Response Improvement of Liquid Crystal-Loaded NRD Waveguide Type Terahertz Variable Phase Shifter
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. LC loaded NRD Waveguide Type Terahertz Phase Shifter
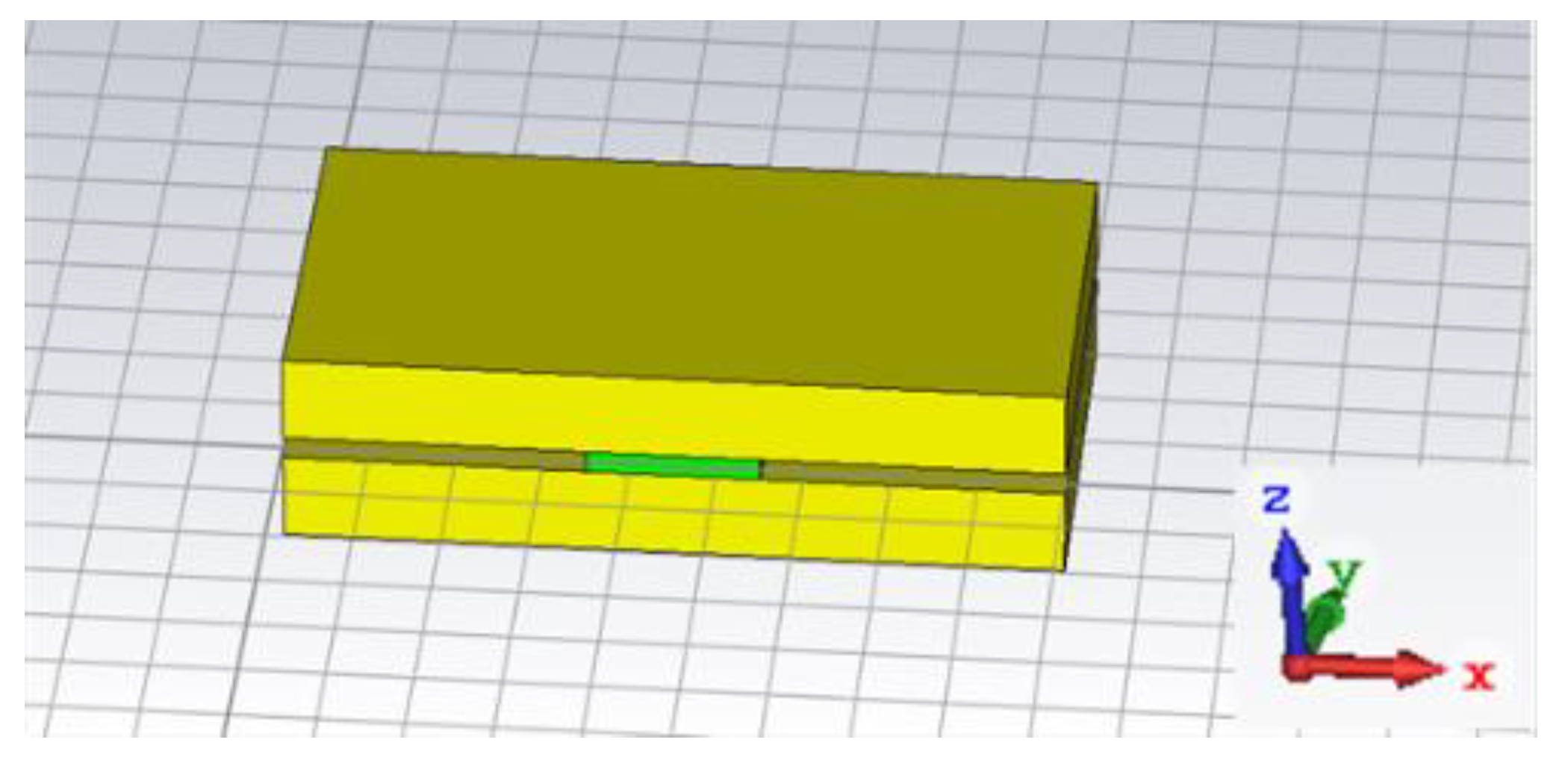
2.1. NRD Waveguide
2.1.1. Basic Structure and Operation
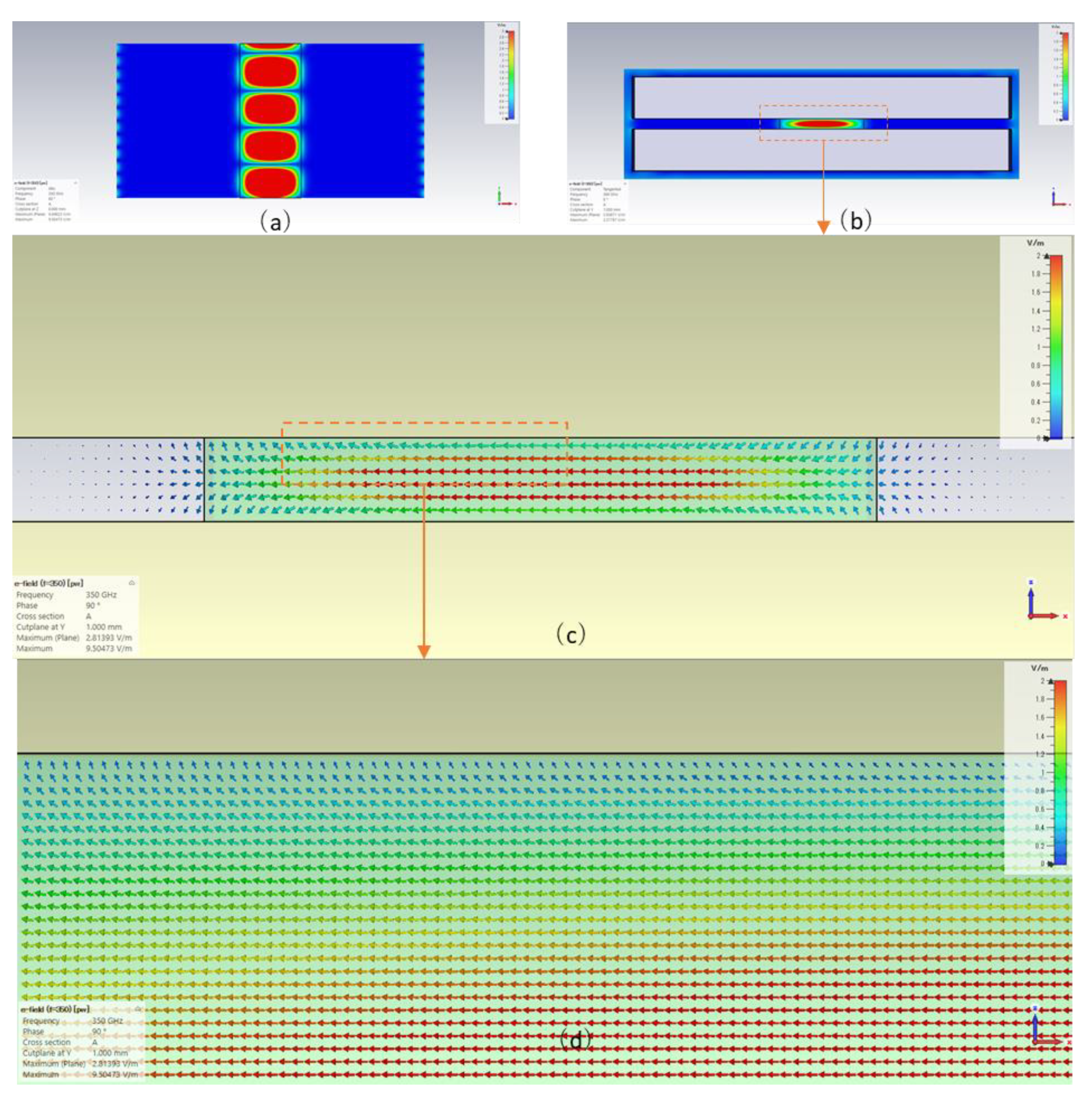
2.1.2. NRD Waveguide Operation by Simulation
2.2. LC loaded NRD Waveguide Type Terahertz Phase Shifter
2.2.1. Phase Change Mechanism of Terahertz Wave by the Liquid Crystal
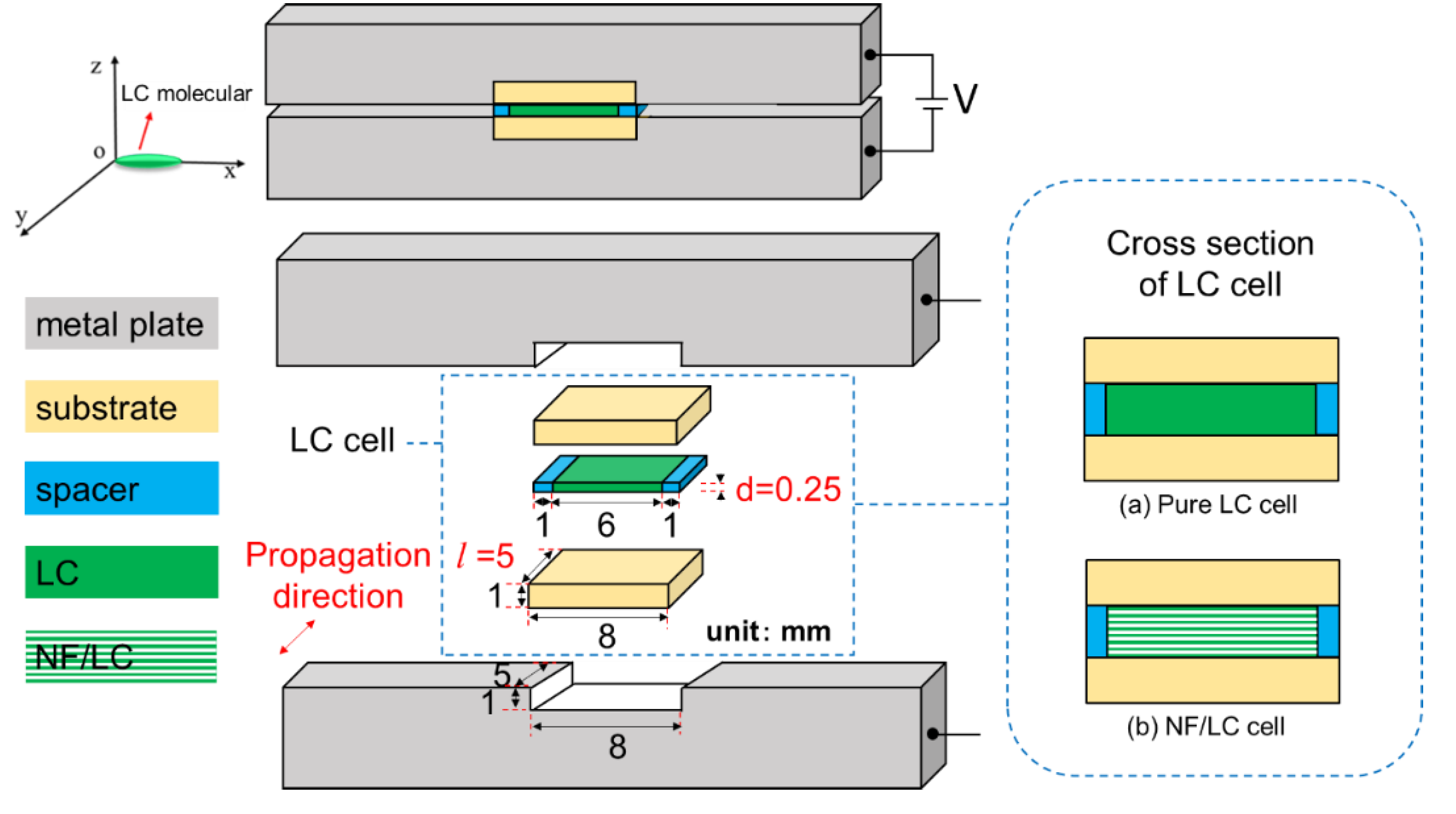
2.2.2. Structure of the Device
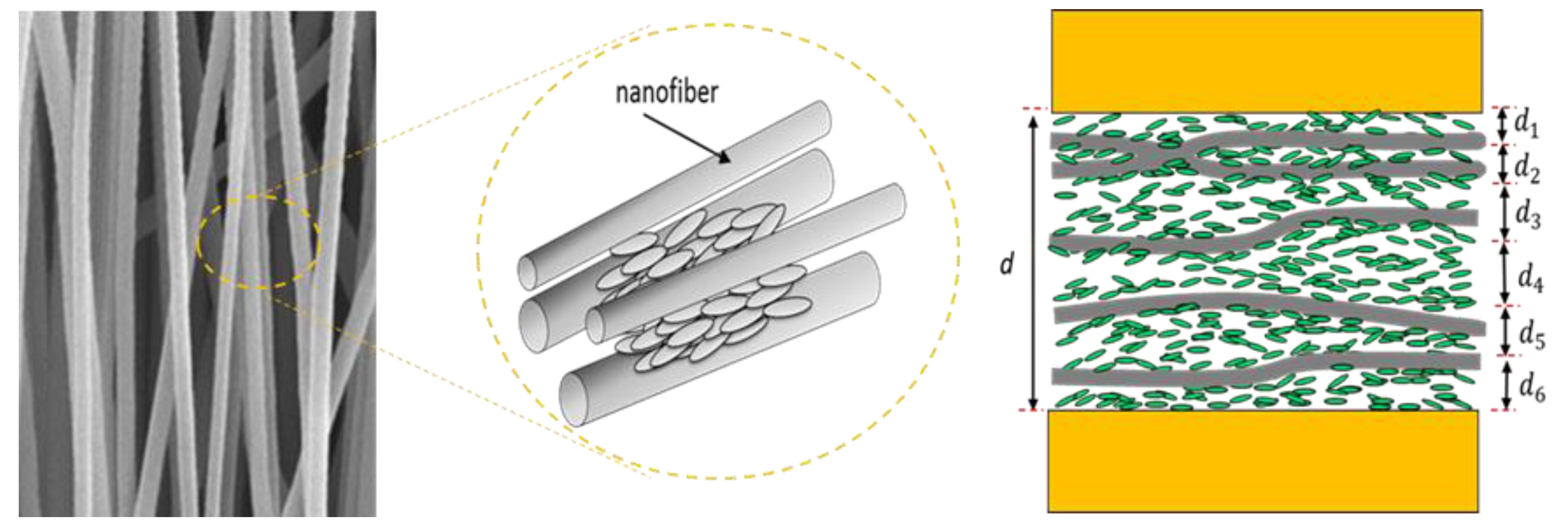
3. Improvement Principle
4. Measurement System
4.1. Permittivity Measurement System
4.2. Terahertz Wave Measurement System
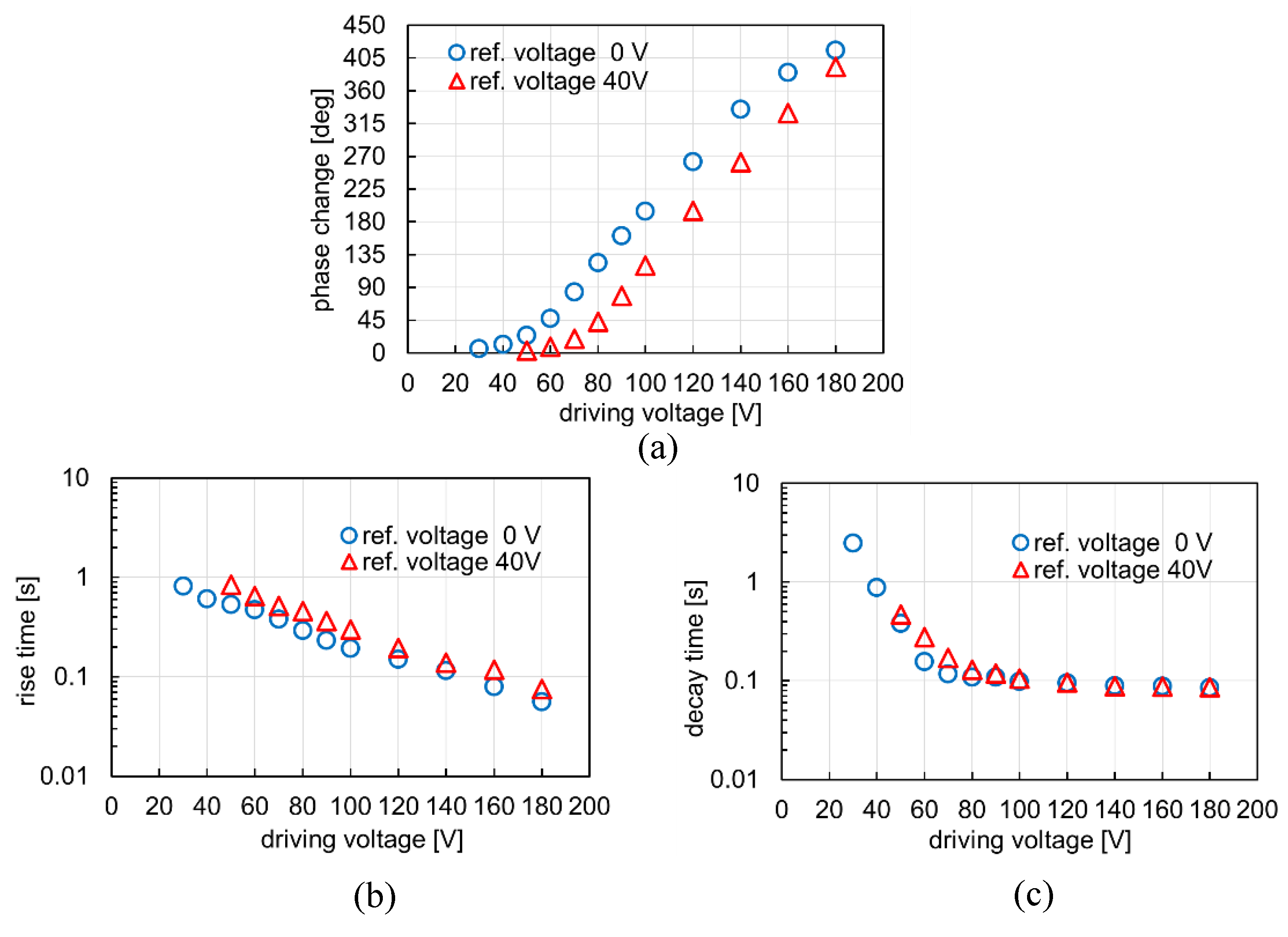
5. Improvement
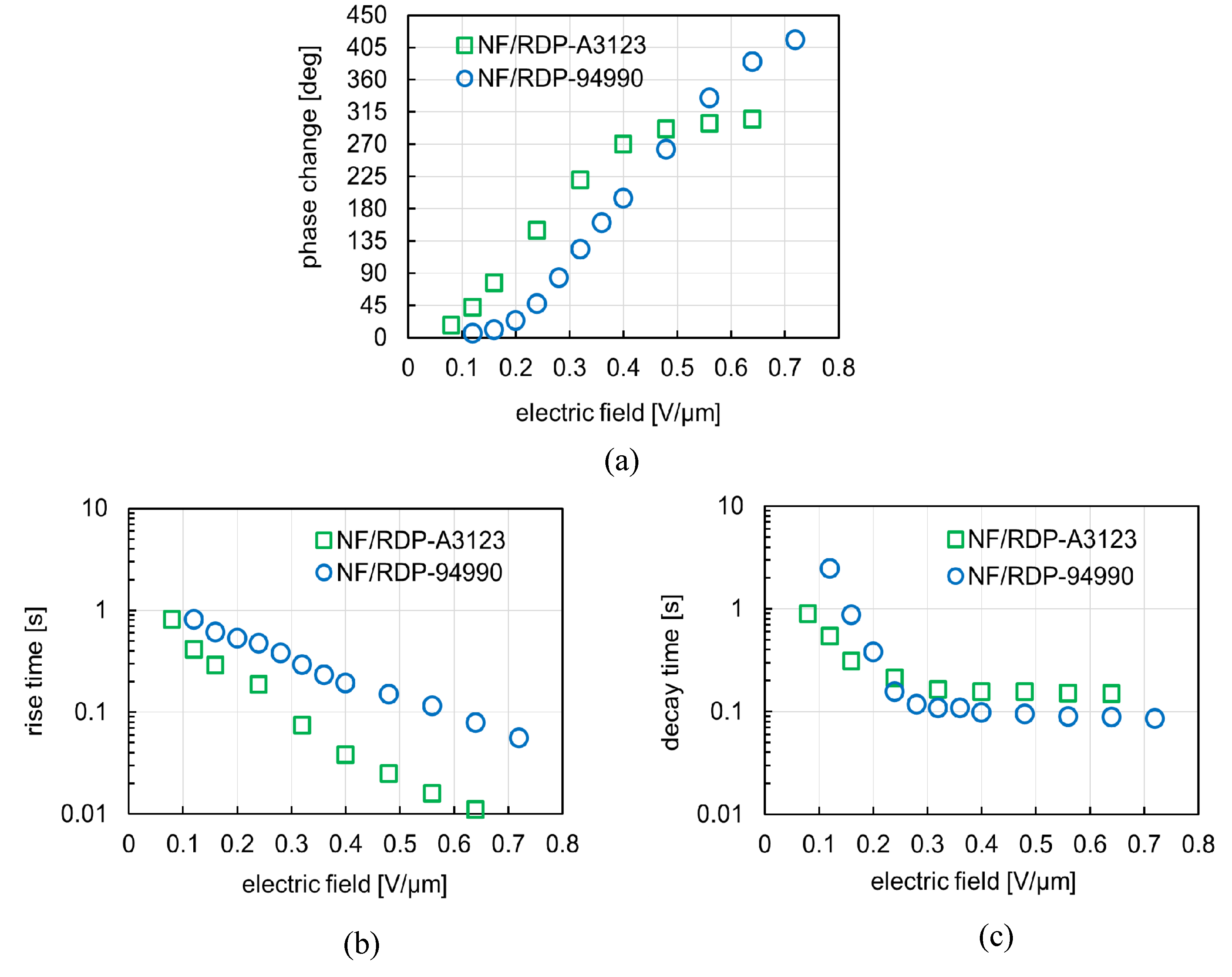
5.1. Two NLCs of RDP-A3123 and RDP-94990
5.2. Improvement Results
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Itoh, T.; Rivera, J. A Comparative Study of Millimeter-Wave Transmission Lines. Infrared Millim. Waves 1983, 9, 95–132. [Google Scholar]
- Khoo, I.C.; Wu, S.T. Optics and Nonlinear Optics of Liquid Crystals; World Scientific: Singapore, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Savo, S.; Shrekenhamer, D.; Padilla, W.J. Padilla, Liquid Crystal Metamaterial Absorber Spatial Light Modulator for THz Applications. Adv. Opt. Mater. 2014, 2, 275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L. Self-activating liquid crystal devices for smart laser protection. Liq. Cryst. 2016, 43, 2062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Urbas, A.M.; Li, Q. Nature-Inspired Emerging Chiral Liquid Crystal Nanostructures: From Molecular Self-Assembly to DNA Mesophase and Nanocolloids. Adv. Mater. 2018, 30, 1801335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Utsumi, Y.; Kamei, T.; Naito, R.; Saito, K. Measurement methods of nematic liquid crystal response time. Mol. Cryst. Liq. Cryst. 2005, 434, 337–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, K.C.; Margerum, J.D.; Lackner, A.M. Liquid crystal millimeter wave electronic phase shifter. Appl. Phys. Lett. 1993, 62, 1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bui, V.B.; Inoue, Y.; Moritake, H. NRD waveguide type terahertz phase shifter using Nematic liquid crystal. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 2019, 58, 22001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoneyama, T. NRD Guide: New Approach to Millimeter Wave. IEEJ 1996, 116, 20–23. (In Japanese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kuroki, F.; Sugioka, M.; Matsukawa, S.; Ikeda, K.; Yoneyama, T. High Speed ASK Transceiver Based on the NRD Guide Technology at 60GHz band. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 1998, 46, 806–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoneyama, T. Millimeter wave integrated circuits using nonradiative dielectric waveguide. IEICE Trans. 1990, J73-C-I, 87–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekisho, B.H.I. Ekisho Binran; Maruzen Kabushikigaisha: Tokyo, Japan, 2000; pp. 108, 477. (In Japanese) [Google Scholar]
- Utsumi, Y.; Kamei, T.; Saito, K.; Moritake, H. Increasing the speed of microstrip-line-type polymer-dispersed liquid-crystal loaded variable phase shifter. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 2005, 53, 3345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geary, J.M.; Goodby, J.W.; Kmetz, A.R.; Patel, J.S. The mechanism of polymer alignment of liquid-crystal materials. J. Appl. Phys. 1987, 62, 4100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Kumar, S. Submillisecond switching of nematic liquid crystal in cells fabricated by anisotropic phase-separation of liquid crystal and polymer mixture. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2005, 86, 71119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fujikake, H.; Kuki, T.; Nomoto, T.; Tsuchiya, Y.; Utsumi, Y. Thick polymer-stabilized liquid crystal films for microwave phase control. J. Appl. Phys. 2001, 89, 5295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucchetta, D.E.; Karapinar, R.; Manni, A.; Simoni, F. Phase-only modulation by nanosized polymer-dispersed liquid crystals. J. Appl. Phys. 2002, 91, 6060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moritake, H.; Umeno, S.; Nguyen, T.; Higuchi, H.; Kikuchi, H. Microstrip-Line-Type Microwave Variable Phase Shifter Using Polymer Stabilized Nematic Liquid Crystal. In Proceedings of the 24th International Liquid Crystal Conference, Mainz, Germany, 19–24 August 2012; p. 176. [Google Scholar]
- Umeno, S.; Nguyen, T.; Higuchi, H.; Kikuchi, H.; Moritake, H. Polymer Stabilized Nematic Liquid Crystal with Thermal Polymerization for Microwave Application. In Proceedings of the 1st Asian Liquid Crystal Conference, Yamanashi, Japan, 16–18 December 2012; p. 52. [Google Scholar]
- Nguyen, T.; Umeno, S.; Higuchi, H.; Kikuchi, H.; Moritake, H. Improvement of decay time in nematic-liquid-crystal-loaded coplanar-waveguide-type microwave phase shifter by polymer stabilizing method. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 2014, 53, 01AE08. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bui, V.B.; Inoue, Y.; Higuchi, H.; Kikuchi, H.; Moritake, H. Response improvement of microstrip line type microwave millimeter wave phase shifter using photopolymerizable polymer stabilized nematic liquid crystal. IEEJ Trans. FM 2017, 137, 356–362. (In Japanese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duong, T.Q.; Kobayashi, H.; Inoue, Y.; Moritake, H. Improved response time of thick liquid crystal device by using electrospun nanofiber. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 2017, 56, 61701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sill, T.J.; von Recum, H.A. Electrospinning: Applications in drug delivery and tissue engineering. Biomaterials 2008, 29, 1989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolanda, E.D.; Colemana, B.D.; Barnesa, C.P.; Simpsonb, D.G.; Wnekc, G.E.; Bowlina, G.L. Electrospinning polydioxanone for biomedical applications. Acta Biomater. 2005, 1, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.Y.; Jeong, L.; Kang, Y.O.; Lee, S.J.; Park, W.H. Electrospinning of polysaccharides for regenerative medicine. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2009, 61, 1020–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shah, P.N.; Manthe, R.L.; Lopina, S.T.; Yun, Y.H. Electrospinning of L-tyrosine polyurethanes for potential biomedical applications. Polymer 2009, 50, 2281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nirmala, R.; Navamathavan, R.; Kang, H.S.; El-Newehy, M.H.; Kim, H.Y. Preparation of polyamide-6/chitosan composite nanofibers by a single solvent system via electrospinning for biomedical applications. Biointerfaces 2011, 83, 173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agarwal, S.; Wendorff, J.H.; Greiner, A. Use of electrospinning technique for biomedical applications. Polymer 2008, 49, 5603–5621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dong, Z.; Kennedy, S.J.; Wu, Y. Electrospinning materials for energy-related applications and devices. J. Power Sources 2011, 196, 4886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raut, H.K.; Nair, A.S.; Dinachali, S.S.; Ganesh, V.A.; Walsh, T.M.; Ramakrishna, S. Porous SiO2 anti-reflective coatings on large-area substrates by electrospinning and their application to solar modules. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 2013, 111, 9–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Ding, C.X.; Zhang, L.C.; Xu, H.W.; Zhang, D.W.; Cheng, T.; Chen, C.H. A novel carbon–silicon composite nanofiber prepared via electrospinning as anode material for high energy-density lithium ion batteries. J. Power Sources 2010, 195, 5052–5056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Gao, C.; Wang, J.; Lu, B.; Chen, W.; Song, J.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, Z.; Pan, X.; Xie, E. TiO2 films with rich bulk oxygen vacancies prepared by electrospinning for dye-sensitized solar cells. J. Power Sources 2012, 214, 244–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasani-Sadrabadi, M.M.; Shabani, I.; Soleimani, M.; Moaddel, H. Novel nanofiber-based triple-layer proton exchange membranes for fuel cell applications. J. Power Sources 2011, 196, 4599–4603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sivakkumar, S.R.; Oh, J.S.; Kim, D.W. Polyaniline nanofibres as a cathode material for rechargeable lithium-polymer cells assembled with gel polymer electrolyte. J. Power Sources 2006, 163, 573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, I.; Hori, F.; Muko, A. Ekisho Nyumon; Saiwai Shobou: Tokyo, Japan, 1992; p. 168. (In Japanese) [Google Scholar]
- Setsuhara, H. Ekisho No Butsuri; Uchida Rokakuho: Tokyo, Japan, 2004; p. 50. (In Japanese) [Google Scholar]
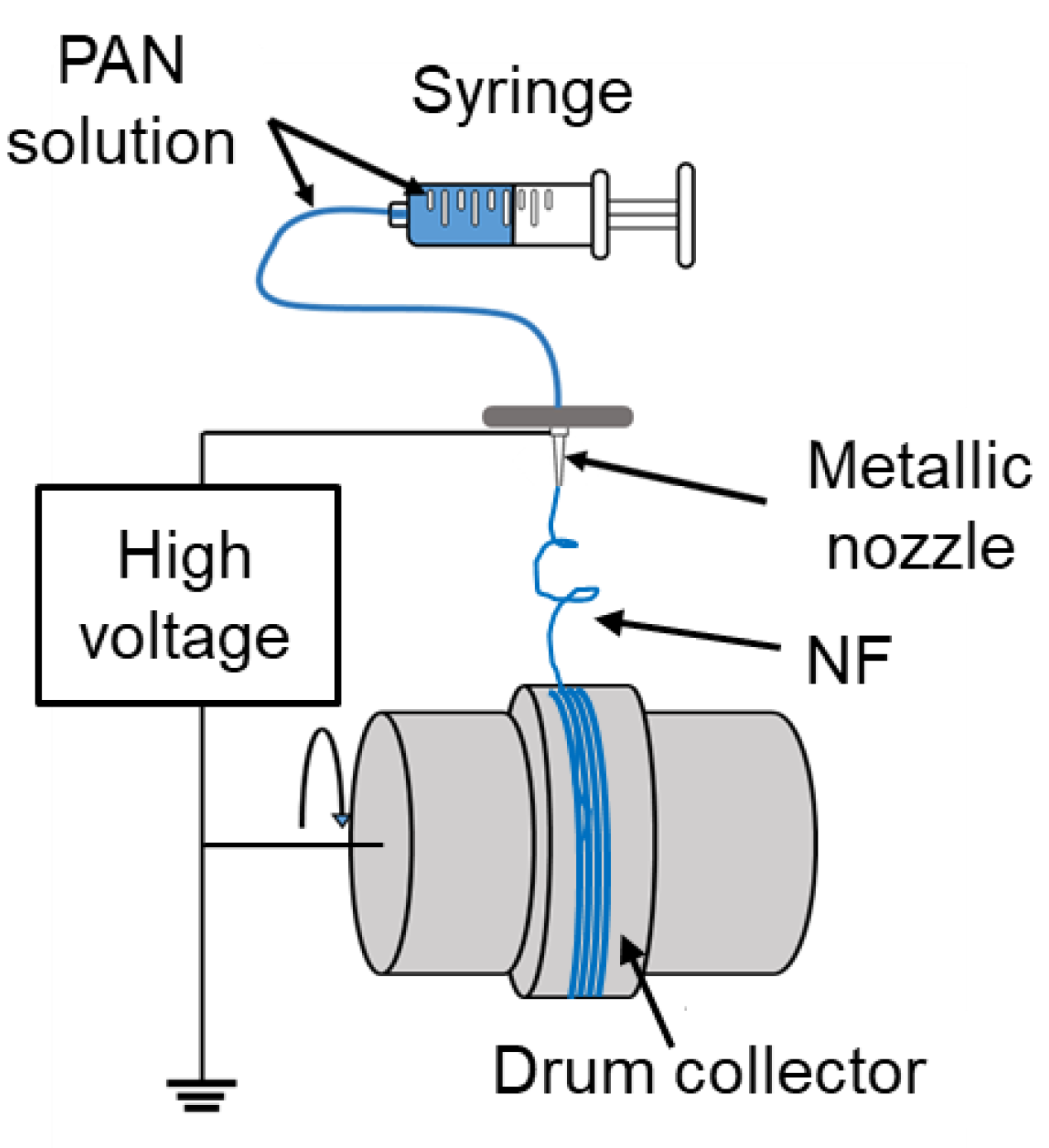


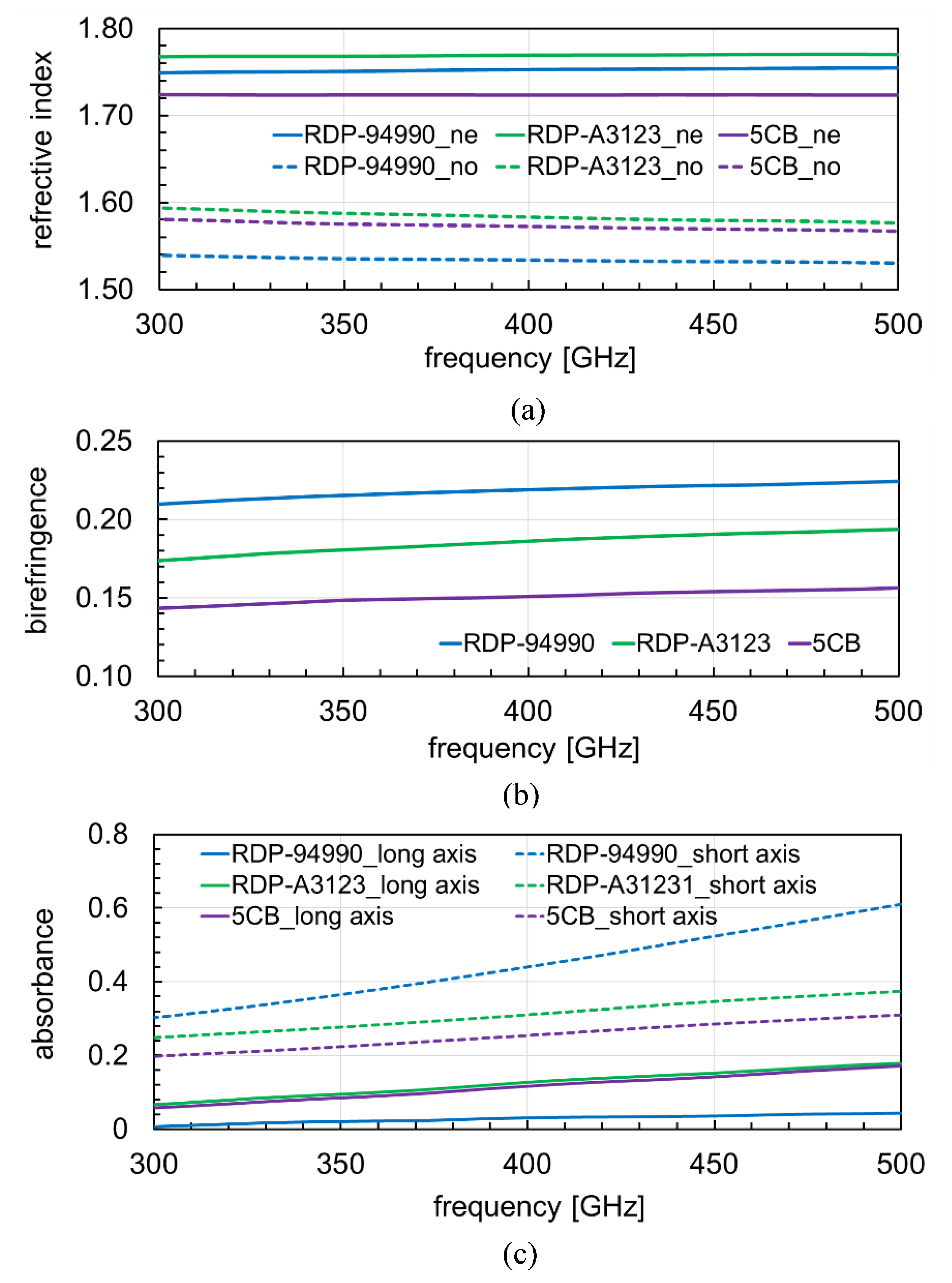

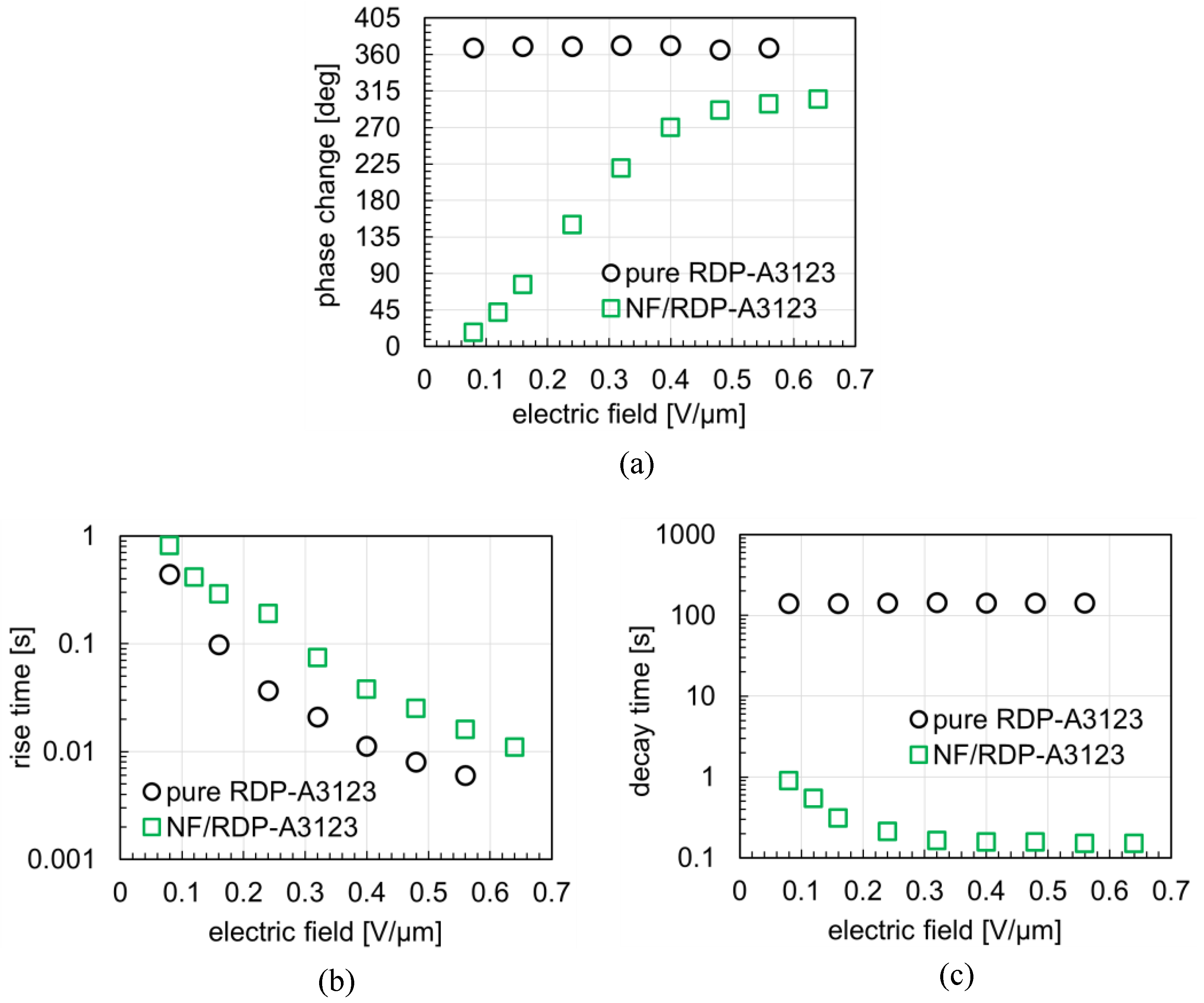
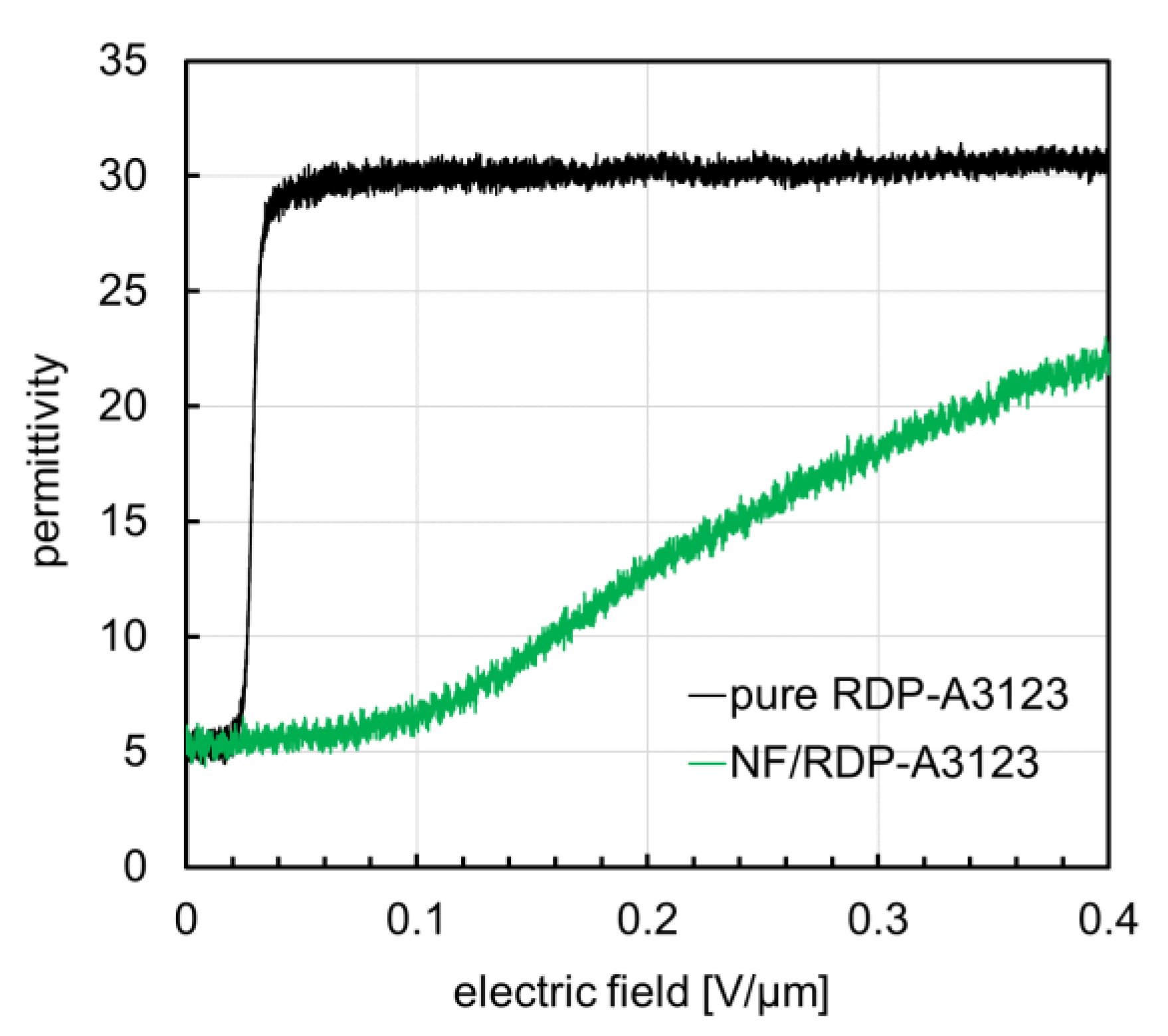
| NLCs | Phase Transition Temperature (°C) | Viscosity (mPa·s) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Crystal-Nematic | Nematic-Isotropic | ||
| 5CB | 24 | 35 | 22.5 |
| RDP-A3123 | −38 | 89 | 60.4 |
| RDP-94990 | −30 | 86 | 40.9 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lang, T.N.; Bui, V.B.; Inoue, Y.; Moritake, H. Response Improvement of Liquid Crystal-Loaded NRD Waveguide Type Terahertz Variable Phase Shifter. Crystals 2020, 10, 307. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst10040307
Lang TN, Bui VB, Inoue Y, Moritake H. Response Improvement of Liquid Crystal-Loaded NRD Waveguide Type Terahertz Variable Phase Shifter. Crystals. 2020; 10(4):307. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst10040307
Chicago/Turabian StyleLang, Trong Nghia, Van Bao Bui, Yo Inoue, and Hiroshi Moritake. 2020. "Response Improvement of Liquid Crystal-Loaded NRD Waveguide Type Terahertz Variable Phase Shifter" Crystals 10, no. 4: 307. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst10040307
APA StyleLang, T. N., Bui, V. B., Inoue, Y., & Moritake, H. (2020). Response Improvement of Liquid Crystal-Loaded NRD Waveguide Type Terahertz Variable Phase Shifter. Crystals, 10(4), 307. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst10040307





