Performance Evaluation of Cementitious Composites Containing Granulated Rubber Wastes, Silica Fume, and Blast Furnace Slag
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Test Procedures
2.1. Materials
2.2. Mixture Proportions and Sample Preparation
2.3. Test Procedures
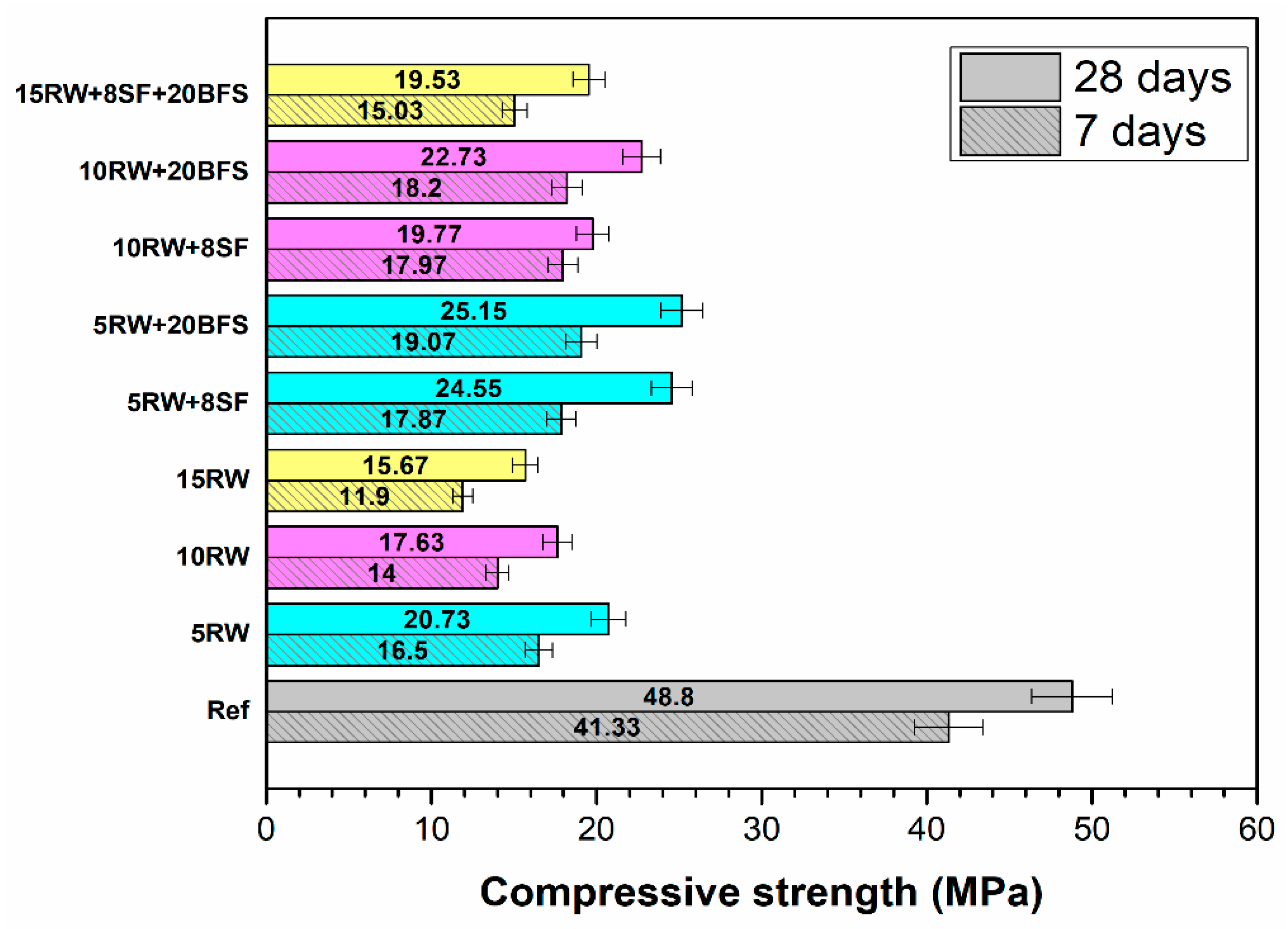
2.3.1. Compressive Strength
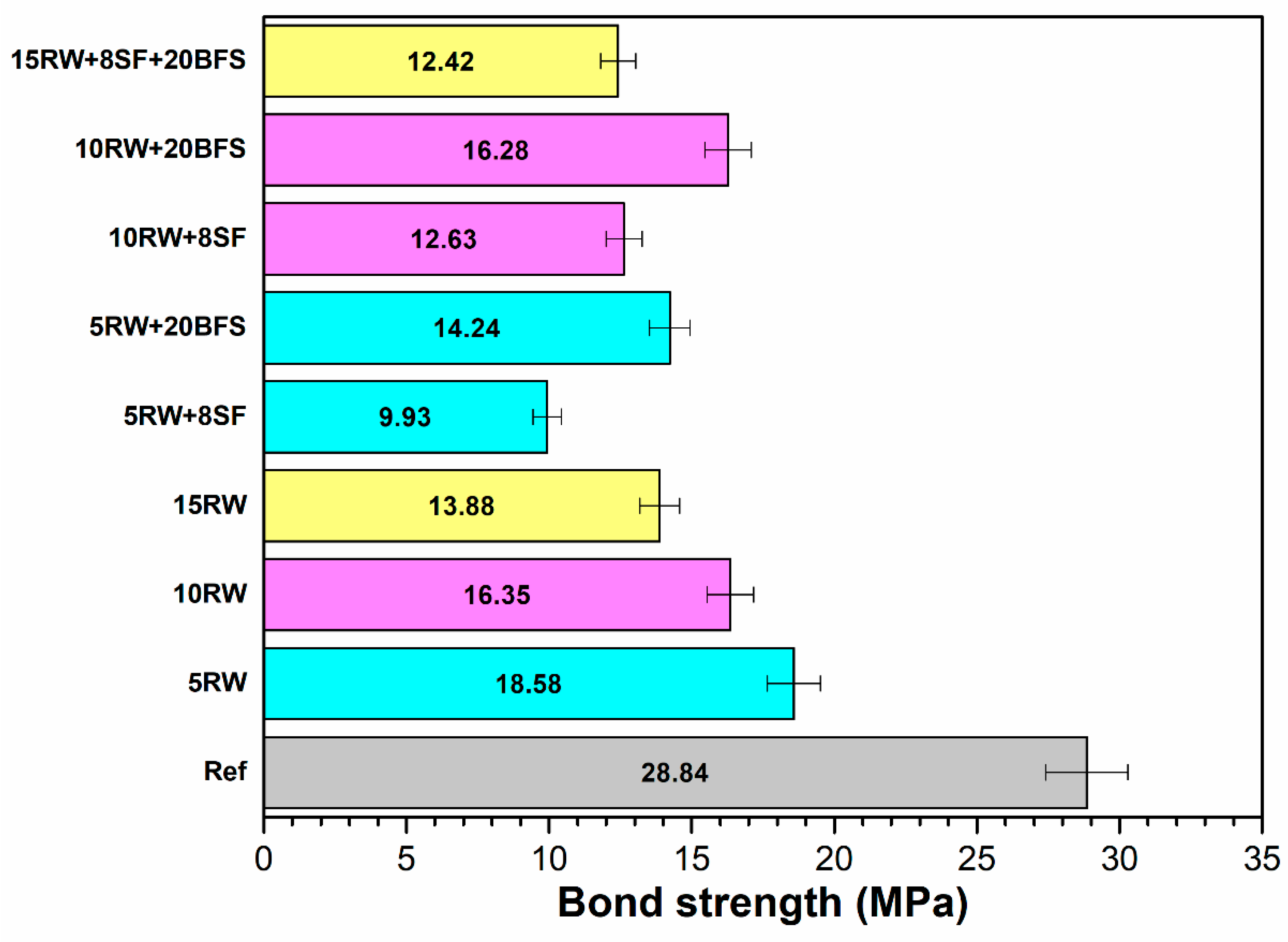
2.3.2. Bond Strength
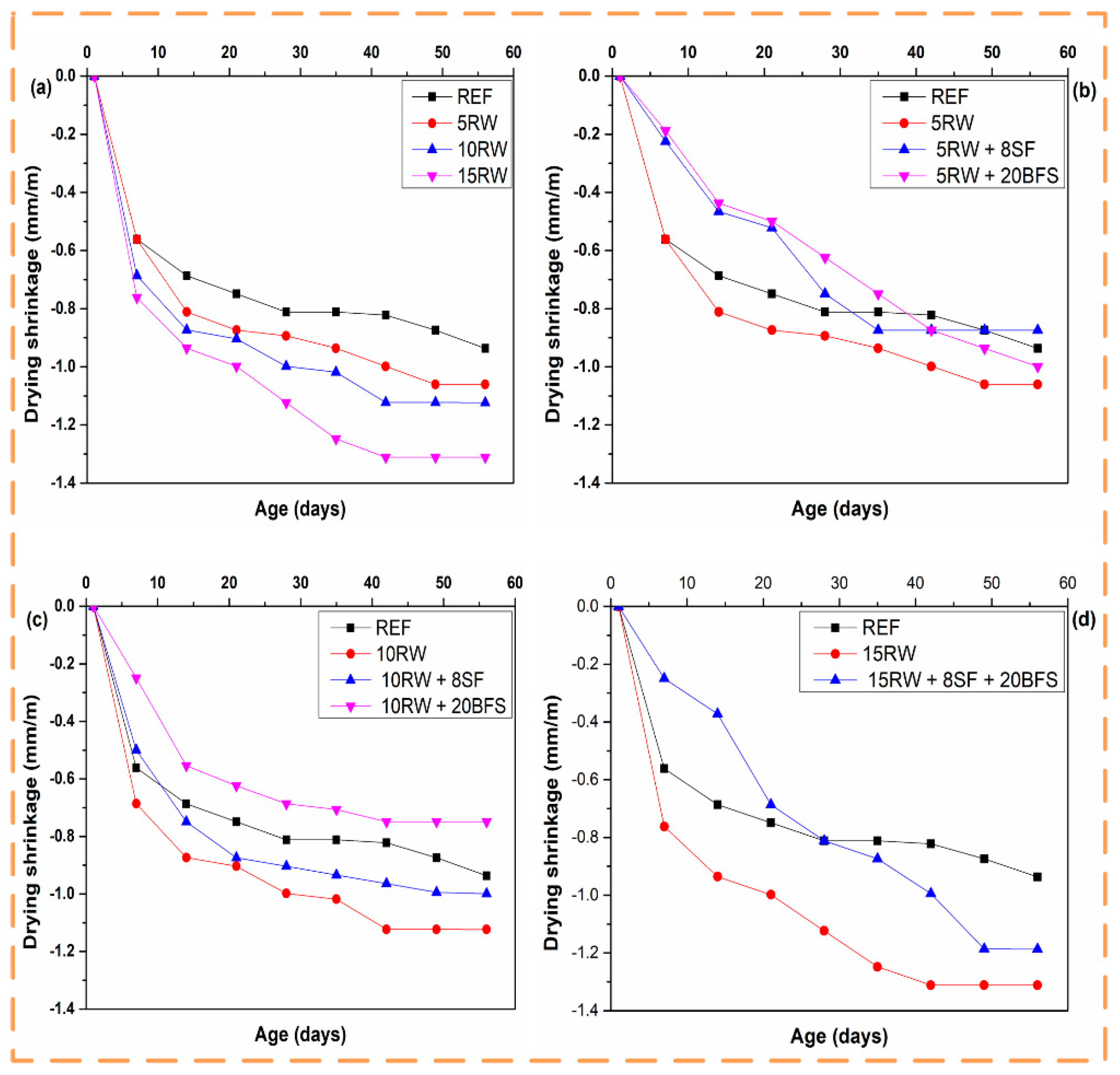
2.3.3. Drying Shrinkage
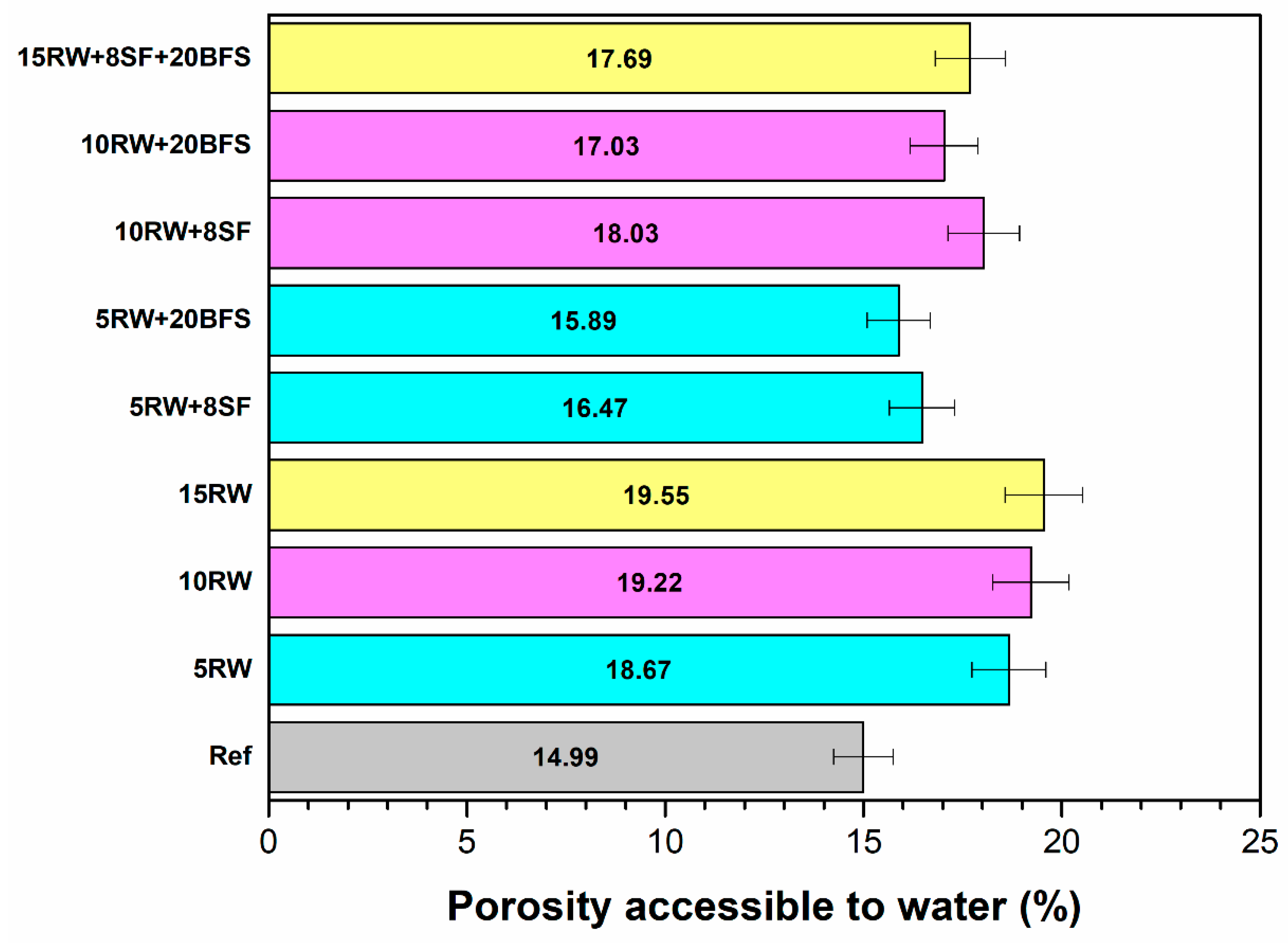
2.3.4. Porosity Accessible to Water
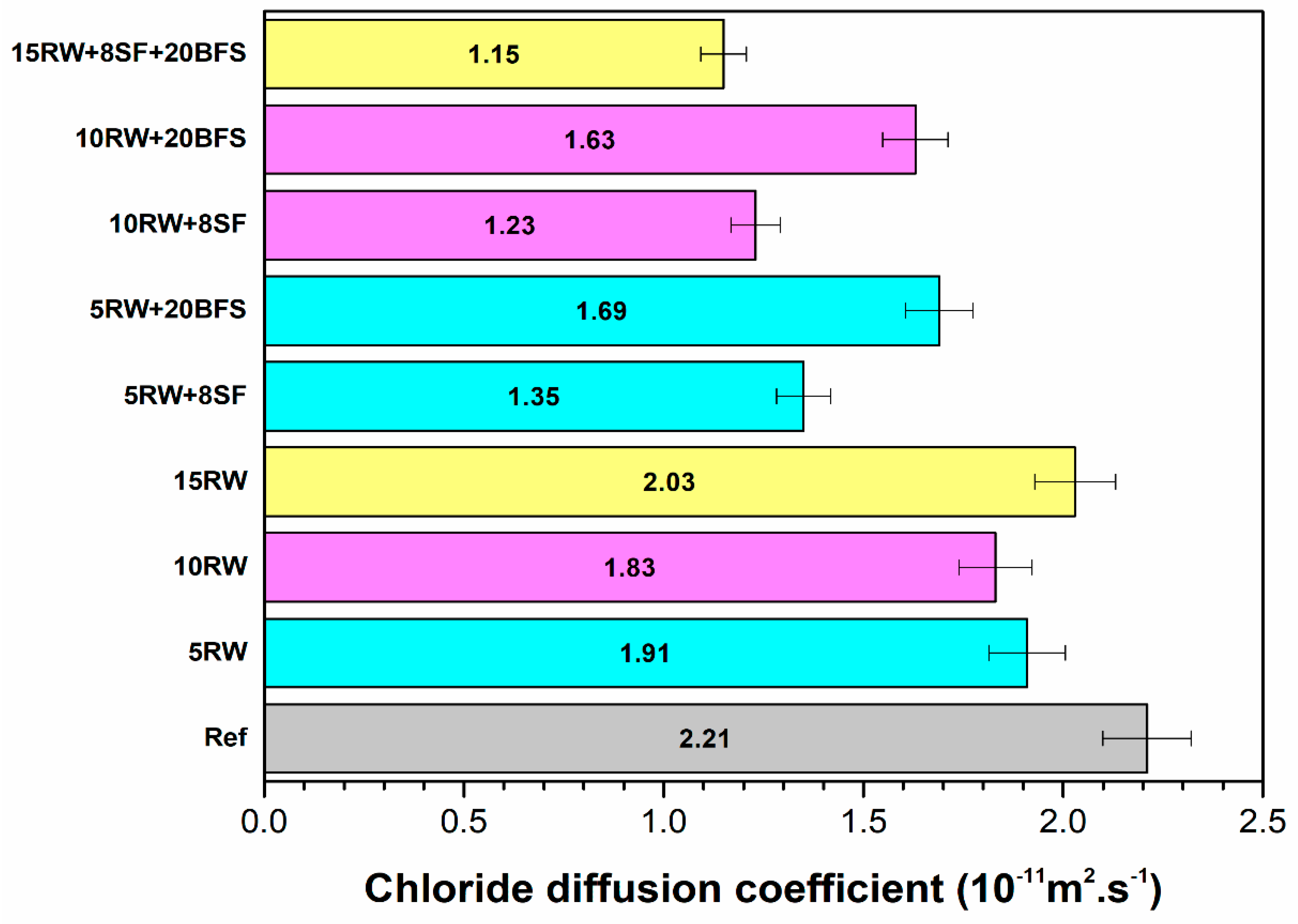
2.3.5. Rapid Chloride Migration
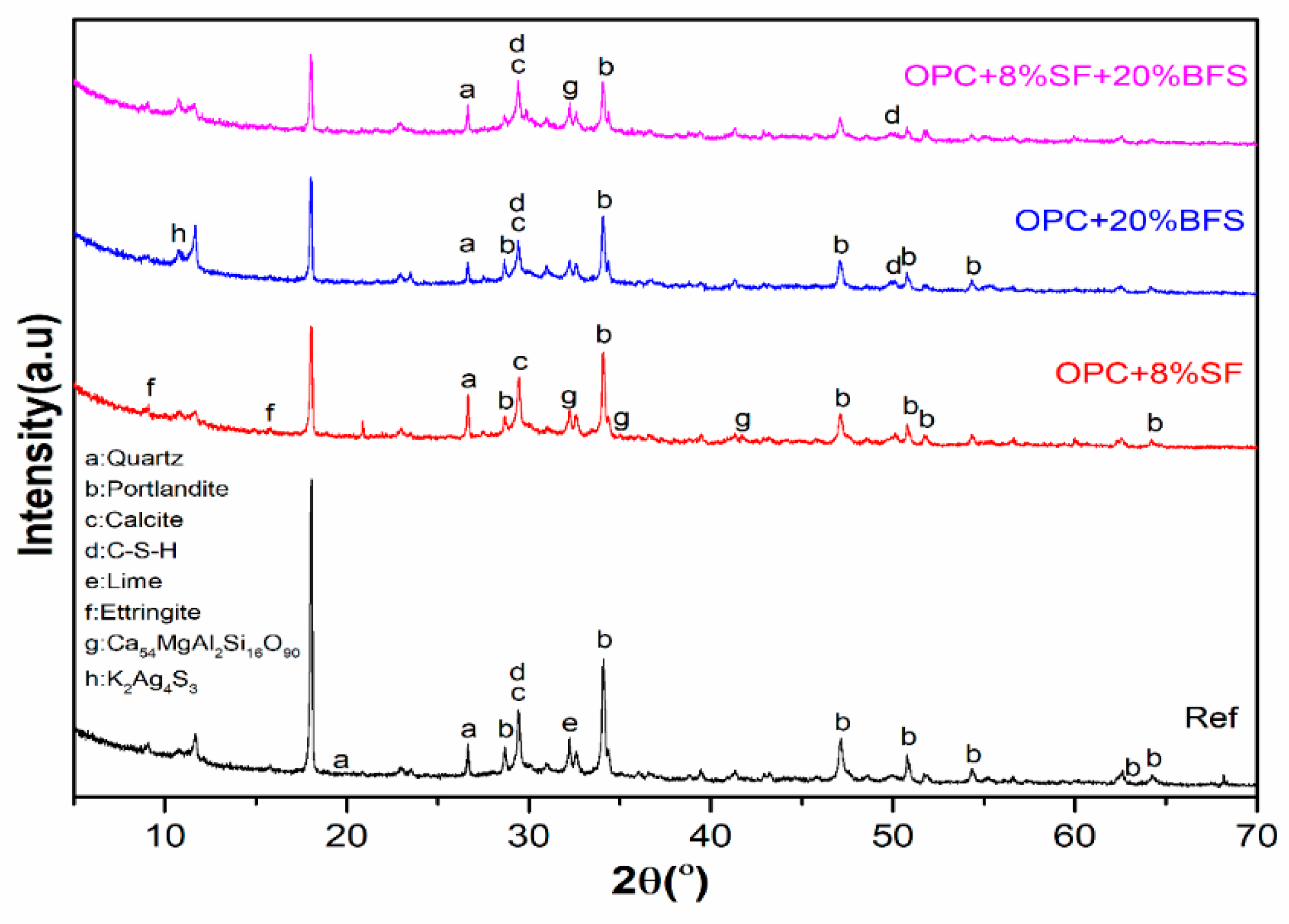
2.3.6. XRD Analysis
2.3.7. SEM Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Compressive Strength
3.2. Bond Strength
3.3. Drying Shrinkage
3.4. Porosity Accessible to Water
3.5. Rapid Chloride Migration
3.6. XRD Analysis
3.7. SEM Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yung, W.H.; Yung, L.C.; Hua, L.H. A study of the durability properties of waste tire rubber applied to self-compacting concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2013, 41, 665–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suhendro, B. Toward green concrete for better sustainable environment. Procedia Eng. 2014, 95, 305–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehta, P.K. Reducing the Environmental Impact of Concrete. Concr. Int. 2001, 23, 61–66. [Google Scholar]
- Boukour, S.; Benmalek, M.L. Performance evaluation of a resinous cement mortar modified with crushed clay brick and tired rubber aggregate. Constr. Build. Mater. 2016, 120, 473–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karakurt, C. Microstructure properties of waste tire rubber composites: An overview. J. Mater. Cycles Waste Manag. 2015, 17, 422–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gigli, S.; Landi, D.; Germani, M. Cost-benefit analysis of a circular economy project: A study on a recycling system for end-of-life tyres. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 229, 680–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, J.S.; Tiwari, S.K. The impact of end-of-life tires on the mechanical properties of fine-grained soil: A Review. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2019, 21, 485–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.Z.; Wang, N.N.; Tseng, M.L.; Huang, Y.M.; Li, N.L. Waste tire recycling assessment: Road application potential and carbon emissions reduction analysis of crumb rubber modified asphalt in China. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 249, 119411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edeskär, T. Use of Tyre Shreds in Civil Engineering Applications: Technical and Environmental Properties. Ph.D. Thesis, Lulea University of Technology, Luleå, Sweden, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Siddique, R. Waste Materials and By-Products in Concrete; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin, Germany, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Connor, K.; Cortesa, S.; Issagaliyeva, S.; Meunier, A.; Bijaisoradat, O.; Kongkatigumjorn, N.; Wattanavit, K. Developing a Sustainable Waste Tire Management Strategy for Thailand; Worcester Polytechnic Institute: Worcester, MA, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, H.S.; Mead, J.L.; Stacer, R.G. Environmental Impacts of Recycling Rubber in Light Fill Applications: Summary and Evaluation of Existing Literature; University of Massachusetts, Chelsea Center for Recycling and Economic Development: Amherst, MA, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Thomas, B.S.; Gupta, R.C. Properties of high strength concrete containing scrap tire rubber. J. Clean. Prod. 2016, 113, 86–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganjian, E.; Khorami, M.; Maghsoudi, A.A. Scrap-tyre-rubber replacement for aggregate and filler in concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2009, 23, 1828–1836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valente, M.; Sibai, A. Rubber/crete: Mechanical properties of scrap to reuse tire-derived rubber in concrete; A review. J. Appl. Biomater. Funct. Mater. 2019, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sambucci, M.; Marini, D.; Sibai, A.; Valente, M. Preliminary Mechanical Analysis of Rubber-Cement Composites Suitable for Additive Process Construction. J. Compos. Sci. 2020, 4, 120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segre, N.; Joekes, I. Use of tire rubber particles as addition to cement paste. Cem. Concr. Res. 2000, 30, 1421–1425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Gammal, A.; Abdel-Gawad, A.K.; El-Sherbini, Y.; Shalaby, A. Compressive strength of concrete utilizing waste tire rubber. J. Emerg. Trends Eng. Appl. Sci. 2010, 1, 96–99. [Google Scholar]
- Aniruddh, A.; Kumar, A.; Khan, M.A. Effect on compressive strength of concrete by using waste rubber as partial replacement of fine aggregate: A review. Int. Res. J. Eng. Technol. 2016, 3, 86–89. [Google Scholar]
- Granju, J.L.; Chausson, H. Serviceability of fiber reinforced thin overlays relation between cracking and debonding. In Proceedings of the ConChem International Exhibition & Conference, Brussels, Belgium, 28–30 November 1995; Verlag für chemische industrie: Thannhausen, Germany; pp. 133–142. [Google Scholar]
- Aslani, F.; Ma, G.; Law, D.; Wan, Y.; Xuan, V.; Le, T. Experimental investigation into rubber granules and their effects on the fresh and hardened properties of self-compacting concrete. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 172, 1835–1847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalil, E.; Abd-Elmohsen, M.; Anwar, A.M. Impact Resistance of Rubberized Self-Compacting Concrete. Water Sci. 2015, 29, 45–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atahan, A.O.; Yücel, A.Ö. Crumb rubber in concrete: Static and dynamic evaluation. Constr. Build. Mater. 2012, 36, 617–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aslani, F. Mechanical properties of waste tire rubber concrete. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2015, 28, 04015152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Topçu, I.B.; Bilir, T. Experimental investigation of some fresh and hardened properties of rubberized self-compacting concrete. Mater. Des. 2009, 30, 3056–3065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grdić, Z.; Topličić-Curčić, G.; Ristić, N.; Grdić, D.; Mitković, P. Hydro-abrasive resistance and mechanical properties of rubberized concrete. Građevinar 2014, 66, 11–20. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, X.; Ranade, R.; Ni, W.; Li, V.C. On the use of recycled tire rubber to develop low E-modulus ECC for durable concrete repairs. Constr. Build. Mater. 2013, 46, 134–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raghavan, D.; Huynh, H.; Ferraris, C.F. Workability, mechanical properties and chemical stability of a recycled tyre rubber filled cementitious composite. J. Mater. Sci. 1998, 33, 1745–1752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cairns, R.A.; Kew, H.Y.; Kenny, M.J. The Use of Recycled Rubber Tyres in Concrete Construction; The University of Strathclyde: Glasgow, Scotland, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Oikonomou, N.; Stefanidou, M.; Mavridou, S. Improvement of the bonding between rubber tire particles and cement paste in cement products. In Proceedings of the 15th Conference of the Technical Chamber of Greece, Alexandroupoli, Greece, 25–27 October 2006; pp. 234–242. [Google Scholar]
- Chou, L.H.; Lin, C.N.; Lu, C.K.; Lee, C.H.; Lee, M.T. Improving rubber concrete by waste organic sulfur compounds. Waste Manag. Res. 2010, 28, 29–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Q.; Huang, B.; Shu, X. Rubber modified concrete improved by chemically active coating and silane coupling agent. Constr. Build. Mater. 2013, 48, 116–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, J.; Fang, C.; Lu, Z.; Li, Z.; Li, L. Effects of the addition of silica fume and rubber particles on the compressive behaviour of recycled aggregate concrete with steel fibres. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 197, 656–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Copetti, C.M.; Borges, P.M.; Squiavon, J.Z.; da Silva, S.R.; de Oliveira Andrade, J.J. Evaluation of tire rubber surface pre-treatment and silica fume on physical-mechanical behavior and microstructural properties of concrete. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 256, 120670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Akhras, N.M.; Smadi, M.M. Properties of tire rubber ash mortar. Cem. Concr. Comp. 2004, 26, 821–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yilmaz, A.; Degirmenci, N. Possibility of using waste tire rubber and fly ash with Portland cement as construction materials. Waste Manag. 2009, 29, 1541–1546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turki, M.; Zarrad, I.; Bretagne, E.; Quéneudec, M. Influence of filler addition on mechanical behavior of cementitious mortar-rubber aggregates: Experimental study and modeling. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2012, 24, 1350–1358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aslani, F.; Gedeon, R. Experimental investigation into the properties of self-compacting rubberised concrete incorporating polypropylene and steel fibers. Struct. Concr. 2018, 20, 267–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadiq, M.R.; Javed, M.F.; Ullah, S.; Din, N. Effect of PVA on Rubberized Concrete. In Proceedings of the 1st Conference on Sustainability in Civil Engineering, Capital University of Science and Technology, Islamabad, Pakistan, 1 August 2019; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Han, Q.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Yu, J.; Hou, D.; Dong, B. Insights into the interfacial strengthening mechanism of waste rubber/cement paste using polyvinyl alcohol: Experimental and molecular dynamics study. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2020, 114, 103791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Wang, N.; Wang, M.; Zhang, J.; Hou, D. Recyclable rubber-cement composites produced by interfacial strengthened strategy from polyvinyl alcohol. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 264, 120541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Dai, Q.; Si, R.; Guo, S. Investigation of properties and performances of Polyvinyl Alcohol (PVA) fiber-reinforced rubber concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 193, 631–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Güneyisi, E.; Gesoǧlu, M.; Özturan, T. Properties of rubberized concretes containing silica fume. Cem. Concr. Res. 2004, 34, 2309–2317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noaman, A.T.; Bakar, B.H.A.; Akil, H.M. Experimental investigation on compression toughness of rubberized steel fibre concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2016, 115, 163–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Fonteboa, B.; Martínez-Abella, F. Concretes with aggregates from demolition waste and silica fume. Mater. Mech. Prop. Build. Environ. 2008, 43, 429–437. [Google Scholar]
- Onuaguluchi, O.; Panesar, D.K. Hardened properties of concrete mixtures containing pre-coated crumb rubber and silica fume. J. Clean. Prod. 2014, 82, 125–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Na, O.; Xi, Y. Mechanical and durability properties of insulation mortar with rubber powder from waste tires. J. Mater. Cycles Waste Manag. 2017, 19, 763–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gesoglu, M.; Güneyisi, E.; Hansu, O.; Ipek, S.; Asaad, D.S. Influence of waste rubber utilization on the fracture and steel—Concrete bond strength properties of concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2015, 101, 1113–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bompa, D.V.; Elghazouli, A.Y. Bond-slip response of deformed bars in rubberised concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 154, 884–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramezanianpour, A.A.; Moeini, M.A. Mechanical and durability properties of alkali activated slag coating mortars containing nanosilica and silica fume. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 163, 611–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedro, D.; de Brito, J.; Veiga, R. Mortars made with fine granulate from shredded tires. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2012, 25, 519–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benazzouk, A.; Douzane, O.; Langlet, T.; Mezreb, K.; Roucoult, J.M.; Quéneudec, M. Physico-mechanical properties and water absorption of cement composite containing shredded rubber wastes. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2007, 29, 732–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sukontasukkul, P.; Tiamlom, K. Expansion under water and drying shrinkage of rubberized concrete mixed with crumb rubber with different size. Constr. Build. Mater. 2012, 29, 520–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benazzouk, A.; Douzane, O.; Mezreb, K.; Que, M. Physico-mechanical properties of aerated cement composites containing shredded rubber waste. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2006, 28, 650–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turgut, P.; Yesilata, B. Physico-mechanical and thermal performances of newly developed rubber-added bricks. Energy Build. 2008, 40, 679–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karahan, O.; Özbay, E.; Hossain, K.M.; Lachemi, M.; Atis, C.D. Fresh, mechanical, transport, and durability properties of self-consolidating rubberized concrete. ACI Mater. J. 2012, 109, 413–420. [Google Scholar]
- Siddique, R.; Naik, T.R. Properties of concrete containing scrap-tire rubber—An overview. Waste Manag. 2004, 24, 563–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sukontasukkul, P. Use of crumb rubber to improve thermal and sound properties of pre-cast concrete panel. Constr. Build. Mater. 2009, 23, 1084–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benazzouk, A.; Douzane, O.; Langlet, T.; Mezreb, K.; Labbani, F.; Roucoult, J.M. Effet des granulats de caoutchouc sur les propriétés d’un mortier de ciment. In Réunion Internationale des Laboratoires et Experts des Matériaux; Université Claude Bernard Lyon 1: Villeurbanne, France, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Bravo, M.; De Brito, J. Concrete made with used tyre aggregate: Durability-related performance. J. Clean. Prod. 2012, 25, 42–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, T.; Siddique, S.; Sharma, R.K.; Chaudhary, S. Behaviour of waste rubber powder and hybrid rubber concrete in aggressive environment. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 217, 283–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.; Liang, J.; Xu, J.; Bo, M.; Li, J.; Tang, B. Research on anti-chloride ion penetration property of crumb rubber concrete at different ambient temperatures. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 189, 42–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamsheer, A.F.; Kupwade-Patil, K.; Büyüköztürk, O.; Bumajdad, A. Analysis of engineered cement paste using silica nanoparticles and metakaolin using 29Si NMR, water adsorption and synchrotron X-ray Diffraction. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 180, 698–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raffoul, S.; Garcia, R.; Pilakoutas, K.; Guadagnini, M.; Medina, N.F. Optimisation of rubberised concrete with high rubber content: An experimental investigation. Constr. Build. Mater. 2016, 124, 391–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Najim, K.B.; Hall, M.R. Crumb rubber aggregate coatings/pre-treatments and their effects on interfacial bonding, air entrapment and fracture toughness in self-compacting rubberised concrete (SCRC). Mater. Struct. 2013, 46, 2029–2043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelisser, F.; Zavarise, N.; Longo, T.A.; Bernardin, A.M. Concrete made with recycled tire rubber: Effect of alkaline activation and silica fume addition. J. Clean. Prod. 2011, 19, 757–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, T.; Chaudhary, S.; Sharma, R.K. Assessment of mechanical and durability properties of concrete containing waste rubber tire as fine aggregate. Constr. Build. Mater. 2014, 73, 562–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| OPC | SF | BFS | OPC | SF | BFS | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Oxydes | (%) | Oxydes | (%) | ||||
| CO2 | - | 3.263 | −1.621 | MnO | - | 0.091 | 0.091 |
| Na2O | - | 1.000 | 0.326 | ZnO | - | 0.009 | - |
| MgO | 3.56 | 5.954 | 7.976 | SeO2 | - | 0.005 | - |
| Al2O3 | 4.89 | 10.134 | 15.495 | Br | - | 0.002 | - |
| SiO2 | 20.93 | 23.941 | 32.823 | Rb2O | - | 0.004 | 0.003 |
| P2O5 | - | 0.034 | 0.018 | SrO | - | 0.110 | 0.125 |
| SO3 | 2.27 | 13.473 | 2.494 | Y2O3 | 0.008 | 0.010 | |
| Cl | - | 0.040 | - | ZrO2 | - | 0.040 | 0.051 |
| K2O | 0.56 | 0.727 | 0.478 | BaO | - | 0.087 | 0.337 |
| CaO | 60.42 | 38.677 | 38.853 | CeO2 | - | 0.054 | - |
| TiO2 | - | 0.554 | 0.649 | ||||
| Fe2O3 | 2.89 | 1.796 | 0.273 | ||||
| Loss on ignition | 3.60 | - | - | ||||
| Mortar Mixture | OPC | Fine Aggregates | Water | RW | BFS | SF | Stabilizer | SP-Plast | Resinous Latex |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ref | 450 | 1350 | 202.5 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 9.95 | 0 |
| 5RW | 450 | 1282.5 | 202.5 | 31.91 | 0 | 0 | 0.45 | 5.22 | 31.5 |
| 10RW | 450 | 1215 | 202.5 | 63.81 | 0 | 0 | 0.45 | 4.82 | 31.5 |
| 15RW | 450 | 1147.5 | 202.5 | 95.72 | 0 | 0 | 0.45 | 5.49 | 31.5 |
| 5RW+8SF | 414 | 1282.5 | 202.5 | 31.91 | 0 | 36 | 0.45 | 7.38 | 31.5 |
| 5RW+20BFS | 360 | 1282.5 | 202.5 | 31.91 | 90 | 0 | 0.45 | 3.96 | 31.5 |
| 10RW+8SF | 414 | 1215 | 202.5 | 63.81 | 36 | 0.45 | 6.12 | 31.5 | |
| 10RW+20BFS | 360 | 1215 | 202.5 | 63.81 | 90 | 0 | 0.45 | 3.92 | 31.5 |
| 15RW+8SF+20BFS | 324 | 1147.5 | 202.5 | 95.72 | 90 | 36 | 0.45 | 6.53 | 31.5 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tagba, M.; Li, S.; Jiang, M.; Gao, X.; Benmalek, M.L.; Boukour, S.; Liu, C. Performance Evaluation of Cementitious Composites Containing Granulated Rubber Wastes, Silica Fume, and Blast Furnace Slag. Crystals 2021, 11, 632. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst11060632
Tagba M, Li S, Jiang M, Gao X, Benmalek ML, Boukour S, Liu C. Performance Evaluation of Cementitious Composites Containing Granulated Rubber Wastes, Silica Fume, and Blast Furnace Slag. Crystals. 2021; 11(6):632. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst11060632
Chicago/Turabian StyleTagba, Maléki, Shujin Li, Mingjie Jiang, Xu Gao, Mohamed Larbi Benmalek, Salima Boukour, and Chuanqi Liu. 2021. "Performance Evaluation of Cementitious Composites Containing Granulated Rubber Wastes, Silica Fume, and Blast Furnace Slag" Crystals 11, no. 6: 632. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst11060632
APA StyleTagba, M., Li, S., Jiang, M., Gao, X., Benmalek, M. L., Boukour, S., & Liu, C. (2021). Performance Evaluation of Cementitious Composites Containing Granulated Rubber Wastes, Silica Fume, and Blast Furnace Slag. Crystals, 11(6), 632. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst11060632








