Effects of Vacuum-Stirring Purification Process on Al-6Mg Alloy Melt
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
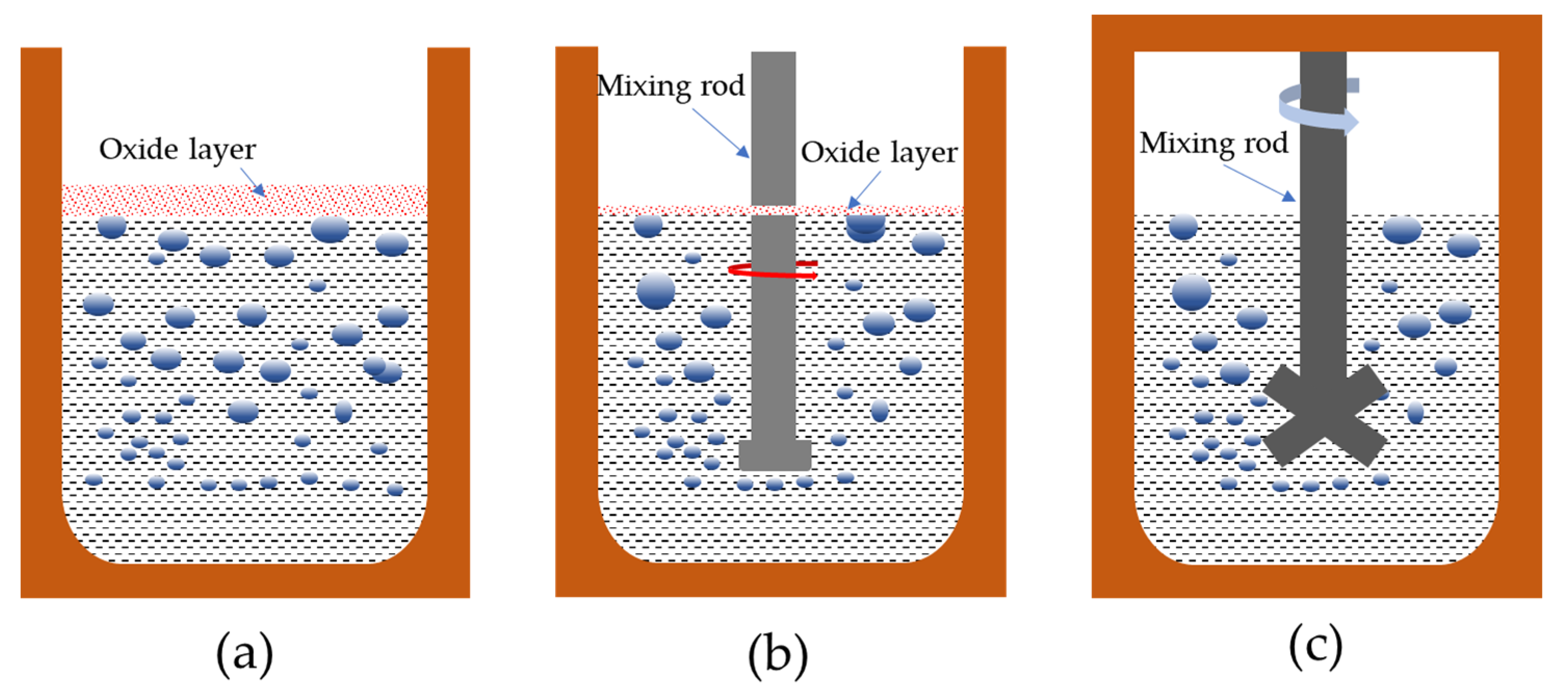
2.2. Methods and Equipment
2.3. Testing Methods
3. Results
3.1. Hydrogen Removal Effect of Al-6Mg Alloy Melt
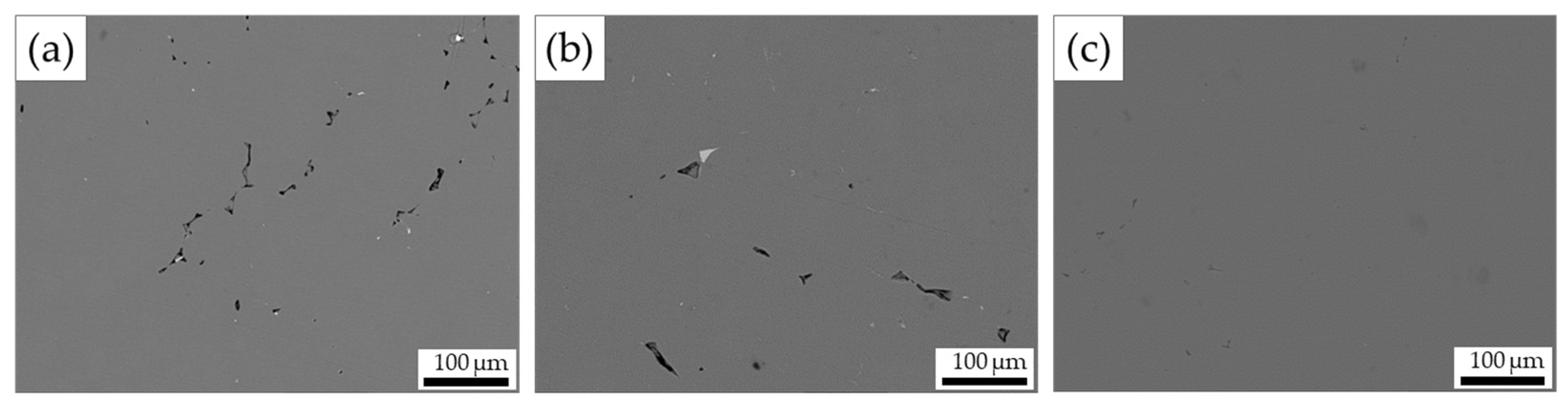
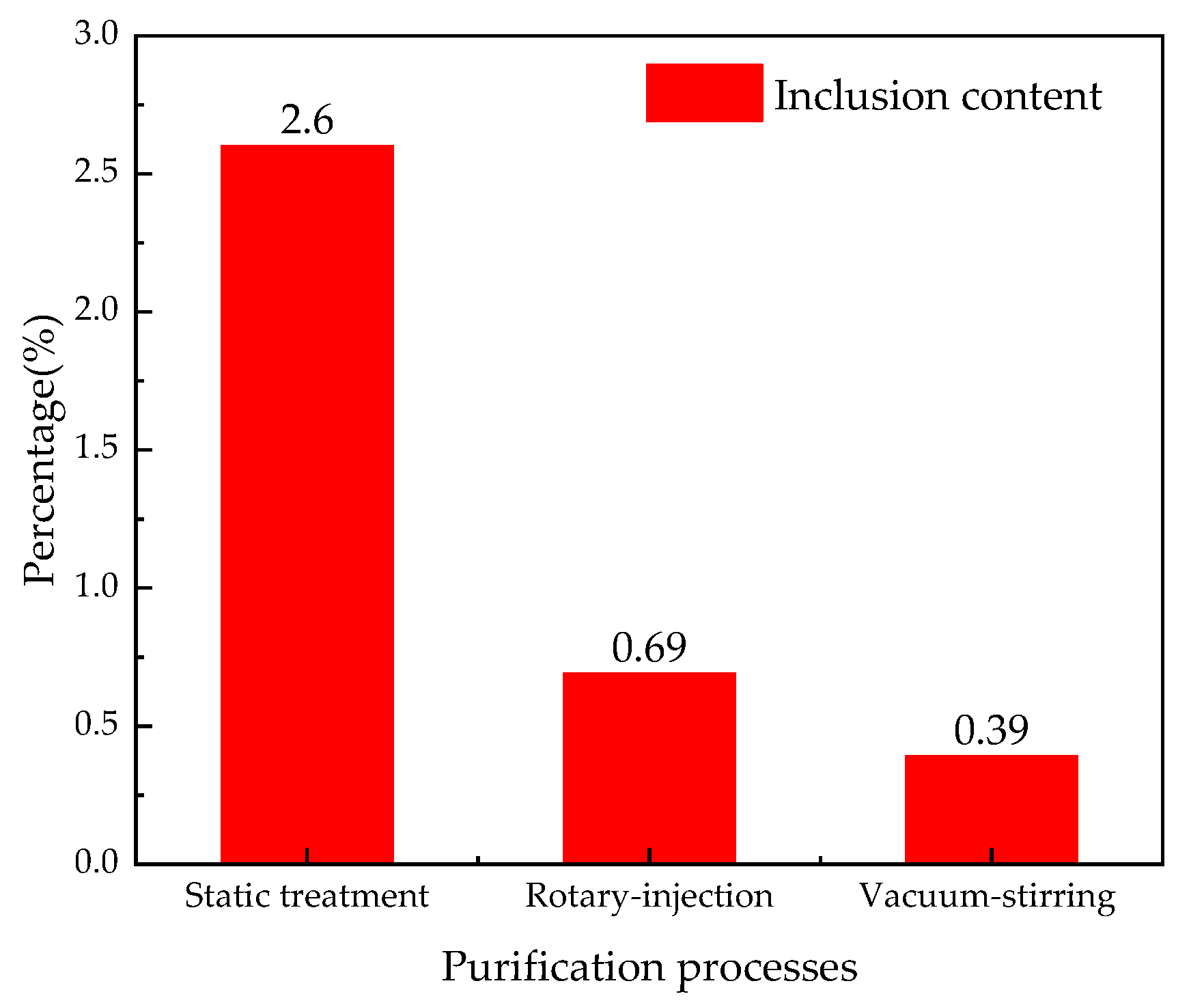
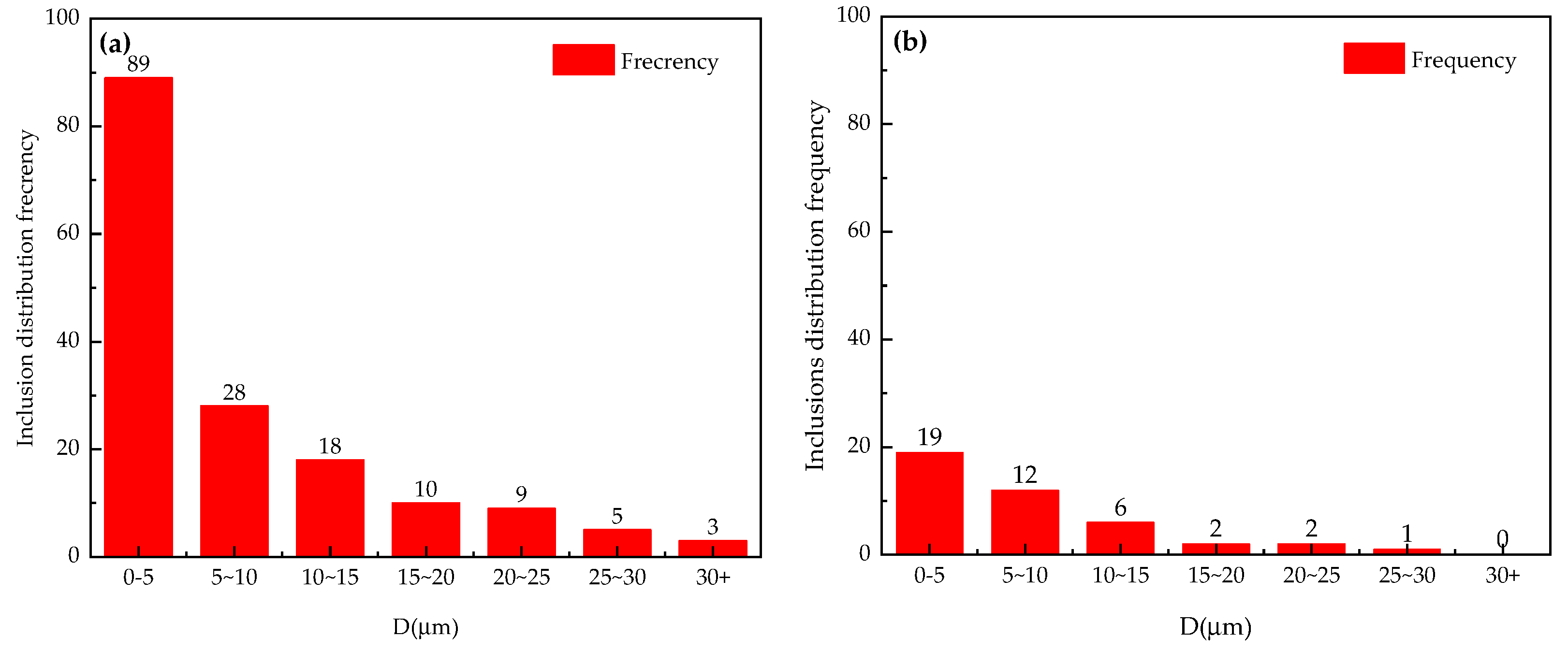
3.2. Inclusions Removal Effect of Al-6Mg Alloy Melt
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
- The hydrogen content of the melt decreases from 0.48 mL/100 gAl in the non-vacuum static treatment to 0.32 mL/100 gAl in the non-vacuum rotary-injection purification process and to 0.10 mL/100 gAl in the vacuum-stirring purification process.
- The inclusion content of the melt decreases from 2.6% in the non-vacuum static treatment to 0.69% in the non-vacuum rotary-injection purification process and to 0.39% in the vacuum-stirring purification process.
- The vacuum-stirring purification process increases the mass transfer driving force and diffusion precipitation of hydrogen, significantly reduces the equivalent pressure of the bubbles, greatly accelerates the hydrogen removal speed and significantly improves the purification effect.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Schlesinger, M.E. Aluminum Recycling; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2007; pp. 13–15. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, D.; Wu, A.; Zhao, Y.; Shan, J.; Liu, X. Effects of Al-Mg c Al-Cu wire on the properties of 2219 aluminum alloy TIG-welded joint. Int. J. Mod. Phys. B 2021, 35, 2150139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, W.; Ma, L.; Lu, Y.; Li, S.Y.; Ji, Z.; Ding, M. Effects of Solution Treatment Temperatures on Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of TIG–MIG Hybrid Arc Additive Manufactured 5356 Aluminum Alloy. Met. Mater. Int. 2018, 24, 1346–1358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Bao, S.; Akhtar, S.; Li, Y. Oxide Film Inclusions and Inoculation Particles TiB2 in Aluminum Melt. Metall. Mater. Trans. B 2021, 52, 2497–2508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toda, H.; Hidaka, T.; Kobayashi, M.; Uesugi, K.; Takeuchi, A.; Horikawa, K. Growth behavior of hydrogen micropores in aluminum alloys during high-temperature exposure. Acta Mater. 2009, 57, 2277–2290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, G.A., Jr.; Scully, J.R. The diffusion and trapping of hydrogen in high purity aluminum. Acta Mater. 1998, 46, 6337–6349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anyalebechi, P.N. Analysis of the effects of alloying elements on hydrogen solubility in liquid aluminum alloys. Scr. Metall. Mater. 1995, 33, 1209–1216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Wang, J.; Shu, D.; Zhang, S.; Sun, B. Removal of Non-Metallic Inclusions from Aluminum by Electroslag Refining. Mater. Trans. 2011, 52, 2266–2269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warke, V.S.; Shankar, S.; Makhlouf, M.M. Mathematical modeling and computer simulation of molten aluminum cleansing by the rotating impeller degasser: Part II. Removal of hydrogen gas and solid particles. J. Mater. Processing Technol. 2005, 168, 119–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shih, T.S.; Weng, K.Y. Effect of A Degassing Treatment on the Quality of Al-7Si and A356 Melts—Degassing Diffusers. Mater. Trans. 2004, 45, 1852–1858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Engh, T.A. Principles of Metal Refining; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Birnbaum, H.K.; Buckley, C.; Zeides, F.; Sirois, E.; Rozenak, P.; Spooner, S.; Lin, J.S. Hydrogen in aluminum. J. Alloy. Compd. 1997, 253–254, 260–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, H.; Sun, B.; Jiang, H.; Ding, W. Effects of rotating impeller degassing on microstructure and mechanical properties of the A356 scraps. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2003, 352, 294–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walek, J.; Michalek, K.; Tkadleková, M.; Saternus, M. Modelling of Technological Parameters of Aluminium Melt Refining in the Ladle by Blowing of Inert Gas through the Rotating Impeller. Met. Open Access Metall. J. 2021, 11, 284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dsa, B.; Zd, A.; Ao, W.A.; Gga, B.; Ming, W.A. Motion and mass transfer models for single bubble in an aluminum melt under a compound field of ultrasonic and rotating flow. Results Phys. 2020, 19, 103386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popescu, G.; Gheorghe, I.; Dnil, F.; Moldovan, P. Vacuum Degassing of Aluminium Alloys. Mater. Sci. Forum 1996, 217–222, 147–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voigt, C.; Hubálková, J.; Zienert, T.; Fankhänel, B.; Stelter, M.; Charitos, A.; Aneziris, C.G. Aluminum Melt Filtration with Carbon Bonded Alumina Filters. Materials 2020, 13, 3962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, Z.; Ye, P.; Liao, H.; Wang, Q. Degassing of aluminum alloys during re-melting. Mater. Lett. 2012, 66, 328–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Kumar, S.; Mukhopadhyay, N.K. Introduction to magnesium alloy processing technology and development of low-cost stir casting process for magnesium alloy and its composites. J. Magnes. Alloy. 2018, 6, 245–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, Y.; Zhao, H.; Shen, X.; Wang, X.; Zheng, H. Simulation of α-Al grain formation in high vacuum die-casting Al-Si-Mg alloys with multi-component quantitative cellular automaton method. China Foundry 2022, 19, 99–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zheng, Y.L.; Lin, Z.Y.; Hu, Z.L.; Zeng, J.M. Quantitative Analysis of Inclusions in Aluminum. Adv. Mater. Res. 2012, 476–478, 453–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mi, G.; Qi, S.; Liu, X.; Niu, J. Research on water simulation experiment of the rotating impeller degassing process. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2009, 499, 195–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Y.; Zhuang, L.; Meng, Z.; Chen, Z.; Tang, X. Calculation of Hydrogen Solubility in Al-Melt under Vacuum Condition. Spec. Cast. Nonferrous Alloy. 2020, 40, 1131–1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, F.R.; Wang, M.; Xie, X.J.; Huang, W.D. Analysis on Thermodynamics and Kinetics of Vacuum Degassing from Aluminum Melt during Adjusted Pressure Casting. Foundry Technol. 2009, 30, 41–43. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, Y.; Ma, W.; Wei, K.; Yu, W.; Dai, Y.; Morita, K. Degassing of aluminum alloys via the electromagnetic directional solidification. Vacuum 2014, 109, 82–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da, S.; Sun, B.; Ke, L.; Li, T.; Xu, Z.; Zhou, Y. Continuous separation of non-metallic inclusions from aluminum melt using alternating magnetic field. Mater. Lett. 2002, 55, 322–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Elements | Mg | Mn | Cr | Ti | Al |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Content (wt.%) | 6.0 | 0.15 | 0.10 | 0.10 | Bal. |
| Purification Process | Non-Vacuum Static Melt Treatment | Non-Vacuum Rotary-Injection Purification | Vacuum-Stirring Purification |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pores area/Full area | 36.05% | 1.22% | 0.36% |
| Purification Process | Non-Vacuum Static Melt Treatment | Non-Vacuum Rotary-Injection Purification | Vacuum-Stirring Purification |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hydrogen content (ml/100 gAl) | 0.48 | 0.32 | 0.10 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, S.; Bai, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Jiang, L. Effects of Vacuum-Stirring Purification Process on Al-6Mg Alloy Melt. Crystals 2022, 12, 675. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst12050675
Li S, Bai Y, Zhang Z, Jiang L. Effects of Vacuum-Stirring Purification Process on Al-6Mg Alloy Melt. Crystals. 2022; 12(5):675. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst12050675
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Shilin, Yuelong Bai, Zhifeng Zhang, and Long Jiang. 2022. "Effects of Vacuum-Stirring Purification Process on Al-6Mg Alloy Melt" Crystals 12, no. 5: 675. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst12050675
APA StyleLi, S., Bai, Y., Zhang, Z., & Jiang, L. (2022). Effects of Vacuum-Stirring Purification Process on Al-6Mg Alloy Melt. Crystals, 12(5), 675. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst12050675






