Abstract
The purpose of this study was to investigate the wetting behavior and interfacial reactions of Sn-Ti alloys, which has been widely applied to join ceramics with metals, on Si3N4 substrates. The isothermal wetting process of Sn-xTi alloys (x = 0.5, 1.0, 1.5, 2.0 and 2.5 wt.%) on Si3N4 was systematically studied from 1223 K to 1273 K through sessile drop methods. The microstructures of the interface were characterized by X-ray diffraction (XRD) and microscope (SEM). The active Ti element remarkably enhanced the wettability of Sn-xTi melts on Si3N4 substrates because of the formation of metallic reaction layers (Ti5Si3 and TiN). With the Ti content rising, thicker Ti5Si3 layer formed on the TiN phase inducing a lower equilibrium contact angle. The value of the lowest contact angle was 6°, which was obtained in the Sn-2.0Ti/Si3N4 system at 1273 K. Larger Ti5Si3 grains were found in Sn-2.5Ti melt and a higher final contact angle was obtained. Lower temperature increased the final contact angle and slowed down the spreading rate. The formation of reaction products was calculated thematically, and the spreading kinetics was calculated according to the reaction-driven theory. The spreading behavior of Sn-Ti alloy on Si3N4 ceramic was composed of rapid-spreading stage and sluggish-spreading stage. The calculated activity energy of spreading was 395 kJ/mol. Eventually, the wetting process of Sn-2.0Ti/Si3N4 system was successfully elucidated. These results provide significant guidance information for the brazing between metals and Si3N4 ceramic.
1. Introduction
Silicon nitride (Si3N4) has attracted much attention as a structural ceramic due to its outstanding mechanical properties, excellent tribological and wear performance, high temperature conductivity and high resistivity [1,2,3,4]. Si3N4 has been extensively used in many fields, such as heat exchangers, aerospace applications and high-power electronic devices [5,6,7]. However, Si3N4 is hard to manufacture into delicate and large devices. Therefore, joining Si3N4 ceramic to other metals is an effective way to extend its industrial applications [8,9,10]. Brazing is regarded as one of the most economical and effective techniques to bond ceramics to other materials [11,12]. It is generally known that an excellent wettability is a crucial factor in obtaining the expected ceramic/metal joints [13]. The influence of reactive elements (such as Ti, Cr and Zr et al.) [14,15,16,17] on the wetting of ceramic substrates has been extensively studied. Particularly, it has been acknowledged that the addition of Ti element can significantly enhance the wettability of filler metals by reacting with ceramic substrates. Recently, Sn-based filler alloys are commonly used for the production of ceramics/ceramics or ceramics/metals joints and metallize surface of ceramics at low temperature. However, the study of the wetting of Si3N4 ceramic by the addition of Ti in Sn-based alloys is limited. In order to better understand the wetting process, the research about the wetting of Ti addition in Sn-based, Cu-based and Ag-Cu-based alloys, which have widely been applied, are summarized as follows:
Fu et al. [18] researched the isothermal wetting and spreading behaviors of Sn-Ti alloy on ZrO2. When Ti concentration increased from 0 to 2.0 at%, the final contact angle decreased from 144° to 42°, resulting from the formation of Ti2O3 phase at the interface. With 4.0%Ti added, an equilibrium contact angle of 22° was acquired because of the Ti11.31Sn3O10 layer forming at the interface in replacement of Ti2O3. Lee et al. [19] studied the wetting behavior of Cu-5 at% Ti alloy on the SiC ceramic at 1273 K. A value of 40° for the final contact angle was observed. Moreover, the microstructure analysis indicated the diffusion of Ti toward SiC, which induced that the SiC substrate was violently decomposed. Therefore, the released Si and C reacted with the solute element Ti forming TiC and Ti5Si3 phase at the interface. A lower value of 20° for contact angle was achieved in Ag-Cu-4.5 wt% Ti/SiC system at 1023 K [20], while only TiSi2 phase was found in the interfacial layer. A similar contact angle was obtained in Sn-5 at.% Ti/SiC wetting system [21]. However, no decomposition of SiC could be found in Sn-Ti/SiC system. The solute element Ti directly reacted with SiC, forming TiC phase, and released Si into melt, then the free Si reacted with Ti to form Ti5Si3 at the interface. These works above have given opinions on the formation of metallic phases at the interface, which could significantly improve the wettability of alloys with Ti addition on ceramic substrates.
Luz et al. [22] analyzed the wetting of Ti-Cu on Si3N4 by sessile drop methods. The research revealed that the decrease of contact angle is due to the reaction of active element Ti with Si3N4 forming TiN and Ti5Si3 phases at the interface. The wettability increased with Ti concentration and increasing temperature. Studies on the process of wetting of Si3N4 ceramics by Ag-Cu-Ti alloys also confirmed the reaction products [23]. The lowest contact angel of 14.6° was obtained at 7.28 at% Ti concentration. The spreading process was inspired by the penetration of molten alloys into Si3N4 substrates. With the Ti concentration further increasing, more TiCu particles hindered the penetration behavior to some degree, which accounted for the higher contact angle. Nomura et al. [24] analyzed the nanostructure of the interfacial reaction products forming at the triple line in Ag-Cu-Ti/Si3N4 system by TEM. A double-layer structure consisting of an upper Ti5Si3 layer and a lower TiN layer was observed at the interface. However, the studies of the wetting and spreading behavior of Sn-Ti alloys on the Si3N4 surfaces are scale and lack of systematization.
This work is aimed to investigate the wetting behavior and interfacial reaction of Sn-xTi alloys on Si3N4. Therefore, the wetting process of Sn-xTi alloys with various Ti content and different isothermal temperatures is studied by sessile drop method. The interfacial microstructure is analyzed by SEM and XRD. Furthermore, the evolution of microstructures is discussed according to the thermodynamic calculation of reaction products. The spreading kinetics are calculated based on the reaction-driven theory.
2. Experimental Materials and Methods
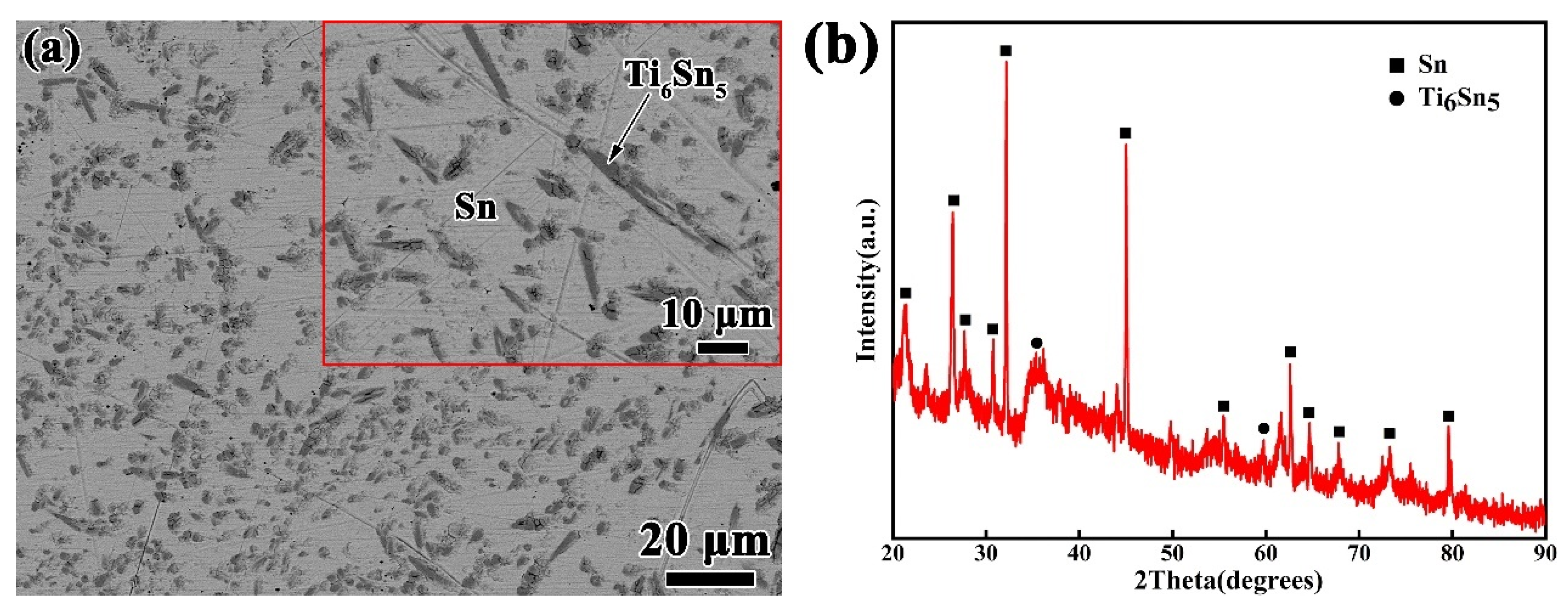
The Si3N4 ceramic applied in this experiment is gas pressing sintered Si3N4 in a dimension of 15 mm × 15 mm × 5 mm, supplied by Huaya Optical Ceramics Factory Shanghai, China. Before the wetting experiments, the Si3N4 ceramic substrates were grinded by diamond grinding discs and polished with a slurry of 0.25 micron diamond particles. The Sn-xTi alloys (x = 0.5, 1, 1.5, 2 and 2.5 wt.%) were processed by arc melting of Sn (99.98 wt.%) and Ti (99.95 wt.%) at purified Ar atmosphere. In order to eliminate the oxygen in the furnace, a piece of zirconium was melted each time before the alloy was melted. The Sn-xTi alloys were melted several times to guarantee a homogeneous alloy composition. As an illustration, Figure 1 shows the microstructure and XRD results of the prepared Sn-2.0Ti, which reveals that Ti has reacted with Sn to form Ti6Sn5, and the Ti6Sn5 phase distributes homogeneously in the Sn matrix. The Si3N4 substrates and Sn-xTi alloys were cleaned in acetone by ultrasonic vibration for 20 min prior to the tests.
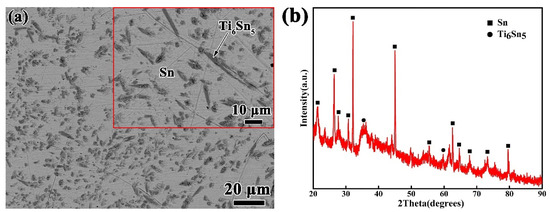
Figure 1.
Microstructural analyses of Sn-2Ti alloy. (a) SEM image (b) XRD pattern.
Wetting tests were performed by the sessile droplet method in a high-vacuum environment using a specially designed furnace [13]. The Si3N4 ceramic substrate was placed on a BN supporter and adjusted to be horizontal. The Sn-xTi alloys were put into a stainless-steel flexible tube connected with an alumina drip pipe on the top of the furnace. The furnace was firstly pumped to a vacuum better than 3.0 × 10−3 Pa and then heated to experimental temperature (ranging from 1223 K to 1273 K) at a rate of 15 K/min. In order to remove the contaminants on the surface, the Si3N4 substrate was heated to 1373 K in the furnace and then the temperature decreased to testing temperature at a rate of 10 K/min. After the temperature of the furnace chamber has stabilized, the solid Sn-Ti bulk fell from the aluminum tube onto Si3N4 substrate. Throughout the course of the wetting experiments, the drop profiles were photographed by a high-resolution camera at a rate of 1 frame/s. The outline of Sn-Ti melt during the wetting procedure was processed with an image analysis software. The error value between the measured and exact value of the contact angle is estimated to be ±2° [25].
After the wetting test, the specimens were firstly fixed by epoxy and then cut perpendicular to the contact interface by diamond blade. The cutting surface was polished to a high gloss. The microstructure of the obtained wetting interfaces was observed by a field-emission scanning electron microscopy (SEM, MERLIN Compact, ZEISS, Jena, German) equipped with energy dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDX, OCTANCE PLUS, EDAX, Bowen, USA). In order to have a further investigation of the interfacial products, the solid Sn-Ti drop was etched off by 30 vol.% HCL, 30 vol.% HNO3 and 40 vol.% deionized water. The exposed interfacial layer was identified by X-ray diffraction (XRD, DX-2700, Taiwan)
3. Results
3.1. Wetting Behavior of Sn-Ti on Si3N4
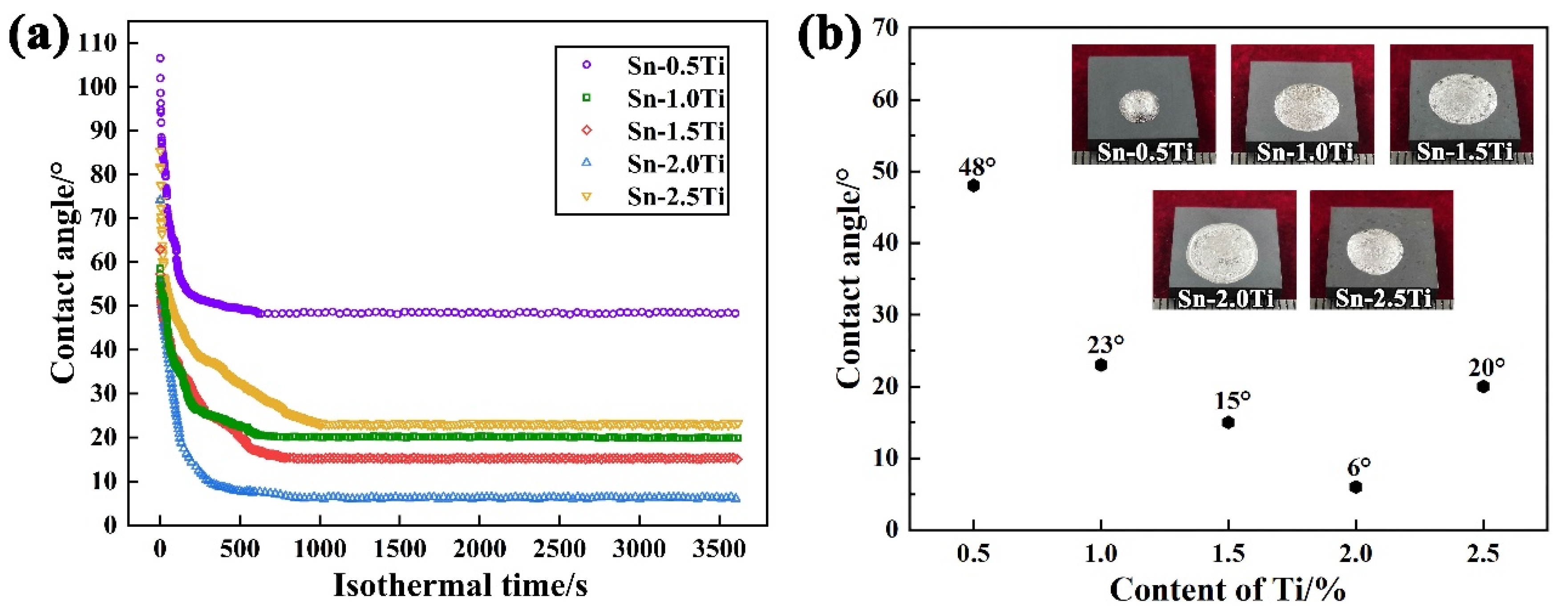
The effect of Ti concentration on the contact angle at 1273 K for Sn-xTi (x = 0.5, 1, 1.5, 2 and 2.5 wt.%) alloys on Si3N4 substrates at 1273 K is presented in Figure 2. The wetting process consists of two different stages, (1) rapid-spreading stage and (2) sluggish-spreading stage (Figure 2a). In the initial stage of the wetting experiment, the contact angle decreases sharply and then a slower decrease of the contact angle was observed.
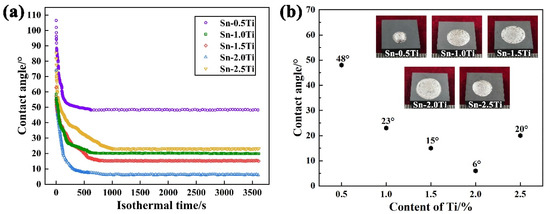
Figure 2.
Effect of Ti concentration on the contact angle at 1273 K. (a) Variation of contact angle with isothermal time, (b) final contact angle of different Ti content and the solid droplet at room temperature.
Generally, the spreading of Sn-Ti alloys on Si3N4 reaches equilibrium after 1000 s. As depicted in Figure 2b, value of the final contact angle decreases first and then increases with the increase of Ti addition in Sn-xTi alloys. As 0.5 at.% Ti is added into Sn matrix, the equilibrium contact angle of 48° is eventually obtained. In the range of 0.5–2.0% Ti, a higher improvement of wettability occurred as more Ti is introduced and the minimum contact angel of 6° is obtained using Sn-2.0Ti. While the final contact angle increases to 20° with the further increase of Ti content in Sn-2.5Ti/Si3N4 wetting system. Moreover, the spreading area of Sn-xTi melts on Si3N4 substrates has a trend of increasing first and then decreasing, which is corresponding to the evolution trend of contact angle.
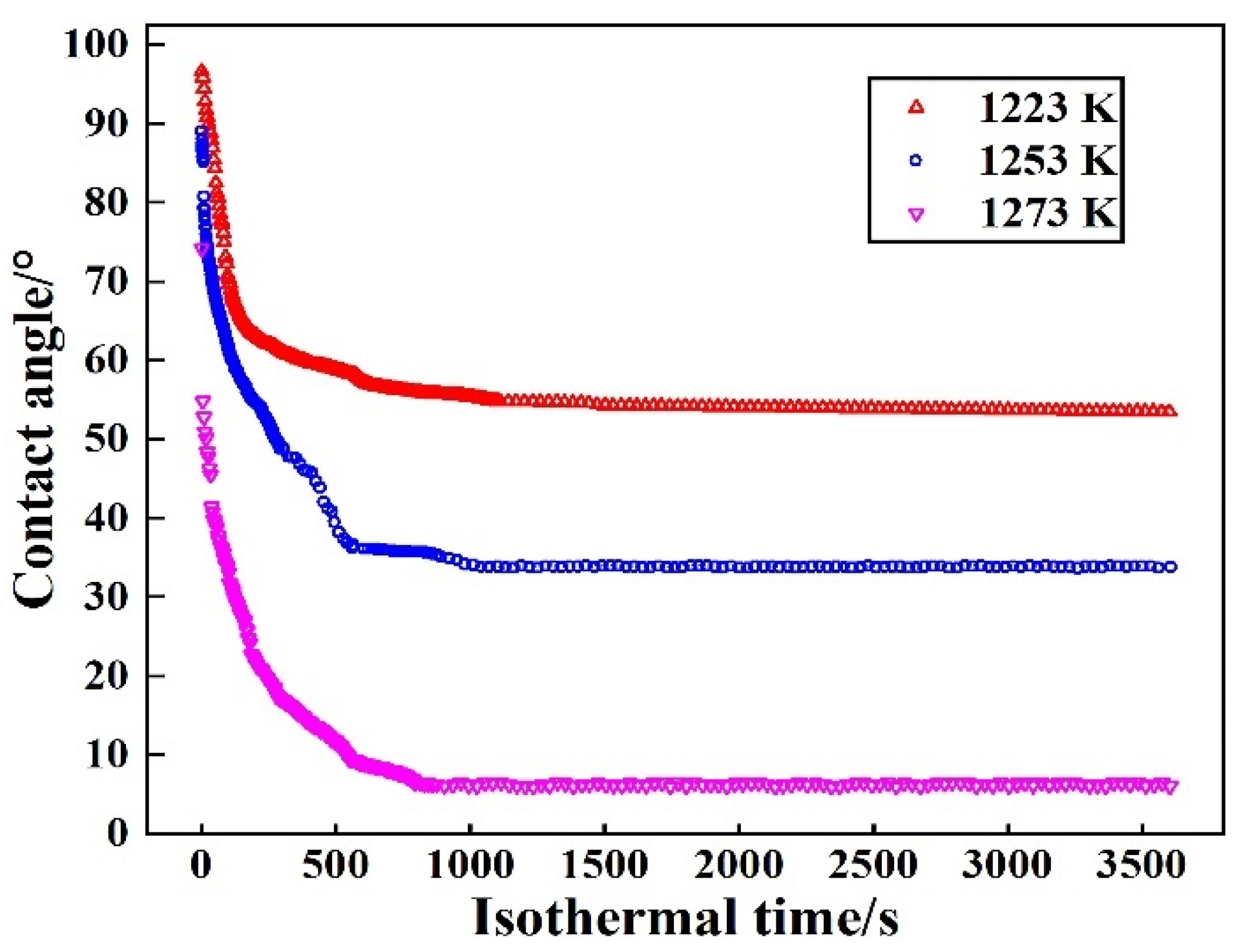
The isothermal wetting experiments to investigate the wetting behavior of Sn–2.0Ti/Si3N4 system were conducted at different temperatures (1223 K, 1253 K and 1273 K). The change of wetting behavior is related to the temperature. The value of different contact angles at various isothermal temperatures holding for 3600 s is shown in Figure 3.
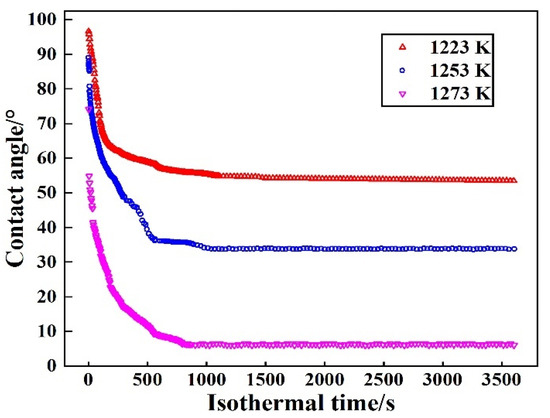
Figure 3.
Change of contact angle of Sn-2Ti/Si3N4 system at various isothermal temperatures.
The spreading process shows a similar trend as the results of the isothermal wetting tests for various Ti content at 1273 K, which consists of (1) rapid-spreading stage and (2) sluggish-spreading stage. Both of the wettability and the spreading rate of Sn-2.0Ti on Si3N4 is improved with the increase of isothermal temperature. The results reveal that isothermal temperature significantly influences the spreading behavior along with the final contact angles of Sn-Ti/Si3N4 system. The lowest contact angle and fastest spreading rate are obtained at 1273 K.
3.2. Interfacial Microstructure of Sn-xTi/Si3N4 Wetting System
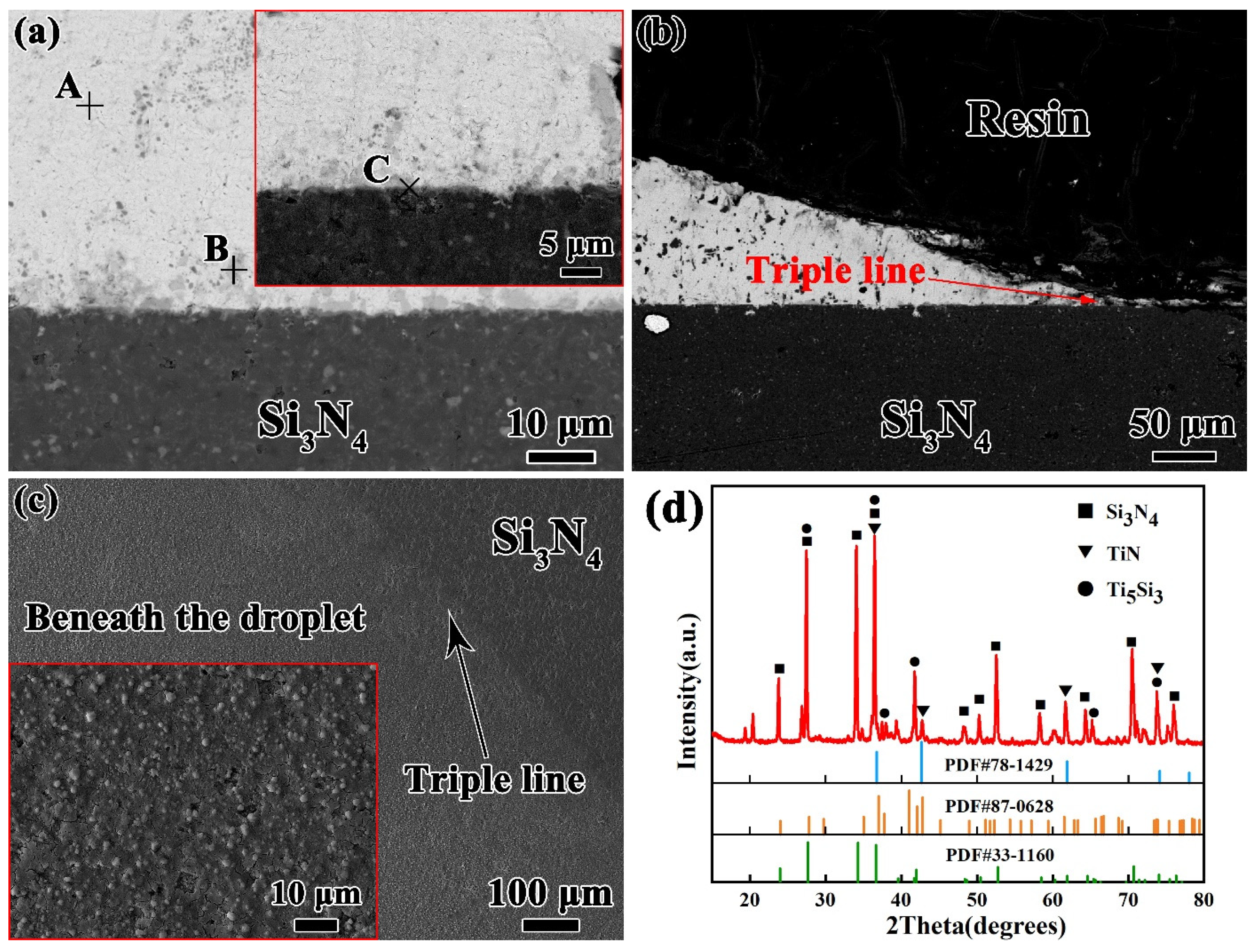
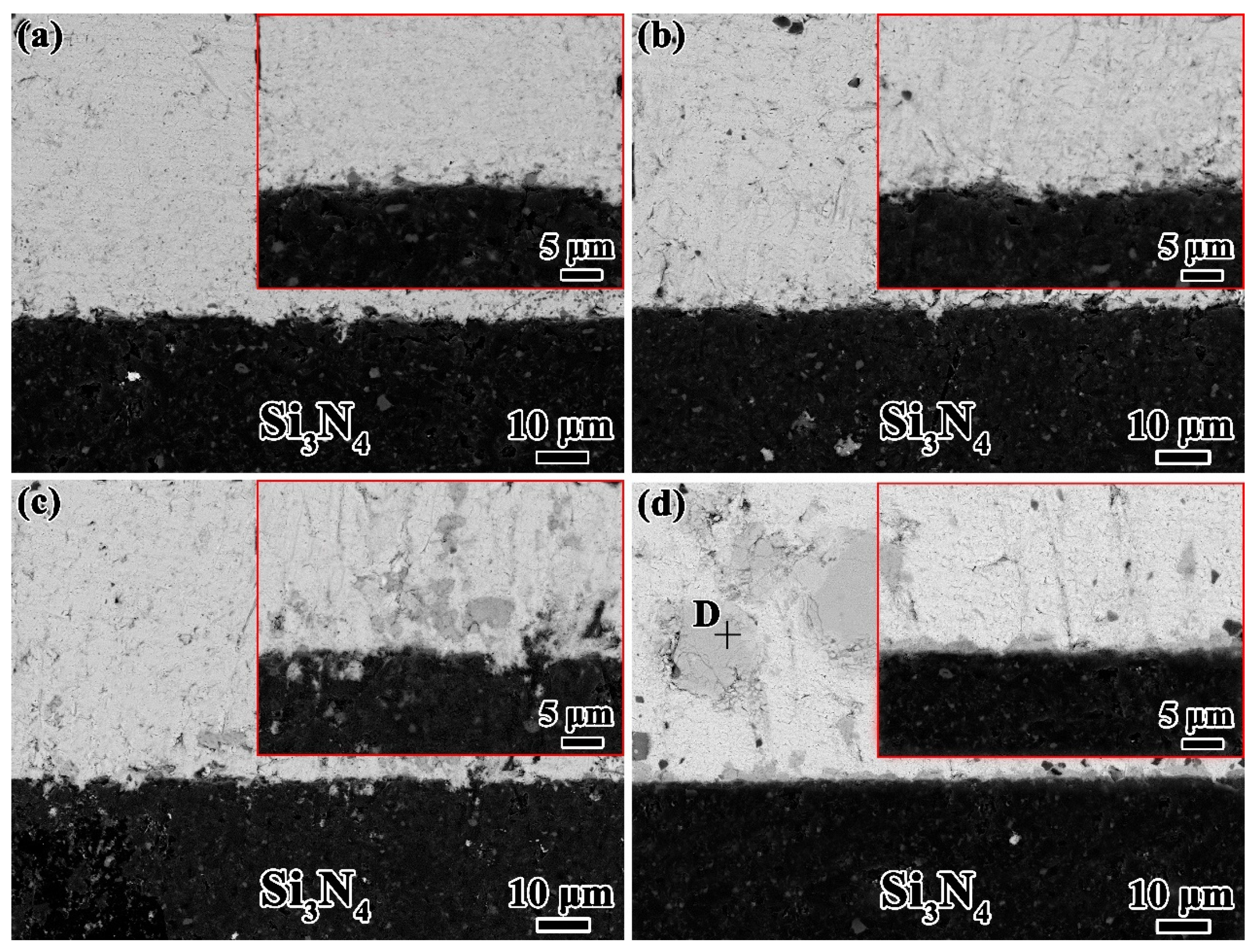
To further understanding the wetting process of Sn-xTi alloys on Si3N4 ceramic, the microstructure of Sn–2Ti/Si3N4 wetting system at 1273 K shown in Figure 4 is analyzed as the typical interface.
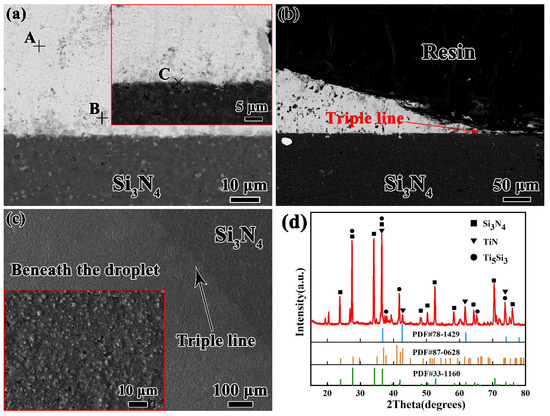
Figure 4.
Typical interfacial microstructure of Sn-2.0Ti/Si3N4 system at 1273K. (a) in middle area and (b) near triple line, (c) top review of reaction layer after etching off droplet, (d) XRD pattern of (c). (Si3N4 PDF#33-1160, TiN PDF#87-0628, Ti5Si3 PDF#78-1429).
According to the typical microstructures shown in Figure 4a and the corresponding EDS results and possible phase identification listed in Table 1, it reveals that the matrix of solid Sn-2Ti droplet is β-Sn and Ti6Sn5 phase distributes in Sn matrix. It seems that some Ti6Sn5 particles absorbed above the droplet/Si3N4 interface. A continuous reaction layer consisting of Ti-Si and Ti-N compounds in thickness of ~1 μm was formed at the interface. The distribution of Ti-N and Ti-Si compounds shows an intense reaction between active Ti and Si3N4 substrate at the interface. The microstructures near triple line, shown in Figure 4b is similar to that in the middle area of the droplet, which indicates that the horizontal growth of reaction later is uniform at the interface.

Table 1.
EDS results of the spots marked in SEM pictures. (wt.%).
Based on the EDS results, it can be seen that some Ti–N and Ti–Si compounds have formed at the interface. However, it is difficult to determine the interface reaction products. In order to make a further identification, the droplet was etched off by strong acid. The reaction layers were exposed and analyzed by X-ray diffusion. The morphology of interfacial layer shown in Figure 4c reveals that a continuous layer covers the Si3N4 substrate. The corresponding XRD result is shown in Figure 4d. It shows that the reaction layer includes Ti5Si3 phase and a small amount of TiN phase, which proves that the active Ti element has reacted with Si3N4 violently.
Respectively, Figure 5a–d shows the evolution of microstructure in Sn-xTi/Si3N4 (x = 0.5, 1.0, 1.5 and 2.5%) wetting systems, which indicates the effect of Ti content on the microstructures of Sn-Ti/Si3N4 interface. Obviously, good bonding between Sn-Ti droplet and Si3N4 substrate is obtained in all the wetting systems with various Ti content. With the increase of Ti concentration, the amount of Ti6Sn5 phases absorbed above the interface increases and the reaction layers covering the Si3N4 substrates thicken gradually, which corresponds to the research conducted by G. Blugan et al. [26] In particular, compared to the Sn-2.0Ti/Si3N4 system, Ti6Sn5 can hardly be found in the solidified Sn-0.5Ti and Sn-1.0Ti droplets shown in Figure 5a,b. The matrix of droplet is Sn and no obvious reaction layer can be observed at the interface. The dimension of Ti6Sn5 phase changes from small grains in Sn-1.5Ti droplet into large blocks in the solidified Sn-2.5Ti droplets (Figure 5c,d). Moreover, the continuous reaction layers are finally obtained when 2.5%Ti added. The thickness of reaction layer is less than 1μm, which are similar with that in Sn-2.0/Si3N4 system.
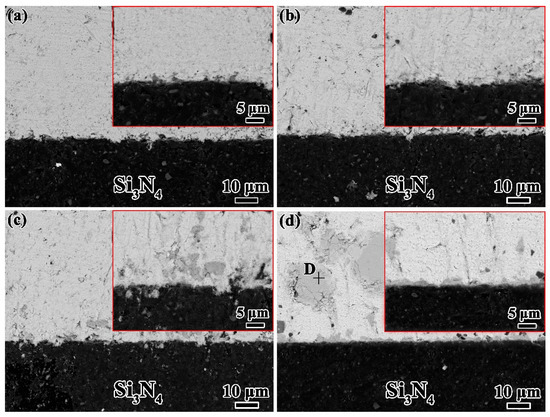
Figure 5.
Interfacial microstructures of various Sn-Ti/Si3N4 system at 1273K. (a) Sn-0.5Ti/Si3N4; (b) Sn-1.0Ti/Si3N4; (c) Sn-1.5Ti/Si3N4 and (d) Sn-2.5Ti/Si3N4.
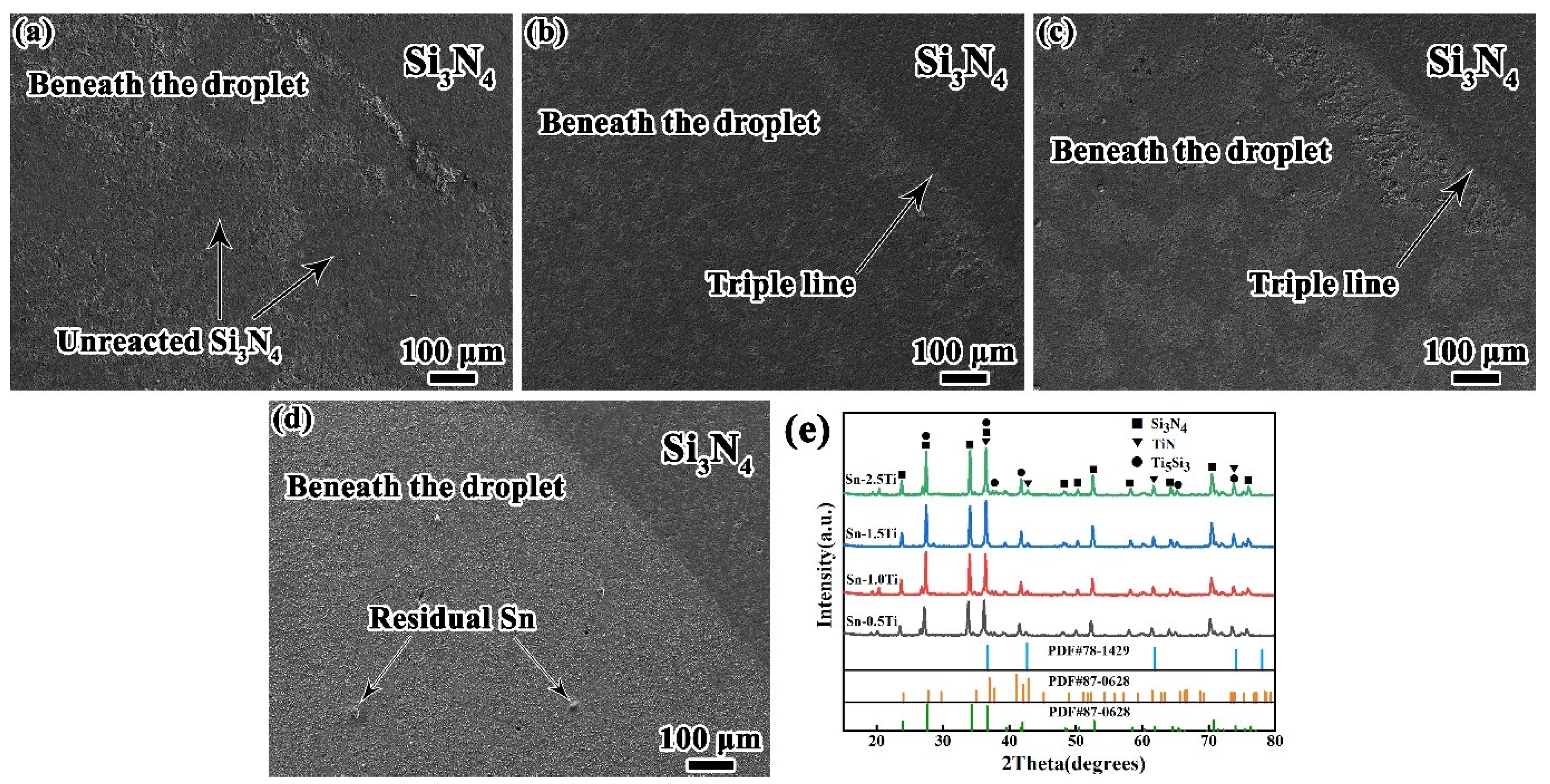
To identify the reaction products at the interface, the Sn-Ti droplets were etched off and the interfacial layers were analyzed by X-ray diffraction (XRD). As depicted in Figure 6. The reaction layer beneath droplets is formed by the white phases. According to Ref. [24], the reaction products are double-layered, consisting of the upper Ti5Si3 phase and the lower TiN phase, the composition of which is corresponding to the XRD results. For Sn-xTi/Si3N4 system (x = 0.5, 1.0 and 1.5 wt%), the richness of reaction products can be obviously observed at the triple line. With the increase of Ti concentration, the coverage of reaction products gradually increases, which corresponds to the evolution of cross-sectional microstructure shown in Figure 5. In the Sn-0.5Ti/Si3N4 system (Figure 6a), few reaction products are formed beneath the droplet. For the 1.0Ti/Si3N4 system, the reaction layers distribute on the Si3N4 substrate discontinuously. With Ti content increasing to 1.5%, more areas have been covered by the reaction products. Moreover, as the Ti content increasing to 2.5%, a continues reaction layer is observed in the Figure 6d. For all the Sn-Ti/Si3N4 wetting system, Ti5Si3 and TiN phases are detected at different Ti concentration. With more Ti element is added to Sn matrix, the diffraction peaks of Ti5Si3 and TiN become stronger at higher Ti content, which indicates that more reaction products is generated at interfacial layer. According to In addition, no new reaction products occurred at the interface because no new diffraction peaks are detected at various Ti content according to the XRD results.
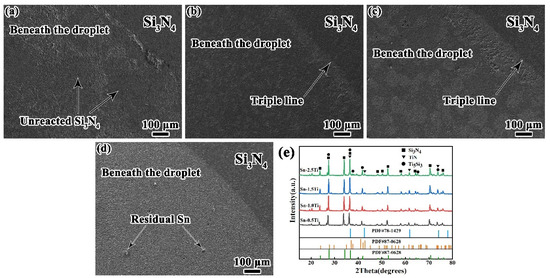
Figure 6.
Top observation of reaction layer after etching off Sn-Ti droplet, (a) Sn-0.5Ti/Si3N4; (b) Sn-1.0Ti/Si3N4; (c) Sn-1.5Ti/Si3N4, (d) Sn-2.5Ti/Si3N4, and (e) XRD patterns of (a–d). (Si3N4 PDF#33-1160, TiN PDF#87-0628, Ti5Si3 PDF#78-1429).
4. Discussion
4.1. Thermodynamic Analysis of Reactions between Sn-xTi and Si3N4
In different wetting experiments with various Ti content and temperature, the wetting behavior of Sn-xTi alloys on Si3N4 ceramic show different characteristics. The final contact angle changes from 48° to 6° ithin the level of Ti content reach 2.0% and then increases to 20° when 2.5%Ti is added. The lower temperature leads to an increase of the contact angle and spreading rate of Sn-Ti/Si3N4 system. With Ti content increasing, a constant reaction layer consisting of TiN and Ti5Si3 phases is observed at the interface. Apparently, the wettability of Sn-Ti on Si3N4 is influenced by interaction between Ti and Si3N4 substrate. After the interfacial reactions occurred, the interface between molten Sn-Ti and Si3N4 turned from Sn-Ti/Si3N4 to the Sn-Ti/reaction products. Consequently, the wettability is determined by the character of the reaction products layer at the interface [27]. To have a better understanding of the wetting behavior, it is significant to investigate the evolution of interfacial reactions.
The interfacial reaction between Sn-Ti melt and Si3N4 includes two main processes [23,28]: (1) the enriched Ti element at the interface reacts with Si3N4, forming the TiN layer and releasing Si into the melt. (2) Ti reacts with Si, generating Ti5Si3. Both TiN and Ti5Si3 formed almost simultaneously, in fact. The formation of TiN is deeply influenced by the concentration of Ti. The thermodynamic calculation of the reactions between Ti and Si3N4 was described as:
The Gibbs free energy of formation of TiN (ΔGr (1)) and Ti5Si3 (ΔGr (2)) at 1273 K can be calculated as:
where the is the standard Gibbs free energy for the formation of TiN and Ti5Si3, which have been reported as −562.1 kJ/mol and −168.6 kJ/mol at 1273 K [29], respectively. The activity of Ti element in molten Sn is denoted as:
where represents the concentration of Ti element in the Sn-Ti melt, represents the activity coefficient of Ti at infinite dilution in the liquid phase. Suppose that the melted Sn matrix is a regular solution, so the value of can be obtained by following calculation [30]:
where is the partial enthalpy of mixing of Ti in Sn solvent equaling to 74 kJ/mol, which is the value at infinitely dilution, . [31] The solubility of Ti element in the liquid Sn phase at 1273 K is acquired from the phase diagram [32]. The Gibbs free energy of reaction (1) and (2) can be calculated as Table 2. According to the calculation results, both of reaction (1) and (2) have the negative Gibbs free energy, indicating that both of the reactions are thermodynamically favorable. The results proves that TiN and Ti5Si3 can form at the interface. Moreover, the values of Gibbs free energy of reaction (1) are lower compared to reaction (2), which reveals that TiN phase tends to form preferentially [33]. The critical Ti concentration necessary for the interfacial reactions to occur can be calculated by the following formulas:
where the and is the molar Gibbs energy of the formation of TiN and Ti5Si3, respectively [34]. Assuming that the value of activity of Si3N4 () is 1, the concentration thresholds of Ti required for TiN and Ti5Si3 to generate are calculated to be 1.05 × 10−20 and 3.8 × 10−5, respectively, which is lower than the actual content of Ti element in the melt. This calculation result further provides the province for the formation of TiN and Ti5Si3 phases at the interface. Moreover, TiN phase can be preferentially generated than Ti5Si3 during the interfacial reaction process.

Table 2.
The results of Gibbs energy calculated of the formation of TiN and Ti5Si3 phases at 1273 K.
According to calculation, the process of interfacial reaction can be estimated. Once the molten Sn-Ti alloy contacts the Si3N4 substrate, the Ti element becomes enriched at the interface and reacts with Si3N4. With the formation of a reaction layer at the surface of Si3N4, the interface between liquid and solid turns from original Sn-Ti /Si3N4 into Sn-Ti/(TiN+Ti5Si3) interface. It is generally known that TiN and Ti5Si3 phases are equipped with metallic characteristics [35]. The previous work shows that compounds with metallic character can reduces the interfacial energy between ceramic and alloy melt. Therefore, the newly formed Sn-Ti/(TiN+Ti5Si3) interface leads to the decrease of the final contact angle. Meanwhile, the wettability is closely related to the amount of Ti element in Sn matrix. In the Sn-0.5Ti/Si3N4 wetting system, a discontinuous reaction layer form on the Si3N4 surface. Based on the Cassie wetting model [36], the equilibrium contact angle () can be evaluated as the following equation:
where is the rate of coverage of α phase, and and represent the final contact angle on α phase and β phase, respectively. Based on the former discussions, the α phase is the interfacial reaction layer consisting of TiN and Ti5Si3 phases, while the β phase is Si3N4 ceramic. Obviously, the higher coverage of reaction layer promotes the contact angle to decrease remarkably. With more Ti added, the continuous layers of TiN and Ti5Si3 phases form at the interface, which leads to a further decrease of contact angle. The lowest value of contact angle is 6°, which is observed in the Sn-2.0Ti/Si3N4 system, eventually. In conclusion, the interface exhibits a stronger metallic character with the increase of Ti content, in which way the wettability of Sn-Ti alloy on Si3N4 ceramic is further improved. Specially, a higher equilibrium contact angle is founded in Sn-2.5Ti/Si3N4 wetting system at 1273 K. It has been reported that intermetallic can increase the viscosity of the melt [37]. Thus, the increase of contact angle is likely due to the attendance of the large block of Ti6Sn5 phase when 2.5Ti is introduces (as shown in Figure 5d), which hinders the movement of the active element towards the edge and impairs the spreading capacity of liquid. In short, the final contact angle is mainly determined by the adequacy of the interfacial reaction and is partly influenced by the viscosity of liquid droplets.
4.2. Spreading Kinetics and Mechanism
According to the previous discussions, the formation of interfacial products result in the improve of final equilibrium wettability and the extraordinary diminishing of the contact angle from 48° to 6°. Therefore, the wetting mechanism of the Sn-Ti on Si3N4 can be depicted by reaction-driven wetting theory. The reaction-limited wetting model [38] is given to express the process:
where , and represent the value of initial, equilibrium and dynamic contact angle, respectively, and is the dynamic constant connected with the activity of element in reactions and the experimental temperature.
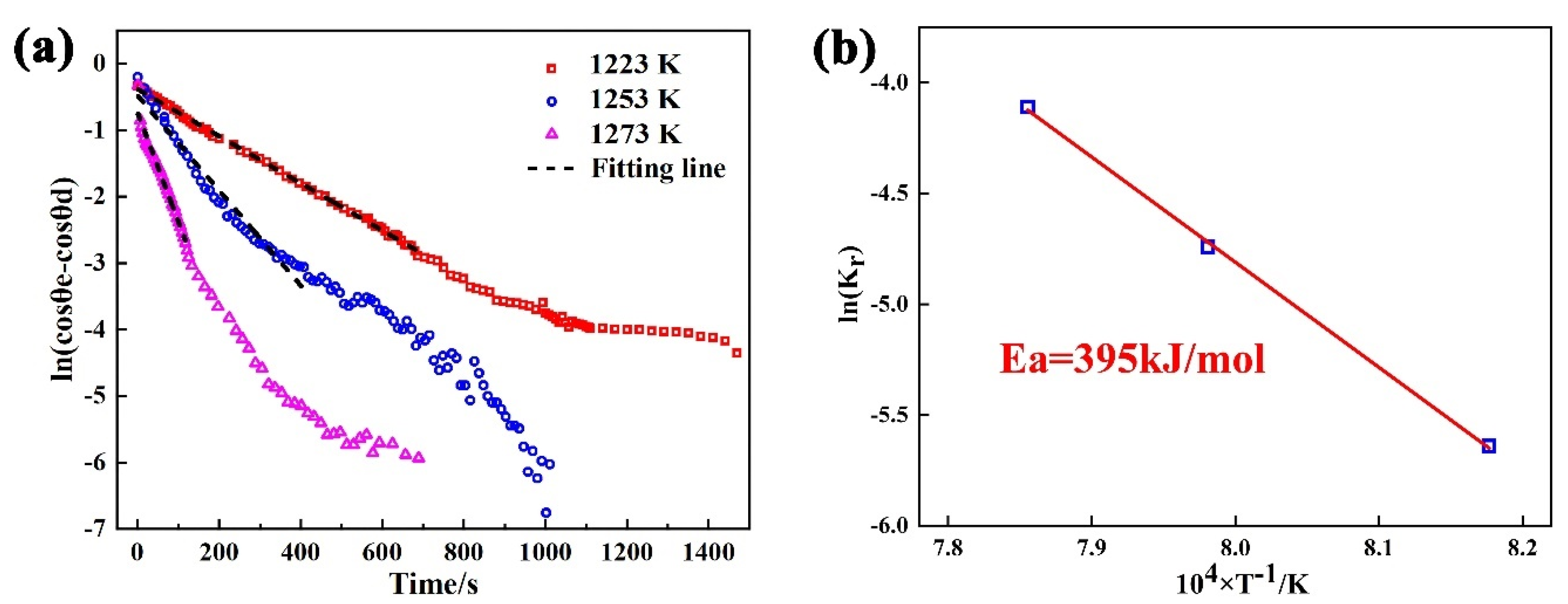
The spreading kinetics for the Sn-Ti/Si3N4 system can be evaluated by Equation (10). Changes in the value of with isothermal time at 1223 K–1273 K and the fitting line are shown in Figure 7a. According to the fitting results, the values of are 2.3 × 10−3, 1.8 × 10−2, and 7.8 × 10−2 at 1223 K, 1253 K, and 1273 K, respectively. Obviously, increases with the increase of experimental temperature, revealing that the spreading process is deeply influenced by isothermal temperature. Based on Arrhenius law and the calculated value of [38], the calculation result for the activation energy of the spreading of Sn-2Ti/Si3N4 system is 395 kJ/mol (Figure 7b), which further verifies the reaction-controlled spreading at triple line.
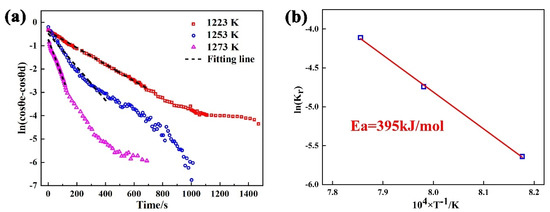
Figure 7.
(a) Logarithm of versus time for Sn-2Ti/Si3N4 at 1223–1273 K, (b) Arrhenius plot of the kinetic constant.
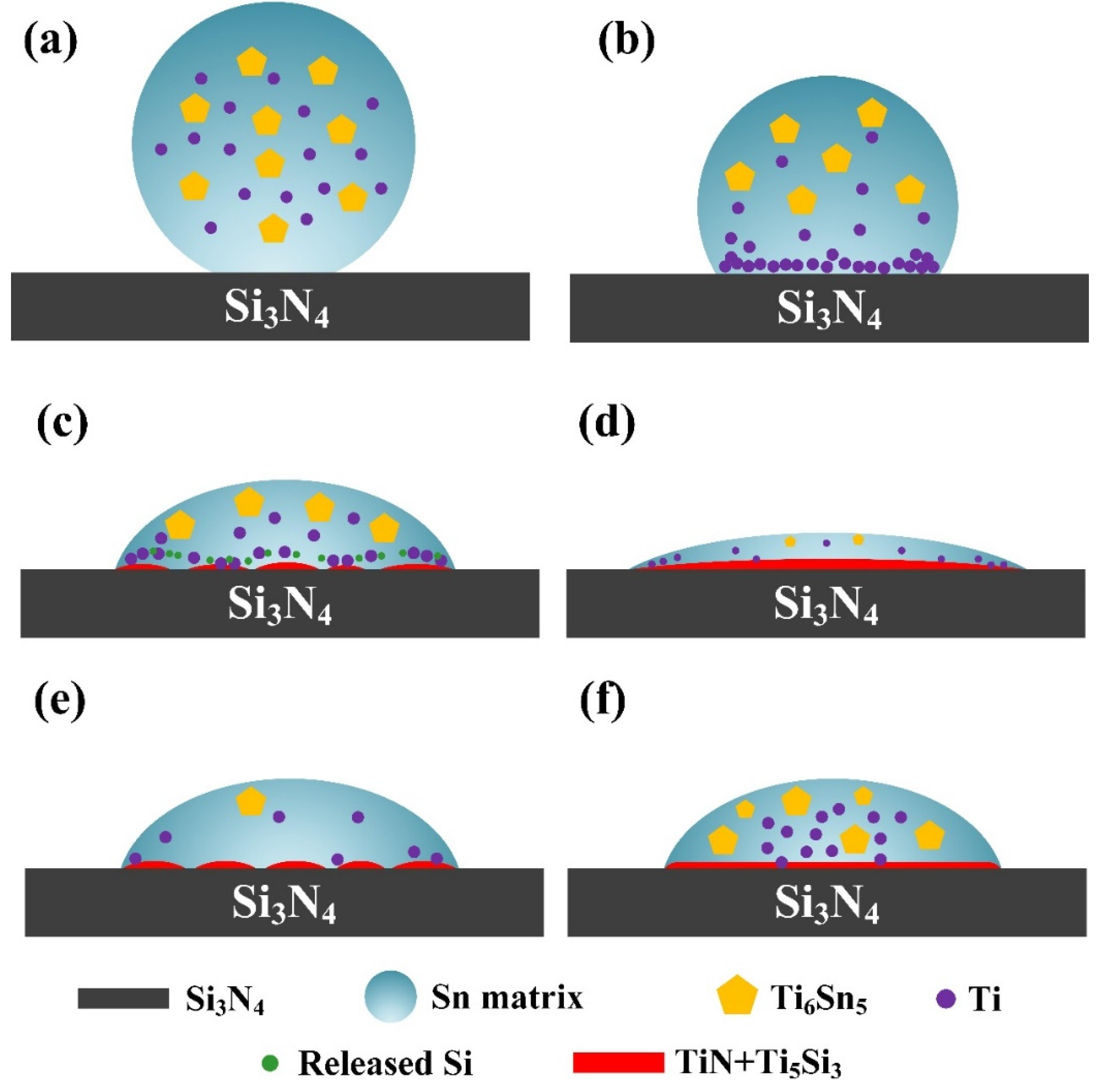
According to the analysis above, the wetting mechanism of Sn-Ti alloy on Si3N4 ceramic can be illustrated as Figure 8. Take the Sn-2Ti/Si3N4 wetting system at 1273 K as an example (Figure 8a–d), at the beginning stage of wetting, Sn-Ti alloy begins to melt on the surface of Si3N4 substrate and Ti element is released from Ti6Sn5 (as shown in Figure 8a). Because of the relatively high activity of Ti in the melted Sn phase, Ti starts to enrich at the interface between Si3N4 and molten droplet. In this stage, the concentration of Ti element is at a high level so that plenty of Ti can diffuse towards the triple line (Figure 8b). According to the previous calculation result, the content of Ti element is sufficient for the interface reaction to occur. Immediately, Ti reacts with Si3N4 substrate and TiN phase forms at the interface between Sn-Ti droplet and Si3N4, during which free Si is released into Sn melt. Along with the formation of TiN, Ti also reacts with the released Si and generates Ti5Si3 phase. The metallic character of TiN and Ti5Si3 phase decreases the interfacial energy between Sn melt and Si3N4 ceramic, which accounts for the improvement of wettability of liquid Sn phase on Si3N4 surface (Figure 8c). With the reaction and spreading process further proceeding, the reaction layer gradually becomes continues and more active Ti is consumed in reaction. Additionally, the movement of triple line increases the diffusion distance of Ti, which results in the limited reaction near the triple line. As a consequence, the spreading slows down because of the decrease of Ti concentration and the increase of diffusion distance. (Figure 8d). When the concentration of Ti is lower than 2% (Figure 8e), the weakness of active Ti limits the further reaction at the interface and hinders the spreading of droplet. In Sn-2.5Ti system (Figure 8f), the spreading process is limited by the appearance of large Ti6Sn5 bulks which decrease the fluidity of Sn-Ti melt. Moreover, the higher temperature mainly increases the identity of the reactions at triple line, which improves the wettability of droplet.
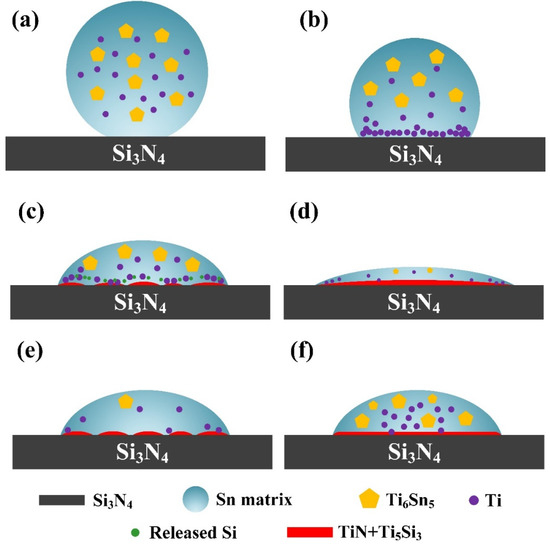
Figure 8.
Wetting mechanism of Sn-xTi/Si3N4 system. (a) Beginning stage of wetting. (b) Enrich of Ti element at the beginning of rapid-spreading stage. (c) Improvement of wettability with the formation of TiN+Ti5Si3 phases at the interface. (d) Further spreading with the formation of continuous reaction layer. (e) Limited interfacial reaction caused by the lack of active Ti. (f) Limited wetting process due to the large bulk of Ti6Sn5 phase.
5. Conclusions
The wetting and spreading behavior of Si3N4 substrates by Sn-Ti alloys was investigated through the modified sessile drop method. The concentration of added Ti significantly affects the wettability of Sn-Ti alloy on Si3N4 by affecting the reactions at the interface. The interfacial microstructure are analyzed and spreading kinetics are calculated. Some conclusions in detail can be drawn as follows:
- 1.
- As Ti element is added, the contact angle of Sn on Si3N4 is dramatically decreased due to the metallic TiN and Ti5Si3 phases formed by reactions between Ti and Si3N4. With a higher Ti concentration, the reaction layer thickens and the final contact angle becomes lower. The lowest value θ = 6o was achieved in Sn-2Ti system. However, the final contact increases when 2.5Ti is added, resulting from the resistance caused by large Ti6Sn5 bulks.
- 2.
- The Ti element reacts with Si3N4 to form the TiN phase, releasing free Si, then the free Si element reacts with active Ti to generate the Ti5Si3 layer. As the addition of Ti increases, coverage of the reaction products on substrates increases gradually. When Ti content is lower than 2.0 wt. %, the discontinuous reaction layers beneath the droplets and the richness of reaction products near the triple line can be observed. The continuous reaction layers are obtained in Sn-2.0Ti and Sn-2.5Ti/Si3N4 wetting systems.
- 3.
- The whole wetting process can be split into two different stages: (i) rapid-spreading and (ii) sluggish-decrease. In the first stage, adequate active Ti diffuses towards the triple line and react with the Si3N4 substrate. Consequently, a fast-spreading process of melted Sn droplet on Si3N4 is obtained. During the following isothermal stage, sufficient active Ti element is consumed by the interfacial reaction and the triple line keeps moving. The lower Ti content and the further distance from the middle area to the edge hinder the diffusion of Ti towards the triple line. Therefore, the sluggish spreading stage is observed because of the weaker reaction.
- 4.
- Temperature presents an immense effect on the spreading process. The spreading kinetic constant increases from 2.3 × 10−3 to 7.8 × 10−2 with isothermal temperature changing from 1223 K to 1273 K. The spreading activation energy for the Sn-Ti alloy on Si3N4 is calculated to be 395 kJ/mol. This work can provide a reference for the addition of active Ti elements during the metallization and brazing process of Si3N4 ceramics with other metals, which can be beneficial for the performance of the metal/ceramic joints.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, W.F.; methodology, H.W.; software, Y.X.; validation, M.G.; formal analysis, M.G.; investigation, H.W.; resources, S.H. (Shihui Huo); data curation, H.W.; writing—original draft preparation, H.W.; writing—review and editing, W.F.; visualization, Y.X.; supervision, S.H. (Shengpeng Hu); project administration, X.S.; funding acquisition, W.F. and X.S. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This project is supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (grant Nos. 52175307, 52105330 and 52005385); the Natural Science Foundation of Shandong Province (Nos. ZR2020QE175 and ZR2019PEE042) and the Taishan Scholars Foundation of Shandong Province (No. tsqn201812128).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
The authors gratefully acknowledge the financial support from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (grant Nos. 52175307, 52105330 and 52005385); the Natural Science Foundation of Shandong Province (Nos. ZR2020QE175 and ZR2019PEE042) and the Taishan Scholars Foundation of Shandong Province (No. tsqn201812128).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Song, Y.; Liu, D.; Jin, G.; Zhu, H.; Chen, N.; Hu, S.; Song, X.; Cao, J. Fabrication of Si3N4/Cu direct-bonded heterogeneous interface assisted by laser irradiation. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2022, 99, 169–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gui, X.; Zhang, M.; Xu, P.; Liu, G.; Guo, Q.; Zhang, X.; Meng, H.; Qiao, G. Experimental and theoretical study on air reaction wetting and brazing of Si3N4 ceramic by Ag-CuO filler metal: Performance and interfacial behavior. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2022, 42, 432–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Zhang, C.; Li, D.; Xie, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Lu, X. Wettability and interfacial reaction mechanism between Ag–Cu alloy and Si3N4 ceramics in air atmosphere. Ceram. Int. 2021, 47, 33078–33088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.M.; Zhang, J.; Liu, C.F.; Sun, Y. Microstructure and mechanical properties of Si3N4/Si3N4 joint brazed with Ag–Cu–Ti+SiCp composite filler. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2010, 527, 2819–2825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fei, S.O.; Tobe, H.; Fujii, G.; Sato, E. Microstructural evolution and mechanical characterization of Nb-interlayer-inserted Ti–6Al–4V/Si3N4 joints brazed with AuNiTi filler. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2020, 778, 139093. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Y.X.; Wang, M.R.; Cao, J.; Song, X.G.; Tang, D.Y.; Feng, J.C. Brazing TC4 alloy to Si3N4 ceramic using nano-Si3N4 reinforced AgCu composite filler. Mater. Des. 2015, 76, 40–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Yao, D.; Chen, H.; Xia, Y.; Zuo, K.; Yin, J.; Liang, H.; Zeng, Y.P. ZrSi2–MgO as novel additives for high thermal conductivity of β-Si3N4 ceramics. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2020, 103, 2090–2100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.F.; Zhang, J.; Zhou, Y.; Meng, Q.C.; Naka, M. Effect of Ti content on microstructure and strength of Si3N4/Si3N4 joints brazed with Cu–Pd–Ti filler metals. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2008, 491, 483–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Dong, D.; Yang, X.; Huang, P.; Shi, K.; Ma, T.; Zhu, D.; Liu, L. Microstructure and Shear Strength of Brazing High Entropy TiZrHfNbMo Alloy and Si3N4 Ceramics Joints. Crystals 2021, 11, 472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elsawy, A.; Fahmy, M. Brazing of Si3N4 ceramic to copper. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 1998, 77, 266–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Si, X.; Li, C.; Cao, J. Reactive Air Brazing of TiAl Alloy Using Ag-CuO: Microstructure and Joint Properties. Crystals 2021, 11, 1496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, B.; Li, T.; Zhang, H.; Hou, J. Interface Behavior of Brazing between Zr-Cu Filler Metal and SiC Ceramic. Crystals 2021, 11, 727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, W.; Song, X.G.; Zhao, Y.X.; Cao, J.; Feng, J.C.; Jin, C.; Wang, G.D. Effect of Ti content on the wetting behavior of Sn0.3Ag0.7Cu/AlN system. Mater. Des. 2017, 115, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, M.; Fan, Z.; Fu, W.; Wang, Q.; Hu, S.; Song, X. Effect of Cr content on the wetting behavior of Cu–Cr/SiC system. Vacuum 2021, 194, 110591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ceccone, G.; Nicholas, M.; Peteves, S.; Kodentsov, A.; Kivilahti, J.; Van Loo, F. The brazing of Si3N4 with Ni-Cr-Si alloys. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 1995, 15, 563–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fan, Z.; Guo, M.; Fu, W.; Xue, Y.; Hu, S.; Song, X. Wettability and spreading behavior of Sn–Cr alloys on SiC. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2021, 272, 124979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simhan, D.R.; Ghosh, A. Vacuum brazing of cubic boron nitride to medium carbon steel with Zr added passive and Ti activated eutectic Ag-Cu alloys. Ceram. Int. 2018, 44, 4891–4899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, W.; Passerone, A.; Bian, H.; Hu, S.; Zhao, Y.; Song, X.; Wang, M.; Valenza, F. Wetting and interfacial behavior of Sn–Ti alloys on zirconia. J. Mater. Sci. 2018, 54, 812–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.K.; Lee, J.Y. A study of the wetting, microstructure and bond strength in brazing SiC by Cu-X (X = Ti, V, Nb, Cr) alloys. J. Mater. Sci. 1996, 31, 4133–4140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Huang, J.; Ye, Z.; Chen, S.; Ji, R.; Zhao, Y. Influence of interfacial reaction on reactive wettability of molten Ag-Cu-X wt.%Ti filler metal on SiC ceramic substrate and mechanism analysis. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2018, 436, 768–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, X.; Passerone, A.; Fu, W.; Hu, S.; Niu, C.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, M.; Valenza, F. Wetting and spreading behavior of Sn–Ti alloys on SiC. Materialia 2018, 3, 57–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luz, A.P.; Ribeiro, S. Wetting behaviour of silicon nitride ceramics by Ti–Cu alloys. Ceram. Int. 2008, 34, 305–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, X.; Zhao, Y.; Hu, S.; Cao, J.; Fu, W.; Feng, J. Wetting of AgCu-Ti filler on porous Si3N4 ceramic and brazing of the ceramic to TiAl alloy. Ceram. Int. 2018, 44, 4622–4629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nomura, M.; Iwamoto, C.; Tanaka, S.I. Nanostructure of wetting triple line in a Ag–Cu–Ti/Si3N4 reactive system. Acta Mater. 1999, 47, 407–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liggieri, L.; Passerone, A. An automatic technique for measuring the surface tension of liquid metals. High Temp. Technol. 1989, 7, 82–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blugan, G.; Janczak-Rusch, J.; Kuebler, J. Properties and fractography of Si3N4/TiN ceramic joined to steel with active single layer and double layer braze filler alloys. Acta Mater. 2004, 52, 4579–4588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kritsalis, P.; Drevet, B.; Valignat, N.; Eustathopoulos, N. Wetting transitions in reactive metal/oxide systems. Scr. Metall. Mater. 1994, 30, 1127–1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Liu, J.; Wang, T. Microstructure and brazing mechanism of porous Si3N4/Invar joint brazed with Ag-Cu-Ti/Cu/Ag-Cu multi-layered filler. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2018, 34, 713–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barin, I.; Platzki, G. Thermochemical Data of Pure Substances; Wiley Online Library: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1989; Volume 304. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, L.; Shen, P.; Lin, Q.; Qiu, F.; Jiang, Q. Effect of Cr on the wetting in Cu/graphite system. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2011, 257, 6276–6281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eustathopoulos, N.; Nicholas, M.G.; Drevet, B. Wettability at High Temperatures; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Okamoto, H. Sn-Ti (tin-titanium). J. Phase Equilibria Diffus. 2010, 31, 202–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, J.; Jiang, Z.; Zhao, Q.; Chen, Z. Brazing of Si3N4 with amorphous Ti40Zr25Ni15Cu20 filler. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2009, 507, 155–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, W.; Song, X.; Tian, R.; Lei, Y.; Long, W.; Zhong, S.; Feng, J. Wettability and joining of SiC by Sn-Ti: Microstructure and mechanical properties. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2020, 40, 15–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, D.; Shen, Y.; Lu, Z. Preparation of TiN–Ti5Si3 in-situ composites by selective laser melting. Mater. Lett. 2009, 63, 1577–1579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cassie, A.B.D.; Baxter, S. Wettability of porous surfaces. Trans. Faraday Soc. 1944, 40, 546–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, W.; Hu, S.; Song, X.; Li, J.; Cao, J.; Feng, J.; Wang, G. Wettability and bonding of graphite by Sn0.3Ag0.7Cu-Ti alloys. Carbon 2017, 121, 536–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dezellus, O.; Hodaj, F.; Eustathopoulos, N. Chemical reaction-limited spreading: The triple line velocity versus contact angle relation. Acta Mater. 2002, 50, 4741–4753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).