Dental Applications of Systems Based on Hydroxyapatite Nanoparticles—An Evidence-Based Update
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Characterization and Biocompatibility of Systems Based on Hydroxyapatite Nanoparticles
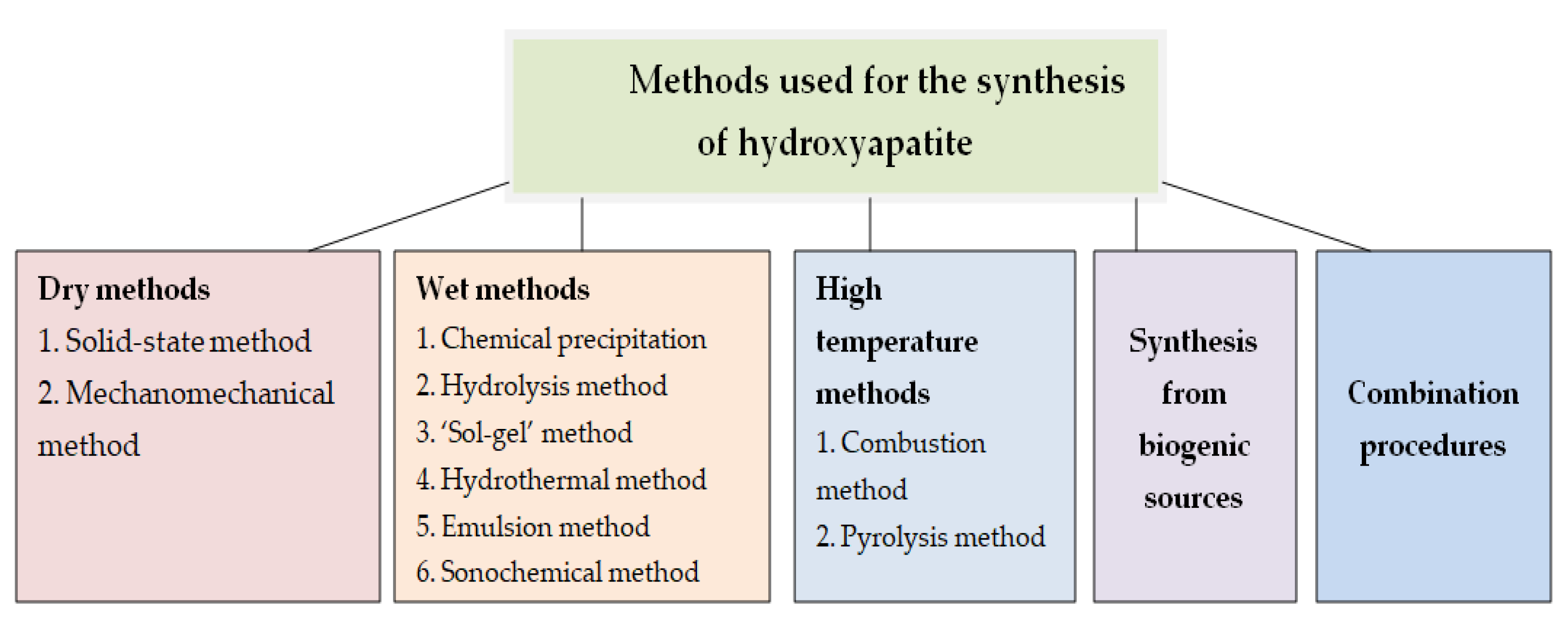
2.1. Synthesis of Hydroxyapatite Nanoparticles
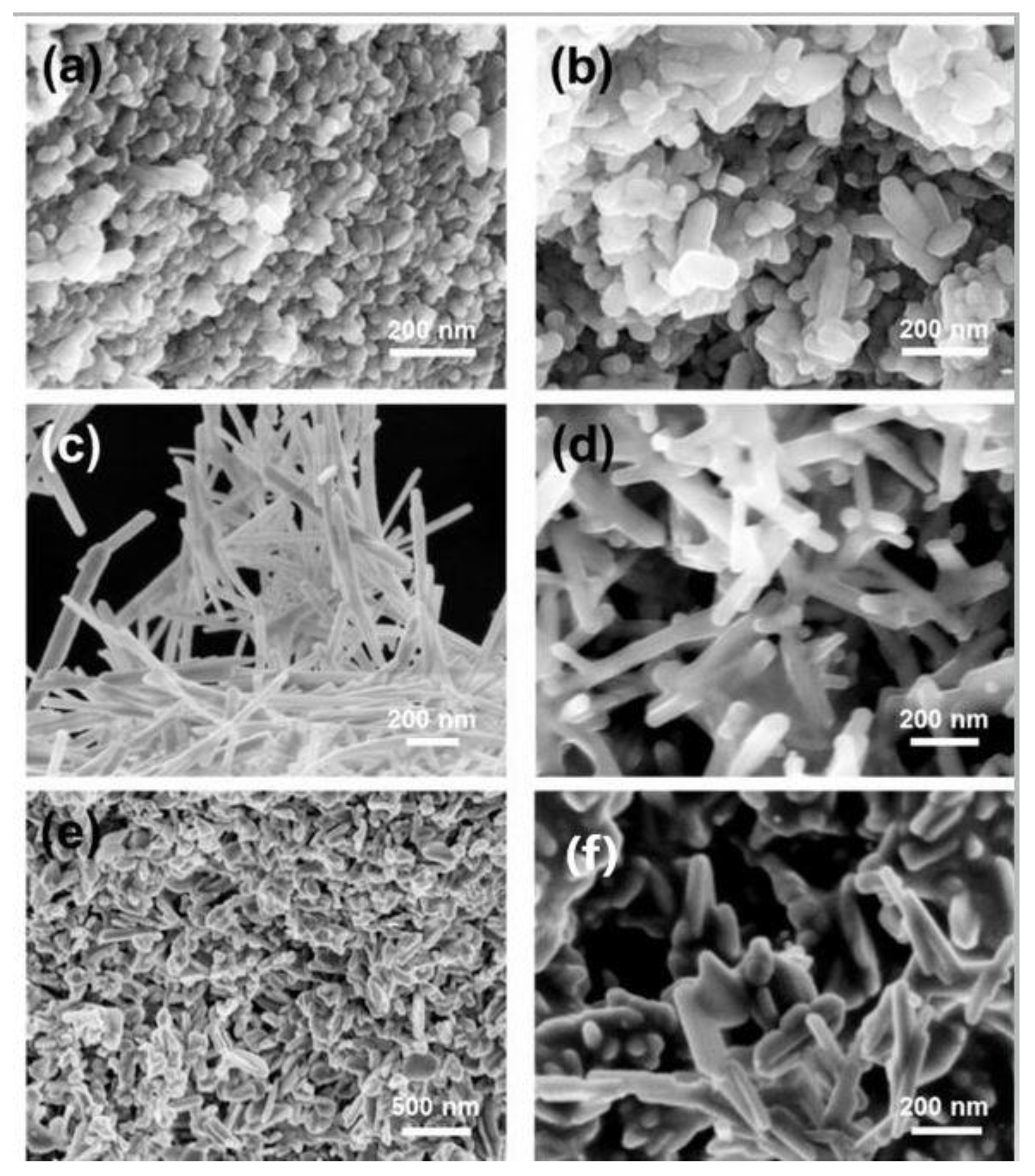
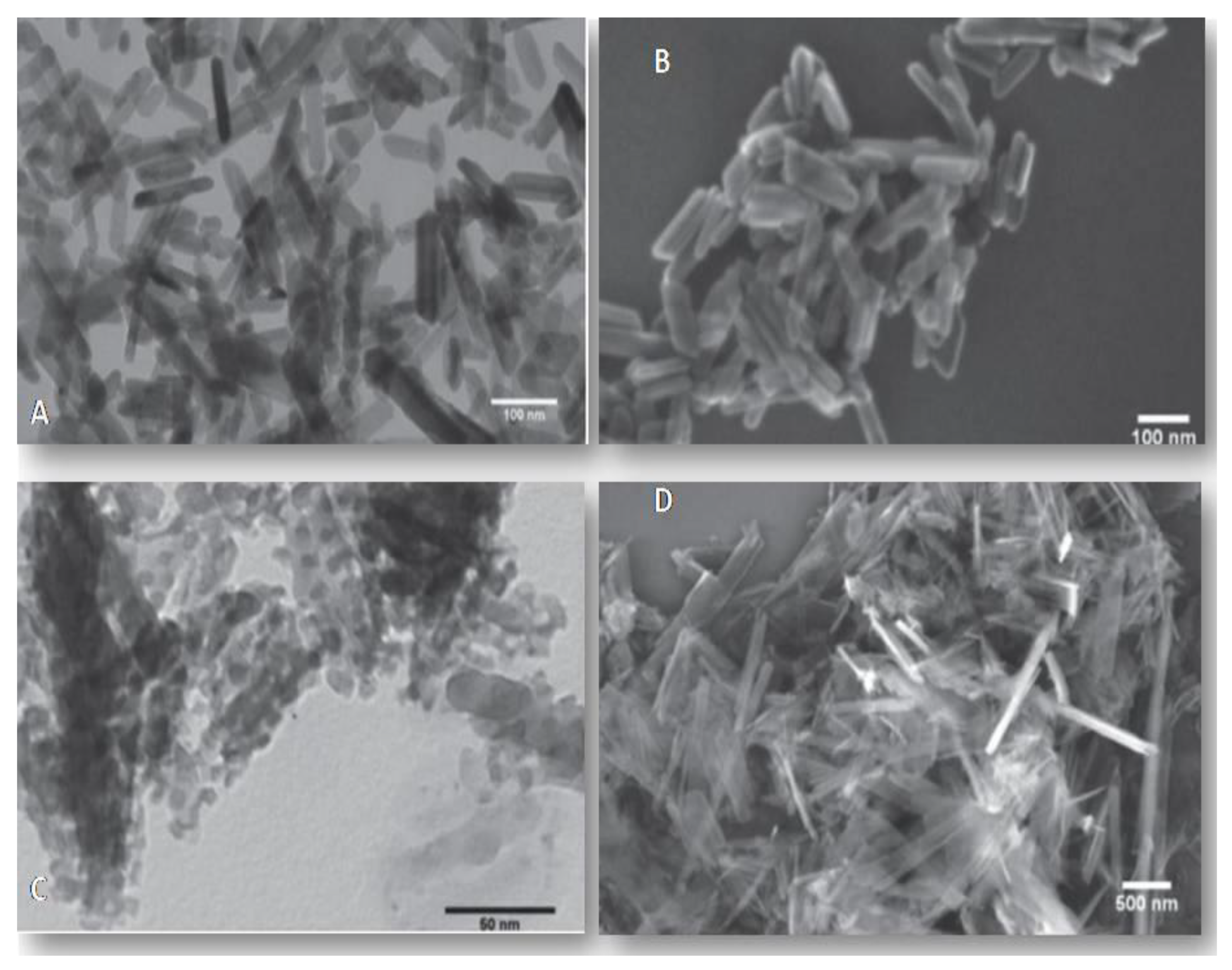
2.2. Characterization of Hydroxyapatite Particles
2.3. Synthesis of Hydroxyapatite Nanocomposites
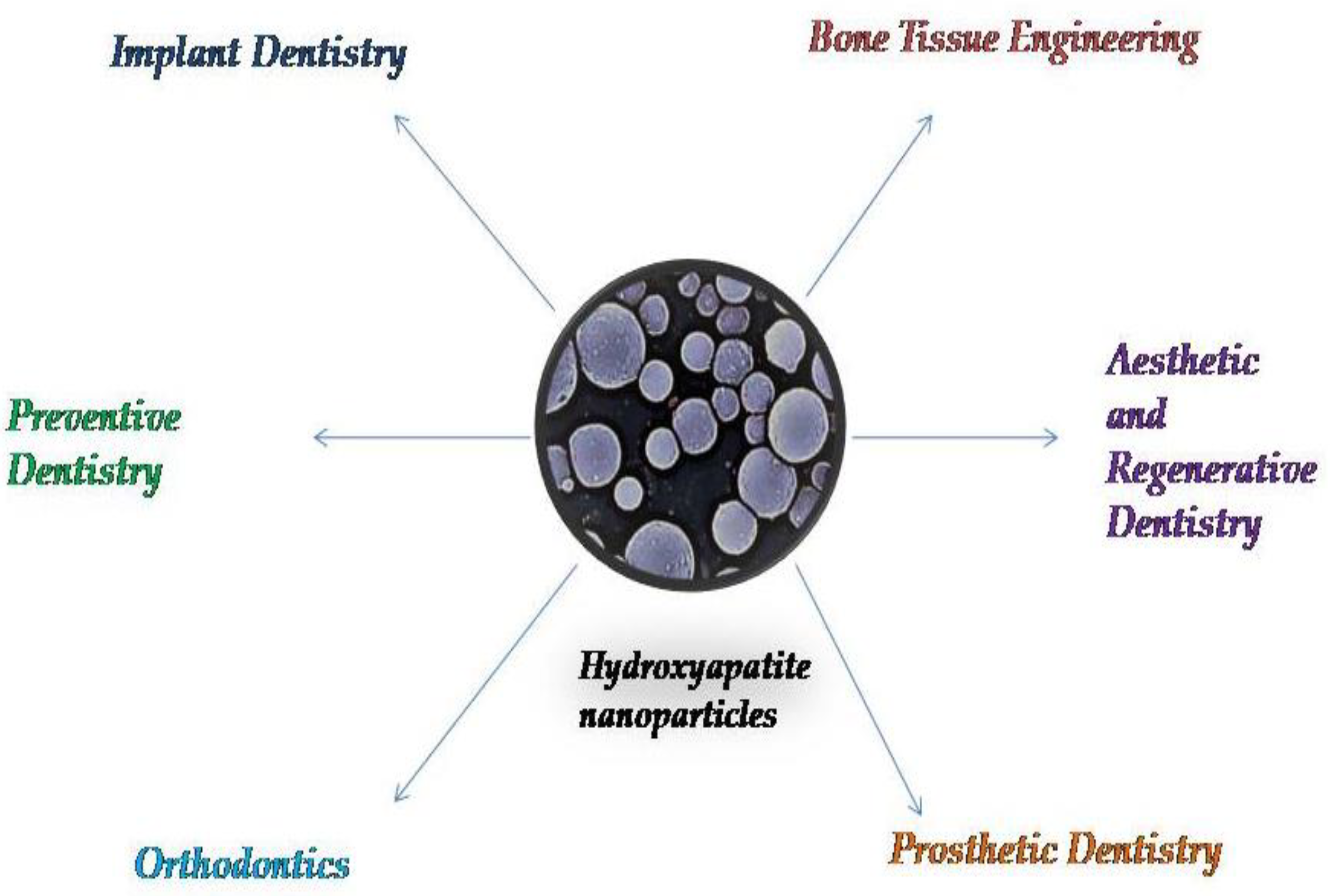
3. Applications of Systems Based on Hydroxyapatite Nanoparticles in Dental Science
3.1. Hydroxyapatite Nanoparticles in Prophylactic and Regenerative Dentistry
3.2. Hydroxyapatite Nanoparticles in Aesthetic and Conservative Dentistry
3.3. Hydroxyapatite Nanoparticles in Restorative Dentistry
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kuśnieruk, S.; Wojnarowicz, J.; Chodara, A.; Chudoba, T.; Gierlotka, S.; Lojkowski, W. Influence of hydrothermal synthesis parameters on the properties of hydroxyapatite nanoparticles. Beilstein. J. Nanotechnol. 2016, 7, 1586–1601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- De Dios Teruel, J.; Alcolea, A.; Hernández, A.; Ruiz, A.J.O. Comparison of chemical composition of enamel and dentine in human, bovine, porcine and ovine teeth. Arch. Oral. Biol. 2015, 60, 768–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antoniac, I.; Miculescu, F.; Cotrut, C.; Ficai, A.; Rau, J.V.; Grosu, E.; Antoniac, A.; Tecu, C.; Cristescu, I. Controlling the Degradation Rate of Biodegradable Mg-Zn-Mn Alloys for Orthopedic Applications by Electrophoretic Deposition of Hydroxyapatite Coating. Materials 2020, 13, 263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Szcześ, A.; Ho, L.; Chibowski, E. Synthesis of hydroxyapatite for biomedical applications. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2017, 249, 321–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sans, J.; Sanz, V.; Puiggalí, J.; Turon, P.; Alemán, C. Controlled Anisotropic Growth of Hydroxyapatite by Additive-Free Hydrothermal Synthesis. Cryst. Growth Des. 2020, 2, 748–756. [Google Scholar]
- Ghiasi, B.; Sefidbakht, Y.; Mozaffari-Jovin, S.; Gharehcheloo, B.; Mehrarya, M.; Khodadadi, A.; Rezaei, M.; Ranaei Siadat, S.O.; Uskoković, V. Hydroxyapatite as a biomaterial–A gift that keeps on giving. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2020, 46, 1035–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arantes, T.M.; Coimbra, L.M.M.; Cristovan, F.H.; Arantes, T.M.; Rosa, G.M.; Lião, L.M. Synthesis and optimization of colloidal hydroxyapatite nanoparticles by hydrothermal processes. J. Braz Chem. Soc. 2018, 29, 1894–1903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coelho, C.C.; Grenho, L.; Gomes, P.S.; Quadros, P.A.; Fernandes, M.H. Nano-hydroxyapatite in oral care cosmetics: Characterization and cytotoxicity assessment. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sadat-Shojai, M.; Khorasani, M.-T.; Dinpanah-Khoshdargi, E.; Jamshidi, A. Synthesis methods for nanosized hydroxyapatite with diverse structures. Acta Biomater. 2013, 9, 7591–7621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molino, G.; Palmieri, M.C.; Montalbano, G.; Fiorilli, S.; Vitale-Brovarone, C. Biomimetic and mesoporous nano-hydroxyapatite for bone tissue application: A short review. Biomed. Mater. 2020, 27, 022001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorozhkin, S.V. Nanosized and nanocrystalline calcium orthophosphates. Acta Biomater. 2010, 6, 715–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varadarajan, N.; Balu, R.; Rana, D. Accelerated Sonochemical Synthesis of Calcium Deficient Hydroxyapatite Nanoparticles: Structural and Morphological Evolution. J. Biomater Tissue Eng. 2014, 4, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Khajuria, D.K.; Vasireddi, R.; Trebbin, M.; Karasik, D.; Razdan, R. Novel therapeutic intervention for osteoporosis prepared with strontium hydroxyapatite and zoledronic acid: In vitro and pharmacodynamic evaluation. Mater. Sci. Eng. C Mater. Biol. Appl. 2017, 71, 698–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sahana, H.; Khajuria, D.K.; Razdan, R.; Mahapatra, D.R.; Bhat, M.R.; Suresh, S.; Rao, R.R.; Mariappan, L. Improvement in bone properties by using risedronate adsorbed hydroxyapatite novel nanoparticle based formulation in a rat model of osteoporosis. J. Biomed. Nanotechnol. 2013, 9, 193–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khajuria, D.K.; Zahra, S.F.; Razdan, R. Effect of locally administered novel biodegradable chitosan based risedronate/zinc-hydroxyapatite intra-pocket dental film on alveolar bone density in rat model of periodontitis. J. Biomater. Sci. Polym. Ed. 2018, 29, 74–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Juntavee, N.; Juntavee, A.; Plongniras, P. Remineralization potential of nano-hydroxyapatite on enamel and cementum surrounding margin of computer-aided design and computer-aided manufacturing ceramic restoration. Int. J. Nanomed. 2018, 13, 2755–2765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hannig, M.; Hannig, C. Nanotechnology and its role in caries therapy. Adv.Dent. Res. 2012, 24, 53–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Y.; Liu, Y.; Yan, W.; Hu, Q.; Tao, J.; Zhang, M. Role of Hydroxyapatite Nanoparticle Size in Bone Cell Proliferation Role of hydroxyapatite nanoparticle size in bone cell proliferation. J. Mater. Chem. 2007, 17, 3780–3787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldberg, M.; Kulkarni, A.B.; Young, M.; Boskey, A. Dentin: Structure, composition and mineralization. Front. Biosci. 2011, 3, 711–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.B.; Gao, S.S.; Yu, H.Y. Effect of nano-hydroxyapatite concentra- tion on remineralization of initial enamel lesion in vitro. Biomed. Mater. 2009, 4, 034104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shi, H.; Zhou, Z.; Li, W.; Fan, Y.; Li, Z.; Wei, J. Hydroxyapatite based materials for bone tissue engineering: A brief and comprehensive introduction. Crystals 2021, 11, 149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pajor, K.; Pajchel, L.; Kolmas, J. Hydroxyapatite and Fluorapatite in Conservative Dentistry and Oral Implantology—A Review. Materials 2019, 12, 2683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Awasthi, S.; Pandey, S.K.; Arunan, E.; Srivastava, C. A review on hydroxyapatite coatings for the biomedical applications: Experimental and theoretical perspectives. J. Mater. Chem. B 2020, 9, 228–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohd Pu’ad, N.A.S.; Abdul Haq, R.H.; Mohd Noh, H.; Abdullah, H.Z.; Idris, M.I.; Lee, T.C. Synthesis method of hydroxyapatite: A review. Mater. Today Proc. 2019, 29, 233–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferraz, M.P.; Monteiro, F.J.; Manuel, C.M. Hydroxyapatite nanoparticles: A review of preparation methodologies. J. Appl. Biomater Biomech. 2004, 2, 74–80. [Google Scholar]
- Webster, T.J.; Siegel, R.W.; Bizios, R. Enhanced surface and mechanical properties of nano phase ceramics to achieve orthopaedic/dental implant efficacy. Key Eng. Mater. 2001, 192, 321–324. [Google Scholar]
- Webster, T.J.; Ergun, C.; Doremus, R.H.; Siegel, R.W.; Bizios, R. Enhanced functions of osteoblasts on nanophase ceramics. Biomaterials 2000, 21, 1803–1810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webster, T.J. Specific proteins mediate enhanced osteoblast adhesion on nanophase ceramics. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 2000, 51, 475–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pataquiva Mateus, A.; Monteiro, F.J.; Pía Ferraz, M. Nanoparticles of hydroxyapatite: Preparation, characterization and cellular approach-An Overview. Rev. Mutis 2013, 3, 43–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fox, K.; Tran, P.A.; Tran, N. Recent advances in research applications of nanophase hydroxyapatite. Chemphyschem 2012, 13, 2495–2506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loo, S.C.; Moore, T.; Banik, B.; Alexis, F. Biomedical applications of hydroxyapatite nanoparticles. Curr. Pharm. Biotechnol. 2010, 11, 333–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paz, A.; Guadarrama, D.; López, M.E.; González, J.; Brizuela, N.; Aragón, J. A comparative study of hydroxyapatite nanoparticles synthesized by different routes. Química Nova, 2012; 35, 1724–1727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agbeboh, N.I.; Oladele, I.O.; Daramola, O.O.; Adediran, A.A.; Olasukanmi, O.O.; Tanimola, M.O. Heliyon Environmentally sustainable processes for the synthesis of hydroxyapatite. Heliyon 2020, 6, e03765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shih, W.J.; Wang, M.C.; Hon, M.H. Morphology and crystallinity of the nanosizedhydroxyapatite synthesized by hydrolysis using cetyltrimethylammonium bromide(CTAB) as a surfactant. J. Cryst. Growth 2005, 275, 2339–2344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanosh, K.P.; Chu, M.C.; Balakrishnan, A. Preparation and characterization of nano-hydroxyapatite powder using sol-gel technique. Bull. Mater. Sci. 2009, 32, 465–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yeon, K.C.; Wang, J.; Ng, S.C. Mechanochemical synthesis of nanocrystalline hydroxyapatite from CaO and CaHPO4. Biomaterials 2001, 22, 2705–2712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turon, P.; del Valle, L.J.; Alemán, C.; Puiggalí, J. Biodegradable and biocompatible systems based on hydroxyapatite nanoparticles. Appl. Sci. 2017, 7, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Leena, M.; Rana, D.; Webster, T.J.; Ramalingam, M. Accelerated synthesis of biomimetic nano hydroxyapatite using simulated body fluid. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2016, 180, 166–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Yang, J.; Quan, Z.; Yang, P.; Li, C.; Hou, Z.; Lin, J. Hydroxyapatite nano- and microcrystals withmultiform morphologies: Controllable synthesis and luminescence properties. Cryst. Growth Des. 2009, 9, 2725–2733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, F.; Leng, Y.; Ding, Y.; Wang, K. Hydrothermal growth of biomimetic carbonated apatite nanoparticles with tunable size, morphology and ultrastructure. Cryst. Eng. Commun. 2013, 15, 2137–2146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, M.; Wang, Y.; Guo, C.; Qi, Y.; Hu, C. Preparation of ultrahigh-aspect-ratio hydroxyapatite nanofibers in reverse micelles under hydrothermal conditions. Langmuir 2004, 20, 4784–4786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, M.G. Hierarchically nanostructured hydroxyapatite: Hydrothermal synthesis, morphology control, growth mechanism, and biological activity. Int. J. Nanomed. 2012, 7, 1781–1791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- McCaffrey, R.; Long, H.; Jin, Y.; Sanders, A.; Park, W.; Zhang, W. Template Synthesis of gold nanoparticles with an organic molecular cage. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2014, 136, 1782–1785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.L.; Liu, X.Y.; Wang, X.G.; Wang, R.Y. Controlling nanoparticle formation via sizable cages of supramolecular soft materials. Langmuir 2011, 27, 7820–7827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, D.S.; Liu, X.Y.; Li, J.L.; Xu, H.Y.; Lin, H.; Chen, Y.Y. Design and fabrication of a new class of nano hybrid materials based on reactive polymeric molecular cages. Langmuir 2013, 29, 11498–11505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Chi, W.; Zhao, D.; Liu, H.; Deng, Y. Molecular-cage method: An improvement of the precipitation method in synthesinzing nanoparticles. Ind. Eng. 2016, 55, 8403–8408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haider, A.; Haider, S.; Han, S.S.; Kang, I.K. Recent advances in the synthesis, functionalization and biomedical applications of hydroxyapatite: A review. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 7442–7458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Arcos, D.; Vallet-Regí, M. Substituted hydroxyapatite coatings of bone implants. J. Mater. Chem. B 2020, 8, 1781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ika, D.A. Bioceramics and Biocomposites-From Research to Clinical Practice; Antoniac, I., Ed.; John Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2019; pp. 248–251. [Google Scholar]
- Surmenev, R.A.; Surmeneva, M.A.; Ivanova, A.A. Significance of Calcium Phosphate Coatings for the Enhancement of New Bone Osteogenesis–A Review. Acta Biomater. 2014, 10, 557–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewandrowski, K.U.; Bondre, S.P.; Wise, D.L.; Trantolo, D.J. Enhanced bioactivity of a poly(propylene fumarate) bone graft substituteby augmentation with nano-hydroxyapatite. Biomed. Mater. 2003, 13, 115–124. [Google Scholar]
- Ramay, H.R.; Li, Z.; Shum, E.; Zhang, M. Chitosan-Alginate Porous Scaffolds Reinforced by Hydroxyapatite Nano- and Micro-Particles: Structural, Mechanical, and Biological Properties. J. Biomed. Nanotechnol. 2005, 1, 151–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Dou, Y.; Yang, J.; Yin, Y.; Zhang, H.; Yao, F.; Wang, H.; Yao, K. Surface characterization and biocompatibilityof micro- and nano-hydroxyapatite/chitosan-gelatin network films. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2009, 29, 1207–1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okada, M.; Matsumoto, T. Fabrication methods of hydroxyapatite nanocomposites. Nano Biomed. 2016, 8, 15–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muzzarelli, R.A.A.; Boudrant, J.; Meyer, D.; Manno, N.; Demarchis, M.; Paoletti, M.G. Current views on fungal chitin/chitosan, human chitinases, food preservation, glucans, pectins and inulin: A tribute to Henri Braconnot, precursor of the carbohydrate polymers science, on the chitin bicentennial. Carbohydr. Polym. 2012, 87, 995–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaya, M.; Baran, T.; Asan-Ozusaglam, M.; Cakmak, Y.S.; Tozak, K.O.; Mol, A.; Mentes, A.; Sezen, G. Extraction and characterization of chitin and chitosan with antimicrobial and antioxidant activities from cosmopolitan Orthoptera species (Insecta). Biotechnol. Bioproc. Eng. 2015, 20, 168–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaya, M.; Cakmak, Y.S.; Baran, T.; Asan-Ozusaglam, M.; Mentes, A.; Tozak, K.O. New chitin, chitosan, and O-carboxymethyl chitosan sources from resting eggs of Daphnia longispina (Crustacea) with physicochemical characterization, and antimicrobial and antioxidant activities. Biotechnol. Bioproc. E 2014, 19, 58–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, P.; Zhao, Y.; Shen, Q.; Wang, D.J.; Xu, D.F. The effect of carboxymethyl-chitosan on the precipitation of calcium carbonate. J. Cryst. Growth 2004, 261, 571–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dumont, V.C.; Mansur, A.A.P.; Carvalho, S.M.; Medeiros Borsagli, F.G.L.; Pereira, M.M.; Mansur, H.S. Chitosan and carboxymethyl-chitosan capping ligands: Effects on the nucleation and growth of hydroxyapatite nanoparticles for producing biocomposite membranes. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2016, 59, 265–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, D.Y.; Johnson, M.A.; Vohden, R.A.; Chen, D.; Martin, D.C. Tailored nanofiber morphologies using modulated electrospinning for biomedical applications. Mater. Res. Soc. Symp. Proc. 2003, 736, D3.8.1–D3.8.6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Both, S.; Yang, X.; Walboomers, X.; Jansen, J. Development of an electrospun nano-apatite/PCL composite membrane for GTR/GBR application. Acta Biomater. 2009, 5, 3295–3304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, T.; Cui, X.; Kao, Y.; Wang, H.; Wen, J. Electrospinning PTMC/Gt/OA-HA composite fiber scaffolds and the biocompatibility with mandibular condylar chondrocytes. Colloids Surf. A 2016, 499, 123–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, X.; Ling, F.; Ma, L.; Yang, C.; Chen, X. Electrospun hydroxyapatite grafted poly(L-lactide)/poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid) nanofibers for guided bone regeneration membrane. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2013, 79, 8–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, P.N.; Chang, L.; Thian, E.S. Development of nanosized silver-substituted apatite for biomedicalapplications: A review. Nanomed. NBM 2015, 11, 1331–1344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rauschmann, M.A.; Wichelhaus, T.A.; Stirnal, V.; Dingeldein, E.; Zichner, L.; Schnettler, R.; Alt, V. Nanocrystalline hydroxyapatite and calcium sulphate as biodegradable composite carrier material forlocal delivery of antibiotics in bone infections. Biomaterials 2005, 26, 2677–2684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hahn, M.A.; Singh, A.K.; Sharma, P.; Brown, S.C.; Moudgil, B.M. Nanoparticles as contrast agents for in vivobioimaging: Current status and future perspectives. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2011, 399, 3–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pankhurst, Q.A.; Connolly, J.; Jones, S.; Dobson, J. Applications of magnetic nanoparticles in biomedicine. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2003, 36, R167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Laranjeira, M.S.; Moço, A.; Ferreira, J.; Coimbra, S.; Costa, E.; Santos-Silva, A.; Ferreira, P.J.; Monteiro, F.J. Different hydroxyapatite magnetic nanoparticles for medical imaging: Its effects on hemostatic, hemolyticactivity and cellular cytotoxicity. Colloid Surface B 2016, 146, 363–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheang, T.-Y.; Lei, Y.Y.; Zhang, Z.Q.; Zhou, H.Y.; Ye, R.Y.; Lin, Y.; Wang, S. Graphene oxide–hydroxyapatite nanocomposites effectively deliver HSV-TK suicide gene to inhibit human breast cancer growth. J. Biomater. Appl. 2018, 33, 216–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, C.H.; Lin, Y.W.; Lin, F.H.; Sun, J.S.; Chao, Y.H.; Lin, H.Y.; Chang, Z.C. Biomimetic Synthesis of Nanocrystalline Hydroxyapatite Composites: Therapeutic Potential and Effects on Bone Regeneration. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 6002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Thomas, S.C.; Kumar Mishra, P.; Talegaonkar, S. Ceramic nanoparticles: Fabrication methods andapplications in drug delivery. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2015, 21, 6165–6188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, S.C.; Sharma, H.; Rawat, P.; Verma, A.; Leekha, A.; Kumar, V.; Tyagi, A.; Gurjar, B.S.; Iqbal, Z.; Talegaonkar, S. Synergistic anticancer efficacy of bendamustine hydrochloride loaded bioactivehydroxyapatite nanoparticles: In-vitro, ex-vivo and in-vivo evaluation. Colloids Surf. B Biointerface 2016, 146, 852–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bordea, R.I.; Candrea, S.; Alexescu, G.T.; Bran, S.; Băciuț, M.; Băciuț, G.; Lucaciu, O.; Dinu, C.M.; Todea, D.M. Nano-hydroxyapatite use in dentistry: A systematic review. Drug Metab. Rev. 2020, 52, 319–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buzea, C.; Pacheco, I.I.; Robbie, K. Nanomaterials and nanoparticles: Sources and toxicity. Biointerphases 2007, 2, MR17–MR71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yazdani, J.; Ahmadian, E.; Sharifi, S.; Shahi, S.; Maleki Dizaj, S. A short view on nanohydroxyapatite as coating of dental implants. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2018, 105, 553–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shashirekha, G.; Jena, A.; Mohapatra, S. Nanotechnology in Dentistry: Clinical Applications, Benefits, and Hazards. Compend. Cont. Educ. Dent. 2017, 38, e1–e4. [Google Scholar]
- Aeran, H.; Kumar, V.; Uniyal, S.; Tanwer, P. Nanodentistry: Is just a fiction or future. J. Oral Biol. Craniofac. Res. 2015, 5, 207–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hannig, M.; Hannig, C. Nanomaterials in preventive dentistry. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2010, 5, 565–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Najibfard, K.; Ramalingam, K.; Chedjieu, I.; Amaechi, B.T. Remineralization of early caries by a nano-hydroxyapatite dentifrice. J.Clin. Dent. 2011, 22, 139–143. [Google Scholar]
- Koul, V.; Kharbanda, O.P. Applications of Nanomaterials in Dental Science: A Review. J. Nanosci. Nacotechnol. 2017, 17, 2235–2255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgan, M.V.; Adams, G.G.; Bailey, D.L.; Tsao, C.E.; Fischman, S.L.; Reynolds, E.C. The anticariogenic effect of sugar-free gum containing CPP-ACP nanocomplexes on approximal caries determined using digital bitewing radiography. Caries Res. 2008, 42, 171–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tschoppe, P.; Zandim, D.L.; Martus, P.; Kielbassa, A.M. Enamel and dentine remineralization by nano-hydroxyapatite toothpastes. J. Dent. 2011, 39, 430–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Esteves-Oliveira, M.; Santos, N.M.; Meyer-Lueckel, H.; Wierichs, R.J.; Rodrigues, J.A. Caries-preventive effect of anti-erosive and nano-hydroxyapatite-containing toothpastes in vitro. Clin. Oral Investig. 2017, 21, 291–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Souza, B.M.; Comar, L.P.; Vertuan, M.; Fernandes Neto, C.; Buzalaf, M.A.R.; Magalhaes, A.C. Effect of an experimental paste with hydroxyapatite nanoparticles and fluoride on dental demineralisation and remineralisation in situ. Caries Res. 2015, 49, 499–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, A.; Rao, A.; Shenoy, R.; Suprabha, B.S. Comparative evaluation of nano-hydroxyapatite and casein phospho- peptide-amorphous calcium phosphate on the remineral- ization potential of early enamel lesions: An in vitro study. J. Orofac. Sci. 2017, 9, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Utneja, S.; Talwar, S.; Nawal, R.; Sapra, S.; Mittal, M.; Rajain, A.; Verma, M. Evaluation of remineralization potential and mechanical properties of pit and fissure sealants forti- fied with nano-hydroxyapatite and nano-amorphous cal- cium phosphate fillers: An in vitro study. J. Conserv. Dent. 2018, 21, 681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jena, A.; Kala, S.; Shashirekha, G. Comparing the effective- ness of four desensitizing toothpastes on dentinal tubule occlusion: A scanning electron microscope analysis. J. Conserv. Dent. 2017, 20, 269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vijayasankari, V.; Asokan, S.; GeethaPriya, P.R. Evaluation of remineralisation potential of experimental nano hydroxyapatite pastes using scanning electron microscope with energy dispersive X-ray analysis: An in-vitro trial. Eur.Arch. Paediatr. Dent. 2019, 20, 529–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Magalhães, A.C.; Francisconi-Dos-Rios, L.F.; Calabria, M.P.; Araújo, D.; Buzalaf, M.; Lauris, J.; Pereira, J.C. Treatment of Dentin Hypersensitivity Using Nano-Hydroxyapatite Pastes: A Randomized Three-Month Clinical Trial. Oper. Dent. 2016, 41, E93–E101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gopinath, N.M.; John, J.; Nagappan, N.; Prabhu, S.; Kumar, E.S. Evaluation of Dentifrice Containing Nano-hydroxyapatite for Dentinal Hypersensitivity: A Randomized Controlled Trial. J. Int. Oral Health 2015, 7, 118–122. [Google Scholar]
- Lhamed, M.; Almalki, F.; Alselami, A.; Alotaibi, T.; Elkwatehy, W. Effect of different remineralizing agents on the initial carious lesions—A comparative study. Saudi Dent. J. 2020, 32, 390–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konagala, R.K.; Mandava, J.; Anwarullah, A.; Uppalapati, L.V.; Karumuri, S.; Angadala, P.L. Synergistic Effect of Arginine on Remineralization Potential of Fluoride Varnish and Nanohydroxyapatite on Artificial Caries Lesions: An In VitroStudy. J. Contemp. Dent. Pract. 2020, 21, 1048–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vano, M.; Derchi, G.; Barone, A.; Genovesi, A.; Covani, U. Tooth bleaching with hydrogen peroxide and nano- hydroxyapatite: A 9-month follow-up randomized clinical trial. Int. J. Dent. Hygiene 2015, 13, 301–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kutuk, Z.B.; Ergin, E.; Cakir, F.Y.; Gurgan, S. Effects of in- office bleaching agent combined with different desensitiz- ing agents on enamel. J. Appl. Oral. Sci. 2018, 27, e80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khalid, H.; Syed, M.R.; Rahbar, M.I.; Iqbal, H.; Ahmad, S.; Kaleem, M.; Matinlinna, J.P.; Khan, A.S. Effect of nano-bioceramics on monomer leaching and degree of conversion of resin-based composites. Dent. Mater. J. 2018, 37, 940–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lung, C.Y.; Sarfraz, Z.; Habib, A.; Khan, A.S.; Matinlinna, J.P. Effect of silanization of hydroxyapatite fillers on physical and mechanical properties of a bis-GMA based resin composite. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2016, 54, 283–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lung, C.Y.K.; Matinlinna, J.P. Aspects of silane coupling agents and surface conditioning in dentistry: An overview. Dent. Mater. J. 2012, 28, 467–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nobre, C.M.G.; Pütz, N.; Hannig, M. Adhesion of Hydroxyapatite Nanoparticles to Dental Materials under Oral Conditions. Scanning 2020, 2020, 6065739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jardim, R.N.; Rocha, A.A.; Rossi, A.M.; de Almeida Neves, A.; Portela, M.B.; Lopes, R.T.; Moreira da Silva, E. Fabrication and characterization of remineralizing dental composites containing hydroxyapatite nanoparticles. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2020, 109, 103817–doi:10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sodagar, A.; Akhavan, A.; Hashemi, E.; Arab, S.; Pourhajibagher, M.; Sodagar, K.; Kharrazifard, M.J.; Bahador, A. Evaluation of the antibacterial activity of a conventional orthodontic composite containing silver/hydroxyapatite nanoparticles. Prog. Orthodont. 2016, 17, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gilani, M.A.H.; Ameli, N.; Ghorbani, R.; Akhavan, A.; Rabiei, A.; Zeinabadi, M.S.; Kameli, S. Effect of Adding Nano Silver-Hydroxyapatite to the Orthodontic Primer on Bracket-Enamel Shear Bond Strength. J. Evol. Med. Dent. Sci. 2020, 9, 3457–3462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasan, L.A. Evaluation the properties of orthodontic adhesive incorporated with nano-hydroxyapatite particles. Saudi Dent. J. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kheur, M.; Kantharia, N.; Iakha, T.; Kheur, S.; Husain, N.A.-H.; Özcan, M. Evaluation of mechanical and adhesion properties of glass ionomer cement incorporating nano-sized hydroxyapatite particles. Odontology 2020, 108, 66–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sidhu, S.K.; Nicholson, J.W. A review of glass-ionomer cements for clinical dentistry. J. Funct. Biomater. 2016, 7, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alatawi, R.A.S.; Elsayed, N.H.; Mohamed, W.S. Influence of hydroxyapatite nanoparticles on the properties of glass ionomer cement. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2019, 8, 344–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noorani, T.Y.; Luddin, N.; Rahman, I.A.; Masudi, S.M. In Vitro Cytotoxicity Evaluation of Novel Nano-Hydroxyapatite-Silica Incorporated Glass Ionomer Cement. J. Clin. Diagn. Res. 2017, 11, ZC105–ZC109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pagano, S.; Chieruzzi, M.; Balloni, S.; Lombardo, G.; Torre, L.; Bodo, M.; Cianetti, S.; Marinucci, L. Biological, thermal and mechanical characterization of modified glass ionomer cements: The role of nanohydroxyapatite, ciprofloxacin and zinc l-carnosine. Mater. Sci. Eng. C Mater. Biol. Appl. 2019, 94, 76–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Technique | Technique’s Features | Technique’s Limitations | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Spectroscopic techniques | Fourier-transform infrared (FTIR) | It measures the intensity over a narrow range of wavelengths at a time and no external calibration is required; it provides accurate results, and identifies even small concentrations of contaminants | Inorganic materials are not easily analyzed |
| Raman spectroscopy | Highly specific (provides a chemical fingerprint of the material); inorganic materials are easier to analyze by Raman spectroscopy than by FTIR | The detection requires a sensitive and highly optimized instrument; fluorescence of the impurities or of the sample itself can hide the Raman spectrum; sample heating by the intense laser radiation can destroy the sample or cover the Raman spectrum. | |
| X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) | Provides unique information about the chemical composition of a material | Slow, poor spatial resolution, requires high vacuum | |
| X-ray diffraction (XRD) | Powerful and rapid(<20 min) technique, provides an unambiguous mineral determination; data interpretation is relatively straight forward | Homogeneous and single-phase materials are best for identification of an unknown; peak overlay may occur, and it is worse for high angle reflections | |
| Energy-dispersive spectroscopy (EDS) | Chemical microanalysis technique used in conjunction with SEM; provides unique peaks characteristic of the atomic structure of the atoms; quick and versatile technique | Comparatively lower precision | |
| Direct visualization | Scanning electron microscopy (SEM) | Direct visualization, high resolution | Nanoparticle aggregation during sample preparation |
| Transmission electron microscopy (TEM) | Direct visualization, high resolution | Nanoparticle aggregation during the sample preparation, electron beam damage, preference for electron-dense atomic | |
| Atomic force microscopy (AFM) | High size resolution, 3D profile | Slow speed, limited scanning area |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Balhuc, S.; Campian, R.; Labunet, A.; Negucioiu, M.; Buduru, S.; Kui, A. Dental Applications of Systems Based on Hydroxyapatite Nanoparticles—An Evidence-Based Update. Crystals 2021, 11, 674. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst11060674
Balhuc S, Campian R, Labunet A, Negucioiu M, Buduru S, Kui A. Dental Applications of Systems Based on Hydroxyapatite Nanoparticles—An Evidence-Based Update. Crystals. 2021; 11(6):674. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst11060674
Chicago/Turabian StyleBalhuc, Silvia, Radu Campian, Anca Labunet, Marius Negucioiu, Smaranda Buduru, and Andreea Kui. 2021. "Dental Applications of Systems Based on Hydroxyapatite Nanoparticles—An Evidence-Based Update" Crystals 11, no. 6: 674. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst11060674
APA StyleBalhuc, S., Campian, R., Labunet, A., Negucioiu, M., Buduru, S., & Kui, A. (2021). Dental Applications of Systems Based on Hydroxyapatite Nanoparticles—An Evidence-Based Update. Crystals, 11(6), 674. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst11060674








