Topological Defect Arrays in Nematic Liquid Crystals Assisted by Polymeric Pillar Arrays: Effect of the Geometry of Pillars
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Effect of the Diameter in Cylindrical Pillars on the Switching Between Patterns
3.2. Electro-Optic Properties Depending on the Diameter and Height of Cylindrical Pillars
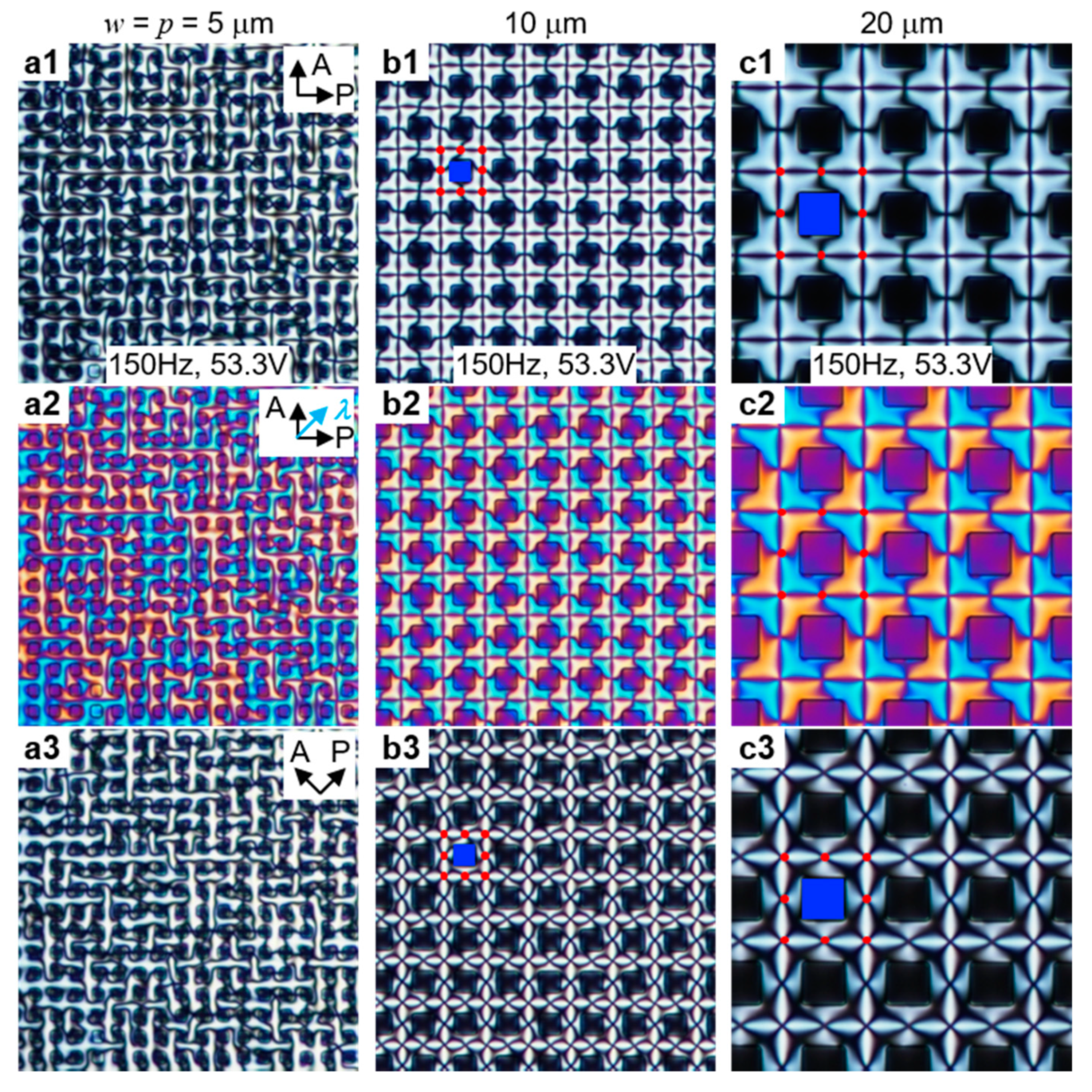
3.3. Effect of Square-Shaped Pillars on the Defect Array Formation
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Blanc, C.; Coursault, D.; Lacaze, E. Ordering nano- and microparticles assemblies with liquid crystals. Liq. Cryst. Rev. 2013, 1, 83–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muševič, I. Integrated and topological liquid crystal photonics. Liq. Cryst. 2014, 41, 418–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bukusoglu, E.; Bedolla Pantoja, M.; Mushenheim, P.C.; Wang, X.; Abbott, N.L. Design of responsive and active (soft) materials using liquid crystals. Annu. Rev. Chem. Biomol. Eng. 2016, 7, 163–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Gennes, P.-G.; Prost, J. The Physics of Liquid Crystals, 2nd ed.; Oxford University Press Press: Oxford, UK, 1993; ISBN 0198512856. [Google Scholar]
- Kléman, M. Defects in liquid crystals. Rep. Prog. Phys. 1989, 52, 555–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poulin, P.; Stark, H.; Lubensky, T.C.; Weitz, D.A. Novel colloidal interactions in anisotropic fluids. Science 1997, 275, 1770–1773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nych, A.; Ognysta, U.; Škarabot, M.; Ravnik, M.; Žumer, S.; Muševič, I. Assembly and control of 3D nematic dipolar colloidal crystals. Nat. Commun. 2013, 4, 1489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Beller, D.A.; Boniello, G.; Serra, F.; Stebe, K.J. Tunable colloid trajectories in nematic liquid crystals near wavy walls. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowick, M.J.; Chandar, L.; Schiff, E.A.; Srivastava, A.M. The cosmological Kibble mechanism in the laboratory: String formation in liquid crystals. Science 1994, 263, 943–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tkalec, U.; Ravnik, M.; Čopar, S.; Žumer, S.; Muševič, I. Reconfigurable knots and links in chiral nematic colloids. Science 2011, 333, 62–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senyuk, B.; Liu, Q.; He, S.; Kamien, R.D.; Kusner, R.B.; Lubensky, T.C.; Smalyukh, I.I. Topological colloids. Nature 2013, 493, 200–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brasselet, E. Tunable optical vortex arrays from a single nematic topological defect. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2012, 108, 087801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Serra, F.; Eaton, S.M.; Cerbino, R.; Buscaglia, M.; Cerullo, G.; Osellame, R.; Bellini, T. Nematic liquid crystals embedded in cubic microlattices: Memory effects and bistable pixels. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2013, 23, 3990–3994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez-Leon, T.; Bates, M.A.; Fernandez-Nieves, A. Defect coalescence in spherical nematic shells. Phys. Rev. E-Stat. Nonlinear Soft Matter Phys. 2012, 86, 030702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lavrentovich, O.D. Topological defects in dispersed liquid crystals, or words and worlds around liquid crystal drops. Liq. Cryst. 1998, 24, 117–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamien, R.D. The geometry of soft materials: A primer. Rev. Mod. Phys. 2002, 74, 953–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stein, D.L. Topological theorem and its applications to condensed matter systems. Phys. Rev. A 1979, 19, 1708–1711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keber, F.C.; Loiseau, E.; Sanchez, T.; DeCamp, S.J.; Giomi, L.; Bowick, M.J.; Marchetti, M.C.; Dogic, Z.; Bausch, A.R. Topology and dynamics of active nematic vesicles. Science 2014, 345, 1135–1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serra, F. Curvature and defects in nematic liquid crystals. Liq. Cryst. 2016, 43, 1920–1936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, C.; Turiv, T.; Guo, Y.; Wei, Q.H.; Lavrentovich, O.D. Command of active matter by topological defects and patterns. Science 2016, 354, 882–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murray, B.S.; Pelcovits, R.A.; Rosenblatt, C. Creating arbitrary arrays of two-dimensional topological defects. Phys. Rev. E-Stat. Nonlinear Soft Matter Phys. 2014, 90, 052501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasaki, Y.; Jampani, V.S.R.; Tanaka, C.; Sakurai, N.; Sakane, S.; Le, K.V.; Araoka, F.; Orihara, H. Large-scale self-organization of reconfigurable topological defect networks in nematic liquid crystals. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 13238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Migara, L.K.; Song, J.-K. Standing wave-mediated molecular reorientation and spontaneous formation of tunable, concentric defect arrays in liquid crystal cells. NPG Asia Mater. 2018, 10, e459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.S.; Serra, F. Tunable dynamic topological defect pattern formation in nematic liquid crystals. Adv. Opt. Mater. 2020, 8, 1900991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.S.; Serra, F. Tunable large-scale regular array of topological defects in nematic liquid crystals. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 35640–35645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beller, D.A.; Gharbi, M.A.; Liu, I.B. Shape-controlled orientation and assembly of colloids with sharp edges in nematic liquid crystals. Soft Matter 2015, 11, 1078–1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.S.; Čopar, S.; Tkalec, U.; Yoon, D.K. Mosaics of topological defects in micropatterned liquid crystal textures. Sci. Adv. 2018, 4, eaau8064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lohr, M.A.; Cavallaro, M., Jr.; Beller, D.A.; Stebe, K.J.; Kamien, R.D.; Collings, P.J.; Yodh, A.G. Elasticity-dependent self-assembly of micro-templated chromonic liquid crystal films. Soft Matter 2014, 10, 3477–3484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| a1 (μm) | 4 | 6 | 8 | ||||||
| h2 (μm) | 2 | 3 | 5 | 2 | 3 | 5 | 2 | 3 | 5 |
| f3 (Hz) | 220 | 240 | 240 | 210 | 220 | 220 | 200 | 200 | 180 |
| V4 (V) | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 |
| τon5 (s) | 0.49 | 0.34 | 0.26 | 0.44 | 0.27 | 0.28 | 0.28 | 0.28 | 0.37 |
| τoff6 (s) | 0.24 | 0.19 | 0.14 | 0.17 | 0.16 | 0.16 | 0.19 | 0.20 | 0.19 |
| τon error | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.04 | 0.04 | 0.04 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.04 |
| τoff error | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.04 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.03 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, M.; Serra, F. Topological Defect Arrays in Nematic Liquid Crystals Assisted by Polymeric Pillar Arrays: Effect of the Geometry of Pillars. Crystals 2020, 10, 314. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst10040314
Kim M, Serra F. Topological Defect Arrays in Nematic Liquid Crystals Assisted by Polymeric Pillar Arrays: Effect of the Geometry of Pillars. Crystals. 2020; 10(4):314. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst10040314
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, MinSu, and Francesca Serra. 2020. "Topological Defect Arrays in Nematic Liquid Crystals Assisted by Polymeric Pillar Arrays: Effect of the Geometry of Pillars" Crystals 10, no. 4: 314. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst10040314
APA StyleKim, M., & Serra, F. (2020). Topological Defect Arrays in Nematic Liquid Crystals Assisted by Polymeric Pillar Arrays: Effect of the Geometry of Pillars. Crystals, 10(4), 314. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst10040314





