A Wearable Fingertip Force Feedback Device System for Object Stiffness Sensing
Abstract
:1. Introduction
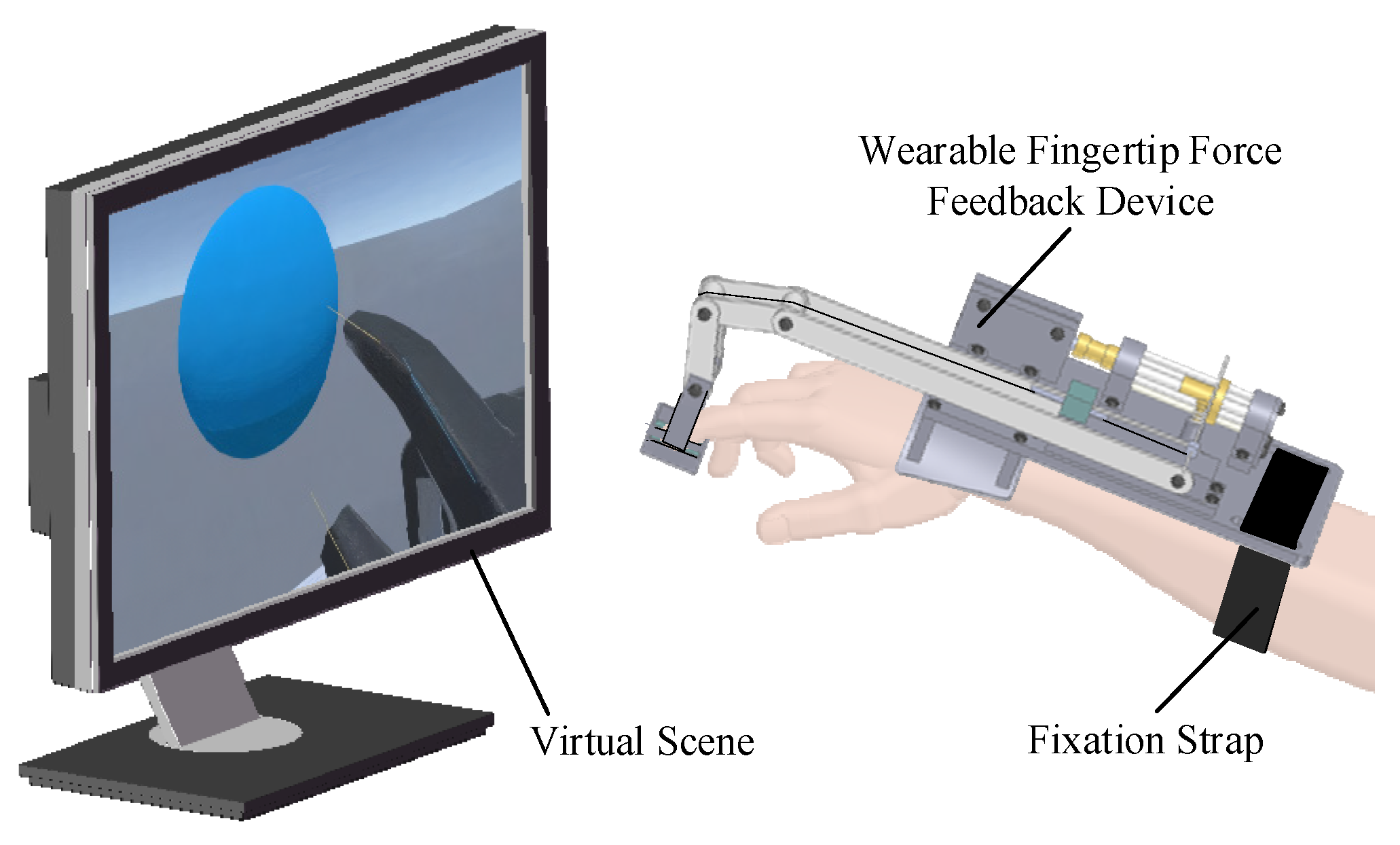
2. Wearable Fingertip Force Feedback Device
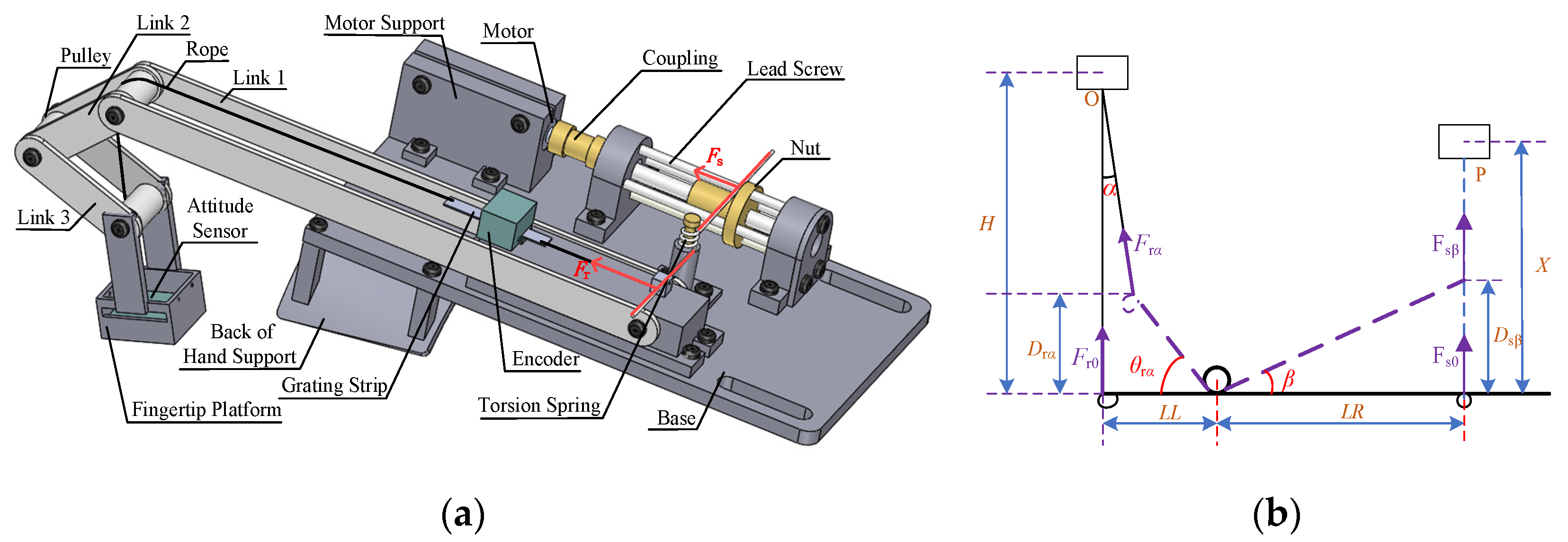
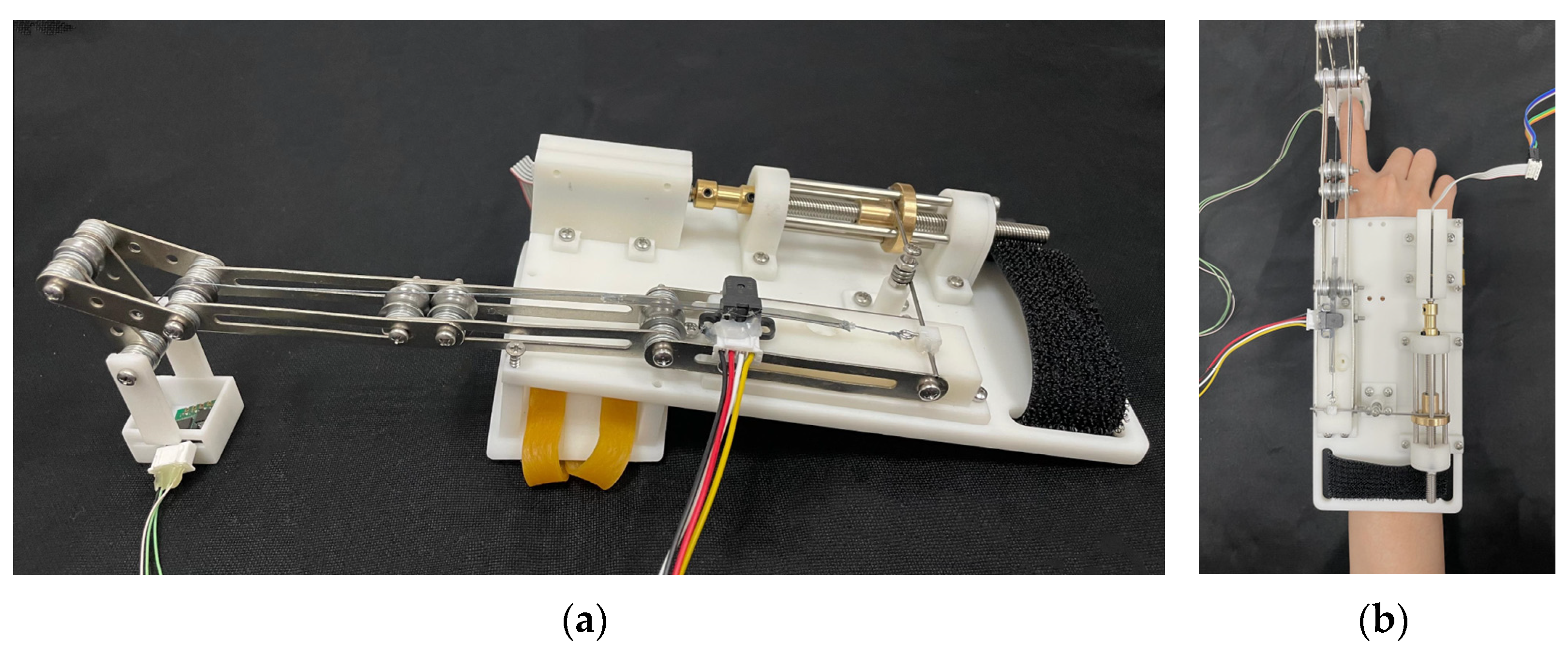
2.1. Mechanical Design
2.2. Mechanical Analysis
2.3. Part Selection
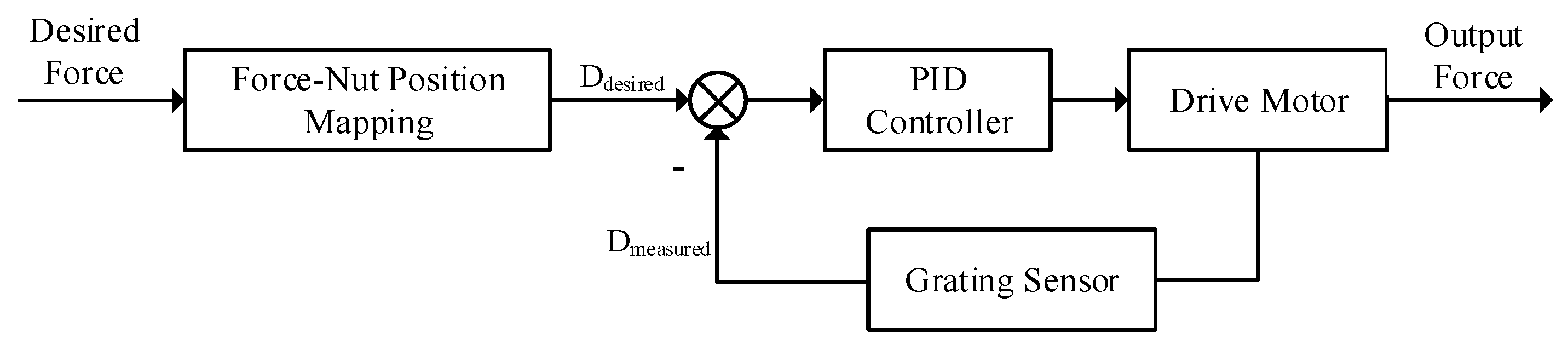
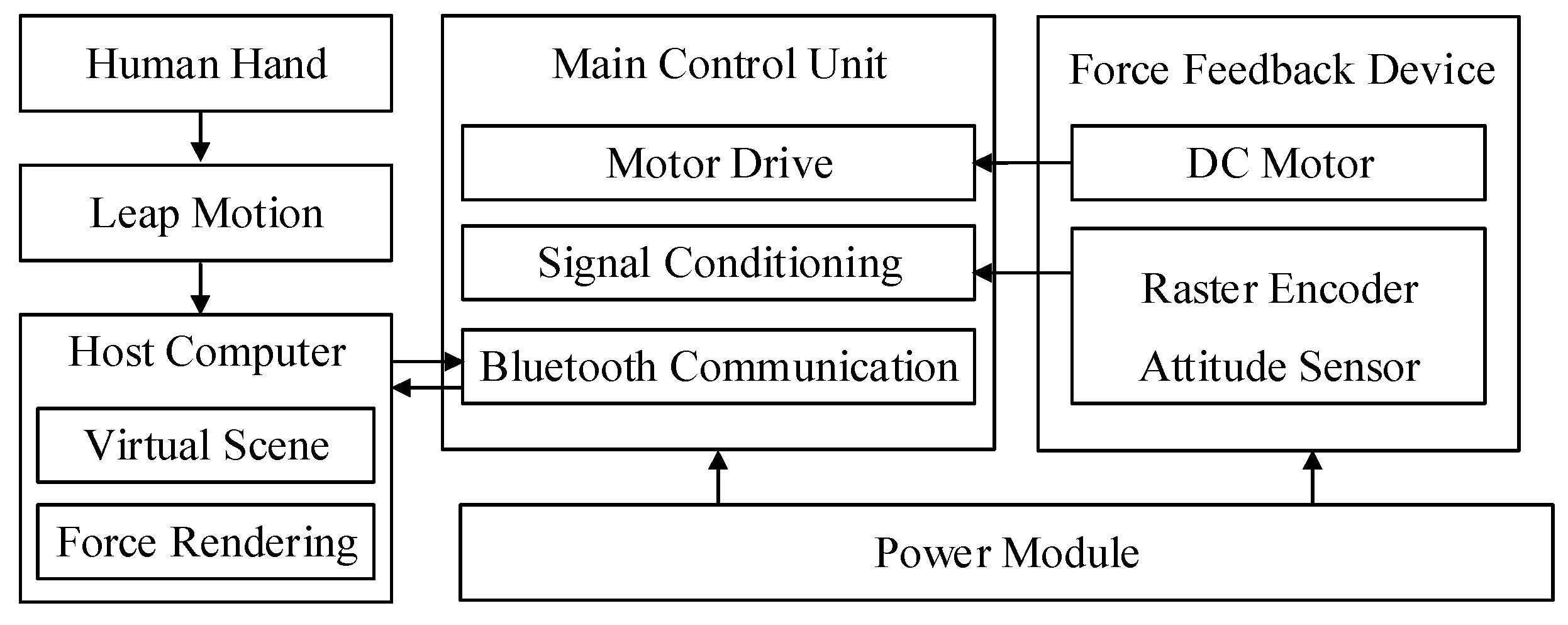
3. Measurement and Control System
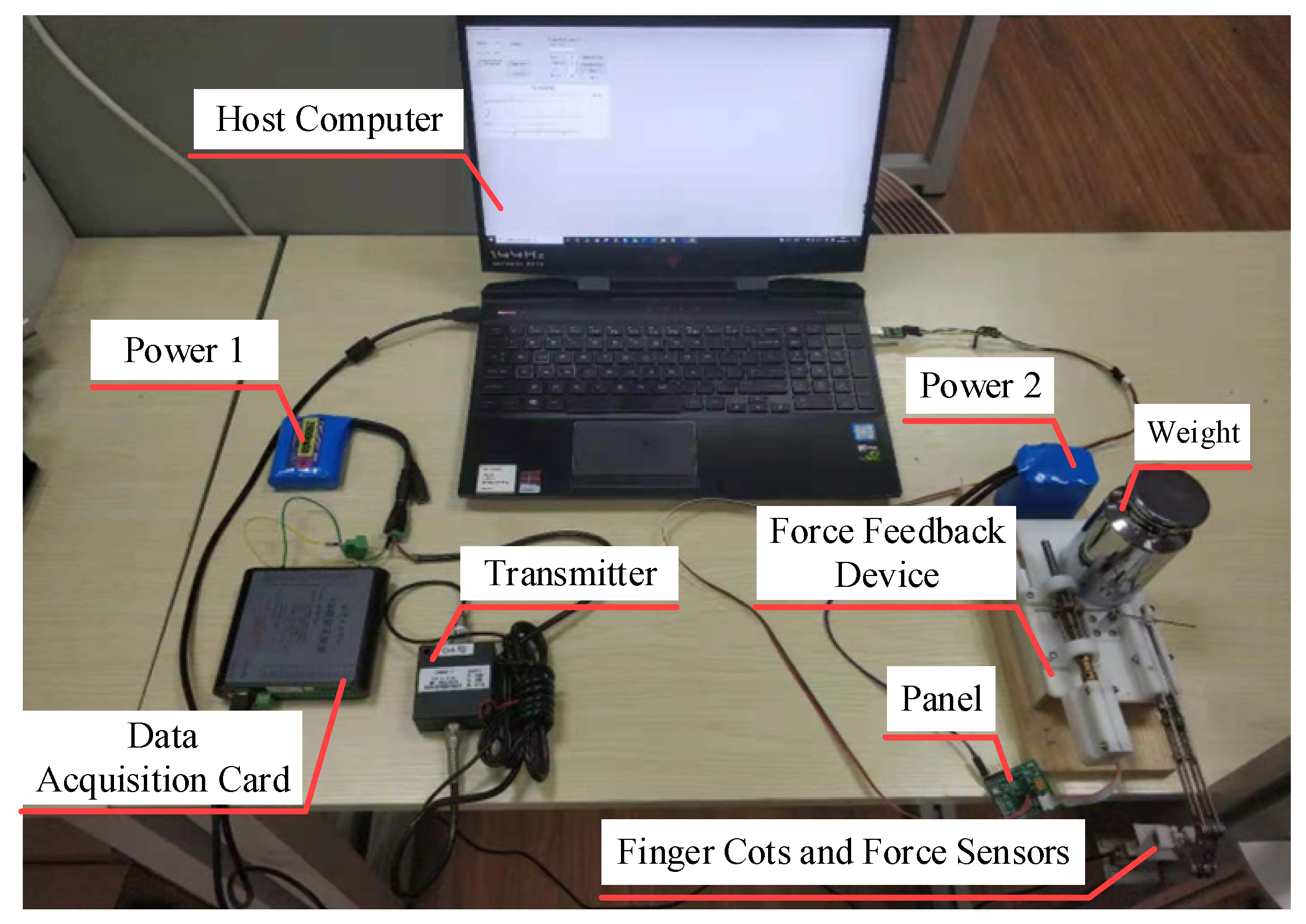
4. Device Performance Evaluation
4.1. Static Performance Test Experiment
- (1)
- Accuracy
- (2)
- Consistency
- (3)
- Repeatability
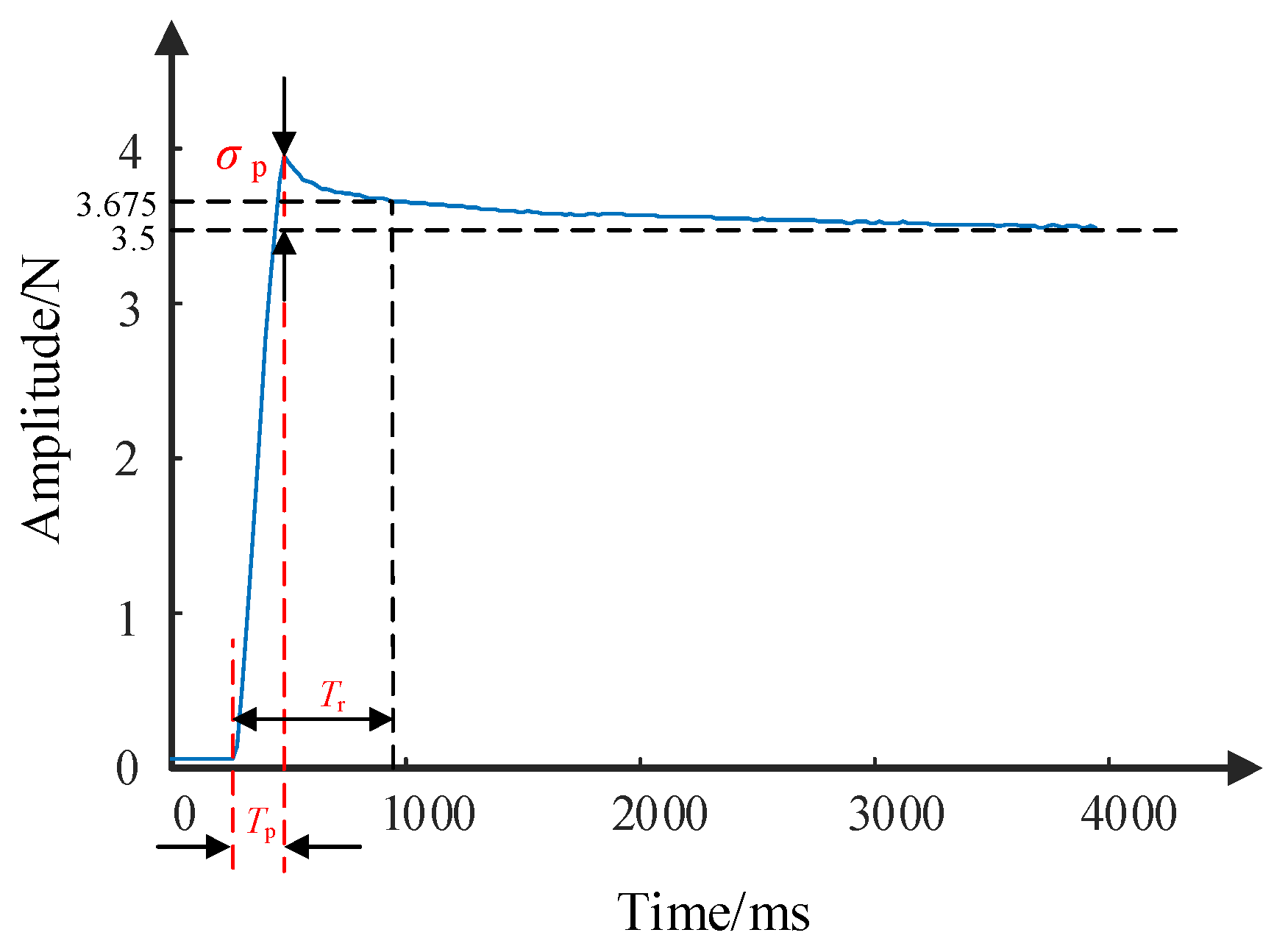
4.2. Dynamic Performance Test Experiment
5. Object Stiffness Reproduction Experiment
5.1. Experimental Method
5.2. Experiment Procedure
5.3. Analysis of Results
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Okamura, A.M.; Webster, R.J.; Nolin, J.T.; Johnson, K.W.; Jafry, H. The Haptic Scissors: Cutting in Virtual Environments. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, Taipei, Taiwan, 14–19 September 2003; Volume 1, pp. 828–833. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, S.; Yu, M.; Geng, X.; Cheng, X.; Wang, P. A Lightweight Exoskeleton Force Feedback Glove. Actuators 2023, 12, 199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, D.T.G.; Nguyen, L. An Efficient Force-Feedback Hand Exoskeleton for Haptic Applications. Int. J. Intell. Robot. Appl. 2021, 5, 395–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, J.; Hinchet, R.; Shea, H.; Majidi, C. Wearable Soft Technologies for Haptic Sensing and Feedback. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2021, 31, 2007428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kudry, P.; Cohen, M. Development of a Wearable Force-Feedback Mechanism for Free-range Haptic Immersive Experience. Front. Virtual Real. 2022, 3, 824886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Lou, G.; Zhang, J.; Zhao, Y. Research on Force Feedback Controller of Interventional Robot Based on Pneumatic Drive. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Mechatronics and Automation (ICMA), Harbin, China, 6–9 August 2023; pp. 784–789. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, K.; Chen, Z.; Tai, Y.; Peng, J.; Shi, J.; Xia, C. A System Design for Virtual Reality Visualization of Medical Image. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Geoinformatics, Kunming, China, 10–12 November 2018; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Ye, R.; Ishibashi, Y.; Huang, P.; Tateiwa, Y. Comparison of Collaboration Methods between Users in Remote Robot Systems with Force Feedback. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer and Communications (ICCC), Chengdu, China, 10–13 December 2021; pp. 1052–1056. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, J.; Yang, B.; Song, A.; Liu, K.; Sun, D.; Tang, Z. The Development of Tactile Feedback Devices. In Proceedings of the SPIE Ninth International Symposium on Sensors, Mechatronics, and Automation System (ISSMAS), Nanjing, China, 11–13 August 2023; Volume 12981, pp. 737–743. [Google Scholar]
- Pawluk, D.T.V.; Adams, R.J.; Kitada, R. Designing Haptic Assistive Technology for Individuals Who are Blind or Visually Impaired. IEEE Trans. Haptics 2015, 8, 258–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, Y.; Yang, C.; Wang, X.; Su, C.-Y. Kinematics Modeling of Geomagic Touch X Haptic Device Based on Adaptive Parameter Identification. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Real-Time Computing and Robotics (RCAR), Angkor Wat, Cambodia, 6–9 June 2016; pp. 295–300. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, B.; Wu, Z.; Li, Q.; Xu, K. CombX: Design of a Haptic Device for Teleoperation. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Biomimetics (ROBIO), Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, 12–15 December 2018; pp. 1969–1974. [Google Scholar]
- Fazlollahi, F.; Seifi, H.; MacLean, K.; Kuchenbecker, K.J. How Do Expert Hapticians Evaluate Grounded Force-feedback Devices? In Proceedings of the IEEE World Haptics Conference (WHC), Montreal, QC, Canada, 6–9 July 2021; p. 341. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, D.; Song, A.; Hu, X.; Fu, L.; Ouyang, Q. A Spherical Actuator-based Hand-held Haptic Device for Touch Screen Interaction. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 15125–15139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arezoo, K.; Tarvirdizadeh, B.; Alipour, K.; Hadi, A.; Arezoo, J. Design, Fabrication and Control of a Handheld Force-Feedback Device. In Proceedings of the IEEE 9th RSI International Conference on Robotics and Mechatronics (ICRoM), Tehran, Iran, 17–19 November 2021; pp. 85–90. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Y.; Yao, K.; Li, J.; Li, D.; Jia, H.; Liu, Y.; Yiu, C.K.; Park, W.; Yu, X. Recent Advances in Multi-mode Haptic Feedback Technologies towards Wearable Interfaces. Mater. Today Phys. 2022, 22, 100602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Yan, Y.; Qi, B.; Qian, H.; Sun, J.; Quigley, A. Contactless Haptic Display Through Magnetic Field Control. IEEE Trans. Haptics 2022, 15, 328–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, D.; Wang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Wen, L.; Zhang, Y. A two-fingered force feedback glove using soft actuators. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE Haptics Symposium (HAPTICS), San Francisco, CA, USA, 25–28 March 2018; pp. 186–191. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; Wang, D.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, J.; Wen, L.; Xu, W.; Zhang, Y. A three-fingered force feedback glove using fiber-reinforced soft bending actuators. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2019, 67, 7681–7690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Yimit, A.; Lu, X.; Hagihara, Y. Design of a two-point-contact fingertip tactile force feedback device. In Proceedings of the 2017 2nd International Conference on Cybernetics, Robotics and Control (CRC), Chengdu, China, 21–23 July 2017; pp. 71–74. [Google Scholar]
- See, A.R.; Choco, J.A.G.; Chandramohan, K. Touch, Texture and Haptic Feedback: A Review on How We Feel the World Around Us. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 4686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.; Lee, S.; Lee, D. Wearable Haptic Device for Stiffness Rendering of Virtual Objects in Augmented Reality. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 6932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez-Hernandez, U.; Al, G.A. Wearable Fingertip with Touch, Sliding and Vibration Feedback for Immersive Virtual Reality. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics (SMC), Prague, Czech Republic, 9–12 October 2022; pp. 293–298. [Google Scholar]
- Chinello, F.; Pacchierotti, C.; Malvezzi, M.; Prattichizzo, D. A Three Revolute-Revolute-Spherical Wearable Fingertip Cutaneous Device for Stiffness Rendering. IEEE Trans. Haptics 2017, 11, 39–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.; Son, B.; Han, I.; Lee, W. Effect of Cutaneous Feedback on the Perception of Virtual Object Weight During Manipulation. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 1357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Song, A.; Tian, L.; Fu, L.; Zeng, H. FW-Touch: A Finger Wearable Haptic Interface with an MR Foam Actuator for Displaying Surface Material Properties on a Touch Screen. IEEE Trans. Haptics 2019, 12, 281–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuang, L.; Ferro, M.; Malvezzi, M.; Prattichizzo, D.; Giordano, P.R.; Chinello, F.; Pacchierotti, C. A Wearable Haptic Device for the Hand with Interchangeable End-effectors. IEEE Trans. Haptics 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bolanowski, S.J., Jr.; Gescheider, G.A.; Verrillo, R.T.; Checkosky, C.M. Four Channels Mediate the Mechanical Aspects of Touch. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1988, 84, 1680–1694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dargahi, J.; Najarian, S. Human Tactile Perception as a Standard for Artificial Tactile Sensing—A Review. Int. J. Med. Robot. Comput. Assist. Surg. 2004, 1, 23–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]





| Parameter | Index |
|---|---|
| H | 200 mm |
| LL | 25 mm |
| LR | 30 mm |
| X | 35 mm |
| Drα | 0~24.8 mm |
| θrα | 0~1.446 rad |
| Dsβ | 0~20 mm |
| β | 0~0.588 rad |
| Amplitude/N | Maximum Overshoot/% | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 4.0 | 12.86 | 220 | 660 |
| 3.5 | 13.6 | 200 | 620 |
| 3.0 | 13.36 | 160 | 680 |
| 2.5 | 11.00 | 140 | 720 |
| 2.0 | 11.86 | 100 | 640 |
| 1.5 | 12.5 | 100 | 920 |
| 1.0 | 10.67 | 100 | 900 |
| 0.5 | 10.42 | 80 | 660 |
| Statements | Average Rating |
|---|---|
| S1: The device can enhance the authenticity of the interaction. | 7 |
| S2: I can clearly distinguish between three different stiffness levels of the sphere. | 5.625 |
| S3: During the use of the device, I am very satisfied with the interactive comfort. | 5.75 |
| S4: The visual 3D imaging synchronization is very good. | 6.125 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wu, C.; Ren, J.; Cao, Q.; Yue, Z.; Fang, T.; Song, A. A Wearable Fingertip Force Feedback Device System for Object Stiffness Sensing. Micromachines 2024, 15, 693. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi15060693
Wu C, Ren J, Cao Q, Yue Z, Fang T, Song A. A Wearable Fingertip Force Feedback Device System for Object Stiffness Sensing. Micromachines. 2024; 15(6):693. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi15060693
Chicago/Turabian StyleWu, Changcheng, Jianli Ren, Qingqing Cao, Zeran Yue, Ting Fang, and Aiguo Song. 2024. "A Wearable Fingertip Force Feedback Device System for Object Stiffness Sensing" Micromachines 15, no. 6: 693. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi15060693
APA StyleWu, C., Ren, J., Cao, Q., Yue, Z., Fang, T., & Song, A. (2024). A Wearable Fingertip Force Feedback Device System for Object Stiffness Sensing. Micromachines, 15(6), 693. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi15060693






