Microwave Irradiation to Produce High Performance Thermoelectric Material Based on Al Doped ZnO Nanostructures
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
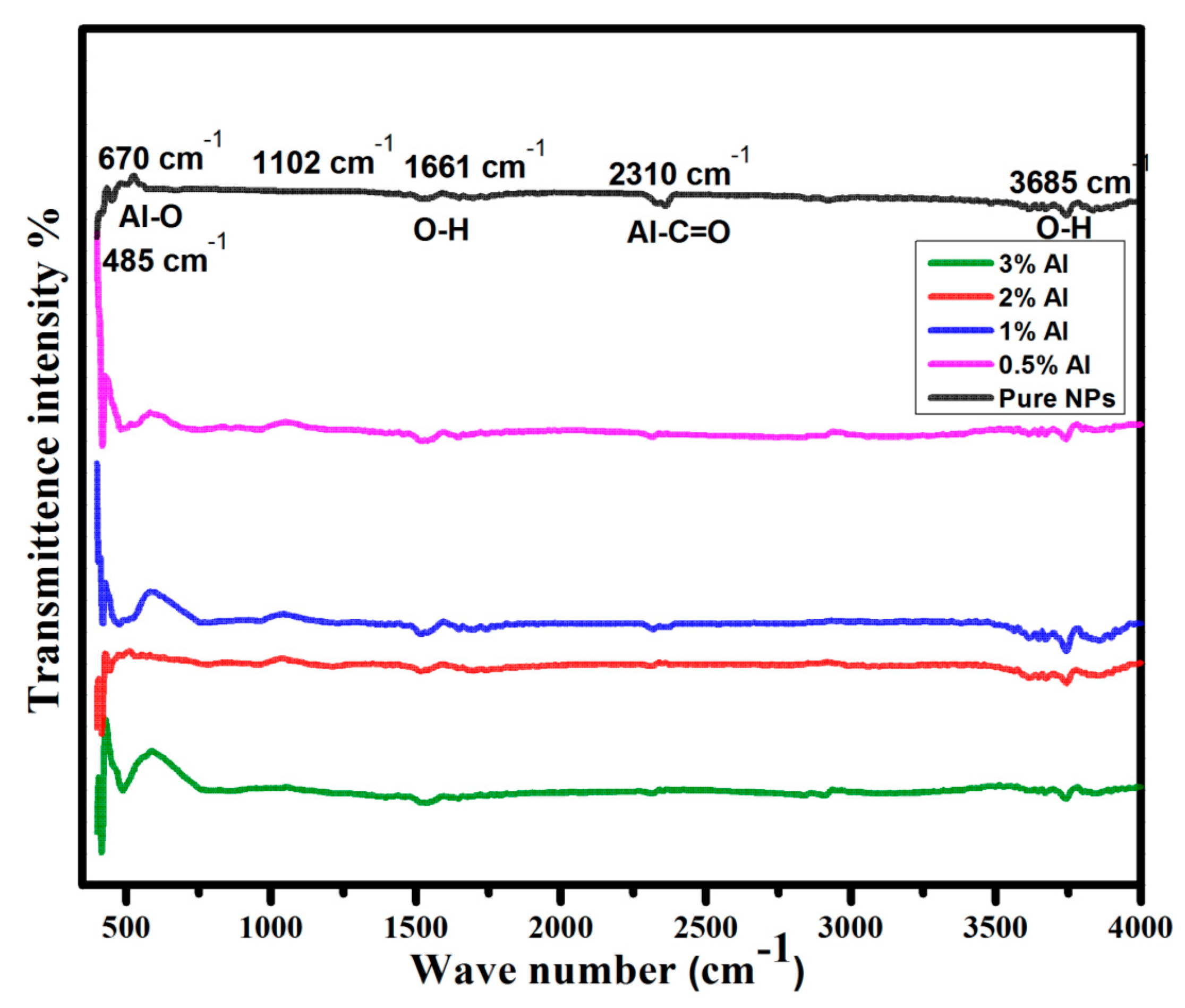
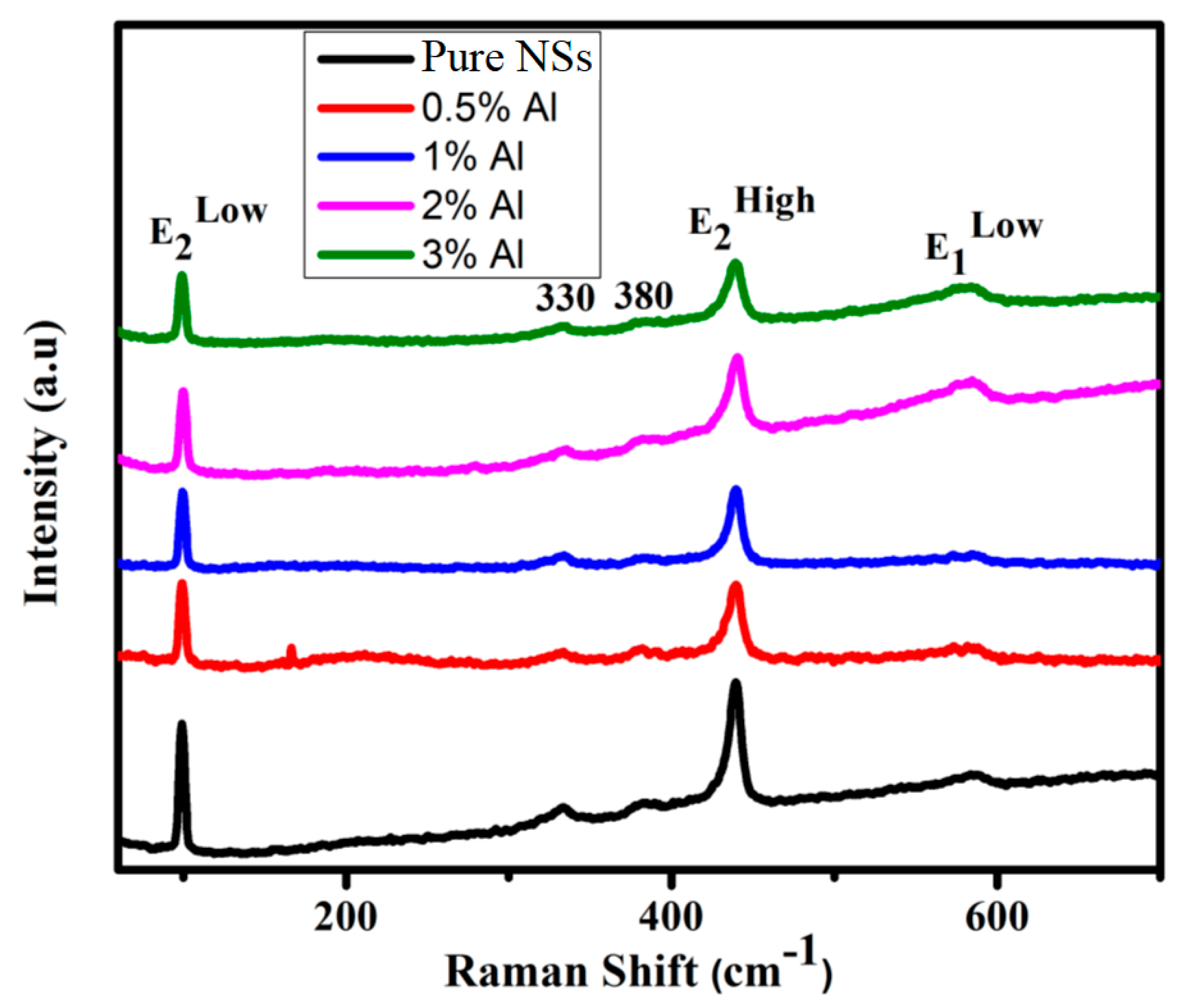
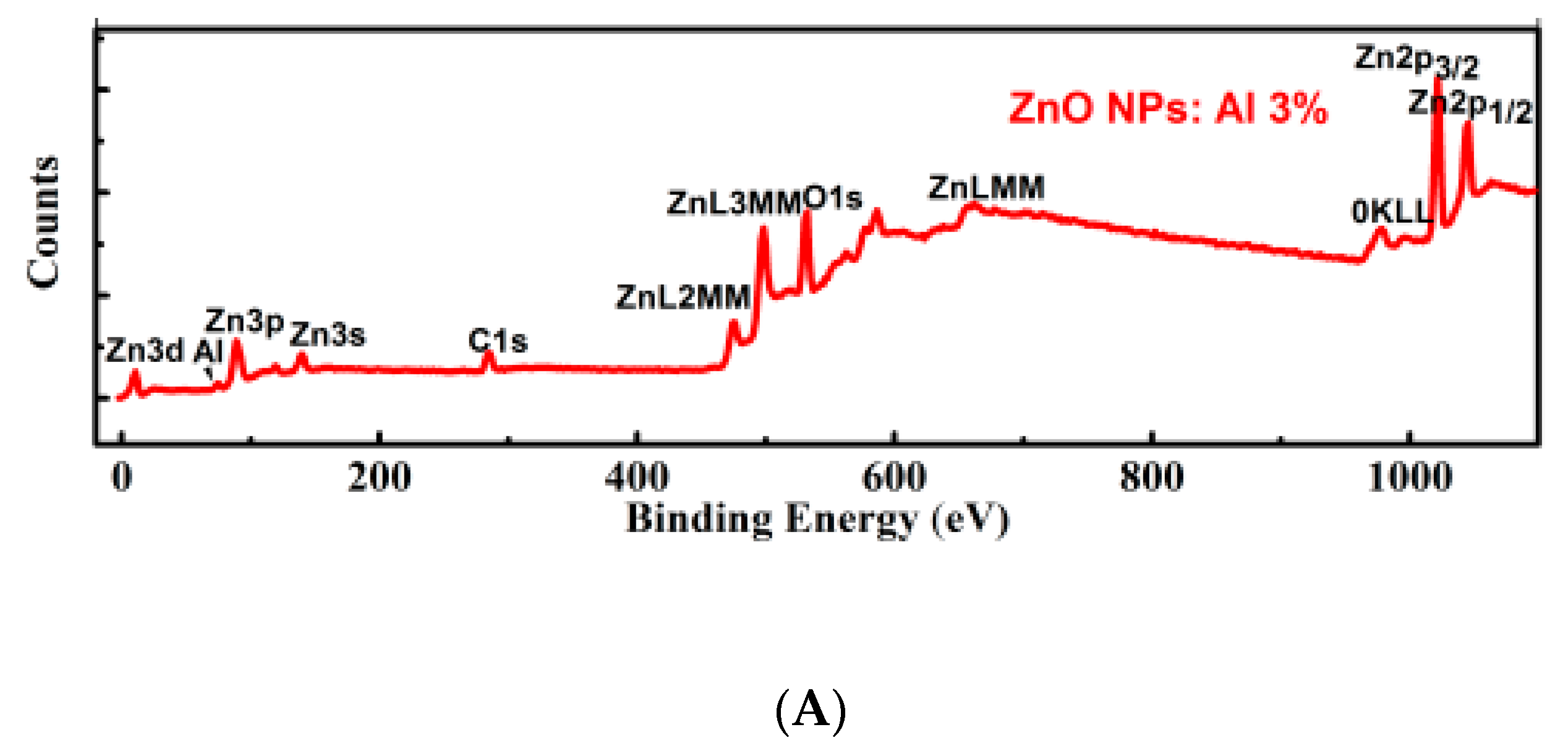
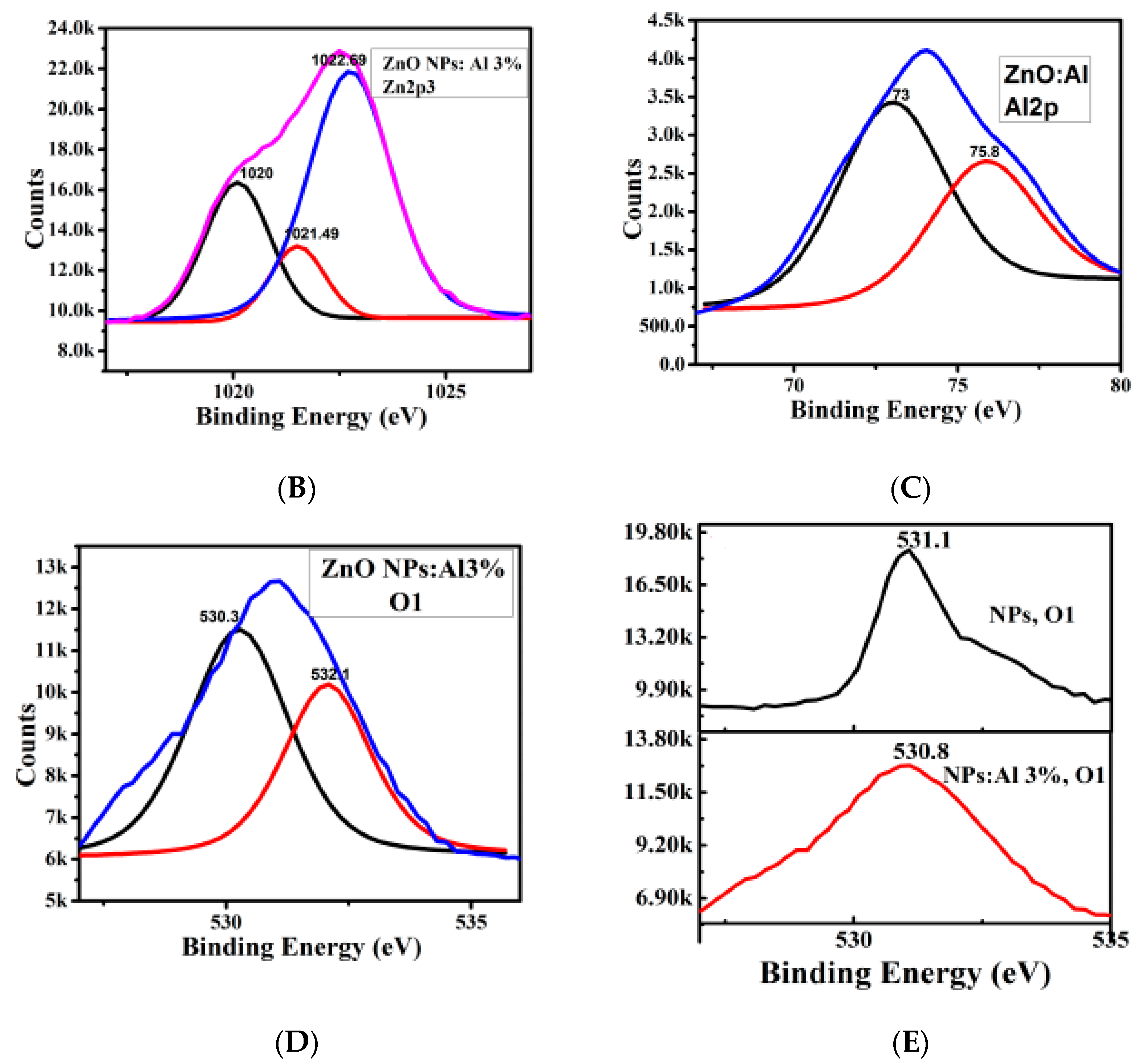
3.1. Structural Properties
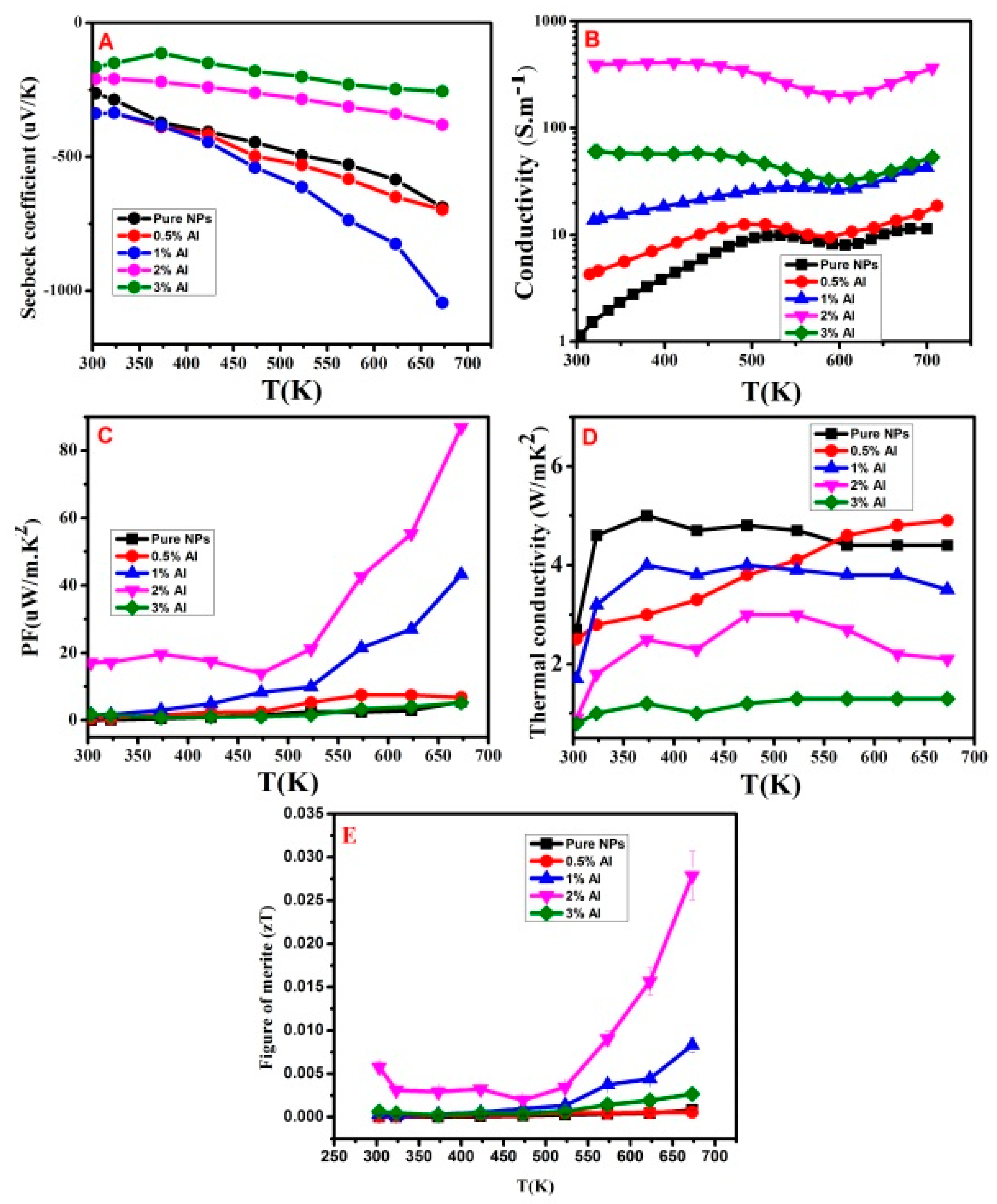
3.2. Thermoelectric Properties
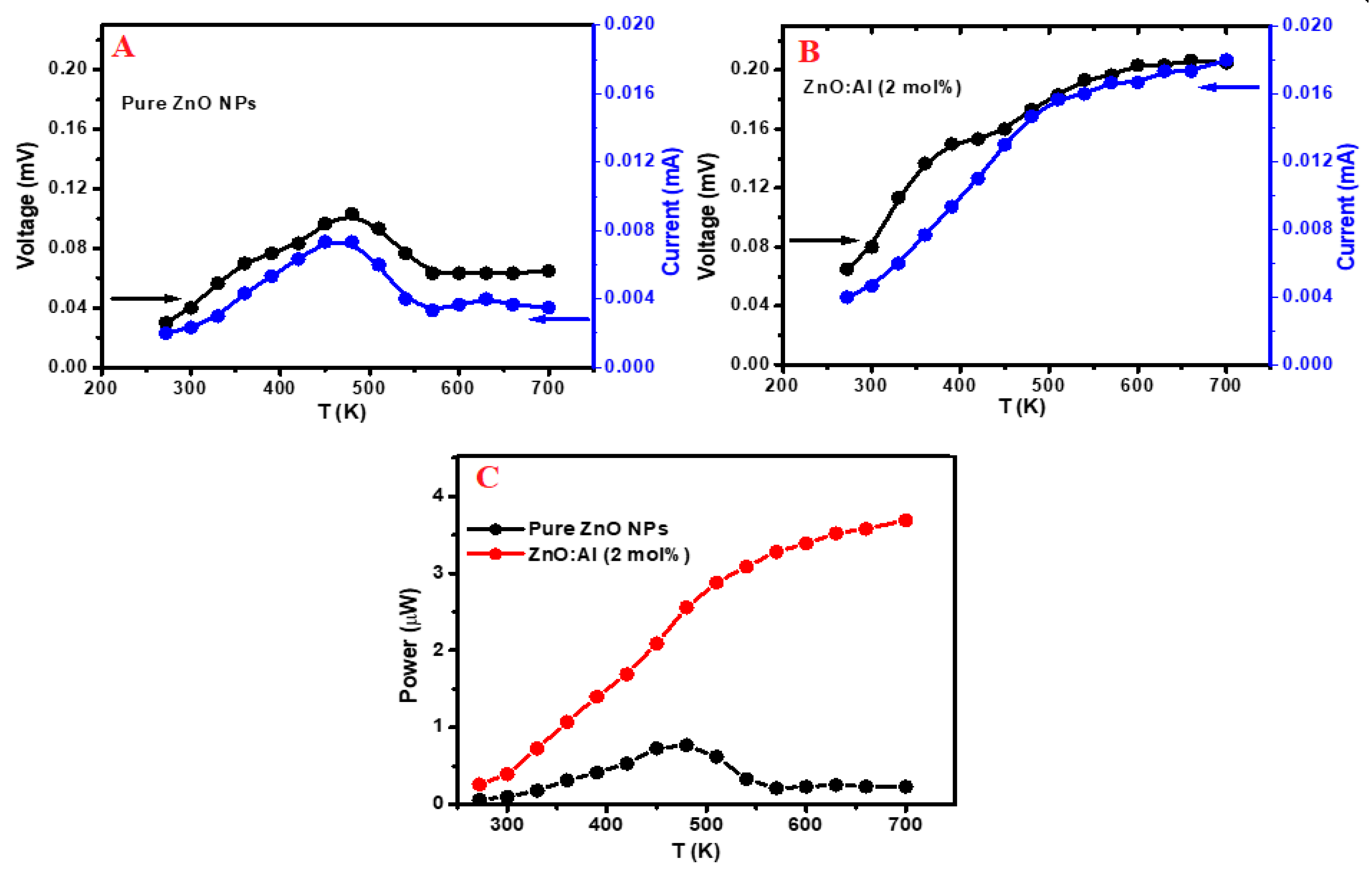
3.3. Power Measurements
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dresselhaus, M.S.; Chen, G.; Tang, M.Y.; Yang, R.G.; Lee, H.; Wang, D.Z.; Ren, Z.F.; Fleurial, J.-P.; Gogna, P. New directions for low-dimensional thermoelectric materials. Adv. Mater. 2007, 19, 1043–1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Backhaus-Ricoult, M.; Rustad, J.; Moore, L.; Smith, C.; Brown, J. Semiconducting large bandgap oxides as potential thermoelectric materials for high-temperature power generation? Appl. Phys. A 2014, 116, 433–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hébert, S.; Berthebaud, D.; Daou, R.; Bréard, Y.; Pelloquin, D.; Guilmeau, E.; Gascoin, F.; Lebedev, O.; Maignan, A. Searching for new thermoelectric materials: Some examples among oxides, sulfides and selenides. J. Phys. Condens. Matter. 2015, 28, 013001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Weintraub, B.; Zhou, Z.; Li, Y.; Deng, Y. Solution synthesis of one-dimensional ZnO nanomaterials and their applications. Nanoscale 2010, 2, 1573–1587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janotti, A.; Van de Walle, C.G. New insights into the role of native point defects in ZnO. J. Cryst. Growth 2006, 287, 58–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jood, P.; Mehta, R.J.; Zhang, Y.; Peleckis, G.; Wang, X.; Siegel, R.W.; Borca-Tasciuc, T.; Dou, S.X.; Ramanath, G. Al-Doped Zinc Oxide nanocomposites with enhanced thermoelectric properties. Nano Lett. 2011, 11, 4337–4342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, K.-M.; Choi, Y.-J.; Yeom, G.Y.; Park, H.-H. Thickness-dependent growth orientation of F-doped ZnO films formed by atomic layer deposition. J. Vac. Sci. Technol. A 2016, 34, 01A144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, Y.; Lian, J. Optical and electrical properties of aluminum-doped ZnO thin films grown by pulsed laser deposition. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2007, 253, 3727–3730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mickan, M.; Helmersson, U.; Rinnert, H.; Ghanbaja, J.; Muller, D.; Horwat, D. Room temperature deposition of homogeneous, highly transparent and conductive Al-doped ZnO films by reactive high power impulse magnetron sputtering. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 2016, 157, 742–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vettumperumal, R.; Kalyanaraman, S.; Thangavel, R. Photoconductive UV detectors based heterostructures of Cd and Mg doped ZnO sol gel thin films. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2014, 145, 237–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, K.C.; Ma, D.Y.; Kim, K.H. The physical properties of Al-doped zinc oxide films prepared by RF magnetron sputtering. Thin Solid Films 1997, 305, 201–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salah, N.; Al-Shawafi, W.M.; Alshahrie, A.; Baghdadi, N.; Soliman, Y.M.; Memic, A. Size controlled, antimicrobial ZnO nanostructures produced by the microwave assisted route. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2019, 99, 1164–1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, M.; Lee, K.E.; Hahn, S.H.; Kim, E.J.; Kim, S.; Chung, J.S.; Shin, E.W.; Park, C. Optical and photoluminescent properties of sol-gel Al-doped ZnO thin films. Mater. Lett. 2007, 61, 1118–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Xu, J.; Xu, Q.; Fang, G. Preparation and characterization of Al doped ZnO thin films by sol–gel process. J. Alloys Compd. 2012, 542, 151–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mote, V.D.; Purushotham, Y.; Dole, B.N. Williamson-Hall analysis in estimation of lattice strain in nanometer-sized ZnO particles. J. Theor. Appl. Phys. 2012, 6, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Park, K.; Ko, K.Y. Effect of TiO2 on high-temperature thermoelectric properties of ZnO. J. Alloys Compd. 2007, 430, 200–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohtaki, M.; Tsubota, T.; Eguchi, K. Thermoelectric properties of oxide solid solutions based on Al-doped ZnO; Proceedings ICT98 (Cat. No.98TH8365). In Proceedings of the Seventeenth International Conference on Thermoelectrics, Piscataway, NJ, USA, 24–28 May 1998; pp. 610–613. [Google Scholar]
- Shirouzu, K.; Ohkusa, T.; Hotta, M.; Enomoto, N.; Hojo, J. Distribution and solubility limit of Al in Al2O3-doped ZnO sintered body. J. Ceram. Soc. Jpn. 2007, 115, 254–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hong, M.-H.; Choi, H.; Shim, D.I.; Cho, H.H.; Kim, J.; Park, H.-H. Study of the effect of stress/strain of mesoporous Al-doped ZnO thin films on thermoelectric properties. Solid State Sci. 2018, 82, 84–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallika, A.; RamachandraReddy, A.; SowriBabu, K.; Reddy, K.V. Synthesis and optical characterization of aluminum doped ZnO nanoparticles. Ceram. Int. 2014, 40, 12171–12177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, C.-L.; Guan, H.-Y.; Wen, S.-B.; Chen, B.; Han, D.-X.; Gong, J.; Yang, X.-H.; Liu, Y.-C. Preparation and characterization of NiO nanofibers via an electrospinning technique. Chem. J. Chin. Univ. Chin. Ed. 2004, 25, 1015–1017. [Google Scholar]
- Yogamalar, N.R.; Bose, A.C. Absorption–emission study of hydrothermally grown Al: ZnO nanostructures. J. Alloys Compd. 2011, 509, 8493–8500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jule, L.; Dejene, F.; Ali, A.G.; Roro, K.; Mwakikunga, B. Defect-induced room temperature ferromagnetic properties of the Al-doped and undoped ZnO rod-like nanostructure. Mater. Lett. 2017, 199, 151–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Decremps, F.; Pellicer-Porres, J.; Saitta, A.M.; Chervin, J.-C.; Polian, A. High-pressure Raman spectroscopy study of wurtzite ZnO. Phys. Rev. B 2002, 65, 092101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, J.; Wang, J.; Zhuo, R.; Yan, D.; Feng, J.; Zhang, F.; Yan, P. The effect of Al doping on the morphology and optical property of ZnO nanostructures prepared by hydrothermal process. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2009, 255, 3959–3964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, W.S. Reaction Sintering of ZnO-Al2O3. Master’s Thesis, University of California, Berkeley, CA, USA, May 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Lindsay, J.R.; Rose, H.J.; Swartz, W.E.; Watts, P.H.; Rayburn, K.A. X-ray photoelectron spectra of aluminum oxides: Structural effects on the “chemical shift”. Appl. Spectrosc. 1973, 27, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nefedov, V.; Firsov, M.; Shaplygin, I. Electronic structures of MRhO2, MRh2O4, RhMO4 and Rh2MO6 on the basis of X-ray spectroscopy and ESCA data. J. Electron. Spectrosc. Relat. Phenom. 1982, 26, 65–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, S.; Guo, T.; Zhao, Y.; Luo, R.; Li, D.; Chen, A.; Liu, C.C. Mechanism enhancing gas sensing and first-principle calculations of Al-doped ZnO nanostructures. J. Mater. Chem. A 2013, 1, 11335–11342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Li, Y.; Kong, Y.; Zhou, J.; Wu, J.; Wu, X.; Qin, W.; Jiao, Z.; Jiang, L. Non-fluorinated superhydrophobic and micro/nano hierarchical Al doped ZnO film: The effect of Al doping on morphological and hydrophobic properties. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 81024–81029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uma, K.; Rusop, M.; Soga, T.; Jimbo, T. Effects of Al content on Zn0.95Mg0.05O thin films deposited by sol–gel spin coating. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 2007, 46, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinemuchi, Y.; Ito, C.; Kaga, H.; Aoki, T.; Watari, K. Thermoelectricity of Al-doped ZnO at different carrier concentrations. J. Mater. Res. 2007, 22, 1942–1946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mondarte, E.A.; Copa, V.; Tuico, A.; Vergara, C.J.; Estacio, E.; Salvador, A.; Somintac, A. Al-doped ZnO and N-doped CuxO thermoelectric thin films for self-powering integrated devices. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. 2016, 45, 27–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, H.; Xu, X.; Hng, H.; Ma, J. Characterization of Al-doped ZnO thermoelectric materials prepared by RF plasma powder processing and hot press sintering. Ceram. Int. 2009, 35, 3067–3072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohtaki, M.; Araki, K.; Yamamoto, K. High thermoelectric performance of dually doped ZnO ceramics. J. Electron. Mater. 2009, 38, 1234–1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, K.; Müller, E.; Drašar, C.; Mrotzek, A. Preparation and thermoelectric properties of Al-doped ZnO ceramics. Mater. Sci. Eng. B 2003, 104, 45–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.M.; Yi, D.Q.; Yu, Z.M.; Xiao, L.R.; Li, J. Preparation of aluminum doped zinc oxide films and the study of their microstructure, electrical and optical properties. Thin Solid Films 2007, 515, 6909–6914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujishiro, Y.; Miyata, M.; Awano, M.; Maeda, K. Effect of microstructural control on thermoelectric properties of hot-pressed Aluminum-Doped Zinc Oxide. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2003, 86, 2063–2066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katsuyama, S.; Takagi, Y.; Ito, M.; Majima, K.; Nagai, H.; Sakai, H.; Yoshimura, K.; Kosuge, K. Thermoelectric properties of (Zn1−yMgy)1−xAlxO ceramics prepared by the polymerized complex method. J. Appl. Phys. 2002, 92, 1391–1398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Özgür, Ü.; Alivov, Y.I.; Liu, C.; Teke, A.; Reshchikov, M.; Doğan, S.; Avrutin, V.; Cho, S.-J.; Morkoç, H. A comprehensive review of ZnO materials and devices. J. Appl. Phys. 2005, 98, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tsubota, T.; Ohtaki, M.; Eguchi, K.; Arai, H. Thermoelectric properties of Al-doped ZnO as a promising oxidematerial for high-temperature thermoelectric conversion. J. Mater. Chem. 1997, 7, 85–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugahara, T.; Ohtaki, M.; Souma, T. Fabrication and power generation characteristics of p-NaCo2O4/n-ZnO oxide thermoelectric modules. In Proceedings of the 25th International Conference on Thermoelectrics, Vienna, Austria, 6–10 August 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Kulsi, C.; Dhara, P.; Mitra, M.; Kargupta, K.; Ganguly, S.; Banerjee, D. Effect of solvent on nanostructure and thermoelectric properties of bismuth. Indian J. Phys. 2016, 90, 557–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, T.; Bardhan, M.; Bhattacharya, M.; Satpati, B. Study of inelastic mean free path of metal nanostructures using energy filtered transmission electron microscopy imaging. J. Microsc. 2015, 258, 253–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
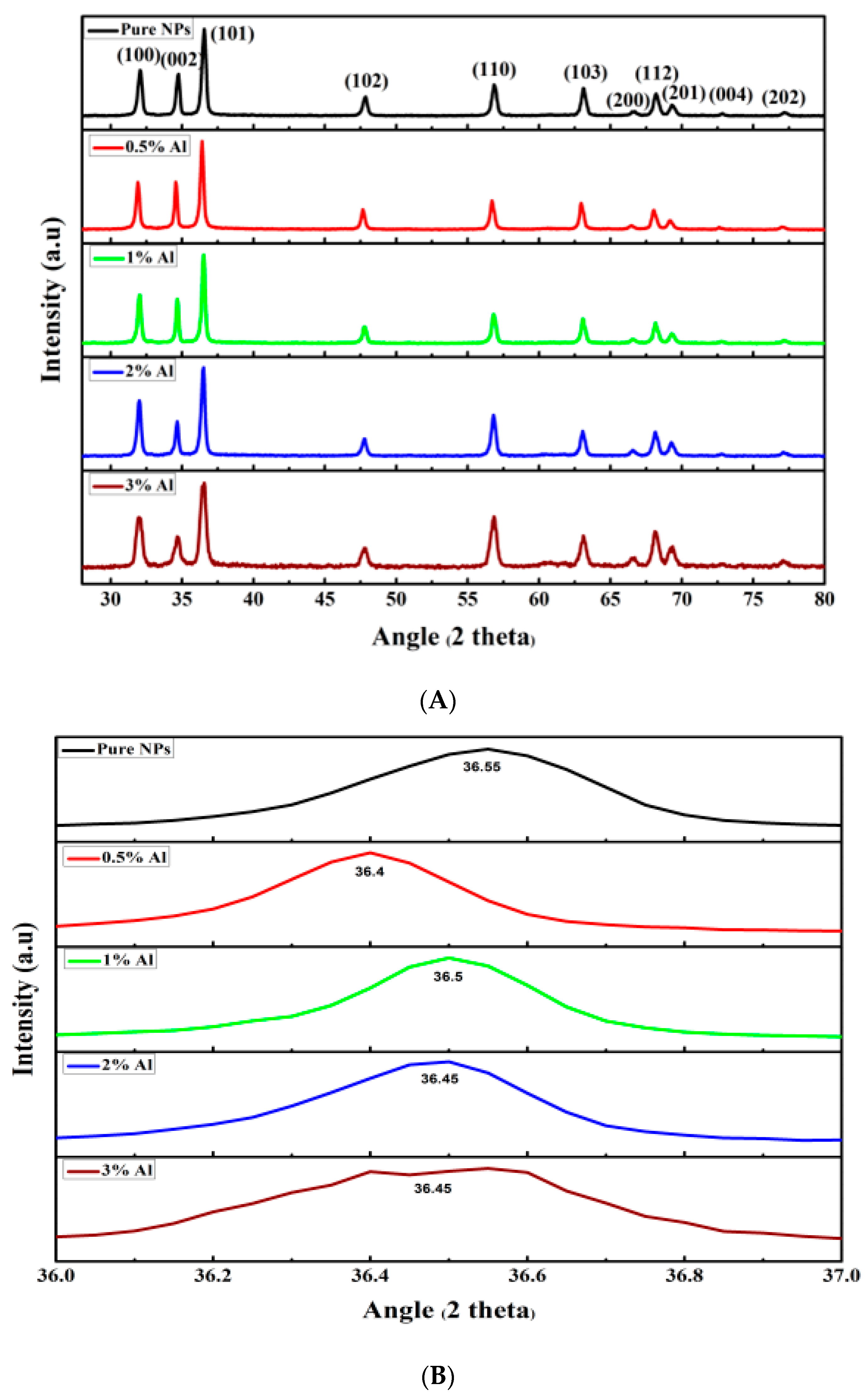
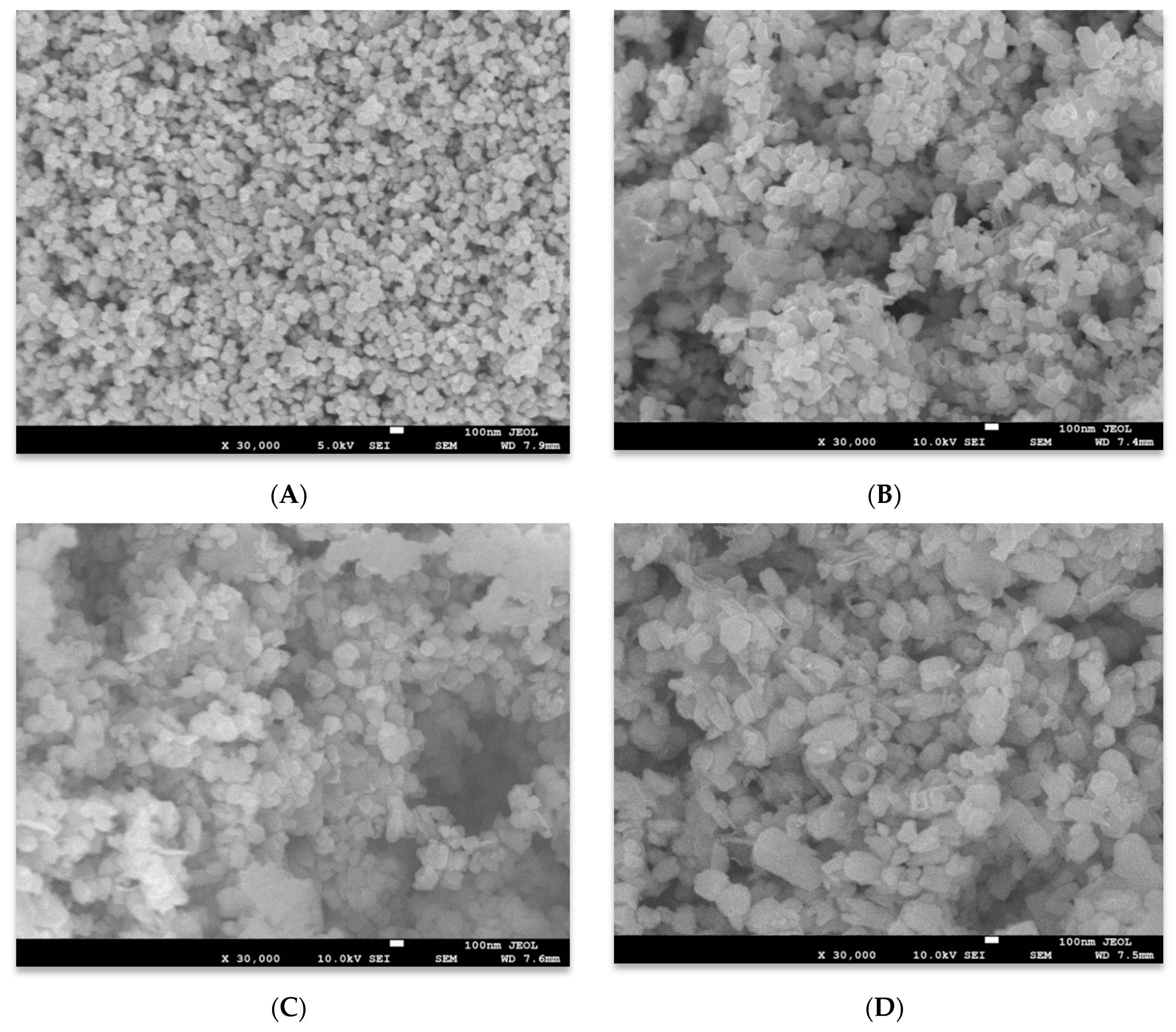
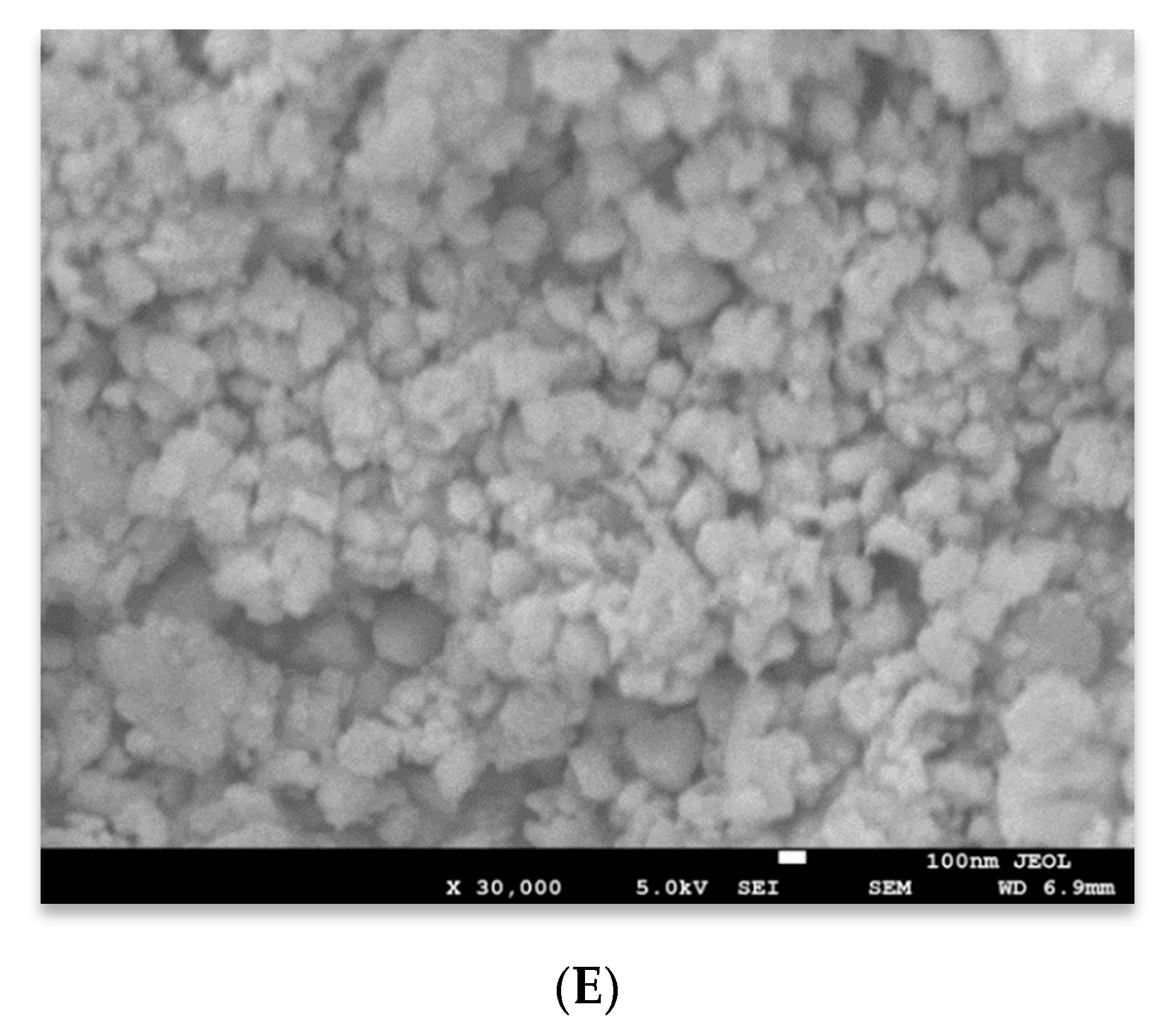

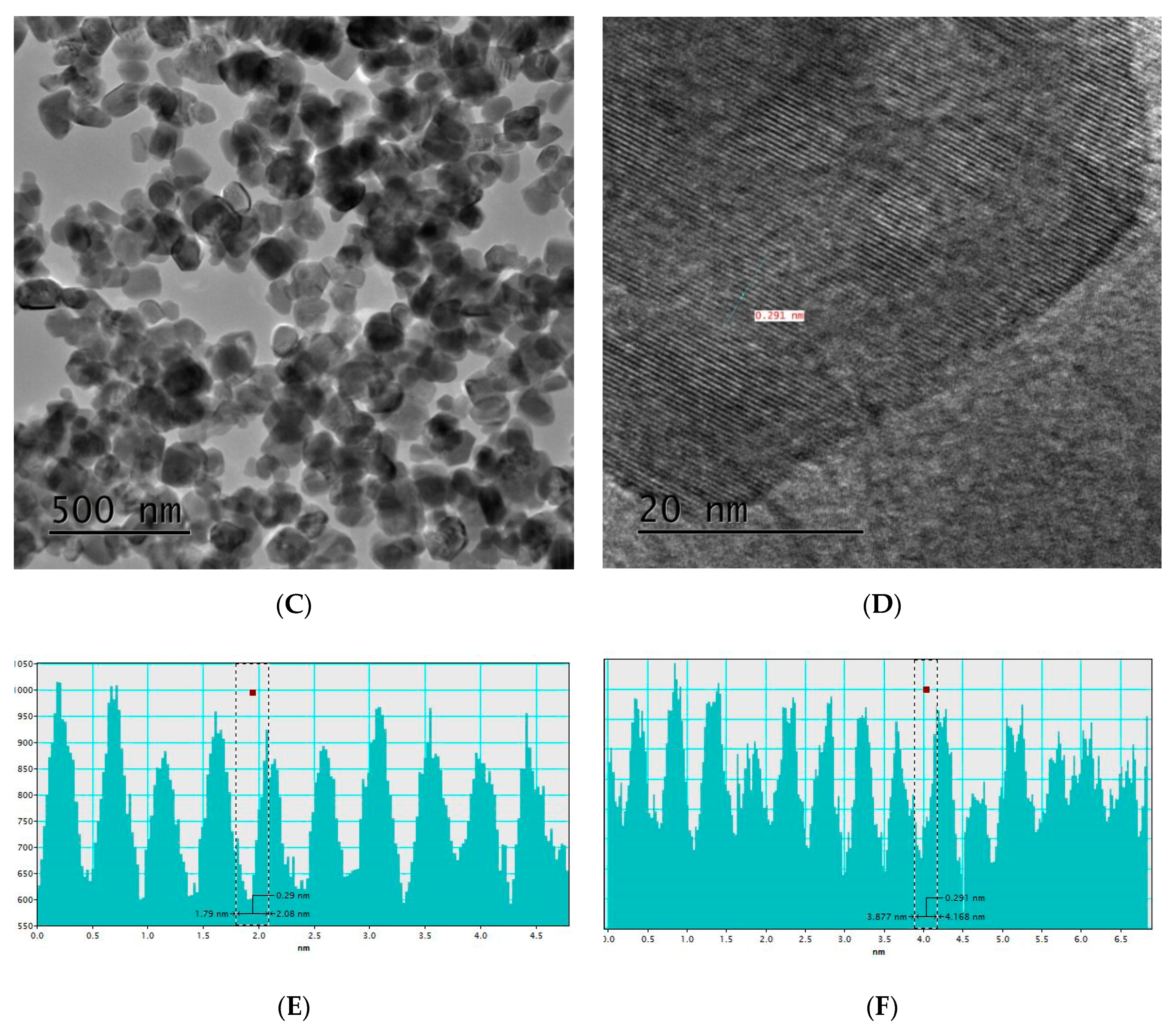
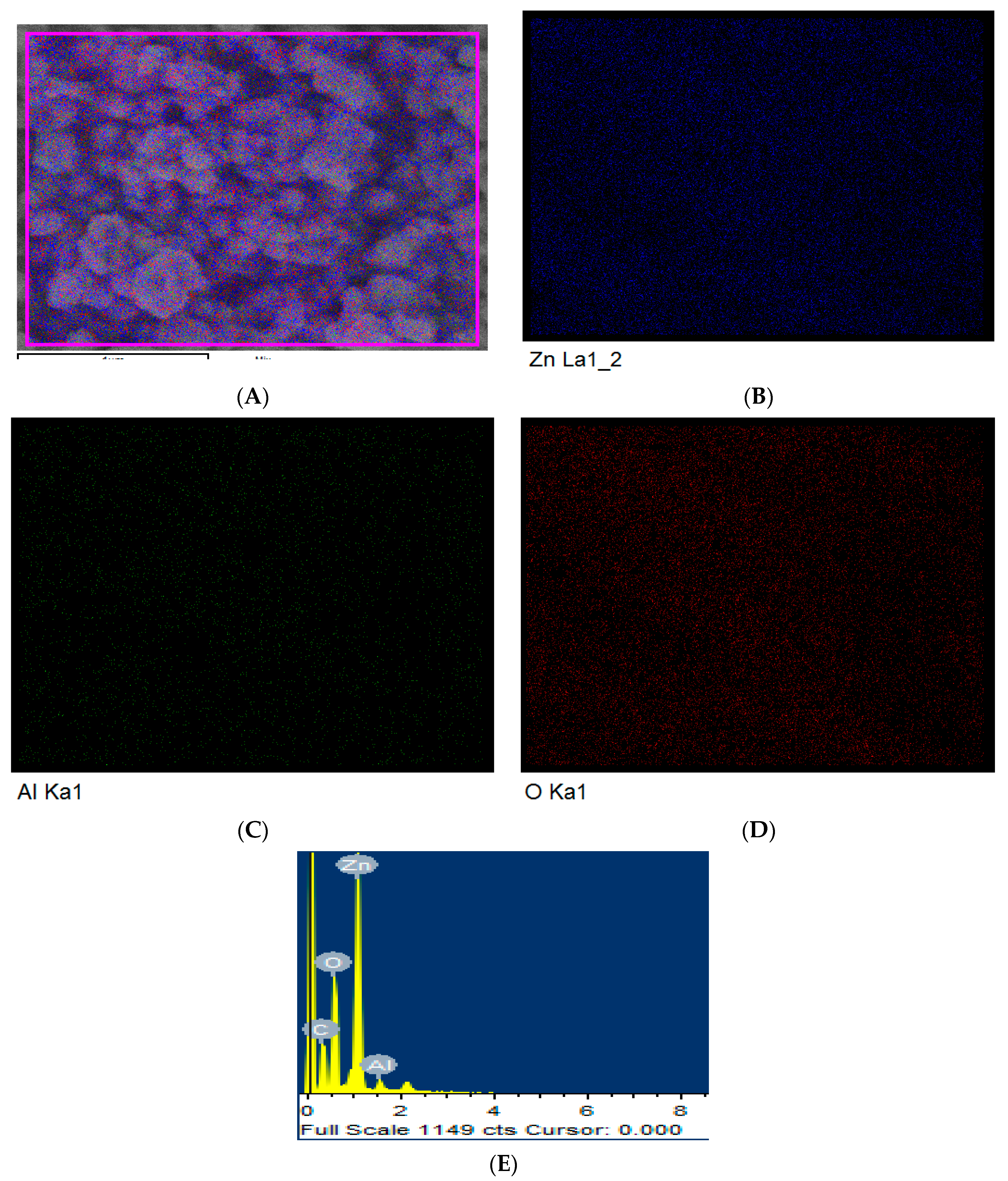
| Materials | Lattice Constant Parameter (Å) | Crystallite Size | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| a | b | c | c/a | ||
| Un-doped ZnO NPs | 3.249 | 3.249 | 5.208 | 1.603 | 18.7 nm |
| ZnO:Al NPs (0.5 mol %) | 3.232 | 3.232 | 5.178 | 1.602 | 23.5 nm |
| ZnO:Al NPs (1 mol %) | 3.236 | 3.236 | 5.186 | 1.602 | 27.6 nm |
| ZnO:Al NPs (2 mol %) | 3.234 | 3.234 | 5.184 | 1.603 | 24.1 nm |
| ZnO:Al NSs (3 mol %) | 3.238 | 3.238 | 5.179 | 1.600 | 17.6 nm |
| Element | Weight% | Atomic% |
|---|---|---|
| C K | 11.97 | 30.04 |
| O K | 19.62 | 36.96 |
| Al K | 2.22 | 2.48 |
| Zn | 66.18 | 30.51 |
| Materials | Temperature (°C) | Thermal Conductivity (W/m·K) | Specific Heat (J/K·Kg) | Thermal Diffusivity (m2·s−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pure ZnO NSs | R.T. * | 2.7 | 0.36 | 0.029 |
| 400 | 4.3 | 0.94 | 0.013 | |
| ZnO Al 0.5% Al | R.T. * | 2.8 | 0.34 | 0.021 |
| 400 | 4.8 | 1.96 | 0.010 | |
| ZnO Al 1% Al | R.T. * | 1.7 | 0.35 | 0.020 |
| 400 | 3.5 | 1.28 | 0.011 | |
| ZnO Al 2% Al | R.T. * | 0.97 | 0.34 | 0.012 |
| 400 | 2.1 | 0.84 | 0.010 | |
| ZnO Al 3% Al | R.T. * | 0.92 | 0.31 | 0.010 |
| 400 | 1.22 | 0.57 | 0.006 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Baghdadi, N.; Salah, N.; Alshahrie, A.; Koumoto, K. Microwave Irradiation to Produce High Performance Thermoelectric Material Based on Al Doped ZnO Nanostructures. Crystals 2020, 10, 610. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst10070610
Baghdadi N, Salah N, Alshahrie A, Koumoto K. Microwave Irradiation to Produce High Performance Thermoelectric Material Based on Al Doped ZnO Nanostructures. Crystals. 2020; 10(7):610. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst10070610
Chicago/Turabian StyleBaghdadi, Neazar, Numan Salah, Ahmed Alshahrie, and Kunihito Koumoto. 2020. "Microwave Irradiation to Produce High Performance Thermoelectric Material Based on Al Doped ZnO Nanostructures" Crystals 10, no. 7: 610. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst10070610
APA StyleBaghdadi, N., Salah, N., Alshahrie, A., & Koumoto, K. (2020). Microwave Irradiation to Produce High Performance Thermoelectric Material Based on Al Doped ZnO Nanostructures. Crystals, 10(7), 610. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst10070610






