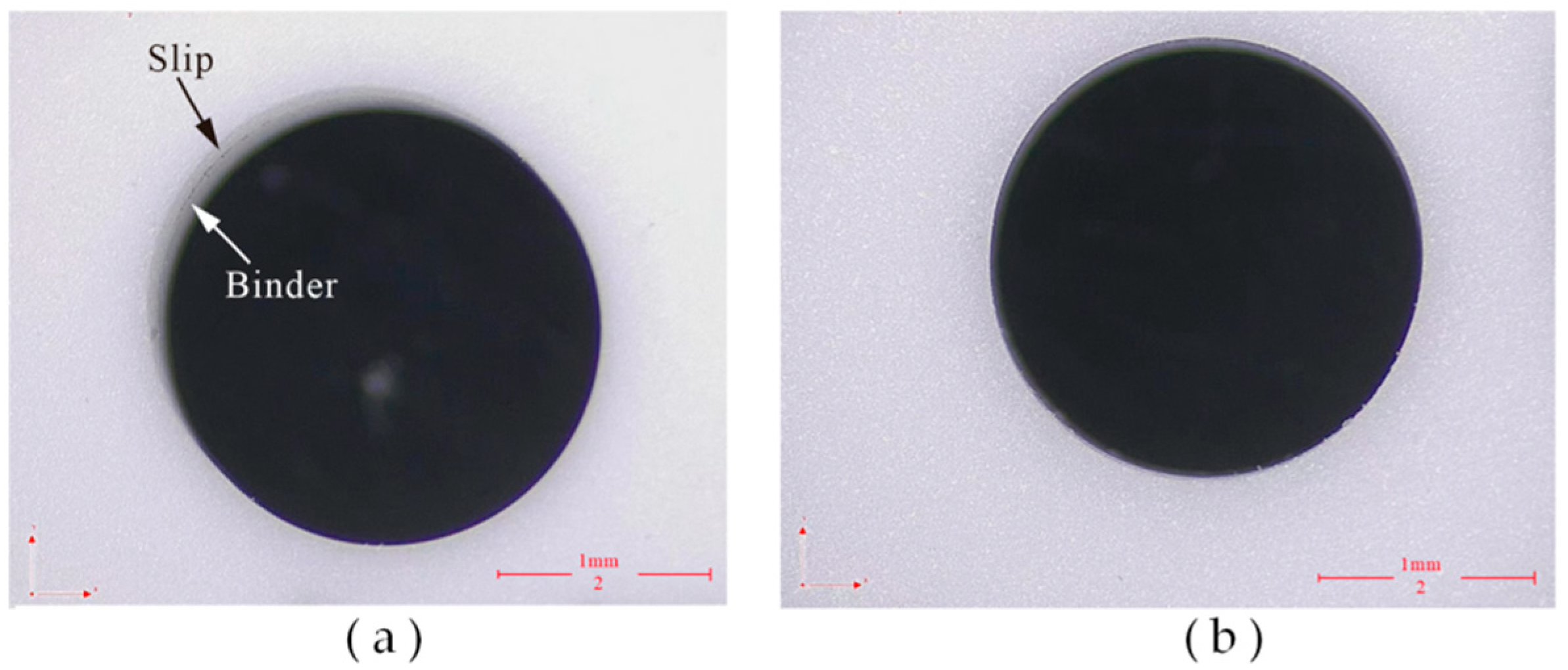
- The experimental results show that compared with DGM, HRUM can effectively reduce axial cutting forces, reducing binder adhesion and suppressing slippage while also improving tool-cutting ability and extending tool life under the same machining parameters. At the initial machining stage, HRUM successfully reduces chipping and other defects. However, it is not as effective in later stages of hole machining, where chipping still occurs. Moreover, the size of grit used impacts cutting forces, tool wear, and the number of holes machined. Larger grit sizes result in fewer machined holes.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fang, S.X.; Zhao, H.L.; Zhang, Q.J. The application status and development trends of ultrasonic machining technology. J. Mech. Eng. 2017, 53, 22–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, A.; Kalsia, M.; Uppal, A.S.; Babbar, A.; Dhawan, V. Machining of hard and brittle materials: A comprehensive review. Mater. Today Proc. 2022, 50, 1048–1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, J.; Singh, C.; Singh, K. Rotary ultrasonic machining of advance materials: A review. Mater. Today Proc. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Legge, P. Machining without abrasive slurry. Ultrasonic 1966, 4, 157–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, G.L.; Zhang, W.X.; Hou, W.B.; Feng, Z.Q.; Wang, G.R. Development of T3030-3/ZV ultrasonic rotary machining machine and its application. In Proceedings of the Fifth National Academic Conference on Electrical Machining, Nanjing, China, 1 October 1986; pp. 143–152. Available online: https://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/detail.aspx?FileName=NSOD198610004014&DbName=CPFD2007 (accessed on 4 May 2023).
- Zheng, S.Y.; Feng, P.F.; Xu, X.P. Development trends of rotary ultrasonic machining technology. J. Tsinghua Univ. Sci. Technol. 2009, 49, 1799–1804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.N. Study on Rotary Ultrasonic Processing Technology and Equipment for Microporous Microwave Ferrite Materials. Master’s Thesis, Tianjin University, Tianjin, China, 2014. Available online: https://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/detail.aspx?FileName=1016186806.nh&DbName=CMFD2017 (accessed on 6 May 2023).
- Zhou, R.F. Research on Performance Enhancement of Rotary Ultrasonic Grinding Tool System. Master’s Thesis, North University of China, Taiyuan, China, 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.H.; Geng, D.X.; Zhang, D.Y.; Zhai, Y.D.; Liu, L.X.; Sun, Z.F.; Shao, Z.Y.; Zhang, M.L.; Jiang, X.G. Cutting performance and surface integrity for rotary ultrasonic elliptical milling of Inconel 718 with the ball end milling cutter. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2023, 319, 118094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.F.; Geng, D.X.; Zheng, W.; Liu, Y.H.; Liu, L.X.; Ying, E.Z.; Jiang, X.G.; Zhang, D.Y. An innovative study on high-performance milling of carbon fiber reinforced plastic by combining ultrasonic vibration assistance and optimized tool structures. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2023, 22, 2131–2146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.H.; Zhang, D.Y.; Geng, D.X.; Shao, Z.Y.; Zhou, Z.H.; Sun, Z.F.; Jiang, Y.G.; Jiang, X.G. Ironing effect on surface integrity and fatigue behavior during ultrasonic peening drilling of Ti-6Al-4V. Chin. J. Aeronaut. 2023, 36, 486–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.M.; Lin, B.; Liu, L.P. Efficiency-based compensations and the mechanical load dependencies of rotary transformer for rotary ultrasonic machining applications. IET Power Electron. 2015, 8, 986–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.B.; Chen, T.; Duan, Z.Y.; Zhang, Y.W.; Li, H.T. Performances of resonant frequency tracking methods and compensation strategies for rotary ultrasonic machining device with contactless energy transfer. Appl. Acoust. 2022, 197, 108959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.Y. Research on High Power Induction Power Transmission Technology Based on Loosely Coupled Transformers. Master’s Thesis, Harbin Institute of Technology, Harbin, China, 2010. Available online: https://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?dbname=CMFD2012&filename=1011259752.nh (accessed on 10 May 2023).
- Jiang, X.G.; Wang, K.Q.; Shao, R.J.; Mills, J.K.; Zhang, D.Y. Self-Compensation Theory and Design of Contactless Energy Transfer and Vibration System for Rotary Ultrasonic Machining. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2018, 33, 8650–8660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, X.P.; Wu, Y.B.; Chen, M.H.; Niu, Y. Modeling and optimization of the magnetically coupled resonant wireless power transfer used in rotary ultrasonic machining process. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2023, 354, 114290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.H. Development of Rotary Ultrasonic Machining Tool Holder and Experimental Research on Rock Slab Drilling Process. Master’s Thesis, Guangdong University of Technology, Guangzhou, China, 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Babitsky, V.I. Finite element modeling of a micro-drill and experiments on high speed ultrasonically assisted micro-drilling. J. Sound Vib. 2011, 330, 2124–2137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zai, P.H.; Tong, J.L.; Liu, Z.Q.; Zhang, Z.P.; Song, C.S.; Zhao, B. Analytical model of exit burr height and experimental investigation on ultrasonic-assisted high-speed drilling micro-holes. J. Manuf. Process. 2021, 68, 807–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sui, H.; Zhang, X.Y.; Zhang, D.Y.; Jiang, X.G.; Wu, R.B. Feasibility study of high-speed ultrasonic vibration cutting titanium alloy. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2017, 247, 111–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.Y.; Peng, Z.L.; Liu, L.B. A transient cutting temperature prediction model for high-speed ultrasonic vibration turning. J. Manuf. Process. 2022, 83, 257–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Z.H.; Zhang, D.Y.; Zhang, X.Y.; Peng, Z.L. Effects of high-pressure coolant on cutting performance of high-speed ultrasonic vibration cutting titanium alloy. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2020, 279, 116584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.C.; Jiao, Y.; Deines, T.W.; Pei, Z.J.; Treadwell, C. Rotary ultrasonic machining of ceramic matrix composites: Feasibility study and designed experiments. Int. J. Mach. Tools Manuf. 2005, 45, 1402–1411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.Z.; Zhang, D.Z.; Wang, H.; Ye, G.H.; He, R.; Cong, W.L. Theoretical and experimental investigations on rotary ultrasonic surface micro-machining of brittle materials. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2022, 89, 106162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, F.; Bie, W.B.; Wang, X.B.; Zhao, B. Longitudinal-torsional coupled rotary ultrasonic machining of ZrO2 ceramics: An experimental study. Ceram. Int. 2022, 48, 28154–28162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ning, F.D.; Wang, H.; Cong, W.L.; Fernando, P.K.S.C. A mechanistic ultrasonic vibration amplitude model during rotary ultrasonic machining of CFRP composite. Ultrasonics 2017, 76, 44–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ning, F.D.; Cong, W.L.; Pei, Z.J.; Treadwell, C. Rotary ultrasonic machining of CFRP: A comparison with grinding. Ultrasonics 2016, 66, 125–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lv, D.X.; Wang, H.X.; Tang, Y.J.; Huang, Y.H.; Li, Z.P. Influences of vibration on surface formation in rotary ultrasonic machining of glass BK7. Precis. Eng. 2013, 37, 839–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ning, F.D.; Wang, H.; Hu, Y.B.; Cong, W.L.; Zhang, M.; Li, Y.Z. Rotary Ultrasonic Surface Machining of CFRP Composites: A Comparison with Conventional Surface Grinding. Procedia Manuf. 2017, 10, 557–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.J.; Guo, Z.N.; Zhang, Y.J.; Chen, M. Development of CNC rotary ultrasonic machining machine and its process experiment. Electromachining Mould 2013, 46–50+59. Available online: https://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/detail.aspx?FileName=DJGU201304011&DbName=CJFQ2013 (accessed on 21 July 2023).
- Wang, J.J.; Feng, P.F.; Zhang, J.F.; Guo, P. Experimental study on vibration stability in rotary ultrasonic machining of ceramic matrix composites: Cutting force variation at hole entrance. Ceram. Int. 2018, 44, 14386–14392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.J.; Feng, P.F.; Zhang, J.F.; Shen, H. Experimental investigation on the effects of thermomechanical loading on the vibrational stability during rotary ultrasonic machining. Mach. Sci. Technol. 2017, 21, 239–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.Y.; Feng, X.J.; Wang, L.J.; Chen, D.C. Study on the drill skidding motion in ultrasonic vibration microdrilling. Int. J. Mach. Tools Manuf. 1994, 34, 847–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Analog Input | Analog Output |
|---|---|
| Channel number: 8 differentials/16 single-ended | Channel number: 2 |
| ADC resolution ratio: 16 bit | DAC resolution ratio: 16 bit |
| Sampling rate: Maximum—2.00 MS/s single-channel, 1.0 MS/s multi-channel; Minimum—none; Timing precision—50 ppm/sampling rate; Timer resolution—10 ns | Maximum update rate: 2.00 MS/s Timing precision: 50 ppm/sampling rate Timer resolution: 10 ns |
| Input coupling: DC | Output coupling: DC |
| Input range: ±10 V, ±5 V, ±2 V; ±1 V; ±0.5 V; ±0.2 V and ±0.1 V | Output range: ±10 V, ±5 V and ±external reference |
| Component | Material | Density (kg/m3) | Longitudinal Wave Velocity-c (m/s) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Piezoceramic | PZT-8 | 7.6 × 103 | 4720 |
| Post matching block | 45 steel | 7.9 × 103 | 5169 |
| Front matching block | Titanium alloy | 4.5 × 103 | 5070 |
| Main components | 99% Al2O3 | |
| Material properties | Density | 3.8 g/cm3 |
| Physical properties | Hardness | HV 1700 |
| Flexural strength | 3500 Kgf/cm2 | |
| Compressive strength | 30,000 Kgf/cm2 | |
| Fracture toughness | 4 Mpa m 1/2 | |
| Group | Test | Grain Size (Mesh/mm) | Ultrasonic Power (%) | Feed Speed (mm/s) | Rotation Speed (r/min) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | HRUM | 80/0.18 | 60 | 0.01 | 10,000 |
| 2 | 160/0.11 | ||||
| 3 | 200/0.09 | ||||
| 4 | DGM | 80/0.18 | 0 | 0.01 | 10,000 |
| 5 | 160/0.11 | ||||
| 6 | 200/0.09 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, S.; Gong, M.; Lian, H.; Wu, J.; Zhu, W.; Ou, Z. Design of a High-Speed Rotary Ultrasonic Machining Machine Tool for Machining Microstructure of Brittle Materials. Micromachines 2023, 14, 1544. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi14081544
Zhang S, Gong M, Lian H, Wu J, Zhu W, Ou Z. Design of a High-Speed Rotary Ultrasonic Machining Machine Tool for Machining Microstructure of Brittle Materials. Micromachines. 2023; 14(8):1544. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi14081544
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Shanhua, Manfeng Gong, Haishan Lian, Jianfeng Wu, Weijie Zhu, and Zhengwei Ou. 2023. "Design of a High-Speed Rotary Ultrasonic Machining Machine Tool for Machining Microstructure of Brittle Materials" Micromachines 14, no. 8: 1544. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi14081544
APA StyleZhang, S., Gong, M., Lian, H., Wu, J., Zhu, W., & Ou, Z. (2023). Design of a High-Speed Rotary Ultrasonic Machining Machine Tool for Machining Microstructure of Brittle Materials. Micromachines, 14(8), 1544. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi14081544





