Size-Dependent and Property-Independent Passive Microdroplet Sorting by Droplet Transfer on Dot Rails
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Principle
3. Device Design and Fabrication
3.1. Computational Analysis
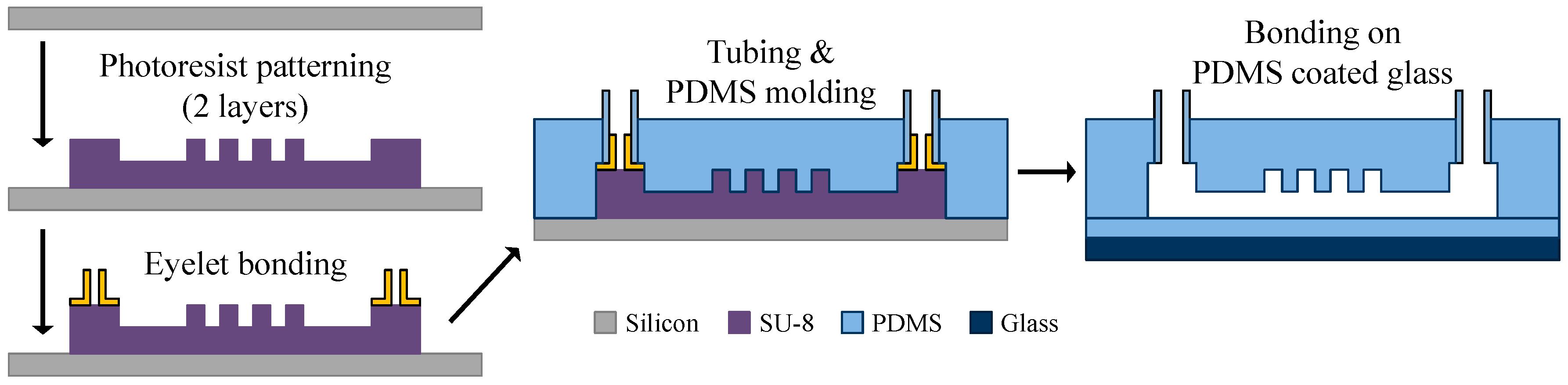
3.2. Device Design and Fabrication
3.3. Materials and Experimental Setup
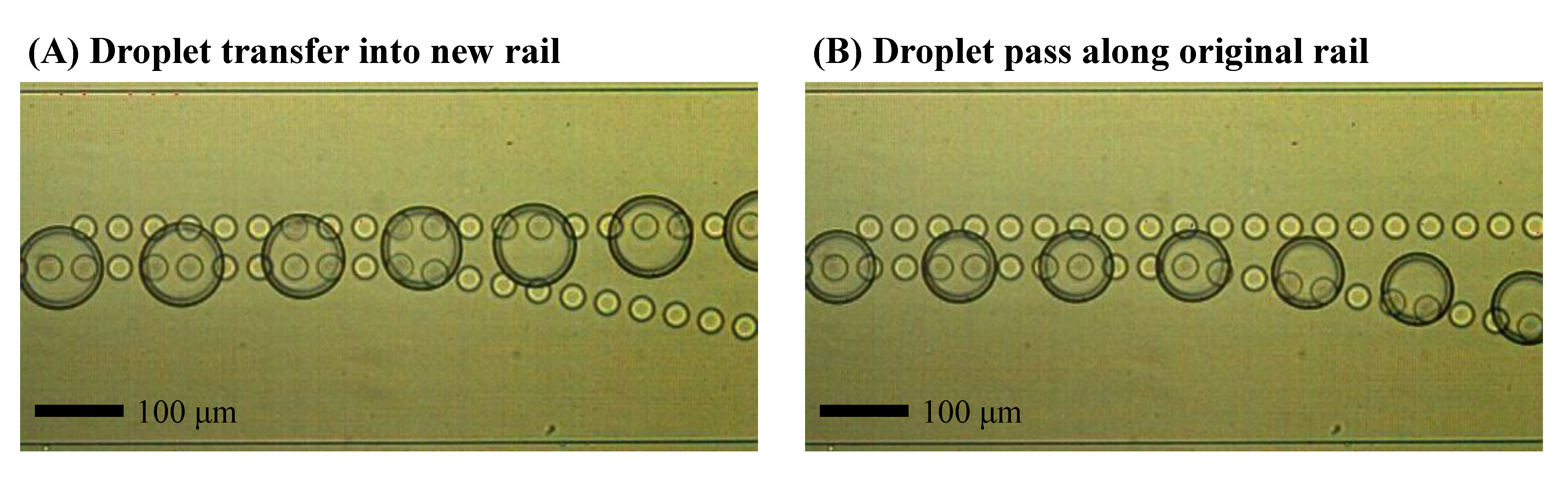
4. Results and Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ohno, K.; Tachikawa, K.; Manz, A. Microfluidics: Applications for analytical purposes in chemistry and biochemistry. Electrophoresis 2008, 29, 4443–4453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Young, E.W.K.; Beebe, D.J. Fundamentals of microfluidic cell culture in controlled microenvironments. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2010, 39, 1036–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, H.; Chen, D.L.; Ismagilov, R.F. Reactions in droplets in microfluidic channels. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2007, 45, 7336–7356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hosokawa, M.; Hoshino, Y.; Nishikawa, Y.; Hirose, T.; Yoon, D.H.; Mori, T.; Sekiguchi, T.; Shoji, S.; Takeyama, H. Droplet-based microfluidics for high-throughput screening of a metagenomic library for isolation of microbial enzymes. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2015, 67, 379–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakamura, K.; Iizuka, R.; Nishi, S.; Yoshida, T.; Hatada, Y.; Takaki, Y.; Iguchi, A.; Yoon, D.H.; Sekiguchi, T.; Shoji, S.; Funatsu, T. Culture-independent method for identification of microbial enzyme-encoding genes by activity-based single-cell sequencing using a water-in-oil microdroplet platform. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 22259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Saint Vencent, M.R.; Wunenburger, R.; Delville, J.-P. Laser switching and sorting for high speed digital microfluidics. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2008, 92, 154105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fradet, E.; McDougall, C.; Abbyad, P.; Dangla, R.; McGloin, D.; Baroud, C.N. Combining rails and anchors with laser forcing for selective manipulation within 2D droplet arrays. Lab Chip 2011, 11, 4228–4234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahn, B.; Lee, K.; Louge, R.; Oh, K.W. Concurrent droplet charging and sorting by electrostatic actuation. Biomicrofluidics 2009, 3, 044102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Link, D.R.; Grasland-Mongrain, E.; Duri, A.; Sarrazin, F.; Cheng, Z.; Cristobal, G.; Marquez, M.; Weitz, D.A. Electric control of droplets in microfluidic devices. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2006, 45, 2556–2560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yap, Y.-F.; Tan, S.-H.; Nguyen, N.-T.; Murshed, S.M.S.; Wong, T.-N.; Yobas, L. Thermally mediated control of liquid microdroplets at a bifurcation. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2009, 42, 065503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miralles, V.; Huerre, A.; Williams, H.; Fournie, B.; Jullien, M.-C. A versatile technology for droplet-based microfluidics: Thermomechanical actuation. Lab Chip 2015, 15, 2133–2139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sesen, M.; Alan, T.; Neild, A. Microfluidic plug steering using surface acoustic waves. Lab Chip 2015, 15, 3030–3038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmid, L.; Weitz, D.A.; Franke, T. Sorting droplet and cells with acoustics: Acoustic microfluidic fluorescence-activated cell sorter. Lab Chip 2014, 14, 3710–3718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoon, D.H.; Wakui, D.; Nakahara, A.; Sekiguchi, T.; Shoji, S. Selective droplet sampling using a minimum number of horizontal pneumatic actuators in a high aspect ratio and highly flexible PDMS device. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 2070–2074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Chen, P.; Dong, Y.; Feng, X.; Liu, B.-F. Encapsulation of single cells on a microfluidic device integrating droplet generation with fluorescence-activated droplet sorting. Biomed. Microdevices 2013, 15, 553–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, S.-T.; Joshipura, I.D.; Lin, Y.; Kakantar-Zadeh, K.; Mitchell, A.; Khoshmanesh, K.; Dickey, M.D. Liquid-metal microdroplets formed dynamically with electrical control of size and rate. Adv. Mater. 2016, 28, 604–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Desbois, L.; Padirac, A.; Kaneda, S.; Genot, A.J.; Rondelez, Y.; Hober, D.; Collard, D.; Fujii, T. A microfluidic device for on-chip Agarose microbead generation with ultralow reagent consumption. Biomicrofluidics 2012, 6, 044101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ke, Y.; Liu, G.; Guo, T.; Zhang, Y.; Li, C.; Xue, W.; Wu, G.; Wang, J.; Du, C. Size controlling of monodisperse carboxymethyl cellulose microparticles via a microfluidic process. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2014, 131, 40663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trantidou, T.; Elani, Y.; Parsons, E.; Ces, O. Hydrophilic surface modification of PDMS for droplet microfluidics using a simple, quick, and robust method via PVA deposition. Microsyst. Nanoeng. 2017, 3, 16091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rakszewska, A.; Tel, J.; Chokkalingam, V.; Huck, W.T.S. One droplet at a time: Toward droplet microfluidics as a versatile tool for single-cell analysis. NPG Asia Mater. 2014, 6, e133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brouzes, E.; Medkova, M.; Savenelli, N.; Marran, D.; Twardowski, M.; Hutchison, J.B.; Rothberg, J.M.; Link, D.R.; Perrimon, N.; Samuels, M.L. Droplet microfluidic technology for single-cell high-throughput screening. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 14195–14200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eastburn, D.J.; Sciambi, A.; Abate, A.R. Ultrahigh-throughput mammalian single-cell reverse-transcriptase polymerase chain reaction in microfluidic drops. Anal. Chem. 2013, 85, 8016–8021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maenaka, H.; Yamada, M.; Yasuda, M.; Seki, M. Continuous and size-dependent sorting of emulsion droplets using hydrodynamics in pinched microchannels. Langmuir 2009, 24, 4405–4410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kok, M.P.; Segers, T.; Versluis, M. Bubble sorting in pinched microchannels for ultrasound contrast agent enrichment. Lab Chip 2015, 15, 3716–3722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joensson, H.N.; Uhlen, M.; Svahn, H.A. Droplet size based separation by deterministic lateral displacement-separating droplets by cell-induced shrinking. Lab Chip 2011, 11, 1305–1310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inglis, D.W. Efficient microfluidic particle separation arrays. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2009, 94, 013510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, H.M.; Samper, V.; Chen, Y.; Heng, C.K.; Lim, T.M.; Yobas, L. Silicon-based microfilters for whole blood cell separation. Biomed. Microdevices 2008, 10, 251–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, R.; Ung, W.L.; Heyman, J.A.; Weitz, D.A. Sensitive and predictable separation of microfluidic droplets by size using in-line passive filter. Biomicrofluidics 2017, 11, 014114. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Carlo, D.D.; Irimia, D.; Tompkins, R.G.; Toner, M. Continuous inertial focusing, ordering, and separation of particles in microchannels. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 18892–18897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hatch, A.C.; Patel, A.; Beer, N.R.; Lee, A.P. Passive droplet sorting using viscoelastic flow focusing. Lab Chip 2013, 13, 1308–1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoon, D.H.; Ha, J.B.; Bahk, Y.K.; Arakawa, T.; Shoji, S.; Go, J.S. Size-selective separation of micro beads by utilizing secondary flow in a curved rectangular microchannel. Lab Chip 2009, 9, 87–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, M.G.; Choi, S.; Park, J.-K. Inertial separation in a contraction-expansion array microchannel. J. Chromatogr. A 2011, 1218, 4138–4143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazutis, L.; Griffiths, A.D. Preparation of monodisperse emulsions by hydrodynamic size fractionation. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2009, 95, 204103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuntaegowdanahalli, S.S.; Bhagat, A.A.S.; Kumar, G.; Papautsky, I. Inertial microfluidics for continuous particle separation in spiral microchannels. Lab Chip 2009, 9, 2973–2980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoon, D.H.; Numakunai, S.; Nakahara, A.; Sekiguchi, T.; Shoji, S. Hydrodynamic on-rail droplet pass filter for fully passive sorting of droplet-phase samples. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 37721–37725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, D.H.; Xie, Z.; Tanaka, D.; Sekiguchi, T.; Shoji, S. A high-resolution passive droplet-phase sample sorter using multi-stage droplet transfer. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 36750–36754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbyad, P.; Dangla, R.; Alexandrou, A.; Baroud, C.N. Rails and anchors: Guiding and trapping droplet microreactors in two dimensions. Lab Chip 2011, 11, 813–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dangla, R.; Lee, S.; Baroud, C.N. Trapping microfluidic drops in wells of surface energy. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2011, 107, 124501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, J.; Ahn, B.; Lee, H.; Xu, L.; Lee, K.; Panchapakesan, R.; Oh, K.W. Droplet-based microfluidic device for multiple-droplet clustering. Lab Chip 2012, 12, 725–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, L.; Lee, H.; Panchapakesan, R.; Oh, K.W. Fusion and sorting of two parallel trains of droplets using a railroad-like channel network and guiding tracks. Lab Chip 2012, 12, 3936–3942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bak, A.; Podgorska, W. Interfacial and surface tensions of toluene/water and air/water systems with nonionic surfactants Tween 20 and Tween 80. Colloids Surf. A 2016, 504, 412–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, N.-S. Formula for the viscosity of a glycerol-water mixture. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2008, 47, 3285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yoon, D.H.; Tanaka, D.; Sekiguchi, T.; Shoji, S. Size-Dependent and Property-Independent Passive Microdroplet Sorting by Droplet Transfer on Dot Rails. Micromachines 2018, 9, 513. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi9100513
Yoon DH, Tanaka D, Sekiguchi T, Shoji S. Size-Dependent and Property-Independent Passive Microdroplet Sorting by Droplet Transfer on Dot Rails. Micromachines. 2018; 9(10):513. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi9100513
Chicago/Turabian StyleYoon, Dong Hyun, Daiki Tanaka, Tetsushi Sekiguchi, and Shuichi Shoji. 2018. "Size-Dependent and Property-Independent Passive Microdroplet Sorting by Droplet Transfer on Dot Rails" Micromachines 9, no. 10: 513. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi9100513
APA StyleYoon, D. H., Tanaka, D., Sekiguchi, T., & Shoji, S. (2018). Size-Dependent and Property-Independent Passive Microdroplet Sorting by Droplet Transfer on Dot Rails. Micromachines, 9(10), 513. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi9100513




