Effect of Bi Content on the Microstructure and Mechanical Performance of Sn-1Ag-0.5Cu Solder Alloy
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
- (1)
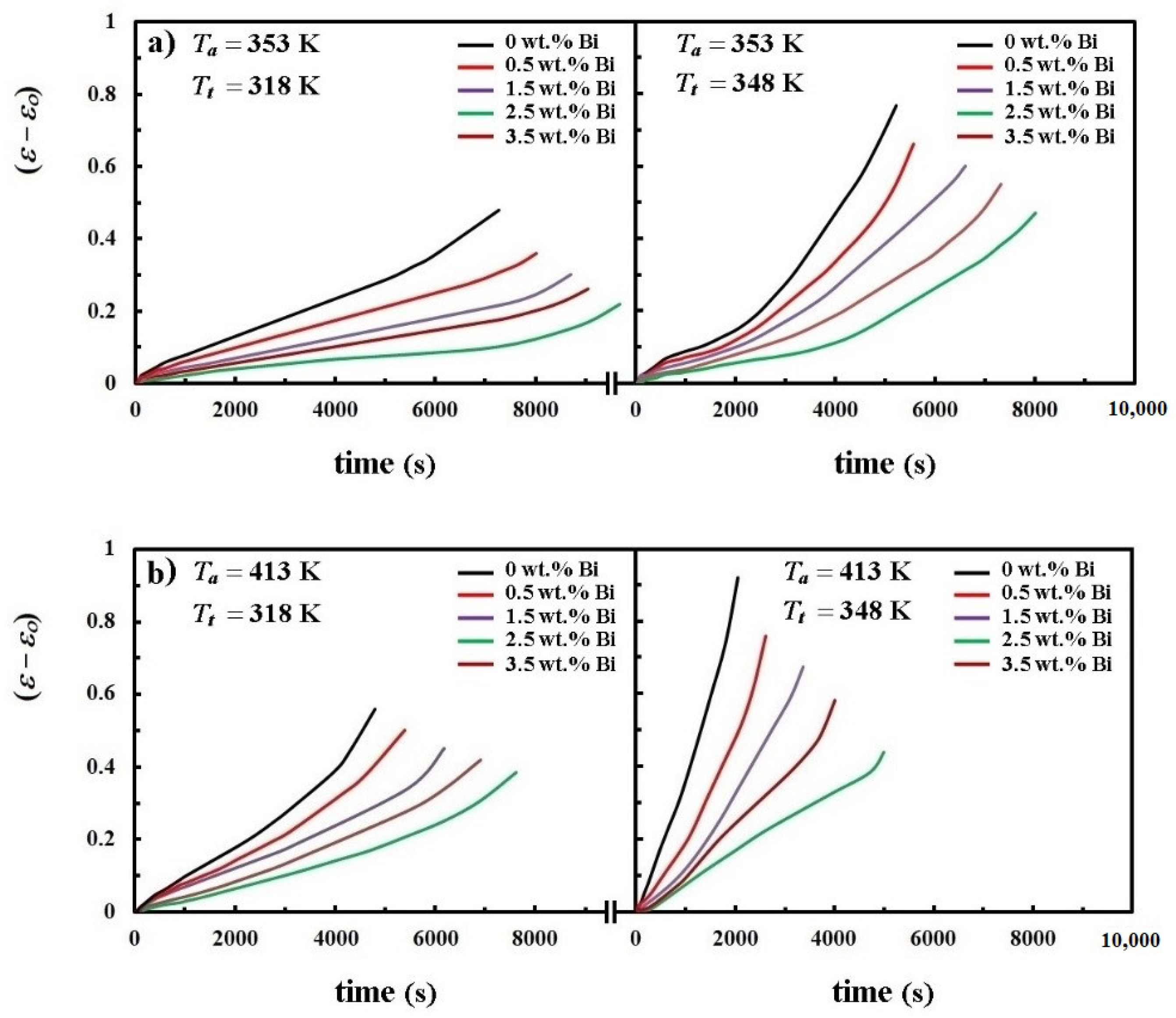
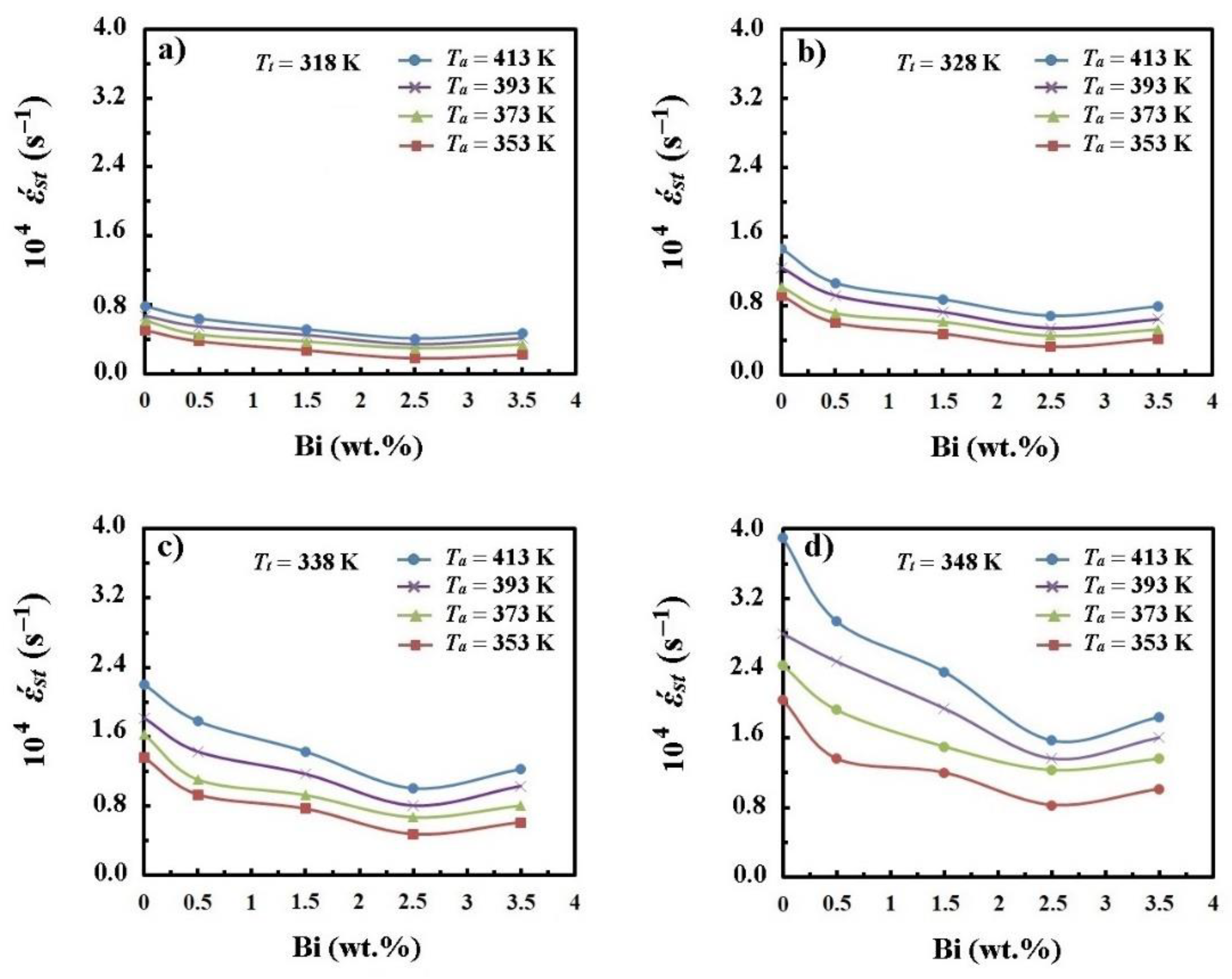
- The steady-state creep rate values were decreased continuously as Bi concentration was elevating up to 2.5 wt.%; above this weight ratio, the trend runs in the opposite direction.
- (2)
- The steady-state creep rate values for all Bi-containing solders increased as the aging and/or testing temperatures raised.
- (3)
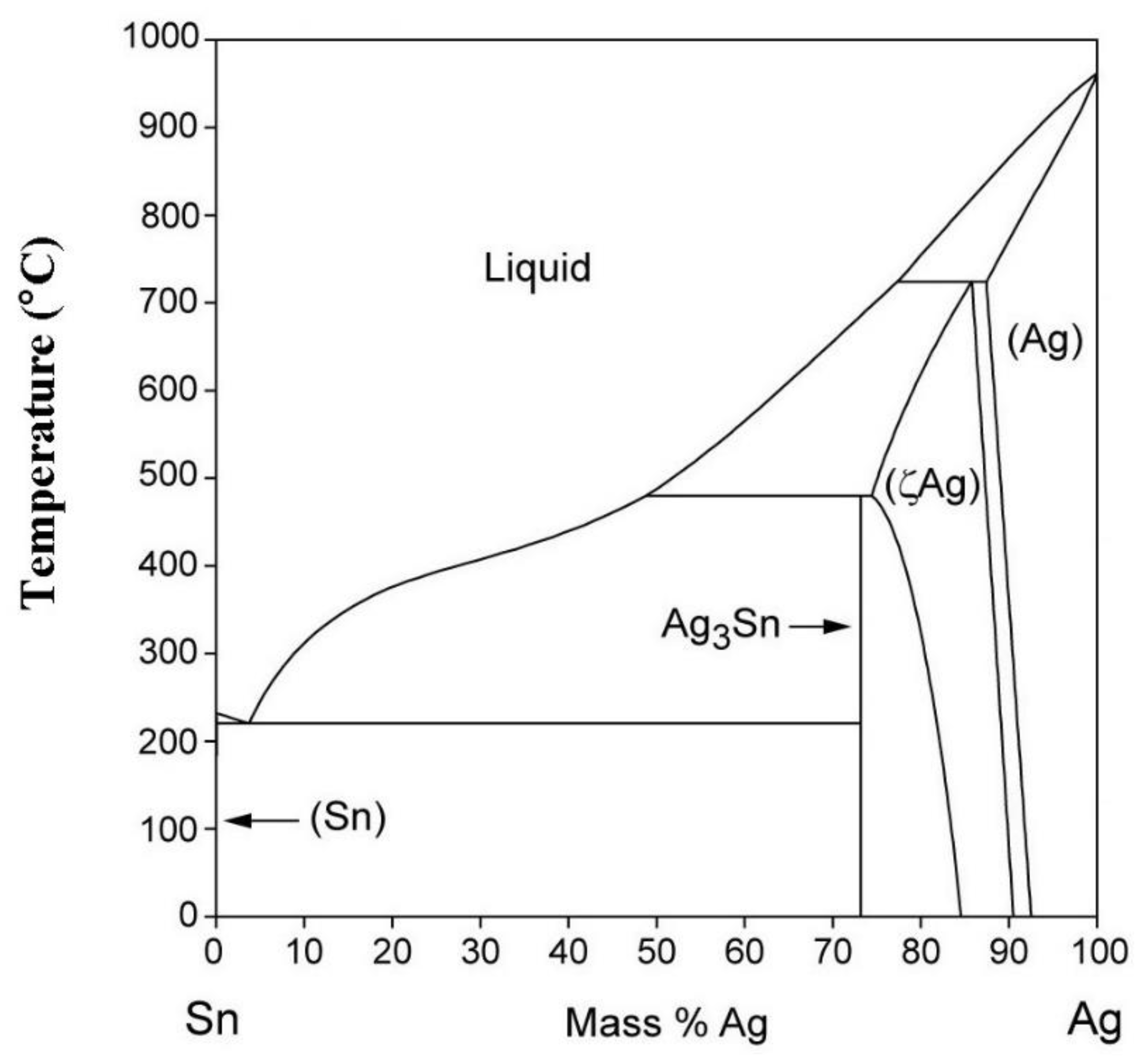
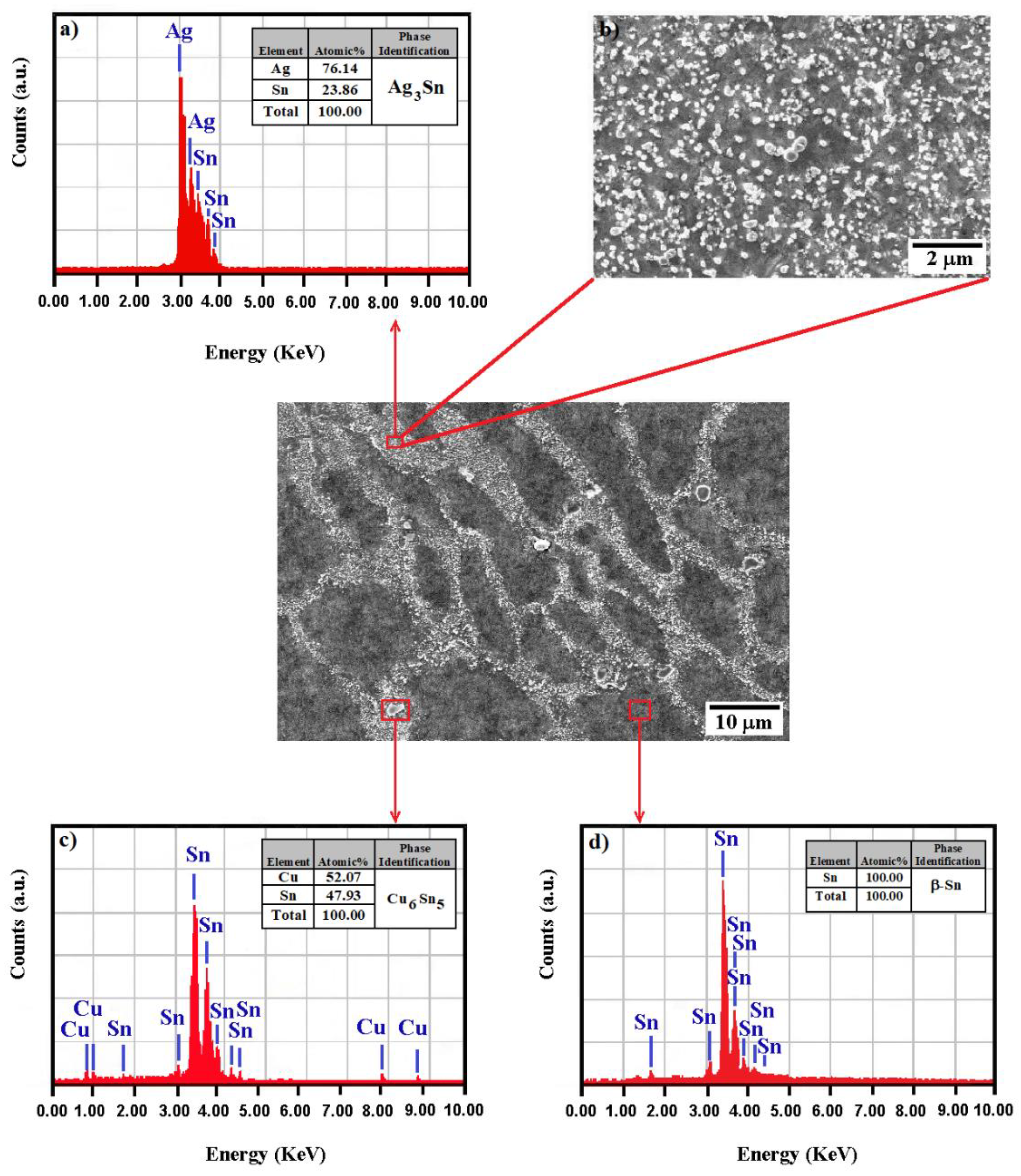
- The steady-state creep rate alterations with Bi ratio and aging temperature were attributed to the formation, growth, coarsening, and coalescence of Ag3Sn and Cu6Sn5 precipitates.
- (4)
- According to the activation energy mean value, the dislocation climb through the core diffusion was the predominant creep mechanism.
- (5)
- The unit cell volume, the lattice constants a and c of the Sn-matrix vary depending on the change in the bismuth content and aging temperature variations
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- El-Daly, A.A.; Eladly, S.A.; Mohamed, A.; Elmosalami, T.A.; Dawood, M.S. Improvement of strength-ductility trade-off in a Sn–0.7Cu–0.2Ni lead-free solder alloys through Al-microalloying. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2020, 31, 8649–8661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yavuzer, B.; Özyürek, D.; Tunçay, T. Microstructure and mechanical properties of Sn 9Zn-xAl and Sn-9Zn-xCu lead-free solder alloys. Mater. Sci. Pol. 2020, 38, 34–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abd El-Rehim, A.F.; Mahmoud, A.S.; Abdelaziz, S.M. Influence of Sb2O3 nanoparticles addition on the thermal, microstructural and creep properties of hypoeutectic Sn–Bi solder alloy. Sci. Adv. Mater. 2021, 13, 20–29. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, J.; Xue, S.; Wang, J.; Wu, M. Coupling effects of rare-earth Pr and Al2O3 nanoparticles on the microstructure and properties of Sn-0.3Ag-0.7Cu low-Ag solder. J. Alloys Compd. 2019, 784, 471–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, H.; Guo, H.; Wang, L.; Wei, J.; Xu, L.; Han, Y. Influence of Ag-modified graphene nanosheets addition into Sn–Ag–Cu solders on the formation and growth of intermetallic compound layers. J. Alloys Compd. 2017, 702, 669–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.; Habib, A.H.; Pickel, A.D.; McHenry, M.E. Magnetic nanoparticle-based solder composites for electronic packaging applications. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2015, 67, 95–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayyadi, R.; Naffakh-Moosavy, H. The Role of Intermetallic Compounds in Controlling the Microstructural, Physical and Mechanical Properties of Cu-[Sn-Ag-Cu-Bi]-Cu Solder Joints. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- El-Daly, A.; Al-Ganainy, G.; Fawzy, A.; Younis, M. Structural characterization and creep resistance of nano-silicon carbide reinforced Sn–1.0Ag–0.5Cu lead-free solder alloy. Mater. Des. 2014, 55, 837–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Zhang, L.; Xu, L.; Zhong, S.-J.; Ma, J.; Bao, L. Effect of nano-Al addition on properties and microstructure of low-Ag content Sn–1Ag–0.5Cu solders. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2016, 27, 7665–7673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spinelli, J.E.; Garcia, A. Development of solidification microstructure and tensile mechanical properties of Sn-0.7Cu and Sn-0.7Cu-2.0Ag solders. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2014, 25, 478–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, F.; Gao, F.; Zhang, J.; Jin, W.; Xiao, X. Tensile properties and wettability of SAC0307 and SAC105 low Ag lead-free solder alloys. J. Mater. Sci. 2011, 46, 3424–3429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, B.; Sabri, M.F.M.; Jauhari, I. Microstructural behavior of iron and bismuth added Sn-1Ag-Cu solder under elevated temperature aging. In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Functional Materials and Metallurgy (ICOFM 2016), Penang, Malaysia, 28 May 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Lin, Y.; Tu, C.; Kao, C. Effects of minor Fe, Co, and Ni additions on the reaction between SnAgCu solder and Cu. J. Alloys Compd. 2009, 478, 121–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, S.; Huang, C.-M.; Pecht, M. A review of lead-free solders for electronics applications. Microelectron. Reliab. 2017, 75, 77–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shnawah, D.A.; Said, S.B.M.; Sabri, M.F.M.; Badruddin, I.A.; Che, F.X. High-Reliability Low-Ag-Content Sn-Ag-Cu Solder Joints for Electronics Applications. J. Electron. Mater. 2012, 41, 2631–2658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shnawah, D.A.-A.; Said, S.B.M.; Sabri, M.F.M.; Badruddin, I.A.; Che, F.X. Microstructure, mechanical, and thermal properties of the Sn–1Ag–0.5Cu solder alloy bearing Fe for electronics applications. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2012, 551, 160–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Qi, L.; Wang, X.-M.; Wang, L. Influence of Bi on microstructures evolution and mechanical properties in Sn–Ag–Cu lead-free solder. J. Alloys Compd. 2004, 375, 196–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chuang, C.; Tsao, L.; Lin, H.; Feng, L. Effects of small amount of active Ti element additions on microstructure and property of Sn3.5Ag0.5Cu solder. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2012, 558, 478–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahdavifard, M.; Sabri, M.; Shnawah, D.; Said, S.; Badruddin, I.; Rozali, S. The effect of iron and bismuth addition on the microstructural, mechanical, and thermal properties of Sn–1Ag–0.5Cu solder alloy. Microelectron. Reliab. 2015, 55, 1886–1890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, H.-K.; Huang, C.-W.; Lee, H.; Wang, Y.-L.; Liu, T.-F.; Chen, C.-M. Interfacial reactions between Cu and SnAgCu solder doped with minor Ni. J. Alloys Compd. 2015, 622, 529–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, H.Y.; Zhu, Q.S.; Wang, Z.G.; Shang, J.K.; Lu, M. Effects of Zn addition on microstructure and tensile properties of Sn–1Ag–0.5Cu alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2010, 527, 1343–1350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanlayasiri, K.; Mongkolwongrojn, M.; Ariga, T. Influence of indium addition on characteristics of Sn–0.3Ag–0.7Cu solder alloy. J. Alloys Compd. 2009, 485, 225–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yassin, A.M.; Zahran, H.Y.; El-Rehim, A.F.A. Effect of TiO2 Nanoparticles Addition on the Thermal, Microstructural and Room-Temperature Creep Behavior of Sn-Zn Based Solder. J. Electron. Mater. 2018, 47, 6984–6994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wollgramm, P.; Burger, D.; Parsa, A.B.; Neuking, K.; Eggeler, G. The effect of stress, temperature and loading direction on the creep behaviour of Ni-base single crystal superalloy miniature tensile specimens. Mater. High Temp. 2016, 33, 346–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilshire, B.; Whittaker, M.T. Grain boundaries: Their influence on creep strain accumulation. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2010, 26, 793–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Rehim, A.F.A.; Zahran, H.Y. Effect of aging treatment on microstructure and creep behaviour of Sn–Ag and Sn–Ag–Bi solder alloys. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2013, 30, 434–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abd El-Rehim, A.F. Effect of grain size on the primary and secondary creep behaviour of Sn–3 wt.% Bi alloy. J. Mater. Sci. 2008, 43, 1444–1450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sona, M.; Prabhu, K.N. Review on microstructure evolution in Sn–Ag–Cu solders and its effect on mechanical integrity of solder joints. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2013, 24, 3149–3169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, H.; Suhling, J.C. A review of mechanical properties of lead-free solders for electronic packaging. J. Mater. Sci. 2009, 44, 1141–1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abd El-Rehim, A.F.; Zahran, H.Y.; AlFaify, S. The mechanical and microstructural changes of Sn-Ag-Bi solders with cooling rate and Bi content variations. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2018, 27, 344–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Daly, A.A.; Fawzy, A.; Mansour, S.F.; Younis, M.J. Novel SiC nanoparticles-containing Sn–1.0 Ag–0.5 Cu solder with good drop impact performance. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2013, 578, 62–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganesan, S.; Pecht, M. Lead-Free Electronics; Wiley-Interscience Publication: New York, NY, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, M.L.; Wang, L. Effects of Cu, Bi, and In on microstructure and tensile properties of Sn-Ag-X(Cu, Bi, In) solders. Met. Mater. Trans. A 2005, 36, 1439–1446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, S.-K.; Kang, S.K.; Shih, D.-Y.; Lee, H.M. The evolution of microstructure and microhardness of Sn–Ag and Sn–Cu solders during high temperature aging. Microelectron. Reliab. 2009, 49, 288–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fix, A.R.; Nüchter, W.; Wilde, J. Microstructural changes of lead-free solder joints during long-term ageing, thermal cycling and vibration fatigue. Solder. Surf. Mt. Technol. 2008, 20, 13–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dieter, G.E. Mechanical Metallurgy, 3rd ed.; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 1986. [Google Scholar]
- El-Rehim, A.F.A.; Zahran, H.Y.; Yassin, A.M. Microstructure evolution and tensile creep behavior of Sn–0.7Cu lead-free solder reinforced with ZnO nanoparticles. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2018, 30, 2213–2223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Fu, N.; Ahmed, S.; Suhling, J.C.; Lall, P. Investigation of Microstructural Evolution in SAC Solders Exposed to Short-Term and Long-Term Aging. In Proceedings of the 2018 17th IEEE Intersociety Conference on Thermal and Thermomechanical Phenomena in Electronic Systems (ITherm), San Diego, CA, USA, 29 May–1 June 2018. [Google Scholar]
- El-Daly, A.; El-Hosainy, H.; Elmosalami, T.; Desoky, W. Microstructural modifications and properties of low-Ag-content Sn–Ag–Cu solder joints induced by Zn alloying. J. Alloys Compd. 2015, 653, 402–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Jing, H.; Nai, S.; Xu, L.; Tan, C.; Wei, J. Temperature Dependence of Creep and Hardness of Sn-Ag-Cu Lead-Free Solder. J. Electron. Mater. 2010, 39, 223–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Rehim, A.F.A.; Mahmoud, M.A. Transient and steady state creep of age-hardenable Al–5 wt% Mg alloy during superimposed torsional oscillations. J. Mater. Sci. 2012, 48, 2659–2669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahiem, A.; El-Daly, A. Investigation on multi-temperature short-term stress and creep relaxation of Sn-Ag-Cu-In solder alloys under the effect of rotating magnetic field. Microelectron. Reliab. 2019, 98, 10–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Witkin, D. Creep Behavior of Bi-Containing Lead-Free Solder Alloys. J. Electron. Mater. 2012, 41, 190–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olofinjana, A.; Haque, R.; Mathir, M.; Voo, N. Studies of the solidification characteristics in Sn-Ag-Cu-Bi solder alloys. Procedia Manuf. 2019, 30, 596–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.S.; Huh, S.H.; Suganuma, K. Effects of intermetallic compounds on properties of Sn–Ag–Cu lead-free soldered joints. J. Alloys Compd. 2003, 352, 226–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayyadi, R.; Naffakh-Moosavy, H. Physical and mechanical properties of synthesized low Ag/lead-free Sn-Ag- Cu-xBi (x=0, 1, 2.5, 5wt%) solders. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2018, 735, 367–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Ezzi, A.; Al-Bawee, A.; Dawood, F.; Shehab, A.A. Effect of Bismuth Addition on Physical Properties of Sn-Zn Lead-Free Solder Alloy. J. Electron. Mater. 2019, 48, 8089–8095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


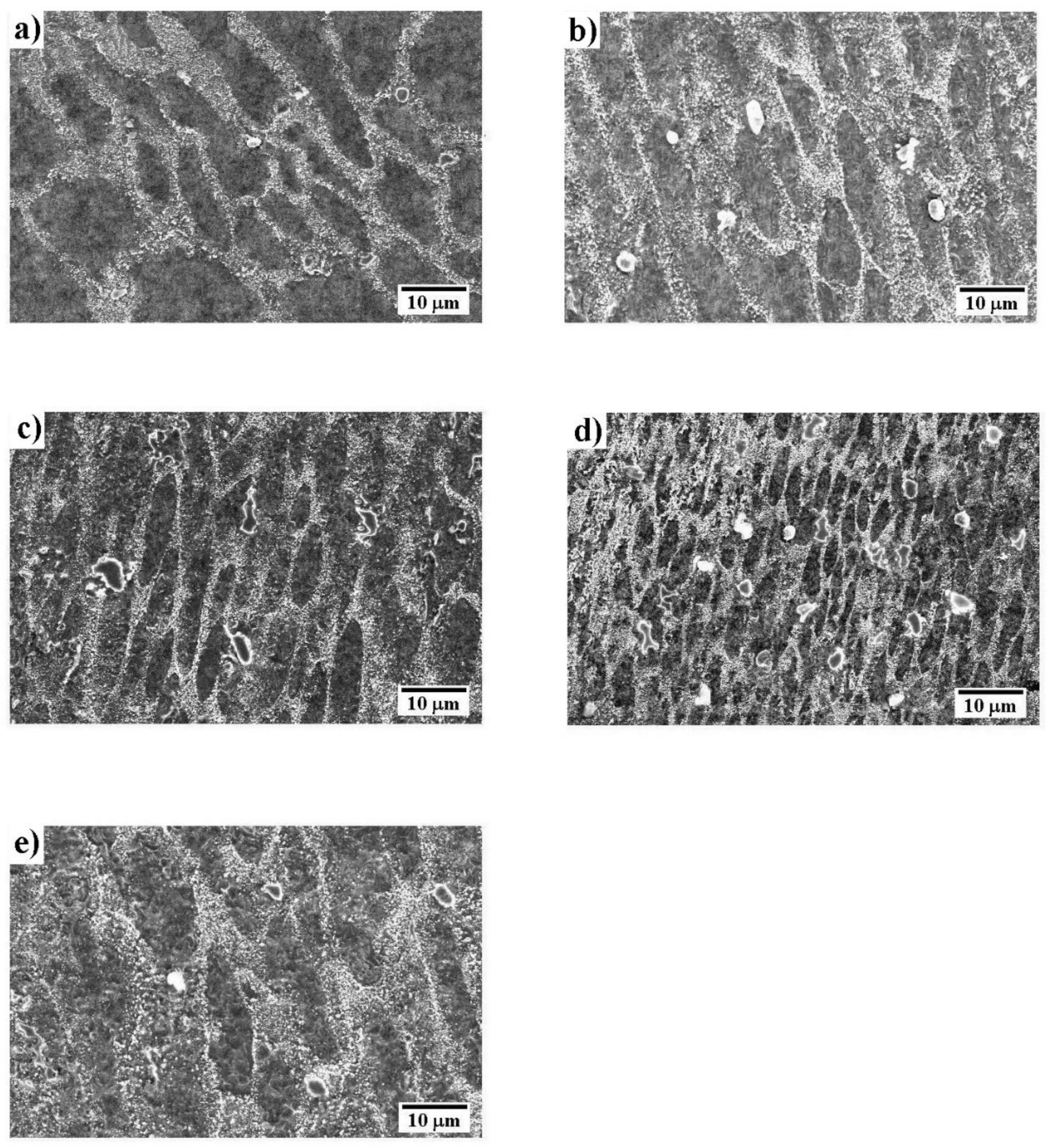
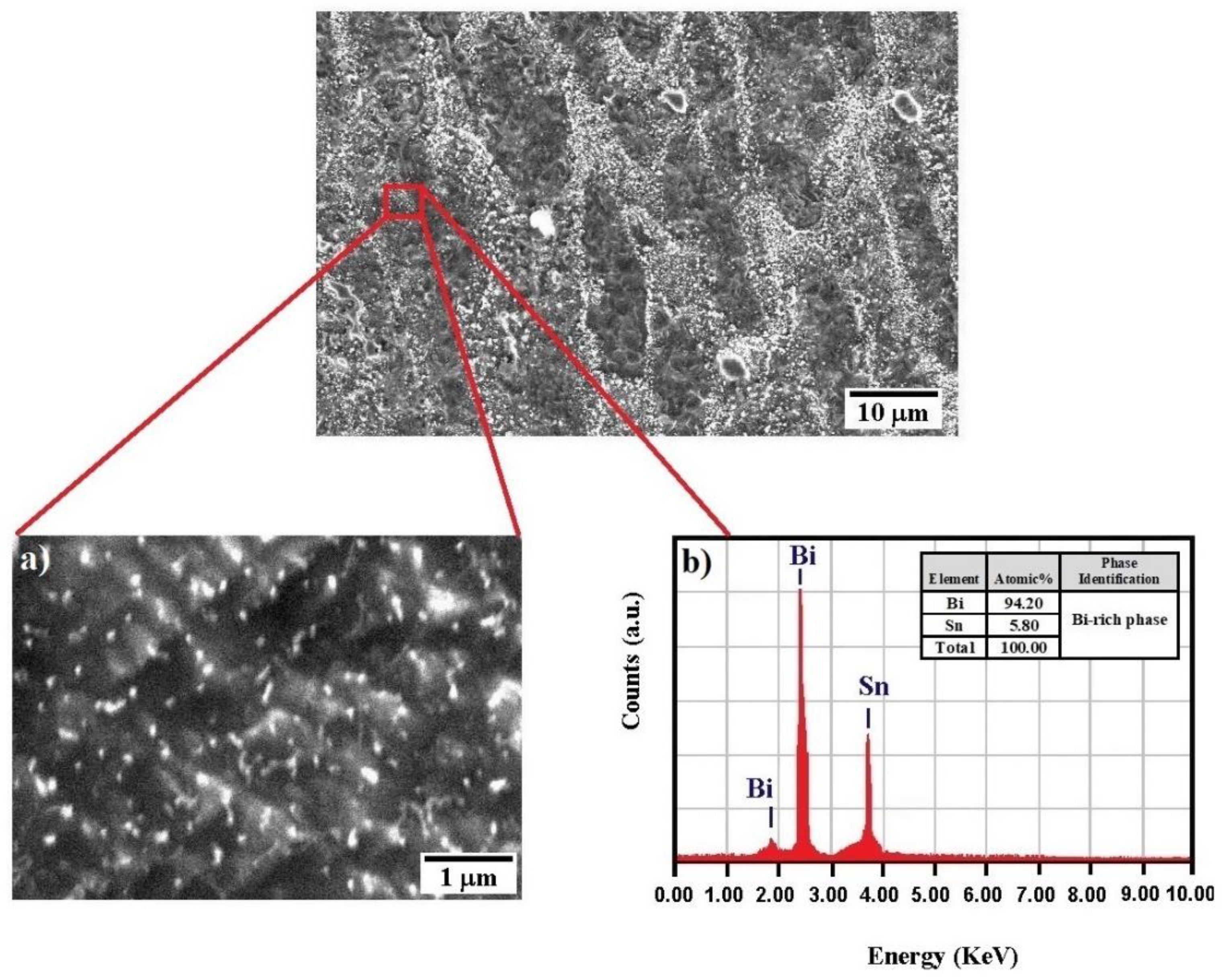



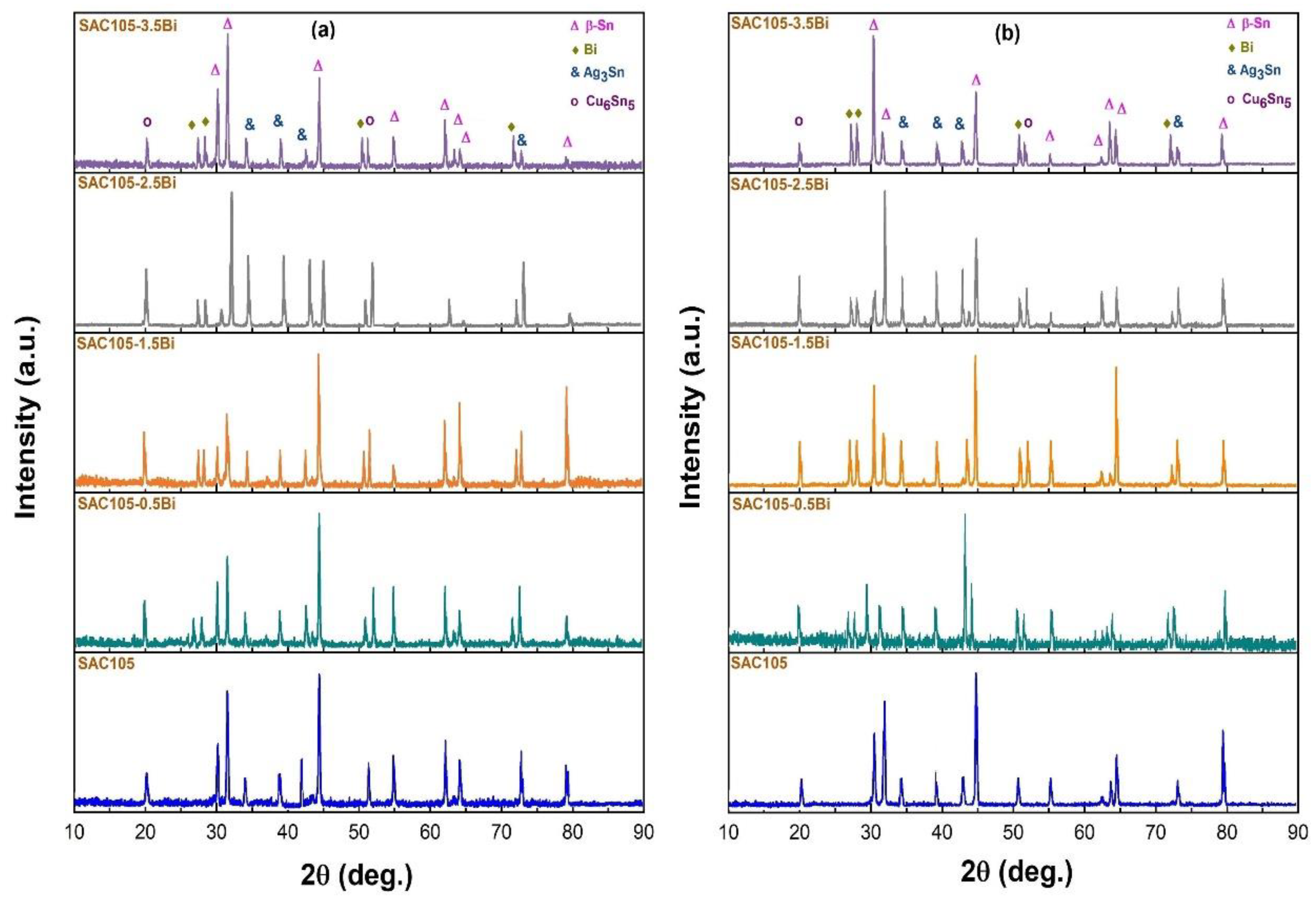
| Solder | Element Content | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ag | Cu | Bi | Sn | |
| SAC105 | 0.97 | 0.48 | 0 | balance |
| SAC105-0.5Bi | 0.94 | 0.46 | 0.49 | balance |
| SAC105-1.5Bi | 0.93 | 0.43 | 1.45 | balance |
| SAC105-2.5Bi | 0.88 | 0.40 | 2.42 | balance |
| SAC105-3.5Bi | 0.85 | 0.39 | 3.40 | balance |
| Lattice Parameter | Aging Temperature (K) | SAC105 | Error % | SAC105-0.5Bi | Error % | SAC105-1.5Bi | Error % | SAC105-2.5Bi | Error % | SAC105-3.5Bi | Error % |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| a (Å) | 353 | 5.9153 | 1.44 | 5.93 | 1.697 | 5.822 | 0.139 | 5.8235 | 0.127 | 5.880 | 0.840 |
| 373 | 5.8453 | 0.246 | 5.83 | 0.017 | 5.815 | 0.257 | 5.7576 | 1.258 | 5.867 | 0.618 | |
| 393 | 5.8579 | 0.462 | 5.8944 | 1.088 | 5.776 | 0.928 | 5.776 | 0.943 | 5.841 | 0.171 | |
| 413 | 5.8692 | 0.655 | 5.7796 | 0.88 | 5.730 | 1.716 | 5.800 | 0.530 | 5.850 | 0.337 | |
| c (Å) | 353 | 3.2355 | 1.682 | 3.1646 | 0.545 | 3.067 | 3.597 | 3.1689 | 0.409 | 3.160 | 0.691 |
| 373 | 3.1984 | 0.516 | 3.1853 | 0.104 | 3.128 | 1.685 | 3.1918 | 0.309 | 3.099 | 2.599 | |
| 393 | 3.2058 | 0.748 | 3.0818 | 3.146 | 3.184 | 0.080 | 3.2522 | 2.206 | 3.136 | 1.431 | |
| 413 | 3.1909 | 0.280 | 3.1506 | 0.986 | 3.180 | 0.042 | 3.2129 | 0.973 | 3.126 | 1.734 | |
| c/a | 353 | 0.5469 | 0.233 | 0.5336 | 2.205 | 0.526 | 3.462 | 0.5441 | 0.281 | 0.537 | 1.518 |
| 373 | 0.5471 | 0.270 | 0.5463 | 0.122 | 0.537 | 1.430 | 0.5543 | 1.588 | 0.528 | 3.198 | |
| 393 | 0.5472 | 0.285 | 0.5228 | 4.188 | 0.551 | 1.018 | 0.5630 | 3.180 | 0.536 | 1.599 | |
| 413 | 0.5436 | 0.372 | 0.5451 | 0.106 | 0.555 | 1.704 | 0.5539 | 1.512 | 0.534 | 2.065 | |
| V (Å)3 | 353 | 113.21 | 4.645 | 111.28 | 2.860 | 104.006 | 3.866 | 107.472 | 0.662 | 109.256 | 0.986 |
| 373 | 109.28 | 1.013 | 108.26 | 0.070 | 105.818 | 2.191 | 105.81 | 2.197 | 106.685 | 1.389 | |
| 393 | 110.01 | 1.683 | 107.07 | 1.026 | 106.275 | 1.768 | 108.50 | 0.288 | 107.007 | 1.092 | |
| 413 | 109.91 | 1.599 | 105.24 | 2.721 | 104.463 | 3.443 | 108.087 | 0.093 | 107.032 | 1.069 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zahran, H.Y.; Mahmoud, A.S.; Abd El-Rehim, A.F. Effect of Bi Content on the Microstructure and Mechanical Performance of Sn-1Ag-0.5Cu Solder Alloy. Crystals 2021, 11, 314. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst11030314
Zahran HY, Mahmoud AS, Abd El-Rehim AF. Effect of Bi Content on the Microstructure and Mechanical Performance of Sn-1Ag-0.5Cu Solder Alloy. Crystals. 2021; 11(3):314. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst11030314
Chicago/Turabian StyleZahran, Heba Y., Ashraf S. Mahmoud, and Alaa F. Abd El-Rehim. 2021. "Effect of Bi Content on the Microstructure and Mechanical Performance of Sn-1Ag-0.5Cu Solder Alloy" Crystals 11, no. 3: 314. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst11030314
APA StyleZahran, H. Y., Mahmoud, A. S., & Abd El-Rehim, A. F. (2021). Effect of Bi Content on the Microstructure and Mechanical Performance of Sn-1Ag-0.5Cu Solder Alloy. Crystals, 11(3), 314. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst11030314







