Liquid Vibration Energy Harvesting Device Using Ferrofluids
Abstract
:1. Introduction
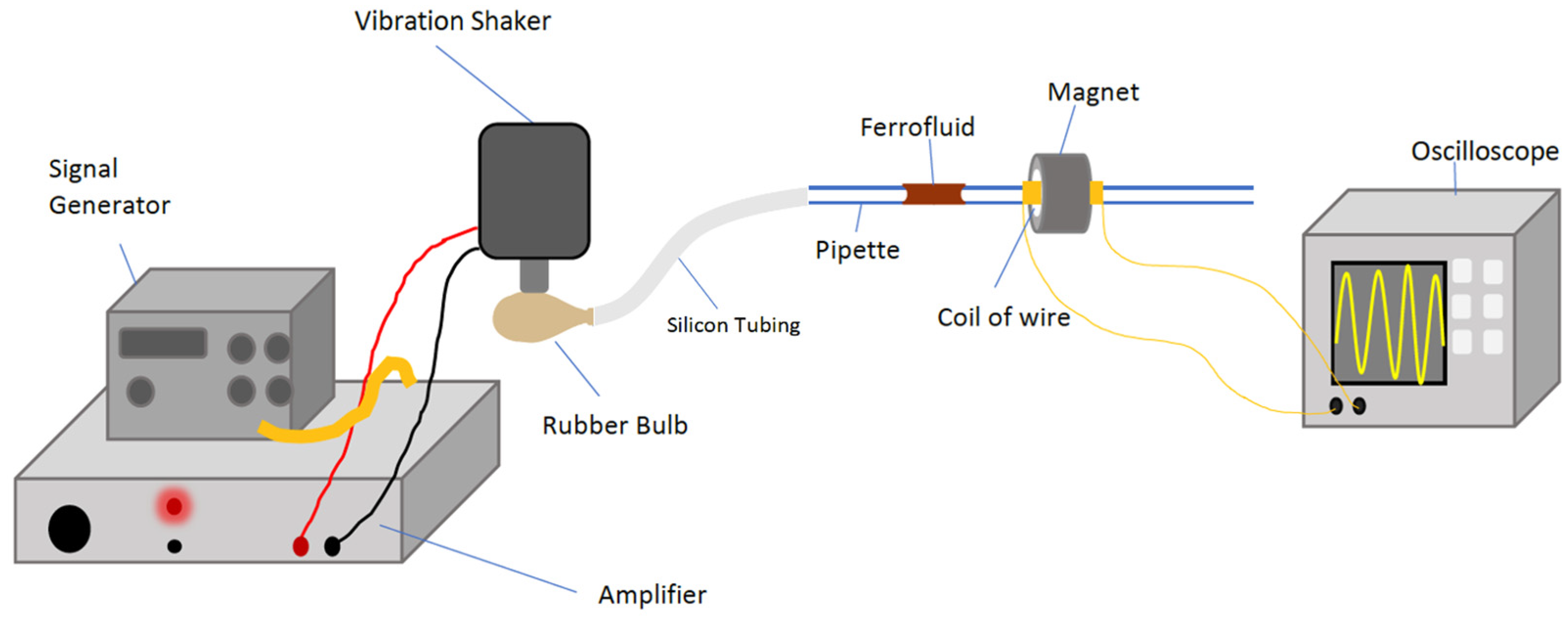
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, H.; Tian, C.; Deng, Z.D. Energy harvesting from low frequency applications using piezoelectric materials. Appl. Phys. Rev. 2014, 1, 041301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kiziroglou, M.E.; Yeatman, E.M. Materials and techniques for energy harvesting. In Functional Materials for Sustainable Energy Applications; Woodhead Publishing: Soston, UK, 2012; pp. 541–572. [Google Scholar]
- Malik, N.N.; Alosaimi, W.; Uddin, M.I.; Alouffi, B.; Alyami, H. Wireless sensor network applications in healthcare and precision agriculture. J. Healthc. Eng. 2020, 2020, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Priya, S.; Inman, D.J. (Eds.) Energy Harvesting Technologies; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2009; Volume 21, p. 2. [Google Scholar]
- Bowen, C.R.; Kim, H.A.; Weaver, P.M.; Dunn, S. Piezoelectric and ferroelectric materials and structures for energy harvesting applications. Energy Environ. Sci. 2014. 7, 25–44. [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Beeby, S.P.; O’Donnell, T. Electromagnetic energy harvesting. In Energy Harvesting Technologies; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 2009; pp. 129–161. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J.; Wang, Z.L. Reviving vibration energy harvesting and self-powered sensing by a triboelectric nanogenerator. Joule 2017, 1, 480–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Wang, Y.; Kim, E.S. Electromagnetic energy harvester with flexible coils and magnetic spring for 1–10 Hz resonance. J. Microelectromech. Syst. 2015. 24, 1193–1206. [CrossRef]
- Rosensweig, R.E. Ferrohydrodynamics; Courier Corporation: Chelmsford, MA, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Bibo, A.; Masana, R.; King, A.; Li, G.; Daqaq, M.F. Electromagnetic ferrofluid-based energy harvester. Phys. Lett. A 2012, 376, 2163–2166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purohit, V.; Mazumder, B.; Jena, G.; Mishra, M. Ferrofluid based micro-electrical energy harvesting. In Proceedings of the APS March Meeting Abstracts 2013, Baltimore, MD, USA, 18–22 March 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Oh, D.W.; Sohn, D.Y.; Byun, D.G.; Kim, Y.S. Analysis of electromotive force characteristics and device implementation for ferrofluid based energy harvesting system. In Proceedings of the 17th International Conference on Electrical Machines and Systems (ICEMS), Hangzhou, China, 22–25 October 2014; pp. 2033–2038. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, Y.S. Analysis of electromotive force characteristics for electromagnetic energy harvester using ferrofluid. J. Magn. 2015, 20, 252–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alazmi, S.; Xu, Y.; Daqaq, M.F. Harvesting energy from the sloshing motion of ferrofluids in an externally excited container: Analytical modeling and experimental validation. Phys. Fluids 2016. 28, 077101. [CrossRef]
- Seol, M.L.; Jeon, S.B.; Han, J.W.; Choi, Y.K. Ferrofluid-based triboelectric-electromagnetic hybrid generator for sensitive and sustainable vibration energy harvesting. Nano Energy 2017, 31, 233–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, W.G.; Kim, D.W.; Tcho, I.W.; Kim, J.K.; Kim, M.S.; Choi, Y.K. Triboelectric nanogenerator: Structure, mechanism, and applications. ACS Nano 2021, 15, 258–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khairul, M.A.; Doroodchi, E.; Azizian, R.; Moghtaderi, B. Advanced applications of tunable ferrofluids in energy systems and energy harvesters: A critical review. Energy Convers. Manag. 2017, 149, 660–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Alazemi, S.F.; Daqaq, M.F.; Li, G. A ferrofluid based energy harvester: Computational modeling, analysis, and experimental validation. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2018, 449, 105–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Liu, Y.; Li, D.; Wang, H. An electromagnetic energy harvester using ferrofluid as a lubricant. Mod. Phys. Lett. B 2018, 32, 1840084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zabek, D.; Taylor, J.; Ayel, V.; Bertin, Y.; Romestant, C.; Bowen, C.R. A novel pyroelectric generator utilising naturally driven temperature fluctuations from oscillating heat pipes for waste heat recovery and thermal energy harvesting. J. Appl. Phys. 2016, 120, 024505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Monroe, J.G.; Bhandari, M.; Fairley, J.; Myers, O.J.; Shamsaei, N.; Thompson, S.M. Energy harvesting via thermo-piezoelectric transduction within a heated capillary. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2017, 111, 043902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, N.; Yang, F.; Luo, T.; Qin, L. Design and Experimental Investigation of an Ultra-Low Frequency, Low-Intensity, and Multidirectional Piezoelectric Energy Harvester with Liquid as the Energy-Capture Medium. Micromachines 2023, 14, 369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Monroe, J.G.; Kumari, S.; Leontsev, S.O.; Vasquez, E.S.; Thompson, S.M.; Berg, M.J.; Walters, D.K.; Walters, K.B. Analytical model for electromagnetic induction in pulsating ferrofluid pipe flows. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2021, 175, 121325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monroe, J.G.; Vasquez, E.S.; Aspin, Z.S.; Fairley, J.D.; Walters, K.B.; Berg, M.J.; Thompson, S.M. Energy harvesting via ferrofluidic induction. Energy Harvest. Storage Mater. Devices Appl. VI 2015, 9493, 89–95. [Google Scholar]
- Esser, F.; Masselter, T.; Speck, T. Silent pumpers: A comparative topical overview of the peristaltic pumping principle in living nature, engineering, and biomimetics. Adv. Intell. Syst. 2019, 1, 1900009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rascón, C.; Parry, A.O.; Aarts, D.G. Geometry-induced capillary emptying. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 12633–12636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Needham, D.; Kinoshita, K.; Utoft, A. Micro-surface and-interfacial tensions measured using the micropipette technique: Applications in ultrasound-microbubbles, oil-recovery, lung-surfactants, nanoprecipitation, and microfluidics. Micromachines 2019, 10, 105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Available online: https://ferrofluid.ferrotec.com/products/ferrofluid-emg/water/emg-707/ (accessed on 14 June 2023).
- O’handley, R.C. Modern Magnetic Materials: Principles and Applications; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]






Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hannon, N.; Harrison, C.W.; Kraśny, M.J.; Zabek, D. Liquid Vibration Energy Harvesting Device Using Ferrofluids. Micromachines 2023, 14, 1588. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi14081588
Hannon N, Harrison CW, Kraśny MJ, Zabek D. Liquid Vibration Energy Harvesting Device Using Ferrofluids. Micromachines. 2023; 14(8):1588. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi14081588
Chicago/Turabian StyleHannon, Nia, Christopher W. Harrison, Marcin J. Kraśny, and Daniel Zabek. 2023. "Liquid Vibration Energy Harvesting Device Using Ferrofluids" Micromachines 14, no. 8: 1588. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi14081588
APA StyleHannon, N., Harrison, C. W., Kraśny, M. J., & Zabek, D. (2023). Liquid Vibration Energy Harvesting Device Using Ferrofluids. Micromachines, 14(8), 1588. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi14081588





