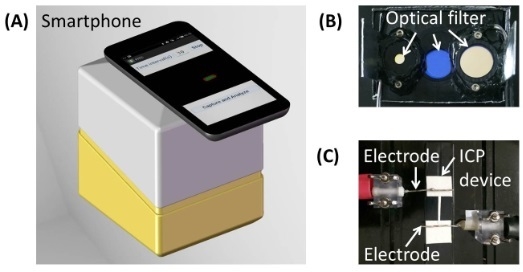
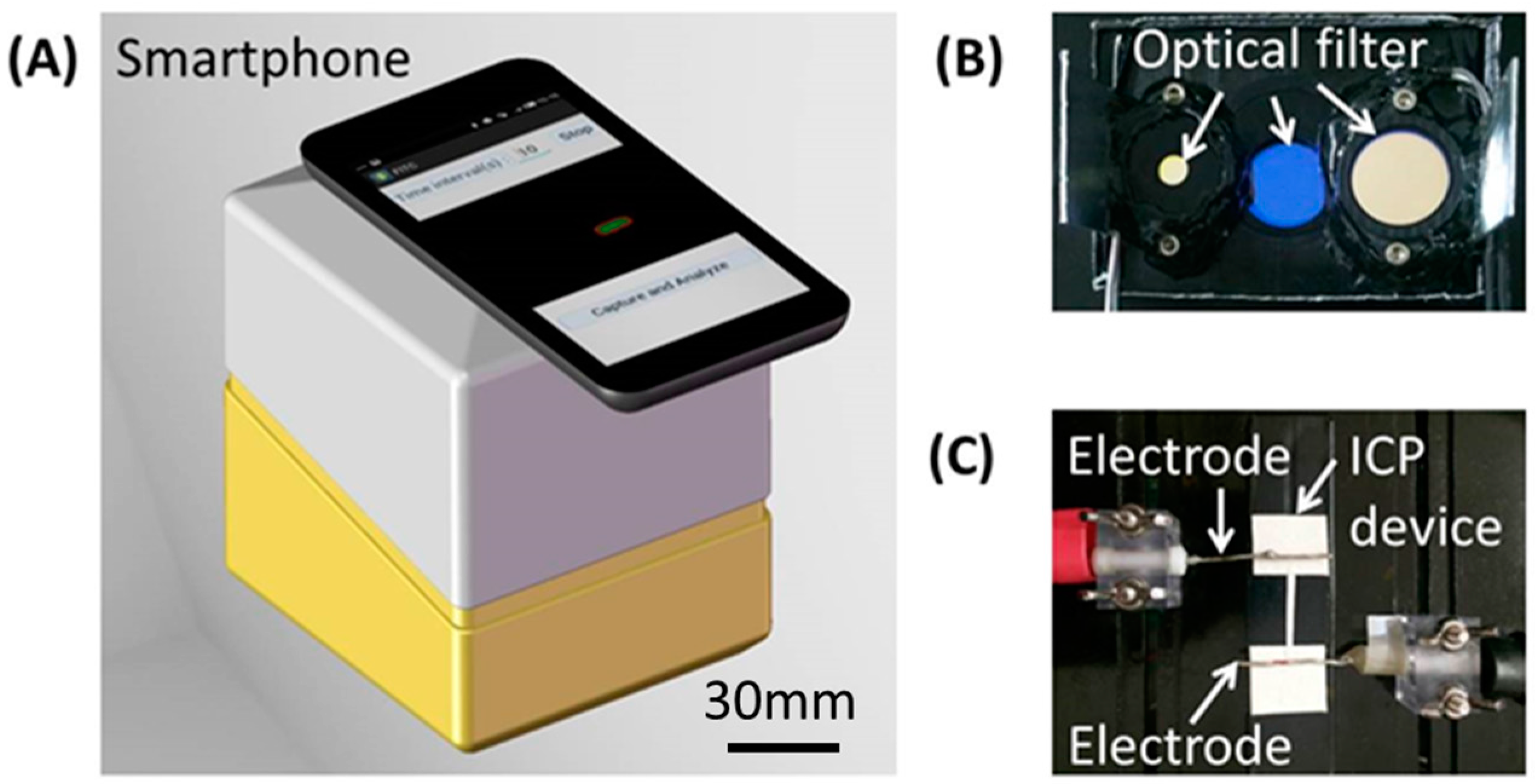
Microfluidic Paper-Based Sample Concentration Using Ion Concentration Polarization with Smartphone Detection
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Design and Fabrication of Paper-Based ICP Device
2.2. Experimental Setup with Smartphone Detection
2.3. Image Processing for Quantitative Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. ICP Devices with Different Fabrication Methods
3.2. ICP Device with Adjusted Dimensions
3.3. ICP Device with Two Jointed Nitrocellulose Membrane Parts
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Höltzel, A.; Tallarek, U. Ionic conductance of nanopores in microscale analysis systems: Where microfluidics meets nanofluidics. J. Sep. Sci. 2007, 30, 1398–1419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.J.; Ko, S.H.; Kang, K.H.; Han, J. Direct seawater desalination by ion concentration polarization. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2010, 5, 297–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Macdonald, B.D.; Gong, M.M.; Zhang, P.; Sinton, D. Out-of-plane ion concentration polarization for scalable water desalination. Lab Chip 2013, 14, 681–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scarff, B.; Escobedo, C.; Sinton, D. Radial sample preconcentration. Lab Chip 2011, 11, 1102–1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeon, H.; Lim, G. Development of continuous cell lysis and separation device using repulsive force generated by ion concentration polarization. In Proceedings of the 18th International Conference on Miniaturized Systems for Chemistry and Life Sciences, San Antonio, TX, USA, 26–30 October 2014; pp. 2459–2461.
- Corstjens, P.L.A.M.; Chen, Z.; Michel, Z.; Bau, H.H.; Abrams, W.R.; Malamud, D.; Sam, N.R.; Tanke, H.J. Rapid Assay Format for Multiplex Detection of Humoral Immune Responses to Infectious Disease Pathogens (HIV, HCV, and TB). Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2007, 1098, 437–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, Y.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Ge, S.; Tang, Z.; Qiu, X. Point-of-care test for C-reactive protein by a fluorescence-based lateral flow immunoassay. Instrum. Sci. Technol. 2014, 42, 635–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, X.; Liu, C.; Mauk, M.G.; Hart, R.W.; Chen, D.; Qiu, J.; Kientz, T.; Fiene, J.; Bau, H.H. A portable analyzer for pouch-actuated, immunoassay cassettes. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2011, 160, 1529–1535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, X.; Thompson, J.A.; Chen, Z.; Liu, C.; Chen, D.; Ramprasad, S.; Mauk, M.G.; Ongagna, S.; Barber, C.; Abrams, W.R.; et al. Finger-actuated, self-contained immunoassay cassettes. Biomed. Microdevices 2009, 11, 1175–1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.; Qiu, X.; Ongagna, S.; Chen, D.; Chen, Z.; Abrams, W.R.; Malamud, D.; Corstjens, P.L.A.M.; Bau, H.H. A timer-actuated immunoassay cassette for detecting molecular markers in oral fluids. Lab Chip 2009, 9, 768–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- López-Marzo, A.M.; Merkoçi, A. Paper-based sensors and assays: A success of the engineering design and the convergence of knowledge areas. Lab Chip 2016, 16, 3150–3176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lankelma, J.; Nie, Z.; Carrilho, E.; Whitesides, G.M. Paper-Based Analytical Device for Electrochemical Flow-Injection Analysis of Glucose in Urine. Anal. Chem. 2012, 84, 4147–4152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gerbers, R.; Foellscher, W.; Chen, H.; Anagnostopoulos, C.; Faghri, M. A new paper-based platform technology for point-of-care diagnostics. Lab Chip 2014, 14, 4042–4049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, J.; Wang, S.; Wang, L.; Li, F.; Pingguan-Murphy, B.; Lu, T.; Xu, F. Advances in paper-based point-of-care diagnostics. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2014, 54, 585–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.; Anand, R.K. Recent advancements in ion concentration polarization. Analyst 2016, 141, 3496–3510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, M.M.; Nosrati, R.; Gabriel, M.C.S.; Zini, A.; Sinton, D. Direct DNA Analysis with Paper-Based Ion Concentration Polarization. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2015, 137, 13913–13919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pu, Q.; Yun, J.; Temkin, H.; Liu, S. Ion-Enrichment and Ion-Depletion Effect of Nanochannel Structures. Nano Lett. 2004, 4, 1099–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hung, L.; Wang, H.; Yang, R. A portable sample concentrator on paper‑based microflidic devices. Microfluid Nanofluid 2016, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, R.; Pu, H.; Wang, H. Ion concentration polarization on paper-based microfluidic devices and its application to preconcentrate dilute sample solutions. Biomicrofluidics 2015, 9, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phan, D.T.; Shaegh, S.A.M.; Yang, C.; Nguyen, N. Sample concentration in a microfluidic paper-based analytical device using ion concentration polarization. Sens. Actuators B 2016, 222, 735–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeh, S.; Chou, K.; Yang, R. Sample pre-concentration with high enrichment factors at a fixed location in paper-based microfluidic devices. Lab Chip 2016, 16, 925–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, K.; Peretz-Soroka, H.; Liu, Y.; Lin, F. Novel developments in mobile sensing based on the integration of microfluidic devices and smartphones. Lab Chip 2016, 16, 943–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, D.; Liu, Q. Biosensors and bioelectronics on smartphone for portable biochemical detection. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2016, 75, 273–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.; Cheng, G.; Edwards, P.; Zhou, M.; Zheng, S.; Liu, Z. G-Fresnel smartphone spectrometer. Lab Chip 2016, 16, 246–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, H.; Yaglidere, O.; Su, T.; Tseng, D.; Ozcan, A. Cost-effective and compact wide-field fluorescent imaging on a cell-phone. Lab Chip 2011, 11, 315–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mancuso, M.; Cesarman, E.; Erickson, D. Detection of Kaposi’s sarcoma associated herpesvirus nucleic acids using a smartphone accessory. Lab Chip 2014, 14, 3809–3816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Y.; Shi, W.; Qin, J.; Lin, B. Low cost, portable detection of gold nanoparticle-labeled microfluidic immunoassay with camera cell phone. Electrophoresis 2009, 30, 579–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, M.M.; Zhang, P.; Macdonald, B.D.; Sinton, D. Nanoporous Membranes Enable Concentration and Transport in Fully Wet Paper-Based Assays. Anal. Chem. 2014, 86, 8090–8097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mauritz, K.A.; Moore, R.B. State of Understanding of Nafion. Chem. Rev. 2004, 104, 4535–4585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thormann, W.; Zhang, C.; Caslavska, J.; Gebauer, P.; Mosher, R.A. Modeling of the impact of ionic strength on the electroosmotic flow in capillary electrophoresis with uniform and discontinuous buffer systems. Anal. Chem. 1998, 70, 549–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Canny, J. A Computational Approach to Edge Detection. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 1986, 8, 679–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]







© 2016 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, X.; Niu, Y.; Chen, Y.; Wu, D.; Yi, L.; Qiu, X. Microfluidic Paper-Based Sample Concentration Using Ion Concentration Polarization with Smartphone Detection. Micromachines 2016, 7, 199. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi7110199
Li X, Niu Y, Chen Y, Wu D, Yi L, Qiu X. Microfluidic Paper-Based Sample Concentration Using Ion Concentration Polarization with Smartphone Detection. Micromachines. 2016; 7(11):199. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi7110199
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Xue, Yanan Niu, Yunyi Chen, Di Wu, Long Yi, and Xianbo Qiu. 2016. "Microfluidic Paper-Based Sample Concentration Using Ion Concentration Polarization with Smartphone Detection" Micromachines 7, no. 11: 199. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi7110199
APA StyleLi, X., Niu, Y., Chen, Y., Wu, D., Yi, L., & Qiu, X. (2016). Microfluidic Paper-Based Sample Concentration Using Ion Concentration Polarization with Smartphone Detection. Micromachines, 7(11), 199. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi7110199