Timing Fluctuation Correction of A Femtosecond Regenerative Amplifier
Abstract
:1. Introduction
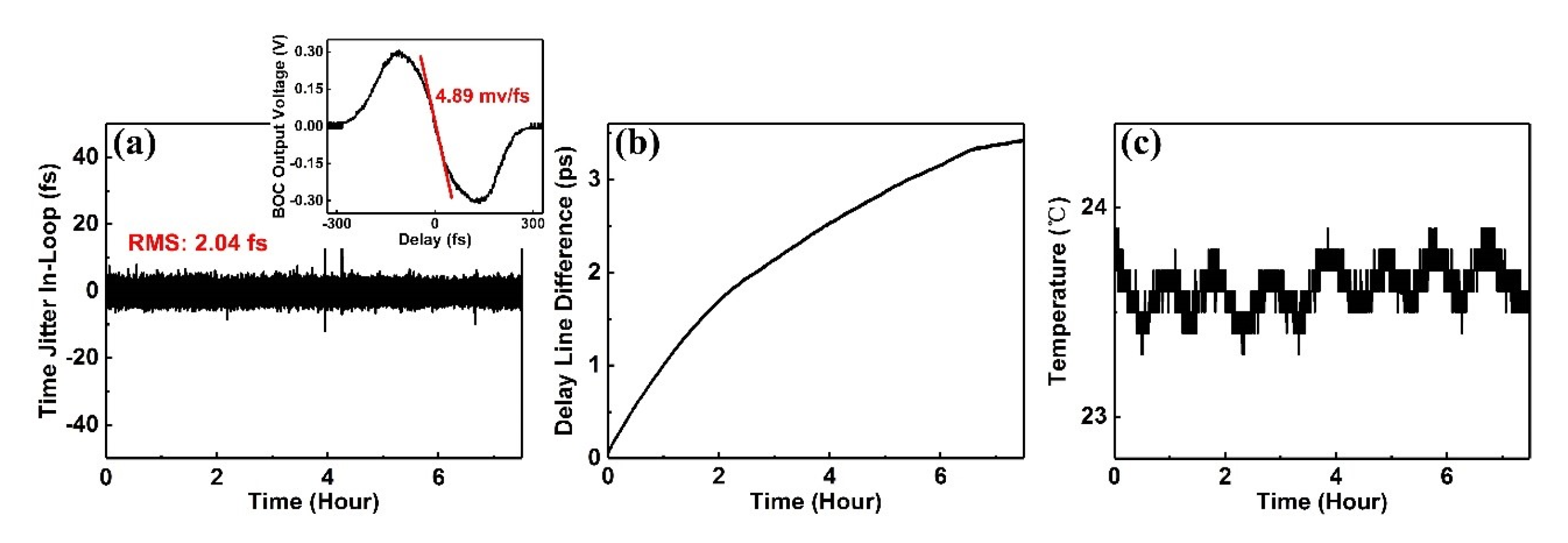
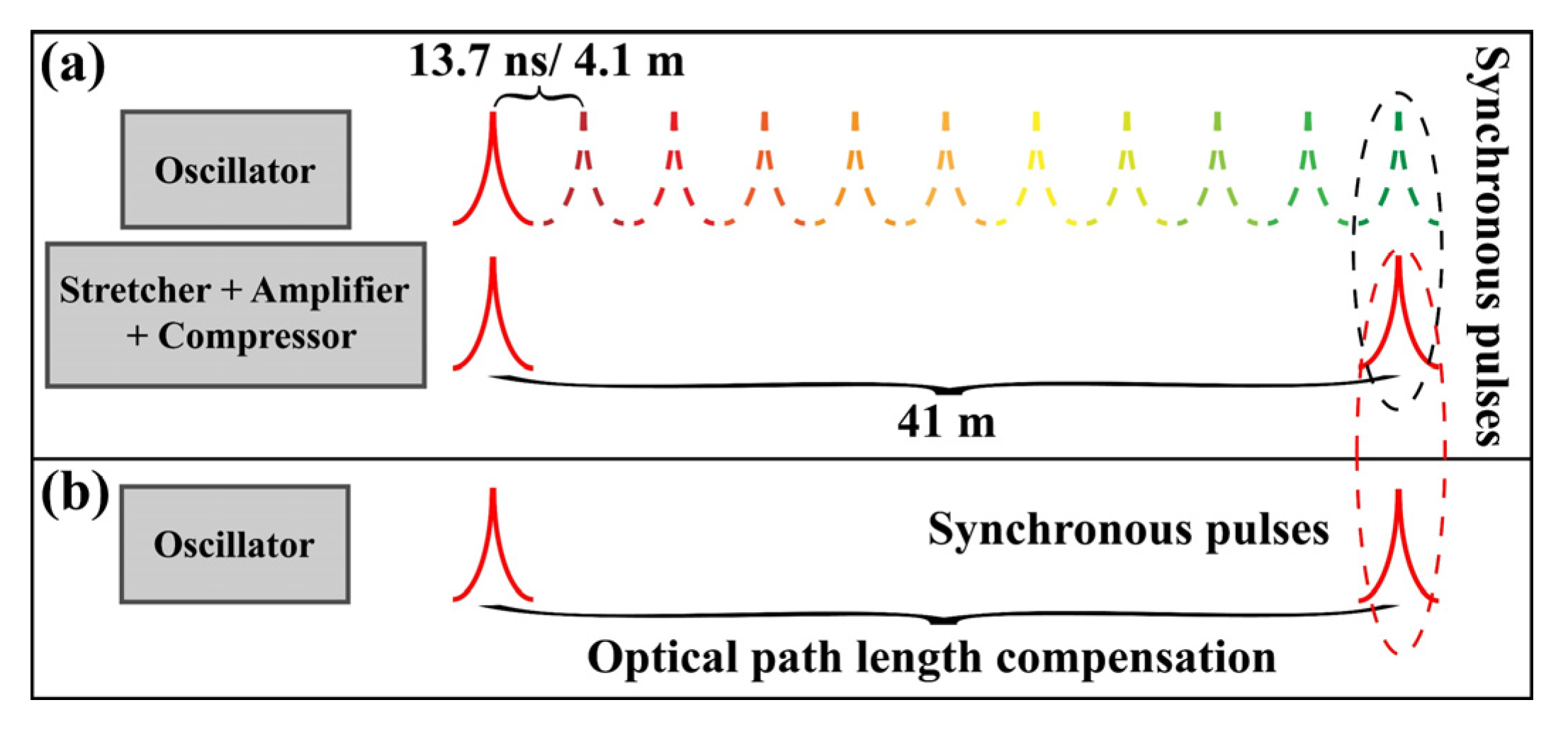
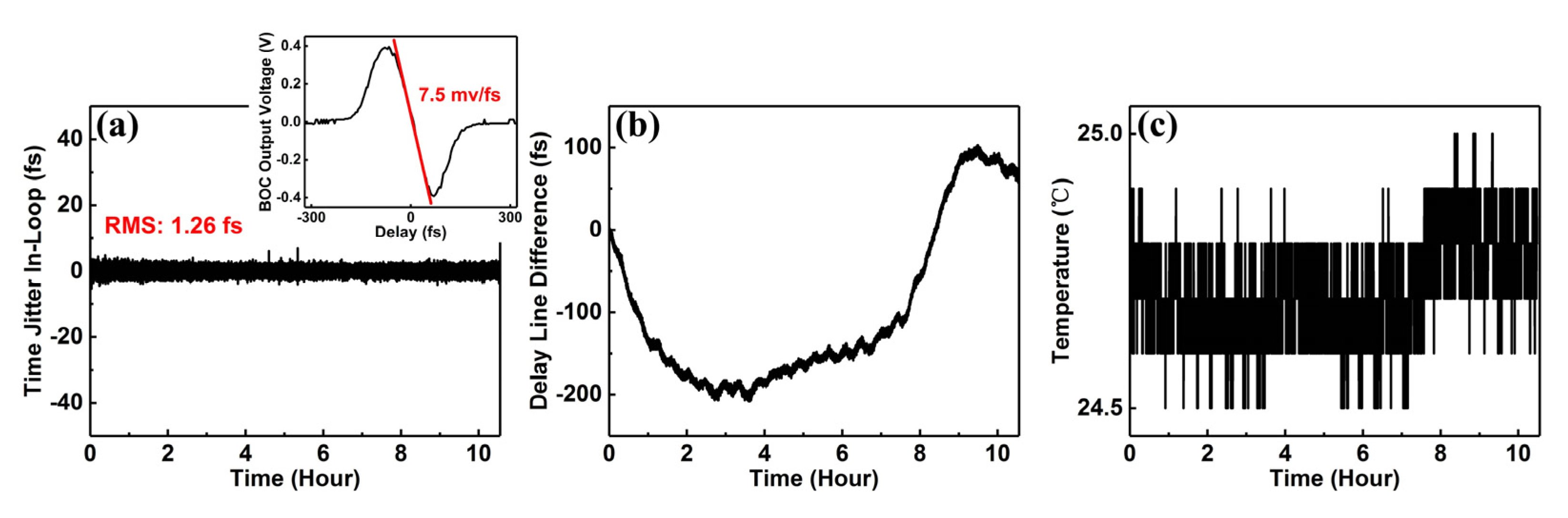
2. Experimental Implementation
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Strickland, D.; Mourou, G. Compression of amplified chirped optical pulses. Opt. Commun. 1985, 56, 219–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubietis, A.; Jonušauskas, G.; Piskarskas, A. Powerful femtosecond pulse generation by chirped and stretched pulse parametric amplification in BBO crystal. Opt. Commun. 1992, 88, 437–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aoyama, M.; Yamakawa, K.; Akahane, Y.; Ma, J.; Inoue, N.; Ueda, H.; Kiriyama, H. 085-PW, 33-fs Ti:sapphire laser. Opt. Lett. 2003, 28, 1594–1596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, L.; Yu, L.; Liang, X.; Chu, Y.; Hu, Z.; Ma, L.; Xu, Y.; Wang, C.; Lu, X.; Lu, H.; et al. High-energy noncollinear optical parametric–chirped pulse amplification in LBO at 800 nm. Opt. Lett. 2013, 38, 4837–4840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sung, J.H.; Lee, H.W.; Yoo, J.Y.; Yoon, J.W.; Lee, C.W.; Yang, J.M.; Son, Y.J.; Jang, Y.H.; Lee, S.K.; Nam, C.H. 42 PW, 20 fs Ti:sapphire laser at 01 Hz. Opt. Lett. 2017, 42, 2058–2061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, X.; Zhou, K.; Zuo, Y.; Zhu, Q.; Su, J.; Wang, X.; Wang, X.; Huang, X.; Jiang, X.; Jiang, D.; et al. Multi-petawatt laser facility fully based on optical parametric chirped-pulse amplification. Opt. Lett. 2017, 42, 2014–2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- le Garrec, B.; Papadopoulos, D.N.; le Blanc, C.; Zou, J.P.; Chériaux, G.; Georges, P.; Druon, F.; Martin, L.; Fréneaux, L.; Beluze, A.; et al. Design update and recent results of the Apollon 10 PW facility. Proc. SPIE 2017, 10238, 102380Q. [Google Scholar]
- Li, W.; Gan, Z.; Yu, L.; Wang, C.; Liu, Y.; Guo, Z.; Xu, L.; Xu, M.; Hang, Y.; Xu, Y.; et al. 339 J high-energy Ti:sapphire chirped-pulse amplifier for 10 PW laser facility. Opt. Lett. 2018, 43, 5681–5684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lureau, F.; Matras, G.; Chalus, O.; Derycke, C.; Morbieu, T.; Radier, C.; Casagrande, O.; Laux, S.; Ricaud, S.; Rey, G.; et al. High-energy hybrid femtosecond laser system demonstrating 2 × 10 PW capability. High Power Laser Sci. Eng. 2020, 8, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danson, C.N.; Haefner, C.; Bromage, J.; Butcher, T.; Chanteloup, J.C.-F.; Chowdhury, E.A.; Galvanauskas, A.; Gizzi, L.A.; Hein, J.; Hillier, D.I.; et al. Petawatt and exawatt class lasers worldwide. High Power Laser Sci. Eng. 2019, 7, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cartlidge, E. The light fantastic. Science 2018, 359, 382–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuegel, J.D.; Bahk, S.W.; Begishev, I.A.; Bromage, J.; Dorrer, C.; Okishev, A.V.; Oliver, J.B. Status of high-energy OPCPA at LLE and future prospects. In Proceedings of the 2014 Conference on Lasers and Electro-Optics (CLEO)—Laser Science to Photonic Applications, San Jose, CA, USA, 8–13 June 2014; pp. 1–2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaykin, A.; Kostyukov, I.; Sergeev, A.; Khazanov, E. Prospects of PEARL 10 and XCELS Laser Facilities. Rev. Laser Eng. 2014, 42, 141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cartlidge, E. Eastern Europe’s laser centers will debut without a star. Science 2017, 355, 785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kodama, R.; Norreys, P.A.; Mima, K.; Dangor, A.E.; Evans, R.G.; Fujita, H.; Kitagawa, Y.; Krushelnick, K.; Miyakoshi, T.; Miyanaga, N.; et al. Fast heating of ultrahigh-density plasma as a step towards laser fusion ignition. Nat. Cell Biol. 2001, 412, 798–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mourou, G.A.; Tajima, T.; Bulanov, S.V. Optics in the relativistic regime. Rev. Mod. Phys. 2006, 78, 309–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fujioka, S.; Takabe, H.; Yamamoto, N.; Salzmann, D.; Wang, F.; Nishimura, H.; Li, Y.; Dong, Q.; Wang, S.; Zhang, Y.; et al. X-ray astronomy in the labora-tory with a miniature compact object produced by laser-driven implosion. Nat. Phys. 2009, 5, 821–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Daido, H.; Nishiuchi, M.; Pirozhkov, A. Review of laser-driven ion sources and their applications. Rep. Prog. Phys. 2012, 75, 056401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, B.; Li, Y.; Peng, Y.; Wang, P.; Qian, J.; Leng, Y.; Li, R. Broad-bandwidth high-temporal-contrast carri-er-envelope-phase-stabilized laser seed for 100 PW lasers. Opt. Lett. 2020, 45, 2215–2218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batysta, F.; Antipenkov, R.; Green, J.T.; Naylon, J.A.; Novák, J.; Mazanec, T.; Hříbek, P.; Zervos, C.; Bakule, P.; Rus, B. Pulse synchronization system for picosecond pulse-pumped OPCPA with femtosecond-level relative timing jitter. Opt. Express 2014, 22, 30281–30286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prinz, S.; Häfner, M.; Schultze, M.; Teisset, C.Y.; Bessing, R.; Michel, K.; Kienberger, R.; Metzger, T. Active pump-seed-pulse synchronization for OPCPA with sub-2-fs residual timing jitter. Opt. Express 2014, 22, 31050–31056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casanova, A.; D’Acremont, Q.; Santarelli, G.; Dilhaire, S.; Courjaud, A. Ultrafast amplifier additive timing jitter character-ization and control. Opt. Lett. 2016, 41, 898–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xin, M.; Şafak, K.; Kärtner, F.X. Ultra-precise timing and synchronization for large-scale scientific instruments. Optica 2018, 5, 1564–1578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, M.; Şafak, K.; Peng, M.Y.; Callahan, P.T.; Kärtner, F.X. One-femtosecond, long-term stable remote laser synchronization over a 35-km fiber link. Opt. Express 2014, 22, 14904–14912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Şafak, K.; Xin, M.; Callahan, P.T.; Peng, M.Y.; Kartner, F.X. All fiber-coupled, long-term stable timing distribution for free-electron lasers with few-femtosecond jitter. Struct. Dyn. 2015, 2, 041715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Chen, J.; Cox, J.; Kärtner, F.X. Attosecond-resolution timing jitter characterization of free-running mode-locked lasers. Opt. Lett. 2007, 32, 3519–3521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kärtner, F.; Wong, F.; Kim, J. Compact Background-Free Balanced Cross-Correlators. U.S. Patent 7,940,390 B2, 10 May 2011. [Google Scholar]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, K.; Li, H.; Wang, X.; Liu, Y.; Song, L.; Leng, Y. Timing Fluctuation Correction of A Femtosecond Regenerative Amplifier. Crystals 2021, 11, 1242. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst11101242
Liu K, Li H, Wang X, Liu Y, Song L, Leng Y. Timing Fluctuation Correction of A Femtosecond Regenerative Amplifier. Crystals. 2021; 11(10):1242. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst11101242
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Keyang, Hongyang Li, Xinliang Wang, Yanqi Liu, Liwei Song, and Yuxin Leng. 2021. "Timing Fluctuation Correction of A Femtosecond Regenerative Amplifier" Crystals 11, no. 10: 1242. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst11101242
APA StyleLiu, K., Li, H., Wang, X., Liu, Y., Song, L., & Leng, Y. (2021). Timing Fluctuation Correction of A Femtosecond Regenerative Amplifier. Crystals, 11(10), 1242. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst11101242






