Effect of Solvent and Catalyst Types on Stability and Properties of Zinc Phthalocyanine in the Organic–Inorganic Hybrid Materials
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experiments
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of Samples
2.3. Methods of Experiments
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. SEM and XRD Study
3.2. UV-Vis Analyzes
3.3. FTIR Study
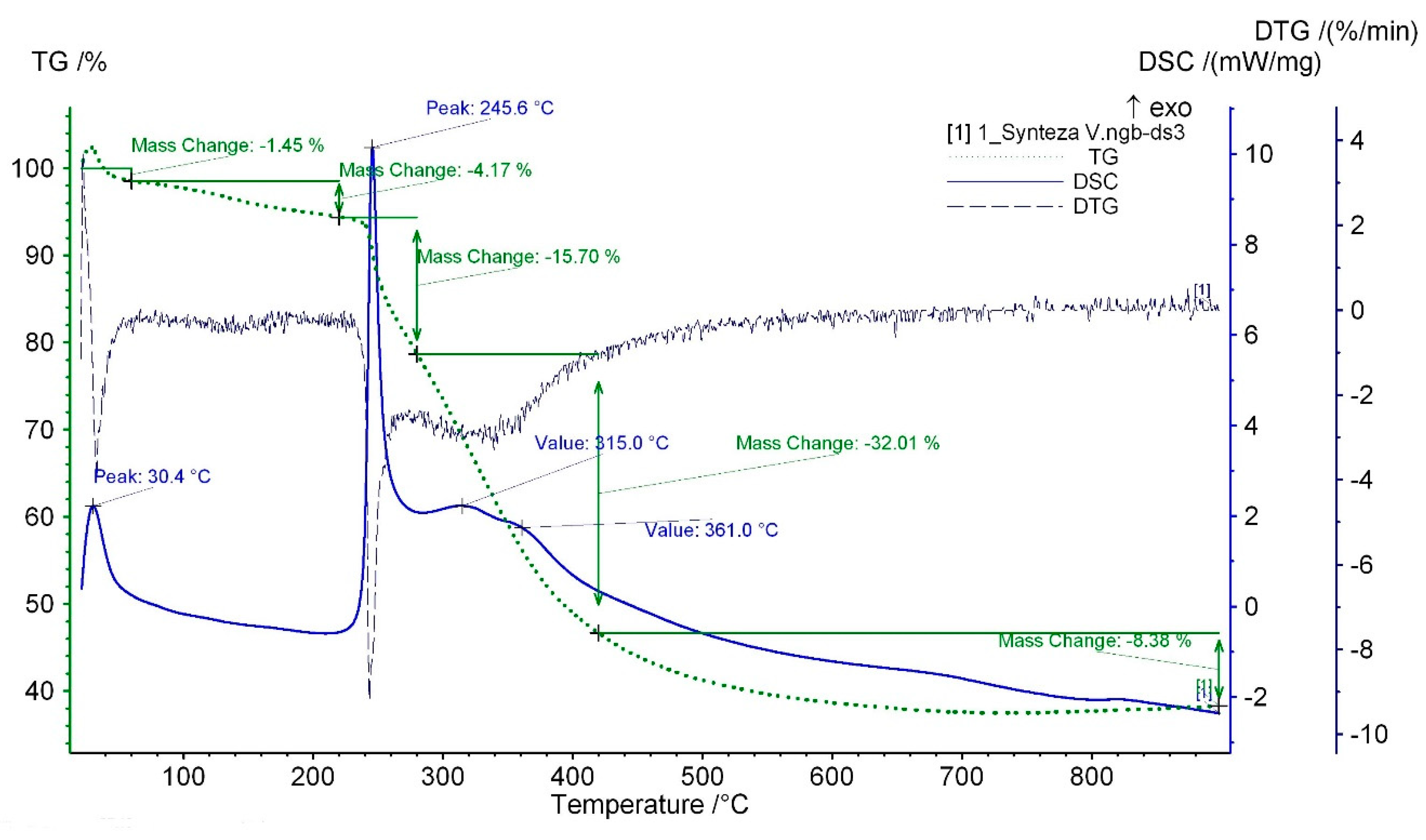
3.4. Thermal Analysis
3.5. Luminescence
3.5.1. Thermoluminescence (TL)
3.5.2. Optically Stimulated Luminescence (OSL)
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shirota, Y.; Kageyama, H. Handbook of Organic Materials for Optical Devices; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Kalyani, N.T.; Swart, H.; Dhoble, S. Principles and Applications of Organic Light Emitting Diodes (OLEDs); Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Arslan, S. Phthalocyanines: Structure, synthesis, purification and applications. J. Life Sci. 2016, 6, 188–197. [Google Scholar]
- Trytek, M.; Makarska, M.; Polska, K.; Radzki, S.; Fiedurek, J. Porfiryny i ftalocyjaniny Cz, I. Właściwości i niektóre zastosowania. Biotechnologia 2005, 71, 109–127. [Google Scholar]
- Isago, H. Optical Spectra of Phthalocyanines and Related Compounds; Springer: Tokyo, Japan, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Słota, R.; Dyrda, G. UV Photostability of Metal phthalocyanines in organic solvents. Inorg. Chem. 2003, 42, 5743–5750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kadish, K.M.; Smith, K.M.; Guilard, R. Handbook of Porphyrin Science: With Applications to Chemistry, Physics, Materials Science, Engineering, Biology and Medicine; World Scientific: Singapore, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Belogorokhov, I.A.; Ryabchikov, Y.V.; Tikhonov, E.V. Photoluminescence in semiconductor structures based on butyl-substituted erbium phthalocyanine complexes. Semiconductors 2008, 42, 321–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eastwood, D.; Edwards, L.; Gourterman, M. Spectra of porphyrins part VII: Vapor absorption and emission of phthalocyanines. J. Mol. Spectrosc. 1966, 20, 381–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dyrda, G.; Zakrzyk, M.; Broda, M.A. Hydrogen bond-mediated conjugates involving lanthanide diphthalocyanines and trifluoroacetic acid (LnPc2@TFA): Structure, photoactivity and stability. Molecules 2020, 25, 3638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simon, J.; Andre, J.J. Molecular Semiconductors: Photoelectrical Properties and Solar Cells; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Hunger, K. Industrial Dyes: Chemistry, Properties, Application; Wiley VCH: Weinheim, Germany, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Xia, H.; Nogami, M. Copper phthalocyanine bonding with gel and their optical properties. Opt. Mater. 2000, 15, 93–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guglielmi, M.; Brusatin, G.; Della Giustina, G. Hybrid glass-like films through sol–gel techniques. J. Non Cryst. Solids 2007, 353, 1681–1687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng-Shane, C. Optical fiber oxygen sensor based on Pd(II) complex embedded in sol–gel matrix. J. Lumin. 2013, 135, 5–9. [Google Scholar]
- Dash, S.; Mishra, S.; Patel, S.; Mishra, B.K. Organically modified silica: Synthesis and applications due to its surface interaction with organic molecules. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2008, 140, 77–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamimura, Y.; Kurumada, K. Percolation transition of siloxane domain in partially phenylated organic/inorganic hybrid glass. J. Non Cryst. Solids 2007, 353, 2521–2527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuniyoshi, M.; Takahashi, M.; Tokuda, Y.; Yoko, T. Thermosoftening phenyl siloxane glasses prepared via sol concentration. J. Non Cryst. Solids 2007, 353, 4162–4169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamimura, Y.; Kurumada, K. Evaluation of molecular volume of siloxane bonding phenyl group in partially phenylated organic/inorganic hybrid glass. J. Non Cryst. Solids 2008, 354, 3414–3417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ou, D.L.; Seddon, A.B. Near-and mid-infrared spectroscopy of sol–gel derived ormosils: Vinyl phenyl silicates. J. Non Cryst. Solids 1997, 210, 187–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; You, L.; Xiang, H.; Jiang, Y. Comparison of dye adsorption by mesoporous hybrid gels: Understanding the interactions between dyes gel surfaces. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2006, 303, 346–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ulatowska, A.; Kudrawiec, K.; Podbielska, H.; Bryja, L.; Misiewicz, J. Transmittance examination in sol-gel derived matrices for optoelectronic application. Opt. Mater. 2001, 17, 247–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, A.C.; Feller, S.A.; Hannon, A.C. (Eds.) Borate Glasses, Crystals and Melts. The Society of Glass Technology: Sheffield, UK, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Ghani, F.; Kristen, J.; Riegler, H. Solubility properties of unsubstituted metal phthalocyanines in different types of solvents. J. Chem. Eng. Data 2012, 57, 439–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogunsipe, A.O.; Idowu, M.A.; Ogunbayo, T.B.; Akinbulu, I.A. Protonation of some non-transition metal phthalocyanines—Spectral photophysicochemical consequences. J. Porphyr. Phthalocyanines 2012, 16, 885–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogunsipe, A.; Maree, D.; Nyokong, T. Solvent effects on the photochemical fluorescence properties of zinc phthalocyanine derivatives. J. Mol. Struct. 2003, 650, 131–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuznetsova, N.A.; Kaliya, O.L. Oxidative photobleaching of phthalocyanines in solution. J. Porphyr. Phthalocyanines 2012, 16, 705–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldovi, H.G.; Blas-Ferrando, V.M.; Ortiz, J.; Garcia, H.; Fernández-Lázaro, F.; Sastre-Santos, Á. Phthalocyanine–Gold Nanoparticle Hybrids: Modulating Quenching with a Silica Matrix Shell. Chem. Phys. Chem. 2016, 17, 1579–1585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerasymchuk, Y.S.; Chernii, V.Y.; Tomachynski, L.A.; Legendziewicz, L.; Radzki, S. Spectroscopic characterization of zirconium(IV) and hafniumf(IV) gallate phthalocyanines in monolithic silica gels obtained by sol–gel method. Opt. Mater. 2005, 27, 1484–1494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purcar, V.; Stamatin, I.; Cinteza, O.; Petcu, C.; Raditoiu, V.; Ghiurea, M.; Miclaus, T.; Andronie, A. Fabrication of hydrophobic and antireflective coatings based on hybrid silica films by sol–gel proces. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2012, 206, 4449–4454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moriones, P.; Ríos, X.; Echeverría, J.C.; Garrido, J.J.; Pires, J.; Pinto, M. Hybrid organic–inorganic phenyl stationary phases for the gas separation of organic binary mixtures Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2011, 389, 69–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández-Escolano, M.; Ramis, X.; Jiménez-Morales, A.; Juan-Díaz, M.; Suay, J. Study of the thermal degradation of bioactive sol–gel coatings for the optimization of its curing process. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2012, 107, 499–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Al-Oweini, R.; El-Rassy, H. Synthesis and characterization by FTIR spectroscopy of silica aerogels prepared using several Si(OR)4 and R”Si(OR0)3 precursors. J. Mol. Struct. 2009, 919, 140–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yong-Ho, K.; Byunghwan, L.; Kwang-Ho, C.; Sang-June, C. Selective adsorption of bisphenol A by organic–inorganic hybrid mesoporous silicas. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2011, 138, 184–190. [Google Scholar]
- Juan-Díaz, M.J.; Martínez-Ibáñez, M.; Lara-Sáez, I.; da Silva, S.; Izquierdo, R.; Gurruchaga, M.; Goñi, I.; Suay, J. Development of hybrid sol–gel coatings for the improvement of metallic biomaterials performance. Prog. Org. Coat. 2016, 96, 42–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ying-Sing, L.; Yu, W.; Sorrie, C. Vibrational spectra of phenyltriethoxysilane, phenyltrimethoxysilane and their sol–gels. Spectrochim. Acta A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2009, 71, 1819–1824. [Google Scholar]
- Jana, R.N.; Bhunia, H. Thermal stability and proton conductivity of silane based nanostructured composite membranes. Solid State Ion. 2008, 178, 1872–1878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, K.H.; Chao, C.M.; Yang, C.J.; Chang, T.C. Synthesis and characterization of polydimethylsiloxane-cured organically modified silicate hybrid coatings. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2006, 91, 2917–2923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Kanezashi, M.; Tsuru, T. Preparation of organic–inorganic hybrid silica membranes using organoalkoxysilanes: The effect of pendant groups. J. Membr. Sci. 2011, 379, 287–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
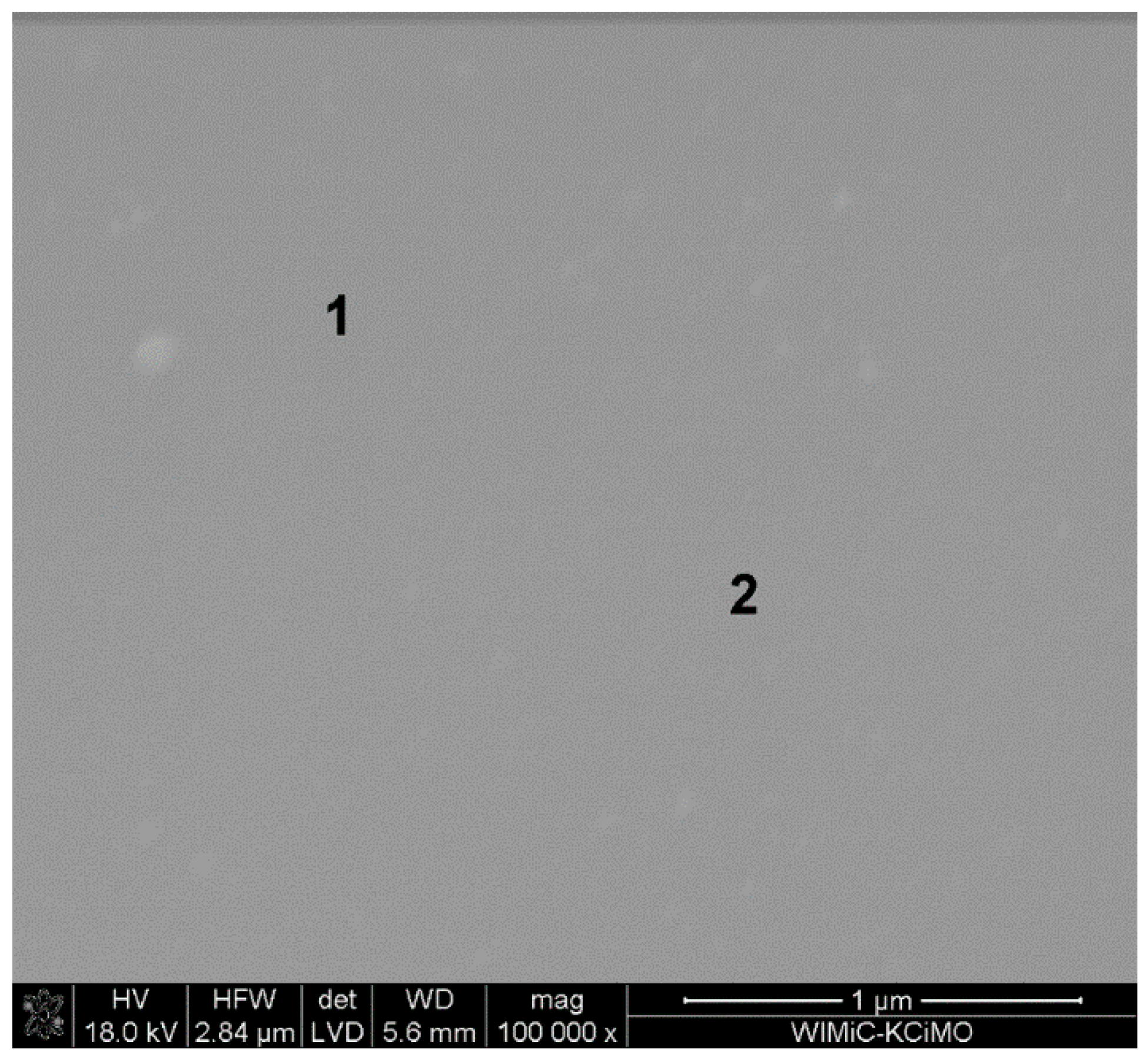
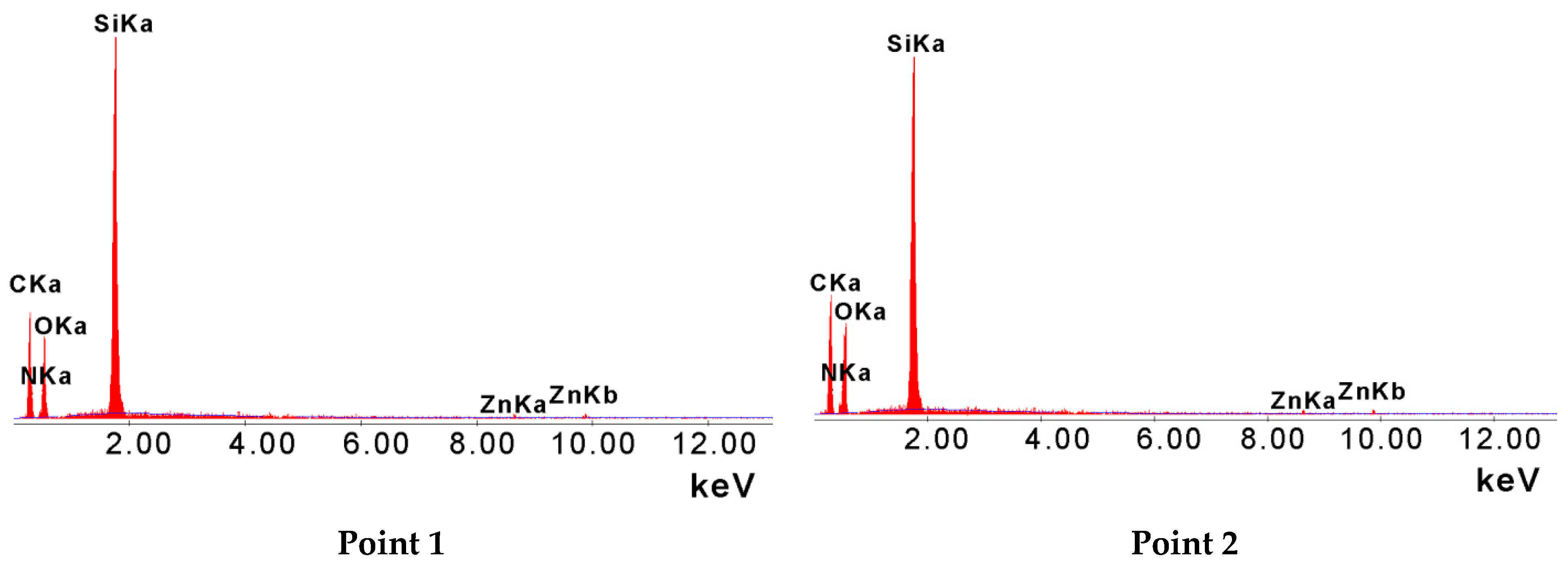
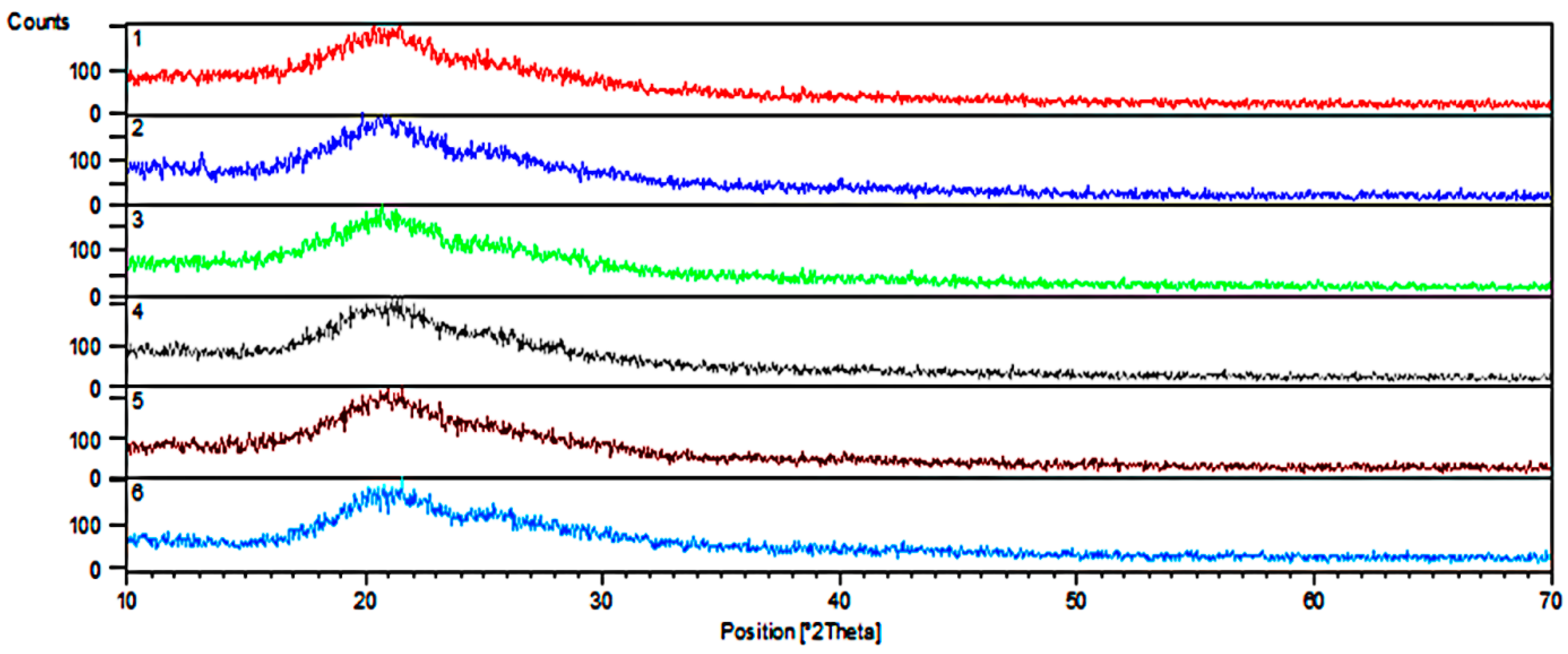
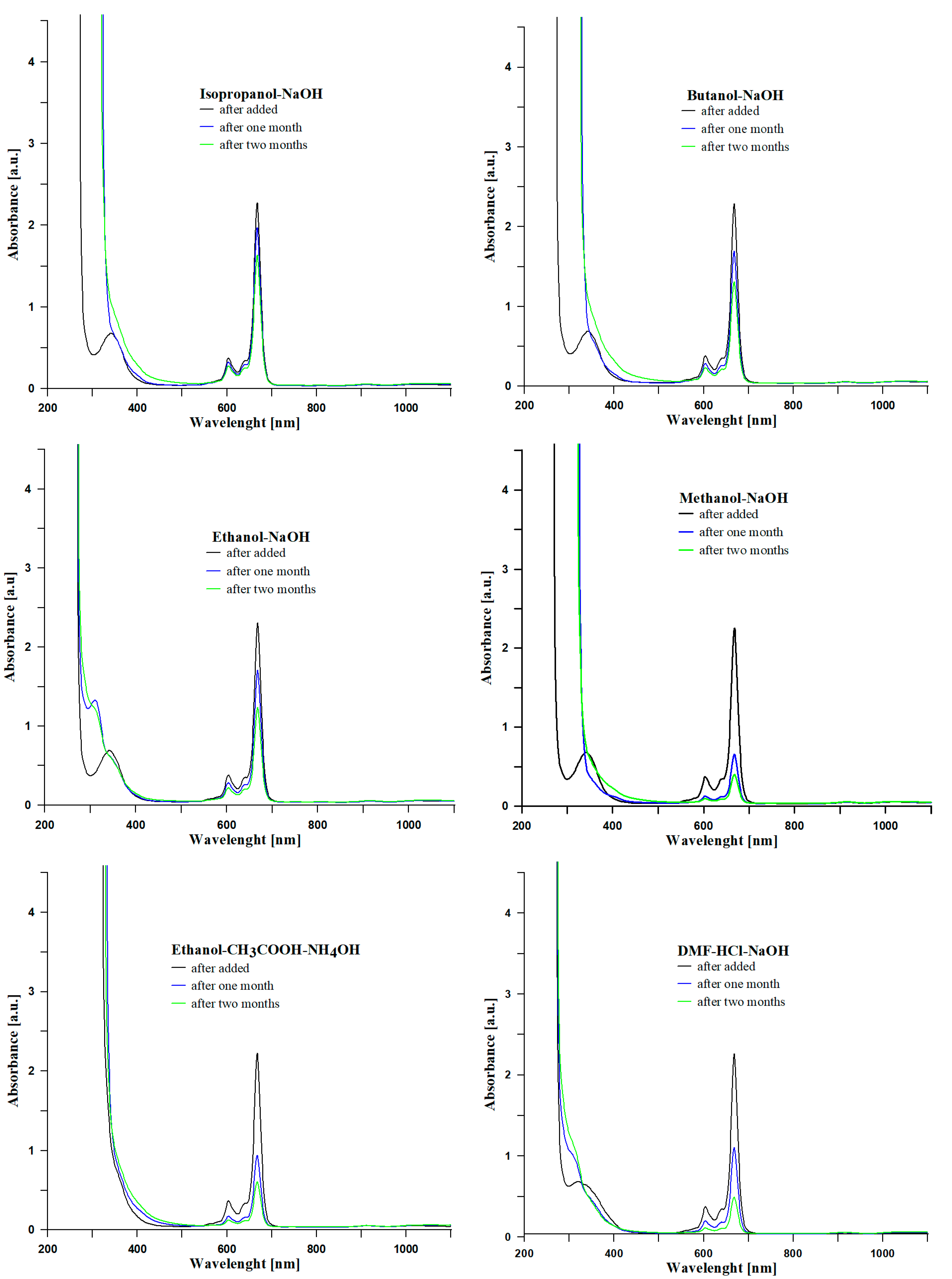
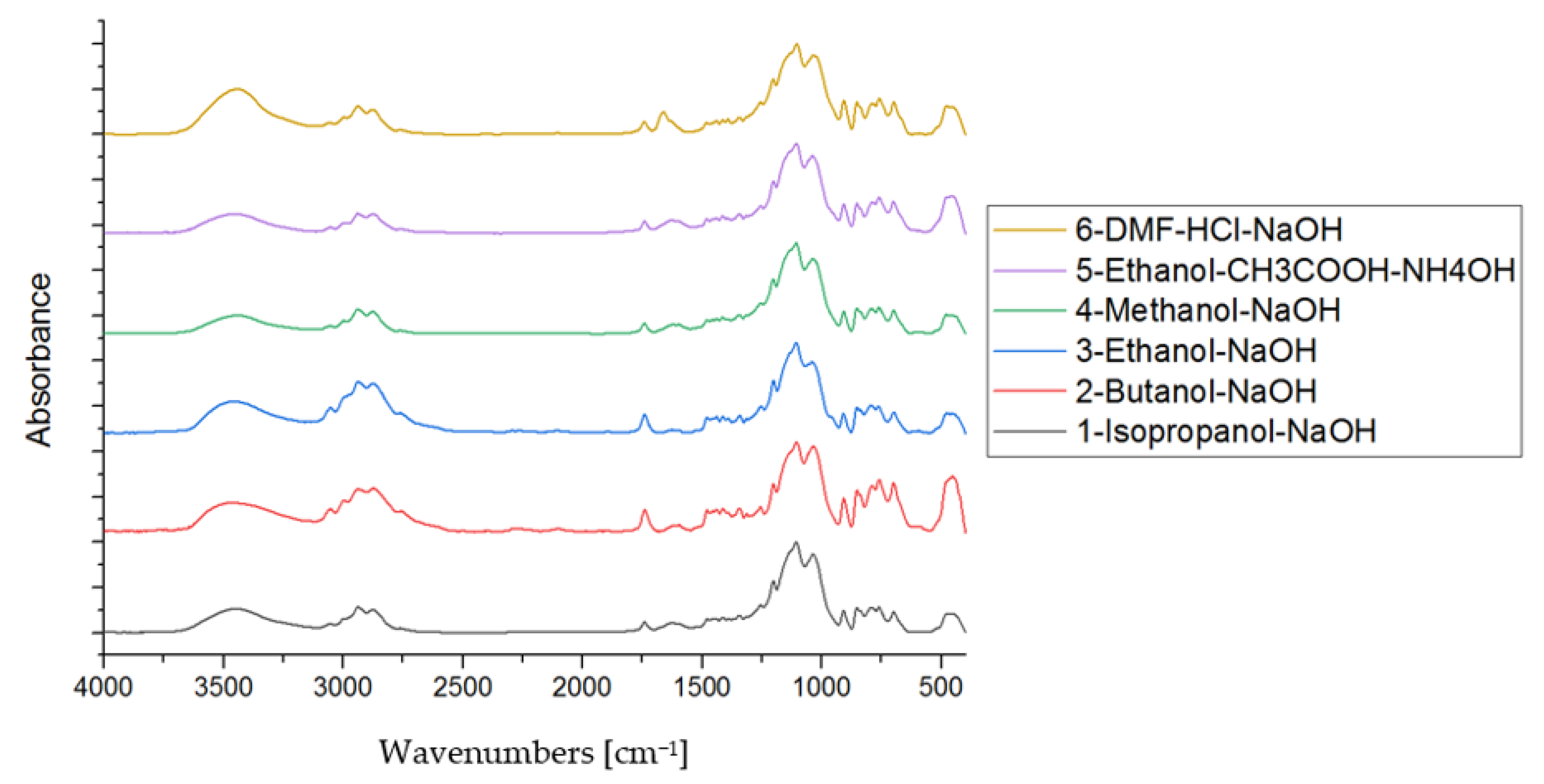

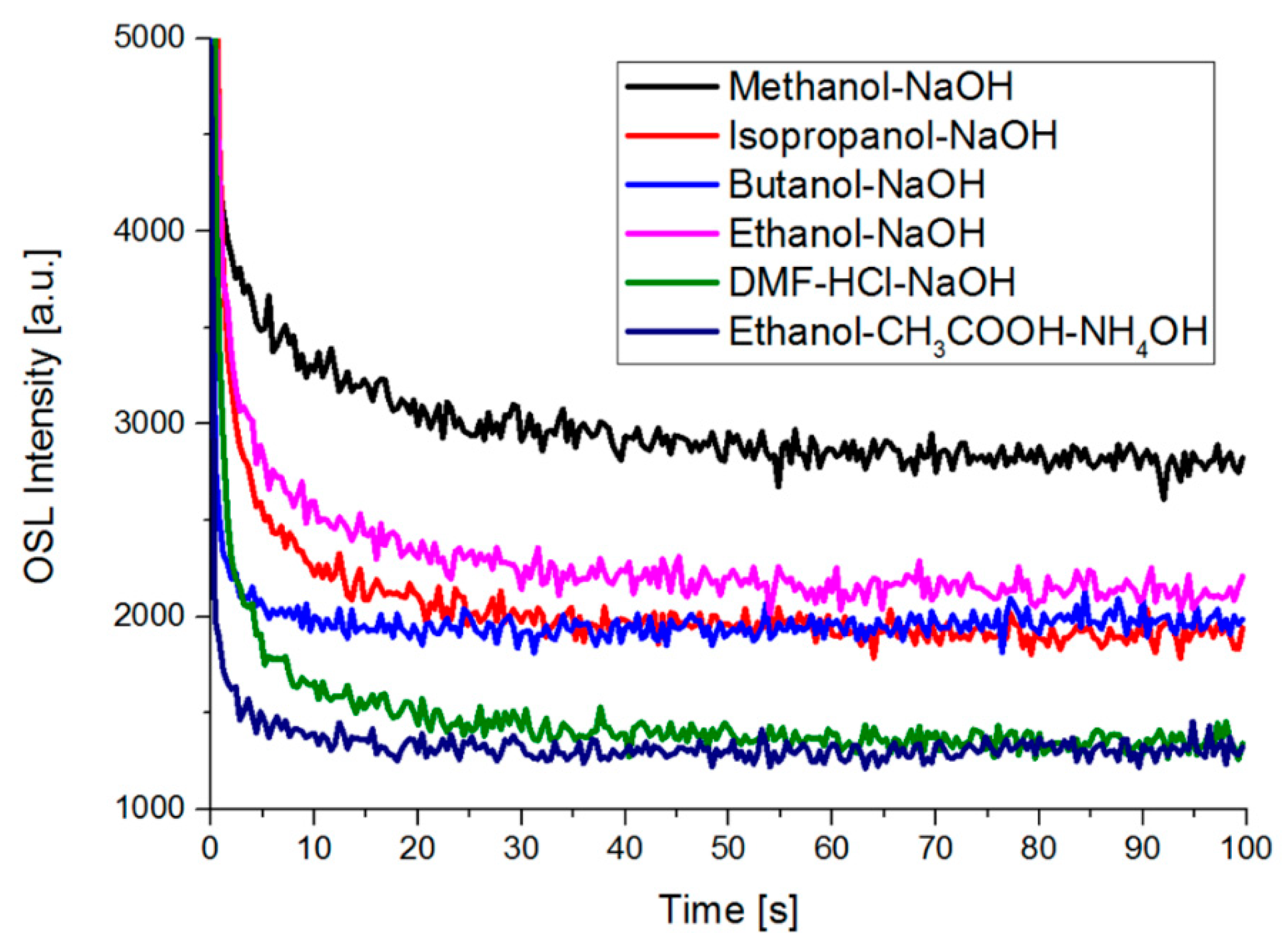
| No. | Name | Solvent | Catalyst | Second Catalyst |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Isopropanol-NaOH | Isopropanol | NaOH | |
| 2 | Butanol-NaOH | Butanol | NaOH | |
| 3 | Ethanol-NaOH | Ethanol | NaOH | |
| 4 | Methanol-NaOH | Methanol | NaOH | |
| 5 | Ethanol-CH3COOH-NH4OH * | Ethanol | CH3COOH | NH4OH |
| 6 | DMF-HCl-NaOH * | DMF | HCl | NaOH |
| Sample No. | 1st Exothermic Effect [°C] | Mass Loss Connected with 1st Exothermic Effect [%] | 2nd, 3rd, and 4th Exothermic Effect [°C] | Total Mass Loss Connected with 2nd, 3rd, and 4th Exothermic Effects [%] |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 30 | 1.45 | 246, 315, 361 | 15.70 |
| 2 | 30 | 1.31 | 256, 299, 337 | 37.57 |
| 3 | 33 | 1.41 | 238, 332 | 32.63 |
| 4 | 31 | 1.54 | 257, 297 | 44.19 |
| 5 | 31 | 2.75 | 253, 282 | 41.30 |
| 6 | 31 | 4.53 | 251, 300, 329 | 45.20 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Popanda, B.; Środa, M.; Cholewa-Kowalska, K. Effect of Solvent and Catalyst Types on Stability and Properties of Zinc Phthalocyanine in the Organic–Inorganic Hybrid Materials. Crystals 2021, 11, 592. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst11060592
Popanda B, Środa M, Cholewa-Kowalska K. Effect of Solvent and Catalyst Types on Stability and Properties of Zinc Phthalocyanine in the Organic–Inorganic Hybrid Materials. Crystals. 2021; 11(6):592. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst11060592
Chicago/Turabian StylePopanda, Barbara, Marcin Środa, and Katarzyna Cholewa-Kowalska. 2021. "Effect of Solvent and Catalyst Types on Stability and Properties of Zinc Phthalocyanine in the Organic–Inorganic Hybrid Materials" Crystals 11, no. 6: 592. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst11060592
APA StylePopanda, B., Środa, M., & Cholewa-Kowalska, K. (2021). Effect of Solvent and Catalyst Types on Stability and Properties of Zinc Phthalocyanine in the Organic–Inorganic Hybrid Materials. Crystals, 11(6), 592. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst11060592







