Zeolitic Imidazolate Framework 67-Derived Ce-Doped CoP@N-Doped Carbon Hollow Polyhedron as High-Performance Anodes for Lithium-Ion Batteries
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
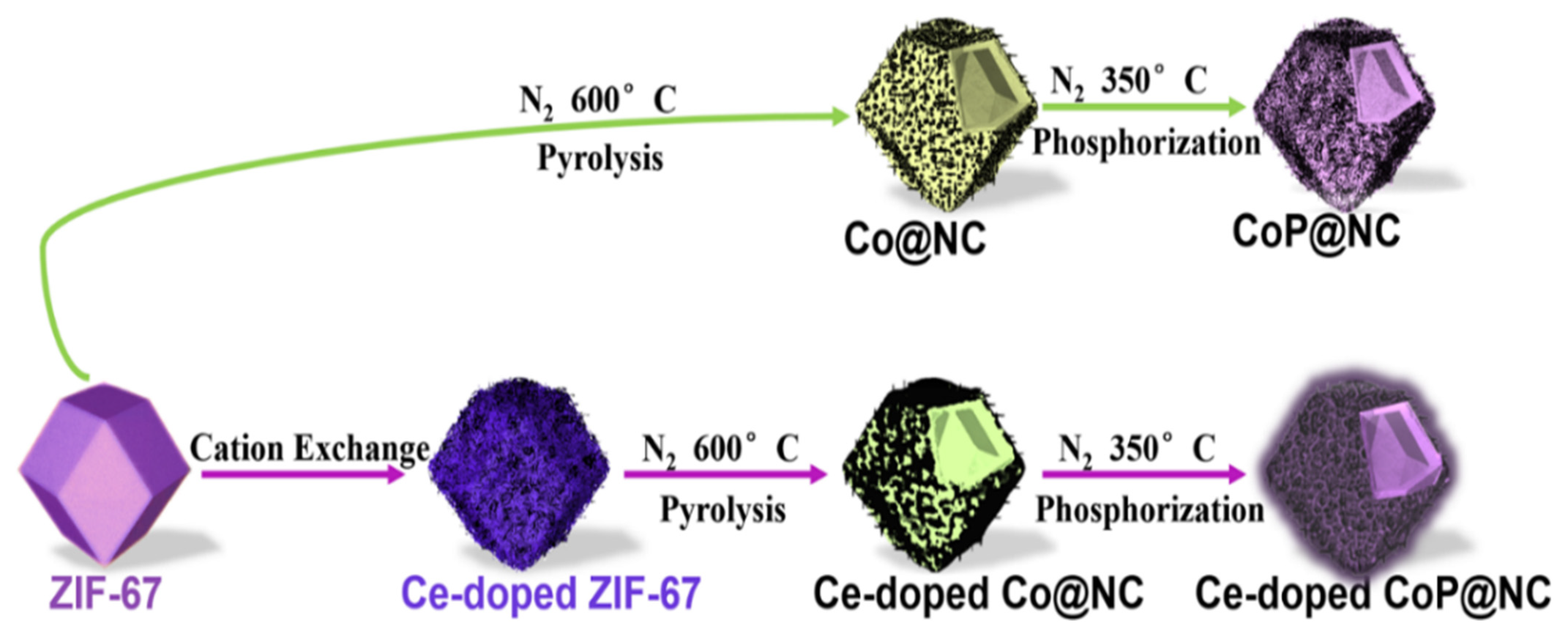
2.1. The synthesis of Hollow Polyhedron Structured Ce-CoP@NC Composite
2.2. Materials Characterization
2.3. Electrochemical Measurements
3. Results
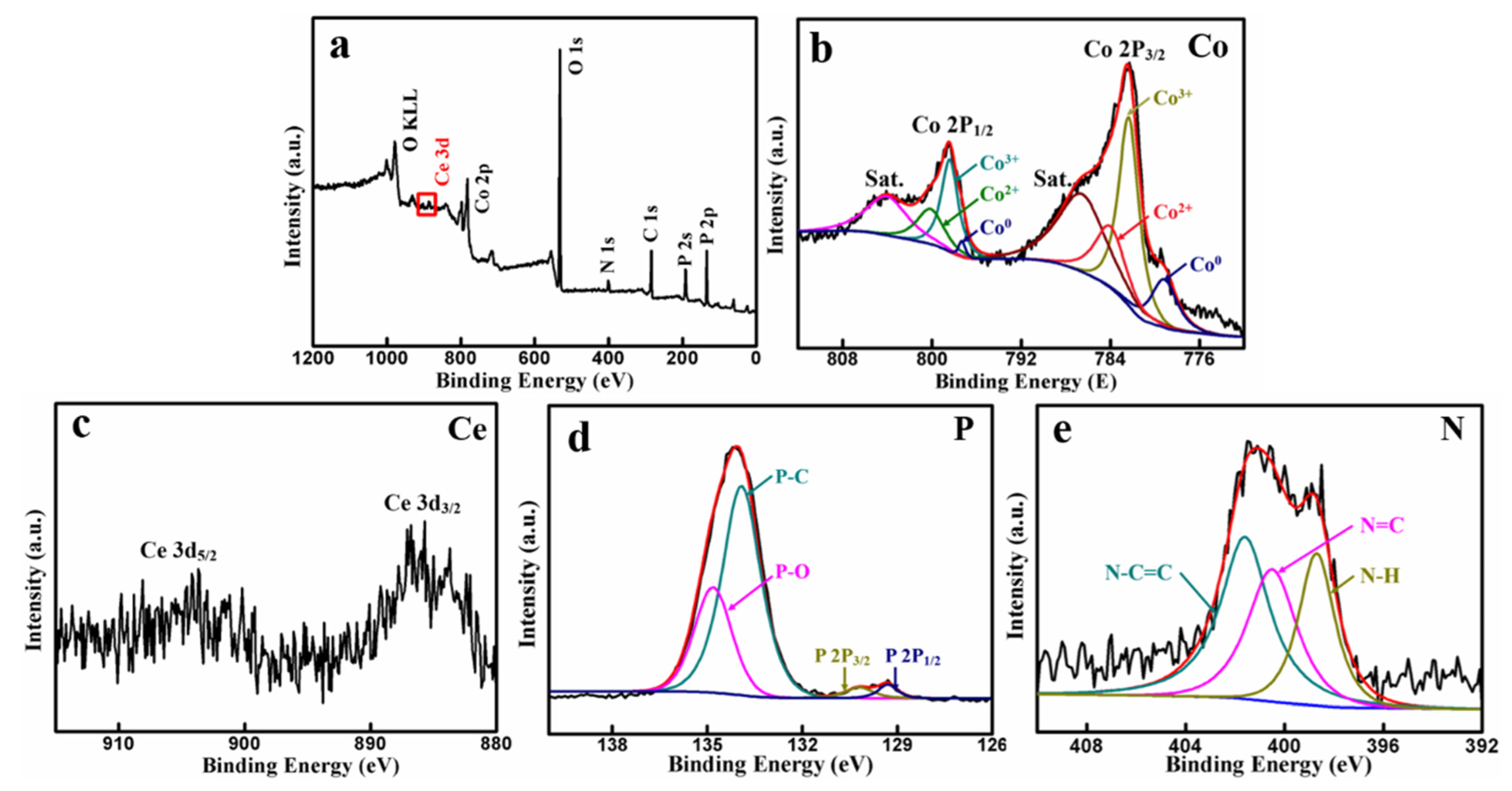
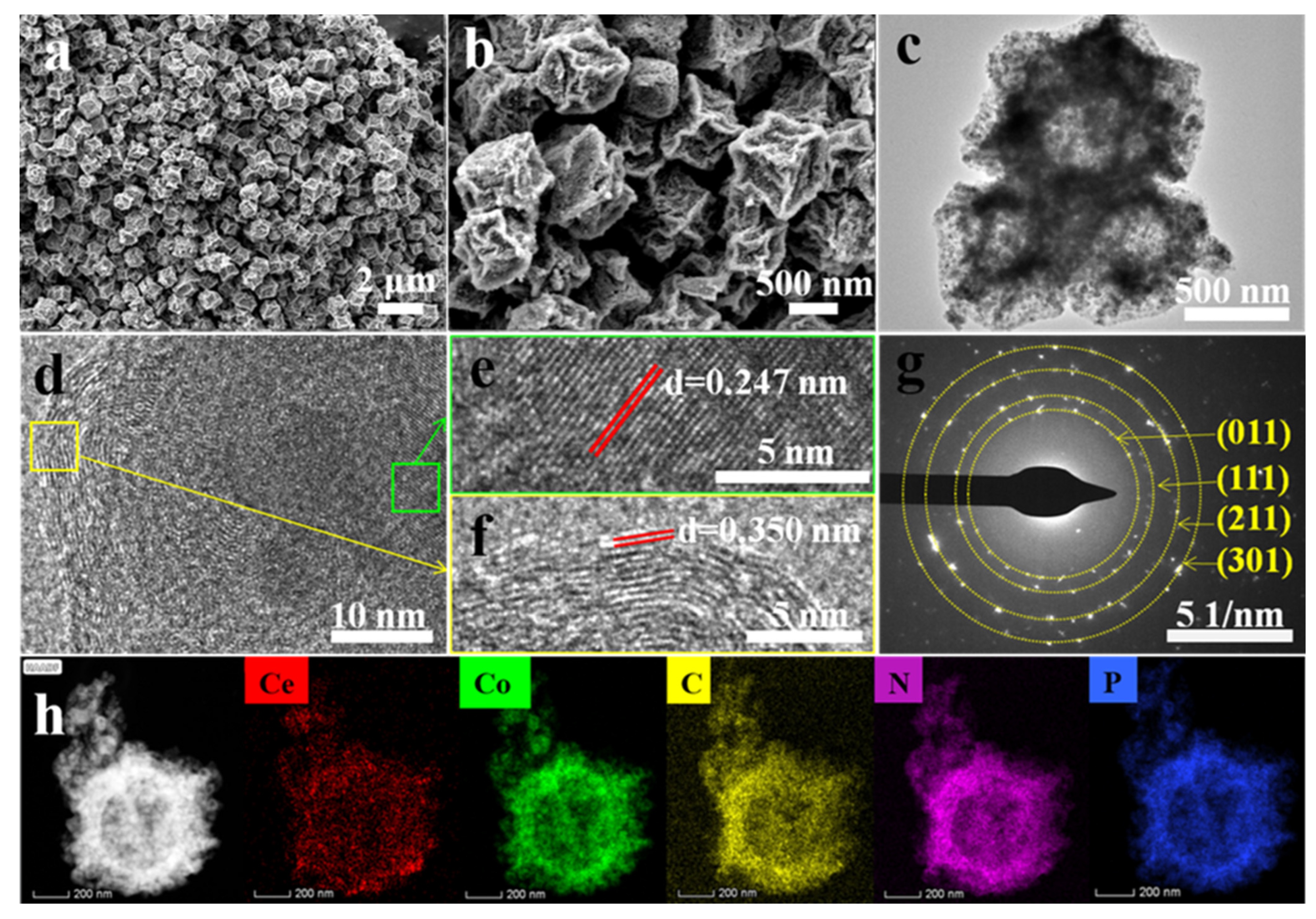
3.1. Composition and Microstructures of the Composite Materials
3.2. Electrochemical Property in Half-Cells
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dunn, B.; Kamath, H.; Tarascon, J.M. Electrical energy storage for the grid: A battery of choices. Science 2011, 334, 928–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, M.; Lu, J.; Chen, Z.W.; Amine, K. 30 Years of Lithium-Ion Batteries. Adv. Mater. 2018, 30, 1800561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zong, H.; Hu, L.; Wang, Z.G.; Qi, R.J.; Yu, K.; Zhu, Z.Q. Metal-organic frameworks-derived CoP anchored on MXene toward an efficient bifunctional electrode with enhanced lithium storage. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 416, 129102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, R.M.; Wang, X.; Chen, Z.H.; She, Z.W.; Wang, L.; Sun, Y.M. Promises and challenges of the practical implementation of prelithiation in lithium-ion batteries. Adv. Energy Mater. 2021, 11, 2101565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Yu, L.; Lou, X.W.D. Nanostructured Conversion-type Anode Materials for Advanced Lithium-Ion Batteries. Chem 2018, 4, 972–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Muhammad, I.; Jabeen, M.; Wang, P.R.; He, Y.S.; Liao, X.Z.; Ma, Z.F. Spray-dried assembly of 3D N, P-Co-doped graphene microspheres embedded with core–shell CoP/MoP@C nanoparticles for enhanced lithium-ion storage. Dalton Trans. 2021, 50, 4555–4566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.N.; Bai, Z.C.; Fang, Z.W.; Zhang, X.; Xu, X.; Du, Y.; Liu, L.; Dou, S.; Yu, G. General synthetic strategy for pomegranate-like transition-metal phosphides@N-doped carbon nanostructures with high lithium storage capacity. ACS Mater. Lett. 2019, 1, 265–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.; Guo, H.N.; Li, W.Q.; Wang, Y.J. MOF-derived core-shell CoP@NC@TiO2 composite as a high-performance anode material for Li-ion batteries. Chem. Asian J. 2021, 16, 322–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.M.; Li, M.Y.; Yu, Y.F.; Zhang, B. Recent advances in nanostructured transition metal phosphides: Synthesis and energy-related applications. Energy Environ. Sci. 2020, 13, 4564–4582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, K.J.; Liu, J.; Li, S.T.; Liu, L.L.; Yang, L.Y.; Liu, S.L.; Wang, H.; Xie, T. Ultrafine cobalt phosphide nanoparticles embedded in nitrogen-doped carbon matrix as a superior anode material for lithium ion batteries. Adv. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 4, 1700377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Zhu, P.P.; Li, C.; Yu, J.; Cai, J.X.; Yang, Z.Y. Needle-like cobalt phosphide arrays grown on carbon fiber cloth as a binder-free electrode with enhanced lithium storage performance. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2021, 32, 154–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.J.; Wang, F.; Liu, K.Y.; Zhu, J.F.; Chen, T.G.; Gu, Z.Y.; Yin, S. Cobalt phosphide nanoparticles grown on Ti3C2 nanosheet for enhanced lithium ions storage performances. J. Alloys Compd. 2021, 853, 157136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, F.F.; Yu, W.; Shi, R.T.; Wan, S.H.; Zhang, H.; Wang, B.; Cao, R. Enhanced lithium storage performance guided by intricate-cavity hollow cobalt phosphide. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2021, 563, 150395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.J.; Liu, J.; Hu, R.Z.; Liu, J.W.; Ouyang, L.Z.; Zhu, M. Self-Supported CoP nanorod arrays grafted on stainless steel as an advanced integrated anode for stable and long-life lithium ion batteries. Chem. Eur. J. 2017, 23, 5198–5204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, B.B.; Chen, K.; Wang, G.; Liu, X.J.; Wang, H.; Bai, J.T. A multidimensional and hierarchical carbon confined cobalt phosphide nanocomposite as an advanced anode for lithium and sodium storage. Nanoscale 2019, 11, 968–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.X.; Na, Z.L.; Yin, D.M.; Wang, C.L.; Wu, Y.M.; Huang, G.; Wang, L. Phytic acid-assisted formation of hierarchical porous CoP/C nanoboxes for enhanced lithium storage and hydrogen generation. ACS Nano 2018, 12, 12238–12246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.L.; Yang, S.J.; Sun, B.X.; Chang, X.H.; Zheng, J.; Li, X.G. A Peapod-like CoP@C nanostructure from phosphorization in a low temperature molten salt for high-performance lithium-ion batteries. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2018, 130, 10344–10348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, L.S.; Chen, G.; Liu, X.H.; Han, J.; Xiao, X.; Zhang, N.; Liang, S.; Qiu, G.; Ma, R. Self-supported Fe-doped CoP nanowire arrays grown on carbon cloth with enhanced properties in lithium-ion batteries. ACS Appl. Energy Mater. 2019, 2, 406–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.L.; Zhao, R.F.; Zhou, K.H.; Shen, C.; Zhang, X.E.; Wu, H.Y.; Ni, L.; Yan, H.; Diao, G.; Chen, M. Cage-structured MxPy@CNCs (M = Co and Zn) from MOF confined growth in carbon nanocages for superior lithium storage and hydrogen evolution performance. J. Mater. Chem. A 2019, 7, 8443–8450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, K.K.; Xi, B.J.; Wei, R.C.; Li, H.B.; Feng, J.K.; Xiong, S.L. Hierarchical microcables constructed by CoP@C⊂Carbon framework intertwined with carbon nanotubes for efficient lithium storage. Adv. Energy Mater. 2020, 10, 1902913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, P.P.; Zhang, Z.; Zhao, P.F.; Zhang, B.W.; Cao, X.; Yu, J.; Cai, J.; Huang, Y.; Yang, Z. Rational design of intertwined carbon nanotubes threaded porous CoP@carbon nanocubes as anode with superior lithium storage. Carbon 2019, 142, 269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.J.; Zhou, L.; Huang, L.; Chen, L.L.; Long, L.; Wang, S.Y.; Xu, X.; Liu, M.; Yang, W.; Jia, J. ZIF-67 derived hierarchical hollow sphere-like CoNiFe phosphide for enhanced performances in oxygen evolution reaction and energy storage. Electrochim. Acta 2019, 318, 883–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.R.; Yang, X.C.; Xue, H.G.; Pang, H.; Xu, Q. Metal–organic frameworks as a platform for clean energy applications. EnergyChem 2020, 2, 100027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, M.; Kong, L.; Li, N.; Liu, Y.Y.; Zhu, J.; Bu, X.H. Synthesis of MOF-derived nanostructures and their applications as anodes in lithium and sodium ion batteries. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2019, 388, 172–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, Y.J.; Xu, L.Q.; Qian, Y.T. Ce-doped α-FeOOH nanorods as high-performance anode material for energy storage. J. Power Sources 2016, 327, 423–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, H.X.; Bai, Y.; Wang, X.R.; Ni, Q.; Wang, Z.H.; Li, Y.; Chen, G.; Wu, F.; Xu, H.; Wu, C. High-capacity interstitial Mn-incorporated MnxFe3-xO4/graphene nanocomposite for sodium-ion battery anodes. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 37812–37821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, P.; Zhuge, F.W.; Zhang, Q.F.; Chen, Y.Q.; Lv, L.; Huang, Y.; Li, H.; Zhai, T. Doping engineering and functionalization of two-dimensional metal chalcogenides. Nanoscale Horiz. 2019, 4, 26–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, W.; Yan, M.; Cheung, H.Y.; Xia, Z.M.; Zhou, X.M.; Qin, Y.B.; Wong, C.Y.; Ho, J.C.; Chang, C.R.; Qu, Y. Modulating electronic structure of CoP electrocatalysts towards enhanced hydrogen evolution by Ce chemical doping in both acidic and basic media. Nano Energy 2017, 38, 290–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.Z.; Huang, J.Z.; Wang, X.J.; Gao, T.L.; Zhang, Y.M.; Yao, T.; Song, B. Ruthenium incorporated cobalt phosphide nanocubes derived from a prussian blue analog for enhanced hydrogen evolution. Front. Chem. 2018, 6, 521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Han, X.Y.; Cui, Y.P.; Liu, H.W. Ce-doped Mn3O4 as high-performance anode material for lithium ion batteries. J. Alloys Compd. 2020, 814, 152348–152356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.Y.; Zheng, G.T.; Guo, G.Z.; Wang, Z.C.; Tang, J.; Li, S.; Wen, Z.; Ji, S.; Sun, J. Ce-doped V2O5 microspheres with improved electrochemical performance for high-power rechargeable lithium ion batteries. J. Alloys Compd. 2019, 784, 574–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.Y.; Li, J.M.; Qiao, R.; Dai, X.; Jing, W.T.; Song, J.X.; Chen, Y.; Guo, S.; Sun, J.; Tan, Q.; et al. Binder-free flexible zinc-ion batteries: One-step potentiostatic electrodeposition strategy derived Ce doped-MnO2 cathode. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 431, 133387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, X.Y.; Zhang, Y.H.; Sun, P.P.; Gao, J.; Shi, F.N. Lithium-lanthanide bimetallic metal-organic frameworks towards negative electrode materials for lithium-ion batteries. Chem. Eur. J. 2020, 26, 5654–5661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ge, P.; Yuan, S.H.; Zhao, W.Q.; Zhao, L.M.; Yang, Y.; Xie, L.L.; Zhu, L.; Cao, X. Rare earth metal La-doped induced electrochemical evolution of LiV3O8 with an oxygen vacancy toward a high energy-storage capacity. J. Mater. Chem. A 2021, 9, 1845–1858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, D.D.; Xu, M.; Liang, X.; Wang, J.Y.; Fang, W.Y.; Zhu, C.G.; Wang, F. Facile synthesis of Pr-doped Co3O4 nanoflakes on the nickel-foam for high performance supercapacitors. Electrochim. Acta 2022, 406, 139815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, C.F.; Guo, L.J.; Li, H.B.; Zhang, B.; Gao, X.; Tian, F.; Qian, Y.; Wang, D.; Xu, L. Rational fabrication of CoS2/Co4S3@N-doped carbon microspheres as excellent cycling performance anode for half/full sodium ion batteries. Energy Storage Mater. 2020, 25, 679–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, F.H.; Li, S.Q.; Yan, Y.; Lu, X.M.; Guo, C.F.; Ji, Z.Y.; Hu, P.; Shen, X. Facile fabrication of Fe0.8Mn1.2O3 with various nanostructures for high-performance lithium-ion batteries. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 427, 131697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, L.B.; Ren, H.P.; Xing, Z.; Zhao, Y.L.; Ju, Z.C. Hierarchical porous CoxFe3−xO4 nanocubes obtained by calcining prussian blue analogous as anode for lithium-ion batteries. New J. Chem. 2020, 44, 12546–12555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, D.; Yi, J.G.; Zhao, X.D.; Yang, J.Q.; Lu, H.R.; Fan, L.Z. Confining ultrasmall CoP nanoparticles into nitrogen-doped porous carbon via synchronous pyrolysis and phosphorization for enhanced potassium-ion storage. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 413, 127508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, S.; Xu, J.Q.; Xie, T.H.; Chu, S.Q.; Wu, D.J.; Qian, B. Regulating the electronic structure of CoP nanoflowers by molybdenum incorporation for enhanced lithium and sodium storage. J. Power Sources 2021, 500, 229975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.Y.; Fu, Y.Y.; Liao, W.H.; Zhang, Y.Q.; Qian, M.; Dai, H.J.; Tong, X.; Yang, Q. Fabrication of Cerium-Doped CoMoP/MoP@C Heterogeneous Nanorods with High Performance for Overall Water Splitting. Energy Fuels 2021, 35, 14169–14176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, C.Z.; Liu, K.F.; Tao, J.; Kang, X.T.; Hou, H.Y.; Cheng, C.; Zhang, D. Self-template synthesis of hybrid porous Co3O4-CeO2 hollow polyhedrons for high performance supercapacitors. Chem. Asian J. 2018, 4, 111–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xing, H.N.; Long, G.K.; Zheng, J.M.; Zhao, H.Y.; Zong, Y.; Li, X.H.; Wang, Y.; Zhu, X.; Zhang, M.; Zheng, X. Interface engineering boosts electrochemical performance by fabricating CeO2@CoP schottky conjunction for hybrid supercapacitors. Electrochim. Acta 2020, 337, 135817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vijayakumar, E.; Ramakrishnan, S.; Sathiskumar, C.; Dong, J.Y.; Balamurugan, J.; Noh, H.S.; Kwon, D.; Kim, Y.H.; Lee, H. MOF-derived CoP-nitrogen-doped carbon@NiFeP nanoflakes as an efficient and durable electrocatalyst with multiple catalytically active sites for OER, HER, ORR and rechargeable zinc-air batteries. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 428, 131115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.Y.; Xin, S.S.; Li, J.; Cui, H.T.; Liu, Y.Y.; Yang, Y.Z.; Wang, M. Synergistic regulation of polysulfides immobilization and conversion by MOF-derived CoP-HNC nanocages for high-performance lithium-sulfur batteries. Nano Energy 2021, 85, 106011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.F.; Pan, A.Q.; Ding, L.; Zhou, Z.L.; Wang, Y.P.; Niu, S.Y.; Liang, S.; Cao, G. Nitrogen-doped yolk−shell-structured CoSe/C dodecahedra for high-performance sodium ion batteries. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 3624–3633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.H.; Zhu, Y.Q.; Zhao, K.J.; Fu, Q.; Wang, K.; Wang, Y.P.; Wang, N.; Lv, X.; Jiang, H.; Chen, L. Surface modification of coordination polymers to enable the construction of CoP/N, P-codoped carbon nanowires towards high-performance lithium storage. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2020, 565, 503–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.N.; Hu, Z.; Liang, Y.R.; Li, L.; Zou, C.; Jin, H.L.; Wang, S.; Lu, H.; Gu, Q.; Chou, S.L.; et al. Facile synthesis of hierarchical hollow CoP@C composites with superior performance for sodium and potassium storage. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2020, 59, 5159–5164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Q.Q.; Jin, Y.H.; Jia, M.; Yuan, Q.; Zhao, C.C.; Ji, M.Q. Sulfur-doped CoP@ nitrogen-doped porous carbon hollow tube as an advanced anode with excellent cycling stability for sodium-ion batteries. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2020, 575, 61–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabassum, H.; Zou, R.; Mahmood, A.; Liang, Z.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, H.; Gao, S.; Qu, C.; Guo, W.; Guo, S. A universal strategy for hollow metal oxide nanoparticles encapsulated into B/N co-doped graphitic nanotubes as high-performance lithium-ion battery anodes. Adv. Mater. 2018, 30, 1705441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.L.; Zou, G.Q.; Hou, H.S.; Li, J.Y.; Liu, C.; Qiu, X.Q.; Ji, X. Composition engineering boosts voltage windows for advanced sodium-ion batteries. ACS Nano 2019, 13, 10787–10797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhai, Y.; Zhou, S.; Guo, L.; Xin, X.; Zeng, S.; Qu, K.; Wang, N.; Zhang, X. Zeolitic Imidazolate Framework 67-Derived Ce-Doped CoP@N-Doped Carbon Hollow Polyhedron as High-Performance Anodes for Lithium-Ion Batteries. Crystals 2022, 12, 533. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst12040533
Zhai Y, Zhou S, Guo L, Xin X, Zeng S, Qu K, Wang N, Zhang X. Zeolitic Imidazolate Framework 67-Derived Ce-Doped CoP@N-Doped Carbon Hollow Polyhedron as High-Performance Anodes for Lithium-Ion Batteries. Crystals. 2022; 12(4):533. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst12040533
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhai, Yanjun, Shuli Zhou, Linlin Guo, Xiaole Xin, Suyuan Zeng, Konggang Qu, Nana Wang, and Xianxi Zhang. 2022. "Zeolitic Imidazolate Framework 67-Derived Ce-Doped CoP@N-Doped Carbon Hollow Polyhedron as High-Performance Anodes for Lithium-Ion Batteries" Crystals 12, no. 4: 533. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst12040533
APA StyleZhai, Y., Zhou, S., Guo, L., Xin, X., Zeng, S., Qu, K., Wang, N., & Zhang, X. (2022). Zeolitic Imidazolate Framework 67-Derived Ce-Doped CoP@N-Doped Carbon Hollow Polyhedron as High-Performance Anodes for Lithium-Ion Batteries. Crystals, 12(4), 533. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst12040533






