Design and Modeling of Polysilicon Electrothermal Actuators for a MEMS Mirror with Low Power Consumption
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Design and Modeling
2.1. Structural Configuration
2.2. Electrical Model of Electrothermal Actuators
2.3. Analytical Modeling of the Electrothermal and Structural Behavior
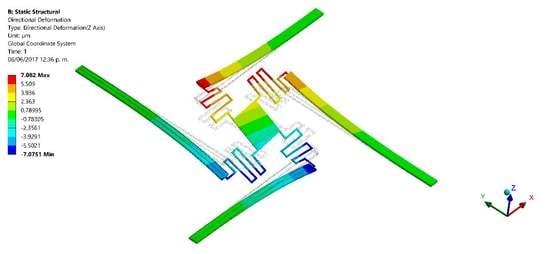
3. Results and Discussions
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chang, C.I.; Tsai, M.H.; Liu, Y.C.; Sun, C.M.; Fang, W. Pick-and-place process for sensitivity improvement of the capacitive type CMOS MEMS 2-axis tilt sensor. J. Micromech. Microeng. 2013, 23, 095029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juárez-Aguirre, R.; Domínguez-Nicolás, S.M.; Manjarrez, E.; Tapia, J.A.; Figueras, E.; Vázquez-Leal, H.; Aguilera-Cortés, L.A.; Herrera-May, A.L. Digital Signal Processing by Virtual Instrumentation of a MEMS Magnetic Field Sensor for Biomedical Applications. Sensors 2013, 13, 15068–15084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, J.Q.; Li, F.; Zhao, M.; Wang, K.A. Surface Micromachined CMOS MEMS Humidity Sensor. Micromachines 2015, 6, 1569–1576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hung, A.C.-L.; Lai, H.Y.-H.; Lin, T.-W.; Fu, S.-G.; Lu, M.S.-C. An electrostatically driven 2D micro-scanning mirror with capacitive sensing for projection display. Sens. Actuators A 2015, 222, 122–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Xu, J.; Zhong, S.; Wu, Y. Large size MEMS scanning mirror with vertical comb drive for tunable optical filter. Opt. Lasers Eng. 2013, 51, 54–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmström, S.T.S.; Baran, U.; Urey, H. MEMS laser scanners: A review. J. Microelectromech. Syst. 2014, 23, 259–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Chen, J.; Zivkovic, A.S.; Tanguy, Q.A.A.; Xie, H. A compact Fourier transform spectrometer on a silicon optical bench with an electrothermal MEMS mirror. J. Microelectromech. Syst. 2016, 25, 347–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Wang, E.; Zhang, X.; Liang, W.; Li, X.; Xie, H. MEMS-based 3D confocal scanning microendoscope using MEMS scanner for both lateral and axial scan. Sens. Actuators A 2014, 215, 89–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, L.Y.; Keeler, E.G. Progress of MEMS scanning micromirrors for optical bio-imaging. Micromachines 2015, 6, 1675–1689. [Google Scholar]
- Haindl, R.; Trasischker, W.; Baumann, B.; Pircher, M.; Hitzenberger, C.K. Three-beam Doppler optical coherence tomography using a facet prism telescope and MEMS mirror for improved transversal solution. J. Mod. Opt. 2015, 62, 1781–1788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, W.; McCormick, D.; Ahn, Y.; Sepehr, A.; Brenner, M.; Wong, B.; Tien, N.; Chen, Z. In vivo tree-dimensional spectral domain endoscopic optical coherence tomography using a microelectromechanical system mirror. Opt. Lett. 2007, 32, 3239–3241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, W.; McCormick, D.T.; Zhang, J.; Wang, L.; Tien, N.C.; Chen, Z. Three-dimensional endoscopic optical coherence tomography by use of a two-axis microelectromechanical scanning mirror. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2006, 88, 163901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solgaard, O.; Godil, A.A.; Howe, R.T.; Lee, L.P.; Peter, Y.-A.; Zappe, H. Optical MEMS: From micromirrors to complex systems. J. Microelectromech. Syst. 2014, 23, 517–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.-H.; Jeong, H.; Lee, S.-K.; Ji, C.-H.; Park, J.-H. Electromagnetically actuated biaxial scanning micromirror fabricated with silicon on glass wafer. Microsyst. Technol. 2017, 23, 2075–2085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, A.R.; Han, A.; Ju, S.; Jeong, H.; Park, J.-H.; Kim, I.; Bu, J.-U.; Ji, C.-J. Electromagnetic biaxial microscanner with mechanical amplification at resonance. Opt. Express 2015, 23, 16792–16802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, C.; He, S. A microelectrostatic repulsive-torque rotation actuator with-width finger. J. Micromech. Microeng. 2015, 25, 095006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Duan, C.; Liu, L.; Li, X.; Xie, H. A non-resonant fiber scanner based on a electrothermally-actuated MEMS stage. Sens. Actuators A 2015, 233, 239–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Zhou, L.; Xie, H. A fast, large-stroke electrothermal MEMS mirror based on Cu/W bimorph. Micromachines 2015, 6, 1876–1889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naono, T.; Fujii, T.; Esashi, M.; Tanaka, S. Non-resonant 2-D piezoelectric MEMS optical scanner actuated by Nb doped PZT thin film. Sens. Actuators A 2015, 233, 147–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.D.; Lee, Y.H.; Yeh, C.S. Design and vibration analysis of a piezoelectric-actuated MEMS scanning mirror and its application to laser projection. Smart Mater. Struct. 2014, 23, 125007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, W.; Tang, S.; McCormick, D.T.; Xie, T.; Anh, Y.-C.; Su, J.; Tomov, I.V.; Krasieva, T.B.; Tromberg, B.J.; Chen, Z. Miniaturized probe based on a microelectromechanical system mirror for multiphoton microscopy. Opt. Lett. 2008, 33, 1324–1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, J.; Guo, S.; Wu, L.; Liu, L.; Choe, S.-W.; Sorg, B.S.; Xie, H. 3D in vivo optical coherence tomography based on a low-voltage, large-scan-range 2D MEMS mirror. Opt. Express 2010, 18, 12065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bauer, R.; Li, L.; Uttamchandani, D. Dynamic properties of angular vertical comb-drive scanning micromirros with electrothermally controlled variable offset. J. Microelectromech. Syst. 2014, 23, 999–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Zhou, P.; Wang, T.; He, J.; Yu, H.; Shen, W. A large-size MEMS scanning mirror for speckle reduction application. Micromachines 2017, 8, 140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ataman, C.; Lani, S.; Noell, W.; de Rooij, N. A dual-axis pointing mirror with moving-magnet actuation. J. Micromech. Microeng. 2013, 23, 025002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, Y.-M.; Gorman, J.J.; Dagalakis, N.G.; Yang, S.H.; Kim, Y.; Yoo, J.M. A high-bandwidth electromagnetic MEMS motion stage for scanning applications. J. Micromech. Microeng. 2012, 22, 105012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koh, K.H.; Kobayashi, T.; Lee, C. Investigation of piezoelectric driven MEMS mirrors based on single and double S-shaped PZT actuator for 2-D scanning applications. Sens. Actuators A 2012, 184, 149–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, C.; Wang, D.; Zhou, Z.; Liang, P.; Samuelson, S.; Pozzi, A.; Xie, H. Swept-source common-path optical coherence tomography with a MEMS endoscopic imaging probe. In Proceedings of the SPIE Optical Coherence Tomography and Coherence Domain Optical Methods Biomedicine XVIII, San Francisco, CA, USA, 3–5 February 2014; Volume 8934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samuelson, S.R.; Xie, H. A large piston displacement MEMS mirror with electrothermal ladder actuator arrays for ultra-low tilt applications. J. Microelectromech. Syst. 2014, 23, 39–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koh, K.H.; Lee, C. A two-dimensional MEMS scanning mirror using hybrid actuation mechanisms with low operation voltage. J. Microelectromech. Syst. 2012, 21, 1124–1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Q.A.; Lee, N.K.S. Analysis and design of polysilicon thermal flexure actuator. J. Micromech. Microeng. 1999, 9, 64–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres, D.; Wang, T.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, X.; Dooley, S.; Tan, X.; Xie, H.; Sepúlveda, N. VO2-based MEMS mirrors. J. Microelectromech. Syst. 2016, 780–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandia National Laboratories. Available online: http://www.sandia.gov/mstc/_assets/documents/design_documents/SUMMiT_V_Dmanual.pdf (accessed on 3 June 2016).
- Lin, L.; Chiao, M. Electrothermal responses of lineshape microstructures. Sens. Actuators A 1996, 55, 35–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karnovsky, I.A.; Lebed, O. Advanced Methods of Structural Analysis; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2010; pp. 211–270. [Google Scholar]
- Megson, T.H.G. Structural and Stress Analysis, 3rd ed.; Elsevier Ltd.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Kawai, Y.; Kim, J.H.; Inomata, N.; Ono, T. Parametrically actuated resonant micromirror using stiffness tunable torsional springs. Sens. Mater. 2016, 28, 131–139. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.; Xu, D.; Zhang, X.; Chen, Q.; Xie, H.; Li, S. Model-based angular scan error correction of an electrothermally-actuated MEMS mirror. Sensors 2015, 15, 30991–31004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, L.; Pal, S.; Xie, H. MEMS mirrors based on a curved concentric electrothermal actuator. Sens. Actuators A 2012, 188, 349–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Espinosa, A.; Rabenorosoa, K.; Clevy, C.; Komati, B.; Lutz, P.; Zhang, X.; Samuelson, S.R.; Xie, H. Piston motion performance analysis of a 3DOF electrothermal MEMS scanner for medical applications. Int. J. Optomech. 2014, 8, 179–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koh, K.H.; Qian, Y.; Lee, C. Design and characterization of a 3D MEMS VOA driven by hybrid electromagnetic and electrothermal actuation mechanics. J. Micromech. Microeng. 2012, 22, 105031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


















| Parameter | Electrical Resistance (Ω) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Lh = 350 μm | Lh = 450 μm | Lh = 550 μm | |
| R1 | 1576.6 | 2027 | 2077.4 |
| R2 | 105.1 | 135.1 | 165.2 |
| R3 | 1.7 | 1.7 | 1.7 |
| Property | Value |
|---|---|
| Young’s Modulus, | 169 GPa |
| Thermal expansion, | 2.5 × 10−6 K−1 |
| Thermal conductivity, | 125 W·m−1·K−1 |
| Substrate Temperature, | 300 K |
| Linear temperature coefficient, ξ | 1.25 × 10−3 K−1 |
| Resistivity at , | 20.27 × 10−6 Ω·m |
| Density | 2330 kg·m−3 |
| Poisson ratio | 0.23 |
| Authors | Mirror Size | Device Footprint (μm × μm) | Maximum Displacement (μm) | Bias Voltage (V) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Zhang et al. [18] | 900 μm × 900 μm | 2500 × 2500 | 312 | 3 |
| Kawai et al. [37] | 3000 μm diameter | 5000 × 5000 | *- | 20 |
| Zhang et al. [38] | 1000 μm × 1000 μm | 1500 × 1500 | 70 | 2 |
| Li et al. [39] | 1000 μm diameter | 2000 × 2000 | 227 | 0.8 |
| Espinosa et al. [40] | 1000 μm × 1000 μm | 1500 × 1500 | 174 | 3.5 |
| Koh et al. [41] | 1500 μm × 1000 μm | 6000 × 6000 | *- | 5 |
| Our work | 100 μm × 100 μm | 1028 × 1028 | 59.2 | 5 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lara-Castro, M.; Herrera-Amaya, A.; Escarola-Rosas, M.A.; Vázquez-Toledo, M.; López-Huerta, F.; Aguilera-Cortés, L.A.; Herrera-May, A.L. Design and Modeling of Polysilicon Electrothermal Actuators for a MEMS Mirror with Low Power Consumption. Micromachines 2017, 8, 203. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi8070203
Lara-Castro M, Herrera-Amaya A, Escarola-Rosas MA, Vázquez-Toledo M, López-Huerta F, Aguilera-Cortés LA, Herrera-May AL. Design and Modeling of Polysilicon Electrothermal Actuators for a MEMS Mirror with Low Power Consumption. Micromachines. 2017; 8(7):203. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi8070203
Chicago/Turabian StyleLara-Castro, Miguel, Adrian Herrera-Amaya, Marco A. Escarola-Rosas, Moisés Vázquez-Toledo, Francisco López-Huerta, Luz A. Aguilera-Cortés, and Agustín L. Herrera-May. 2017. "Design and Modeling of Polysilicon Electrothermal Actuators for a MEMS Mirror with Low Power Consumption" Micromachines 8, no. 7: 203. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi8070203
APA StyleLara-Castro, M., Herrera-Amaya, A., Escarola-Rosas, M. A., Vázquez-Toledo, M., López-Huerta, F., Aguilera-Cortés, L. A., & Herrera-May, A. L. (2017). Design and Modeling of Polysilicon Electrothermal Actuators for a MEMS Mirror with Low Power Consumption. Micromachines, 8(7), 203. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi8070203