Towards Independent Control of Multiple Magnetic Mobile Microrobots †
Abstract
:1. Introduction

2. System Architecture

3. Path Planning
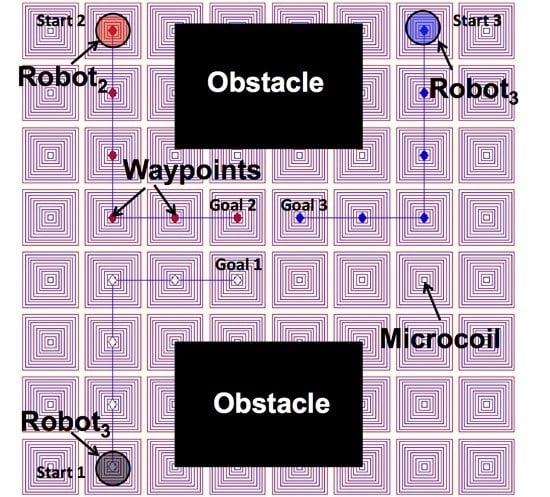
3.1. Problem Formulation
- Initial states of n robots to be transported in X, where X is the discretized operating space of the entire magnetic operating field;
- Goal states of n robots represented as grid locations within X;
- Static and dynamic obstacles represented either as other objects or other moving robots.
- Collision-free paths for n robots to move their goal states .
3.2. Approach
3.3. State-Action Space Presentation

3.4. Cost Function
4. Controller Design
4.1. Problem Formulation
- The dynamics of the i-th robot, where m is the mass of the robot, γ is the drag force coefficient of the surrounding medium, is the driving magnetic force, is the surface frictional force, and ;
- A reference state the robot needs to follow;
- A measurement of the robot state.
- A feedback control input to determine the required magnetic force such that the robot can follow the reference state .
4.2. Approach
5. Computation of Currents
5.1. Overview


5.2. Optimization Problem Formulation
5.3. Approach
6. Results and Discussion
6.1. Simulation Results
| Parameters | 64-Coil System |
|---|---|
| Static Friction Coefficient, | |
| Dynamic Friction Coefficient, | |
| Number of turns, | 10 |
| Permeability of air, (N/m) | |
| Current limit (A), – | |
| Susceptibility of robot, χ | 0.05 |
| Robot diameter (mm) | 2.0 |

| () | () | (A) | (A) | (A) | (A) | (A) | (A) | (A) | (A) | (A) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1.2 | 0 | −0.4 | −0.6 | 0.4 | −0.5 | −0.8 | 0.8 | −0.5 | −0.6 | 0.4 |
6.2. Experimental Results


7. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chowdhury, S.; Švec, P.; Wang, C.; Seale, K.T.; Wikswo, J.P.; Losert, W.; Gupta, S.K. Automated Cell Transport in Optical Tweezers-Assisted Microfluidic Chambers. IEEE Trans. Autom. Sci. Eng. 2013, 10, 980–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donald, B.R.; Levey, C.G.; McGray, C.D.; Paprotny, I.; Rus, D. An untethered, electrostatic, globally controllable MEMS micro-robot. J. Microelectromech. Syst. 2006, 15, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, W.; Chen, X.; Lyttle, S.; Fu, Z.; Shi, Y.; Cappelleri, D. Design of a magnatostrictive thin microrobot. In Proceedings of ASME International Design Engineering Technical Conferences & Computers and Information in Engineering Conference, Vancouver, Canada, 12–18 November 2010.
- Jing, W.; Chen, X.; Lyttle, S.; Fu, Z.; Shi, Y.; Cappelleri, D. A magnetic thin film microrobot with two operating modes. In Proceedings of the 2011 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Shanghai, China, 09–13 May 2011; pp. 96–101.
- Li, G.; Xi, N.; Chen, H.; Saeed, A.; Yu, M. Assembly of nanostructure using AFM based nanomanipulation system. In Proceedings of the 2004 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation ( ICRA’04), New Orleans, LA, USA, 26 April–1 May 2004; pp. 428–433.
- Bista, S.; Chowdhury, S.; Gupta, S.K.; Varshney, A. Using GPUs for realtime prediction of optical forces on microsphere ensembles. J. Comput. Inf. Sci. Eng. 2013, 13, 031002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowdhury, S.; Thakur, A.; Švec, P.; Wang, C.; Losert, W.; Gupta, S. Automated Manipulation of Biological Cells Using Gripper Formations Controlled By Optical Tweezers. IEEE Trans. Autom. Sci. Eng. 2014, 11, 338–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thakur, A.; Chowdhury, S.; Švec, P.; Wang, C.; Losert, W.; Gupta, S.K. Indirect pushing based automated micromanipulation of biological cells using optical tweezers. Int. J. Robot. Res. 2014, 33, 1098–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cappelleri, D.; Fu, Z.; Fatovic, M. Caging for 2D and 3D micromanipulation. J. Micro-Nano Mechatron. 2012, 7, 115–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cappelleri, D.J.; Fu, Z. Towards flexible, automated microassembly with caging micromanipulation. In Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Karlsruhe, Germany, 6–10 May 2013; pp. 1427–1432.
- Das, A.N.; Zhang, P.; Lee, W.H.; Popa, D.; Stephanou, H. μ3: Multiscale, deterministic micro-nano assembly system for construction of on-wafer microrobots. In Proceedings of the 2007 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, Roma, Italy, 10–14 April 2007; pp. 461–466.
- Diller, E.; Pawashe, C.; Floyd, S.; Sitti, M. Assembly and disassembly of magnetic mobile micro-robots towards deterministic 2-D reconfigurable micro-systems. Int. J. Robot. Res. 2011, 30, 1667–1680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diller, E.; Floyd, S.; Pawashe, C.; Sitti, M. Control of multiple heterogeneous magnetic microrobots in two dimensions on nonspecialized surfaces. IEEE Trans. Robot. 2012, 28, 172–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelrine, R.; Wong-Foy, A.; McCoy, B.; Holeman, D.; Mahoney, R.; Myers, G.; Herson, J.; Low, T. Diamagnetically levitated robots: An approach to massively parallel robotic systems with unusual motion properties. In Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), St. Paul, MN, USA, 14–18 May 2012; pp. 739–744.
- Peng, T.; Balijepalli, A.; Gupta, S.K.; LeBrun, T. Algorithms for on-line monitoring of micro spheres in an optical tweezers-based assembly cell. J. Comput. Inf. Sci. Eng. 2007, 7, 330–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, A.G.; Pomerance, A.; Losert, W.; Gupta, S.K. Developing a Stochastic Dynamic Programming Framework for Optical Tweezer-Based Automated Particle Transport Operations. IEEE Trans. Autom. Sci. Eng. 2010, 7, 218–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, A.G.; Chowdhury, S.; Losert, W.; Gupta, S.K. Real-Time Path Planning for Coordinated Transport of Multiple Particles using Optical Tweezers. IEEE Trans. Autom. Sci. Eng. 2012, 9, 669–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, A.; Chowdhury, S.; Gupta, S. Optical Tweezers: Autonomous Robots for the Manipulation of Biological Cells. IEEE Robot. Autom. Mag. 2014, 21, 81–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowdhury, S.; Svec, P.; Wang, C.; Seale, K.; Wikswo, J.P.; Losert, W.; Gupta, S.K. Automated cell transport in optical tweezers assisted microfluidic chamber. IEEE Trans. Autom. Sci. Eng. 2013, 10, 980–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, S.; Sun, D. Automated transportation of biological cells with a robot-tweezer manipulation system. Int. J. Robot. Res. 2011, 30, 1681–1694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ju, T.; Liu, S.; Yang, J.; Sun, D. Apply RRT-based Path Planning to Robotic Manipulation of Biological Cells with Optical Tweezer. In Proceedings of the International Conference Mechatronics Automation, Shanghai, China, 6–7 January 2011; pp. 221–226.
- Wu, Y.; Sun, D.; Huang, W.; Xi, N. Dynamics Analysis and Motion Planning for Automated Cell Transportation With Optical Tweezers. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatron. 2013, 18, 706–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, W.; Ishii, K.S.; Ohta, A.T. Micro-assembly using optically controlled bubble microrobots. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2011, 99, 094103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, W.; Pagano, N.; Cappelleri, D.J. A micro-scale magnetic tumbling microrobot. In Proceedings of the ASME 2012 International Design Engineering Technical Conferences and Computers and Information in Engineering Conference, Chicago, IL, USA, 12–15 August 2012; pp. 187–196.
- Jing, W.; Pagano, N.; Cappelleri, D.J. A tumbling magnetic microrobot with flexible operating modes. In Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Karlsruhe, Germany, 6–10 May 2013; pp. 5514–5519.
- Jing, W.; Pagano, N.; Cappelleri, D.J. A novel micro-scale magnetic tumbling microrobot. J. Micro-Bio Robot. 2013, 8, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steager, E.B.; Sakar, M.S.; Magee, C.; Kennedy, M.; Cowley, A.; Kumar, V. Automated biomanipulation of single cells using magnetic microrobots. Int. J. Robot. Res. 2013, 32, 346–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, W.; Cappelleri, D.J. Towards Functional Mobile Magnetic Microrobots. In Small-Scale Robotics. From Nano-to-Millimeter-Sized Robotic Systems and Applications; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2014; pp. 81–100. [Google Scholar]
- Jing, W.; Cappelleri, D. Incorporating in-situ force sensing capabilities in a magnetic microrobot. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS 2014), Chicago, IL, USA, 14-18 September 2014; pp. 4704–4709.
- Chowdhury, S.; Jing, W.; Cappelleri, D. Controlling multiple microrobots: recent progress and future challenges. J. Micro-Bio Robot. 2015, 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- LaValle, S.M. Planning algorithms; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Hart, P.; Nilsson, N.; Raphael, B. A Formal Basis for the Heuristic Determination of Minimum Cost Paths. IEEE Trans. Syst. Sci. Cybern. 1968, 4, 100–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kavraki, L.E.; Švestka, P.; Latombe, J.C.; Overmars, M.H. Probabilistic roadmaps for path planning in high-dimensional configuration spaces. IEEE Trans. Robot. Autom. 1996, 12, 566–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amato, N.M.; Wu, Y. A randomized roadmap method for path and manipulation planning. In Proceedings of the 1996 IEEE International Conference on IEEE Robotics and Automation, Minneapolis, MN, USA, 22–28 April 1996; Volume 1, pp. 113–120.
- LaValle, S.M.; Kuffner, J.J., Jr. Rapidly-exploring random trees: Progress and prospects. Available online: http://citeseerx.ist.psu.edu/viewdoc/versions?doi=10.1.1.38.1387 (accessed on 23 December 2015).
- Koenig, S.; Likhachev, M. D* Lite. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference of Artificial Intelligence, Alberta, Canada, 28 July–1 August 2002; pp. 476–483.
- Cappelleri, D.; Efthymiou, D.; Goswami, A.; Vitoroulis, N.; Zavlanos, M. Towards Mobile Microrobot Swarms for Additive Micromanufacturing. Int. J. Adv. Robot. Syst. 2014, 11, 150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beyzavi, A.; Nguyen, N.T. Modeling and optimization of planar microcoils. J. Micromechan. Microeng. 2008, 18, 095018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, W.; Cappelleri, D. A magnetic microrobot with in situ force sensing capabilities. Robotics 2014, 3, 106–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vitoroulis, N.E., Jr.; Cappelleri, D.J. Microcoil Design And Analysis for Actuation of Microstructures and Devices. Available online: http://multiscalerobotics.org/wp-content/uploads/2014/09/NikoCappelleriIDETCbreif2013.pdf (accessed on 23 December 2015).
- Pawashe, C.; Floyd, S.; Sitti, M. Modeling and experimental characterization of an untethered magnetic micro-robot. Int. J. Robot. Res. 2009, 28, 1077–1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons by Attribution (CC-BY) license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chowdhury, S.; Jing, W.; Cappelleri, D.J. Towards Independent Control of Multiple Magnetic Mobile Microrobots. Micromachines 2016, 7, 3. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi7010003
Chowdhury S, Jing W, Cappelleri DJ. Towards Independent Control of Multiple Magnetic Mobile Microrobots. Micromachines. 2016; 7(1):3. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi7010003
Chicago/Turabian StyleChowdhury, Sagar, Wuming Jing, and David J. Cappelleri. 2016. "Towards Independent Control of Multiple Magnetic Mobile Microrobots" Micromachines 7, no. 1: 3. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi7010003
APA StyleChowdhury, S., Jing, W., & Cappelleri, D. J. (2016). Towards Independent Control of Multiple Magnetic Mobile Microrobots. Micromachines, 7(1), 3. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi7010003