Microfabricating Mirror-like Surface Precision Micro-Sized Amorphous Alloy Structures Using Jet-ECM Process
Abstract
:1. Introduction
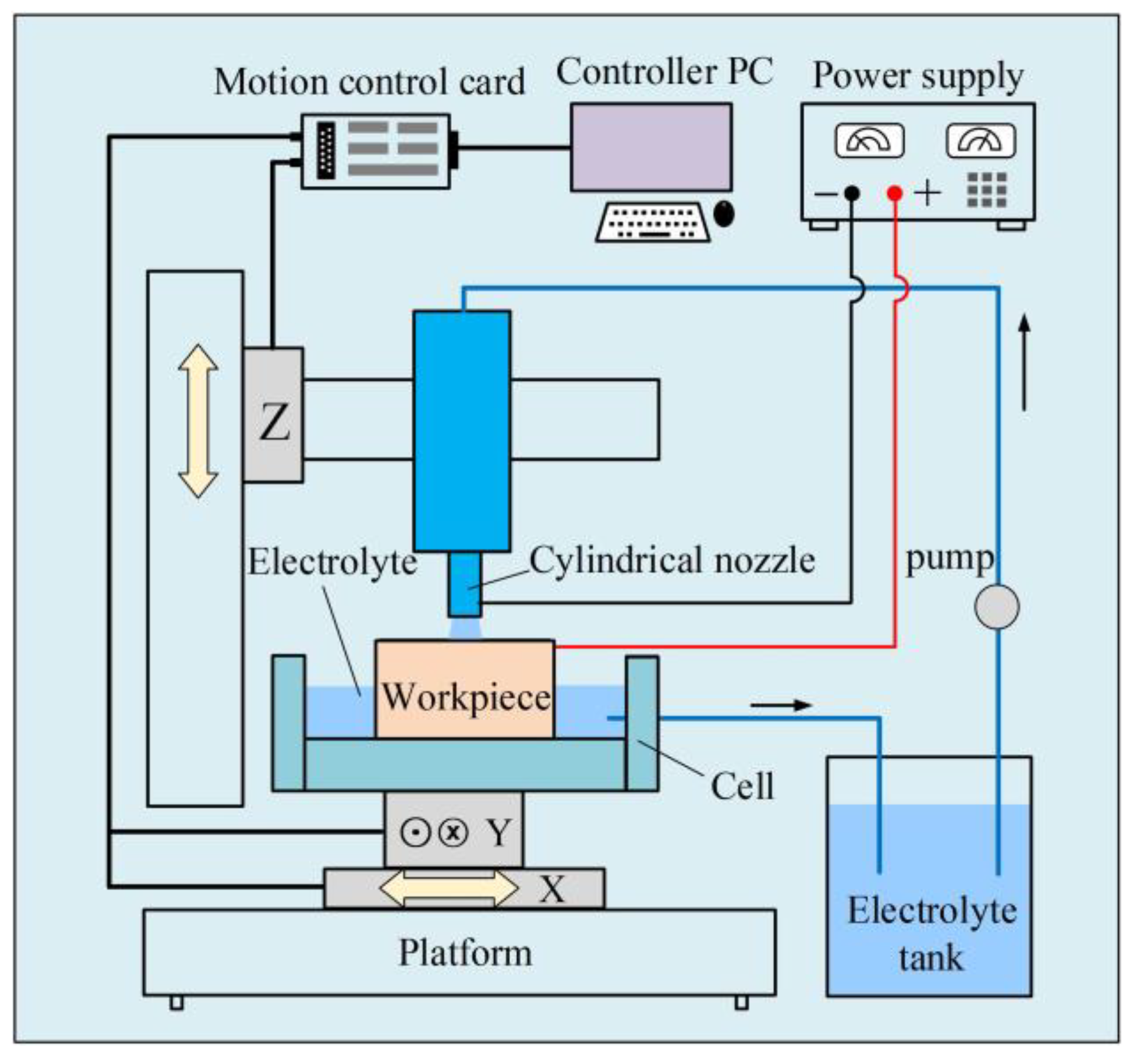
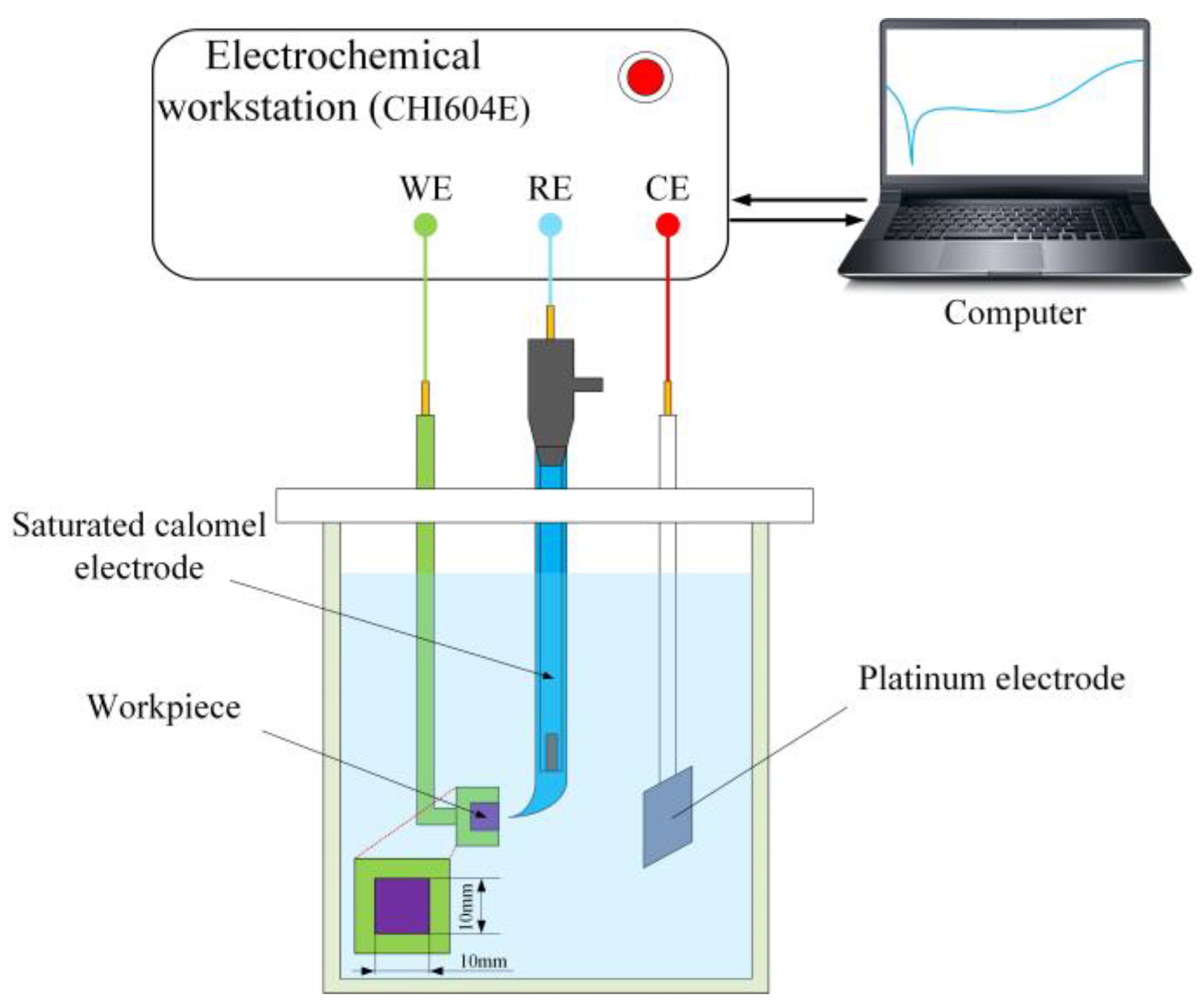
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Electrochemical Characteristic Analysis of Zr-Based Amorphous Alloys
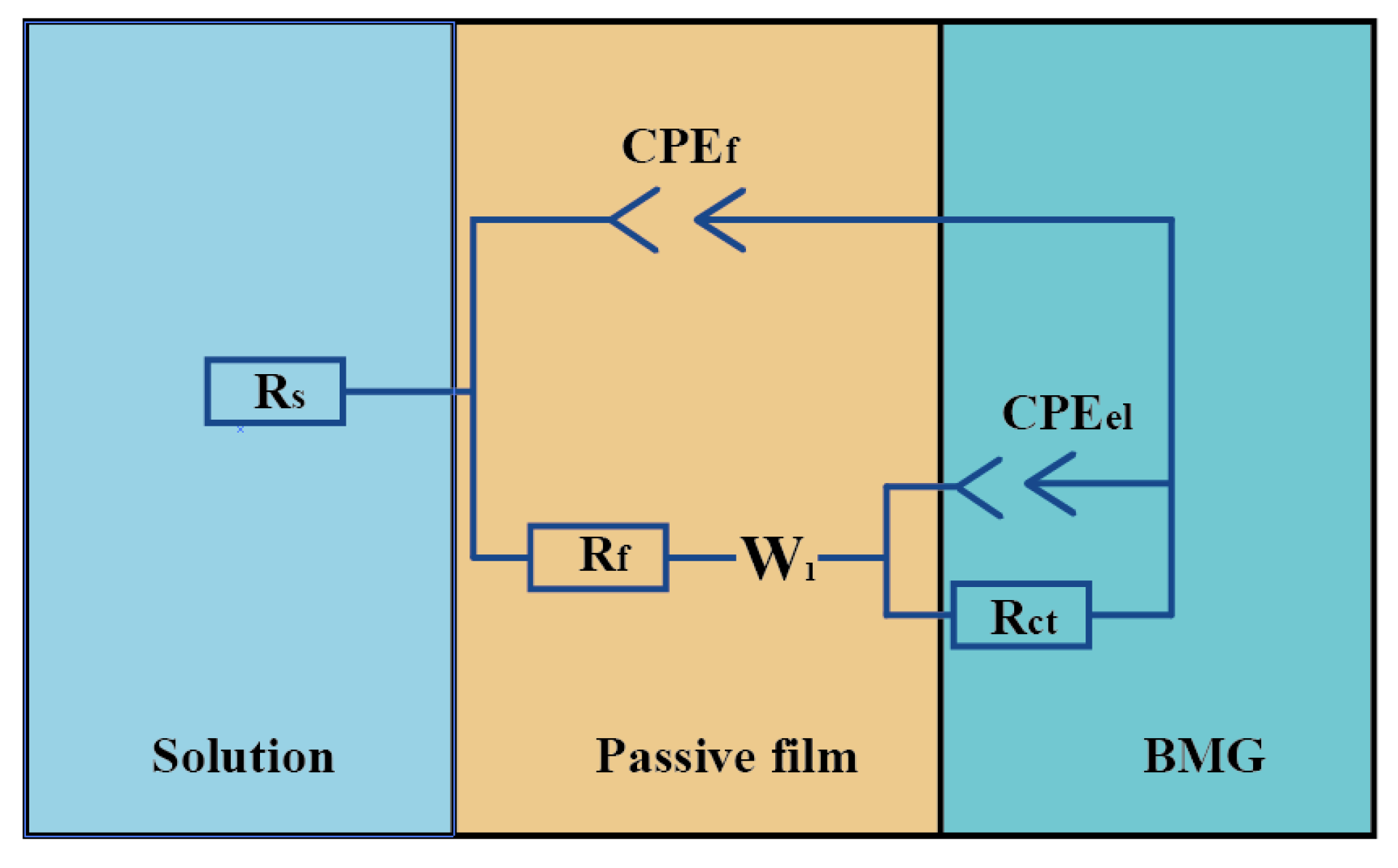
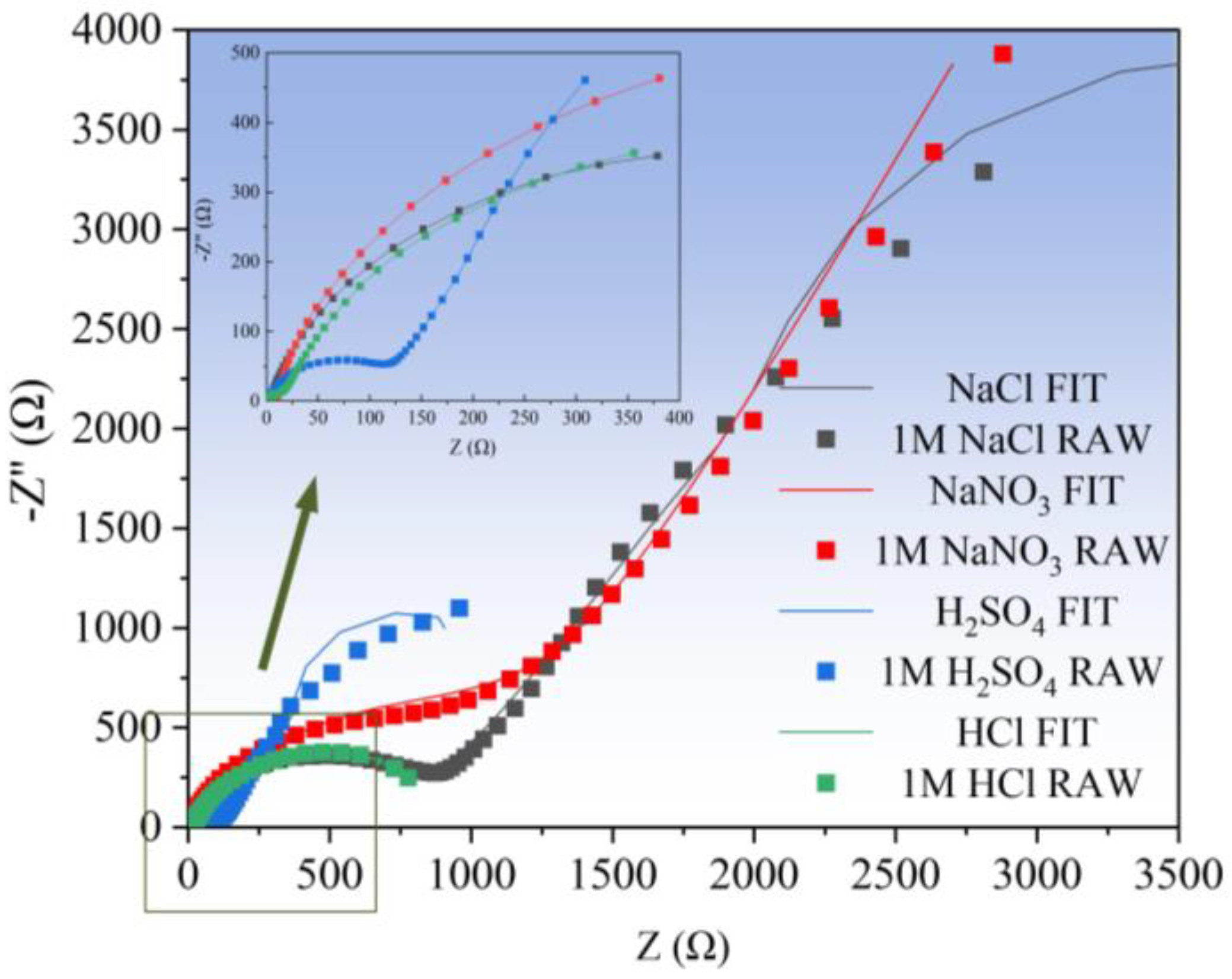
3.1.1. Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy (EIS) Analysis
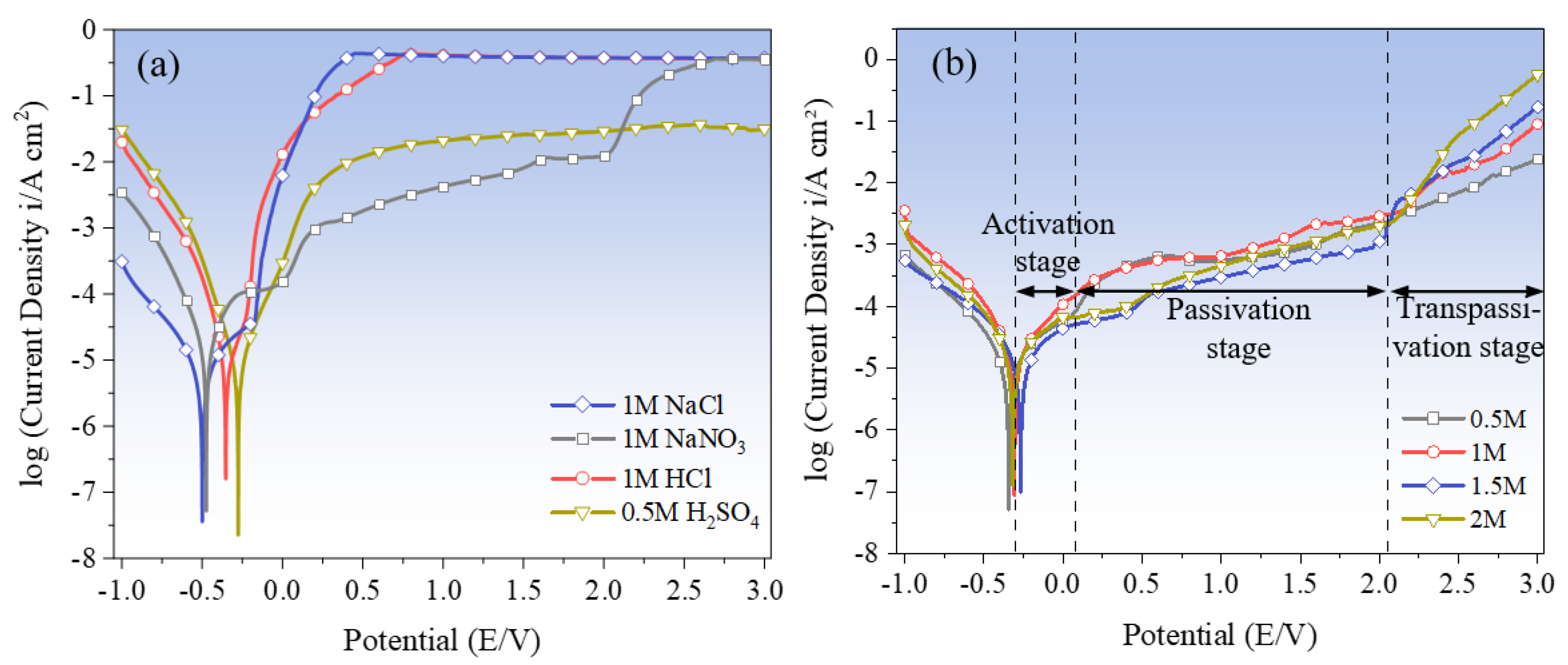
3.1.2. Electrochemical Polarization Characterization
3.1.3. Electrochemical Polarization Characterization
3.2. Fabrication of Micro-Dimples on the AA by Jet-ECM
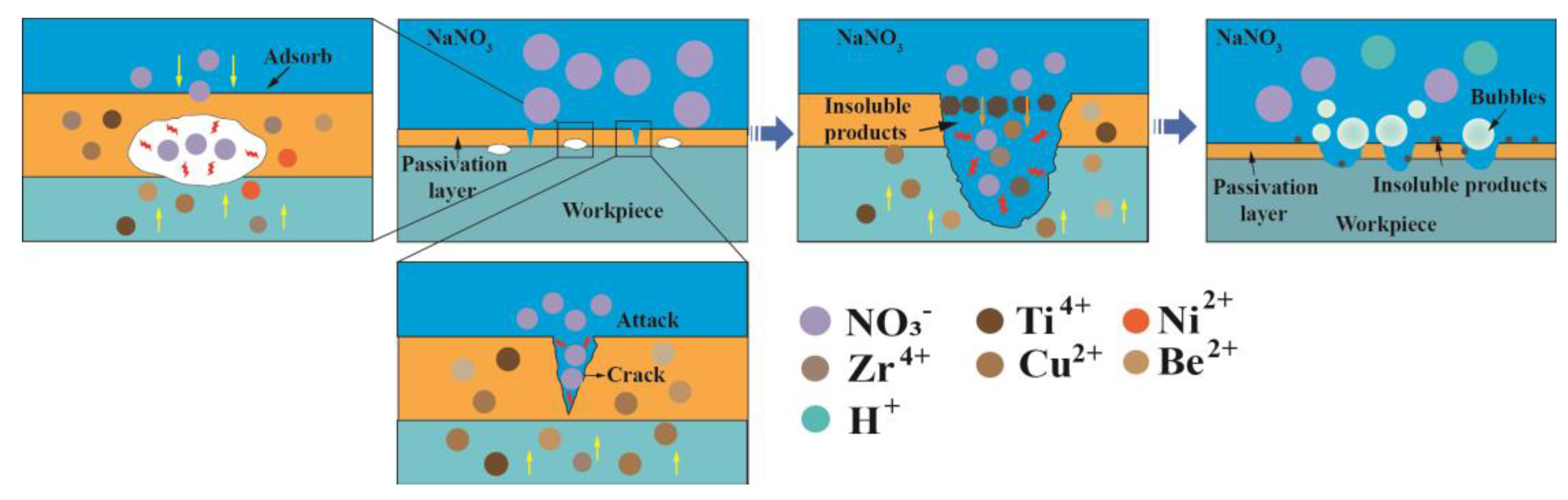
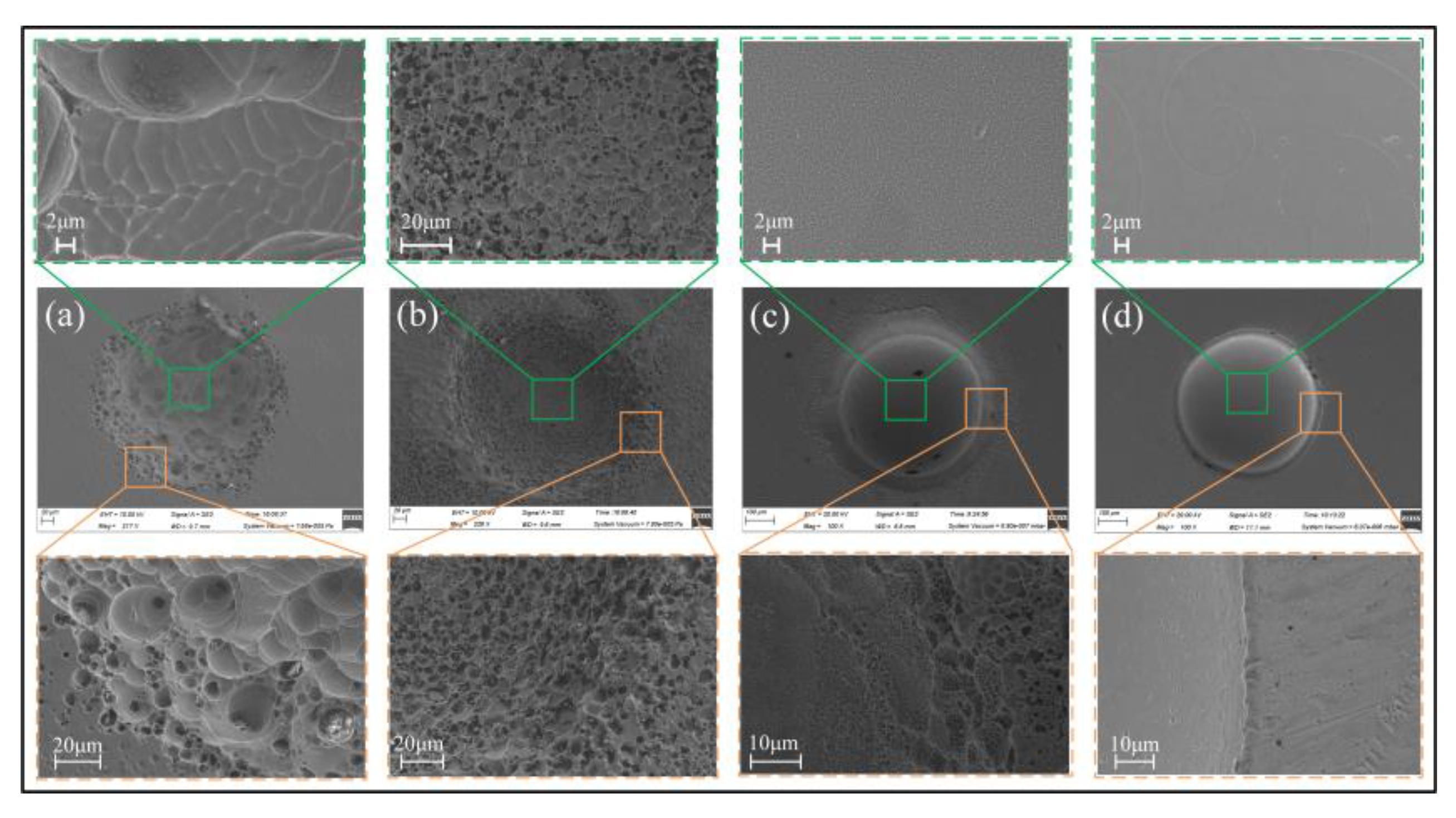
3.2.1. Effect of Electrolyte Compositions
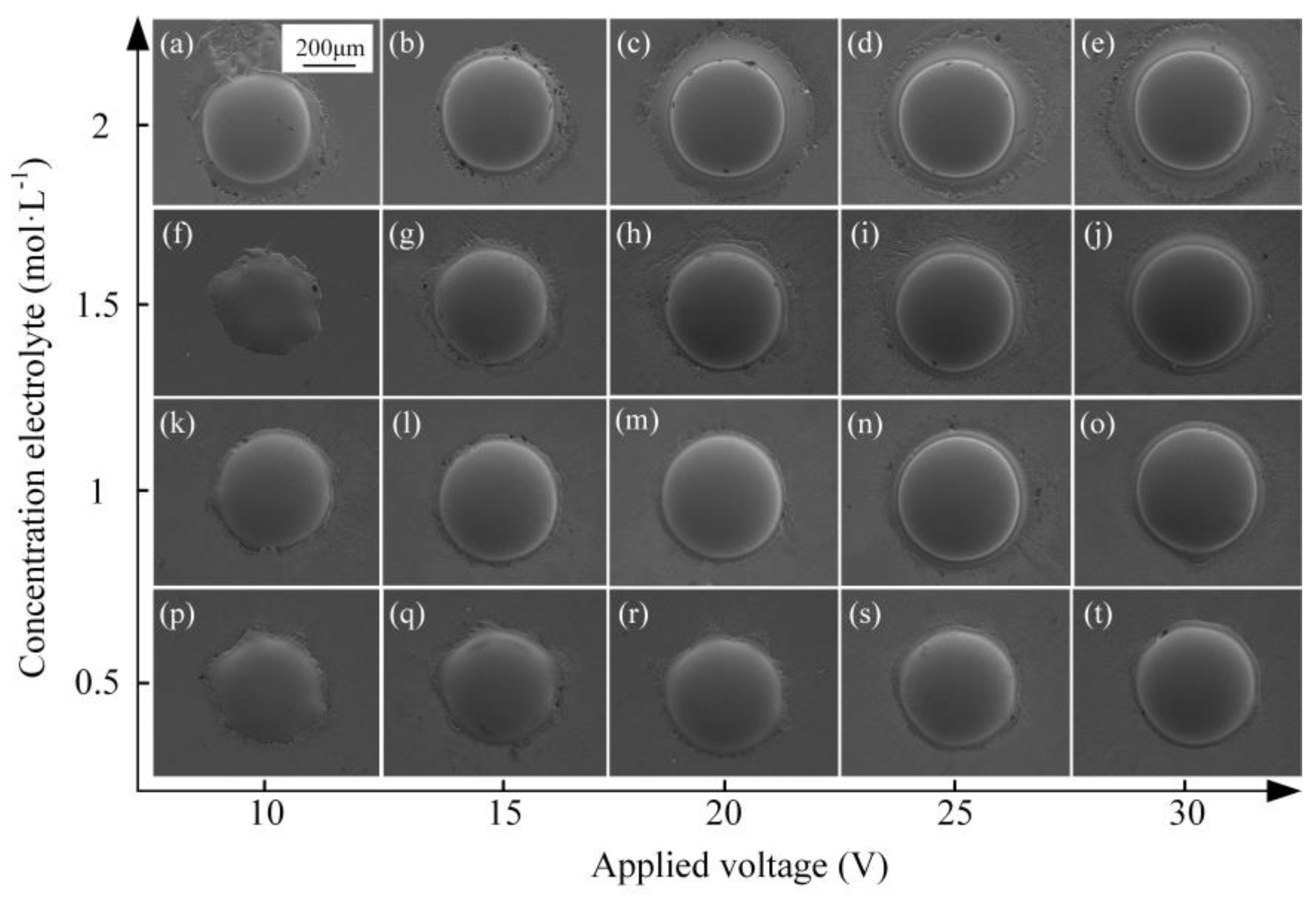
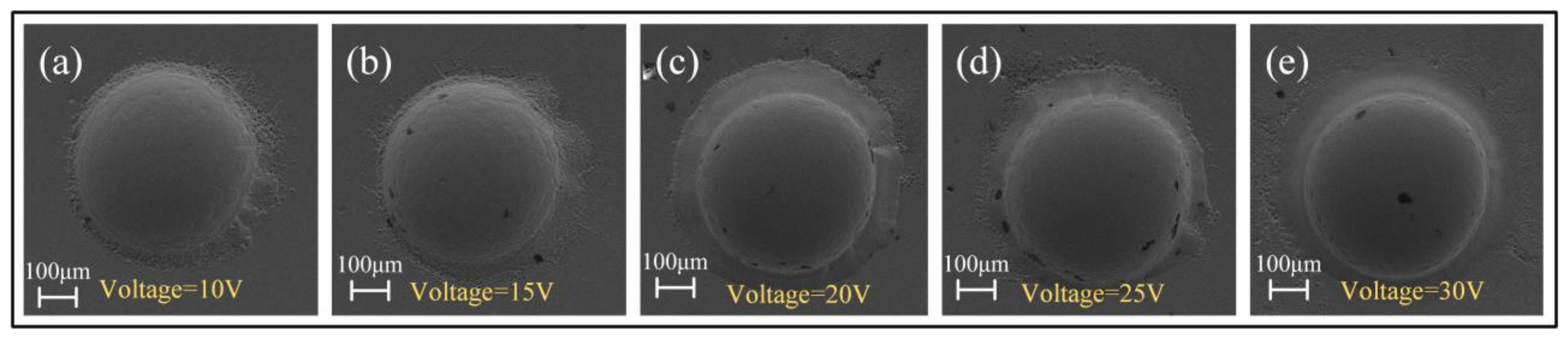
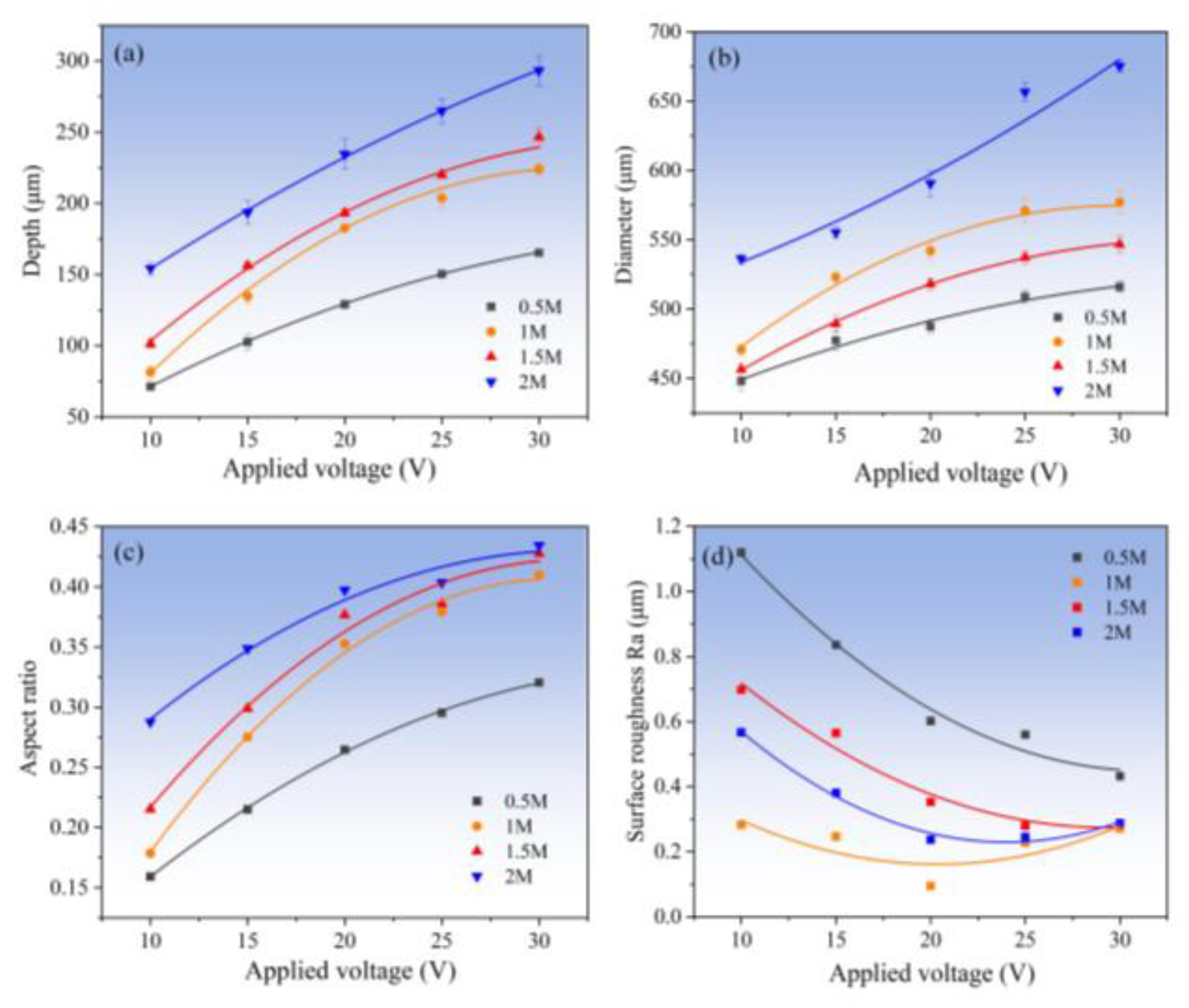
3.2.2. Effect of Electrolyte Concentration
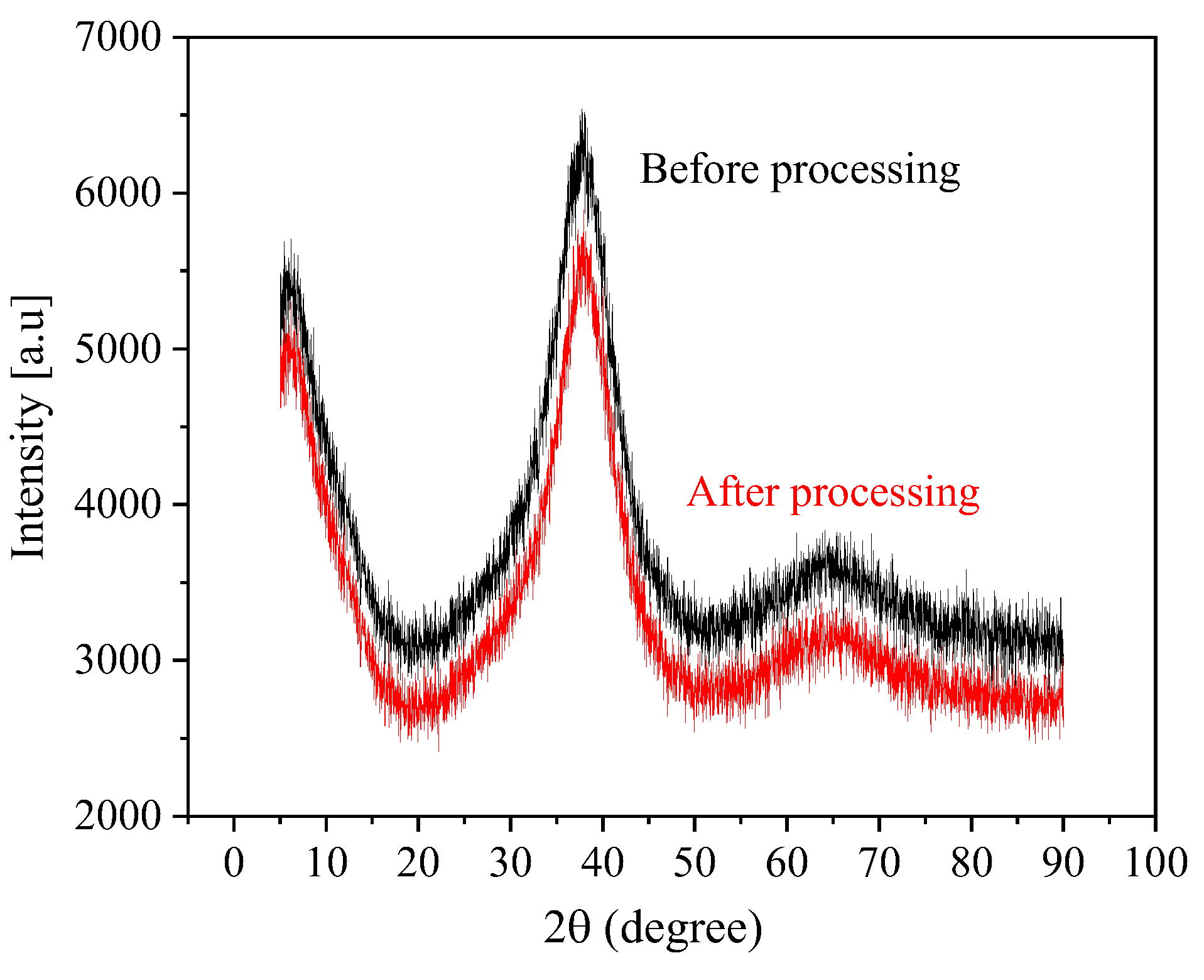
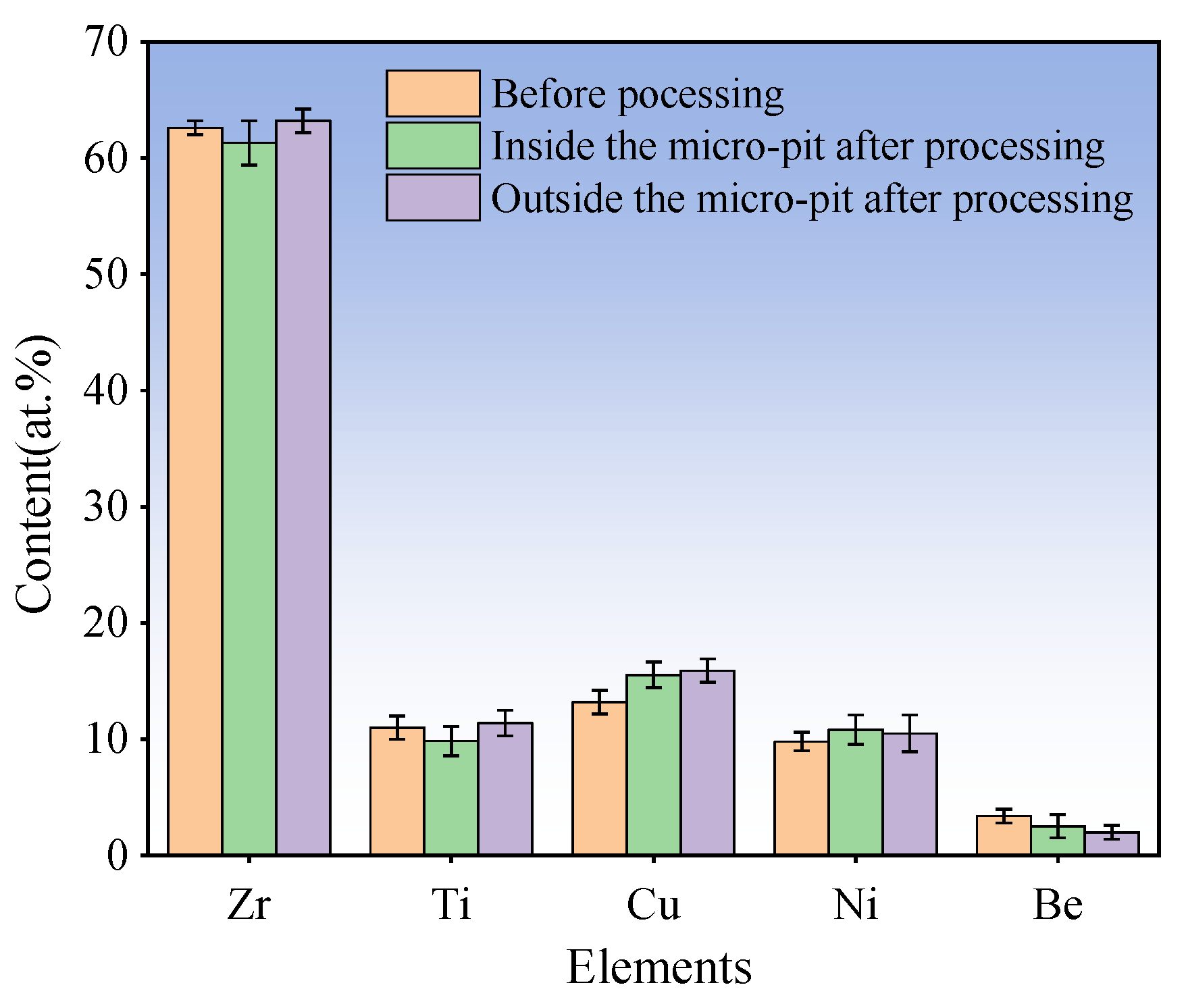
3.3. Fabrication of Micro-Dimples on the AA by Jet-ECM
4. Conclusions
- Oxygen-containing electrolytes such as NaNO3 and H2SO4 are more suitable for the microfabrication of the Zr-based AA by Jet-ECM than chloride-containing electrolytes such as HCl and NaCl, and the NaNO3 electrolyte is the most desirable due to its high oxidization and electrochemical neutrality.
- The material removal of Zr-based AA during Jet-ECM probably follows two mechanisms (defects-inducing mechanism and ion difference-inducing mechanism). Compared with other electrochemical processes, Jet-ECM is more advantageous due to the use of significantly high-speed electrolyte supply.
- The arrayed micro-dimples with mirror-like surface features were fabricated on the surface of Zr-based AA using Jet-ECM, employing optimized processing parameters: 1 M NaNO3, 20 V voltage, 200 μm IEG, 15 s processing time, and 10 m/s impinging electrolyte flow rate. Their depths and diameters measure 206 ± 0.93 μm and 542.6 ± 2.3 μm, respectively, with Ra values less than 100 nm. Jet-ECM is a potentially competitive microfabrication process for Zr-based AA and can achieve mirror-like surface precision microstructures without being crystallized.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Guo, C.; Wu, B.; Xu, B.; Liang, X.; Shen, J.; Wu, X. Electrochemical surface smoothing of spark erosion treated Zr-based bulk metallic glasses in NaCl-ethylene glycol electrolyte. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2021, 116, 1591–1607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, H.; Zhao, W.; Wei, X.; Ding, Y.; Shen, X.; Liu, W. Effect of Ti addition on mechanical properties and corrosion resistance of Ni-free Zr-based bulk metallic glasses for potential biomedical applications. J. Alloy Compd. 2020, 815, 152636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inoue, A.; Takeuchi, A. Recent development and application products of bulk glassy alloys. Acta Mater. 2011, 59, 2243–2267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Telford, M. The case for bulk metallic glass. Mater. Today 2004, 7, 36–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, M.; Zong, H.; Wang, H.; Qi, Y.; Liang, S.; Song, A.; Zhang, W.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, X.; Jing, Q.; et al. The fluidity and molding ability of glass-forming Zr-based alloy melt. Sci. China Ser. G 2008, 51, 438–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kendall, T.; Bartolo, P.; Gillen, D.; Diver, C. A review of physical experimental research in jet electrochemical machining. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2019, 105, 651–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Chen, Y.; Jiang, M.; Li, D.; He, J.; Wu, Y.; Liu, L. A thermoplastic forming map of a Zr-based bulk metallic glass. Acta Mater. 2013, 61, 1921–1931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Xia, T.; Heng, L.; Liu, L. Superhydrophobic Zr-based metallic glass surface with high adhesive force. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2013, 102, 251603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Liao, G.; Pan, J.; Tang, Z.; Peng, P.; Liu, L.; Shi, T. Superplastic micro-forming of Zr65Cu17.5Ni10Al7.5 bulk metallic glass with silicon mold using hot embossing technology. J. Alloy Compd. 2009, 484, 118–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Zhang, H.; Liang, X.; Gong, F.; Ma, J. Fabrication of metallic glass micro grooves by thermoplastic forming. J. Micromech Microeng. 2017, 27, 025009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schroers, J.; Nguyen, T.; O’Keeffe, S.; Desai, A. Thermoplastic forming of bulk metallic glass—Applications for MEMS and microstructure fabrication. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2007, 449–451, 898–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakkal, M.; Liu, C.T.; Watkins, T.R.; Scattergood, R.O.; Shih, A.J. Oxidation and crystallization of Zr-based bulk metallic glass due to machining. Intermetallics 2004, 12, 195–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakkal, M.; Shih, A.J.; Scattergood, R.O.; Liu, C.T. Machining of a Zr–Ti–Al–Cu–Ni metallic glass. Scripta Mater. 2004, 50, 583–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakkal, M.; Shih, A.J.; Scattergood, R.O. Chip formation, cutting forces, and tool wear in turning of Zr-based bulk metallic glass. Int. J. Mach. Tools Manuf. 2004, 44, 915–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Gong, Y.G.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, H.; Li, Q. Microgrinding characteristics of Zr-based bulk metallic glasses. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Tech. 2018, 94, 2401–2417. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Gong, Y.; Liu, W.; Sun, X.; Xu, L. Effect of milling parameters on chip shape and chip morphology for Zr-based bulk metallic glass by using micro-groove milling. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2020, 111, 1587–1602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Wu, X.; Zhang, G.; Xu, B.; Cheng, Y.; Ruan, S. Experimental Study on Machinability of Zr-Based Bulk Metallic Glass during Micro Milling. Micromachines 2020, 11, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sano, T.; Takahashi, M.; Murakoshi, Y.; Suto, S.; Matsuno, K. Abrasive water-jet cutting of amorphous alloys. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 1992, 32, 571–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wessels, V.; Grigoryev, A.; Dold, C.; Wyen, C.; Roth, R.; Weingärtner, E.; Pude, F.; Wegener, K.; Jörg, F.L. Abrasive waterjet machining of three-dimensional structures from bulk metallic glasses and comparison with other techniques. J. Mater. Res. 2012, 27, 1187–1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Lu, P.; Dai, N.; Li, Y.; Liao, C.; Zheng, Q.; Liu, L. Noncrystalline micromachining of amorphous alloys using femtosecond laser pulses. Mater. Lett. 2007, 61, 4290–4293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.; Lee, C.; Hu, T.; Li, C.; Huang, J. Pulsed laser micromachining of Mg–Cu–Gd bulk metallic glass. Opt. Laser Eng. 2012, 50, 883–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, F.; Yang, J.; Zhu, X.; Liang, C.; Wang, H. Femtosecond laser-induced concentric ring microstructures on Zr-based metallic glass. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2010, 256, 3653–3660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Fu, J.; Zheng, C.; Ji, Z. Effect of nanosecond pulse laser ablation on the surface morphology of Zr-based metallic glass. Opt. Laser Technol. 2016, 83, 21–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsieh, S.F.; Chen, S.; Lin, M.H.; Shih, F.O.; Lin, W.; Mao, S. Crystallization and carbonization of an electrical discharge machined Zr-based bulk metallic glass alloy. J. Mater. Res. 2013, 28, 3177–3184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Yan, J. On the surface characteristics of a Zr-based bulk metallic glass processed by microelectrical discharge machining. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2015, 355, 1306–1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koza, J.A.; Sueptitz, R.; Uhlemann, M.; Schiultz, L.; Gebert, A. Electrochemical micromachining of a Zr-based bulk metallic glass using a micro-tool electrode technique. Intermetallics 2011, 19, 437–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cole, K.M.; Kirk, D.W.; Singh, C.V.; Thorpe, S.J. Optimizing electrochemical micromachining parameters for Zr-based bulk metallic glass. J. Manuf. Process. 2017, 25, 227–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, C.; Wu, B.; Xu, B.; Wu, S.; Shen, J.; Wu, X. Investigation of Pulse Electrochemical Machining of Zr-Based Bulk Metallic Glasses in NaNO3-Ethylene Glycol Electrolyte. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2021, 168, 071502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, L.; Zeng, Y.; Zhu, D. Investigation on Wire Electrochemical Micro Machining of Ni-based Metallic Glass. Electrochim. Acta 2017, 233, 274–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, L.; Zeng, Y.; Fang, X.; Zhu, D. Micropatterning of Ni-based metallic glass by pulsed wire electrochemical micro machining. Intermetallics 2017, 81, 16–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hang, Y.; Yang, T.; Xu, Z.; Zeng, Y. Electrochemical micromachining of ZrCu-based amorphous alloy in ethylene glycol solution. Intermetallics 2021, 132, 107155. [Google Scholar]
- Meng, L.; Zeng, Y.; Zhu, D. Wire electrochemical micromachining of Ni-based metallic glass using bipolar nanosecond pulses. Int. J. Mach. Tools Manuf. 2019, 146, 103439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, L.; Zeng, Y.; Fang, X.; Zhu, D. Wire electrochemical micromachining of metallic glass using a carbon nanotube fiber electrode. J. Alloy Compd. 2017, 709, 760–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, L.; Zeng, Y.; Fang, X.; Zhu, D. Micro-shaping of metallic glass by wire electrochemical micro-machining with a reciprocating traveling workpiece. J. Alloy Compd. 2018, 739, 235–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hang, Y.; Zeng, Y.; Yang, T.; Meng, L. The dissolution characteristics and wire electrochemical micromachining of metallic glass Ni82Cr7Si5Fe3B3. J. Manuf. Process. 2020, 58, 884–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Y.; Meng, L.; Fang, X. Surface Characteristics of Ni-Based Metallic Glass in Wire Electrochemical Micro Machining. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2017, 164, E408–E421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hang, Y.; Zeng, Y.; Tao, Y.; Xu, Z.; Xu, K.; Wang, H. The microstructure formation of thick Zr-based amorphous alloy with anode vibration in HClO4 solution by WECMM. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2021, 117, 1459–1472. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, K.; Zeng, Y.; Li, P.; Fang, X.; Zhu, D. Effect of wire cathode surface hydrophilia when using a travelling wire in wire electrochemical micro machining. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2016, 235, 68–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawanaka, T.; Kunieda, M. Mirror-like finishing by electrolyte jet machining. CIRP Ann. 2015, 64, 237–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hackert-Oschätzchen, M.; Meichsner, G.; Zinecker, M.; Martin, A.; Schubert, A. Micro machining with continuous electrolytic free jet. Precis. Eng. 2012, 36, 612–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bisterov, I.; Mitchell-Smith, J.; Speidel, A.; Clare, A.T. Specific and Programmable Surface Structuring by Electrochemical Jet Processing. Procedia CIRP 2018, 68, 460–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Speidel, A.; Bisterov, I.; Saxena, K.K.; Zubayr, M. Electrochemical jet manufacturing technology: From fundamentals to application. Int. J. Mach. Tools Manuf. 2022, 180, 103931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchell-Smith, J.; Speidel, A.; Gaskell, J.; Clare, A.T. Energy distribution modulation by mechanical design for electrochemical jet processing techniques. Int. J. Mach. Tools Manuf. 2017, 122, 32–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Zhao, C.; Qu, N.; Shen, Z. Improving surface quality through macro electrochemical jet milling with novel cathode tool. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2022, 309, 117731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, S.; Huang, K.; Ming, P.; Wang, S.; Zhao, F.; Qin, G.; Liu, H. Jet Electrochemical Micromilling of Ti-6Al-4V Using NaCl–Ethylene Glycol Electrolyte. Micromachines 2024, 15, 173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, B.A.; Meyer, H.M.; Benson, R.S.; Yokoyama, Y.; Liaw, P.K.; Liu, C.T. A study of the corrosion behaviour of Zr50Cu(40−X) Al10PdX bulk metallic glasses with scanning Auger microanalysis. Corros. Sci. 2008, 50, 1825–1832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, H.; Qiao, J.; Yang, H.; Wang, Y.; Liaw, P.K.; Lan, A. The corrosion behavior of in-situ Zr-based metallic glass matrix composites in different corrosive media. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2016, 363, 37–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamachi, M.U.; Baunack, S.; Eckert, J.; Schultz, L.; Gebert, A. Pitting corrosion of bulk glass-forming zirconium-based alloys. J. Alloy Compd. 2004, 377, 290–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, M.; Zhang, S.; Yang, B.; Qiu, S.; Wang, H.; Wang, J. Prominent inhibition efficiency of sodium nitrate to corrosion of Al-based amorphous alloy. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2020, 530, 147211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Jin, Z.; Sun, W.; Xia, C.; Ma, M.; Zhang, X.; Li, G.; Liu, R. A study on the corrosion behavior of the in-situ Ti-based bulk metallic glass matrix composites in acid solutions. J. Alloy Compd. 2019, 782, 927–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Parameter | Property or Value |
|---|---|
| Density (g·cm−3) | 6.12 |
| Hardness (HV) | 568–619 |
| Poisson ratio | 0.30 |
| Specific conductance (MS/m) | 0.52–0.53 |
| Thermal conductivity (W·m−1·K−1) | 4.601 |
| Element | Zr | Ti | Cu | Ni | Be |
| Element content (at.%) | 62.6% | 11% | 13.2% | 9.8% | 3.4% |
| Parameters | NaNO3 | HCl | H2SO4 | NaCl |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ecorr (V) | −0.47 | −0.35 | −0.28 | −0.50 |
| Epassi (V) | 0.02 | −0.18 | −0.05–0.25 | −0.19–0.10 |
| Etrans (V) | 2.02 | 0.21 | 0.39 | 0.14 |
| Icorr (A·cm2) | −0.81 | −6.79 | −7.64 | −7.44 |
| Itrans (A·cm2) | −1.91 | −0.57 | −2.42 | −1.05 |
| Machining Parameter | Property or Value |
|---|---|
| Nozzle material | SUS 304 |
| Nozzle diameter/μm | ID: 220 ± 2; OD: 450 ± 3 |
| Electrolyte composition | NaNO3, H2SO4, HCl and NaCl |
| Concentration/(mol/L) | 0.5 or 1 |
| Machining gap/μm | 200 |
| Machining voltage/V | 10, 15, 20, 25, 30 |
| Electrolyte velocity (m/s) | 10 |
| Machining time/s | 15 |
| Temperature of electrolyte/°C | 25 ± 2 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Han, L.; Ming, P.; Niu, S.; Yang, G.; Li, D.; Cheng, K. Microfabricating Mirror-like Surface Precision Micro-Sized Amorphous Alloy Structures Using Jet-ECM Process. Micromachines 2024, 15, 375. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi15030375
Han L, Ming P, Niu S, Yang G, Li D, Cheng K. Microfabricating Mirror-like Surface Precision Micro-Sized Amorphous Alloy Structures Using Jet-ECM Process. Micromachines. 2024; 15(3):375. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi15030375
Chicago/Turabian StyleHan, Lei, Pingmei Ming, Shen Niu, Guangbin Yang, Dongdong Li, and Kuaile Cheng. 2024. "Microfabricating Mirror-like Surface Precision Micro-Sized Amorphous Alloy Structures Using Jet-ECM Process" Micromachines 15, no. 3: 375. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi15030375
APA StyleHan, L., Ming, P., Niu, S., Yang, G., Li, D., & Cheng, K. (2024). Microfabricating Mirror-like Surface Precision Micro-Sized Amorphous Alloy Structures Using Jet-ECM Process. Micromachines, 15(3), 375. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi15030375






