Disposable Optical Stretcher Fabricated by Microinjection Moulding
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Device and µIM Mould Design
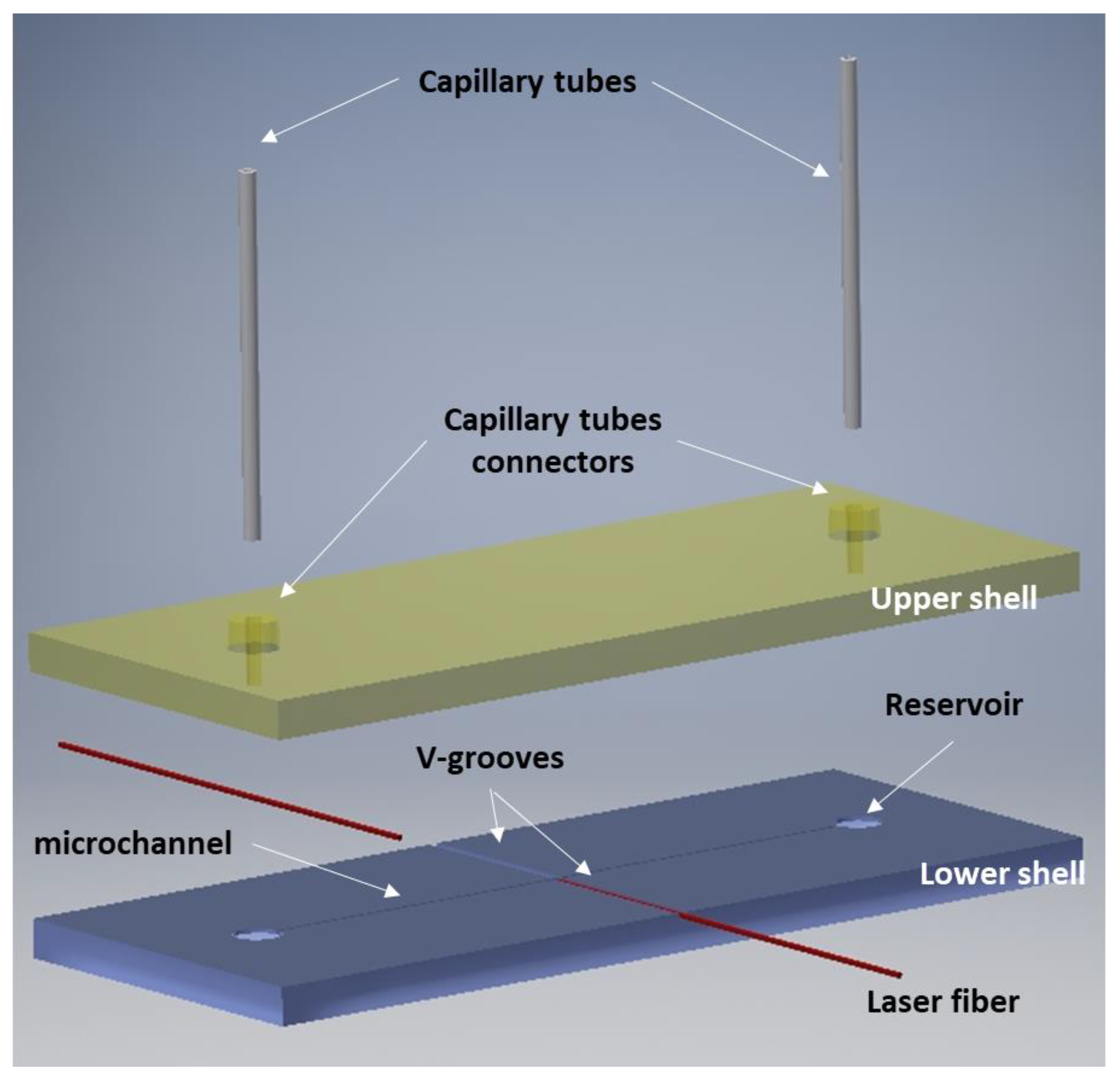
2.1. Optical Stretcher Design
2.2. Microinjection Moulding
3. Fabrication
3.1. Inserts Manufacturing
3.1.1. FLM
3.1.2. µEDM
3.1.3. µIM Shells Manufacturing
4. Optical Stretcher Demonstration
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- El-Ali, J.; Sorger, P.K.; Jensen, K.F. Cells on Chips. Nature 2006, 442, 403–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Souza, N. Single-cell methods. Nat. Methods 2011, 9, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lautenschläger, F.; Paschke, S.; Schinkinger, S.; Bruel, A.; Beil, M.; Guck, J. The regulatory role of cell mechanics for migration of differentiating myeloid cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 15696–15701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Guck, J.; Ananthakrishnan, R.; Mahmood, H.; Moon, T.J.; Cunningham, C.C.; Käs, J. The optical stretcher: a novel laser tool to micromanipulate cells. J. Biophys. 2001, 81, 767–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhuri, P.K.; Warkiani, M.E.; Jing, T.; Lim, C.T. Microfluidics for research and applications in oncology. Analyst 2016, 141, 504–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bellini, N.; Vishnubhatla, K.C.; Bragheri, F.; Ferrara, L.; Minzioni, P.; Ramponi, R.; Cristiani, I.; Osellame, R. Femtosecond laser fabricated monolithic chip for optical trapping and stretching of single cells. Opt. Express 2010, 18, 4679–4688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bragheri, F.; Ferrara, L.; Bellini, N.; Vishnubhatla, K.C.; Minzioni, P.; Ramponi, R.; Osellame, R.; Cristiani, I. Optofluidic chip for single cell trapping and stretching fabricated by a femtosecond laser. J. Biophotonics 2010, 3, 234–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khanafer, K.; Duprey, A.; Schlicht, M.; Berguer, R. Effects of strain rate, mixing ratio, and stress–strain definition on the mechanical behavior of the polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) material as related to its biological applications. Biomed. Microdevices 2009, 11, 503–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sui, G.; Wang, J.; Lee, C.C.; Lu, W.X.; Lee, S.P.; Leyton, J.V.; Wu, A.M.; Tseng, H.R. Solution-phase surface modification in intact poly(dimethylsiloxane) microfluidic channels. Anal. Chem. 2006, 78, 5543–5551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klapperich, C.M. Microfluidic diagnostics: time for industry standards. Expert Rev. Med. Devices 2009, 6, 211–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Attia, U.M.; Marson, S.; Alcock, J.R. Micro-injection moulding of polymer microfluidic devices. Microfluid. Nanofluid. 2009, 7, 1–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Becker, H.; Locascio, L.E. Polymer microfluidic devices. Talanta 2002, 56, 267–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arvelo, M.K.; Matteucci, M.; Sorensen, K.T.; Bilenberg, B.; Vannahme, C.; Kristensen, A.; Berg-Sørensen, K. Optical manipulation with two beam traps in microfluidic polymer systems. In Proceedings of the 20th Microoptics Conference (MOC), Fukuoka, Japan, 25–28 October 2015; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA; pp. 1–2. [Google Scholar]
- De Coster, D.; Ottevaere, H.; Vervaeke, M.; Van Erps, J.; Callewaert, M.; Wuytens, P.; Simpson, S.H.; Hanna, S.; De Malsche, W.; Thienpont, H. Mass-manufacturable polymer microfluidic device for dual fiber optical trapping. Opt. Express 2015, 23, 30991–31009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matteucci, M.; Triches, M.; Nava, G.; Kristensen, A.; Pollard, M.R.; Berg-Sørensen, K.; Taboryski, R.J. Fiber-Based, Injection-Moulded Optofluidic Systems: Improvements in Assembly and Applications. Micromachines 2015, 6, 1971–1983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Heckele, M.; Schomburg, W.K. Review on micro moulding of thermoplastic polymers. J. Micromech. Microeng. 2004, 14, R1–R14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mair, D.A.; Geiger, E.; Pisano, A.P.; Fréchet, J.M.J.; Svec, F. Injection moulded microfluidic chips featuring integrated interconnects. Lab Chip 2006, 6, 1346–1354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martínez Vázquez, R.; Trotta, G.; Volpe, A.; Bernava, G.; Basile, V.; Paturzo, M.; Ferraro, P.; Ancona, A.; Fassi, I.; Osellame, R. Rapid Prototyping of Plastic Lab-on-a-Chip by Femtosecond Laser Micromachining and Removable Insert Microinjection Moulding. Micromachines 2017, 8, 328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, P.H.; Cheng, C.W.; Chang, C.P.; Wu, T.M.; Wang, J.K. Fabrication of large-area hydrophobic surfaces with femtosecond-laser structured moulds. J. Micromech. Microeng. 2011, 21, 115032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, D.M.; Jiang, J.; Meng, W.J.; Wang, W. Fabrication of high-aspect-ratio microscale Ta mould inserts with micro electrical discharge machining. Microsyst Technol. 2007, 13, 503–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volpe, A.; Di Niso, F.; Gaudiuso, C.; De Rosa, A.; Martínez Vázquez, R.; Ancona, A.; Lugarà, P.M.; Osellame, R. Welding of PMMA by a femtosecond fiber laser. Opt. Express 2015, 23, 4114–4124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costa, F.; Tosello, G.; Whiteside, B. Best practice strategies for validation of micro moulding process simulation. In Proceedings of the Polymer Process Engineering Conference, Bradford, UK, 27–28 Octorber 2009; Coates, P., Ed.; University of Bradford: Bradford, UK; pp. 331–364. [Google Scholar]
- Marhöfer, D.M.; Tosello, G.; Hansen, H.N.; Islam, A. Advancements on the simulation of the micro injection moulding process. In Proceedings of the Multi-Material Micro Manufacture (4M) Int. Conf., San Sebastian, Spain, 8–10 October 2013; pp. 77–81. [Google Scholar]
- Trotta, G.; Ancona, A.; Volpe, A.; Di Niso, F.; Fassi, I. Improving the flexibility of micro injection moulding by exploiting fs-laser micro milling to realize mould inserts with complex 3D microfeatures. In Proceedings of the 4M/ICOMM2015 Int. Conf., Milano, Italy, 31 March–2 April 2015; pp. 354–357. [Google Scholar]
- De Marco, C.; Eaton, S.M.; Martinez-Vazquez, R.; Rampini, S.; Cerullo, G.; Levi, M.; Turri, S.; Osellame, R. Solvent vapor treatment controls surface wettability in PMMA femtosecond-laser-ablated microchannels. Microfluid. Nanofluid. 2013, 14, 171–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]











| Material | Tmelt (°C) | Tmould (°C) | Vinj (mm/s) | Phold (bar) | thold (s) | tcool (s) | Run (mm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PMMA | 250 | 80 | 100 | 1000 | 5 | 5 | 18 |
| Dimensions measured | Confocal measurement of the mould insert inverse microfeatures (Figure 6) (µm) | Confocal measurements of microfeatures on lower shell (µm) |
|---|---|---|
| µchannel width | 113 ± 0.1 | 113 ± 2.8 |
| µchannel height | 106 ± 0.4 | 105 ± 1.2 |
| V-groove height (depth) | 190 ± 0.7 | 188 ± 1.2 |
| V-groove width | 237 ± 0.6 | 242 ± 1.6 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Trotta, G.; Martínez Vázquez, R.; Volpe, A.; Modica, F.; Ancona, A.; Fassi, I.; Osellame, R. Disposable Optical Stretcher Fabricated by Microinjection Moulding. Micromachines 2018, 9, 388. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi9080388
Trotta G, Martínez Vázquez R, Volpe A, Modica F, Ancona A, Fassi I, Osellame R. Disposable Optical Stretcher Fabricated by Microinjection Moulding. Micromachines. 2018; 9(8):388. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi9080388
Chicago/Turabian StyleTrotta, Gianluca, Rebeca Martínez Vázquez, Annalisa Volpe, Francesco Modica, Antonio Ancona, Irene Fassi, and Roberto Osellame. 2018. "Disposable Optical Stretcher Fabricated by Microinjection Moulding" Micromachines 9, no. 8: 388. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi9080388
APA StyleTrotta, G., Martínez Vázquez, R., Volpe, A., Modica, F., Ancona, A., Fassi, I., & Osellame, R. (2018). Disposable Optical Stretcher Fabricated by Microinjection Moulding. Micromachines, 9(8), 388. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi9080388










