Influence of the Curing and Annealing Temperatures on the Properties of Solution Processed Tin Oxide Thin Films
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussions
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nomura, K.; Ohta, H.; Takagi, A.; Kamiya, T.; Hirano, M.; Hosono, H. Room-Temperature Fabrication of Transparent Flexible Thin-Film Transistors Using Amorphous Oxide Semiconductors. Nature 2004, 432, 488–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hosono, H.; Yasukawa, M.; Kawazoe, H. Novel oxide amorphous semiconductors: Transparent conducting amorphous oxides. J. Non Cryst. Solids 1996, 203, 334–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fortunato, E.; Barquinha, P.; Martins, R. Oxide Semiconductor Thin-Film Transistors: A Review of Recent Advances. Adv. Mater. 2012, 24, 2945–2986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.T.; Shi, X.L.; Liu, W.W.; Zhong, X.H.; Wang, J.N.; Pyrah, L.; Sanderson, K.D.; Ramsey, P.M.; Hirata, M.; Tsuri, K. Influence of Preferred Orientation on the electrical Conductivity of Fluorine doped Tin Oxide Films. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 3679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsunashima, A.; Yoshimizu, H.; Kodaira, K.; Shimada, S.; Matsushita, T. Preparation and properties of Antimony-doped SnO2 films by thermal decomposition of tin 2-ethylexanoate. J. Mater. Sci. 1986, 21, 2731–2734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avis, C.; Kim, Y.; Jang, J. Amorphous Tin Oxide Applied to Solution Processed Thin-Film Transistors. Materials 2019, 12, 3341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jang, J.; Kitsomboonloha, R.; Swisher, S.L.; Park, E.S.; Kang, H.; Subramanian, V. Transparent High-Performance Thin Film Transistors from Solution-Processed SnO2/ZrO2 Gel-like Precursors. Adv. Mater. 2013, 25, 1042–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Zhou, Y.H.; Zhong, D.-Y.; Li, X.-F.; Zhang, J.H. Simultaneous Enhancement of Electrical Performance and Negative Bias Illumination Stability for Low-Temperature Solution-Processed SnO2 Thin-Film Transistors by Fluorine Incorporation. IEEE Trans. Elec. Dev. 2019, 66, 4205–4210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shih, C.; Chin, A.; Lu, C.F.; Su, W.F. Remarkably high mobility ultrathin-film metal-oxide transistor with strongly overlapped orbitals. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nomura, K.; Kamiya, T.; Hosono, H. Ambipolar Oxide Thin-Film Transistor. Adv. Mater. 2011, 23, 3431–3434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sajiz, K.J.; Reena Mary, A.P. Tin Oxide Based P and N-Type Thin Film Transistors Developed by RF Sputtering. ECS J. Solid State Sci. Technol. 2015, 4, Q101–Q104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ponzoni, A. Morphological Effects in SnO2 Chemiresistors for Ethanol Detection: A Review in Terms of Central Performances and Outliers. Sensors 2021, 21, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suematsu, K.; Sasaki, M.; Ma, N.; Yuasa, M.; Shimanoe, K. Antimony-Doped Tin Dioxide Gas Sensors Exhibiting High Stability in the Sensitivity to Humidity Changes. ACS Sens. 2016, 1, 913–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Liu, D.; Wang, Y.; Wang, C.; Zhang, T.; Zhang, P.; Sarvari, H.; Chen, Z.; Li, S. Enhanced performance of planar perovskite solar cells using low temperature solution-processed al-doped SnO2 as electron transport layers. Nano. Res. Lett. 2017, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Q.; Zhang, L.; Wang, H.; Yang, X.; Meng, J.; Liu, H.; Yin, Z.; Wu, J.; Zhang, X.; You, J. Enhanced electron extraction using SnO2 for high efficiency planar-structure HC(NH2)2PbI3-based perovskite solar cells. Nat. Energy 2017, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.B.; Kumar, N.; Ovhal, M.M.; Kim, Y.J.; Song, Y.M.; Kang, J.W. Dopant-Free, Amorphous–Crystalline Heterophase SnO2 Electron Transport Bilayer Enables >20% Efficiency in Triple-Cation Perovskite Solar Cells. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2020, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, S.; Seo, S.; Park, H.; Shin, H. Atomic layer deposition of a SnO2 electron-transporting layer for planar perovskite solar cells with a power conversion efficiency of 18.3%. Chem. Commun. 2019, 55, 2433–2436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, K.-H.; Seo, J.-Y.; Lee, S.; Shin, H.; Park, N.-G. Solution-processed SnO2 thin film for a hysteresis-free planar perovskite solar cell with a power conversion efficiency of 19.2%. J. Mater. Chem. A 2017, 5, 24790–24803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manseki, K.; Splingaire, L.; Schnupf, U.; Sugiura, T.; Vafaei, S. Current Advances in the Preparation of SnO2 Electron Transport Materials for Perovskite Solar Cells. In Proceedings of the 5th Thermal and Fluids Engineering Conference, New Orleans, LA, USA, 5–8 April 2020; pp. 585–592. [Google Scholar]
- Kuang, Y.; Zardetto, V.; van Gils, R.; Karwal, S.; Koushik, D.; Verheijen, M.A.; Black, L.E.; Weijtens, C.; Veenstra, S.; Andriessen, R.; et al. Low-Temperature Plasma-Assisted Atomic-Layer-Deposited SnO2 as an Electron Transport Layer in Planar Perovskite Solar Cells. ACS Appl. Mater. Interf. 2018, 10, 30367–30378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kam, M.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, D.; Fan, Z. Room-Temperature Sputtered SnO2 as Robust Electron Transport Layer for Air-Stable and Efcient Perovskite Solar Cells on Rigid and Flexible Substrates. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koo, H.S.; Lee, J.-A.; Heo, Y.-W.; Lee, J.H.; Lee, H.Y.; Kim, J.J. Effects of oxygen partial pressure on the structural and electrical properties of Al and Sb co-doped p-type ZnO thin films grown by pulsed laser deposition. Thin Solid Film. 2020, 708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, J.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, C.; Yang, X.; Hu, R.; Huang, J.; Yu, J.; Li, L. Low-temperature preparation of ZnO thin film by atmospheric mist chemistry vapor deposition for flexible organic solar cells. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Elec. 2016, 27, 7004–7009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Won, J.H.; Han, S.H.; Park, B.K.; Chung, T.-M.; Han, J.H. Effect of Oxygen Source on the Various Properties of SnO2 Thin Films Deposited by Plasma-Enhanced Atomic Layer Deposition. Coatings 2020, 10, 692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banger, K.K.; Yamashita, Y.; Mori, K.; Peterson, R.L.; Leedham, T.; Rickard, J.; Sirringhaus, H. Low-temperature, high-performance solution-processed metal oxide thin-film transistors formed by a “sol gel on chip” process. Nat. Mater. 2011, 10, 45–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, C.-H.; Lin, L.-Y.; Cheng, C.C.; Chang, C. Printed Oxide Thin Film Transistors: A Mini Review. ECS J. Solid State Sci. Technol. 2015, 4, P3044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lalasari, L.H.; Arini, T.; Andriyah, L.; Firdiyono, F.; Yuwono, A.H. Electrical, optical and structural properties of FTO thin films fabricated by spray ultrasonic nebulizer technique from SnCl4 precursor. AIP Conf. Proc. 2018, 1964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rey, G.; Ternon, C.; Modreanu, M.; Mescot, X.; Consonni, V.; Bellet, D. Electron scattering mechanisms in fluorine doped SnO2 thin films. J. Appl. Phys. 2013, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, S.-S.; Tsai, Y.-S.; Bai, K.-R. Structural and physical properties of tin oxide thin films for optoelectronic applications. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2016, 380, 203–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pusawale, S.N.; Deshmukh, P.R.; Lokhande, C.D. Chemical synthesis and characterization of hydrous tin oxide (SnO2:H2O) thin films. Bull. Mater. Sci. 2011, 34, 1179–1183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, J.; Yim, H.; Cho, Y.-H.; Kang, D.-H.; Choi, J.-W. Optical and Electronic Properties of SnO2 Thin Films Fabricated Using the SILAR Method. J. Sens. Sci. Technol. 2015, 24, 364–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Deyu, G.K. Muñoz-Rojas, D.; Rapenne, L.; Deschanvres, J.L.; Klein, A.; Jiménez, C.; Bellet, D.; SnO2 Films Deposited by Ultrasonic Spray Pyrolysis: Influence of Al Incorporation on the Properties. Molecules 2019, 24, 2797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erken, O.; Ozkendir, O.M.; Gunes, M.; Harputlu, E.; Ulutase, C.; Gumus, C. A study of the electronic and physical properties of SnO2 thin films as a function of substrate temperature. Ceram. Int. 2019, 45, 19086–19092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palanichamy, S.; Mohamed, J.R.; Kumar, P.S.S.; Pandiarajan, S.; Amalraj, L. Physical properties of nebulized spray pyrolysised SnO2 thin films at different substrate temperature. Appl. Phys. A 2018, 124, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.S.; Kim, D.Y.; Kim, W.-B.; Park, I.K. Realization of Eu-doped p-SnO2 thin film by spray pyrolysis deposition. Ceram. Int. 2020, 46, 430–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuliarto, B.; Gumilara, G.; Zulhendria, D.W.; Septiani, N.L.W. Preparation of SnO2 Thin Film Nanostructure for CO Gas Sensor Using Ultrasonic Spray Pyrolysis and Chemical Bath Deposition Technique. Acta Phys. Pol. A 2017, 131, 534–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashina, A.; Battula, R.K.; Chundi, E.R.N.; Sakthivel, S.; Veerappan, G. Dip coated SnO2 film as electron transport layer for low temperature processed planar perovskite solar cells. Appl. Surf. Sci. Adv. 2021, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.E.K.; Oliver, M. Structural, electrical, and optical properties of reactively sputtered SnO2 thin films. Met. Mater. Int. 2010, 16, 441–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jäger, T.; Bissig, B.; Döbeli, M.; Tiwari, A.N.; Romanyuk, Y.E. Thin films of SnO2:F by reactive magnetron sputtering with rapid thermal post-annealing. Thin Solid Film. 2014, 553, 21–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jo, K.-W.; Moon, S.-W.; Cho, W.-J. Fabrication of high-performance ultrathin-body SnO2 thin-film transistors using microwave-irradiation post-deposition annealing. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2015, 106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peale, R.E.; Smith, E.; Abouelkhair, H.; Oladeji, I.O.; Vangala, S.; Cooper, T.; Grzybowski, G.; Khalilzadeh-Rezaie, F.; Cleary, J.W. Electrodynamic properties of aqueous spray-deposited SnO2:F films for infrared plasmonics. Opt. Eng. 2017, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Nadarajah, A.; Carnes, M.E.; Kast, M.G.; Johnson, D.W.; Boettcher, S.W. Aqueous Solution Processing of F-Doped SnO2 Transparent Conducting Oxide Films Using a Reactive Tin(II) Hydroxide Nitrate Nanoscale Cluster. Chem. Mater. 2013, 25, 4080–4087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Dong, G.; Duan, L.; Qiao, J.; Zhang, D.; Wang, L.; Qiu, Y. Impacts of Sn precursors on solution-processed amorphous zinc–tin oxide films and their transistors. RSC Adv. 2012, 2, 5307–5313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitabayashi, S.; Koga, N. Thermal Decomposition of Tin(II) Oxyhydroxide and Subsequent Oxidation in Air: Kinetic Deconvolution of Overlapping Heterogeneous Processes. J. Phys. Chem. C 2015, 119, 16188–16199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patnaik, P. Handbook of Inorganic Chemicals; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Heo, J.; Hock, A.S.; Gordon, R. Low Temperature Atomic Layer Deposition of Tin Oxide. Chem. Mater. 2010, 22, 4964–4973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tauc, J. Optical properties and electronic structure of amorphous Ge and Si. Mat. Res. Bull. 1968, 3, 37–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makuła, P.; Pacia, M.; Macyk, W. How To Correctly Determine the Band Gap Energy of Modified Semiconductor Photocatalysts Based on UV−Vis Spectra. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2018, 9, 6814–6817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanatta, A.R. Revisiting the optical bandgap of semiconductors and the proposal of a unifed methodology to its determination. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viezbicke, B.D.; Patel, S.; Davis, B.E.; Birnie, D.P., III. Evaluation of the Tauc method for optica absorption edge determmination: ZnO thin films as a model system. Phys. Status Solidi B 2015, 8, 1700–1710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pankove, J.I. Optical Processes in Semiconductors; Courier Corporation: Mineola, NY, USA, 1971. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, P.; Longo, P.; Zaslavsky, A.; Pacifici, D. Optical bandgaps of single- and multi-layered amorphous germanium ultra-thin films. J. Appl. Phys. 2016, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, S.S.; Zhang, Y.X.; Teng, X.M.; Li, G.H.; Li, L. Optical properties of nitrogen-doped SnO2 films: Effect of the electronegativity on refractive index and band gap. J. Appl. Phys. 2008, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janicek, P.; Niang, K.M.; Mistric, J.; Palka, K.; Flewitt, A.J. Spectroscopic ellipsometry characterization of ZnO:Sn thin films withvarious Sn composition deposited by remote-plasma reactive sputtering. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2017, 421, 557–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di, M.; Bersch, E.; Diebold, A.; Consiglio, S.; Clark, R.; Leusink, G.; Kaack, T. Comparison of methods to determine bandgaps of ultrathin HfO2 films using spectroscopic ellipsometry. J. Vac. Sci. Tech. A 2011, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forouhi, A.R.; Bloomer, I. Optical Dispersion Relations for Amorphous Semiconductors and Amorphous Dielectrics. Phys. Rev. B 1986, 34, 7018–7026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forouhi, A.R.; Bloomer, I. Optical Properties of Crystalline Semiconductors and Dielectrics. Phys. Rev. B 1988, 38, 1865–1874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, J.; Wang, X.; Fan, X.; Dai, R.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Ding, Z. Temperature dependent optical properties of SnO2 film study by ellipsometry. Opt. Mater. Express 2019, 9, 3691–3699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parra, R.; Joanni, E.; Espinosa, J.W.M.; Tararam, R.; Cilense, M.; Bueno, P.R.; Varela, J.A.; Longo, E. Photoluminescent CaCu3Ti4O12-based thin films synthesized by a sol-gel method. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2008, 91, 4162–4164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
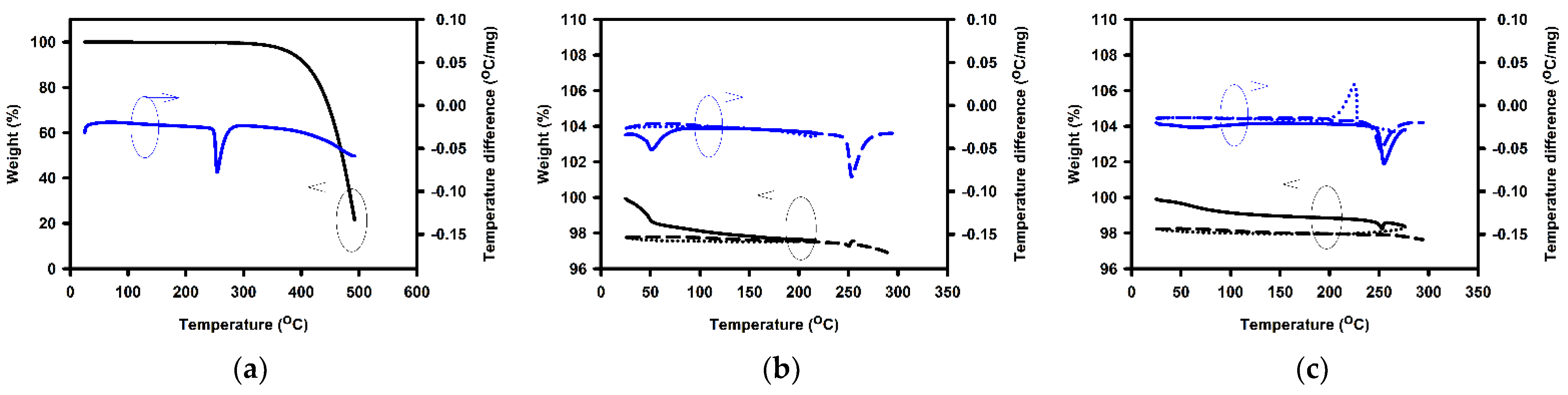
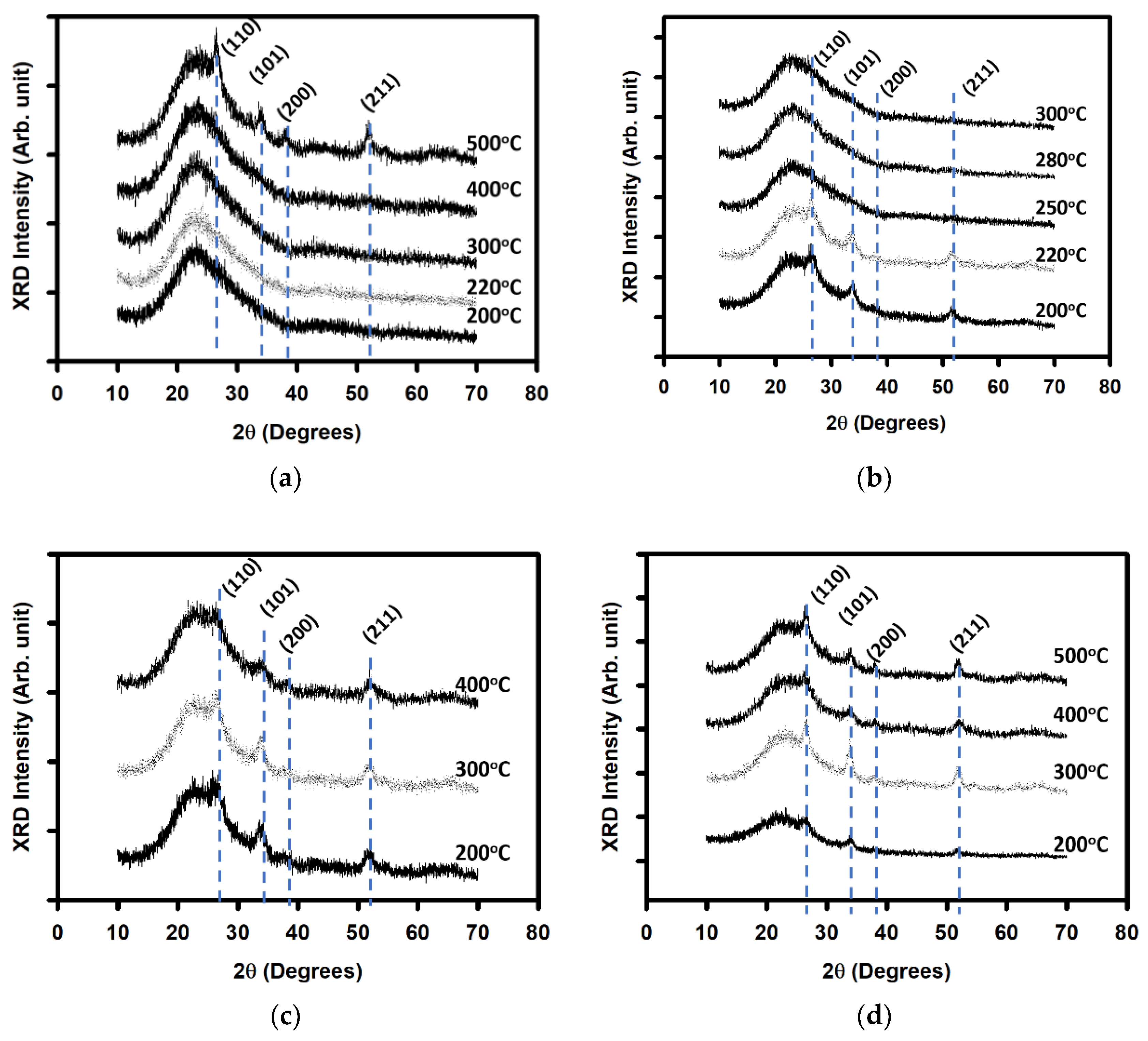

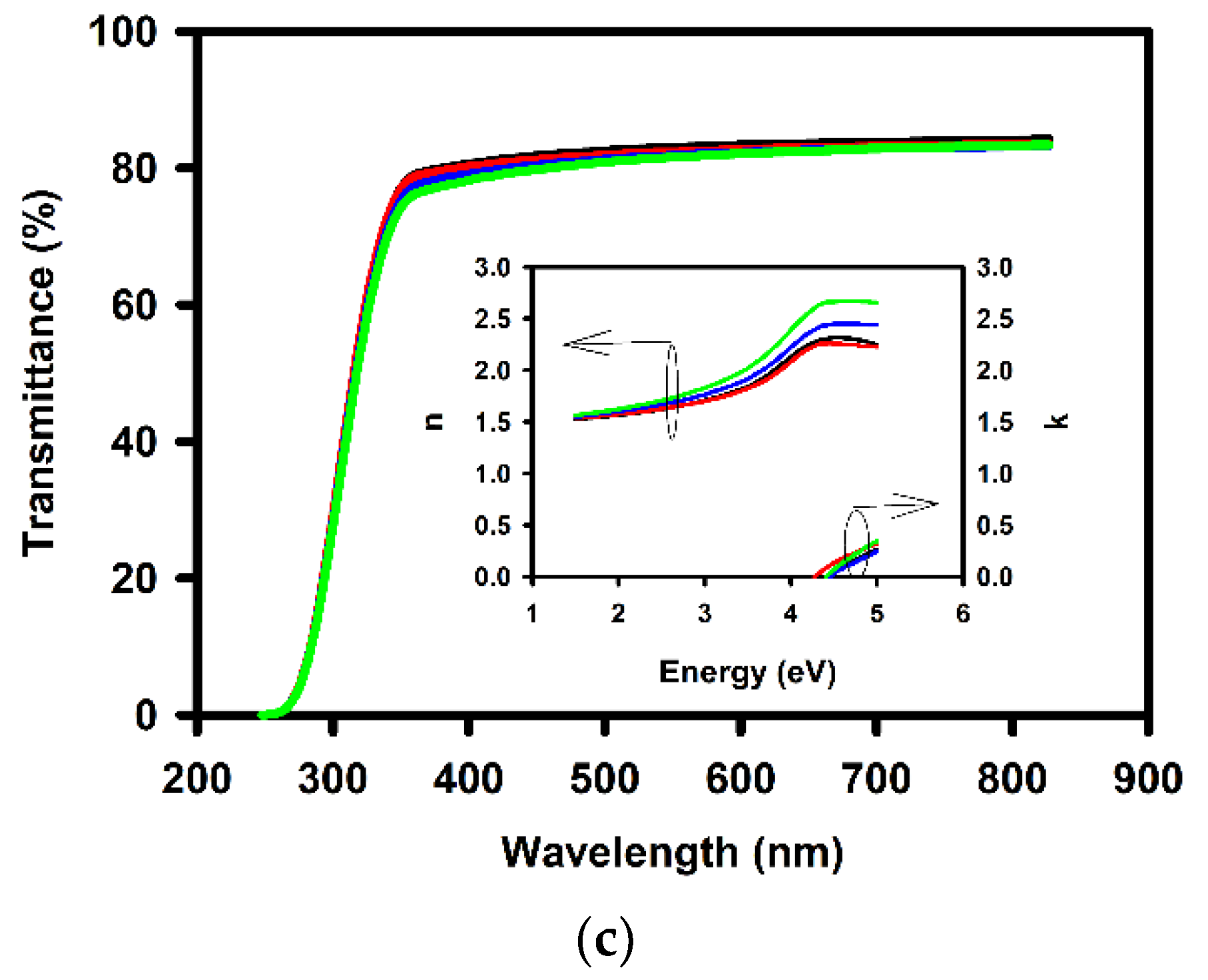
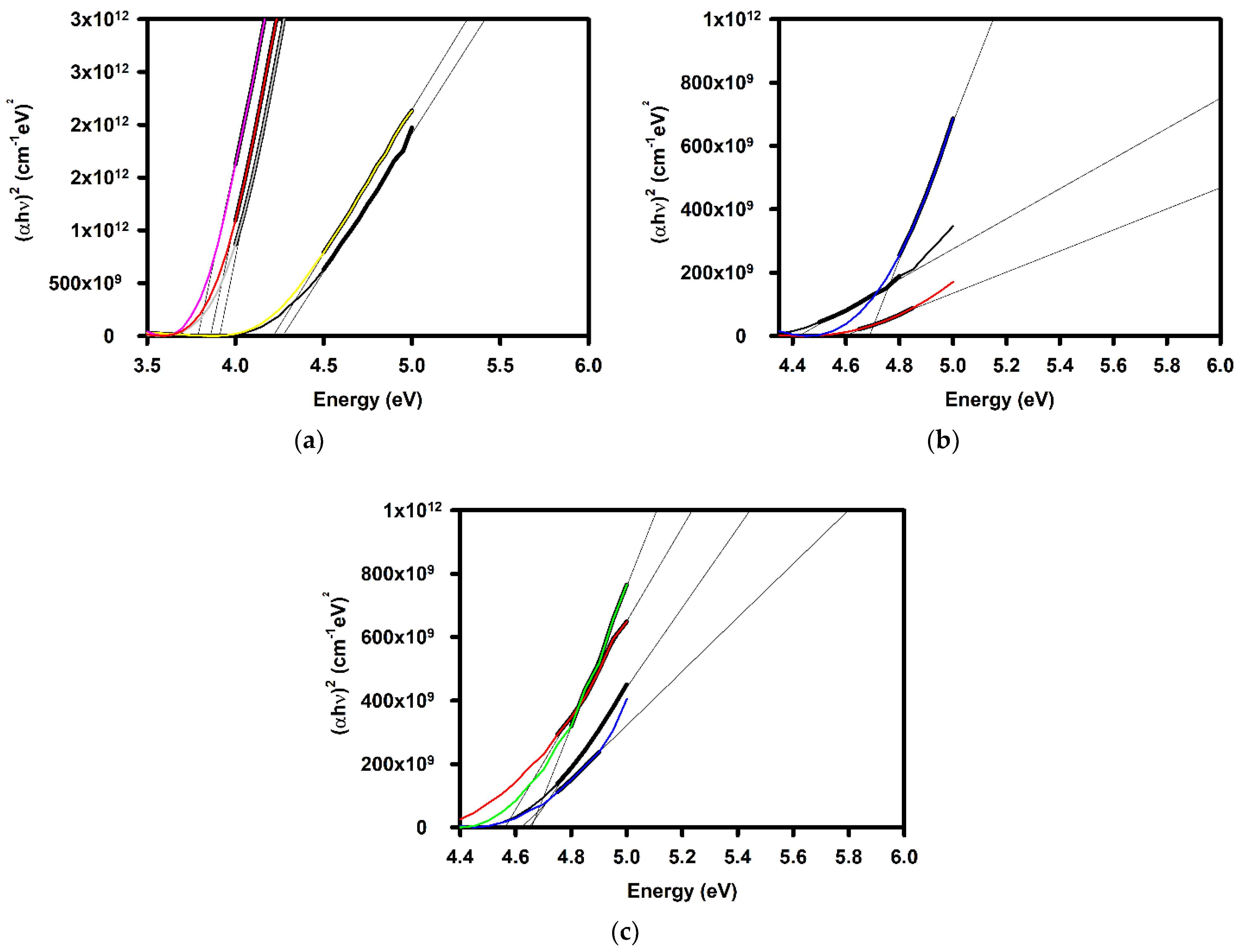


| Annealing Temperature (°C) | Curing Temperature (°C) | Rpv (nm) | Rrms (nm) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 300 | 200 | 4.926 | 0.391 |
| 220 | 5.548 | 0.339 | |
| 250 | 2.277 | 0.261 | |
| 280 | 1.986 | 0.16 | |
| 300 | 1.682 | 0.154 | |
| 400 | 200 | 6.087 | 0.537 |
| 300 | 5.594 | 0.552 | |
| 400 | 10.266 | 1.020 | |
| 500 | 200 | 14.072 | 1.365 |
| 300 | 12.954 | 0.741 | |
| 400 | 5.912 | 0.683 | |
| 500 | 36.022 | 1.566 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Avis, C.; Jang, J. Influence of the Curing and Annealing Temperatures on the Properties of Solution Processed Tin Oxide Thin Films. Crystals 2021, 11, 851. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst11080851
Avis C, Jang J. Influence of the Curing and Annealing Temperatures on the Properties of Solution Processed Tin Oxide Thin Films. Crystals. 2021; 11(8):851. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst11080851
Chicago/Turabian StyleAvis, Christophe, and Jin Jang. 2021. "Influence of the Curing and Annealing Temperatures on the Properties of Solution Processed Tin Oxide Thin Films" Crystals 11, no. 8: 851. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst11080851
APA StyleAvis, C., & Jang, J. (2021). Influence of the Curing and Annealing Temperatures on the Properties of Solution Processed Tin Oxide Thin Films. Crystals, 11(8), 851. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst11080851






