Abstract
Bone supports animal bodies, is the place where blood is produced, and is essential for the immune system, among other important functions. The dominant inorganic component in bone is hydroxyapatite (Hap), the structure and dynamics of which still pose many unsolved puzzles. An updated understanding of HAp is of great significance to osteology, dentistry, and the development of artificial bone and other biomaterials. In this work, HAp nanoparticles were synthesized with the wet chemical precipitation method and their structure and morphologies were controlled by varying pH and adding fluoride ions by two different routes: (1) fluoride ions were added during synthesis, and (2) fluoride ions were introduced after the samples were synthesized by soaking the samples in solutions with fluoride ions. XRD and HRTEM were employed to confirm the composition and structure, while various multinuclear (1H, 19F, 31P) solid-state nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) methods including 1D single pulse, cross-polarization under magic-angle spinning (CPMAS), and 2D heteronuclear correlation (HETCOR) were used to characterize the structure, morphology, and dynamics, validating the general core-shell morphology in these F-HAp samples. It was found that all hydroxide ions were substituted when the fluoride ion concentration was above 0.005 M. An NMR peak corresponding to water structure emerged and the bulk water peak was shifted upfield, indicating that fluoride substitution modifies both the crystalline core and the amorphous shell of F-HAp nanoparticles. With the second route of fluoride substitution, increases in soaking time or fluoride ion concentration could increase fluoride substitution in HAp, but could not achieve complete substitution. Finally, with 1H-31P CPMAS and HETCOR, it was established that there are two types of phosphorous, one in the crystalline core (PO43−) and the other in the amorphous shell (HPO42−). These results are valuable for clarifying the fluoride substitution mechanism in HAp in biomaterials or in organisms, and provide insights for developing next generation replacement materials for bone, tooth, or coating films, drug delivery systems, etc.
1. Introduction
An obvious and essential feature of vertebrate animals is that their bodies contains various types of bone. Their bodies are supported by a sophisticated skeletal system that consists of hundreds of bones of differing sizes, shapes, and biophysical, biochemical, and mechanical properties. Bones are also places where blood is made and some bones such as vertebrae also provide neurological signal pathways for the central nerve system. The importance of bones for vertebrates can never be overemphasized. Similar to other organs, bones may be subject to many diseases and injuries, which are becoming increasingly worse with the growth of the aged population. Research on bones has a long history since ancient times and a huge body of data has been accumulated. The most remarkable achievements are those made in the past century. Significant advances have been achieved in understanding their anatomic structure [1,2,3], physiological functions, and biochemical mechanisms of synthesis, repair, and aging [4,5]. These achievements have revolutionized the medical treatment of various disorders, diseases, and injuries related to bones [4,5,6,7]. Tremendous progress has also been made in the development of artificial bones [8,9] and bone regeneration [10]. Based on our current understanding [11,12,13,14], the main components of bone have been identified as a protein collagen (mostly of type I) and an inorganic compound hydroxyapatite (HAp). The growth and maintenance of a bone are highly complex and involve many cells, proteins, hormones, ions, and, of course, water. Blood vessels and lymphatic systems are also an active participant.
Biophysical chemists and materials scientists are interested in bone for a number of reasons. Firstly, it is a system responsible for a variety of functions from mechanical support, anti-wear, anti-tear, and hormone and ion balancing, to blood-making and neuro signaling. Secondly, it is a good example of a hierarchical multiscale complex system ranging from the nanometer to meter scales, providing good opportunities for demonstrating all kinds of interesting physical chemistry phenomena. Lastly, but not least, it is a typical organic-inorganic hybrid material, so bone studies can offer valuable insights for the understanding of organic-inorganic hybrid materials and the development of better biomimetic, bionic, or biogenic materials. Organic-inorganic hybrid materials have been an important subject of research over the past decades and play a more and more important role in photonics, gas sensing, biomedical detection, replacement biomaterials, etc. [15,16,17,18,19,20,21]. They are also very common in living things [22,23,24,25,26,27,28]. To build a good understanding of certain biological functions, pathological mechanisms, or the effect of a drug or a therapy, or to develop next generation materials, a better understanding of the physicochemical principles underlying this type of material is indispensable.
Hydroxyapatite nanocrystals play an important role in the bone, teeth, joints, shells, and other organs of animals and belong to a class of representative systema that inspires the study and development of biogenic, biomimetic, and bionic materials, and new organic-inorganic hybrid materials [22,23]. In the hierarchical structure, mineralized collagen is believed to be the most important building block and has been intensively studied, although its mass accounts for only 20 wt% to 30 wt%, while the mineral Hap, which accounts for 60 wt% to 70 wt% of the total mass, plays an auxiliary, though essential, role [11,12,13,14]. As the dominant inorganic component, the structure, morphology and dynamics of HAp still hold many unsolved puzzles. An updated understanding of HAp is of great significance to osteology, dentistry, and the development of artificial bone and other biomaterials.
To gain a better understanding of HAp in real animal bones and for the development of next generation HAp-based ceramic materials, as well as bionic materials for bone/tooth replacement, drug delivery, anti-microbial use, and other purposes, it is pertinent to study the structure and morphology of HAp synthesized in conditions similar to the physiological environment (ions and small and large molecules). Therefore, in this work, our HAp samples are synthesized in a simulated body fluid (SBF) [29,30,31,32,33] to mimic the in vivo physiological conditions. Fluoride ions are one of the most common ions in bone, tooth, and other tissues, and SBF used in this work contains all the important ions in real blood and body fluids. The motivation of this work can be summarized as follows: (1) to explore the changes of structure and morphology of HAp synthesized in SBF by varying pH slightly and comparing the outcome with previously published results; (2) to investigate the structure and morphology of fluorine-substituted HAp synthesized with wet precipitation method in SBF; (3) to characterize the structure and morphology of the HAp systems with XRD, HRTEM, and most importantly, solid-state NMR, focusing on the core-shell structure. To achieve these goals, HAp nanoparticles were synthesized with the wet chemical precipitation method and their structure and morphologies were controlled by varying pH and adding fluoride ions by two different routes: (1) fluoride ions were added during synthesis, and (2) fluoride ions were introduced after the samples are synthesized by soaking the samples in solutions with fluoride ions. XRD and HRTEM were employed to confirm the composition and structure, while various solid-state NMR methods including 1D single pulse under high speed -MAS-, 1H-31P CPMAS, 2D 1H-31P, 19F-31P HETCOR were used to characterize the structure, morphology, and dynamics, validating the general core-shell morphology in these F-HAp samples. These results are well supported by each other and are valuable for clarifying the fluoride substitution mechanism in HAp in biomaterials or in organisms, and provide insights for developing next generation replacement materials for bone, tooth, etc.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Preparation
The following chemicals were used in work: sodium chloride produced by Echo Inc. (Northbrook, IL, USA), purity 99%; sodium hydrogen carbonate produced by AencoreTaiwan (Kaohsiung, Taiwan) purity 99.5%; potassium chloride purchased from Showa Inc. (Tokyo, Japan), purity 99.5%; potassium hydrogen phosphate anhydrate purchased from Merck (Tokyo, Japan) purity 99%; magnesium chloride hexahydrate purchased from Aencore Chemicals Taiwan (Kaohsiung, Taiwan), purity 98%; hydrogen chloride aqueous solution (37%) purchased from Nihon Shiyaku Reagent Japan; calcium chloride purchased from Nihon Shiyaku Reagent Japan purity 99%; sodium sulfate purchased from Echo Inc., purity 99%; 2-Amino-2-hydroxymethyl-propane-1,3-diol, tris purchased from Acros Organics USA, purity > 99%; calcium nitrate purchased from Nihon Shiyaku Reagent (Kyoto, Japan) purity 98%; sodium hydrogen phosphate manufactured by Acros Oraganics USA (Carlsbad, CA, USA), purity 98%; sodium fluoride purchased from PanReac AppliChem USA (Chicago, IL, USA), purity 99%.
For pH measurement, a G&B Instruments (Lymington, UK) PL-700 multifunction pH meter for laboratory use was used; buffer solution with pH = 7.00, pH = 4.01, pH = 10.00 produced by Rocker was selected as the standard calibration solution of the pH meter; the pH values of all samples were calibrated prior to measurement with a calibration percentage higher than 90%.
2.1.1. Preparation of Simulation Body Fluid
The SBF used in this work was prepared using the formula published by Koboku [29,30,31,32,33]. Each batch was 1000 mL and all ingredients were accurately weighed to the third decimal place. The procedure of preparation is summarized as follows:
(1) Clean a 1000 mL plastic container and fill it with 900 mL deionized water to control the water temperature to 36.5 ± 1.5 °C; (2) Add the following ingredients in order: NaCl 8.035 g, NaHCO3 0.355 g, KCl 0.225 g, K2HPO4·3H2O 0.231 g, MgCl2·6H2O 0.331 g, 1.0 M HCl 39 mL, Na2SO4 0.072 g; (3) Slowly add 0.292 g of CaCl2 to ensure that all of it is dissolved without precipitation; (4) Verify that the pH value of the solution, which should be 2.0 ± 1.0 at this point; (5) Slowly add Tris (trishydroxymethylaminomethane), and continue to add it after the pH has risen and stabilized. Do not change the pH too much; (6) Continue until 6.118 g Tris is added to make the pH of the solution reach 7.45 ± 0.01; (7) Use a syringe to suck out 1.0 M HCl, and slowly drop it so that the final pH value reaches 7.40 ± 0.01; (8) Rinse the remaining solution on the pH meter into the solution; (9) Fill up to 1000 mL of water; (10) Seal and store it in the refrigerator below 10 °C.
The prepared SBF solution must be used within one month to avoid deterioration and compromised results. Prior to use, it must be heated to 37.5 °C in water.
2.1.2. Synthesis of Fluorinated HAp
In this work, the chemical precipitation method of wet synthesis was used as the synthesis route for calcium hydroxyphosphate. In order to avoid the precipitation reaction of SBF solution in glassware, all the containers used in the work were high-density polyethylene containers.
2.1.2.1. Synthesis of General Calcium Hydroxyphosphate
(1) Weigh 2.5 g of Na2HPO4 and 7 g of Ca(NO3)2, with calcium ions controlled as the limiting reagent. Add each to a beaker of 350 mL containing SBF solution to complete the preparation. Keep them at temperature at 37 °C and stir at 400 rpm for 1 h to ensure that the solutions are completely dissolved;
(2) Mix the two beakers of solutions together, stir the mixture for 10 min, take out the magnet stirrer, seal it with paraffin film, and let it settle for 24 h. The temperature of the solution is kept at 37 °C throughout the process;
(3) After 24 h, open the sealing film and verify that the precipitation is complete; then carefully pour out the supernatant liquid, add 250 mL of deionized water, put in a magnetic stirrer and rotate it at 400 rpm for 10 min, then take the stirrer out and let it stand for 1 h until it settles again;
(4) Repeat Step 3 several times. After confirming that it is clean, pour out the supernatant liquid by decantation method, then place it in an oven and bake it at 60 °C for 24 h so that the water evaporates completely and the final sample of calcium hydroxyphosphate is obtained.
2.1.2.2. Synthesis of Calcium Hydroxyl Phosphate with Changing pH
To prepare SBF with different pH values, in Step 5 of Section 2.1.1, Tris was added slowly to achieve pHs of 7.0 and 7.2 to obtain SBF with pH = 7.0 and pH = 7.2, respectively; then calcium hydroxyphosphate with different pH values was synthesized according to the method described in Section 2.1.2.1.
2.1.2.3. Synthesis of Calcium Hydroxyphosphate Substituted with Fluoride Ion
After the SBF with pH = 7.4 was prepared, 250 mL of SBF was taken out and 0.02625 g, 0.0525 g, and 0.105 g of sodium fluoride were added to make the SBF bionic solution so that solutions with 0.0025 M, 0.005 M, 0.01 M fluoride ion concentrations were prepared, respectively. Then, following the method of Section 2.1.2.1, fluoride ion-added calcium hydroxyphosphate samples were synthesized and numbered as SBF + 0.0025 M, SBF + 0.005 M, and SBF + 0.01 M, respectively.
2.1.2.4. Synthesis of Hydroxy Calcium Phosphate Soaked in Fluoride Ion Solution
Hydroxycalcium phosphate was synthesized with pH = 7.4 according to the method described in Section 2.1.2.1, ground it into fine powder, and prepared in 0.0025 M, 0.005 M, 0.01 M NaF aqueous solutions. Then, 1 g of calcium hydroxyphosphate powder was put into each of the NaF solutions of different concentrations and soaked for 1 day, 3 days, and 7 days, respectively. Then, the samples were taken out, cleaned, and dried according to Step 3 and Step 4 of Section 2.1.2.1. The nine samples were labeled 1d-0.0025 M, 1d-0.005 M, 1d-0.01 M, 3d-0.0025 M, 3d.0005M, 3d-0.01 M, 7d-0.0025 M, 7d-0.005 M, and 7d-0.01 M.
2.2. Instrumental Characterization: XRD, HRTEM and Solid-State NMR
The XRD patterns were obtained on a powder diffractometer Bruker D2-Phaser using a copper target; the characteristic X-ray wavelength formed was 0.154056 nm (Cu-Kα = 0.154056); the 2θ scanning range was 20°~80°; the κ (shape factor) of the calcium hydroxyphosphate sample in the Scherrer Equation was set to about 0.9; the JCPDS phase identification of Ca2+, PO43−, and F− was performed following general diffraction analysis method with MDI JADE.
High resolution TEM images for the samples were obtained on a JEOL TEM-3010 Analytical Scanning Transmission Electron Microscope with a 250 Mesh copper mesh dedicated to TEM and a high-energy electron beam acceleration voltage of 300 kV.
Various 1D and 2D solid-state NMR spectra were obtained on a Varian-Agilent Inova 500 MHz spectrometer and a Bruker AVANCE II 600 MHz solid-state NMR spectrometer. For 19F, 31P and 1H single pulse MAS spectra, 90° pulse and 35 kHz sample spinning speed was used. For 1H-31P CPMAS spectra, 10 kHz sample spinning speed and contact times of 0.2 ms, 0.5 ms, 2 ms, 5 ms, and 10 ms were used. For 1H-31P HETCOR spectra, the sample spinning speed was 35 kHz; the frequency-switched Lee-Goldberg (FSLG) pulse sequence was used to remove 1H-31P dipolar interaction during the t1 evolution period; the contact time for 1H-31P CP was 1 ms.
3. Results and Discussion
The characterization results with XRD, HRTEM, and different solid-state NMR methods are presented as follows and their significance from the perspective of biogenic or biomimetic materials, as well as fluoration, will be discussed.
3.1. XRD
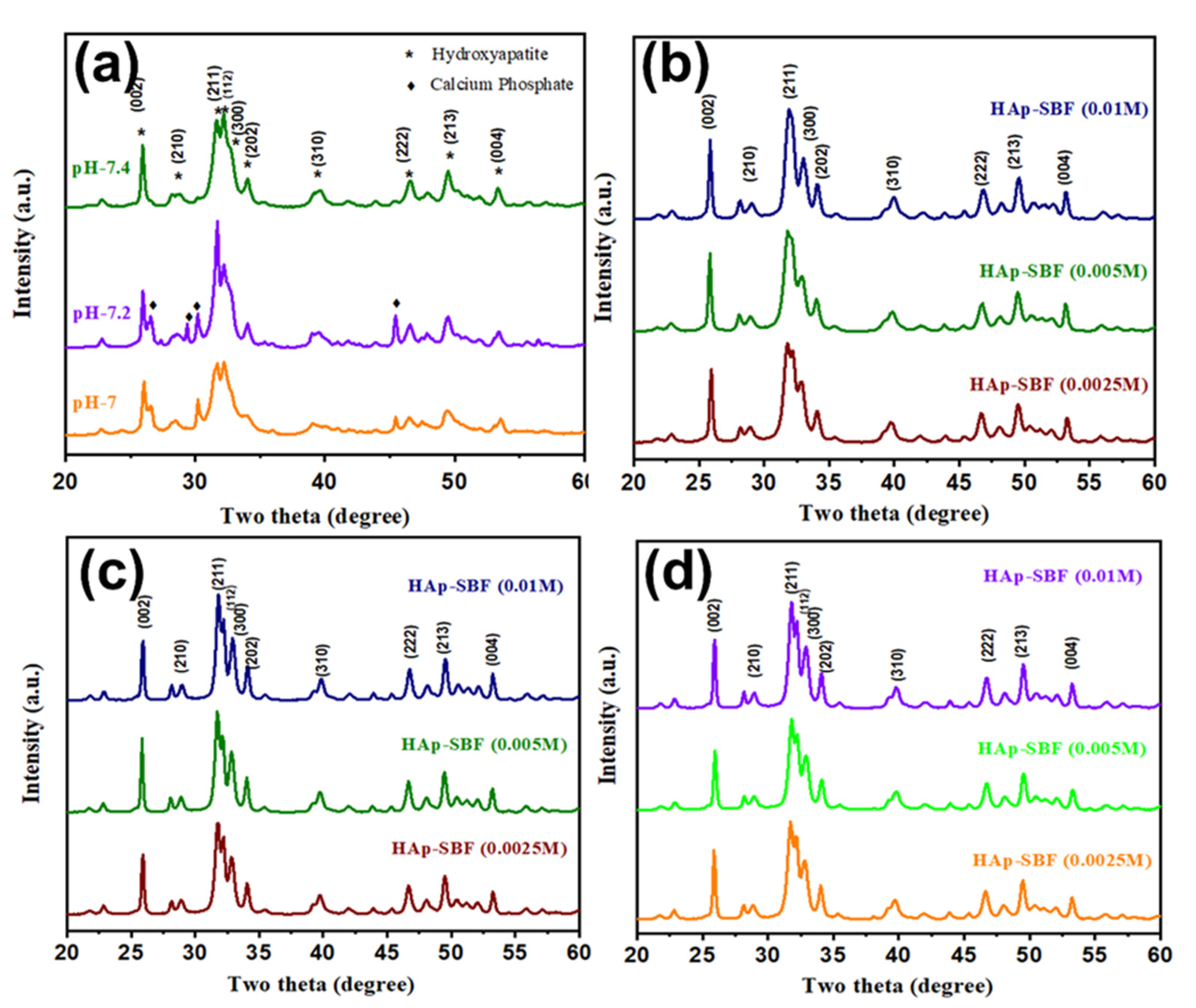
Figure 1 shows the powder XRD spectra of 12 HAp and F-HAp samples synthesized at different pH values, at different NaF concentrations, or soaked in different NaF solutions for different numbers of days. The influence of the pH value is minor, although the crystallinity increases slightly at higher pH values, in agreement with previous observations [34,35,36,37]. Compared to HAp nanoparticles synthesized in ordinary solvents, HAP nanoparticles synthesized in SBF show less crystallinity, implying that HAp nanoparticles grown in vivo may have less crystallinity. This is supported by studies of animal bones [38,39,40,41]. It is interesting to notice that in F-HAp synthesized in SBF and NaF, the crystallinity increased. This is consistent with the previous observation of F-HAp synthesized in ordinary solutions and the fact that fluoride substitution of hydroxy reduces solubility and improves stability [42]. Furthermore, as shown at the bottom of Figure 1, simply soaking HAp (synthesized in SBF) in NaF can improve crystallinity, although it is far less effective than HAp synthesized in NaF. The higher the NaF concentration and the longer the soaking time, the better the crystallinity. However, after about three days of soaking, there is little room for further improvement. These observations are supported by other methods, as shown below.
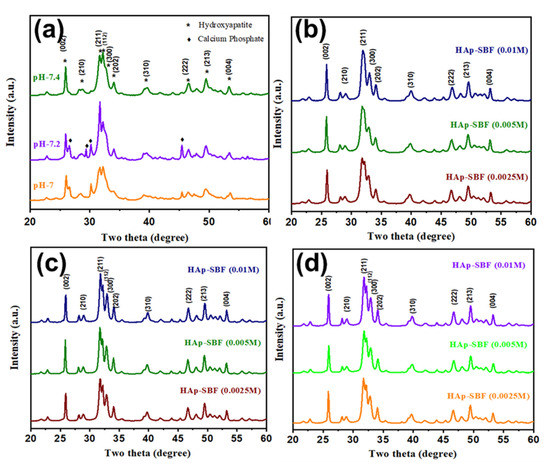
Figure 1.
Powder XRD spectra of HAp and F-HAp (a): HAp synthesized in SBF at different pH values; (b): F-Hap synthesized in SBF at different concentrations of NaF; (c): HAp synthesized in SBF followed by 1 day soaking in solutions of different concentrations of NaF; (d): HAp synthesized in SBF followed by 3 days soaking in solutions of different concentrations of NaF.
3.2. HRTEM
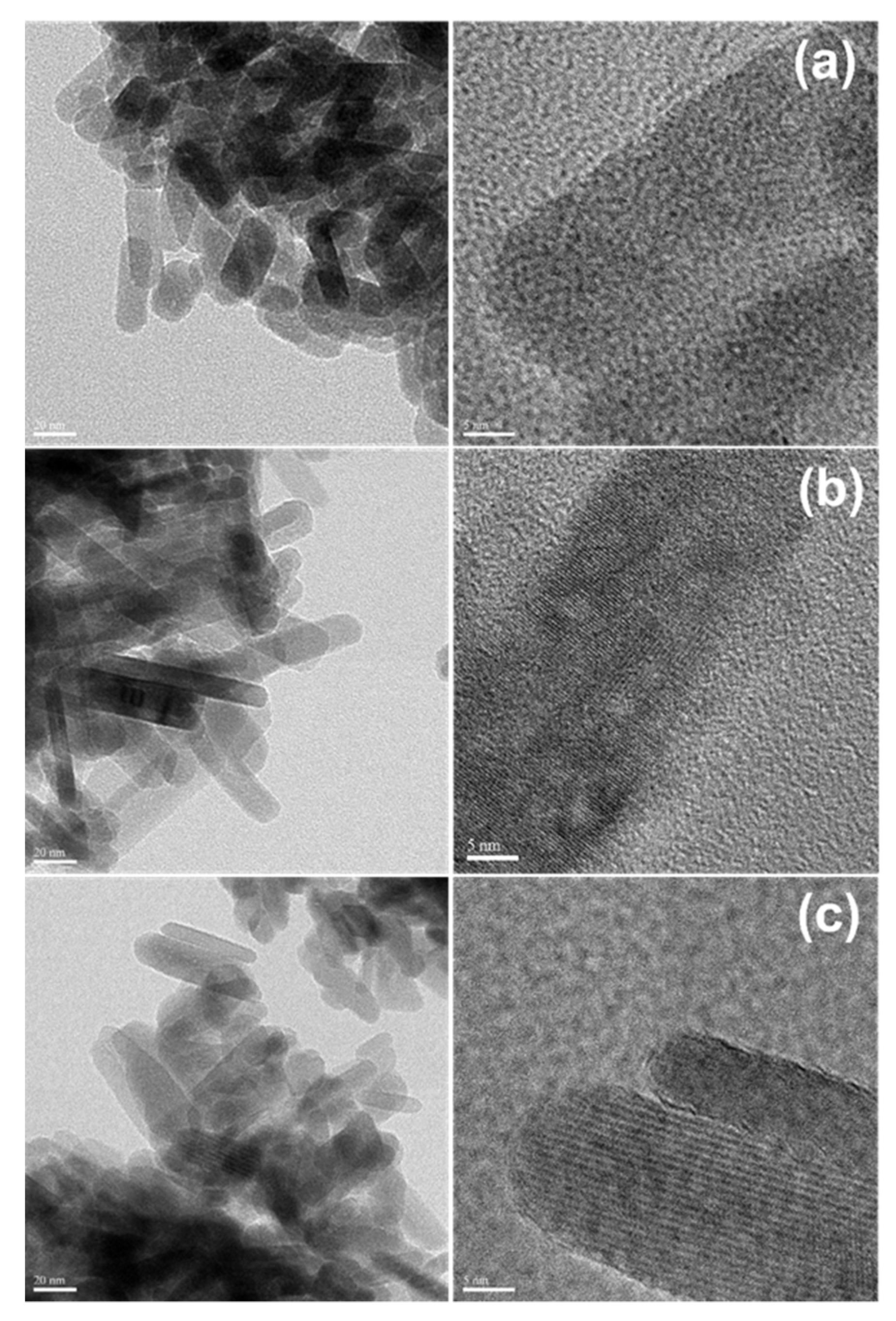
To see how synthesis conditions affect the nanoscale structure and morphology of F-HAp nanoparticles, HRTEM was employed to generate images from the atomic scale to about 100 nm. Figure 2 shows the representative images of F-HAp nanoparticles synthesized in SBF at different NaF concentrations (2.5 mM, 5 mM and 10 mM). They share some common features: (1) all have the general core-shell morphology with a crystalline core and largely amorphous shell regions and (2) the crystalline region for all samples is rod-like. It was found that the crystallinity was improved by increasing the pH value (Figure S1) (see Supplementary Materials), by increasing the NaF concentration (Figure S2), or by increasing the soaking time (Figure S3). These results are consistent with the XRD results above and the solid-state NMR results in the following section.
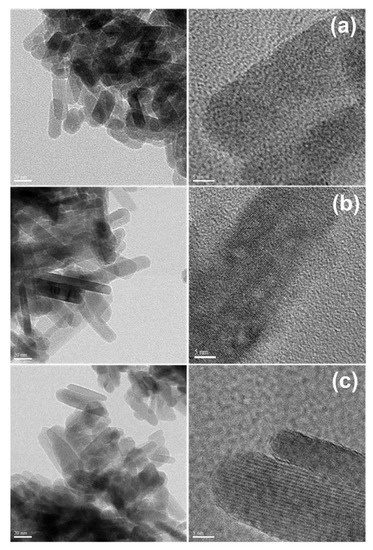
Figure 2.
HRTEM images of F-HAp: (a) F-HAp synthesized in SBF at 0.01 M of NaF, (b) F-HAp synthesized in SBF at 0.005 M of NaF, and (c) F-HAp synthesized in SBF at 0.0025 M of NaF.
3.3. Solid-State NMR
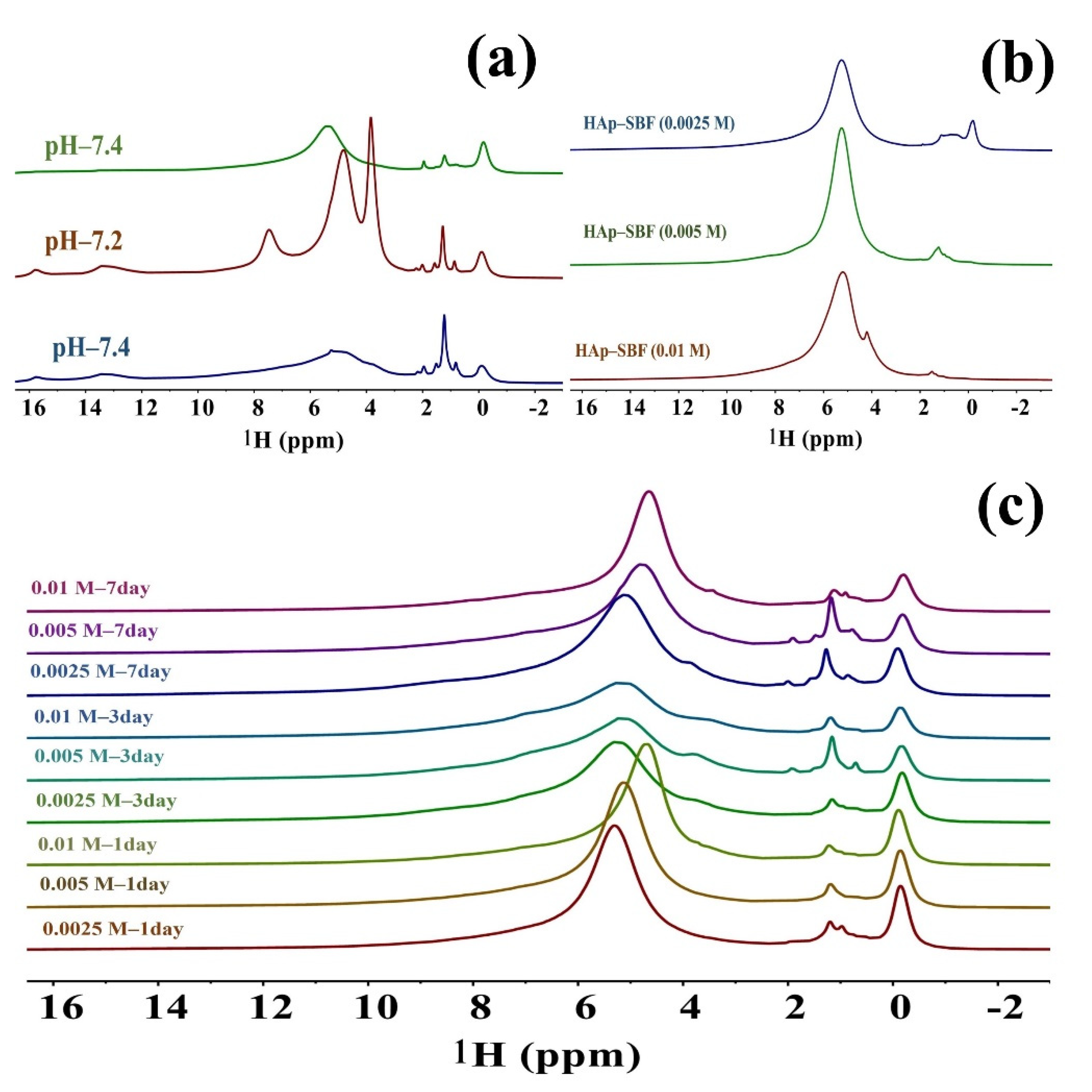
To further investigate how synthesis conditions affect HAp and in particular to see straightforward evidence of fluoride substitution in F-HAp, both 1D and 2D multinuclear (1H, 19F, 31P) solid-state NMR spectra were acquired. Figure 3 is the 1H 35 kHz MAS spectra of various HAp and F-HAP samples. Based on the assignment of 1H spectrum [43], the hydroxyl group corresponds to a peak at around 0.00 ppm; peaks between ~0.5–1.5 ppm are from surface-structured water; peaks above 2 ppm are from HPO42− (bulk, distorted, or surface), except for the large peak at around 5 ppm, which arises from adsorbed water. It must be pointed out that the last region (peaks above ~2 ppm) varies greatly depending on random changes in synthesis conditions such as the rate and order of adding reactants, stirring or vibration modes, humidity, etc. Therefore, huge variations were observed in reported results [43,44,45,46,47,48,49] as well as in the spectra shown in Figure 3 (top left in particular). It is advisable not to make quantitative claims based on the peaks in this region (please refer to the 2D HETCOR spectra discussed, below which offer far more consistent results). In contrast, we can draw far more quantitative conclusions from the region between 0 and ~2 ppm, which is more reliable and much less variable. The top left of Figure 3 indicates that changes in pH have little influence on hydroxide and structured water, indicating that the crystalline region is hardly changed, but that the amorphous region may be changed even with a slight change of pH. Clear evidence of fluoride substitution of hydroxyl is displayed in Figure 3b, where the gradual vanishing of the hydroxide peak at ~0.0 ppm is shown. It is found that all hydroxide ions were substituted when the fluoride concentration was above 50 mM (Figure 3b). In the meantime, a peak corresponding to structural water emerged and the bulk water peak was shifted upfield, indicating that fluoride substitution modifies both the crystalline core and the amorphous shell of F-HAp. With the second route of fluoride substitution, increasing the soaking time or the fluoride ion concentration could increase fluoride substitution in HAp, but could not achieve complete substitution (Figure 3, bottom), as the hydroxide peak was still strong after soaking in a 50 mM NaF solution for 7 days. This phenomenon implies that fluoride substitution of hydroxide in deep regions of bone or tooth is inefficient or unlikely.
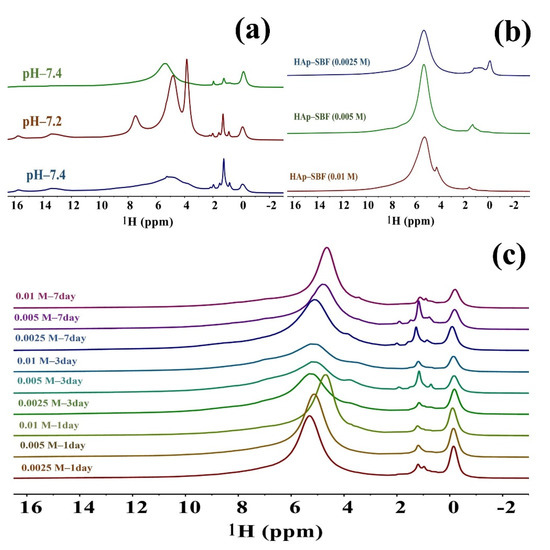
Figure 3.
(a) 1H 35 kHz MAS NMR spectra of HAp synthesized in different pH values; (b) 1H 35 kHz MAS NMR spectra of F-HAp synthesized in BSF at different concentrations; (c) 1H 35 kHz MAS NMR spectra of HAp soaked in NaF solutions with different concentrations and different times.
The 1D 31P 35 kHz MAS spectra of the samples (Figure S3) are much less informative because the difference between the chemical shifts of phosphate and hydrogen phosphate is small. However, some consistent trends are noteworthy. For instance, the 31P peak shifted upfield as the concentration of NaF or the soaking time increased. This means fluoride substitution brings more shielding onto phosphorus than hydroxide. This does not seem to make sense, since fluoride is more electronegative and 31P nuclei should be less shielded after substitution. However, if we notice that the unit cell size of F-HAp (a = 937 pm) is smaller than that of pristine HAp (a = 941 pm), then we can solve this problem. There are two competing facts here: the increased electronegativity and the increased local electronic density; the higher local electronic density overwhelms the effect of increased electronegativity. It is noteworthy that our results and interpretation on F-HAp are in agreement with the enhanced stability of fluorine-substituted organic molecules and proteins, as discussed in recent years [50,51,52,53].
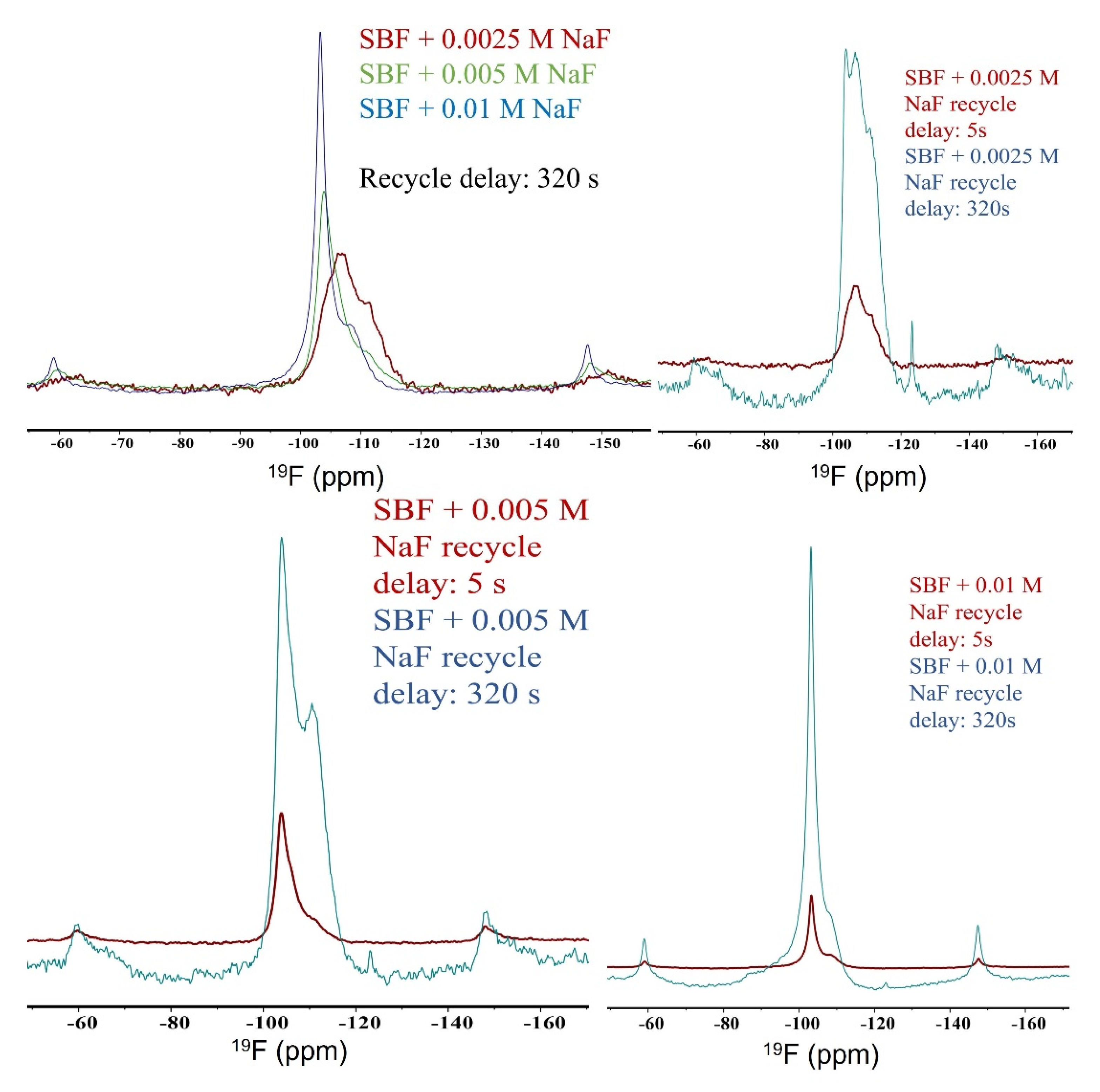
The variations of 19F 35 kHz MAS spectra over samples (Figure 4, Figures S4 and S5) are more appreciable than that of its 31P counterparts. Common to all 19F MAS spectra is the fact that substitution of hydroxide with fluoride leads to an increase of the 19F peak at ~−104 ppm, which should be assigned to crystalline fluoride. The peaks between ~−110 ppm and ~−115 ppm should be assigned to fluoride in the amorphous region. As shown in the top left spectra of Figure 4, increasing the NaF concentration leads to a great increase of crystalline fluoride. A remarkable feature of the 19F MAS NMR spectra shown in Figure 4 is that the spectra show significant change with different recycle delays. This can be explained by the presence of fluoride species in vastly different micro-environments; the fluoride ions in crystalline regions have much shorter longitudinal relaxation T1, whereas the fluoride ions in the amorphous regions have much longer longitudinal relaxation times. The difference in relaxation time in different regions is not surprising; what is surprising here is the magnitude of the difference. The relaxation rate in the amorphous region is more like that of free liquids than that of soft solids. We mention that this phenomenon deserves more extensive investigation, but this is beyond the scope of this work.
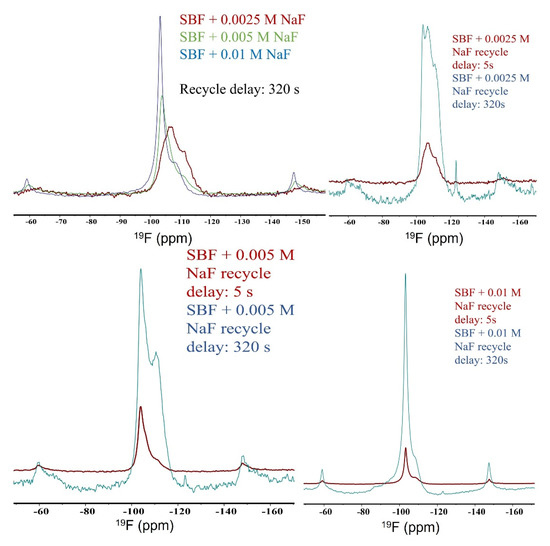
Figure 4.
19F 35 kHz MAS spectra of HAp synthesized in SBF and soaked in solutions at different NaF concentrations (2.5 mM, 5 mM, and 10 mM) for different recycle delays (brown: 5 s; green: 320 s).
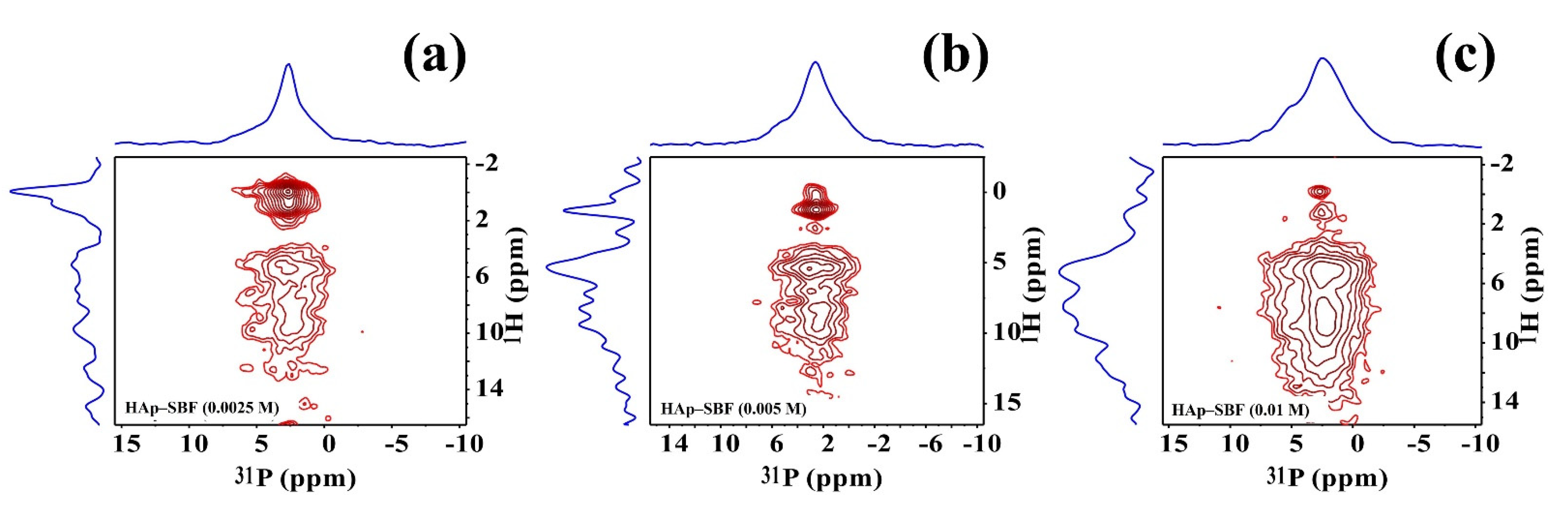
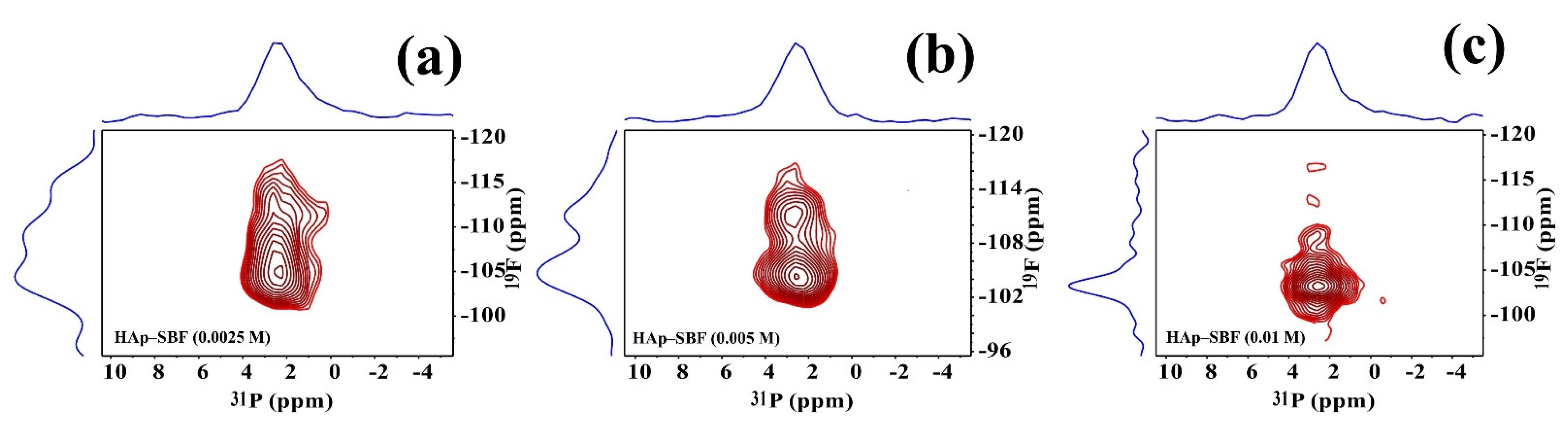
While 1D multinuclear solid-state NMR spectra can offer valuable structural, morphological, and dynamic information on F-HAp, as pointed out above, there are some disadvantages. For instance, for 1H MAS spectra, the peaks above ~2 ppm vary so much that they hardly offer quantitative conclusions; for 31P MAS spectra, the broad peaks have low resolution. Therefore, we also performed a series of 2D heteronuclear correlation solid-state NMR experiments and 1H-31P and 19F-31P HETCOR spectra were obtained, as shown in Figure 5 and Figure 6, Figures S6 and S7, respectively. The most important feature of these 2D 1H-31P and 19F-31P HETCOR spectra is that different 31P sites corresponding to (PO43−) and (HPO42−) in various micro-environments are clearly resolved. In particular, because of the long transverse relaxation time in the mobile regions, 1H-31P and 19F-31P correlation peaks in these regions are not only observable, but also resolvable. The gradual vanishing of the hydroxide peak with increasing NaF concentration correlates well with the increase of hydrogen phosphate, offering straightforward evidence that full fluoride substitution of hydroxide could be achieved at 10 mM concentration of NaF. The remaining strong 1H-31P cross peaks clearly show that these peaks arise from hydrogen phosphate. On the hand, as shown by the conspicuous OH−—31P cross peaks in Figure S6, complete fluoride substitution could not be achieved simply by soaking, although higher NaF concentration and longer soaking time help fluoride substitution.
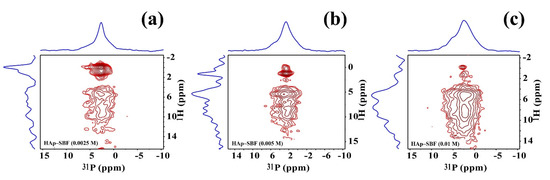
Figure 5.
1H-31P 35 kHz HETCOR spectra of HAp synthesized in SBF and NaF solutions at different concentrations: 2.5 mM (a), 5 mM (b), and 10 mM (c).
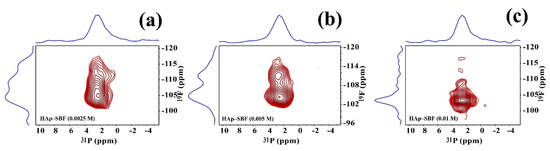
Figure 6.
19F-31P 35 kHz HETCOR spectra of HAp synthesized in SBF and NaF solutions at different concentrations: 2.5 mM (a), 5 mM (b), and 10 mM (c). The gradual decrease of the cross peaks between ~108 to ~114 ppm corresponds to a decrease in the amorphous shell region and an increase of crystallinity.
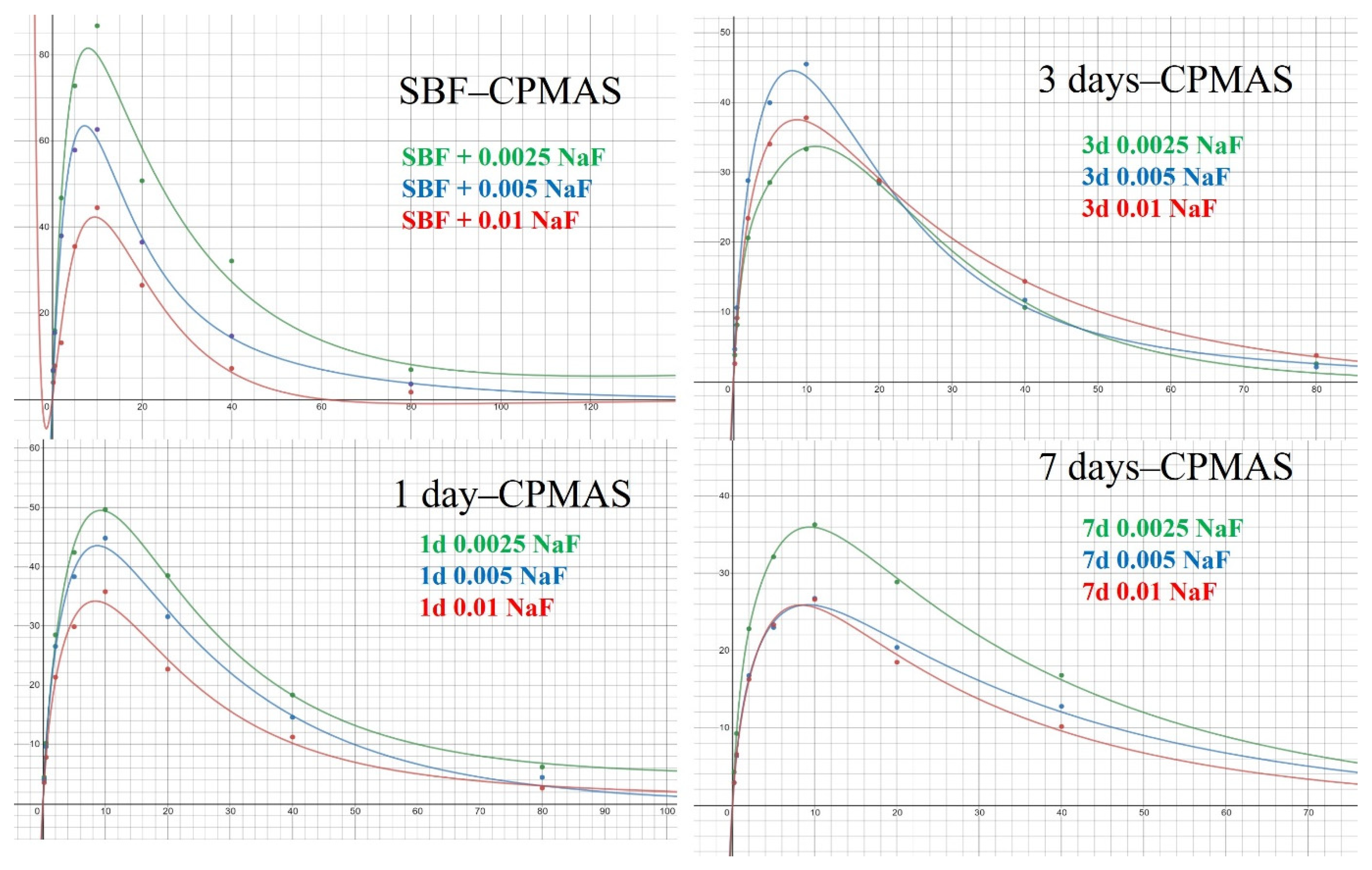
Finally, to obtain quantitative dynamics information in different regions, 1H-31P CPMAS spectra with different contact times for each sample were acquired. Figure 7 shows the CP curves for different samples from which the 1H-31P cross relaxation time TCP and 1H transverse relaxation time during the RF pulse, T1ρ, can be obtained by fitting the CP curves with the following formula:
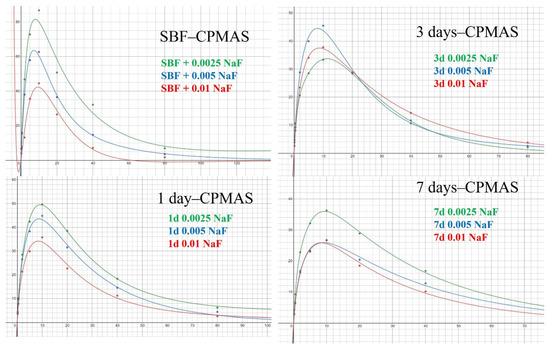
Figure 7.
1H-31P 11 kHz CPMAS spectra of HAp synthesized in SBF and soaked in solutions at different NaF concentrations (2.5 mM, 5 mM, and 10 mM) for different recycle delays (brown: 5 s; green: 320 s).
It is found that best fitting is reached for all samples when a single component model is used. This seems a surprising result since there are at least two types of 31P micro-environments. However, considering the fluoride substitution and the rigid hydroxide in the crystalline region (which means very short T1ρ), it is reasonable to assume that the 1H-31P CPMAS spectra from the signal of HPO42− is dominant. From this result, we may have a more straightforward interpretation of the 1H-31P HETCOR S spectra (Figure 5, Figures S5 and S6), namely, the 1H-31P cross peaks corresponding to a 1H chemical shift larger than ~2.0 ppm arise predominantly from HPO42−, since in the HETCOR pulse sequence, there is a CP block [54].
Research in the past few decades has achieved great progress in the structure, morphology, dynamics, and functions of the HAp system, which enables us to have a deeper understanding of bone structure, bone physiology, and bone pathology, and to develop a large number of related bionic materials, coatings, or drug delivery systems [42,55,56,57,58]. However, there are still many unanswered questions. The effect of ions on the composition, structure, and morphology of the HAp system is an example. This work is a further effort in this direction. It is anticipated that in the future, there will be more research on ionic behavior in the HAp system, such as how interactions between ions and other large and small molecules (hormones, collagen, regulatory proteins, etc.) affect the structure, morphology, and function of HAp. There is also significant room for improvement in experimental methods (including sample preparation, instrument technology, and applications) and theoretical computation and simulation.
4. Conclusions
In summary, some important discoveries based on various characterization methods employed on fluorinated HAp samples have been achieved, particularly from multinuclear solid-state NMR. (1) Morphology changes with pH (7.0~7.4) are minor. Crystalline (core)-amorphous (shell) structure is universal, with the core/shell ratio varying with synthetic condition. (2) Differences between our samples and Kobayashi’s work [32] are significant, indicating the importance of synthetic conditions in controlling morphology. Their method of adding a nucleation center helps rapid crystallization (in ~1 h), in contrast to the wet precipitation method, which requires 24 h before the formation of precipitate. (3) 1D 1H and 19F spectra show that full substitution of hydroxide by fluoride can be reached when the concentration of F− reaches 5 mM. When the concentration of NaF approaches 10 mM, a new peak at ~3.5 ppm arises, supposedly from bulk HPO42−, probably because of the hydrogen bonding between F− and HPO42−. (4) OH− peak diminishing is accompanied with the appearance of peaks at 1~2 ppm corresponding to structural water; the water peak is upfield shifted with the increase of NaF. (5) The 1D 19F MAS NMR spectra show significant change with different recycle delays, indicating the presence of different fluorine environments, which was also confirmed with 2D 19F-31P HETCOR, showing larger CSA for samples synthesized in higher NaF concentrations. (6) Based on the experimental data, single component fitting produced better accuracy; the CP signal is stronger for the brushite region.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/cryst12020139/s1; Figure S1. HRTEM images of HAp synthesized in SBF at different pH values pH = 7.0 (a); pH = 7.2 (b) and pH = 7.4 (c). Figure S2. HRTEM images of HAp synthesized in SBF followed by soaking in NaF solution at 0.0025 M for 1 day (a); 3 days (b) and 7 days (c). Figure S3. (a): 31P 35 kHz MAS NMR spectra of HAp synthesized in different NaF concentrations; (b): 31P 35 kHz MAS NMR spectra of HAp synthesized in BSF and soaked in NaF solutions at different concentrations for 1 days; (c): 31P 35 kHz MAS NMR spectra of HAp synthesized in BSF and soaked in NaF solutions at different concentrations for 3 days; (d): 31P 35 kHz MAS NMR spectra of HAp synthesized in BSF and soaked in NaF solutions at different concentrations for 7 days. Figure S4. (a): 19F 35 kHz MAS NMR spectra of HAp synthesized in SBF solutions with different concentrations of F- ion; (b): 19F 35 kHz MAS NMR spectra of HAp soaked for 1 day in solutions with different concentrations of F- ion; (c): 19F 35 kHz MAS NMR spectra of HAp soaked for different days in solutions with the same concentration of F- ion (2.5 mM). Figure S5. (a): 19F 35 kHz MAS NMR spectra of HAp soaked for 3 days in solutions with different concentrations of F- ion; (b): 19F 35 kHz MAS NMR spectra of HAp soaked for 7 days in solutions with different concentrations of F- ion; (c): 19F 35 kHz MAS NMR spectra of HAp soaked for different days in solutions with the same concentration of F- ion (5 mM); (d): 19F 35 kHz MAS NMR spectra of HAp soaked for different days in solutions with the same concentration of F- ion (10 mM). Figure S6. 1H-31P 35 kHz HETCOR spectra of HAp synthesized in SBF at different pH values: pH = 7 (a); pH = 7.2 (b) and pH = 7.4 (c). Figure S7. 1H-31P 35 kHz HETCOR spectra of HAp synthesized in SBF and soaked in solutions at different NaF concentrations (2.5 mM, 5 mM and 10 mM) for different days (1 day, 3 days, 7 days), respectively.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, S.-W.D., S.-S.L. and H.-Y.C.; methodology, S.-W.D., H.-Y.C., S.-S.L., S.-C.Y., D.T., R.-H.C. and H.-H.W.; software, S.-C.Y., D.T. and H.-H.W.; validation, S.-W.D., Y.-R.H. and H.-Y.C.; formal analysis, S.-W.D., D.T., P.-Y.C., Y.-C.L. and S.-C.Y.; investigation, S.-C.Y., D.T., S.-W.D., R.-H.C., H.-Y.C., P.-Y.C., Y.-C.L.; resources, S.-W.D., S.-S.L., Y.-R.H. and H.-Y.C.; data curation, S.-C.Y., D.T., P.-Y.C., Y.-C.L. and R.-H.C., writing—original draft preparation, S.-C.Y., D.T., S.-W.D. and H.-Y.C.; writing—review and editing, S.-W.D. and H.-Y.C.; visualization, S.-C.Y. and D.T.; supervision, S.-W.D. and H.-Y.C.; project administration, S.-W.D.; funding acquisition, S.-W.D. and H.-Y.C. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Ministry of Science and Technology of Taiwan, grant numbers MOST 104-2113-M-110-010, MOST 110-2113-M-110-016 to S.D.; MOST 110-2113-M-037-019 to H.Y.C.; NSYSU-KHGMH joint project CMRPG8I0351 to S.S.L. and S.D.; and NSYSU-KMU Joint Project 111-P03 to S.-W.D. and H.-Y.C. The APC was funded by the Ministry of Science and Technology of Taiwan.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
The XRD and HRTEM experiments were carried out on the NSYSU high valued instrument center. NSYSU and National Taiwan University (NTU) solid-state NMR spectrometers are acknowledged for the 1D and 2D experiments. In particular, we gratefully acknowledge Shing-Jong Huang of NTU for his professional assistance. The National Center for High-Performance Computing of Taiwan is gratefully acknowledged for providing the computing software and hardware to support this project.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
References
- Bonnucci, E.; Motta, P.M. Ultrastructure of Skeletal Tissues. Bone and Cartilage in Health and Disease; Kluwer Academic Publishers: Boston, MA, USA, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Cowin, S.C. Bone Mechanics Handbook; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Currey, J.D. Bones: Structure and Mechanics; Princeton University Press: Princeton, NJ, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Burr, D.B.; Allen, M.R. Basic and Applied Bone Biology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Brookes, M.; Revell, W.J. Blood Supply of Bone: Scientific Aspects; Springer: London, UK, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- U.S. Department of Health and Human Services. Bone Health and Osteoporosis: A Report of the Surgeon General; U.S. Department of Health and Human Services: Washington, DC, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Leeming, D.J.; Henriksen, K.; Byrjalsen, I.; Qvist, P.; Madsen, S.H.; Garnero, P.; Karsdal, M.A. Is bone quality associated with collagen age? Osteoporos. Int. 2009, 20, 1461–1470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weiner, S.; Wagner, H.D. The material bone: Structure mechanical function relations. Annu. Rev. Mater. Sci. 1998, 28, 271–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.Y.; McKittrick, J.; Meyers, M.A. Biological materials: Functional adaptations and bioinspired designs. Progr. Mater. Sci. 2012, 57, 1492–1704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKay, W.F.; Peckham, S.M.; Badura, J.M. A comprehensive clinical review of recombinant human bone morphogenetic protein-2 (INFUSE (R) Bone Graft). Int. Orthop. 2007, 31, 729–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Beck, K.; Brodsky, B. Supercoiled protein motifs: The collagen triple- helix and the alpha-helical coiled coil. J. Struct. Biol. 1998, 122, 17–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sherman, V.R.; Yang, W.; Meyers, M. The materials science of collagen. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2015, 52, 22–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, W.; Sherman, V.R.; Gludovatz, B.; Schaible, E.; Stewart, P.; Ritchie, R.O.; Meyers, M.A. On the tear resistance of skin. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mehdi, S.S.; Khorasani, M.T.; Dinpanah-Khoshdargi, E.; Jamshidi, A. Synthesis methods for nanosized hydroxyapatite with diverse structures. Acta Biomater. 2013, 98, 7591–7621. [Google Scholar]
- Loyt, D.A.; Shea, K.J. Bridged polysilsesquioxanes. Highly porous hybrid organic-inorganic materials. Chem. Rev. 1995, 95, 1431–1442. [Google Scholar]
- Plass, R.; Pelet, S.; Krueger, J.; Grätzel, M.; Bach, U. Quantum dot sensitization of organic—Inorganic hybrid solar cells. J. Phys. Chem. B 2002, 106, 7578–7580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Kang, Y.; Wang, L.; Zhang, H.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Y. Organic/inorganic hybrid sensors: A review. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2013, 182, 467–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Draxl, C.; Nabok, D.; Hannewald, K. Organic/inorganic hybrid materials: Challenges for ab initio methodology. Acc. Chem. Res. 2014, 47, 3225–3232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vallet-Regí, M.; Colilla, M.; González, B. Medical applications of organic—Inorganic hybrid materials within the field of silica-based bioceramics. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2011, 40, 596–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Shi, L.; Zhou, H.; Zhu, J.; Wang, Z.; Mao, X.; Chi, M.; Sun, L.; Yuan, S. Water-based organic–inorganic hybrid coating for a high-performance separator. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2016, 4, 3794–3802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaushik, A.; Kumar, R.; Arya, S.K.; Nair, M.; Malhotra, B.D.; Bhansali, S. Organic−inorganic hybrid nanocomposite-based gas sensors for environmental monitoring. Chem. Rev. 2015, 115, 4571–4606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonucci, E. Biological Calcification: Normal and Pathological Processes in the Early Stage; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- George, A.; Veis, A. Phosphorylated proteins and control over apatite nucleation, crystal growth, and inhibition. Chem. Rev. 2008, 108, 4670–4693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tomoaia, G.; Pasca, R.D. On the collagen mineralization. A Review. Clujul Med. 2015, 88, 15–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nudelman, F.; Pieterse, K.; George, A.; Bomans, P.H.; Friedrich, H.; Brylka, L.J.; Hilbers, P.A.; de With, G.; Sommerdijk, N.A. The role of collagen in bone apatite formation in the presence of hydroxyapatite nucleation inhibitors. Nat. Mater. 2010, 9, 1004–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Habraken, W.J.; Tao, J.; Brylka, L.J.; Friedrich, H.; Bertinetti, L.; Schenk, A.S.; Verch, A.; Dmitrovic, V.; Bomans, P.H.; Frederik, P.M.; et al. Ion-association complexes unite classical and non-classical theories for the biomimetic nucleation of calcium phosphate. Nat. Commun. 2013, 4, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tintut, Y.; Demer, L.L. Effects of bioactive lipids and lipoproteins on bone. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2014, 25, 53–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Torres, A.M.; Matheny, J.B.; Keaveny, T.M.; Taylor, D.; Rimnac, C.M.; Hernandez, C.J. Material heterogeneity in cancellous bone promotes deformation recovery after mechanical failure. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 2892–2897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kokubo, T.; Kushitani, H.; Sakka, S.; Kitsugi, T.; Yamamuro, T. Solutions able to reproduce in vivo surface-structure changes in bioactive glass-ceramic A-W3. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 1990, 24, 721–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kokubo, T. Bioactive glass ceramics: Properties and applications. Biomaterials 1991, 12, 155–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kokubo, T.; Takadama, H. How useful is SBF in predicting in vivo bone bioactivity? Biomaterials 2006, 27, 2907–2915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kobayashi, T.; Ono, S.; Hirakura, S.; Oaki, Y.; Imai, H. Morphological variation of hydroxyapatite grown in aqueous solution based on simulated body fluid. CrystEngComm 2012, 14, 1143–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kokubo, T.; Yamaguchi, S. Novel bioactive materials developed by simulated body fluid evaluation: Surface-modified Ti metal and its alloys. Acta Biomater. 2016, 44, 16–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Nancollas, G.H. Calcium orthophosphates: Crystallization and dissolution. Chem. Rev. 2008, 108, 4628–4669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gregory, T.M.; Moreno, E.C.; Brown, W.E. Preparation and Solubility of Hydroxyapatite. J. Res. Nat. Bur. Stand. 1968, 74, 773–782. [Google Scholar]
- DeRooij, J.F.; Heughebaert, J.C.; Nancollas, G.H. A pH study of calcium phosphate seeded precipitation. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1984, 100, 350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.-F.; Darvell, B.W.; Leung, V.W.-H. Hydroxyapatite solubility in simple inorganic Solutions. Arch. Oral Biol. 2004, 49, 359–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaflak, A.; Chmielewski, D.; Kolodziejski, W. Solid-state NMR study of discrete environments of bone mineral nanoparticles using phosphorus-31 relaxation. J. Appl. Biomed. 2016, 14, 321–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gelli, R.; Ridi, F.; Baglioni, P. The importance of being amorphous: Calcium and magnesium phosphates in the human body. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2019, 269, 219–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edén, M. Structure and formation of amorphous calcium phosphate and its role as surface layer of nanocrystalline apatite: Implications for bone mineralization. Materialia 2021, 17, 101107–101151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Von Euw, S.; Wang, Y.; Laurent, G.; Drouet, C.; Babonneau, F.; Nassif, N. Bone mineral: New insights into its chemical composition. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 8456–8466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Arcos, D.; Vallet-Regí, M. Substituted hydroxyapatite coatings of bone implants. J. Mater. Chem. B 2020, 8, 1781–1800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osman, M.B.; Diallo-Garcia, S.; Herledan, V.; Dalil Brouri, D.; Yoshioka, T.; Kubo, J.; Millo, Y.; Costentin, G. Discrimination of surface and bulk structure of crystalline hydroxyapatite nanoparticles by NMR. J. Phys. Chem. C 2015, 119, 23008–23020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Von Euw, S.; Fernandes, F.M.; Cassaignon, S.; Selmane, M.; Laurent, G.; Pehau-Arnaudet, G.; Coelho, C.; Bonhomme-Coury, L.; Giraud-Guille, M.M.; et al. Water-mediated structuring of bone apatite. Nat. Mater. 2013, 12, 1144–1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Klimavicius, V.; Kareiva, A.; Balevicius, V. Solid-state NMR study of hydroxyapatite containing amorphous phosphate phase and nanostructured hydroxyapatite: Cut-off averaging of CP-MAS kinetics and size profiles of spin clusters. J. Phys. Chem. C 2014, 118, 28914–28921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coppel, Y.; Prigent, Y.; Grégoire, G. Characterization of hydrogenated dentin components by advanced 1 H solid-state NMR experiments. Acta Biomater. 2021, 120, 156–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kristinaitytė, K.; Dagys, L.; Kausteklis, J.; Klimavicius, V.; Doroshenko, I.; Pogorelov, V.; Valevičienė, N.R.; Balevicius, V. NMR and FTIR studies of clustering of water molecules: From low-temperature matrices to nano-structured materials used in innovative medicine. J. Mol. Liq. 2017, 235, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathew, R.; Turdean-Ionescu, C.; Yu, Y.; Stevensson, B.; Izquierdo-Barba, I.; García, A.; Arcos, D.; Vallet-Regí, M.; Edeń, M. Proton environments in biomimetic calcium phosphates formed from mesoporous bioactive CaO–SiO2–P2O5 glasses in vitro: Insights from solid-state NMR. J. Phys. Chem. C 2017, 121, 13223–13238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kaflak, A.; Moskalewski, S.; Kolodziejskia, W. The solid-state proton NMR study of bone using a dipolar filter: Apatite hydroxyl content versus animal age. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 16909–16919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shah, P.; Westwell, A.D. The role of fluorine in medicinal chemistry. J. Enzym. Inhib. Med. Chem. 2007, 22, 527–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dalvi, V.H.; Rossky, P.J. Molecular origins of fluorocarbon hydrophobicity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 13603–13607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mecinovic, J.; Snyder, P.W.; Mirica, K.A.; Bai, S.; Mack, E.T.; Kwant, R.L.; Moustakas, D.T.; Héroux, A.; Whitesides, G.M. Fluoroalkyl and alkyl chains have similar hydrophobicities in binding to the “hydrophobic wall” of carbonic anhydrase. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2011, 133, 14017–14026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Robalo, J.R.; Huhmann, S.; Koksch, B.; Verde, A.V. The multiple origins of the hydrophobicity of fluorinated apolar amino acids. Chem 2017, 3, 881–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, C.H.; Ramamoorthy, A.; Gierasch, L.M. Simultaneous charac-terization of the amide 1H chemical shift, 1H–15N dipolar, and 15N chemical shift interaction tensors in a peptide bond by three-dimensional solid-state NMR spectroscopy. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1995, 117, 6148–6614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elvis, O.; López, E.O.; Mello, A.; Farina, M.; Rossi, A.M.; Rossi, A.L. Nanoscale analysis of calcium phosphate films obtained by RF magnetron sputtering during the initial stages of deposition. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2015, 279, 16–24. [Google Scholar]
- Mondal, S.; Dorozhkin, S.V.; Pal, U. Recent progress on fabrication and drug delivery applications of nanostructured hydroxyapatite. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Nanomed. Nanobiotechnol. 2018, 10, e1504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S. Hydroxyapatite Coatings for Biomedical Applications; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Mucalo, M. Hydroxyapatite (HAp) for Biomedical Applications; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2015. [Google Scholar]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).