Enhancing the Solubility and Dissolution Performance of Safinamide Using Salts
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Instrumentations and Materials
2.2. Preparation of Safinamide Salts
2.3. Solubility and Intrinsic Dissolution Rate (IDR) Studies
2.4. Stability Studies
3. Results
3.1. Crystal Structure Analysis
3.1.1. Crystal Structure of SAF-HCl (1:1) Salt
3.1.2. Crystal Structure of SAF-HBr (1:1) Salt
3.1.3. Crystal Structure of SAF/MA (1:1) Salt
3.1.4. Crystal Structure of SAF/MA/H2O (1:1:1) Salt Hydrate
3.2. Powder X-ray Diffraction (PXRD) Analyse
3.3. Thermal Analyses
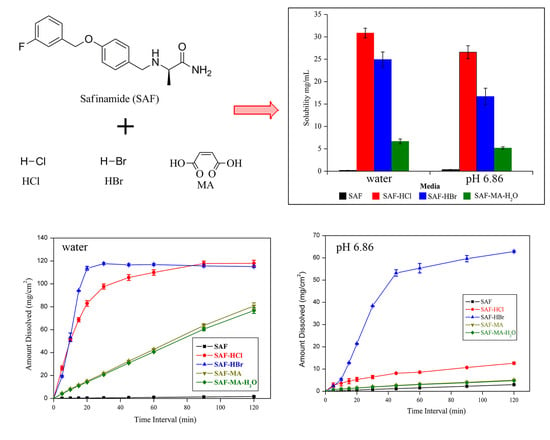
3.4. Solubility and Dissolution Studies
3.5. Stability Studies
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lipinski, C.A.; Lombardo, F.B.; Dominy, W.; Feeney, P.J. Experimental and computational approaches to estimate solubility and permeability in drug discovery and development q settings. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2001, 1–3, 3–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lipinski, C.A. Poor aqueous solubility-An industry wide problem in drug discovery. Am. Pharm. Rev. 2002, 5, 82–85. [Google Scholar]
- Leuner, C.; Dressman, J. Improving drug solubility for oral delivery using solid dispersions. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2000, 50, 47–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hecq, J.; Deleers, M.; Fanara, D.; Vranckx, H.; Amighi, K. Preparation and characterization of nanocrystals for solubility and dissolution rate enhancement of nifedipine. Int. J. Pharm. 2005, 1–2, 167–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmad, I.; Ganie, A.A.; Dar, A.A. Achievement of enhanced solubility and improved optics in the molecular complexes based on sulfonate-pyridinium supramolecular synthon. CrystEngComm 2020, 22, 3933–3942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, N.; Nair, R.H. Engineering cocrystal solubility, stability, and pH(max) by micellar solubilization. J. Pharm. Sci. 2011, 100, 5219–5234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Zhang, B.; Gao, Y.; Zhang, J.; Shi, L. Baicalein-nicotinamide cocrystal with enhanced solubility, dissolution, and oral bioavailability. J. Pharm. Sci. 2014, 103, 2330–2337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanphui, P.; Tothadi, S.; Ganguly, S.; Desiraju, G.R. Salt and cocrystals of sildenafil with dicarboxylic acids: Solubility and pharmacokinetic advantage of the glutarate salt. Mol. Pharm. 2013, 10, 4687–4697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, L.; Zhang, X.R.; Yang, S.P.; Liu, J.J.; Chen, C.J. Improved solubility of vortioxetine using c2-c4 straight-chain dicarboxylic acid salt hydrates. Crystals 2018, 8, 352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, X.L.; Wu, C.; Li, J.H.; Liu, L.C.; He, X.; Lu, T.B.; Chen, J.M. Modulating the solubility and pharmacokinetic properties of 5-fluorouracil via cocrystallization. CrystEngComm 2020, 22, 3670–3682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Couillaud, B.M.; Espeau, P.; Mignet, N.; Corvis, Y. State of the art of pharmaceutical solid forms: From crystal property issues to nanocrystals formulation. ChemMedChem 2019, 14, 8–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sathisaran, I.; Dalvi, S. Engineering Cocrystals of Poorly Water-Soluble Drugs to Enhance Dissolution in Aqueous Medium. Pharmaceutics 2018, 10, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Owoyemi, B.C.D.; da Silva, C.C.; Diniz, L.F.; Souza, M.S.; Ellena, J.A.; Carneiro, R.L. Fluconazolium oxalate: Synthesis and structural characterization of a highly soluble crystalline form. CrystEngComm 2019, 21, 1114–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arabiani, M.R.; Lodagekar, A.; Yadav, B.; Chavan, R.B.; Shastri, N.R.; Purohit, P.Y.; Shelat, P.; Dave, D. Mechanochemical synthesis of brexpiprazole cocrystals to improve its pharmaceutical attributes. CrystEngComm 2019, 21, 800–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, B.; Yoon, W.; Yun, J.; Ban, E.; Yun, H.; Kim, A. Emodin-nicotinamide (1:2) cocrystal identified by thermal screening to improve emodin solubility. Int. J. Pharm. 2019, 557, 26–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Q.; Dun, J.; Chen, J.M.; Liu, S.; Sun, C.C. Improving solid-state properties of berberine chloride through forming a salt cocrystal with citric acid. Int. J. Pharm. 2019, 554, 14–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Childs, S.L.; Hardcastle, K.I. Cocrystals of chlorzoxazone with carboxylic acids. CrystEngComm 2007, 9, 364–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brittain, H.G. Cocrystal Systems of Pharmaceutical Interest: 2011. Cryst. Growth Des. 2012, 12, 1046–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbas, R.; Font-Bardia, M.; Paradkar, A.; Hunter, C.A.; Prohens, R. Combined Virtual/Experimental Multicomponent Solid Forms Screening of Sildenafil: New Salts, Cocrystals and Hybrid Salt-Cocrystals. Cryst. Growth Des. 2018, 18, 7618–7627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nechipadappu, S.K.; Reddy, I.R.; Tarafder, K.; Trivedi, D.R. Salt/Cocrystal of Anti-Fibrinolytic Hemostatic Drug Tranexamic acid: Structural, DFT, and Stability Study of Salt/Cocrystal with GRAS Molecules. Cryst. Growth Des. 2018, 19, 347–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarma, B.; Bora, P.; Saikia, B. Regulation of π…π Stacking Interactions in Small Molecule Cocrystals and/or Salts for Physiochemical Property Modulation. Cryst. Growth Des. 2018, 18, 1448–1458. [Google Scholar]
- Onofrj, M.; Bonanni, L.; Thomas, A. An expert opinion on safinamide in Parkinson’s disease. Expert. Opin. Investig. Drugs 2008, 17, 1115–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borgohain, R.; Kandadai, R.M. Safinamide: A novel anti-Parkinsonian drug with multiple actions. Neurodegener. Dis. Manag. 2013, 3, 231–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stocchi, F.; Arnold, G.; Onofrj, M.; Kwiecinski, H.; Faroello, R.G. Improvement of motor function in early Parkinson disease by safinamide. Neurology 2004, 63, 746–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deeks, E.D. Safinamide: First Global Approval. Drugs 2015, 75, 705–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blair, H.A.; Dhilon, S. Safinamide: A Review in Parkinson’s Disease. CNS Drugs 2017, 31, 169–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheldrick, G.M. SHELXS 97, Program for the Solution of Crystal Structure; University of Göttingen: Göttingen, Germany, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Sheldrick, G.M. SHELXL97, Program for the Refinement of Crystal Structure; University of Göttingen: Göttingen, Germany, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Schultheiss, N. Pharmaceutical Cocrystals and Their Physicochemical Properties. Cryst. Growth Des. 2009, 9, 2950–2967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]










| Title | SAF-HCl | SAF-HBr | SAF-MA | SAF-MA-H2O |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chemical formula | C17H20N2O2F+, Cl− | C17H20N2O2F+, Br− | C17H20N2O2F+, C4H3O4− | C17H20N2O2F+, C4H3O4−, H2O |
| Molecular formula | C17H20N2O2FCl | C17H20N2O2FBr | C21H24N2O6F | C21H25N2O7F |
| Formula weight | 338.80 | 383.26 | 418.41 | 436.43 |
| Crystal system | orthorhombic | orthorhombic | orthorhombic | triclinic |
| Space group | P212121 | P212121 | P212121 | P1 |
| a [Å] | 5.2766(8) | 5.2340(4) | 5.7326(5) | 5.9202(8) |
| b [Å] | 12.174(2) | 13.8352(11) | 9.2498(12) | 8.5781(11) |
| c [Å] | 26.389(5) | 24.0985(17) | 38.155(4) | 11.8413(15) |
| α[°] | 90 | 90 | 90 | 105.072(11) |
| β[°] | 90 | 90 | 90 | 101.299(11) |
| γ[°] | 90 | 90 | 90 | 105.145(11) |
| Z | 4 | 4 | 4 | 1 |
| V (Å3) | 1695.2(5) | 1745.1(2) | 2023.2(4) | 537.57(12) |
| Dcalc (g cm−3) | 1.327 | 1.459 | 1.374 | 1.348 |
| μ (mm−1) | 0.246 | 2.376 | 0.107 | 0.107 |
| R1 (I > 2σ (I)) | 0.0633 | 0.0449 | 0.0809 | 0.0512 |
| wR2 (all data, F2) | 0.0780 | 0.0783 | 0.1372 | 0.1062 |
| GOF | 0.955 | 0.994 | 1.062 | 1.029 |
| Rint | 0.0537 | 0.0588 | 0.0917 | 0.0323 |
| Largest diff. peak and hole (e·Å−3) | 0.200/−0.182 | 0.416/−0.331 | 0.184/−0.205 | 0.153/−0.124 |
| CCDC | 2010647 | 2010646 | 2010649 | 2010648 |
| H-Bond | d(D−H) | d(H···A) | d(D···A) | ∠(DHA) | Symmetry Code |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SAF-HCl | |||||
| N1+−H1A···Cl1 | 0.97 | 2.46 | 3.366(4) | 156 | −x, y−1/2, −z+1/2 |
| N1+−H1B···Cl1 | 0.89 | 2.36 | 3.219(4) | 164 | −x, y−1/2, −z+1/2 |
| N2−H2A···Cl1 | 0.86 | 2.37 | 3.228(4) | 175 | x, y−1, z |
| N2−H2B···Cl1 | 0.89 | 2.56 | 3.332(4) | 145 | x−1, y−1, z |
| SAF-HBr | |||||
| N1+−H1A···Br1 | 0.89 | 2.54 | 3.436(4) | 176 | −x+1, y+1/2, −z+1/2 |
| N1+−H1B···Br1 | 1.04 | 2.45 | 3.410(4) | 152 | −x+1, y+1/2, −z+1/2 |
| N2−H2A···Br1 | 0.86 | 2.79 | 3.503(4) | 141 | x+1, y+1, z |
| N2−H2B···Br1 | 0.86 | 2.59 | 3.443(4) | 170 | x, y+1, z |
| SAF-MA | |||||
| N1+−H1A···O3 | 0.87 | 1.89 | 2.760(5) | 174 | x, y, z |
| N1+−H1B···O4 | 1.01 | 2.05 | 3.049(5) | 169 | x−1, y, z |
| N2−H2A···O2 | 0.96 | 1.97 | 2.908(5) | 163 | −x+1, y−1/2, −z+1/2 |
| N2−H2B···O5 | 0.90 | 2.35 | 3.066(5) | 137 | −x+1, y−1/2, −z+1/2 |
| O5−H5···O4 | 0.94 | 1.51 | 2.439(5) | 173 | x, y, z |
| SAF-MA-H2O | |||||
| N1+−H1A···O7 | 0.90 | 1.92 | 2.787(3) | 161 | x, y−1, z |
| N1+−H1B···O6 | 0.90 | 1.99 | 2.825(3) | 153 | x, y, z |
| N2−H2A···O3 | 0.86 | 2.07 | 2.909(3) | 166 | x+1, y, z+1 |
| N2−H2B···O4 | 0.87 | 2.19 | 3.000(3) | 155 | x, y, z+1 |
| O7−H7C···O6 | 0.90 | 2.09 | 2.846(3) | 141 | x−1, y+1, z |
| O4−H4···O5 | 0.90 | 1.62 | 2.402(3) | 142 | x, y, z |
| Compound | Aqueous Solubility (mg/mL) | Solubility at pH 6.86 (mg/mL) | IDR in Aqueous Medium (mg/cm2/min) | IDR at pH 6.86 (mg/cm2/min) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SAF | 0.19 | 0.39 | 0.013 | 0.024 |
| SAF-HCl | 30.86 | 26.59 | 4.16 | 0.14 |
| SAF-HBr | 24.93 | 16.69 | 6.03 | 1.49 |
| SAF-MA | Unstable | Unstable | 0.67 | 0.037 |
| SAF-MA-H2O | 6.66 | 5.18 | 0.64 | 0.035 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gao, L.; Liu, Q.; Zhang, X.-R. Enhancing the Solubility and Dissolution Performance of Safinamide Using Salts. Crystals 2020, 10, 989. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst10110989
Gao L, Liu Q, Zhang X-R. Enhancing the Solubility and Dissolution Performance of Safinamide Using Salts. Crystals. 2020; 10(11):989. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst10110989
Chicago/Turabian StyleGao, Lei, Qian Liu, and Xian-Rui Zhang. 2020. "Enhancing the Solubility and Dissolution Performance of Safinamide Using Salts" Crystals 10, no. 11: 989. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst10110989
APA StyleGao, L., Liu, Q., & Zhang, X.-R. (2020). Enhancing the Solubility and Dissolution Performance of Safinamide Using Salts. Crystals, 10(11), 989. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst10110989