Deformation Analysis of a Pneumatically-Activated Polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) Membrane and Potential Micro-Pump Applications
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Design and Experiment
2.1. Design Principle and Fabrication



2.2. Control and Measurement System
3. Theoretical and Numerical Methods
3.1. Theoretical Analysis

3.2. Numerical Modeling and Optimizations
4. Results and Discussion
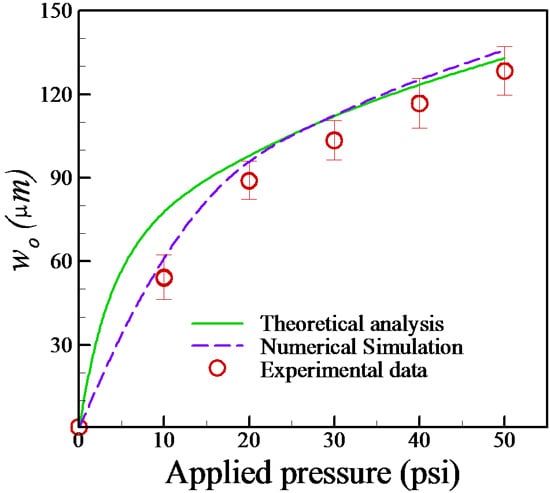
4.1. Estimation of Membrane Deformation



4.2. Evaluation of Pumping Rate

5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Laser, D.J.; Santiago, J.G. A review of micropumps. J. Micromech. Microeng. 2004, 14, R35–R64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, A.Y.; Chou, H.-P.; Spence, C.; Arnold, F.H.; Quake, S.R. An integrated microfabricated cell sorter. Anal. Chem. 2002, 74, 2451–2457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, A.Y.; Spence, C.; Scherer, A.; Arnold, F.H.; Quake, S.R. A microfabricated fluorescence-activated cell sorter. Nat. Biotechnol. 1999, 17, 1109–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maillefer, D.; Gamper, S.; Frehner, B.; Balmer, P. A high-performance silicon micropump for disposable drug delivery systems. In Proceedings of The 14th IEEE International Conference on Micro Electro Mechanical Systems, Interlaken, Switzerland, 25 January 2001; pp. 413–417.
- Hong, J.W.; Studer, V.; Hang, G.; Anderson, W.F.; Quake, S. A nanoliter-scale nucleic acid processor with parallel architecture. Nat. Biotechnol. 2004, 22, 435–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Enzelberger, M.; Quake, S.R. A nanoliter rotary device for polymerase chain reaction. Electrophoresis 2002, 23, 1531–1536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bourouina, T.; Bosseboeuf, A.; Grandchamp, J.P. Design and simulation of an electrostatic micropump for drug-delivery applications. J. Micromech. Microeng. 1997, 7, 186–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saif, M.T.A.; Alaca, B.E.; Sehitoglu, H. Analytical modeling of electrostatic membrane actuator for micro pumps. J. Microelectromech. Syst. 1999, 8, 335–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francais, O.; Dufour, I.; Sarraute, E. Analytical static modeling and optimization of electrostatic micropumps. J. Micromech. Microeng. 1997, 7, 183–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, Q.L.; Zhou, Z.Y.; Yang, Y.H.; Wang, X.H. Design, optimization and simulation on microelectromagnetic pump. Sens. Actuators A 2000, 83, 200–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capanu, M.; Boyd, J.G.; Hesketh, P.J. Design, fabrication, and testing of a bistable electromagnetically actuated microvalve. J. Microelectromech. Syst. 2000, 9, 181–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, O.C.; Konishi, S. Fabrication and drive test of pneumatic PDMS micro pump. Sens. Actuators A 2007, 135, 849–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Unger, M.A.; Chou, H.-P.; Thorsen, T.; Scherer, A.; Quake, S.R. Monolithic microfabricated valves and pumps by multilayer soft lithography. Science 2000, 288, 113–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thorsen, T.; Maerkl, S.J.; Quake, S.R. Microfluidic large-scale integration. Science 2002, 298, 580–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chou, H.P.; Unger, M.A.; Quake, S.R. A microfabricated rotary pump. Biomed. Microdevice 2001, 3, 323–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, O.C.; Yang, S.S. Fabrication and test of a thermopneumatic micropump with a corrugated p+ diaphragm. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2000, 83, 249–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van de Pol, F.C.M.; van Lintel, H.T.G.; Elwenspoek, M.; Fluitman, J.H.J. Therpneumatic micropump based on microengineering techniques. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 1990, 21, 198–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spencer, J.G. Piezoelectric micropump with three valves working peristaltically. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 1990, 21–23, 203–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, C.J.; Forster, F.K. Optimization of a circular piezoelectric bimorph for a micropump driver. J. Micromech. Microeng. 2000, 10, 459–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Husband, B.; Bu, M.; Evans, A.G.R.; Melvin, T. Investigation for the operation of an integrated peristaltic micropump. J. Micromech. Microeng. 2004, 14, S64–S69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Q.; Yang, B.; Xie, J.; Tai, Y.-C. Dynamic simulation of a peristaltic micropump considering coupled fluid flow and structural motion. J. Micromech. Microeng. 2007, 1, 220–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.H.; Lee, G.B. Automatic bio-sampling chips integrated with micropumps and microvalves for multiple disease detection. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2005, 21, 419–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tseng, H.Y.; Wang, C.H.; Lin, W.Y.; Lee, G.B. Membrane-activated microfluidic rotary devices for pumping and mixing. Biomed. Microdevices 2007, 9, 545–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.H.; Lee, G.B. Pneumatically-driven peristaltic micropumps utilizing serpentine-shape channels. J. Micromech. Microeng. 2006, 16, 341–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.L.; Wang, S.S.; Wu, M.H.; Oh-Yang, C.C. Development of an integrated microfluidic perfusion cell culture system for real-time microscopic observation of biological cells. Sensors 2011, 11, 395–411. [Google Scholar]
- Timoshenko, S.; Woinosky-Krieger, S. Theory of Plates and Shells, 2nd ed.; McGraw-hill: New York, NY, USA, 1959; pp. 415–420. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, B.; Song1, G.; Hussain, F. Simulation of a piezoelectrically actuated valveless micropump. Smart Mater. Struct. 2005, 14, 400–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuard, D.; Tzvetkova-Chevolleau, T.; Decossas, S.; Tracqui, P.; Schiavone, P. Optimization of poly-di-methyl-siloxane (PDMS) substrates for studying cellular adhesion and motility. Microelectron. Eng. 2008, 85, 1289–1293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sim, W.; Kim, B.; Choi, B.; Park, J.-O. Theoretical and experimental studies on the parylene diaphragms for microdevices. Microsyst. Technol. 2005, 11, 11–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chiou, C.-H.; Yeh, T.-Y.; Lin, J.-L. Deformation Analysis of a Pneumatically-Activated Polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) Membrane and Potential Micro-Pump Applications. Micromachines 2015, 6, 216-229. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi6020216
Chiou C-H, Yeh T-Y, Lin J-L. Deformation Analysis of a Pneumatically-Activated Polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) Membrane and Potential Micro-Pump Applications. Micromachines. 2015; 6(2):216-229. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi6020216
Chicago/Turabian StyleChiou, Chi-Han, Tai-Yen Yeh, and Jr-Lung Lin. 2015. "Deformation Analysis of a Pneumatically-Activated Polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) Membrane and Potential Micro-Pump Applications" Micromachines 6, no. 2: 216-229. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi6020216
APA StyleChiou, C.-H., Yeh, T.-Y., & Lin, J.-L. (2015). Deformation Analysis of a Pneumatically-Activated Polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) Membrane and Potential Micro-Pump Applications. Micromachines, 6(2), 216-229. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi6020216