Novel Trends in Lyotropic Liquid Crystals
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Lyotropic Liquid Crystals
2.1. Classic Lyotropics from Amphiphiles and Polymers
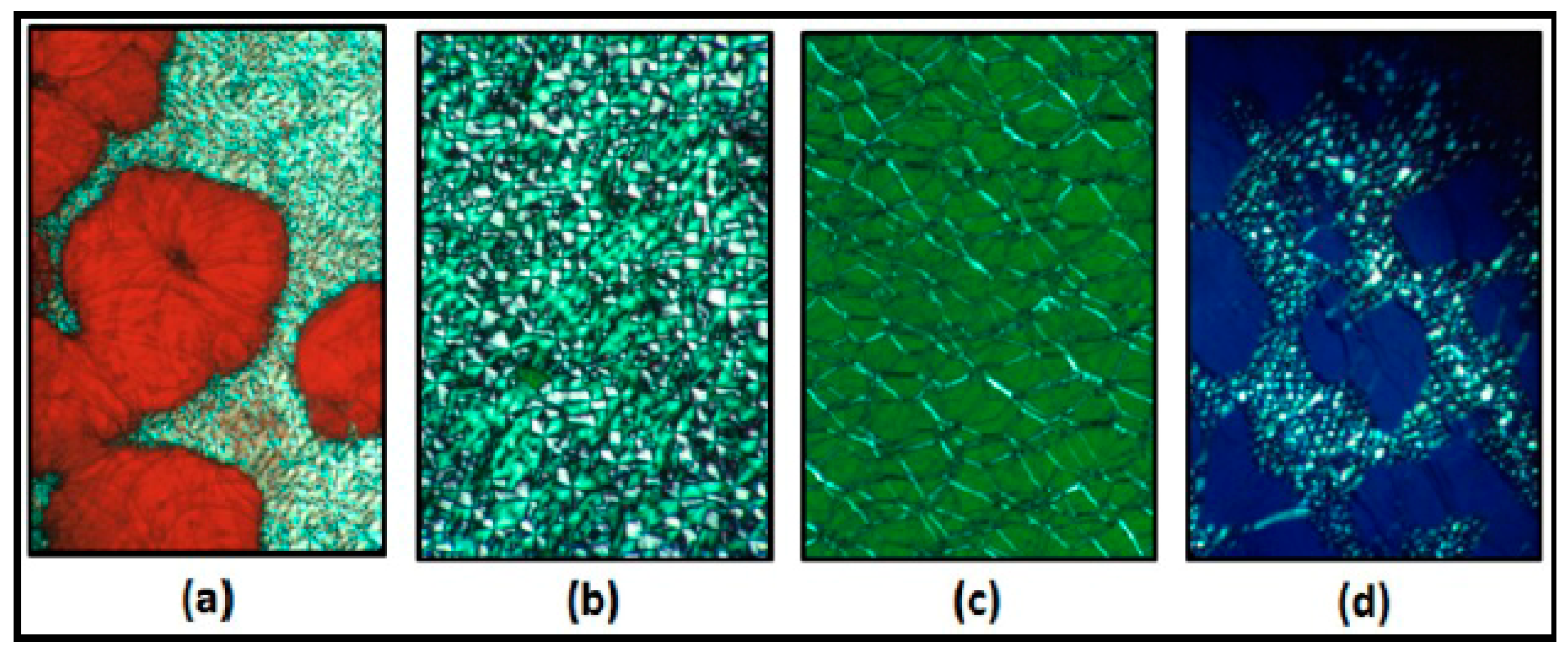
2.2. Inorganic Liquid Crystals
2.3. Clays
2.4. Tobacco Mosaic Virus (TMV) and Other Viruses
2.5. Lyotropic Phases from DNA
2.6. Lyotropic Cholesteric Cellulose Derivatives and Cellulose Nanocrystals
2.7. Nanotubes, Nanorods and Nanowires
2.8. Graphene Oxide and Other 2D Materials
2.9. Chromonics
2.10. Polar Lyotropic Lamellar Phases
2.11. Active and Living Lyotropic Nematics
2.12. Applications
3. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Neto, A.M.F.; Salinas, S.R.A. The Physics of Lyotropic Liquid Crystals: Phase Transitions and Structural Properties; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Petrov, A.G. The Lyotropic State of Matter: Molecular Physics and Living Matter Physics; Taylor & Francis: London, UK, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Reinitzer, F. Beiträge zur Kenntniss des Cholesterins. Monatsh. Chem. 1888, 9, 421–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Virchow, R. Myelinformen. Arch. Pathol. Anatom. Physiol. Klin. Med. 1854, 6, 572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mettenheimer, C. Mittheilung in Betreff mikroskopischer Beobachtungen mit polarisirtem Licht. Correspondenzblatt Vereins Gemeinschaftliche Arb. Förd. Wiss. Heilkd. 1857, 24, 331–332. [Google Scholar]
- Planer, J. Notiz über das Cholestearin. Ann Chem. 1861, 118, 25–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loebisch, W. Zur Kenntniss des Cholesterins. Ber. Deutsch. Chem. Ges. 1872, 5, 510–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rayman, M.B. Contribution à l’histoire de la cholestérine. Bull. Soc. Chim. Paris 1887, 47, 898–901. [Google Scholar]
- Lehmann, O. Über fliessende Krystalle. Z. Phys. Chem. 1889, 4, 462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markovitsi, D.; Mathis, A.; Simon, J.; Wittman, J.C.; Le Moigne, J. Annelides V: A New Type of Lyotropic Mesomorphic PHASE. Mol. Cryst. Liq. Cryst. 1980, 64, 121–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menger, F.M.; Littau, C.A. Gemini-surfactants: Synthesis and properties. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1991, 113, 1451–1452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menger, F.M.; Ding, J. Spiro-Tenside und -Phospholipide: Synthese und Eigenschaften. Angew. Chem. 1996, 108, 2266–2268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schröter, J.A.; Tschierske, C.; Wittenberg, M.; Wendorff, J.H. Formation of Columnar and Lamellar Lyotropic Mesophases by Facial Amphiphiles with Protic and Lipophilic Solvents. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1998, 120, 10669–10675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuhrhop, J.H.; Fritsch, D. Bolaamphiphiles form ultrathin, porous and unsymmetric monolayer lipid membranes. Accounts Chem. Res. 1986, 19, 130–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.J.; Saupe, A. Observation of a Biaxial Nematic Phase in Potassium Laurate-1-Decanol-Water Mixtures. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1980, 45, 1000–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luckhurst, G.R.; Sluckin, T.J. (Eds.) Biaxial Nematic Liquid Crystals: Theory, Simulation, and Experiment; John Wiley & Sons: Chichester, UK, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, L.J.; Saupe, A. Liquid crystalline phases of the sodium decylsulfate/decanol/water system. Nematic-nematic and cholesteric-cholesteric phase transitions. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1980, 102, 4879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruckner, J.R.; Porada, J.H.; Dietrich, C.F.; Dierking, I.; Giesselmann, F. A Lyotropic Chiral Smectic C Liquid Crystal with Polar Electrooptic Switching. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2013, 52, 8934–8937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukherjee, P.K.; Sen, K. On a new topology in the phase diagram of biaxial nematic liquid crystals. J. Chem. Phys. 2009, 130, 141101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quist, P.-O. First order transitions to a lyotropic biaxial nematic. Liq. Cryst. 1995, 18, 623–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akpinar, E.; Otluoglu, K.; Turkmen, M.; Canioz, C.; Reis, D.; Neto, A.M.F. Effect of the presence of strong and weak electrolytes on the existence of uniaxial and biaxial nematic phases in lyotropic mixtures. Liq. Cryst. 2016, 43, 1693–1708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diesselhorst, H.; Freundlich, H. On the double refraction of vanadine pentoxydsol. Phys. Z. 1915, 16, 419–425. [Google Scholar]
- Freundlich, H. Die Doppelbrechung des Vanadinpentoxydsols. Ber. Bunsenges. Phys. Chem. 1916, 22, 27–33. [Google Scholar]
- Zocher, H. Über freiwillige Strukturbildung in Solen. (Eine neue Art anisotrop flüssiger Medien.). Zeitschrift für Anorganische und Allgemeine Chemie 1925, 147, 91–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davidson, P.; Garreau, A.; Livage, J. Nematic colloidal suspensions of V2O5 in water—Or Zocher phases revisited. Liq. Cryst. 1994, 16, 905–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelletier, O.; Sotta, P.; Davidson, P. Deuterium Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Study of the Nematic Phase of Vanadium Pentoxide Aqueous Suspensions. J. Phys. Chem. B 1999, 103, 5427–5433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zocher, H.; Török, C. Neuere Beiträge zur Kenntnis der Taktosole. Colloid Polym. Sci. 1960, 173, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Davidson, P.; Gabriel, J.-C.P.; Levelut, A.M.; Batail, P. A new nematic suspension based on all-inorganic polymer rods. Europhys. Lett. 1993, 21, 317–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zocher, H.; Török, C. Crystals of higher order and their relation to other superphases. Acta Crystallogr. 1967, 22, 751–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonin, A.S. Inorganic lyotropic liquid crystals. J. Mater. Chem. 1998, 8, 2557–2574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mourchid, A.; Delville, A.; Lambard, J.; Lécolier, E.; Levitz, P. Phase diagram of colloidal dispersions of anisotropic charged particles: Equilibrium properties, structure, and rheology of laponite suspensions. Langmuir 1995, 11, 1942–1950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paineau, E.; Antonova, K.; Baravian, C.; Bihannic, I.; Davidson, P.; Dozov, I.; Impéror-Clerc, M.; Levitz, P.; Madsen, A.; Meneau, F.; et al. Liquid-Crystalline Nematic Phase in Aqueous Suspensions of a Disk-Shaped Natural Beidellite Clay. J. Phys. Chem. B 2009, 113, 15858–15869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langmuir, I. The Role of Attractive and Repulsive Forces in the Formation of Tactoids, Thixotropic Gels, Protein Crystals and Coacervates. J. Chem. Phys. 1938, 6, 873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabriel, J.-C.P.; Sanchez, C.; Davidson, P. Observation of Nematic Liquid-Crystal Textures in Aqueous Gels of Smectite Clays. J. Phys. Chem. 1996, 100, 11139–11143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kajiwara, K.; Donkai, N.; Hiragi, Y.; Inagaki, H. Lyotropic mesophase of imogolite, 1. Effect of polydispersity on phase diagram. Makromol. Chem. 1986, 187, 2883–2893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kajiwara, K.; Donkai, N.; Fujiyoshi, Y.; Inagaki, H. Lyotropic mesophase of imogolite, 2. Microscopic observation of imogolite mesophase. Makromol. Chem. 1986, 187, 2895–2907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dierking, I.; Al-Zangana, S. Lyotropic Liquid Crystal Phases from Anisotropic Nanomaterials. Nanomaterials 2017, 7, 305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michot, L.J.; Bihannic, I.; Maddi, S.; Baravian, C.; Levitz, P.; Davidson, P. Sol/Gel and Isotropic/Nematic Transitions in Aqueous Suspensions of Natural Nontronite Clay. Influence of Particle Anisotropy. 1. Features of the I/N Transition. Langmuir 2008, 24, 3127–3139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onsager, L. The effects of shape on the interaction of colloidal particles. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 1949, 51, 627–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barry, E.; Beller, D.; Dogic, Z. A model liquid crystalline system based on rodlike viruses with variable chirality and persistence length. Soft Matter 2009, 5, 2563–2570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayer, A. Über die Mosaikkrankheit des Tabaks. Die Landwirtsch. Versuchsstationen. 1886, 32, 451–467. [Google Scholar]
- Iwanowski, D. Über die Mosaikkrankheit der Tabakspflanze. Bulletin Scientifique Publié Par l’Académie Impériale des Sciences de Saint-Pétersbourg/Nouvelle Serie III 1892, 35, 67–70. [Google Scholar]
- Beijerinck, M.W. Über ein Contagium vivum fluidum als Ursache der Fleckenkrankheit der Tabaksblätter. In Verhandelingen der Koninklijke Akademie van Wetenschappen Te Amsterdam; J. Müller: Brake, Germany, 1898; Volume 65, pp. 1–22. [Google Scholar]
- Kausche, G.A.; Pfankuch, E.; Ruska, H. The visualisation of herbal viruses in surface microscopes. Naturwissenschaften 1939, 27, 292–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bawden, F.C.; Pirie, N.W.; Bernal, J.D.; Fankuchen, I. Liquid Crystalline Substances from Virus-infected Plants. Nature 1936, 138, 1051–1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oldenbourg, R.; Wen, X.; Meyer, R.B.; Caspar, D.L.D. Orientational Distribution Function in Nematic Tobacco-Mosaic-Virus Liquid Crystals Measured by X-Ray Diffraction. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1988, 61, 1851–1854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fraden, S.; Maret, G.; Caspar, D.L.D. Angular correlations and the isotropic-nematic phase transition in suspensions of tobacco mosaic virus. Phys. Rev. E 1993, 48, 2816–2837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Graf, H.; Löwen, H. Phase diagram of tobacco mosaic virus solutions. Phys. Rev. E 1999, 59, 1932–1942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dogic, Z.; Fraden, S. Cholesteric Phase in Virus Suspensions. Langmuir 2000, 16, 7820–7824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dogic, Z.; Fraden, S. Smectic Phase in a Colloidal Suspension of Semiflexible Virus Particles. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1997, 78, 2417–2420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dogic, Z.; Fraden, S. Ordered phases of filamentous viruses. Curr. Opin. Colloid Interface Sci. 2006, 11, 47–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dogic, Z. Filamentous Phages as a Model System in Soft Matter Physics. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, M.; Dogic, Z.; Keller, S.L.; Fraden, S. Entropically driven microphase transitions in mixtures of colloidal rods and spheres. Nature 1998, 393, 349–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leforestier, A.; Livolant, F. The Bacteriophage Genome Undergoes a Succession of Intracapsid Phase Transitions upon DNA Ejection. J. Mol. Boil. 2010, 396, 384–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leforestier, A.; Livolant, F. Supramolecular ordering of DNA in the cholesteric liquid crystalline phase: An ultrastructural study. Biophys. J. 1993, 65, 56–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strzelecka, T.E.; Davidson, M.W.; Rill, R.L. Multiple liquid crystal phases of DNA at high concentrations. Nature 1988, 331, 457–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zanchetta, G.; Nakata, M.; Buscaglia, M.; Clark, N.A.; Bellini, T. Liquid crystal ordering of DNA and RNA oligomers with partially overlapping sequences. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 2008, 20, 494214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smalyukh, I.I.; Zribi, O.V.; Butler, J.C.; Lavrentovich, O.D.; Wong, G.C.L. Structure and Dynamics of Liquid Crystalline Pattern Formation in Drying Droplets of DNA. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2006, 96, 177801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salamonczyk, M.; Zhang, J.; Portale, G.; Zhu, C.; Kentzinger, E.; Gleeson, J.T.; Jakli, A.; De Michele, C.; Dhont, J.K.G.; Sprunt, S.; et al. Smectic phase in suspensions of gapped DNA duplexes. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 13358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Storm, I.M.; Kornreich, M.; Hernandez-Garcia, A.; Voets, I.K.; Beck, R.; Stuart, M.A.C.; Leermakers, F.A.M.; De Vries, R. Liquid Crystals of Self-Assembled DNA Bottlebrushes. J. Phys. Chem. B 2015, 119, 4084–4092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brach, K.; Hatakeyama, A.; Nogues, C.; Olesiak-Banska, J.; Buckle, M.; Matczyszyn, K. Photochemical analysis of structural transitions in DNA liquid crystals reveals differences in spatial structure of DNA molecules organized in liquid crystalline form. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 4528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- George, J.; Sabapathi, S. Cellulose nanocrystals: Synthesis, functional properties, and applications. Nanotechnol. Sci. Appl. 2015, 8, 45–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pääkkö, M.; Ankerfors, M.; Kosonen, H.; Nykänen, A.; Ahola, S.; Österberg, M.; Ruokolainen, J.; Laine, J.; Larsson, P.T.; Ikkala, O.; et al. Enzymatic Hydrolysis Combined with Mechanical Shearing and High-Pressure Homogenization for Nanoscale Cellulose Fibrils and Strong Gels. Biomacromolecules 2007, 8, 1934–1941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kloser, E.; Gray, D.G. Surface Grafting of Cellulose Nanocrystals with Poly(ethylene oxide) in Aqueous Media. Langmuir 2010, 26, 13450–13456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gray, D.G.; Mu, X. Chiral Nematic Structure of Cellulose Nanocrystal Suspensions and Films; Polarized Light and Atomic Force Microscopy. Materials 2015, 8, 7873–7888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gray, D.G. Recent Advances in Chiral Nematic Structure and Iridescent Color of Cellulose Nanocrystal Films. Nanomaterials 2016, 6, 213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lagerwall, J.P.F.; Schütz, C.; Salajkova, M.; Noh, J.; Park, J.H.; Scalia, G.; Bergström, L. Cellulose nanocrystal-based materials: From liquid crystal self-assembly and glass formation to multifunctional thin films. NPG Asia Mater. 2014, 6, e80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azzam, F.; Heux, L.; Jean, B. Adjustment of the Chiral Nematic Phase Properties of Cellulose Nanocrystals by Polymer Grafting. Langmuir 2016, 32, 4305–4312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abitbol, T.; Kam, D.; Levi-Kalisman, Y.; Gray, D.G.; Shoseyov, O. Surface Charge Influence on the Phase Separation and Viscosity of Cellulose Nanocrystals. Langmuir 2018, 34, 3925–3933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spontak, R.J.; El-Nokaly, M.A.; Bartolo, R.G.; Burns, J.L. Polymer Solutions, Blends and Interfaces; Noda, I., Rubingh, D.N., Eds.; Elsevier Science Publishers B.V.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Cowie, J.; Arrighi, V.; Cameron, J.; McEwan, I.; McEwen, I.J. Lyotropic liquid crystalline cellulose derivatives in blends and molecular composites. Polymer 2001, 42, 9657–9663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cowie, J.; Arrighi, V.; Cameron, J.; Robson, D. Lyotropic liquid crystalline cellulose derivatives in blends and molecular composites. Macromol. Symp. 2000, 152, 107–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamide, K.; Okajima, K.; Matsui, T.; Kajita, S. Formation of Lyotropic Liquid Crystals of Cellulose Derivatives Dissolved in Inorganic Acids. Polym. J. 1986, 18, 273–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Onofrei, M.-D.; Dobos, A.M.; Stoica, I.; Olaru, N.; Olaru, L.; Ioan, S. Lyotropic Liquid Crystal Phases in Cellulose Acetate Phthalate/Hydroxypropyl Cellulose Blends. J. Polym. Environ. 2013, 22, 99–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dierking, I.; Scalia, G.; Morales, P.; LeClere, D. Aligning and Reorienting Carbon Nanotubes with Nematic Liquid Crystals. Adv. Mater. 2004, 16, 865–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dierking, I.; Scalia, G.; Morales, P. Liquid crystal–carbon nanotube dispersions. J. Appl. Phys. 2005, 97, 44309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lynch, M.D.; Patrick, D.L. Organizing Carbon Nanotubes with Liquid Crystals. Nano Lett. 2002, 2, 1197–1201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lagerwall, J.P.F.; Scalia, G. Carbon nanotubes in liquid crystals. J. Mater. Chem. 2008, 18, 2890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yakemseva, M.; Dierking, I.; Kapernaum, N.; Usol’Tseva, N.V.; Giesselmann, F. Dispersions of multi-wall carbon nanotubes in ferroelectric liquid crystals. Eur. Phys. J. E 2014, 37, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lagerwall, J.P.F.; Scalia, G.; Haluska, M.; Dettlaff-Weglikowska, U.; Giesselmann, F.; Roth, S. Simultaneous alignment and dispersion of carbon nanotubes with lyotropic liquid crystals. Phys. Status Solidi B 2006, 243, 3046–3049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lagerwall, J.P.F.; Scalia, G.; Haluska, M.; Dettlaff-Weglikowska, U.; Roth, S.; Giesselmann, F. Nanotube Alignment Using Lyotropic Liquid Crystals. Adv. Mater. 2007, 19, 359–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, W.; Yu, B.; Liu, W.; Hao, J. Carbon Nanotubes Incorporated within Lyotropic Hexagonal Liquid Crystal Formed in Room-Temperature Ionic Liquids. Langmuir 2007, 23, 8549–8553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scalia, G.; Von Bühler, C.; Hägele, C.; Roth, S.; Giesselmann, F.; Lagerwall, J.P.F. Spontaneous macroscopic carbon nanotube alignment via colloidal suspension in hexagonal columnar lyotropic liquid crystals. Soft Matter 2008, 4, 570–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.H.; Bai, Y.; Wang, F.M.; Liu, N. Fabrication and Characterizes of TiO2 Nanomaterials Templated by Lyotropic Liquid Crystal. Adv. Mater. Res. 2011, 399, 532–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saliba, S.; Davidson, P.; Impéror-Clerc, M.; Mingotaud, C.; Kahn, M.L.; Marty, J.-D. Facile direct synthesis of ZnO nanoparticles within lyotropic liquid crystals: Towards organized hybrid materials. J. Mater. Chem. 2011, 21, 18191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Somoza, A.M.; Sagui, C.; Roland, C. Liquid-crystal phases of capped carbon nanotubes. Phys. Rev. B 2001, 63, 81403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, W.; Kinloch, I.A.; Windle, A.H. Nematic Liquid Crystallinity of Multiwall Carbon Nanotubes. Science 2003, 302, 1363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, W.; Windle, A.H. Isotropic−Nematic Phase Transition of Dispersions of Multiwall Carbon Nanotubes. Macromolecules 2005, 38, 6181–6188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badaire, S.; Zakri, C.; Maugey, M.; Derré, A.; Barisci, J.N.; Wallace, G.G.; Poulin, P. Liquid Crystals of DNA-Stabilized Carbon Nanotubes. Adv. Mater. 2005, 17, 1673–1676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puech, N.; Blanc, C.; Grelet, E.; Zamora-Ledezma, C.; Maugey, M.; Zakri, C.; Anglaret, E.; Poulin, P. Highly Ordered Carbon Nanotube Nematic Liquid Crystals. J. Phys. Chem. C 2011, 115, 3272–3278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, V.A.; Ericson, L.M.; Parra-Vasquez, A.N.G.; Fan, H.; Wang, Y.; Prieto, V.; Longoria, J.A.; Ramesh, S.; Saini, R.K.; Kittrell, C.; et al. Phase behaviour and rheology of SWNTs in superacids. Macromolecules 2004, 37, 154–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rai, P.K.; Pinnick, R.A.; Parra-Vasquez, A.N.G.; Davis, V.A.; Schmidt, H.K.; Hauge, R.H.; Smalley, R.E.; Pasquali, M. Isotropic−Nematic Phase Transition of Single-Walled Carbon Nanotubes in Strong Acids. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2006, 128, 591–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Majewski, P.W.; Keskar, G.; Pfefferle, L.D.; Osuji, C.O. Lyotropic Self-Assembly of High-Aspect-Ratio Semiconductor Nanowires of Single-Crystal ZnO. Langmuir 2011, 27, 11616–11621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Pelligra, C.I.; Keskar, G.; Majewski, P.W.; Ren, F.; Pfefferle, L.D.; Osuji, C.O. Liquid Crystalline Order and Magnetocrystalline Anisotropy in Magnetically Doped Semiconducting ZnO Nanowires. ACS Nano 2011, 5, 8357–8364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Z.; Chen, C.; Hu, R.; Mai, K.; Qian, G.; Wang, Z. Two-Step Self-Assembly and Lyotropic Liquid Crystal Behavior of TiO2 Nanorods. J. Nanomater. 2012, 2012, 180989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.-S.; Walda, J.; Manna, L.; Alivisatos, A.P.; Alivisatos, A.P. Semiconductor Nanorod Liquid Crystals. Nano Lett. 2002, 2, 557–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.-S.; Alivisatos, A.P. Semiconductor Nanorod Liquid Crystals and Their Assembly on a Substrate. Adv. Mater. 2003, 15, 408–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behabtu, N.; Lomeda, J.R.; Green, M.J.; Higginbotham, A.L.; Sinitskii, A.; Kosynkin, D.V.; Tsentalovich, D.; Parra-Vasquez, A.N.G.; Schmidt, J.; Kesselman, E.; et al. Spontaneous high-concentration dispersions and liquid crystals of graphene. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2010, 5, 406–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Z.; Gao, C. Graphene chiral liquid crystals and macroscopic assembled fibres. Nat. Commun. 2011, 2, 571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.E.; Han, T.H.; Lee, S.H.; Kim, J.Y.; Ahn, C.W.; Yun, J.M.; Kim, S.O.; Lee, J. Graphene Oxide Liquid Crystals. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2011, 50, 3043–3047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Zangana, S.; Iliut, M.; Turner, M.; Vijayaraghavan, A.; Dierking, I. Confinement effects on lyotropic nematic liquid crystal phases of graphene oxide dispersions. 2D Mater. 2017, 4, 041004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dan, B.; Behabtu, N.; Martinez, A.; Evans, J.S.; Kosynkin, D.V.; Tour, J.M.; Pasquali, M.; Smalyukh, I.I. Liquid crystals of aqueous, giant graphene oxide flakes. Soft Matter 2011, 7, 11154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jalili, R.; Aboutalebi, S.H.; Esrafilzadeh, D.; Shepherd, R.L.; Chen, J.; Aminorroaya-Yamini, S.; Konstantinov, K.; Minett, A.I.; Razal, J.M.; Wallace, G.G. Scalable One-Step Wet-Spinning of Graphene Fibers and Yarns from Liquid Crystalline Dispersions of Graphene Oxide: Towards Multifunctional Textiles. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2013, 23, 5345–5354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.Y.; Kim, S.O. Liquid crystals: Electric fields line up graphene oxide. Nat. Mater. 2014, 13, 325–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, S.-H.; Shen, T.-Z.; Song, J.-K. Electro-optical Characteristics of Aqueous Graphene Oxide Dispersion Depending on Ion Concentration. J. Phys. Chem. C 2014, 118, 26304–26312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, T.-Z.; Hong, S.-H.; Song, J.-K. Electro-optical switching of graphene oxide liquid crystals with an extremely large Kerr coefficient. Nat. Mater. 2014, 13, 394–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmad, R.T.M.; Hong, S.-H.; Shen, T.-Z.; Song, J.-K. Optimization of particle size for high birefringence and fast switching time in electro-optical switching of graphene oxide dispersions. Opt. Express 2015, 23, 4435–4440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Narayan, R.; Kim, J.E.; Kim, J.Y.; Lee, K.-E.; Kim, S.O. Graphene Oxide Liquid Crystals: Discovery, Evolution and Applications. Adv. Mater. 2016, 28, 3045–3068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasikala, S.P.; Lim, J.; Kim, I.H.; Jung, H.J.; Yun, T.; Han, T.H.; Kim, S.O. Graphene oxide liquid crystals: A frontier 2D soft material for graphene-based functional materials. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2018, 47, 6013–6045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Draude, A.; Dierking, I. Lyotropic Liquid Crystals from Colloidal Suspensions of Graphene Oxide. Crystals 2019, 9, 455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Zangana, S.; Iliut, M.; Turner, M.; Vijayaraghavan, A.; Dierking, I. Properties of a Thermotropic Nematic Liquid Crystal Doped with Graphene Oxide. Adv. Opt. Mater. 2016, 4, 1541–1548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Zangana, S.; Iliut, M.; Boran, G.; Turner, M.; Vijayaraghavan, A.; Dierking, I. Dielectric spectroscopy of isotropic liquids and liquid crystal phases with dispersed graphene oxide. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 31885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamora-Ledezma, C.; Puech, N.; Zakri, C.; Grelet, E.; Moulton, S.E.; Wallace, G.G.; Gambhir, S.; Blanc, C.; Anglaret, E.; Poulin, P. Liquid Crystallinity and Dimensions of Surfactant-Stabilized Sheets of Reduced Graphene Oxide. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2012, 3, 2425–2430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.J.; Park, J.H.; Yamamoto, J.; Kim, Y.S.; Scalia, G. Electro-optic switching with liquid crystal graphene. Phys. Status Solidi Rapid Res. Lett. 2016, 10, 397–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jalili, R.; Aminorroaya-Yamini, S.; Benedetti, T.R.B.; Aboutalebi, S.H.; Chao, Y.; Wallace, G.G.; Officer, D.L. Processable 2D materials beyond graphene: MoS2 liquid crystals and fibres. Nanoscale 2016, 8, 16862–16867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, Y.; Mathis, T.S.; Zhao, M.-Q.; Anasori, B.; Dang, A.; Zhou, Z.; Cho, H.; Gogotsi, Y.; Yang, S. Thickness-independent capacitance of vertically aligned liquid-crystalline MXenes. Nature 2018, 557, 409–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nicolosi, V.; Chhowalla, M.; Kanatzidis, M.G.; Strano, M.S.; Coleman, J.N. Liquid Exfoliation of Layered Materials. Science 2013, 340, 1226419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Xu, Z.; Gao, W.; Cheng, Z.; Gao, C. Graphene and Other 2D Colloids: Liquid Crystals and Macroscopic Fibers. Adv. Mater. 2017, 29, 1606794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, G.; Yao, T.; Sun, H.; Scott, S.M.; Shao, D.; Wang, G.; Lian, J. Highly thermally conductive and mechanically strong graphene fibers. Science 2015, 349, 1083–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Wong, M.; Zhang, X.; Yao, H.; Ishige, R.; Takahara, A.; Miyamoto, M.; Nishimura, R.; Sue, H. Tunable Lyotropic Photonic Liquid Crystal Based on Graphene Oxide. ACS Photon. 2014, 1, 79–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akbari, A.; Sheath, P.; Martin, S.T.; Shinde, D.B.; Shaibani, M.; Banerjee, P.C.; Tkacz, R.; Bhattacharyya, D.; Majumder, M. Large-area graphene-based nanofiltration membranes by shear alignment of discotic nematic liquid crystals of graphene oxide. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 10891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, L.; Ye, J.; Shuai, M.; Zhu, Z.; Zhou, X.; Wang, Y.; Li, Y.; Su, Z.; Zhang, H.; Chen, Y.; et al. Graphene oxide liquid crystals for reflective displays without polarizing optics. Nanoscale 2015, 7, 1616–1622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lydon, J.E. Chromonics. In Handbook of Liquid Crystals, Vol 2B; Demus, D., Goodby, J., Gray, G.W., Speiss, H.-W., Vi, V., II, Eds.; Wiley-VCH: Weinheim, Germany, 1998; pp. 981–1007. [Google Scholar]
- Lydon, J.E. Chromonic liquid crystal phases. Curr. Opin. Colloid Interface Sci. 1998, 3, 458–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tam-Chang, S.-W.; Huang, L. Chromonic liquid crystals: Properties and applications as functional materials. Chem. Commun. 2008, 17, 1957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nastishin, Y.A.; Liu, H.; Shiyanovskii, S.V.; Lavrentovich, O.; Kostko, A.; Anisimov, M.A. Pretransitional fluctuations in the isotropic phase of a lyotropic chromonic liquid crystal. Phys. Rev. E 2004, 70, 051706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hartshorne, N.H.; Woodard, G.D. Mesomorphism in the System Disodium Chromoglycate-Water. Mol. Cryst. Liq. Cryst. 1973, 23, 343–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kustanovich, I.; Poupko, R.; Zimmermann, H.; Luz, Z.; Labes, M.M. Lyomesophases of the diethylammonium flufenamate-water system studied by deuterium NMR spectroscopy. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1985, 107, 3494–3501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horowitz, V.R.; Janowitz, L.A.; Modic, A.L.; Heiney, P.A.; Collings, P.J. Aggregation behavior and chromonic liquid crystal properties of an anionic monoazo dye. Phys. Rev. E 2005, 72, 041710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kostko, A.; Cipriano, B.H.; Pinchuk, O.A.; Ziserman, L.; Anisimov, M.A.; Danino, D.; Raghavan, S.R. Salt Effects on the Phase Behavior, Structure, and Rheology of Chromonic Liquid Crystals. J. Phys. Chem. B 2005, 109, 19126–19133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sidky, H.; Whitmer, J.K. The Emergent Nematic Phase in Ionic Chromonic Liquid Crystals. J. Phys. Chem. B 2017, 121, 6691–6698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romani, E.; Ferrarini, A.; De Michele, C. Elastic Constants of Chromonic Liquid Crystals. Macromolecules 2018, 51, 5409–5419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, J.; Davidson, Z.S.; Collings, P.J.; Lubensky, T.C.; Yodh, A.G. Chiral symmetry breaking and surface faceting in chromonic liquid crystal droplets with giant elastic anisotropy. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 1742–1747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, S.; Shiyanovskii, S.V.; Park, H.-S.; Lavrentovich, O.D. Fine structure of the topological defect cores studied for disclinations in lyotropic chromonic liquid crystals. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 14974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akpinar, E.; Topcu, G.; Reis, D.; Neto, A.M.F. Effect of the presence of the anionic azo dye Sunset Yellow in lyotropic mixtures with uniaxial and biaxial nematic phases. Submitted.
- Valášek, J. Piezo-Electric and Allied Phenomena in Rochelle Salt. Phys. Rev. 1921, 17, 475–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, R.; Liebert, L.; Strzelecki, L.; Keller, P. Ferroelectric liquid crystals. J. Phys. Lett. 1975, 36, 69–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, N.A.; Lagerwall, S.T. Submicrosecond bistable electro-optic switching in liquid crystals. Appl. Phys. Lett. 1980, 36, 899–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schafheutle, M.A.; Finkelmann, H. Shapes of Micelles and Molecular Geometry Synthesis and Studies on the Phase Behaviour, Surface Tension and Rheology of Rigid Rod-Like Surfactants in Aqueous Solutions. Liq. Cryst. 1988, 3, 1369–1386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ujiie, S.; Yano, Y. Thermotropic and lyotropic behavior of novel amphiphilic liquid crystals having hydrophilic poly(ethyleneimine) units. Chem. Commun. 2000, 1, 79–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harjung, M.D.; Giesselmann, F. Electroclinic effect in the chiral lamellar α phase of a lyotropic liquid crystal. Phys. Rev. E 2018, 97, 032705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harjung, M.D.; Schubert, C.P.J.; Knecht, F.; Porada, J.H.; Lemieux, R.P.; Giesselmann, F. New amphiphilic materials showing the lyotropic analogue to the thermotropic smectic C* liquid crystal phase. J. Mater. Chem. C 2017, 5, 7452–7457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruckner, J.R.; Giesselmann, F. The Lyotropic Analog of the Polar SmC* Phase. Crystals 2019, 9, 568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menzel, A.M. Tuned, driven, and active soft matter. Phys. Rep. 2015, 554, 1–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golestanian, R.; Ramaswamy, S. Active Matter. Eur. Phys. J. E 2013, 36, 54002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Bukusoglu, E.; Pantoja, M.B.; Mushenheim, P.C.; Wang, X.; Abbott, N.L. Design of Responsive and Active (Soft) Materials Using Liquid Crystals. Annu. Rev. Chem. Biomol. Eng. 2016, 7, 163–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doostmohammadi, A.; Ignés-Mullol, J.; Yeomans, J.M.; Sagués, F. Active nematics. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 3246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dombrowski, C.; Cisneros, L.; Chatkaew, S.; E Goldstein, R.; Kessler, J.O. Self-Concentration and Large-Scale Coherence in Bacterial Dynamics. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2004, 93, 098103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Shi, X.-Q.; Huang, M.; Chen, X.; Xiao, M.; Liu, C.; Chaté, H.; Zhang, H.P. Data-driven quantitative modeling of bacterial active nematics. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 116, 777–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanchez, T.; Chen, D.T.N.; DeCamp, S.J.; Heymann, M.; Dogic, Z. Spontaneous motion in hierarchically assembled active matter. Nature 2012, 491, 431–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henkin, G.; DeCamp, S.J.; Chen, D.T.N.; Sanchez, T.; Dogic, Z. Tunable dynamics of microtubule-based active isotropic gels. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. A Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 2014, 372, 20140142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schaller, V.; Weber, C.; Semmrich, C.; Frey, E.; Bausch, A.R. Polar patterns of driven filaments. Nature 2010, 467, 73–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Kumar, N.; Ross, J.L.; Gardel, M.L.; De Pablo, J.J. Interplay of structure, elasticity, and dynamics in actin-based nematic materials. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 2017, 115, E124–E133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, N.; Zhang, R.; De Pablo, J.J.; Gardel, M.L. Tunable structure and dynamics of active liquid crystals. Sci. Adv. 2018, 4, eaat7779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.; Sokolov, A.; Lavrentovich, O.D.; Aranson, I.S. Living Liquid Crystals. Biophys. J. 2014, 106, 420a. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, C.; Turiv, T.; Guo, Y.; Wei, Q.-H.; Lavrentovich, O.D. Command of active matter by topological defects and patterns. Science 2016, 354, 882–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Genkin, M.M.; Sokolov, A.; Lavrentovich, O.D.; Aranson, I.S. Topological Defects in a Living Nematic Ensnare Swimming Bacteria. Phys. Rev. X 2017, 7, 011029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Genkin, M.M.; Sokolov, A.; Aranson, I.S. Spontaneous topological charging of tactoids in a living nematic. New J. Phys. 2018, 20, 043027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woolverton, C.J.; Gustely, E.; Li, L.; Lavrentovich, O.D. Liquid crystal effects on bacterial viability. Liq. Cryst. 2005, 32, 417–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mezzenga, R.; Seddon, J.M.; Drummond, C.J.; Boyd, B.J.; Schröder-Turk, G.E.; Sagalowicz, L. Nature-Inspired Design and Application of Lipidic Lyotropic Liquid Crystals. Adv. Mater. 2019, 31, e1900818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadeghpour, A. Lyotropic Liquid Crystalline Phases for the Formulation of Future Functional Foods. J. Nutr. Health Food Eng. 2016, 5, 553–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garti, N.; Libster, D.; Aserin, A. Lipid polymorphism in lyotropic liquid crystals for triggered release of bioactives. Food Funct. 2012, 3, 700–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larsson, K. Lyotropic liquid crystals and their dispersions relevant in foods. Curr. Opin. Colloid Interface Sci. 2009, 14, 16–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engels, T.; Von Rybinski, W. Liquid crystalline surfactant phases in chemical applications. J. Mater. Chem. 1998, 8, 1313–1320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Negrini, R.; Mezzenga, R. pH-Responsive Lyotropic Liquid Crystals for Controlled Drug Delivery. Langmuir 2011, 27, 5296–5303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aleandri, S.; Speziale, C.; Mezzenga, R.; Landau, E.M. Design of Light-Triggered Lyotropic Liquid Crystal Mesophases and Their Application as Molecular Switches in “On Demand” Release. Langmuir 2015, 31, 6981–6987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, N.-H.; Jahn, A.; Cho, S.-J.; Kim, J.S.; Ki, M.-H.; Kim, D.-D. Lyotropic liquid crystal systems in drug delivery: A review. J. Pharm. Investig. 2014, 45, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, C.; Wang, J.; Cao, F.; Lee, R.J.; Zhai, G. Lyotropic liquid crystal systems in drug delivery. Drug Discov. Today 2010, 15, 1032–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, V.K. Optical Amplification of Ligand-Receptor Binding Using Liquid Crystals. Science 1998, 279, 2077–2080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luan, C.; Luan, H.; Luo, D. Luan Application and Technique of Liquid Crystal-Based Biosensors. Micromachines 2020, 11, 176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shiyanovskii, S.V.; Lavrentovich, O.D.; Schneider, T.; Ishikawa, T.; Smalyukh, I.I.; Woolverton, C.J.; Niehaus, G.D.; Doane, K.J. Lyotropic Chromonic Liquid Crystals for Biological Sensing Applications. Mol. Cryst. Liq. Cryst. 2005, 434, 259–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, H.; Yang, S.; Shen, G.; Yu, R.; Wu, Z. Signal-Enhanced Liquid-Crystal DNA Biosensors Based on Enzymatic Metal Deposition. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2010, 49, 8608–8611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popov, P.; Honaker, L.; Kooijman, E.E.; Mann, E.K.; Jákli, A. A liquid crystal biosensor for specific detection of antigens. Sens. Bio-Sens. Res. 2016, 8, 31–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oton, E.; Oton, J.M.; Caño-García, M.; Escolano, J.M.; Quintana, X.; Geday, M.A. Rapid detection of pathogens using lyotropic liquid crystals. Opt. Express 2019, 27, 10098–10107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Souza, J.F.; Pontes, K.D.S.; Alves, T.F.; Amaral, V.; Rebelo, M.A.; Hausen, M.; Chaud, M.V. Spotlight on Biomimetic Systems Based on Lyotropic Liquid Crystal. Molecules 2017, 22, 419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fowler, C.E.; Shenton, W.; Stubbs, G.; Mann, S. Tobacco Mosaic Virus Liquid Crystals as Templates for the Interior Design of Silica Mesophases and Nanoparticles. Adv. Mater. 2001, 13, 1266–1269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dellinger, T.M.; Braun, P.V. Lyotropic Liquid Crystals as Nanoreactors for Nanoparticle Synthesis. Chem. Mater. 2004, 16, 2201–2207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Chen, D.; Jiao, X. Lyotropic liquid crystal directed synthesis of nanostructured materials. Sci. Technol. Adv. Mater. 2009, 10, 23001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Umadevi, S.; Umamaheswari, R.; Ganesh, V. Lyotropic liquid crystal-assisted synthesis of micro- and nanoparticles of silver. Liq. Cryst. 2017, 44, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salili, S.M.; Worden, M.; Nemati, A.; Miller, D.W.; Hegmann, T. Synthesis of Distinct Iron Oxide Nanomaterial Shapes Using Lyotropic Liquid Crystal Solvents. Nanomaterials 2017, 7, 211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hegmann, T.; Qi, H.; Marx, V.M. Nanoparticles in Liquid Crystals: Synthesis, Self-Assembly, Defect Formation and Potential Applications. J. Inorg. Organomet. Polym. Mater. 2007, 17, 483–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuijk, A.; Van Blaaderen, A.; Imhof, A. Synthesis of Monodisperse, Rodlike Silica Colloids with Tunable Aspect Ratio. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2011, 133, 2346–2349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, J.H.; Noh, J.; Schütz, C.; Salazar-Alvarez, G.; Scalia, G.; Bergström, L.; Lagerwall, J.P.F. Macroscopic Control of Helix Orientation in Films Dried from Cholesteric Liquid-Crystalline Cellulose Nanocrystal Suspensions. ChemPhysChem 2014, 15, 1477–1484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Querejeta-Fernández, A.; Chauve, G.; Méthot, M.; Bouchard, J.; Kumacheva, E. Chiral Plasmonic Films Formed by Gold Nanorods and Cellulose Nanocrystals. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2014, 136, 4788–4793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Campbell, M.G.; Evans, J.S.; Smalyukh, I.I. Orientationally Ordered Colloidal Co-Dispersions of Gold Nanorods and Cellulose Nanocrystals. Adv. Mater. 2014, 26, 7178–7184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, G.; Wang, X.; Chen, T.; Gao, J.; Gai, F.; Wang, Y.; Xu, Y. Optically Tunable Chiral Plasmonic Guest–Host Cellulose Films Weaved with Long-range Ordered Silver Nanowires. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 11863–11870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]













© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dierking, I.; Martins Figueiredo Neto, A. Novel Trends in Lyotropic Liquid Crystals. Crystals 2020, 10, 604. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst10070604
Dierking I, Martins Figueiredo Neto A. Novel Trends in Lyotropic Liquid Crystals. Crystals. 2020; 10(7):604. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst10070604
Chicago/Turabian StyleDierking, Ingo, and Antônio Martins Figueiredo Neto. 2020. "Novel Trends in Lyotropic Liquid Crystals" Crystals 10, no. 7: 604. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst10070604
APA StyleDierking, I., & Martins Figueiredo Neto, A. (2020). Novel Trends in Lyotropic Liquid Crystals. Crystals, 10(7), 604. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst10070604





