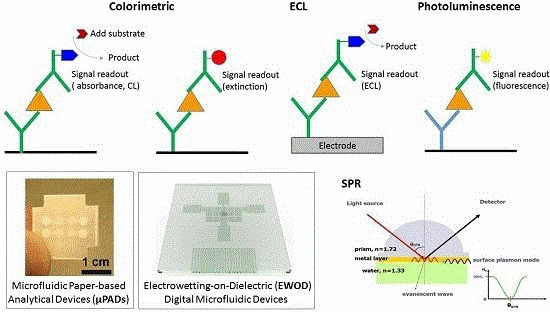
Opto-Microfluidic Immunosensors: From Colorimetric to Plasmonic
Abstract
:1. Introduction
| Detection Methods | Signal Generation | Label | Time Required | Microfluidic Device Types | LOD a Level | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Colormetric detection | Visible light illumination | Enzymatic catalyzed probes for ELISA | Minutes to hours | Microchannel | pg/mL | [28] |
| Microchannel | pg/mL | [29] | ||||
| Strip-based | ng/mL | [30] | ||||
| Disc-based | ng/mL | [31] | ||||
| Chemiluminescence | Chemical reaction | Enzymatic catalyzed probes for CL | Minutes | Opto-microfluidic | pg/mL | [32] |
| Microchannel | pg/mL | [33] | ||||
| μPAD b | ng/mL | [34] | ||||
| Disc-based | ng/mL | [35] | ||||
| EWOD c | μg/mL | [36] | ||||
| Electrochemiluminescence | Electrochemical reaction | ECL probes | Minutes | μPAD | ng/mL | [37] |
| Microchannel | ng/mL | [38] | ||||
| Photoluminescence | Optical excitation | Photoluminescent dyes | Real time | Microchannel | pg/mL | [39] |
| Microchannel | pg/mL | [40] | ||||
| Microchannel | pg/mm2 | [41] | ||||
| Microchannel | ng/mL | [42] | ||||
| EWOD | μg/mL | [43] | ||||
| Surface plasmon resonance | Optical excitation with evanescent waves | Label-free | Real time | Microchannel | ng/mL | [44] |
| EWOD | ng/mL | [45,46] |
2. Immunosensing with Optical Probes

2.1. Colorimetric Detection
2.2. Chemiluminescence (CL)
2.3. Electrochemiluminescence (ECL)
2.4. Photoluminescence
3. Label-Free Immunosensing
3.1. Change of Refractive Index
3.2. Surface-Plasmon-Resonance (SPR) Immunosensor

4. Microfluidics
4.1. Paper-Based Microfluidics (μPADs)


4.2. Electrowetting-on-Dielectric (EWOD) Digital Microfluidic Devices

5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rongen, H.A.; Hoetelmans, R.M.; Bult, A.; van Bennekom, W.P. Chemiluminescence and immunoassays. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 1994, 12, 433–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, P. Dendrimers and their applications in immunoassays and clinical diagnostics. Biotechnol. Appl. Biochem. 2007, 48, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dhawan, S. Signal amplification systems in immunoassays: Implications for clinical diagnostics. Expert Rev. Mol. Diagn. 2006, 6, 749–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wheeler, M.J. Immunoassay techniques. Methods Mol. Biol. 2006, 324, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Afeyan, N.B.; Gordon, N.F.; Regnier, F.E. Automated real-time immunoassay of biomolecules. Nature 1992, 358, 603–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.T.; Juang, R.H.; He, J.L.; Chu, W.Y.; Wang, C.H. Detection of H6 influenza antibody by blocking enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. Vet. Microbiol. 2010, 142, 205–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, J.L.; Hsieh, M.S.; Chiu, Y.C.; Juang, R.H.; Wang, C.H. Preparation of monoclonal antibodies against poor immunogenic avian influenza virus proteins. J. Immunol. Methods 2013, 387, 43–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, J.L.; Hsieh, M.S.; Juang, R.H.; Wang, C.H. A monoclonal antibody recognizes a highly conserved neutralizing epitope on hemagglutinin of H6N1 avian influenza virus. Vet. Microbiol. 2014, 174, 333–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagatani, N.; Yamanaka, K.; Ushijima, H.; Koketsu, R.; Sasaki, T.; Ikuta, K.; Saito, M.; Miyahara, T.; Tamiya, E. Detection of influenza virus using a lateral flow immunoassay for amplified DNA by a microfluidic RT-PCR chip. Analyst 2012, 137, 3422–3426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- MacCallum, R.M.; Martin, A.C.; Thornton, J.M. Antibody-antigen interactions: Contact analysis and binding site topography. J. Mol. Biol. 1996, 262, 732–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Porstmann, T.; Kiessig, S.T. Enzyme immunoassay techniques an overview. J. Immunol. Methods 1992, 150, 5–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bange, A.; Halsall, H.B.; Heineman, W.R. Microfluidic immunosensor systems. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2005, 20, 2488–2503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, S.; Goryll, M.; Sin, L.Y.M.; Wong, P.K.; Chae, J. Microfluidic-based biosensors toward point-of-care detection of nucleic acids and proteins. Microfluid. Nanofluid. 2011, 10, 231–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henares, T.G.; Mizutani, F.; Hisamoto, H. Current development in microfluidic immunosensing chip. Anal. Chim. Acta 2008, 611, 17–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, C.-C.; Wang, J.-H.; Wu, H.-W.; Lee, G.-B. Microfluidic immunoassays. J. Lab. Autom. 2010, 15, 253–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hey, T.; Fiedler, E.; Rudolph, R.; Fiedler, M. Artificial, non-antibody binding proteins for pharmaceutical and industrial applications. Trends Biotechnol. 2005, 23, 514–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jayasena, S.D. Aptamers: An emerging class of molecules that rival antibodies in diagnostics. Clin. Chem. 1999, 45, 1628–1650. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Makaraviciute, A.; Ramanaviciene, A. Site-directed antibody immobilization techniques for immunosensors. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2013, 50, 460–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peluso, P.; Wilson, D.S.; Do, D.; Tran, H.; Venkatasubbaiah, M.; Quincy, D.; Heidecker, B.; Poindexter, K.; Tolani, N.; Phelan, M.; et al. Optimizing antibody immobilization strategies for the construction of protein microarrays. Anal. Biochem. 2003, 312, 113–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vashist, S.K.; Dixit, C.K.; MacCraith, B.D.; O’Kennedy, R. Effect of antibody immobilization strategies on the analytical performance of a surface plasmon resonance-based immunoassay. Analyst 2011, 136, 4431–4436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corry, B.; Uilk, J.; Crawley, C. Probing direct binding affinity in electrochemical antibody-based sensors. Anal. Chim. Acta 2003, 496, 103–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J. Electrochemical biosensors: Towards point-of-care cancer diagnostics. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2006, 21, 1887–1892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zang, D.; Ge, L.; Yan, M.; Song, X.; Yu, J. Electrochemical immunoassay on a 3D microfluidic paper-based device. Chem. Commun. 2012, 48, 4683–4685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fodey, T.L.; Thompson, C.S.; Traynor, I.M.; Haughey, S.A.; Kennedy, D.G.; Crooks, S.R. Development of an optical biosensor based immunoassay to screen infant formula milk samples for adulteration with melamine. Anal. Chem. 2011, 83, 5012–5016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mauriz, E.; Calle, A.; Montoya, A.; Lechuga, L.M. Determination of environmental organic pollutants with a portable optical immunosensor. Talanta 2006, 69, 359–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, S. Electromechanical biosensors for pathogen detection. Microchim. Acta 2012, 178, 245–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mecklenburg, M.; Lindbladh, C.; Li, H.; Mosbach, K.; Danielsson, B. Enzymatic amplification of a flow-injected thermometric enzyme-linked immunoassay for human insulin. Anal. Biochem. 1993, 212, 388–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Novo, P.; Prazeres, D.M.; Chu, V.; Conde, J.P. Microspot-based ELISA in microfluidics: Chemiluminescence and colorimetry detection using integrated thin-film hydrogenated amorphous silicon photodiodes. Lab Chip 2011, 11, 4063–4071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, L.; Li, C.M.; Liu, Y.; Gao, J.; Wang, W.; Gan, Y. Flow-through functionalized PDMS microfluidic channels with dextran derivative for ELISAs. Lab Chip 2009, 9, 1243–1247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, H.; Mao, X.; Zeng, Q.; Wang, S.; Kawde, A.N.; Liu, G. Aptamer-functionalized gold nanoparticles as probes in a dry-reagent strip biosensor for protein analysis. Anal. Chem. 2009, 81, 669–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, B.S.; Lee, J.N.; Park, J.M.; Lee, J.G.; Kim, S.; Cho, Y.K.; Ko, C. A fully automated immunoassay from whole blood on a disc. Lab Chip 2009, 9, 1548–1555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pires, N.M.M.; Dong, T. Ultrasensitive opto-microfluidic immunosensor integrating gold nanoparticle-enhanced chemiluminescence and highly stable organic photodetector. J. Biomed. Opt. 2014, 19, 030504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, P.; Liu, Z.; Tung, S.; Dong, Z.; Liu, L. Fully automated quantification of insulin concentration using a microfluidic-based chemiluminescence immunoassay. J. Lab. Autom. 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ge, L.; Wang, S.; Song, X.; Ge, S.; Yu, J. 3D origami-based multifunction-integrated immunodevice: Low-cost and multiplexed sandwich chemiluminescence immunoassay on microfluidic paper-based analytical device. Lab Chip 2012, 12, 3150–3158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, S.; Ishimatsu, R.; Nakano, K.; Imato, T. Automated chemiluminescence immunoassay for a nonionic surfactant using a recycled spinning-pausing controlled washing procedure on a compact disc-type microfluidic platform. Talanta 2015, 133, 100–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rackus, D.G.; Dryden, M.D.; Lamanna, J.; Zaragoza, A.; Lam, B.; Kelley, S.O.; Wheeler, A.R. A digital microfluidic device with integrated nanostructured microelectrodes for electrochemical immunoassays. Lab Chip 2015, 15, 3776–3784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Ge, L.; Zhang, Y.; Song, X.; Li, N.; Ge, S.; Yu, J. Battery-triggered microfluidic paper-based multiplex electrochemiluminescence immunodevice based on potential-resolution strategy. Lab Chip 2012, 12, 4489–4498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, M.S.; Shi, H.W.; He, L.J.; Xu, J.J.; Chen, H.Y. Microchip device with 64-site electrode array for multiplexed immunoassay of cell surface antigens based on electrochemiluminescence resonance energy transfer. Anal. Chem. 2012, 84, 4207–4213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sang, C.H.; Chou, S.J.; Pan, F.M.; Sheu, J.T. Fluorescence enhancement and multiple protein detection in ZnO nanostructure microfluidic devices. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2016, 75, 285–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, Y.F.; Tang, T.T.; Xu, H.S.; Zhu, C.Q.; Cunningham, B.T. High sensitivity automated multiplexed immunoassays using photonic crystal enhanced fluorescence microfluidic system. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2015, 73, 32–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Yin, H.C.; Que, L. A nanostructured aluminum oxide-based microfluidic device for enhancing immunoassay’s fluorescence and detection sensitivity. Biomed. Microdevices 2014, 16, 771–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rowe, C.A.; Scruggs, S.B.; Feldstein, M.J.; Golden, J.P.; Ligler, F.S. An array immunosensor for simultaneous detection of clinical analytes. Anal. Chem. 1999, 71, 433–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sista, R.S.; Hua, Z.; Thwar, P.; Sudarsan, A.; Srinivasan, V.; Eckhardt, A.E.; Pollack, M.G.; Pamula, V.K. Development of a digital microfluidic platform for point of care testing. Lab Chip 2008, 8, 2091–2104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ouellet, E.; Lausted, C.; Lin, T.; Yang, C.W.T.; Hood, L.; Lagally, E.T. Parallel microfluidic surface plasmon resonance imaging arrays. Lab Chip 2010, 10, 581–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malic, L.; Veres, T.; Tabrizian, M. Biochip functionalization using electrowetting-on-dielectric digital microfluidics for surface plasmon resonance imaging detection of DNA hybridization. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2009, 24, 2218–2224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malic, L.; Veres, T.; Tabrizian, M. Two-dimensional droplet-based surface plasmon resonance imaging using electrowetting-on-dielectric microfluidics. Lab Chip 2009, 9, 473–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuswandi, B.; Nuriman; Huskens, J.; Verboom, W. Optical sensing systems for microfluidic devices: A review. Anal. Chim. Acta 2007, 601, 141–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Engvall, E.; Jonsson, K.; Perlmann, P. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. II. Quantitative assay of protein antigen, immunoglobulin G, by means of enzyme-labelled antigen and antibody-coated tubes. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Protein Struct. 1971, 251, 427–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lequin, R.M. Enzyme immunoassay (EIA)/enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). Clin. Chem. 2005, 51, 2415–2418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schroeder, H.; Adler, M.; Gerigk, K.; Muller-Chorus, B.; Gotz, F.; Niemeyer, C.M. User configurable microfluidic device for multiplexed immunoassays based on DNA-directed assembly. Anal. Chem. 2009, 81, 1275–1279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madou, M.; Zoval, J.; Jia, G.; Kido, H.; Kim, J.; Kim, N. Lab on a CD. Annu. Rev. Biomed. Eng. 2006, 8, 601–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dodeigne, C.; Thunus, L.; Lejeune, R. Chemiluminescence as diagnostic tool. A review. Talanta 2000, 51, 415–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.X.; Sun, L.; Chu, X.G. Chemiluminescence immunoassay. Trends Anal. Chem. 2009, 28, 404–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, A.; Cao, Z.; Li, H.; Kai, M.; Lu, J. Chemiluminescence platforms in immunoassay and DNA analyses. Anal. Sci. 2009, 25, 587–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yakovleva, J.; Davidsson, R.; Lobanova, A.; Bengtsson, M.; Eremin, S.; Laurell, T.; Emneus, J. Microfluidic enzyme immunoassay using silicon microchip with immobilized antibodies and chemiluminescence detection. Anal. Chem. 2002, 74, 2994–3004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baeyens, W.R.; Schulman, S.G.; Calokerinos, A.C.; Zhao, Y.; Garcia Campana, A.M.; Nakashima, K.; de Keukeleire, D. Chemiluminescence-based detection: Principles and analytical applications in flowing streams and in immunoassays. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 1998, 17, 941–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radi, R.; Cosgrove, T.P.; Beckman, J.S.; Freeman, B.A. Peroxynitrite-induced luminol chemiluminescence. Biochem. J. 1993, 290, 51–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Z.; Liu, H.; Zong, C.; Yan, F.; Ju, H. Automated support-resolution strategy for a one-way chemiluminescent multiplex immunoassay. Anal. Chem. 2009, 81, 5484–5489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yacoub-George, E.; Hell, W.; Meixner, L.; Wenninger, F.; Bock, K.; Lindner, P.; Wolf, H.; Kloth, T.; Feller, K.A. Automated 10-channel capillary chip immunodetector for biological agents detection. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2007, 22, 1368–1375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, P.P.; Ge, L.; Yan, M.; Song, X.R.; Ge, S.G.; Yu, J.H. Paper-based three-dimensional electrochemical immunodevice based on multi-walled carbon nanotubes functionalized paper for sensitive point-of-care testing. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2012, 32, 238–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weeks, I.; Sturgess, M.L.; Woodhead, J.S. Chemiluminescence immunoassay: An overview. Clin. Sci. 1986, 70, 403–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, X.; Zhang, K.; Pan, J.; Chen, G.; Liu, A.Q.; Fan, S.K.; Zhou, J. Chemiluminescence detector based on a single planar transparent digital microfluidic device. Lab Chip 2013, 13, 2714–2720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chemical Connection. Available online: http://www.chemicalconnection.org.uk/chemistry/topics/images/ee7b.jpg (accessed on 5 Febuary 2016).
- Hu, L.; Xu, G. Applications and trends in electrochemiluminescence. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2010, 39, 3275–3304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richter, M.M. Electrochemiluminescence (ECL). Chem. Rev. 2004, 104, 3003–3036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forster, R.J.; Bertoncello, P.; Keyes, T.E. Electrogenerated chemiluminescence. Annu. Rev. Anal. Chem. 2009, 2, 359–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Lorimier, R.M.; Smith, J.J.; Dwyer, M.A.; Looger, L.L.; Sali, K.M.; Paavola, C.D.; Rizk, S.S.; Sadigov, S.; Conrad, D.W.; Loew, L.; et al. Construction of a fluorescent biosensor family. Protein Sci. 2002, 11, 2655–2675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Melnyk, O.; Duburcq, X.; Olivier, C.; Urbès, F.; Auriault, C.; Gras-Masse, H. Peptide arrays for highly sensitive and specific antibody-binding fluorescence assays. Bioconjug. Chem. 2002, 13, 713–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, I.H.; Mauer, L.; Irudayaraj, J. In-situ fluorescent immunomagnetic multiplex detection of foodborne pathogens in very low numbers. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2014, 57, 143–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Beéck, K.O.; Vermeersch, P.; Verschueren, P.; Westhovens, R.; Mariën, G.; Blockmans, D.; Bossuyt, X. Antinuclear antibody detection by automated multiplex immunoassay in untreated patients at the time of diagnosis. Autoimmun. Rev. 2012, 12, 137–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Juncker, D.; Bergeron, S.; Laforte, V.; Li, H. Cross-reactivity in antibody microarrays and multiplexed sandwich assays: Shedding light on the dark side of multiplexing. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 2014, 18, 29–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, J.Y.; Liu, T.C.; Lin, G.F.; Li, Z.X.; Zou, L.P.; Li, M.; Wu, Y.S. Development of an immunomagnetic bead-based time-resolved fluorescence immunoassay for rapid determination of levels of carcinoembryonic antigen in human serum. Anal. Chim. Acta 2012, 734, 93–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Zhou, S.; Tu, D.; Chen, Z.; Huang, M.; Zhu, H.; Ma, E.; Chen, X. Amine-functionalized lanthanide-doped zirconia nanoparticles: Optical spectroscopy, time-resolved fluorescence resonance energy transfer biodetection, and targeted imaging. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 15083–15090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Nchimi Nono, K.; Syrjänpää, M.; Charbonnière, L.J.; Hovinen, J.; Härmä, H. Stable and highly fluorescent europium (III) chelates for time-resolved immunoassays. Inorg. Chem. 2013, 52, 8461–8466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, B.; Qiu, J.; Gerstenmeier, J.; Li, P.; Pien, H.; Pepper, J.; Cunningham, B. A label-free optical technique for detecting small molecule interactions. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2002, 17, 827–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, X.; White, I.M.; Shopova, S.I.; Zhu, H.; Suter, J.D.; Sun, Y. Sensitive optical biosensors for unlabeled targets: A review. Anal. Chim. Acta 2008, 620, 8–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bennett, C.A. Principles of Physical Optics; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, G.; Meng, Y.H.; Liu, L.; Niu, Y.; Chen, S.; Cai, Q.; Jiang, T.J. Development of biosensor based on imaging ellipsometry and biomedical applications. Thin Solid Films 2011, 519, 2750–2757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez, S.D.; Li, C.P.; Chiang, C.E.; Schuller, I.K.; Sailor, M.J. A label-free porous alumina interferometric immunosensor. ACS Nano 2009, 3, 3301–3307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mun, K.S.; Alvarez, S.D.; Choi, W.Y.; Sailor, M.J. A stable, label-free optical interferometric biosensor based on TiO2 nanotube arrays. ACS Nano 2010, 4, 2070–2076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Homola, J.; Yee, S.S.; Gauglitz, G. Surface plasmon resonance sensors: Review. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 1999, 54, 3–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pattnaik, P. Surface plasmon resonance: Applications in understanding receptor-ligand interaction. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2005, 126, 79–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanda, V.; Kariuki, J.K.; Harrison, D.J.; McDermott, M.T. Label-free reading of microarray-based immunoassays with surface plasmon resonance imaging. Anal. Chem. 2004, 76, 7257–7262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Willets, K.A.; van Duyne, R.P. Localized surface plasmon resonance spectroscopy and sensing. Annu. Rev. Phys. Chem. 2007, 58, 267–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thanh, N.T.K.; Rosenzweig, Z. Development of an aggregation-based immunoassay for anti-protein a using gold nanoparticles. Anal. Chem. 2002, 74, 1624–1628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Posthuma-Trumpie, G.A.; Korf, J.; van Amerongen, A. Lateral flow (immuno) assay: Its strengths, weaknesses, opportunities and threats. A literature survey. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2009, 393, 569–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lafleur, L.; Stevens, D.; McKenzie, K.; Ramachandran, S.; Spicar-Mihalic, P.; Singhal, M.; Arjyal, A.; Osborn, J.; Kauffman, P.; Yager, P. Progress toward multiplexed sample-to-result detection in low resource settings using microfluidic immunoassay cards. Lab Chip 2012, 12, 1119–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, E.; Liang, T.; Spicar-Mihalic, P.; Houghtaling, J.; Ramachandran, S.; Yager, P. Two-dimensional paper network format that enables simple multistep assays for use in low-resource settings in the context of malaria antigen detection. Anal. Chem. 2012, 84, 4574–4579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ng, A.H.; Uddayasankar, U.; Wheeler, A.R. Immunoassays in microfluidic systems. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2010, 397, 991–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foudeh, A.M.; Fatanat Didar, T.; Veres, T.; Tabrizian, M. Microfluidic designs and techniques using lab-on-a-chip devices for pathogen detection for point-of-care diagnostics. Lab Chip 2012, 12, 3249–3266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, W.; van der Berg, A. Lab on paper. Lab Chip 2008, 8, 1988–1991. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Cheng, C.M.; Martinez, A.W.; Gong, J.; Mace, C.R.; Phillips, S.T.; Carrilho, E.; Mirica, K.A.; Whitesides, G.M. Paper-based ELISA. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2010, 49, 4771–4774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinez, A.W.; Phillips, S.T.; Whitesides, G.M. Three-dimensional microfluidic devices fabricated in layered paper and tape. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 19606–19611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Crooks, R.M. Three-dimensional paper microfluidic devices assembled using the principles of origami. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2011, 133, 17564–17566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ge, L.; Yan, J.X.; Song, X.R.; Yan, M.; Ge, S.G.; Yu, J.H. Three-dimensional paper-based electrochemiluminescence immunodevice for multiplexed measurement of biomarkers and point-of-care testing. Biomaterials 2012, 33, 1024–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tseng, S.C.; Yu, C.C.; Wan, D.; Chen, H.L.; Wang, L.A.; Wu, M.C.; Su, W.F.; Han, H.C.; Chen, L.C. Eco-friendly plasmonic sensors: Using the photothermal effect to prepare metal nanoparticle-containing test papers for highly sensitive colorimetric detection. Anal. Chem. 2012, 84, 5140–5145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, S.K.; Hsieh, T.H.; Lin, D.Y. General digital microfluidic platform manipulating dielectric and conductive droplets by dielectrophoresis and electrowetting. Lab Chip 2009, 9, 1236–1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, S.K.; Hsu, Y.W.; Chen, C.H. Encapsulated droplets with metered and removable oil shells by electrowetting and dielectrophoresis. Lab Chip 2011, 11, 2500–2508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shih, S.C.; Gach, P.C.; Sustarich, J.; Simmons, B.A.; Adams, P.D.; Singh, S.; Singh, A.K. A droplet-to-digital (D2D) microfluidic device for single cell assays. Lab Chip 2015, 15, 225–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rival, A.; Jary, D.; Delattre, C.; Fouillet, Y.; Castellan, G.; Bellemin-Comte, A.; Gidrol, X. An EWOD-based microfluidic chip for single-cell isolation, mRNA purification and subsequent multiplex qPCR. Lab Chip 2014, 14, 3739–3749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, S.K.; Huang, P.W.; Wang, T.T.; Peng, Y.H. Cross-scale electric manipulations of cells and droplets by frequency-modulated dielectrophoresis and electrowetting. Lab Chip 2008, 8, 1325–1331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, S.K.; Yang, H.; Wang, T.T.; Hsu, W. Asymmetric electrowetting—Moving droplets by a square wave. Lab Chip 2007, 7, 1330–1335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wheeler, A.R.; Moon, H.; Kim, C.J.; Loo, J.A.; Garrell, R.L. Electrowetting-based microfluidics for analysis of peptides and proteins by matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization mass spectrometry. Anal. Chem. 2004, 76, 4833–4838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kirby, A.E.; Lafreniere, N.M.; Seale, B.; Hendricks, P.I.; Cooks, R.G.; Wheeler, A.R. Analysis on the go: Quantitation of drugs of abuse in dried urine with digital microfluidics and miniature mass spectrometry. Anal. Chem. 2014, 86, 6121–6129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wheeler, A.R.; Moon, H.; Bird, C.A.; Loo, R.R.; Kim, C.J.; Loo, J.A.; Garrell, R.L. Digital microfluidics with in-line sample purification for proteomics analyses with MALDI-MS. Anal. Chem. 2005, 77, 534–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mei, N.; Seale, B.; Ng, A.H.; Wheeler, A.R.; Oleschuk, R. Digital microfluidic platform for human plasma protein depletion. Anal. Chem. 2014, 86, 8466–8472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanders, R.; Huggett, J.F.; Bushell, C.A.; Cowen, S.; Scott, D.J.; Foy, C.A. Evaluation of digital PCR for absolute DNA quantification. Anal Chem 2011, 83, 6474–6484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- White, R.A., III; Quake, S.R.; Curr, K. Digital PCR provides absolute quantitation of viral load for an occult RNA virus. J. Virol. Methods 2012, 179, 45–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, J.L.; Chen, A.T.; Lee, J.H.; Fan, S.K. Digital microfluidics for manipulation and analysis of a single cell. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 22319–22332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barbulovic-Nad, I.; Yang, H.; Park, P.S.; Wheeler, A.R. Digital microfluidics for cell-based assays. Lab Chip 2008, 8, 519–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yetisen, A.K.; Akram, M.S.; Lowe, C.R. Paper-based microfluidic point-of-care diagnostic devices. Lab Chip 2013, 13, 2210–2251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pollack, M.G.; Pamula, V.K.; Srinivasan, V.; Eckhardt, A.E. Applications of electrowetting-based digital microfluidics in clinical diagnostics. Expert Rev. Mol. Diagn. 2011, 11, 393–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, K.; Ng, A.H.; Fobel, R.; Wheeler, A.R. Digital microfluidics. Annu. Rev. Anal. Chem. 2012, 5, 413–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sista, R.S.; Eckhardt, A.E.; Srinivasan, V.; Pollack, M.G.; Palanki, S.; Pamula, V.K. Heterogeneous immunoassays using magnetic beads on a digital microfluidic platform. Lab Chip 2008, 8, 2188–2196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, E.M.; Ng, A.H.; Uddayasankar, U.; Wheeler, A.R. A digital microfluidic approach to heterogeneous immunoassays. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2011, 399, 337–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vergauwe, N.; Witters, D.; Ceyssens, F.; Vermeir, S.; Verbruggen, B.; Puers, R.; Lammertyn, J. A versatile electrowetting-based digital microfluidic platform for quantitative homogeneous and heterogeneous bio-assays. J. Micromech. Microeng. 2011, 21, 054026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, A.H.; Choi, K.; Luoma, R.P.; Robinson, J.M.; Wheeler, A.R. Digital microfluidic magnetic separation for particle-based immunoassays. Anal. Chem. 2012, 84, 8805–8812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karuwan, C.; Sukthang, K.; Wisitsoraat, A.; Phokharatkul, D.; Patthanasettakul, V.; Wechsatol, W.; Tuantranont, A. Electrochemical detection on electrowetting-on-dielectric digital microfluidic chip. Talanta 2011, 84, 1384–1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shamsi, M.H.; Choi, K.; Ng, A.H.; Wheeler, A.R. A digital microfluidic electrochemical immunoassay. Lab Chip 2014, 14, 547–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsaloglou, M.N.; Jacobs, A.; Morgan, H. A fluorogenic heterogeneous immunoassay for cardiac muscle troponin cTnI on a digital microfluidic device. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2014, 406, 5967–5976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ng, A.H.; Lee, M.; Choi, K.; Fischer, A.T.; Robinson, J.M.; Wheeler, A.R. Digital microfluidic platform for the detection of rubella infection and immunity: A proof of concept. Clin. Chem. 2015, 61, 420–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, K.; Ng, A.H.; Fobel, R.; Chang-Yen, D.A.; Yarnell, L.E.; Pearson, E.L.; Oleksak, C.M.; Fischer, A.T.; Luoma, R.P.; Robinson, J.M.; et al. Automated digital microfluidic platform for magnetic-particle-based immunoassays with optimization by design of experiments. Anal. Chem. 2013, 85, 9638–9646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2016 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons by Attribution (CC-BY) license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
He, J.-L.; Wang, D.-S.; Fan, S.-K. Opto-Microfluidic Immunosensors: From Colorimetric to Plasmonic. Micromachines 2016, 7, 29. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi7020029
He J-L, Wang D-S, Fan S-K. Opto-Microfluidic Immunosensors: From Colorimetric to Plasmonic. Micromachines. 2016; 7(2):29. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi7020029
Chicago/Turabian StyleHe, Jie-Long, Da-Shin Wang, and Shih-Kang Fan. 2016. "Opto-Microfluidic Immunosensors: From Colorimetric to Plasmonic" Micromachines 7, no. 2: 29. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi7020029
APA StyleHe, J.-L., Wang, D.-S., & Fan, S.-K. (2016). Opto-Microfluidic Immunosensors: From Colorimetric to Plasmonic. Micromachines, 7(2), 29. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi7020029