A Bidirectional Neuromodulation Technology for Nerve Recording and Stimulation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Background and Limitations
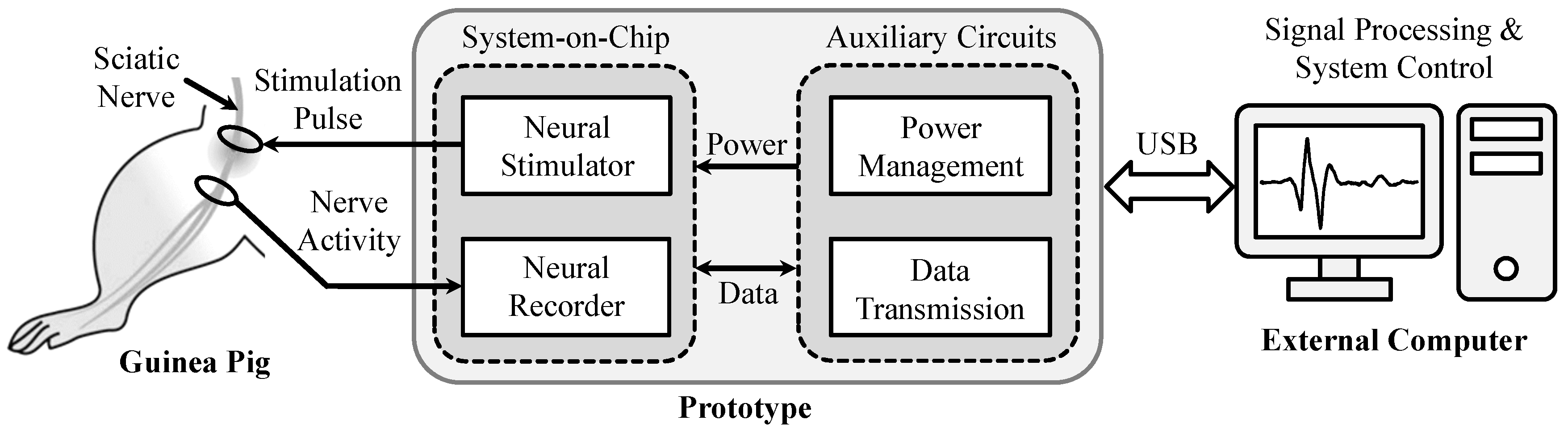
3. Bidirectional Closed-Loop Neuromodulation System Design
3.1. Neural Recorder Design
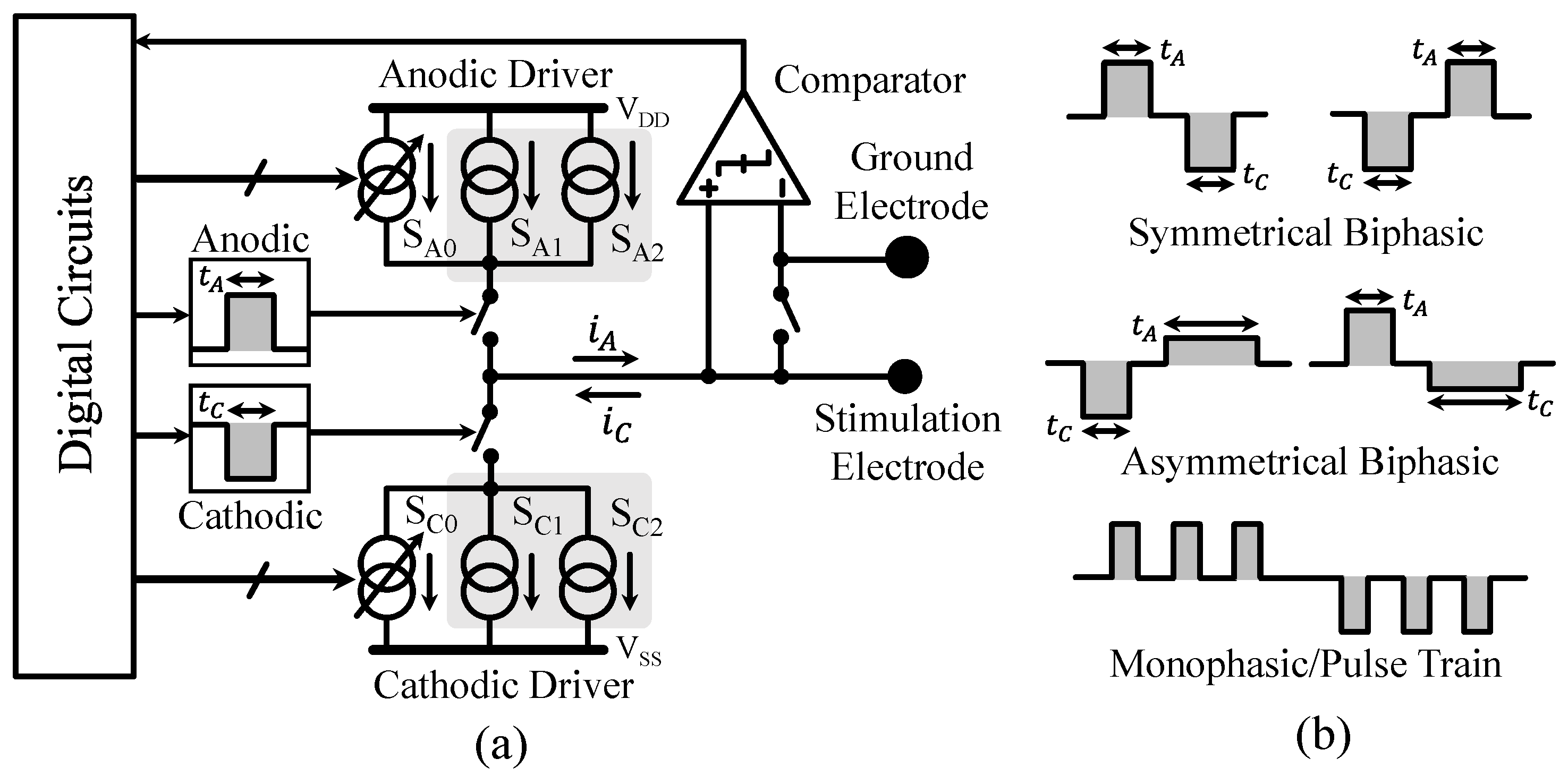
3.2. Neural Stimulator Design
3.3. Auxiliary Circuits Design
4. Experimental Prototype and Animal Experimental Results
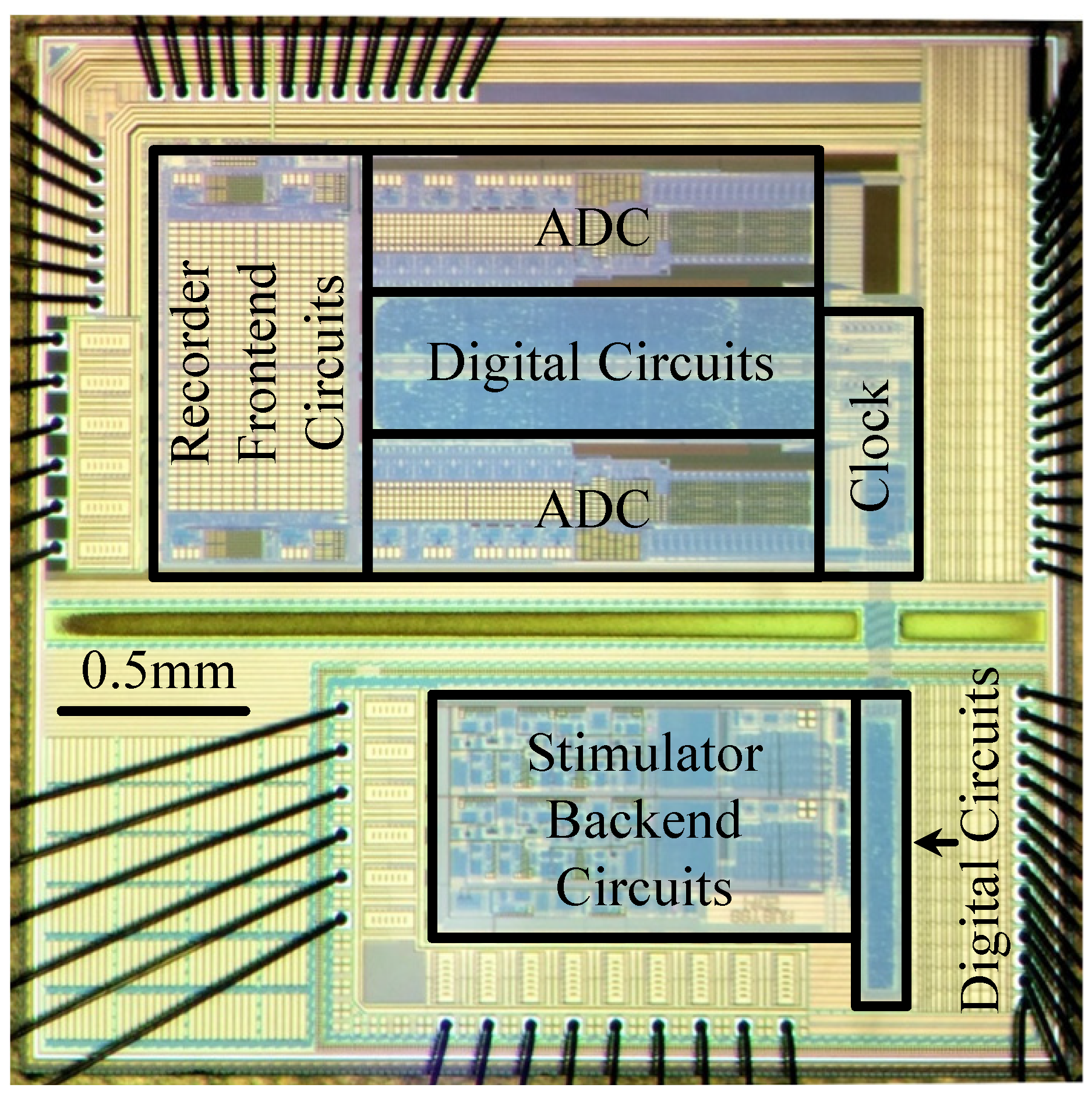
4.1. Experimental Prototype
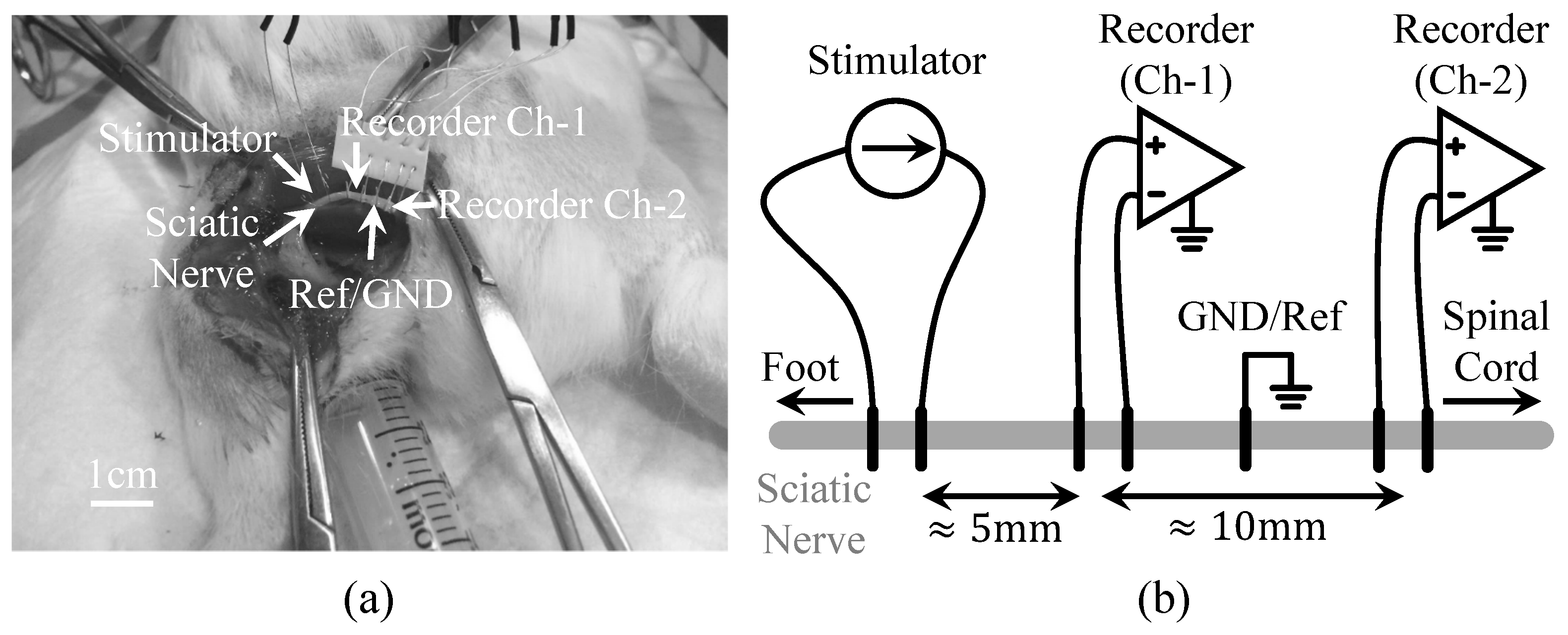
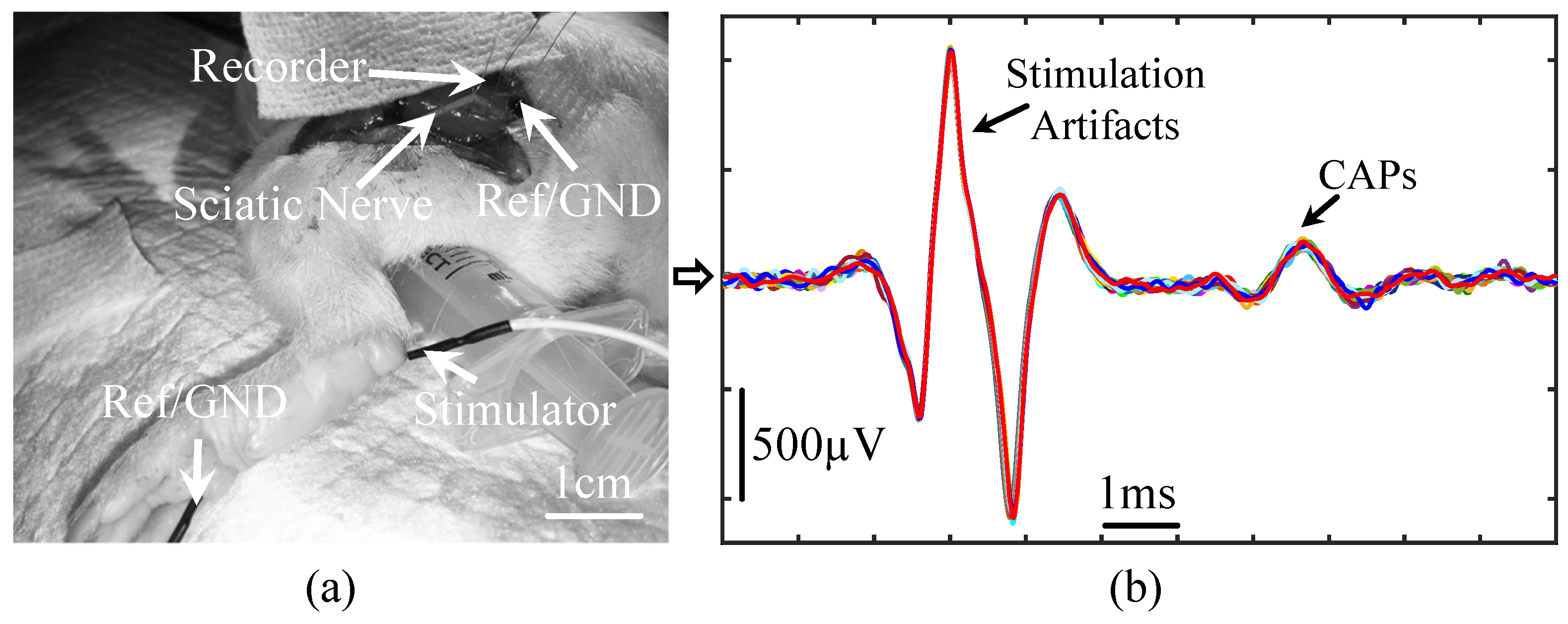
4.2. Animal Surgery and Experimental Preparation
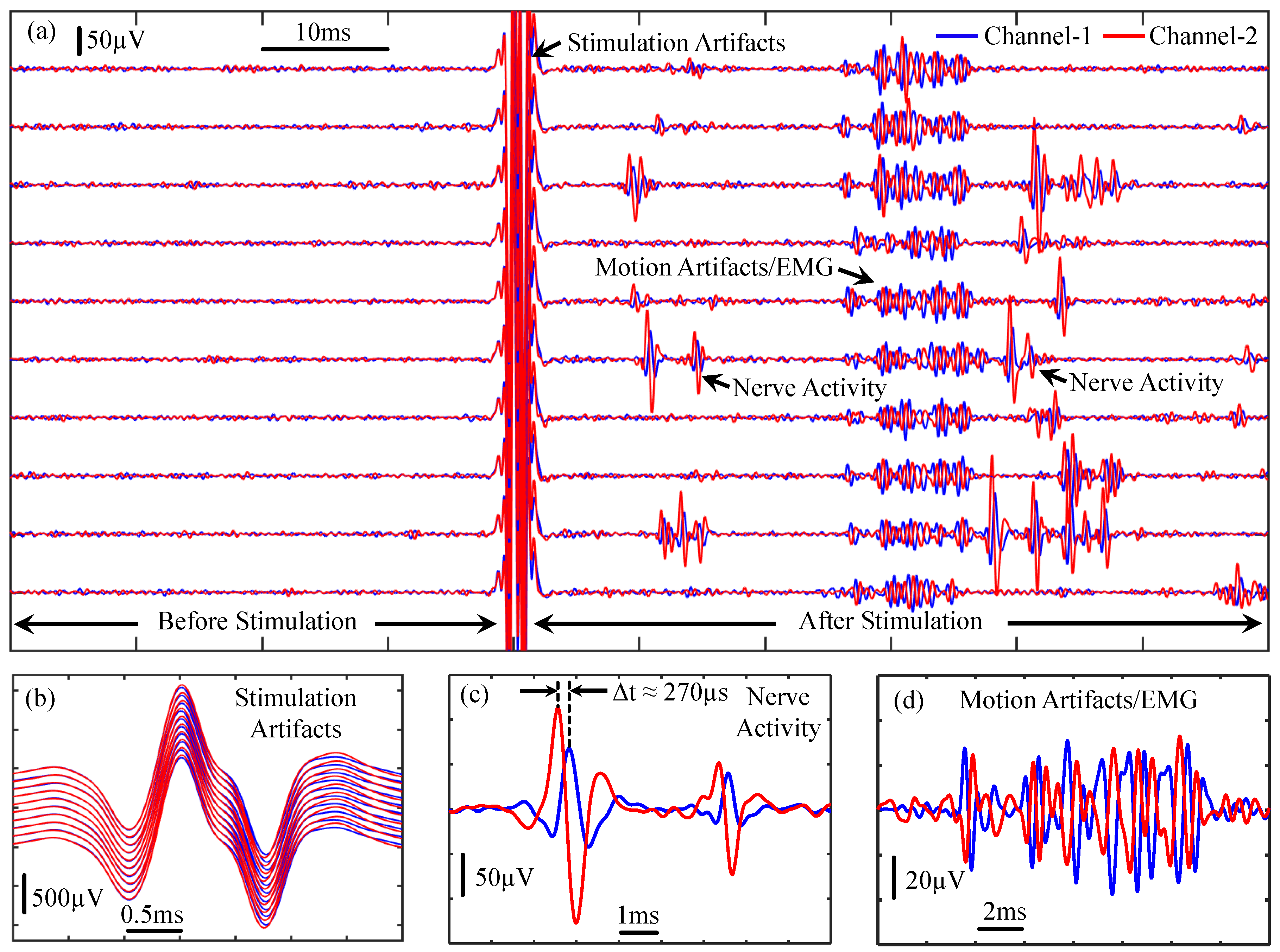
4.3. Animal Experimental Results from the Proposed Prototype
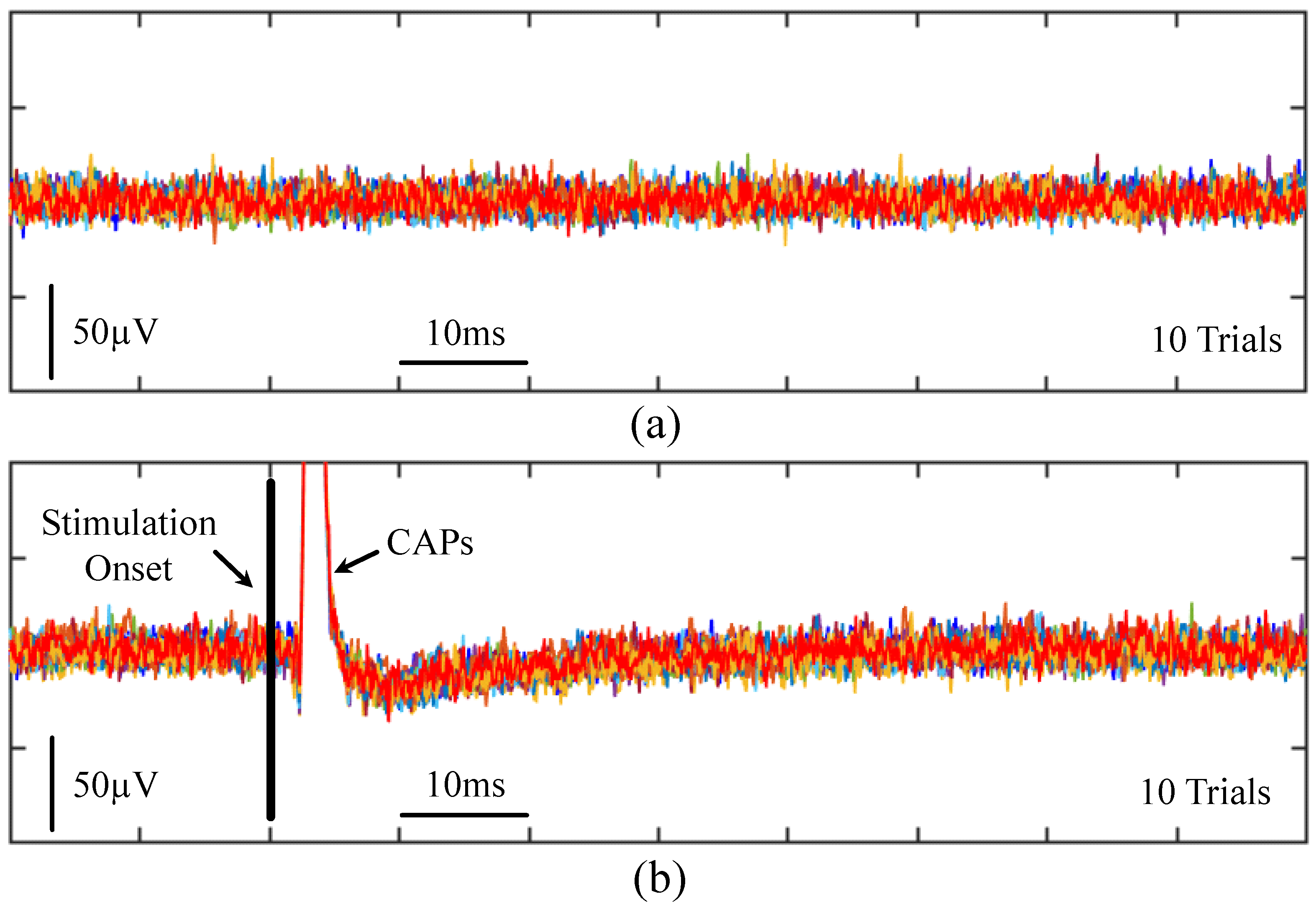
4.4. Animal Experimental Results from Commercial System
5. Conclusions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Burns, J.; Hsieh, Y.H.; Mueller, A.; Chevallier, J.; Sriram, T.S.; Lewis, S.J.; Chew, D.; Achyuta, A.; Fiering, J. High density penetrating electrode arrays for autonomic nerves. In Proceedings of the 38th Annual International of the IEEE EMBS Conference, Orlando, FL, USA, 17–20 August 2016; pp. 2802–2805. [Google Scholar]
- Boretius, T.; Badia, J.; Pascual-Font, A.; Schuettler, M.; Navarro, X.; Yoshida, K.; Stieglitz, T. A transverse intrafascicular multichannel electrode (time) to interface with the peripheral nerve. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2010, 26, 62–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdelhalim, K.; Kokarovtseva, L.; Velazquez, J.; Genov, R. 915-MHz FSK/OOK Wireless Neural Recording SoC With 64 Mixed-Signal FIR Filters. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 2013, 48, 2478–2493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biederman, W.; Yeager, D.; Narevsky, N.; Koralek, A.; Carmena, J.; Alon, E.; Rabaey, J. A Fully Integrated, Miniaturized (0.125 mm2) 10.5 μW Wireless Neural Sensor. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 2013, 48, 960–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reardon, S. Electroceuticals spark interest. Nature 2014, 511, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Famm, K.; Litt, B.; Tracey, K.J.; Boyden, E.S.; Slaoui, M. Drug discovery: A jump-start for electroceuticals. Nature 2013, 496, 159–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bensmaia, S.J.; Miller, L.E. Restoring sensorimotor function through intracortical interfaces: Progress and looming challenges. Nat. Rev. Neuronsci. 2014, 15, 313–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chernyy, N.; Schiff, S.J.; Gluckman, B.J. Time dependence of stimulation/recording-artifact transfer function estimates for neural interface systems. In Proceedings of the 31th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBS 2009), Minneapolis, MN, USA, 3–6 September 2009; pp. 1380–1383. [Google Scholar]
- Clark, G.A.; Ledbetter, N.M.; Warren, D.J.; Harrison, R.R. Recording sensory and motor information from peripheral nerves with utah slanted electrode arrays. In Proceedings of the 33th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBS 2011), Boston, MA, USA, 30 August–3 September 2011; pp. 4641–4644. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Z.; Xu, J.; Nguyen, A.T.; Wu, T.; Zhao, W.; Tam, W.K. Neuronix enables continuous, simultaneous neural recording and electrical microstimulation. In Proceedings of the 38th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBS 2016), Orlando, FL, USA, 16–20 August 2016; pp. 4451–4454. [Google Scholar]
- Rieger, R.; Taylor, J.; Demosthenous, A.; Donaldson, N.; Langlois, P.J. Design of a low noise preamplifier for nerve cuff electrode recording. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 2003, 38, 1373–1379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lotti, F.; Ranieri, F.; Vadala, G.; Zollo, L.; Di Pino, G. Invasive intraneural interfaces: Foreign body reaction issues. Front. Neurosci. 2017, 11, 00497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loi, D.; Carboni, C.; Angius, G.; Angotzi, G.N.; Barbaro, M.; Raffo, L.; Raspopovic, S.; Navarro, X. Peripheral neural activity recording and stimulation system. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Circuits Syst. 2011, 5, 368–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, J.; Yang, Z. A 50 μW/Ch Artifacts-Insensitive Neural Recorder Using Frequency-Shaping Technique. In Proceedings of the IEEE Custom Integrated Circuits Conference (CICC), San Jose, CA, USA, 22–25 September 2013; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, J.; Wu, T.; Yang, Z. A power efficient frequency shaping neural recorder with automatic bandwidth adjustment. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE International Asian Solid-State Circuit Conference (A-SSCC), Kaohsiung, Taiwan, 10–12 November 2014; pp. 197–200. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, J.; Wu, T.; Liu, W.; Yang, Z. A Frequency Shaping Neural Recorder With 3 pF Input Capacitance and 11 Plus 4.5 Bits Dynamic Range. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Circuits Syst. 2014, 8, 510–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, J.; Wu, T.; Yang, Z. A New System Architecture for Future Long-Term High-Density Neural Recording. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. II Express Briefs 2013, 60, 402–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Nguyen, A.T.; Zhao, W.; Guo, H.; Wu, T.; Wiggins, H.; Keefer, E.W.; Lim, H.; Yang, Z. A Low-Noise, Wireless, Frequency-Shaping Neural Recorder. IEEE J. Emerg. Sel. Top. Circuits Syst. 2018, 8, 187–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, A.; Xu, J.; Tam, W.; Zhao, W.; Wu, T.; Yang, Z. A Programmable Fully Integrated Microstimulator for Neural Implants and Instrumentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE Biomedical Circuits and Systems Conference, Shanghai, China, 17–19 October 2016; pp. 472–475. [Google Scholar]
- Navarro, X.; Krueger, T.B.; Lago, N.; Micera, S.; Stieglitz, T.; Dario, P. A critical review of interfaces with the peripheral nervous system for the control of neuroprostheses and hybrid bionic systems. J. Peripher. Nerv. Syst. 2005, 10, 229–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- FitzGerald, J.J.; Lacour, S.P.; McMahon, S.B.; Fawcett, J.W. Microchannels as axonal amplifiers. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2008, 55, 1136–1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cogan, S.F. Neural stimulation and recording electrodes. Annu. Rev. Biomed. Eng. 2008, 10, 275–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lempka, S.; Johnson, M.; Moffitt, M.; Otto, K.; Kipke, D.; McIntyre, C. Theoretical analysis of intracortical microelectrode recordings. J. Neural Eng. 2011, 8, 045006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yang, Z.; Zhao, Q.; Keefer, E.; Liu, W. Noise characterization, modeling, and reduction for in-vivo neural recording. In Proceedings of the Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 7–10 December 2009; pp. 2160–2168. [Google Scholar]
- Scholvin, J.; Kinney, J.P.; Bernstein, J.G.; Moore-Kochlacs, C.; Kopell, N.; Fonstad, C.G.; Boyden, E.S. Close-packed silicon microelectrodes for scalable spatially oversampled neural recording. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2016, 63, 120–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garde, K.; Keefer, E.; Botterman, B.; Galvan, P.; Romero-Ortega, M.I. Early interfaced neural activity from chronic amputated nerves. Front. Neuroeng. 2009, 2, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seo, D.; Neely, R.M.; Shen, K.; Singhal, U.; Alon, E.; Rabaey, J.M.; Carmena, J.M.; Maharbiz, M.M. Wireless recording in the peripheral nervous system with ultrasonic neural dust. Neuron 2016, 91, 529–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Micera, S.; Carpaneto, J.; Raspopovic, S. Control of hand prostheses using peripheral information. IEEE Rev. Biomed. Eng. 2010, 3, 48–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dweiri, Y.M.; Eggers, T.; McCallum, G.; Durand, D.M. Ultra-low noise miniaturized neural amplifier with hardware averaging. J. Neural Eng. 2015, 12, 046024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gao, H.; Walker, R.; Nuyujukian, P.; Makinwa, K.; Shenoy, K.; Murmannn, B.; Meng, T. HermesE: A 96-Channel Full Data Rate Direct Neural Interface in 0.13 μm CMOS. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 2012, 47, 1043–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muller, R.; Gambini, S.; Rabaey, J. A 0.013 mm2, 5 μW, DC-Coupled Neural Signal Acquisition IC With 0.5 V Supply. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 2012, 47, 232–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrison, R.; Watkins, P.; Kier, R.; Lovejoy, R.; Black, D.; Greger, B.; Solzbacher, F. A Low-Power Integrated Circuit for a Wireless 100-Electrode Neural Recording System. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 2007, 42, 123–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrison, R.; Charles, C. A Low-Power Low-Noise CMOS Amplifier for Neural Recording Applications. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 2003, 38, 958–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wattanapanitch, W.; Fee, M.; Sarpeshkar, R. An Energy-Efficient Micropower Neural Recording Amplifier. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Circuits Syst. 2007, 1, 136–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.; Lee, H.; Kiani, M.; Jow, U.; Ghovanloo, M. An Inductively Powered Scalable 32-Channel Wireless Neural Recording System-on-a-Chip for Neuroscience Applications. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Circuits Syst. 2010, 4, 360–371. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Patel, Y.A.; Butera, R.J. Differential fiber-specific block of nerve conduction in mammalian peripheral nerves using kilohertz electrical stimulation. J. Neurophysiol. 2015, 113, 3923–3929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Patel, Y.A.; Willsie, A.; Clements, I.P.; Aguilar, R.; Rajaraman, S.; Butera, R.J. Microneedle cuff electrodes for extrafascicular peripheral nerve interfacing. In Proceedings of the 38th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBC), Orlando, FL, USA, 16–20 August 2016; pp. 1741–1744. [Google Scholar]
- Wenk, H.N.; Brederson, J.D.; Honda, C.N. Morphine Directly Inhibits Nociceptors in Inflamed Skin. J. Neurophysiol. 2006, 95, 2083–2097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Waxman, S.G. Determinants of conduction velocity in myelinated nerve fibers. Muscle Nerve 1980, 3, 141–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xu, J.; Guo, H.; Nguyen, A.T.; Lim, H.; Yang, Z. A Bidirectional Neuromodulation Technology for Nerve Recording and Stimulation. Micromachines 2018, 9, 538. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi9110538
Xu J, Guo H, Nguyen AT, Lim H, Yang Z. A Bidirectional Neuromodulation Technology for Nerve Recording and Stimulation. Micromachines. 2018; 9(11):538. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi9110538
Chicago/Turabian StyleXu, Jian, Hongsun Guo, Anh Tuan Nguyen, Hubert Lim, and Zhi Yang. 2018. "A Bidirectional Neuromodulation Technology for Nerve Recording and Stimulation" Micromachines 9, no. 11: 538. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi9110538
APA StyleXu, J., Guo, H., Nguyen, A. T., Lim, H., & Yang, Z. (2018). A Bidirectional Neuromodulation Technology for Nerve Recording and Stimulation. Micromachines, 9(11), 538. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi9110538



