Martensitic Transformation and Crystalline Structure of Ni50Mn50−xSnx Melt-Spun Heusler Alloys
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
- (i)
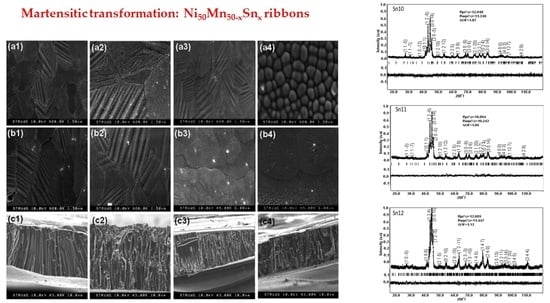
- From XRD Rietveld analysis: alloys with Sn10 and Sn11 have a textured monoclinic 7M martensite structure, while those with Sn12 have a 10M martensite structure. In contrast, the alloy with Sn13 has an austenite cubic L21 structure.
- (ii)
- The results from calorimetric measurements confirmed that all samples present a reversible transition (the austenite to martensite), and the change of the composition has an obvious effect on transformation behavior. With the increase/decrease of Sn/Mn content, the characteristic transformation temperatures (As, Af, Ms, Mf) drop to low temperature, which is due to the decrease of e/a. Consequently, Ms increases as the e/a parameter increases. In addition, the e/a control permits the development of alloys with the desired transformation temperatures. Likewise, the entropy and enthalpy change related to the transformation decreases as the e/a decreases. These trends cannot be extrapolated to further studies on functional response.
- (iii)
- Morphological analysis indicated that the SEM observations exhibit a microstructure with columnar grains and preferential orientation.
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, Z.-H.; Li, Z.; Yang, J.; Li, D.; Yang, B.; Zhang, Y.; Esling, C.; Zhao, X.; Zuo, L. Large magnetic entropy change and magnetostrain in a directionally solidified Ni45.7Co4.2Mn37.3Sb12.8 alloy. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2020, 500, 166379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sokolovskiy, V.; Miroskhina, M.; Zagrebin, M.; Buchelnikov, V. Prediction of giant magnetocaloric effect in Ni40Co10Mn26Al14 Heusler alloys: An insight from ab initio and Monte Carlo calculations. J. Appl. Phys. 2020, 127, 163901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Khabib, S.; Batti, K.P.; Srivastava, V.; James, R.D.; Leighton, C. Nanoscale magnetic phase competition throughout the Ni50−xCoxMn40Sn10 phase diagram: Insights from small-angle neutron scattering. Phys. Rev. Mater. 2019, 3, 104413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouabdallah, M.; Cizeron, G. Differential scanning calorimetry of transformation sequences during slow heating of Cu–Al–Ni shape memory alloys. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2002, 68, 951–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Auguet, C.; Isalgué, A.; Lovey, F.C.; Pelegrina, J.L.; Ruiz, S.; Torra, V. Metastable effects on martensitic transformation in SMA. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2007, 89, 537–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Topel-Zeren, E.; Aksit, A.; Aydogdu, Y. Shape memory effect of polymeric composite materials filled with NiMnSbB shape memory alloy for textile materials. Mater. Res. Express 2020, 7, 055702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canbay, C.A.; Karaduman, O.; Özkul, I. Lagging temperatura problema in DTA/DSC measurement on investigation of NiTi SMA. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González, A.; Bonastre, J.; Escoda, L.; Suñol, J.J. Thermal analysis of Fe (Co, Ni) based alloys prepared by mechanical alloying. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2007, 87, 255–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhobe, P.A.; Priolkar, K.R.; Nigam, A.K. Room temperature magnetocaloriceffect in Ni–Mn–In. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2007, 91, 242503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutou, Y.; Imano, Y.; Koeda, N.; Omori, T.; Kainuma, R.; Ishida, K.; Oikawa, K. Magnetic and martensitic transformations of NiMnX (X = In, Sn, Sb) ferromagnetic shape memory alloys. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2004, 85, 4358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krenke, T.; Acet, M.; Wassermann, E.F.; Moya, X.; Manosa, L.; Planes, A. Martensitic transition and the nature of ferromagnetism in the austenitic and martensitic states of Ni-Mn-Sn alloys. Phys. Rev. B 2005, 72, 014412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, P.J.; Gandy, A.P.; Ishida, K.; Kainuma, R.; Kanomata, T.; Neumann, K.U.; Ouladdiaf, B.; Ziebeck, K.R.A. The magnetic and structural properties of the magnetic shape memory compound Ni2Mn1.44Sn0.56. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 2006, 18, 2249–2259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koyama, K.; Watanabe, K.; Kanomata, T.; Kainuma, R.; Oikawa, K.; Ishida, K. Observation of field-induced reverse transformation in ferromagnetic shape memory alloy Ni50Mn36Sn14. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2006, 88, 132505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrisek, V.; Dusek, M. The Crystallographic Computing System; Institute of Physics: Prague, Czech Republic, 2000; Available online: http://www.xrey.fzu.cz/jana/jana.html (accessed on 1 May 2020).
- Coll, R.; Escoda, L.; Saurina, J.; Hernando, B.; Suñol, J.J. Martensitic transformation in Mn-Ni-Sn Heusler alloys. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2010, 99, 905–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Llamazares, J.L.; Sánchez, T.; Santos, J.-D.; Pérez, M.J.; Sánchez, M.L.; Hernando, B.; Escoda, L.; Suñol, J.J.; Varga, R. Martensitic phase transformation in rapidly solidified Mn50Ni40In10 alloy ribbons. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2008, 92, 012513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bachaga, T.; Daly, R.; Khitouni, M.; Escoda, L.; Saurina, J.; Suñol, J.J. Thermal and Structural Analysis of Mn49.3Ni43.7Sn7.0 Heusler Alloy Ribbons. J. Entropy 2015, 17, 646–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rekik, H.; Krifa, M.; Bachaga, T.; Escoda, L.; Sunol, J.J.; Khitouni, M.; Chemingui, M. Structural and martensitic transformation of MnNiSn shape memory alloys. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2017, 90, 291–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, H.; Wu, D.; Xue, S.; Frenzel, J.; Eggeler, G.; Zhai, Q. Martensitic transformation in rapidly solidified Heusler Ni49Mn39Sn12 ribbons. Acta Mater. 2011, 59, 5692–5699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaufman, L.; Hullert, M. Thermodynamics of martensite transformation. In Martensite; Olson, G.B., Owen, W.S., Eds.; ASM International: Cambridge, UK, 1992; pp. 41–58. [Google Scholar]
- Hernando, B.; Sanchez-Llamazares, J.L.; Santos, J.D.; Sanchez, M.L.; Escoda, L.; Sunol, J.J.; Varga, R.; Garcia, C.; Gonzalez, J. Grain oriented NiMnSn and NiMnIn Heusler alloys ribbons produced by melt spinning: Martensitic transformation and magnetic properties. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2009, 321, 763–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, J.D.; Sanchez, T.; Alvarez, P.; Sanchez, M.L.; Sanchez-Llamazares, J.L.; Hernando, B.; Escoda, L.; Suñol, J.J.; Varga, R. Microstructure and magnetic properties of Ni50Mn37Sn13 Heusler alloy ribbons. J. Appl. Phys. 2008, 103, 07B326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Planes, A.; Manosa, L.; Acet, M. Magnetocaloric effect and its relation to shape-memory properties in ferromagnetic Heusler alloys. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 2009, 21, 233201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanchez-Alarcos, V.; Recarte, V.; Perez-Landazabal, J.L.; Gomez-Polo, C.; Rodriguez-Velamazan, J.A. Role of magnetism on the martensitic transformation in Ni–Mn-based magnetic shape memory alloys. Acta Mater. 2012, 60, 459–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chernenko, V.A. Compositional instability of beta-phase in Ni–Mn–Ga alloys. Scr. Mater. 1999, 40, 523–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krenke, T.; Moya, X.; Aksoy, S.; Acet, M.; Entel, P.; Manosa, L.; Planes, A.; Elerman, Y.; Yücel, A.; Wassermann, E.F. Electronic aspects of the martensitic transition in Ni–Mn based Heusler alloys. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2007, 310, 2788–2789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deltell, A.; Escoda, L.; Saurina, J.; Suñol, J.J. Martensitic transformation in Ni-Mn-Sn-Co Heusler alloys. Metals 2015, 5, 695–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Álvarez-Alonso, P.; Aguilar-Ortiz, C.O.; Villa, E.; Nespoli, A.; Flores-Zúñiga, H.; Chernenko, V.A. Conventional and inverse elastocaloric effect in Ni-Fe-Ga and Ni-Mn-Sn ribbons. Scr. Mater. 2017, 128, 36–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saini, D.; Singh, S.; Banerjee, M.K.; Sachdev, K. Microstructure and phase transformation in Ni50Mn40Sn10 shape memory alloy. Powder Metall. Met. Ceram. 2018, 57, 361–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Billman, J.; Shamberger, P.J. Size effects in the martensitic transformation hysteresis in Ni-Mn-Sn Heusler alloy films. Acta Mater. 2019, 180, 116e125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| Alloy/Sample | Crystallographic Structure | Lattice Parameters/nm |
|---|---|---|
| Sn10 | Monoclinic 7M | a = 0.42824(4) b = 0.57874(7) c = 0.43426(5) β = 93.86° |
| Sn11 | Monoclinic 7M | a = 0.42806(6) b = 0.57277(3) c = 0.43321(8) β = 93.84° |
| Sn12 | Monoclinic 10M | a = 0.43326(2) b = 0.56412(9) c = 2.11706(7) β = 88.32° |
| Sn13 | Cubic L21 | a = 0.59827(5) |
| Sample | e/a | Ms/K | Mf/K | As/K | Af/K | T0/K | ∆H/J mol−1 | ∆S/J mol−1 K−1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sn10 | 8.20 | 418.5 | 392 | 405 | 427 | 422.75 | 1326 (h) 1334 (c) | 3.134 (h) 3.156 (c) |
| Sn11 | 8.17 | 380 | 361 | 367 | 391 | 385.5 | 1112 (h) 1126 (c) | 2.855 (h) 2.921 (c) |
| Sn12 | 8.14 | 345 | 330 | 335 | 361 | 353.2 | 890 (h) 894 (c) | 2. 512 (h) 2.531 (c) |
| Sn13 | 8.11 | 297 | 284 | 293 | 315 | 306 | 669 (h) 665 (c) | 2.186 (h) 2.173 (c) |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ameur, R.; Chemingui, M.; Bachaga, T.; Escoda, L.; Khitouni, M.; Suñol, J.-J. Martensitic Transformation and Crystalline Structure of Ni50Mn50−xSnx Melt-Spun Heusler Alloys. Crystals 2020, 10, 853. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst10100853
Ameur R, Chemingui M, Bachaga T, Escoda L, Khitouni M, Suñol J-J. Martensitic Transformation and Crystalline Structure of Ni50Mn50−xSnx Melt-Spun Heusler Alloys. Crystals. 2020; 10(10):853. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst10100853
Chicago/Turabian StyleAmeur, Rim, Mahmoud Chemingui, Tarek Bachaga, Lluisa Escoda, Mohamed Khitouni, and Joan-Josep Suñol. 2020. "Martensitic Transformation and Crystalline Structure of Ni50Mn50−xSnx Melt-Spun Heusler Alloys" Crystals 10, no. 10: 853. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst10100853
APA StyleAmeur, R., Chemingui, M., Bachaga, T., Escoda, L., Khitouni, M., & Suñol, J.-J. (2020). Martensitic Transformation and Crystalline Structure of Ni50Mn50−xSnx Melt-Spun Heusler Alloys. Crystals, 10(10), 853. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst10100853