A Novel Method for the Preparation of Fibrous CeO2–ZrO2–Y2O3 Compacts for Thermochemical Cycles
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Preparation
2.2. Sample Characterization
2.3. Gas Permeability Test
2.4. Evaluation of Redox Kinetics
3. Results and Discussion
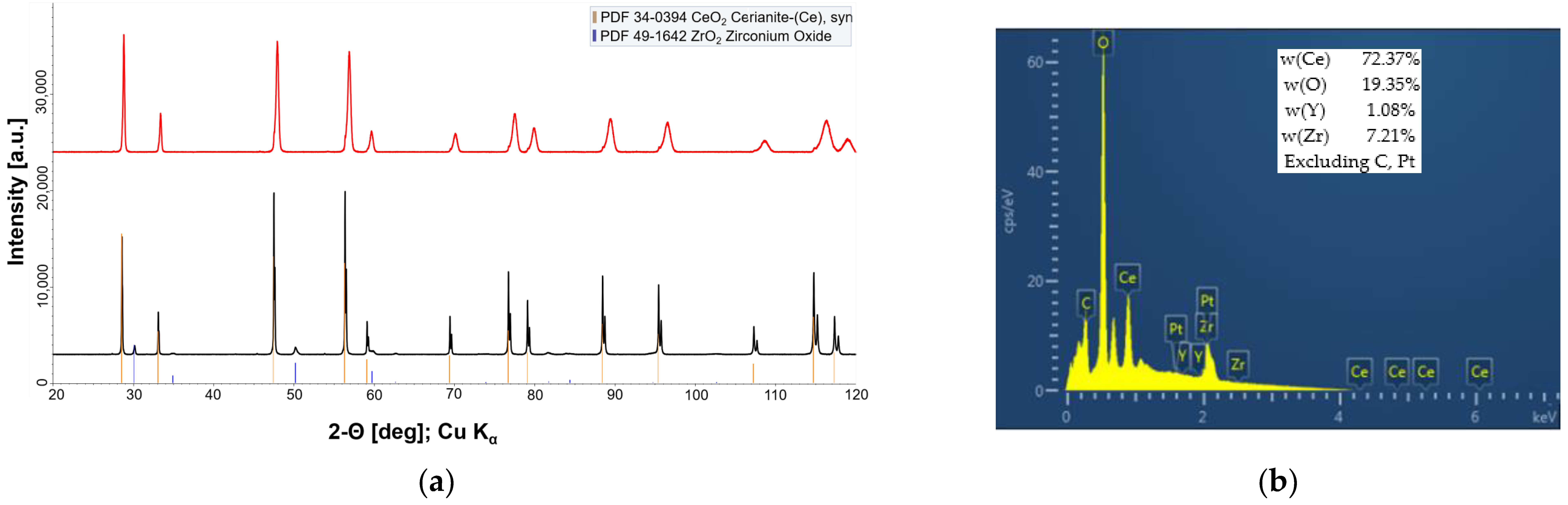
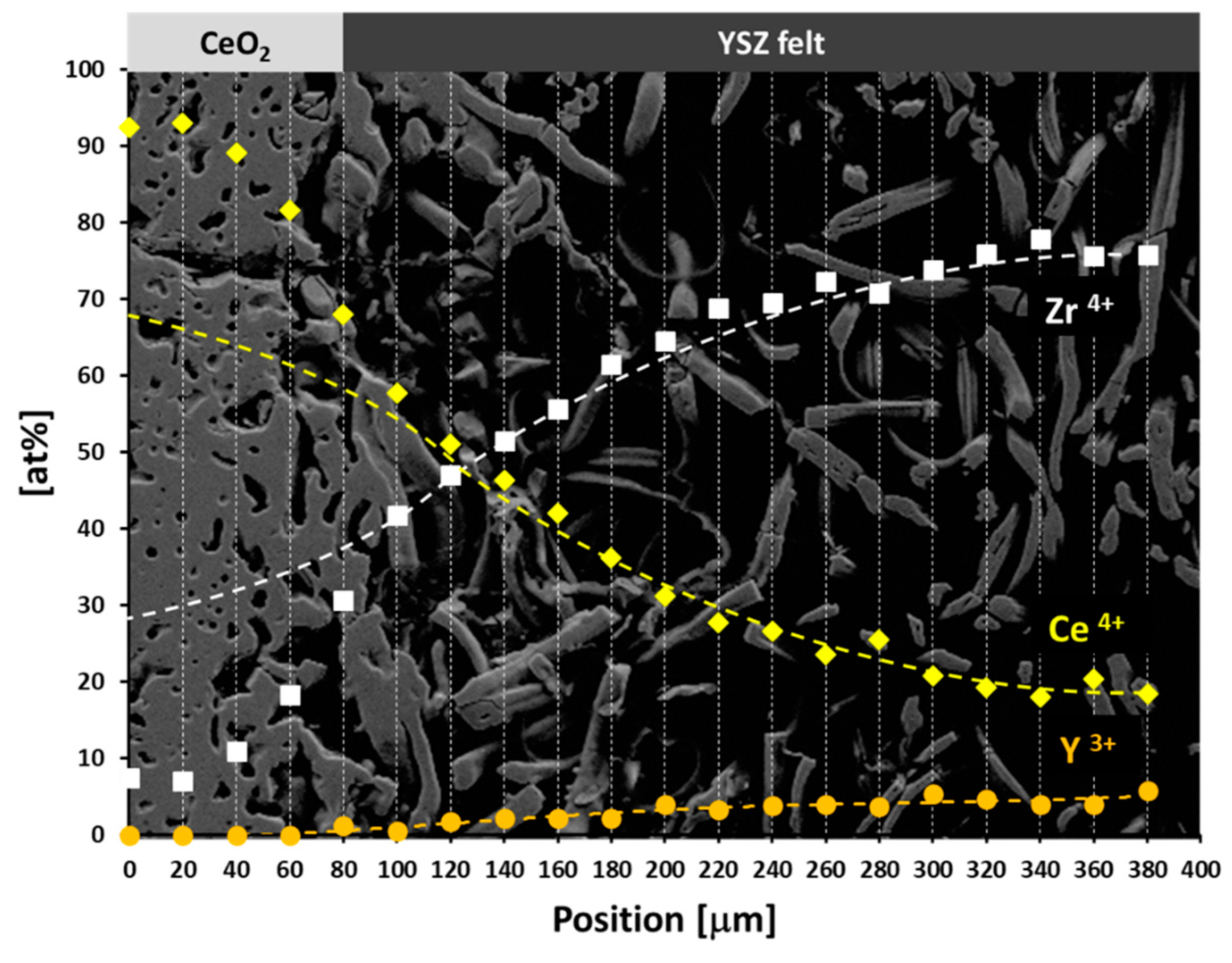
3.1. Fabrication and Microstructural Evolution of Fibrous Y,Zr Co-Doped CeO2 Compacts
3.2. Redox-Kinetics
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- D’Souza, L. Thermochemical hydrogen production from water using reducible oxide materials: A critical review. Mater. Renew. Sustain. Energy 2013, 2, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Roeb, M.; Neises, M.; Monnerie, N.; Call, F.; Simon, H.; Sattler, C.; Schmücker, M.; Pitz-Paal, R. Materials-Related aspects of thermochemical water and carbon dioxide splitting: A review. Materials 2012, 5, 2015–2054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Agrafiotis, C.; Roeb, M.; Sattler, C. A review on solar thermal syngas production via redox pair-based water/carbon dioxide splitting thermochemical cycles. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2015, 42, 254–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abanades, S.; Flamant, G. Thermochemical hydrogen production from a two-step solar-driven water-splitting cycle based on cerium oxides. Sol. Energy 2006, 80, 1611–1623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chueh, W.C.; Haile, S.M. A thermochemical study of ceria: Exploiting an old material for new modes of energy conversion and CO2 mitigation. Philos. Trans. A Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 2010, 368, 3269–3294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Knoblauch, N.; Dörrer, L.; Fielitz, P.; Schmücker, M.; Borchardt, G. Surface controlled reduction kinetics of nominally undoped polycrystalline CeO2. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2015, 17, 5849–5860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, Q.-L.; Lee, C.; Ishihara, T.; Kaneko, H.; Tamaura, Y. Reactivity of CeO2-based ceramics for solar hydrogen production via a two-step water-splitting cycle with concentrated solar energy. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2011, 36, 13435–13441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Call, F.; Roeb, M.; Schmücker, M.; Bru, H.; Curulla-Ferre, D.; Sattler, C.; Pitz-Paal, R. Thermogravimetric analysis of zirconia-doped ceria for thermochemical production of solar fuel. AJAC 2013, 4, 37–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kuhn, M.; Bishop, S.R.; Rupp, J.; Tuller, H.L. Structural characterization and oxygen nonstoichiometry of ceria-zirconia (Ce1−xZrxO2−δ) solid solutions. Acta Mater. 2013, 61, 4277–4288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, P.R.; Kim, T.; Zhou, G.; Fornasiero, P.; Gorte, R.J. Evidence for entropy effects in the reduction of ceria−zirconia solutions. Chem. Mater. 2006, 18, 5363–5369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Q.; Zhou, G.; Jiang, Z.; Li, C. Thermochemical CO2 splitting reaction with CexM1−xO2−δ (M=Ti4+, Sn4+, Hf4+, Zr4+, La3+, Y3+ and Sm3+) solid solutions. Sol. Energy 2014, 99, 55–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Call, F.; Roeb, M.; Schmücker, M.; Sattler, C.; Pitz-Paal, R. Ceria doped with zirconium and lanthanide oxides to enhance solar thermochemical production of fuels. J. Phys. Chem. C 2015, 119, 6929–6938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheffe, J.R.; Jacot, R.; Patzke, G.R.; Steinfeld, A. Synthesis, characterization, and thermochemical redox performance of Hf4+, Zr4+, and Sc3+ doped ceria for splitting CO2. J. Phys. Chem. C 2013, 117, 24104–24114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fornasiero, P.; Kašpar, J.; Graziani, M. On the rate determining step in the reduction of CeO2–ZrO2 mixed oxides. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 1999, 22, L11–L14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yashima, M.; Arashi, H.; Kakihana, M.; Yoshimura, M. Raman scattering study of cubic-tetragonal phase transition in Zr1-xCexO2 Solid Solution. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 1994, 77, 1067–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Gal, A.; Abanades, S. Catalytic investigation of ceria-zirconia solid solutions for solar hydrogen production. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2011, 36, 4739–4748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Gal, A.; Abanades, S.; Bion, N.; Le Mercier, T.; Harlé, V. Reactivity of doped ceria-based mixed oxides for solar thermochemical hydrogen generation via two-step water-splitting cycles. Energy Fuels 2013, 27, 6068–6078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shannon, R.D. Revised effective ionic radii and systematic studies of interatomic distances in halides and chalcogenides. Acta Cryst. A 1976, 32, 751–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaneko, H.; Taku, S.; Tamaura, Y. Reduction reactivity of CeO2–ZrO2 oxide under high O2 partial pressure in two-step water splitting process. Sol. Energy 2011, 85, 2321–2330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemaux, S.; Bensaddik, A.; van der Eerden, A.M.J.; Bitter, J.H.; Koningsberger, D.C. Understanding of enhanced oxygen storage capacity in Ce0.5Zr0.5O2: The presence of an anharmonic pair distribution function in the Zr−O2 subshell as analyzed by XAFS spectroscopy. J. Phys. Chem. B 2001, 105, 4810–4815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, Z.; Woo, T.K.; Hermansson, K. Effects of Zr doping on stoichiometric and reduced ceria: A first-principles study. J. Chem. Phys. 2006, 124, 224704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodriguez, J.A.; Hanson, J.C.; Kim, J.-Y.; Liu, G.; Iglesias-Juez, A.; Fernández-García, M. Properties of CeO2 and Ce1-xZrx nanoparticles: X-ray absorption near-edge spectroscopy, density functional, and time-resolved X-ray diffraction studies. J. Phys. Chem. B 2003, 107, 3535–3543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.-F.; Guo, Y.-L.; Lu, G.-Z.; Hu, P. Maximizing the localized relaxation: The origin of the outstanding oxygen storage capacity of kappa-Ce2Zr2O8. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2009, 48, 8289–8292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, G.; Shah, P.R.; Kim, T.; Fornasiero, P.; Gorte, R.J. Oxidation entropies and enthalpies of ceria–zirconia solid solutions. Catal. Today 2007, 123, 86–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Le Gal, A.; Abanades, S.; Flamant, G. CO2 and H2O splitting for thermochemical production of solar fuels using nonstoichiometric ceria and ceria/zirconia solid solutions. Energy Fuels 2011, 25, 4836–4845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, Y.; Yang, C.-K.; Haile, S.M. Ceria–Zirconia solid solutions (Ce1–xZrxO2−δ, x ≤ 0.2) for solar thermochemical water splitting: A thermodynamic study. Chem. Mater. 2014, 26, 6073–6082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abanades, S.; Legal, A.; Cordier, A.; Peraudeau, G.; Flamant, G.; Julbe, A. Investigation of reactive cerium-based oxides for H2 production by thermochemical two-step water-splitting. J. Mater. Sci. 2010, 45, 4163–4173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Gal, A.; Abanades, S. Dopant incorporation in ceria for enhanced water-splitting activity during solar thermochemical hydrogen generation. J. Phys. Chem. C 2012, 116, 13516–13523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudisill, S.G.; Venstrom, L.J.; Petkovich, N.D.; Quan, T.; Hein, N.; Boman, D.B.; Davidson, J.H.; Stein, A. Enhanced oxidation kinetics in thermochemical cycling of CeO2 through templated porosity. J. Phys. Chem. C 2013, 117, 1692–1700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eufinger, J.-P.; Daniels, M.; Schmale, K.; Berendts, S.; Ulbrich, G.; Lerch, M.; Wiemhöfer, H.-D.; Janek, J. The model case of an oxygen storage catalyst—non-stoichiometry, point defects and electrical conductivity of single crystalline CeO2-ZrO2-Y2O3 solid solutions. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2014, 16, 25583–25600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vidmar, P.; Fornasiero, P.; Kašpar, J.; Gubitosa, G.; Graziani, M. Effects of trivalent dopants on the redox properties of Ce0.6Zr0.4O2 mixed oxide. J. Catal. 1997, 171, 160–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yahiro, H.; Eguchi, Y.; Eguchi, K.; Arai, H. Oxygen ion conductivity of the ceria-samarium oxide system with fluorite structure. J. Appl. Electrochem. 1988, 18, 527–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, X.; Lin, Y.S.; Holt, C.T.; Swartz, S.L. Electric conductivity and oxygen permeability of modified cerium oxides. J. Mater. Sci. 2003, 38, 1073–1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grieshammer, S. Defect interactions in the CeO2–ZrO2–Y2O3 solid solution. J. Phys. Chem. C 2017, 121, 15078–15084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pullar, R.C.; Novais, R.M.; Caetano, A.P.F.; Barreiros, M.A.; Abanades, S.; Oliveira, F.A.C. A review of solar thermochemical CO2 splitting using ceria-based ceramics with designed morphologies and microstructures. Front. Chem. 2019, 7, 601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Furler, P.; Scheffe, J.; Gorbar, M.; Moes, L.; Vogt, U.; Steinfeld, A. Solar thermochemical CO2 splitting utilizing a reticulated porous ceria redox system. Energy Fuels 2012, 26, 7051–7059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furler, P.; Scheffe, J.R.; Steinfeld, A. Syngas production by simultaneous splitting of H2O and CO2 via ceria redox reactions in a high-temperature solar reactor. Energy Environ. Sci. 2012, 5, 6098–6103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takacs, M.; Ackermann, S.; Bonk, A.; Neises-von Puttkamer, M.; Haueter, P.; Scheffe, J.R.; Vogt, U.F.; Steinfeld, A. Splitting CO2 with a ceria-based redox cycle in a solar-driven thermogravimetric analyzer. AIChE J. 2017, 63, 1263–1271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gladen, A.C.; Davidson, J.H. The morphological stability and fuel production of commercial fibrous ceria particles for solar thermochemical redox cycling. Sol. Energy 2016, 139, 524–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gibbons, W.T.; Venstrom, L.J.; de Smith, R.M.; Davidson, J.H.; Jackson, G.S. Ceria-Based electrospun fibers for renewable fuel production via two-step thermal redox cycles for carbon dioxide splitting. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2014, 16, 14271–14280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bishop, S.R. Chemical expansion of solid oxide fuel cell materials: A brief overview. Acta. Mech. Sin. 2013, 29, 312–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crank, J. The-Mathematics-of-Diffusion, 2nd ed.; Oxford University Press: London, UK, 1975; ISBN 0-19-853344-6. [Google Scholar]
- Beschnitt, S.; de Souza, R.A. Impurity diffusion of Hf and Zr in Gd-doped CeO2. Solid State Ion. 2017, 305, 23–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, J.; Li, Q.; Zhu, L.; Liu, X.; Zhong, X.; Meng, J.; Cao, X. Preparation of CeO(2)-ZrO(2) ceramic fibers by electrospinning. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2007, 307, 567–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.; Wang, C.-A.; Zhou, J. Effect of YSZ fiber addition on microstructure and properties of porous YSZ ceramics. J. Mater. Sci. 2012, 47, 6326–6332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, L.; Wang, C.-A.; Huang, Y. Porous yttria-stabilized zirconia ceramics with ultra-low thermal conductivity. J. Mater. Sci. 2010, 45, 3242–3246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darcy, H. Les Fontaines Publiques de la Ville de Dijon; Victor Dalmont: Paris, France, 1856. [Google Scholar]
- Kawagoe, Y.; Oshima, T.; Tomarikawa, K.; Tokumasu, T.; Koido, T.; Yonemura, S. A study on pressure-driven gas transport in porous media: From nanoscale to microscale. Microfluid. Nanofluid. 2016, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Haussener, S.; Steinfeld, A. Effective heat and mass transport properties of anisotropic porous ceria for solar thermochemical fuel generation. Materials 2012, 5, 192–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isobe, T.; Kameshima, Y.; Nakajima, A.; Okada, K.; Hotta, Y. Gas permeability and mechanical properties of porous alumina ceramics with unidirectionally aligned pores. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2007, 27, 53–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knoblauch, N. Synthese, Charakterisierung und Untersuchung zum Redoxverhalten von ceroxidbasierten Materialien zur Erzeugung Solarer Brennstoffe. Ph.D. Thesis, Technische Universität Clausthal, Clausthal-Zellerfeld, Germany, 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]










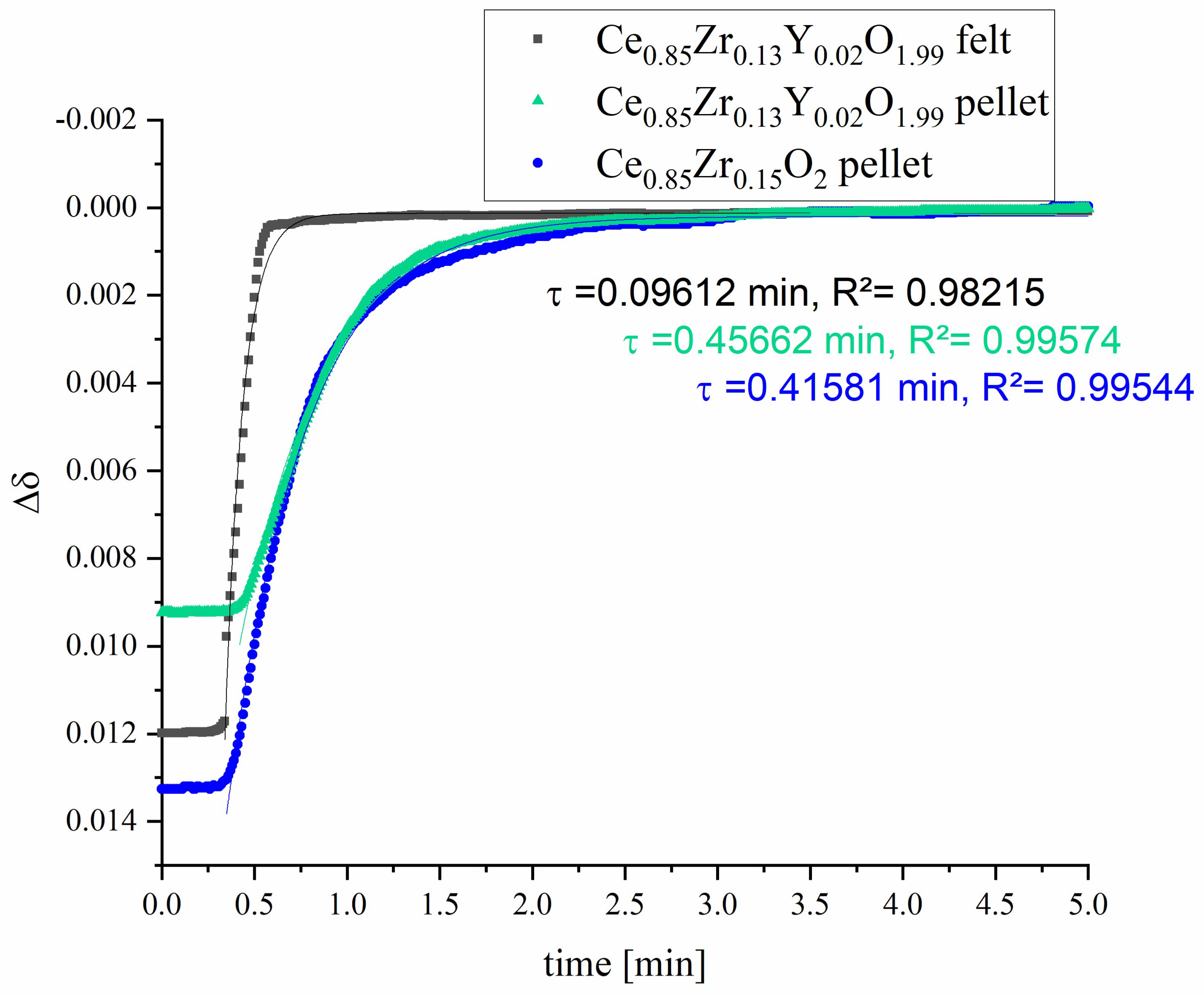

| Sample | Relaxation Time Constant τ [min] | t [min] for Turnover of 95% |
|---|---|---|
| Ce0.85Zr0.13Y0.02O1.99 felt | 0.09612 ± 0.00121 | ~0.29 |
| Ce0.85Zr0.13Y0.02O1.99 pellet | 0.45662 ± 0.00289 | ~1.37 |
| Ce0.85Zr0.15O2 pellet | 0.41581 ± 0.00268 | ~1.25 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Knoblauch, N.; Mechnich, P. A Novel Method for the Preparation of Fibrous CeO2–ZrO2–Y2O3 Compacts for Thermochemical Cycles. Crystals 2021, 11, 885. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst11080885
Knoblauch N, Mechnich P. A Novel Method for the Preparation of Fibrous CeO2–ZrO2–Y2O3 Compacts for Thermochemical Cycles. Crystals. 2021; 11(8):885. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst11080885
Chicago/Turabian StyleKnoblauch, Nicole, and Peter Mechnich. 2021. "A Novel Method for the Preparation of Fibrous CeO2–ZrO2–Y2O3 Compacts for Thermochemical Cycles" Crystals 11, no. 8: 885. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst11080885
APA StyleKnoblauch, N., & Mechnich, P. (2021). A Novel Method for the Preparation of Fibrous CeO2–ZrO2–Y2O3 Compacts for Thermochemical Cycles. Crystals, 11(8), 885. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst11080885






