Mechanism-Oriented Analysis of Core–Shell Structured CIP@SiO2 Magnetic Abrasives for Precision-Enhanced Magnetorheological Polishing
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals and Materials
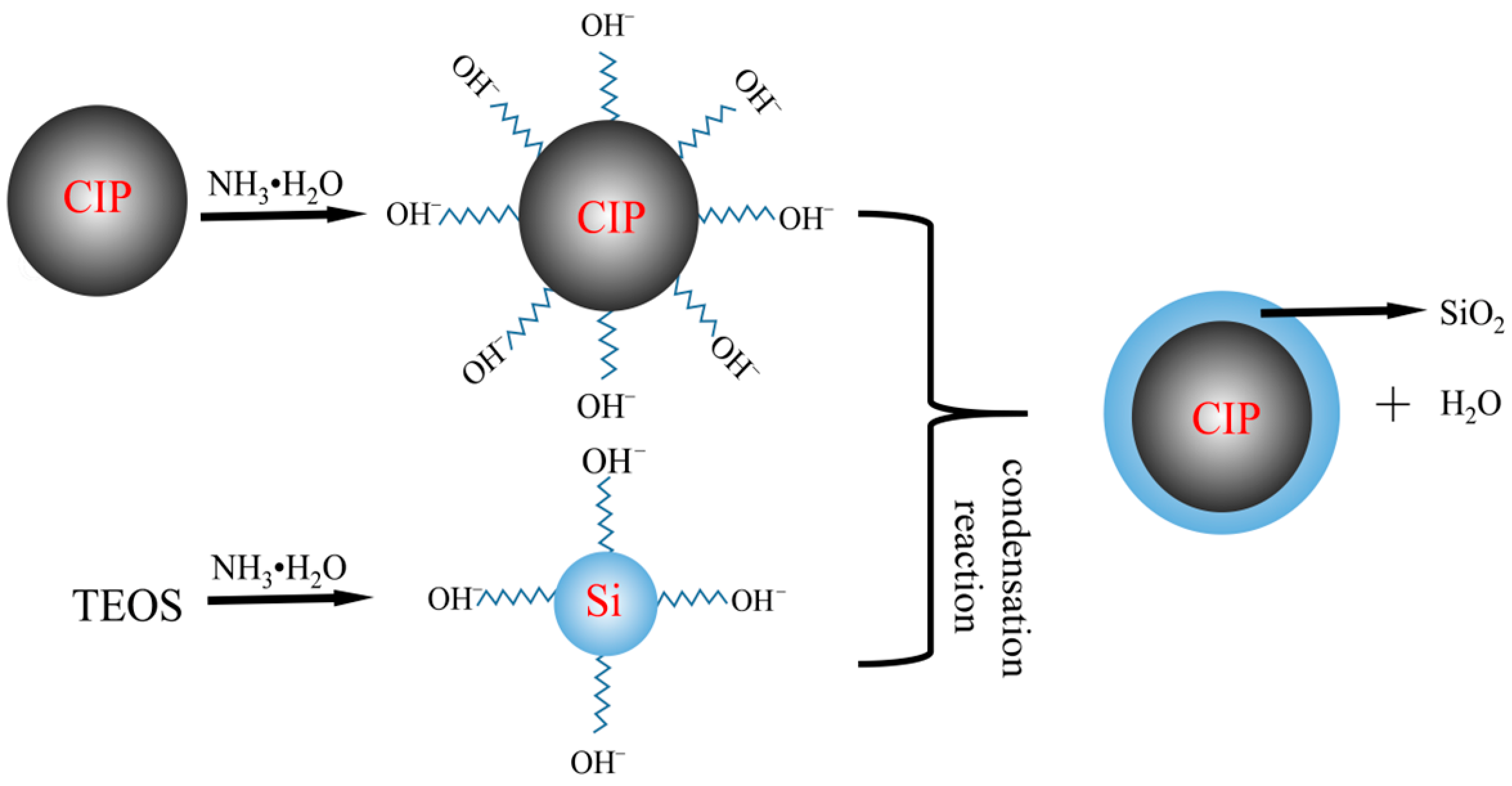
2.2. Preparation Principle and Process of Magnetic Composite Particles
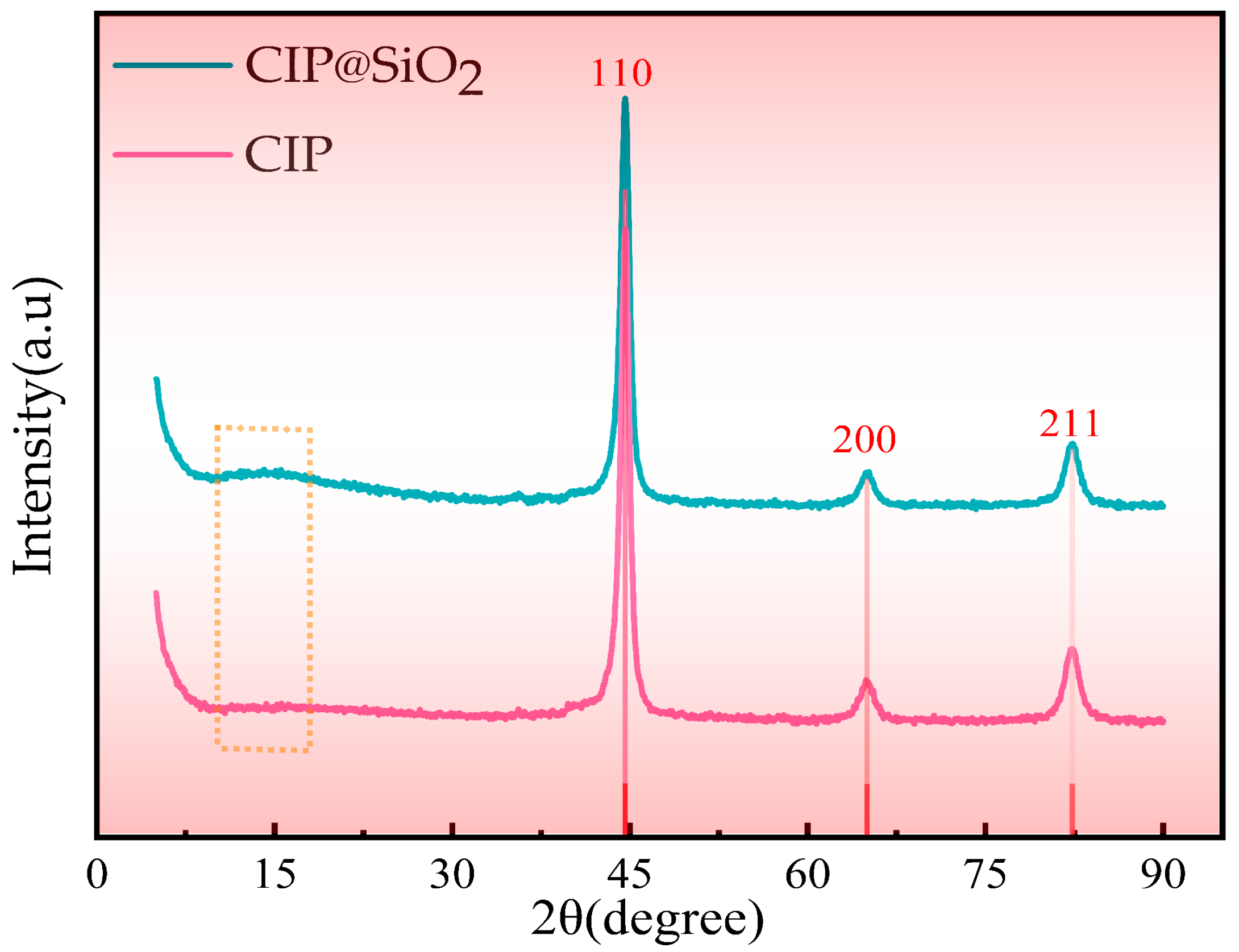
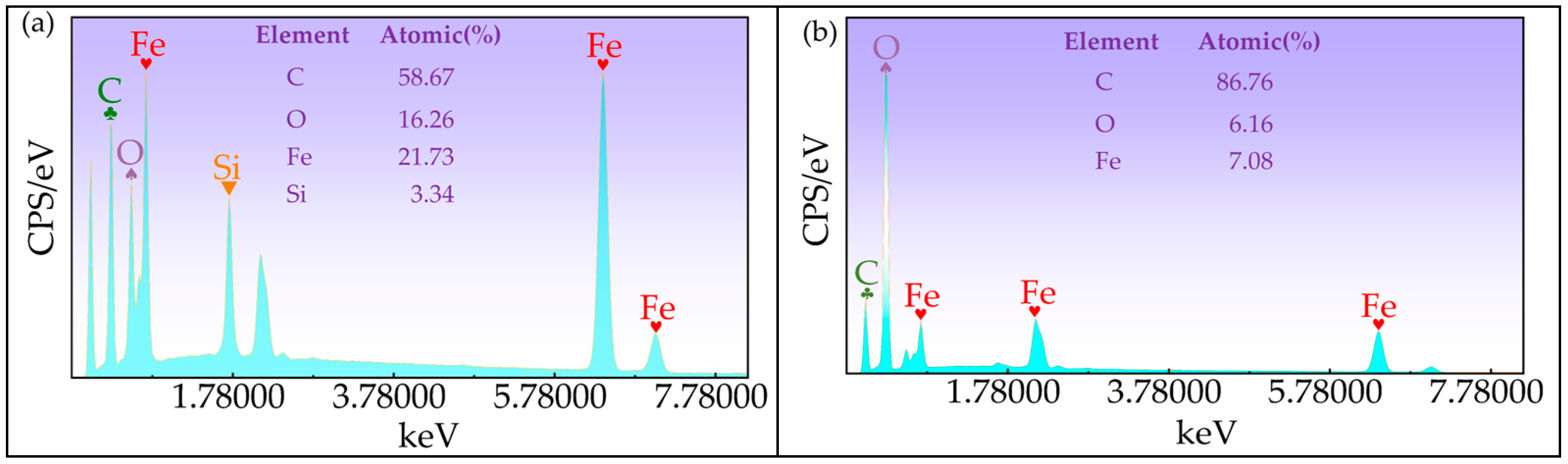
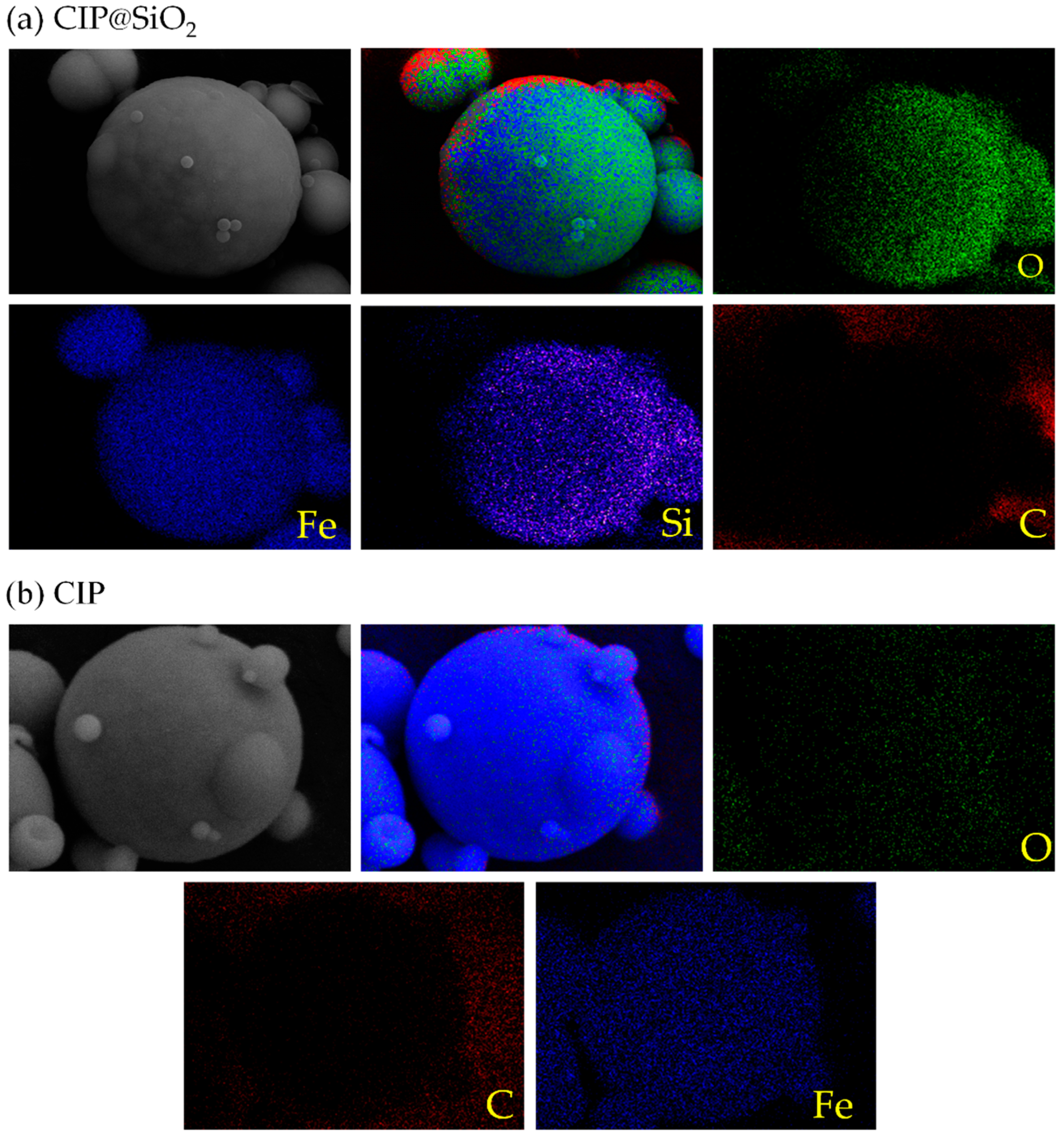
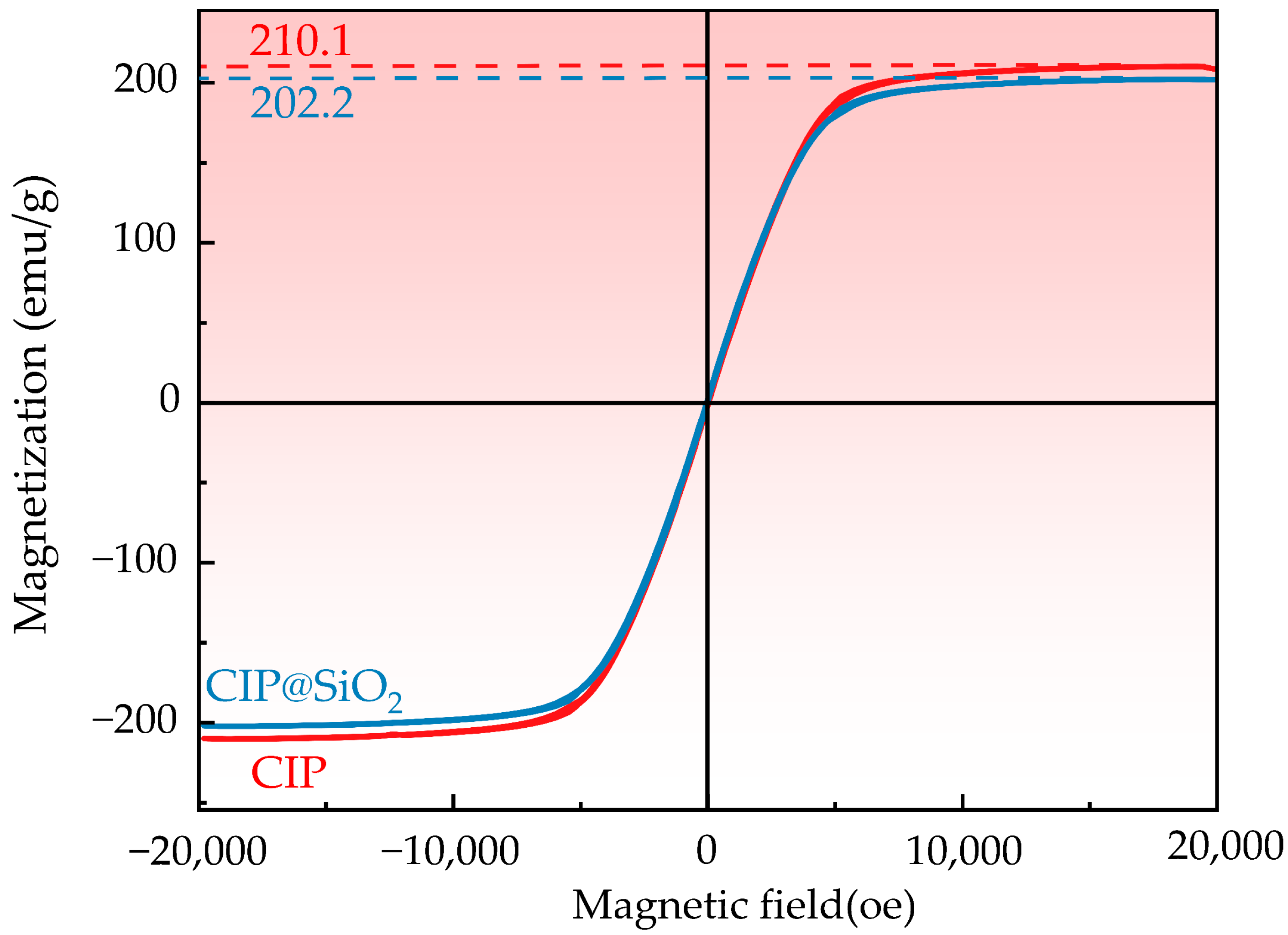
2.3. Property Measurement and Characterization of CIP@SiO2 Magnetic Composite Particles
3. Experiment Design for the MRP
3.1. Principle and Device of Magnetorheological Polishing
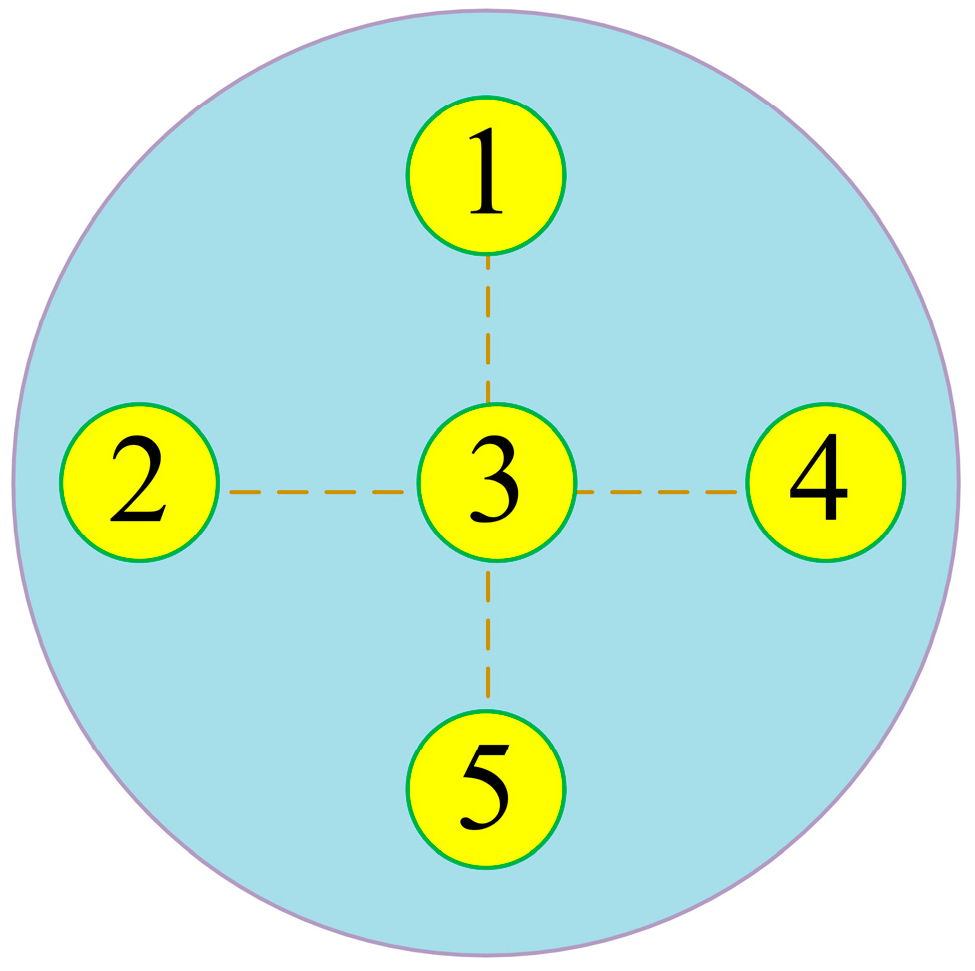
3.2. Parameters Design for the MRP Process
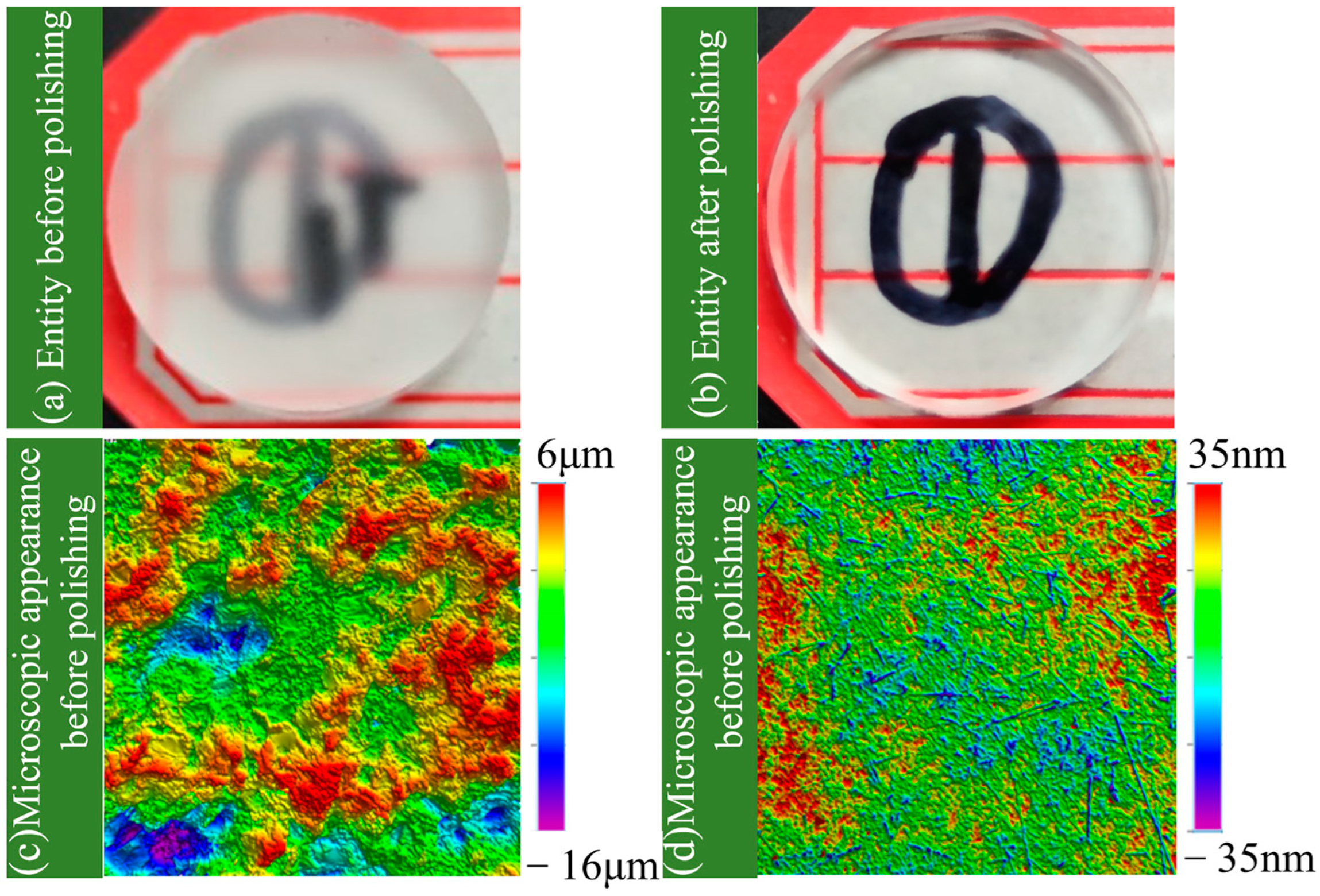
3.3. Measurement and Calculation of Surface Roughness and Material Removal Rate
4. Results and Discussion
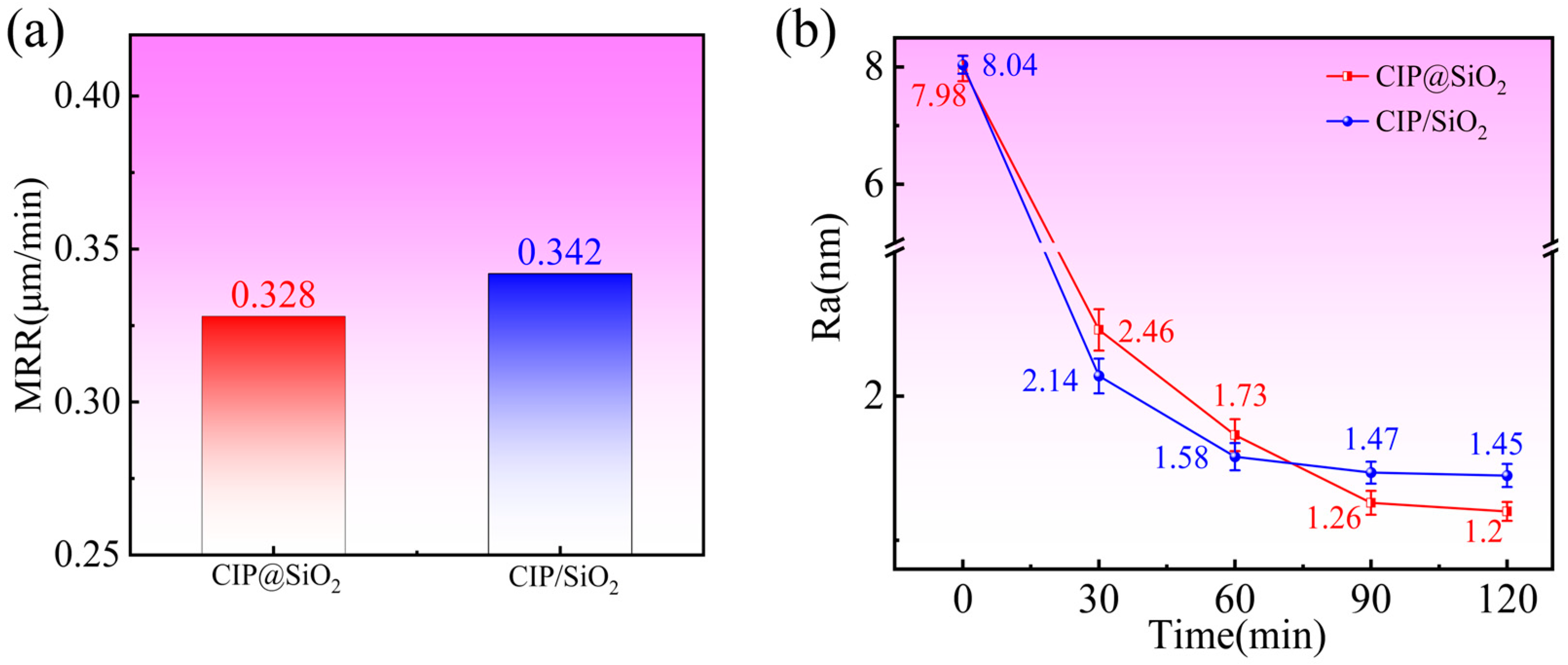
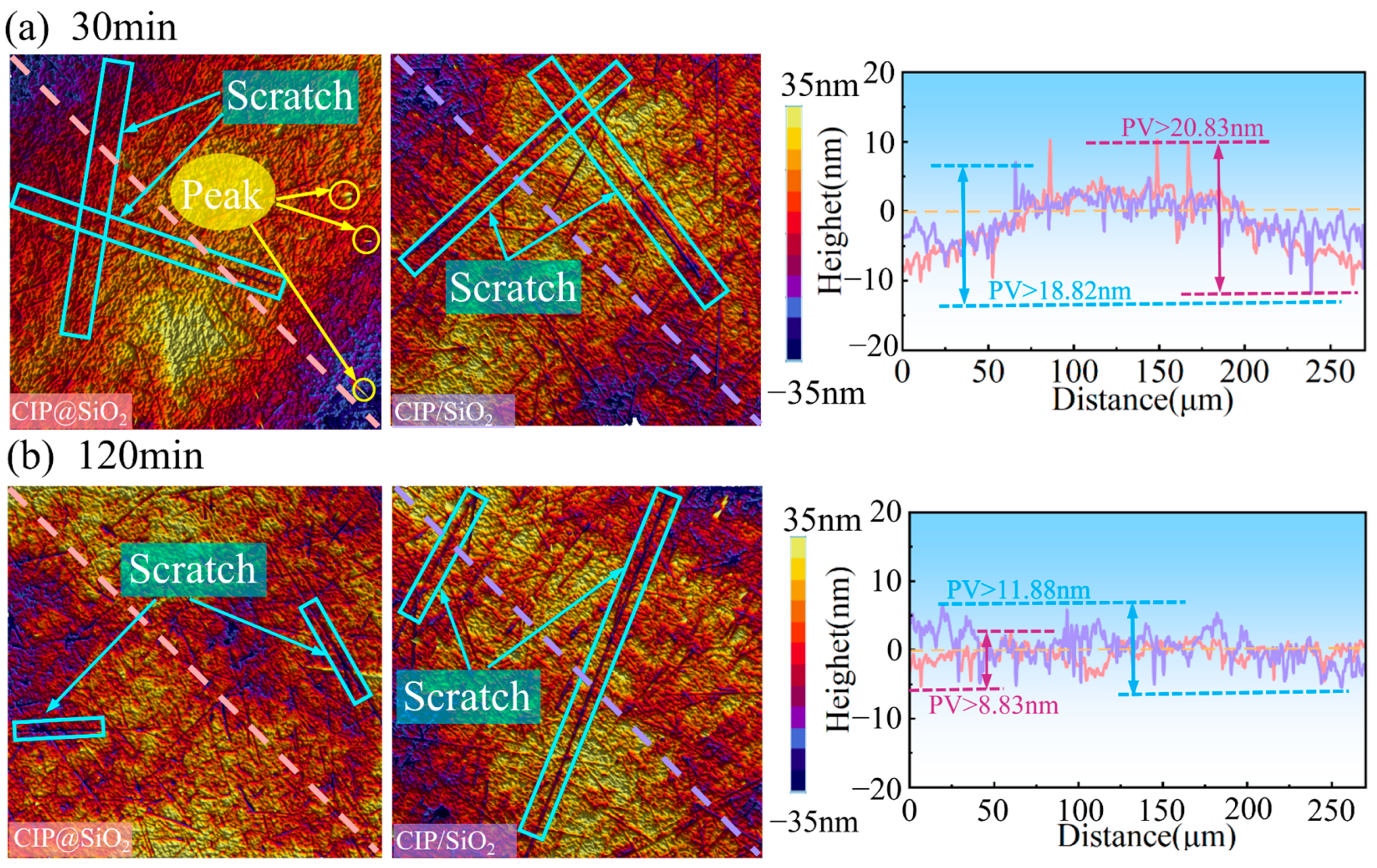
4.1. Effect of Polishing Time on Polishing Effect Under Different Abrasives
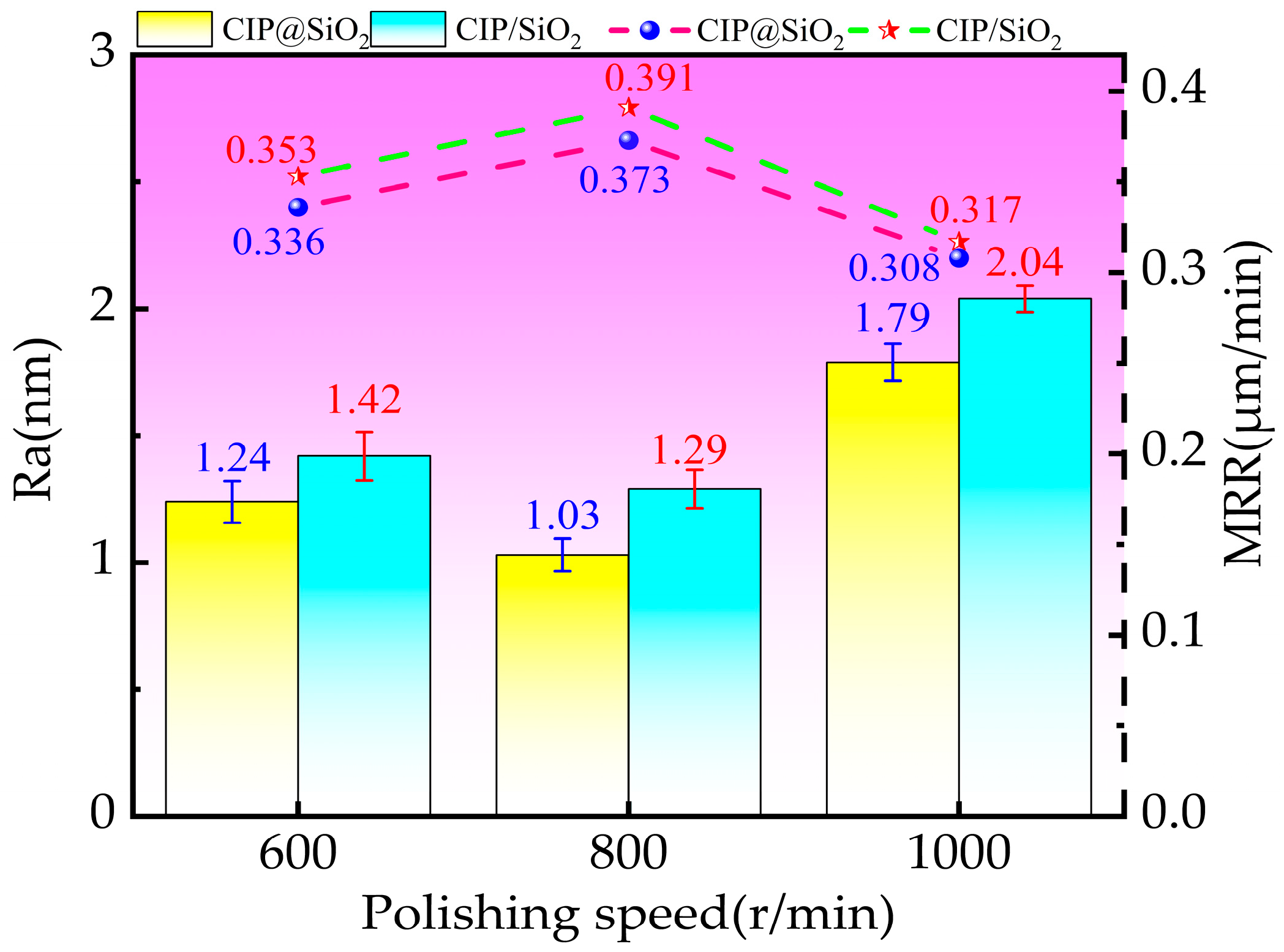
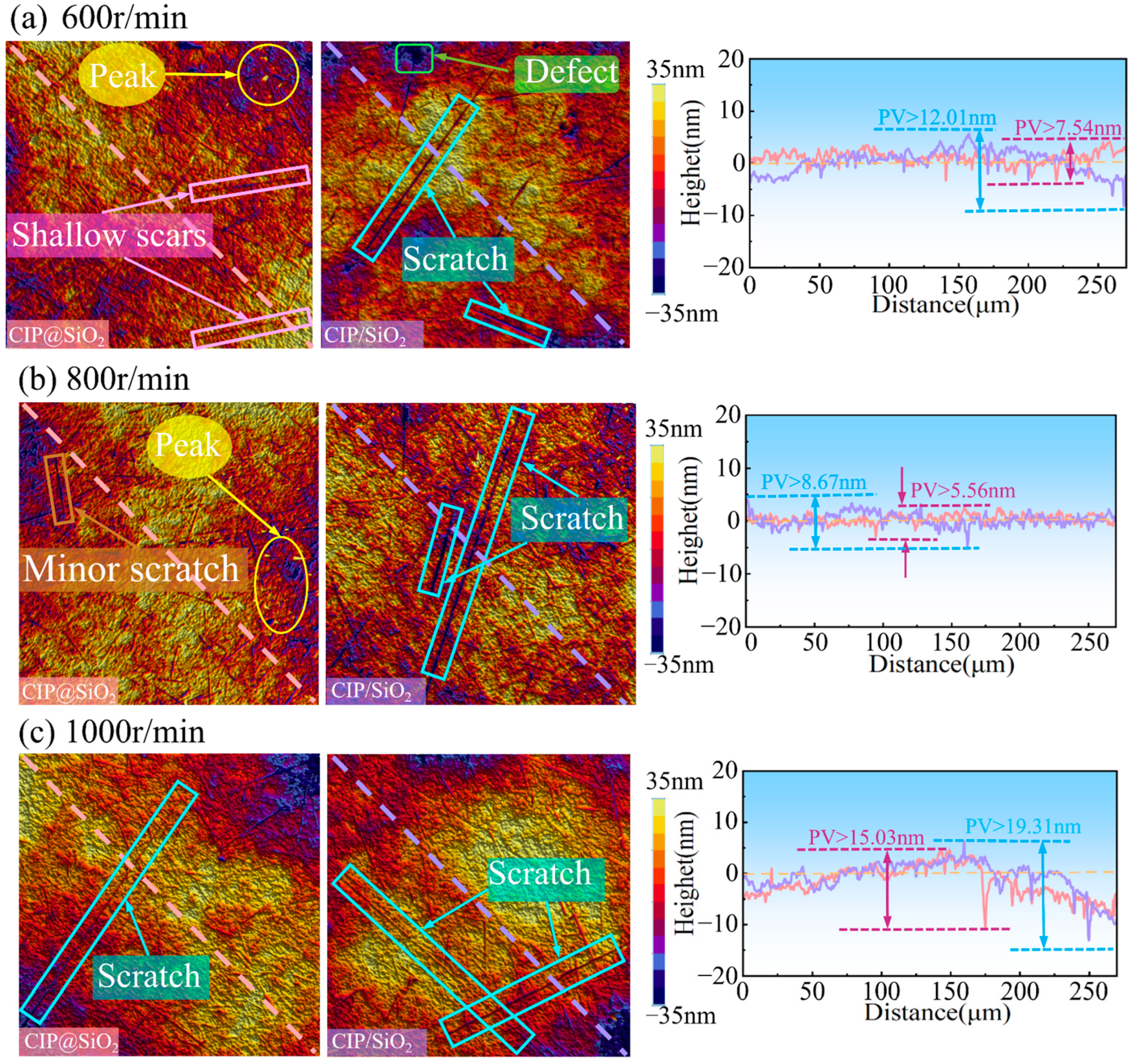
4.2. Effect of Polishing Speed on Polishing Effect Under Different Abrasives
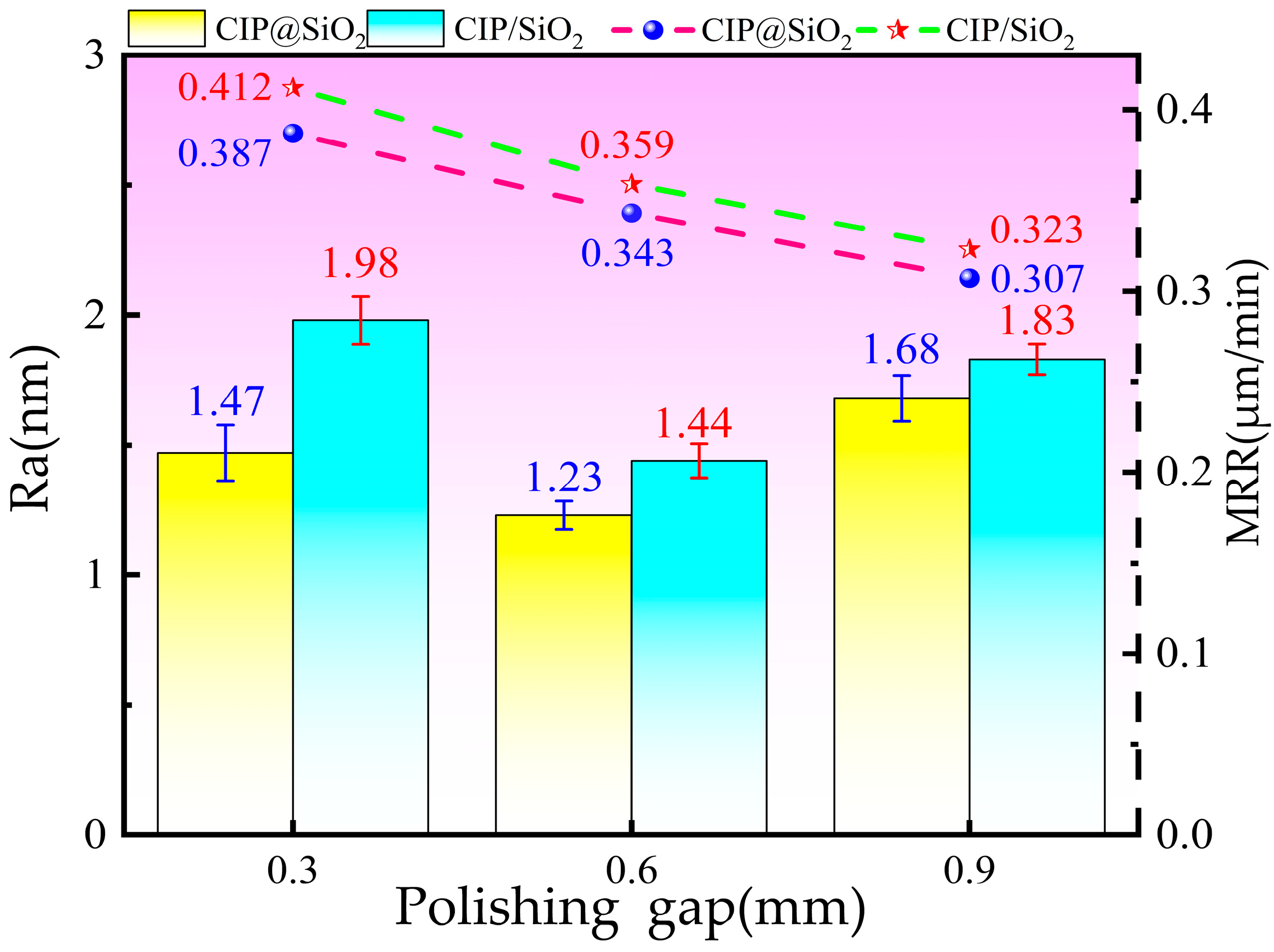
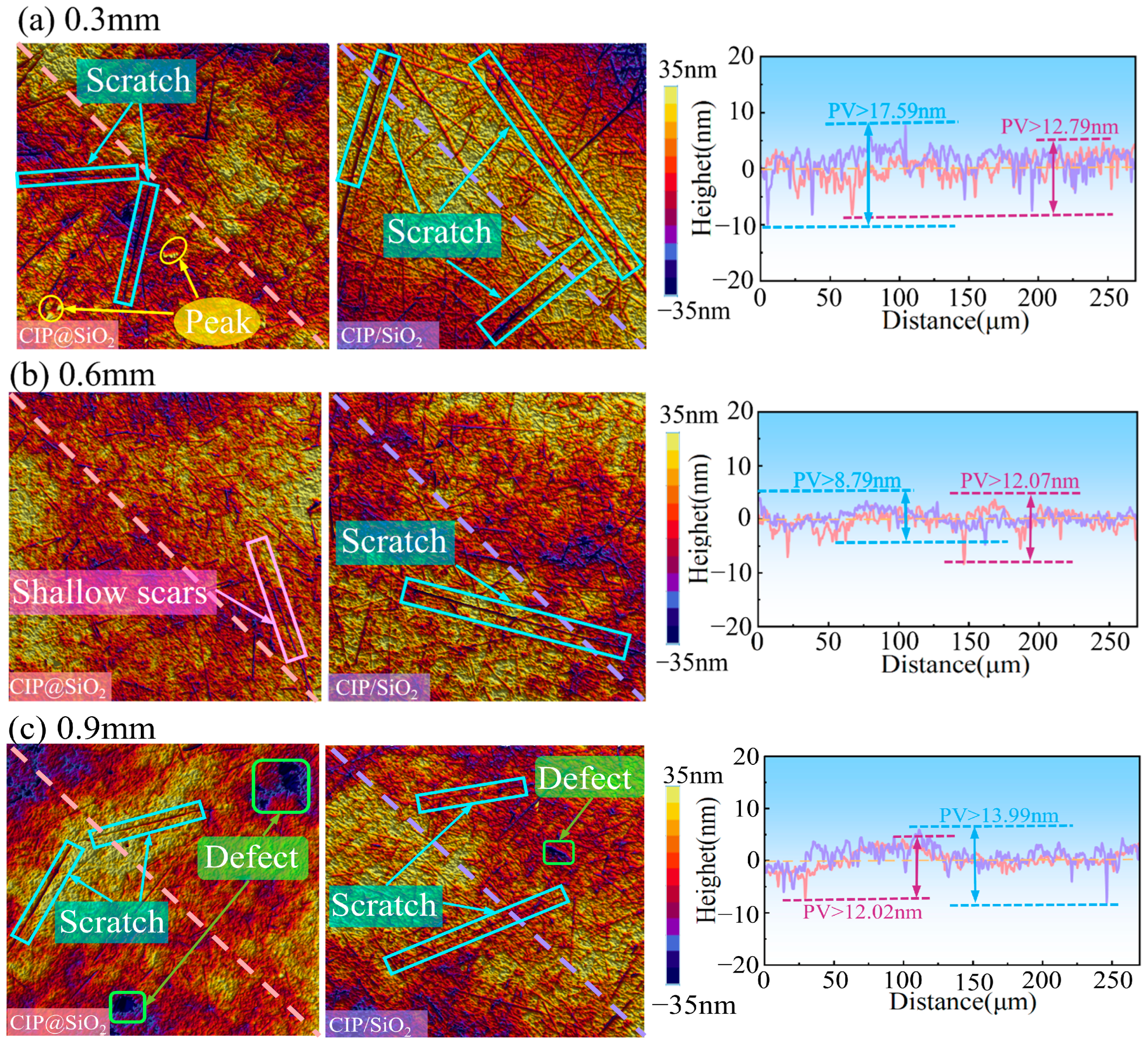
4.3. Effect of Polishing Gap on Polishing Effect Under Different Abrasives
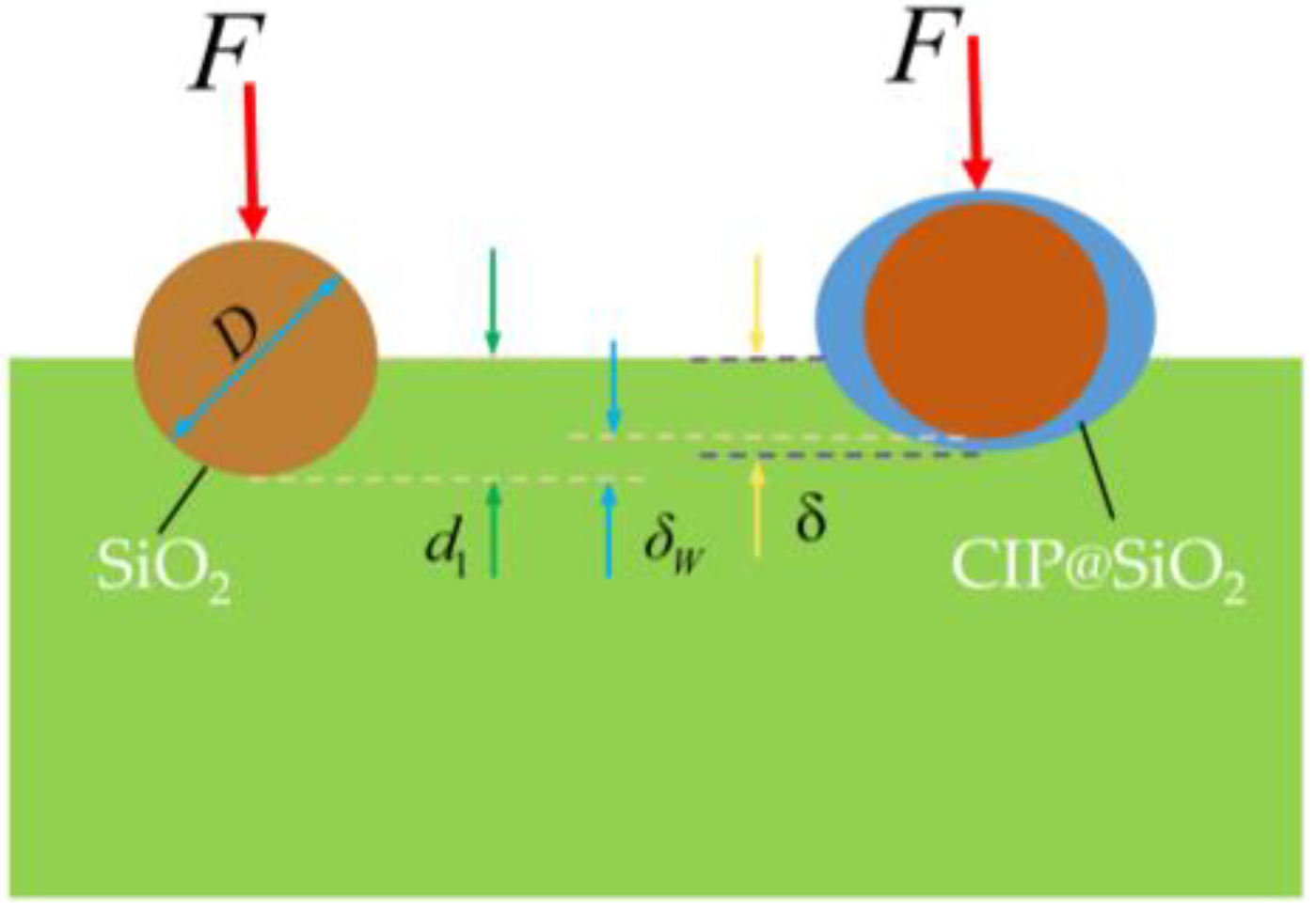
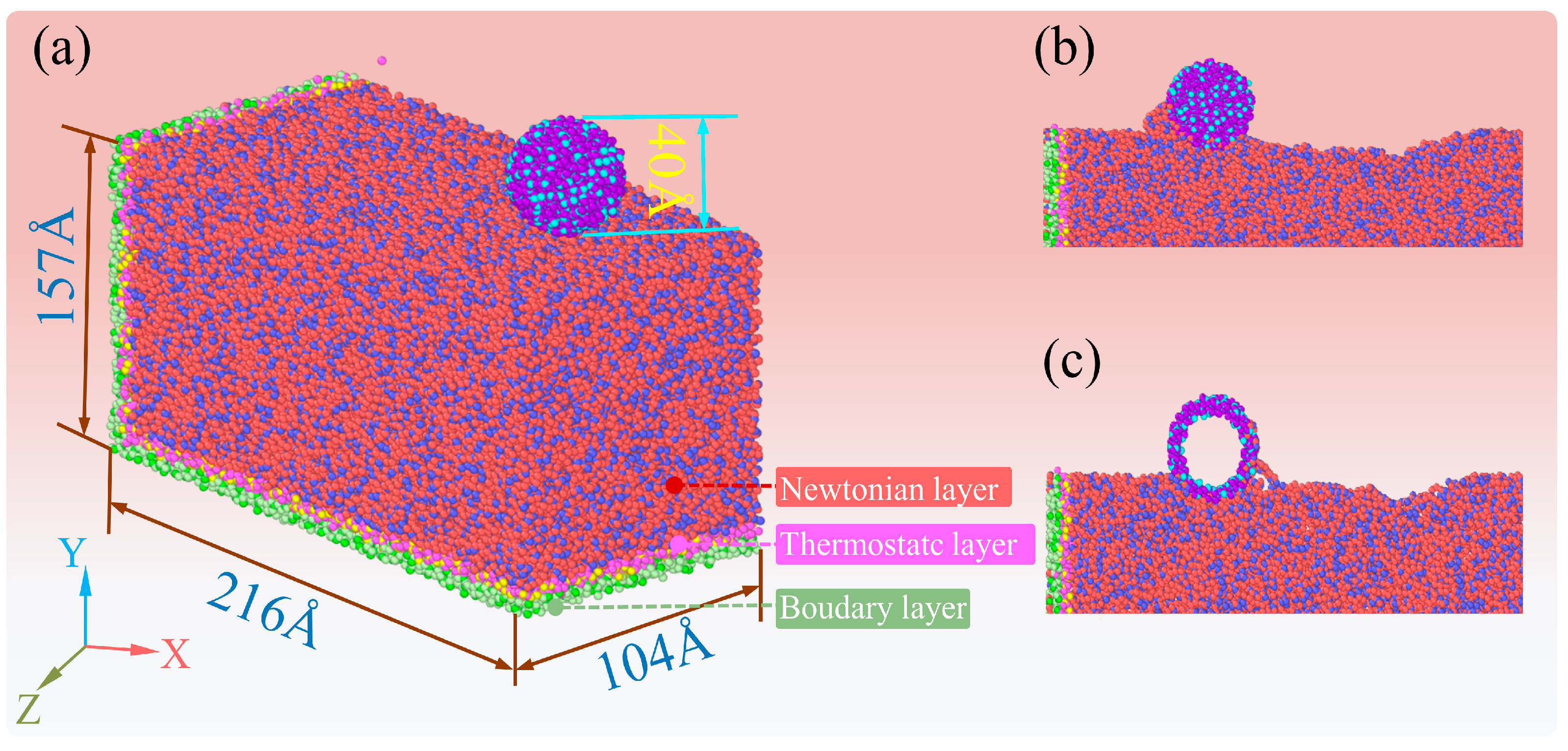
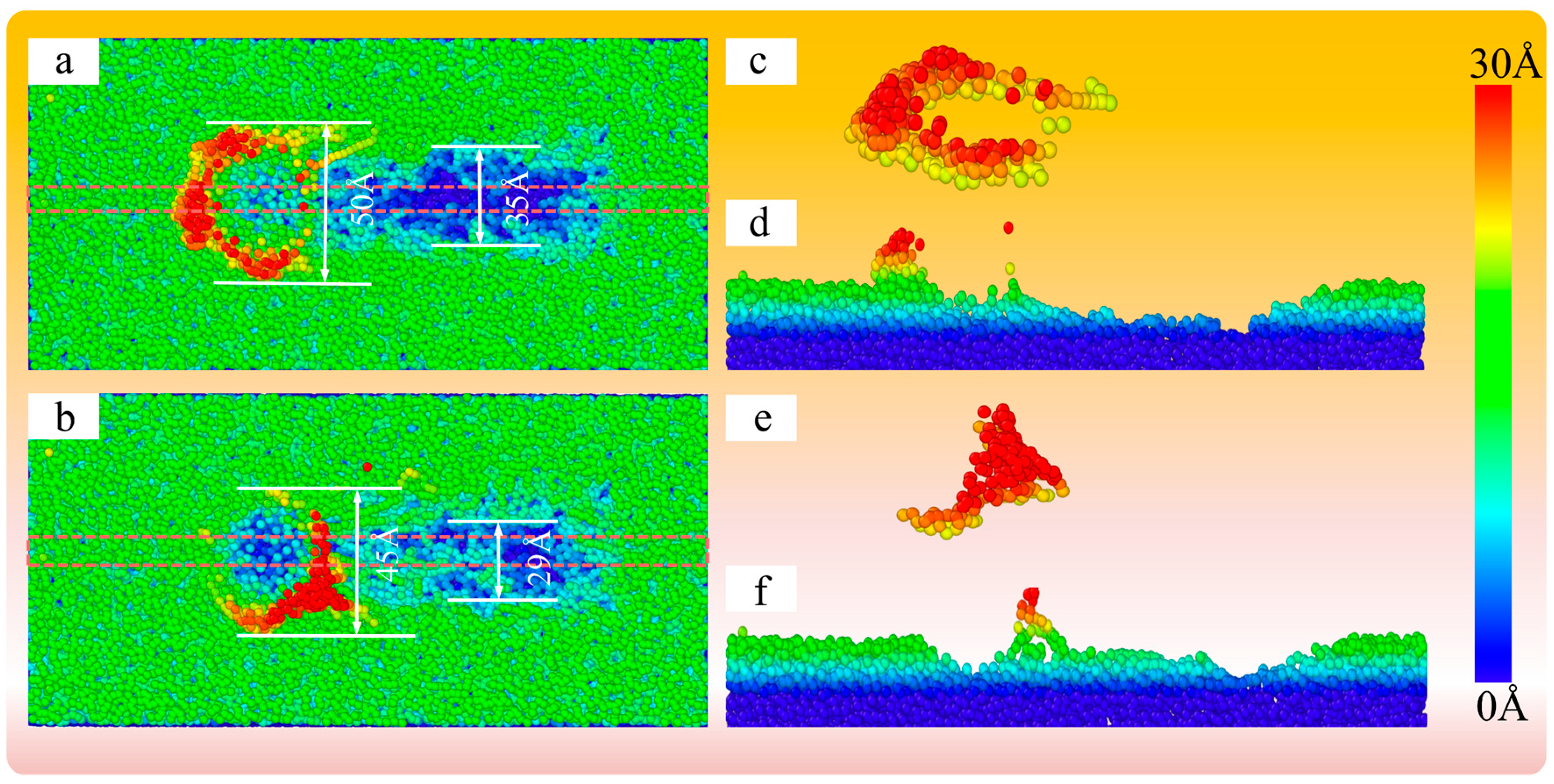
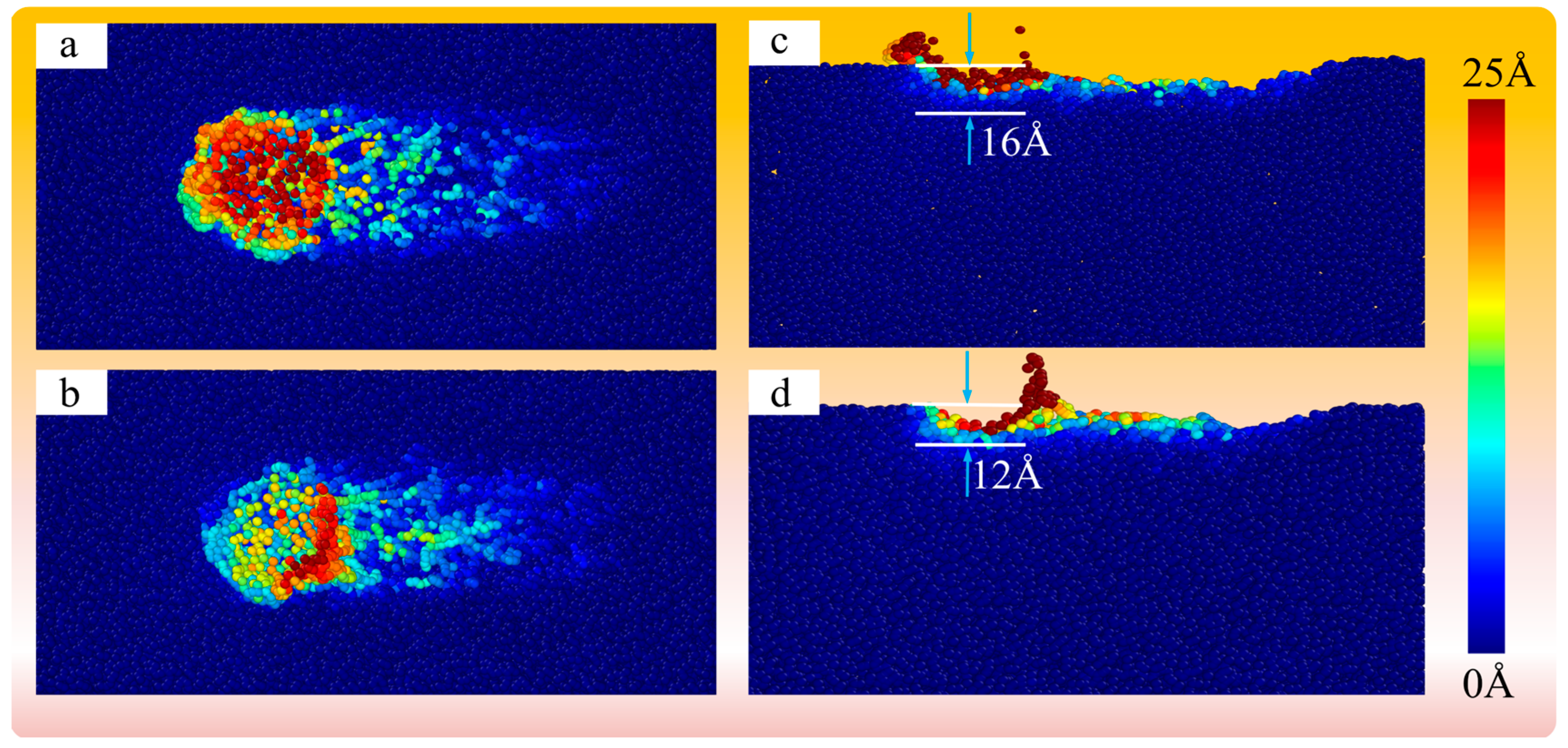
4.4. Mechanism Analysis for the Polishing
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| MRP | magnetorheological polishing |
| CIP | carbonyl iron particle |
| CIP@SiO2 | carbonyl iron particles coated with SiO2 |
References
- Wang, W.; Ji, S.; Zhao, J. Review of magnetorheological finishing on components with complex surfaces. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2024, 131, 3165–3191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Feng, Z. Analyzing and improving surface texture by dual-rotation magnetorheological finishing. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2016, 360, 224–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, M.; Singh Yadav, H.N.; Kumar, A.; Das, M. An overview of magnetorheological polishing fluid applied in nano-finishing of components. J. Micromanuf. 2022, 5, 82–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajput, A.S.; Das, M.; Kapil, S. A comprehensive review of magnetorheological fluid assisted finishing processes. Mach. Sci. Technol. 2022, 26, 339–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, B.; Li, Y.; Yan, Q.; Chai, J.; Song, W.; Lan, X. Cluster magnetorheological global dynamic pressure planarization processing of single crystal sapphire. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2023, 128, 1213–1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, M.M.; Yang, Y.K.; Lin, J.Q.; Du, Y.S.; Zhou, X.Q. Research progress of magnetorheological polishing technology: A review. Adv. Manuf. 2024, 12, 642–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sidpara, A.; Das, M.; Jain, V.K. Rheological characterization of magnetorheological finishing fluid. Mater. Manuf. Process. 2009, 24, 1467–1478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Wang, Q.; Zhu, K.; Jiang, S.; Wu, H.; Yi, L. Preparation and characterization of magnetorheological elastic polishing composites. J. Intell. Mater. Syst. Struct. 2019, 30, 1481–1492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, P.; Du, T.; Ma, N.; Dong, X.; Qi, M. Effect of interfacial shear strength between magnetic particles and carrier liquid on rheological properties of magnetorheological fluids. J. Mol. Liq. 2023, 369, 120929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niranjan, M.; Jha, S.; Kotnala, R.K. Ball end magnetorheological finishing using bidisperse magnetorheological polishing fluid. Mater. Manuf. Process. 2014, 29, 487–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, J.; Ma, Z.; Nie, M. Investigation into Rheological Properties of Magnetorheological Polishing Slurry Using α-Cellulose as an Additive Agent and Its Polishing Performance. Int. J. Precis. Eng. Manuf. 2020, 21, 2041–2050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, D.; Du, H.; Tan, F.; Li, K.; Shao, Q.; Lin, J.; Zhou, X. Analysis of settlement stability of aqueous magnetorheological fluid for magnetorheological jet polishing. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2024, 697, 134444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milde, R.; Moucka, R.; Sedlacik, M.; Pata, V. Iron-sepiolite high-performance magnetorheological polishing fluid with reduced sedimentation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 12187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, Q.; Zhai, W.; Gao, B.; Shi, Y.; Cheng, X. Synthesis and characterization of nanocomposite Fe3O4/SiO2 core–shell abrasives for high-efficiency ultrasound-assisted magneto-rheological polishing of sapphire. Ceram. Int. 2021, 47, 31681–31690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Pan, G.; Gong, H.; Shi, X.; Zou, C. Characterization of sapphire chemical mechanical polishing performances using silica with different sizes and their removal mechanisms. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2017, 513, 153–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.; Xu, X.; Dai, L.; Gong, H.; Lin, S. Chemical-mechanical polishing performance of core-shell structured polystyrene@ceria/nanodiamond ternary abrasives on sapphire wafer. Ceram. Int. 2021, 47, 31691–31701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Ren, G.; Xie, W.; Zhang, J.; Pan, D.; Su, H.; Wang, S. Controllable synthesis of core-shell SiO2@ CeO2 abrasives for chemical mechanical polishing on SiO2 film. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2024, 682, 132901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Pan, J.; Yan, Q.; Huang, Z.; Luan, T. The processing properties of photocatalysis assisted magnetorheological polishing based on TiO2–CI composite particles. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. 2024, 172, 108043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, Q.; Zhai, W.; Gao, B.; Shi, Y.; Cheng, X. Effect of core-diameters and shell-thicknesses of Fe3O4/SiO2 composite abrasives on the performance of ultrasound-assisted magnetorheological polishing for sapphire. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2021, 625, 126871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.W.; Hong, K.P.; Cho, M.W.; Kwon, S.H.; Choi, H.J. Polishing characteristics of optical glass using PMMA-coated carbonyl-iron-based magnetorheological fluid. Smart Mater. Struct. 2015, 24, 065002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sedlacik, M.; Pavlínek, V. A tensiometric study of magnetorheological suspensions’ stability. Rsc Adv. 2014, 4, 58377–58385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Sehgal, R.; Wani, M.; Sharma, M.D. Magnetorheological study of core−shell structured carbonyl iron/2-D graphene oxide microparticles suspensions with improved sedimentation stability. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2023, 579, 170852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, Y.; Singh, H. Experimental investigations on chemo-mechanical magneto-rheological finishing of Al-6061 alloy using composite magnetic abrasive (CIP-Al2O3) developed via microwave-sintering route. J. Manuf. Process. 2023, 99, 765–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, J.; Chen, Z.; Yan, Q. Study on the rheological properties and polishing properties of SiO2@ CI composite particle for sapphire wafer. Smart Mater. Struct. 2020, 29, 114003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Xie, H.; Zhou, W.; Ren, Z. Enhanced antioxidation and microwave absorbing properties of SiO2-coated flaky carbonyl iron particles. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2018, 446, 143–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morel, A.L.; Nikitenko, S.I.; Gionnet, K.; Wattiaux, A.; Lai-Kee-Him, J.; Labrugere, C.; Chevalier, B.; Deleris, G.; Petibois, C.; Brisson, A.; et al. Sonochemical approach to the synthesis of Fe3O4@ SiO2 core−shell nanoparticles with tunable properties. ACS Nano 2008, 2, 847–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, M.; Li, W.; Dong, J.; Zhang, Z.; Yang, B. Synthesis and characterization of superparamagnetic Fe3O4@ SiO2 core-shell composite nanoparticles. World J. Condens. Matter Phys. 2011, 1, 49–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.S.; An, G.S. Surface engineering of Fe3O4@ SiO2 Core–Shell nanoparticles: Role of CTAB/TEOS ratio. Ceram. Int. 2025, 51, 379–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalid, A.; Ahmed, R.M.; Taha, M.; Soliman, T.S. Fe3O4 nanoparticles and Fe3O4@ SiO2 core-shell: Synthesize, structural, morphological, linear, and nonlinear optical properties. J. Alloys Compd. 2023, 947, 169639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, W.; Huang, C.-E.; Yang, J.; Zeng, J.; Qiu, T. Effect of sintering temperature on the properties of fused silica ceramics prepared by gelcasting. J. Electron. Mater. 2014, 43, 2566–2572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, J.; Nagourney, T.; Darvishian, A.; Shiari, B.; Woo, J.-K.; Najafi, K. Fused Silica Micro Birdbath Shell Resonators with 1.2 Million Q and 43 Second Decay Time Constant. In Proceedings of the Hilton Head Solid State Sensors, Actuators, and Microsystems Workshop, Hilton Head Island, SC, USA, 8–12 June 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Li, C.; Yang, M.; Chen, B.; Xu, Y.; Yan, X. Nanoscale understanding of the tribological removal behaviors for additive-fabricated Ti6Al4V alloy under the magnetorheological polishing. Wear 2025, 572–573, 206071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, Y. Modeling the effects of particle deformation in chemical mechanical polishing. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2012, 258, 8469–8474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Factors | Level |
|---|---|
| Abrasive type | 35 vol% CIP@SiO2 composite abrasive, 35 vol% CIP/SiO2 mixed abrasive (CIP 24 vol%, SiO2 11 vol%) |
| Polishing time (min) | 30, 60, 90, 120 |
| Polishing speed (r/min) | 600, 800, 1000 |
| Polishing gap (mm) | 0.3, 0.6, 0.9 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, C.; Chen, S.; Zheng, Z.; Zhu, Y.; Chen, B.; Xu, Y. Mechanism-Oriented Analysis of Core–Shell Structured CIP@SiO2 Magnetic Abrasives for Precision-Enhanced Magnetorheological Polishing. Micromachines 2025, 16, 495. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi16050495
Li C, Chen S, Zheng Z, Zhu Y, Chen B, Xu Y. Mechanism-Oriented Analysis of Core–Shell Structured CIP@SiO2 Magnetic Abrasives for Precision-Enhanced Magnetorheological Polishing. Micromachines. 2025; 16(5):495. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi16050495
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Chunyu, Shusheng Chen, Zhuoguang Zheng, Yicun Zhu, Bingsan Chen, and Yongchao Xu. 2025. "Mechanism-Oriented Analysis of Core–Shell Structured CIP@SiO2 Magnetic Abrasives for Precision-Enhanced Magnetorheological Polishing" Micromachines 16, no. 5: 495. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi16050495
APA StyleLi, C., Chen, S., Zheng, Z., Zhu, Y., Chen, B., & Xu, Y. (2025). Mechanism-Oriented Analysis of Core–Shell Structured CIP@SiO2 Magnetic Abrasives for Precision-Enhanced Magnetorheological Polishing. Micromachines, 16(5), 495. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi16050495






