Numerical Studies of Batch and Inline High Shear Melt Conditioning Technology Using Different Rotors
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Method
2.1. Numerical Method
2.2. Geometry
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Mesh Independence
3.2. Validation with Experimental Data
3.3. Flow Field
3.4. Turbulence Kinetic Viscosity
3.5. Strain Rate
3.6. Volume Flow Rate
3.7. Power Number
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Polmear, I.; St. John, D.; Nie, J.F.; Qian, M. Light Alloys: Metallurgy of the Light Metals, 5th ed.; Butterworth-Heinemann: Oxford, UK, 2017; ISBN 9780080994307. [Google Scholar]
- Campbell, J. An Overview of the Effects of Bifilms on the Structure and Properties of Cast Alloys. Metall. Mater. Trans. B Process Metall. Mater. Process. Sci. 2006, 37, 857–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eskin, D.G.; Tzanakis, I.; Wang, F.; Lebon, G.S.B.; Subroto, T.; Pericleous, K.; Mi, J. Fundamental Studies of Ultrasonic Melt Processing. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2019, 52, 455–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vatansever, F.; Ertürk, A.T.; Karabay, S. Improving Mechanical Properties of AlSi10Mg Aluminum Alloy Using Ultrasonic Melt Treatment Combined with T6 Heat Treatment. Kov. Mater. 2019, 57, 33–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eskin, G.I.; Eskin, D.G. Ultrasonic Treatment of Light Alloy Melts, 2nd ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Tonry, C.E.H.; Djambazov, G.; Dybalska, A.; Griffiths, W.D.; Beckwith, C.; Bojarevics, V.; Pericleous, K.A. Acoustic Resonance for Contactless Ultrasonic Cavitation in Alloy Melts. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2020, 63, 104959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dybalska, A.; Caden, A.; Griffiths, W.D.; Nashwan, Z.; Bojarevics, V.; Djambazov, G.; Tonry, C.E.H.; Pericleous, K.A. Enhancement of Mechanical Properties of Pure Aluminium through Contactless Melt Sonicating Treatment. Materials 2021, 14, 4479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, J.; Zuo, Y.; Fan, Z. Liquid Metal Engineering by Application of Intensive Melt Shearing. In Proceedings of the International Symposium on Liquid Metal Processing and Casting 2013, LMPC 2013, Austin, TX, USA, 22–25 September 2013; Krane, M.J.M., Jardy, A., Williamson, R.L., Beaman, J.J., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2013; pp. 291–299, ISBN 9781510814400. [Google Scholar]
- Patel, J.B.; Yang, X.; Mendis, C.L.; Fan, Z. Melt Conditioning of Light Metals by Application of High Shear for Improved Microstructure and Defect Control. JOM 2017, 69, 1071–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Z.; Wang, Y.; Xia, M.; Arumuganathar, S. Enhanced Heterogeneous Nucleation in AZ91D Alloy by Intensive Melt Shearing. Acta Mater. 2009, 57, 4891–4901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, S.; Prasada Rao, A.K.; Fan, Z. Melt Conditioned Direct Chill (MC-DC) Casting of Al Alloys. Trans. Indian Inst. Met. 2013, 66, 117–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Men, H.; Jiang, B.; Fan, Z. Mechanisms of Grain Refinement by Intensive Shearing of AZ91 Alloy Melt. Acta Mater. 2010, 58, 6526–6534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.T.; Zhao, P.; Yang, R.; Patel, J.B.; Chen, X.; Fan, Z. Grain Refinement and Improvement of Solidification Defects in Direct-Chill Cast Billets of A4032 Alloy by Melt Conditioning. Metall. Mater. Trans. B Process Metall. Mater. Process. Sci. 2017, 48, 2481–2492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Y.; Patel, J.B.; Lazaro-Nebreda, J.; Fan, Z. Improved Defect Control and Mechanical Property Variation in High-Pressure Die Casting of A380 Alloy by High Shear Melt Conditioning. JOM 2018, 70, 2726–2730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lebon, G.S.B.; Li, H.T.; Patel, J.B.; Assadi, H.; Fan, Z. Numerical Modelling of Melt-Conditioned Direct-Chill Casting. Appl. Math. Model. 2020, 77, 1310–1330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazaro-Nebreda, J.; Patel, J.B.; Chang, I.T.H.; Stone, I.C.; Fan, Z. Solidification Processing of Scrap Al-Alloys Containing High Levels of Fe. In Proceedings of the Joint 5th International Conference on Advances in Solidification Processes (ICASP-5) & 5th International Symposium on Cutting Edge of Computer Simulation of Solidification, Casting and Refining (CSSCR-5), Salzburg, Austria, 17–21 June 2019; IOP Publishing: Bristol, UK, 2019; Volume 529. [Google Scholar]
- Lazaro-Nebreda, J.; Patel, J.B.; Scamans, G.M.; Fan, Z. Multi-Purpose High Shear Melt Conditioning Technology for Effective Melt Quality and for Recycling of Al Alloy Scrap. In Proceedings of the 16th International Aluminium Alloys Conference (ICAA16), Montreal, QC, Canada, 17–21 June 2018; p. 401623. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Helal, K.; Lazaro-Nebreda, J.; Patel, J.B.; Scamans, G.M. High-Shear de-Gassing and de-Ironing of an Aluminum Casting Alloy Made Directly from Aluminum End-of-Life Vehicle Scrap. Recycling 2021, 6, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Utomo, A. Flow Patterns and Energy Dissipation Rates in Batch Rotor-Stator Mixers. Ph.D. Thesis, The University of Birmingham, Birmingham, UK, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Doucet, L.; Ascanio, G.; Tanguy, P.A. Hydrodynamics Characterization of Rotor-Stator Mixer with Viscous Fluids. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2005, 83, 1186–1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Håkansson, A. Rotor-Stator Mixers: From Batch to Continuous Mode of Operation-A Review. Processes 2018, 6, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barailler, F.; Heniche, M.; Tanguy, P.A. CFD Analysis of a Rotor-Stator Mixer with Viscous Fluids. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2006, 61, 2888–2894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Utomo, A.T.; Baker, M.; Pacek, A.W. Flow Pattern, Periodicity and Energy Dissipation in a Batch Rotor-Stator Mixer. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2008, 86, 1397–1409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Utomo, A.; Baker, M.; Pacek, A.W. The Effect of Stator Geometry on the Flow Pattern and Energy Dissipation Rate in a Rotor-Stator Mixer. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2009, 87, 533–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lebon, G.S.B.; Lazaro-Nebreda, J.; Patel, J.B.; Fan, Z. Numerical Assessment of in-Line Rotor–Stator Mixers in High-Shear Melt Conditioning (HSMC) Technology. JOM 2020, 72, 4092–4100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vikash; Deshawar, D.; Kumar, V. Hydrodynamics and Mixing Characterization in a Novel High Shear Mixer. Chem. Eng. Process. Process Intensif. 2017, 120, 57–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, M.; Patel, J.B.; Stone, I.; Fan, Z.; Browne, D.J. Identification of Key Liquid Metal Flow Features in the Physical Conditioning of Molten Aluminium Alloy with High Shear Processing. Comput. Mater. Sci. 2017, 131, 35–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weller, H.G. OpenFOAM. 2022. Available online: https://openfoam.org/download/7-source/ (accessed on 12 September 2022).
- Menter, F.R.; Kuntz, M.; Langtry, R. Ten Years of Industrial Experience with the SST Turbulence Model. Turbul. Heat Mass Transf. 2003, 4, 625–632. [Google Scholar]
- Issa, R.I. Solution of the Implicitly Discretised Fluid Flow Equations by Operator-Splitting. J. Comput. Phys. 1986, 62, 40–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caretto, L.S.; Gosman, A.D.; Patankar, S.V.; Spalding, D.B. Two Calculation Procedures for Steady, Three-Dimensional Flows with Recirculation. In Proceedings of the Third International Conference on Numerical Methods In Fluid Mechanics; Lecture Notes in Physics. Cabannes, H., Temam, R., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1973; Volume 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tzanakis, I.; Lebon, G.S.B.; Eskin, D.G.; Pericleous, K.A. Characterizing the Cavitation Development and Acoustic Spectrum in Various Liquids. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2017, 34, 651–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dybalska, A.; Eskin, D.G.; Patel, J.B. Optimal Stator Design for Oxide Films Shearing Found by Physical Modelling. In Minerals, Metals and Materials Series; Lambotte, G., Lee, J., Allanore, A., Wagstaff, S., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; pp. 181–192. ISBN 9783030057275. [Google Scholar]
- Ribes, A.; Caremoli, C. Salomé Platform Component Model for Numerical Simulation. In Proceedings of the International Computer Software and Applications Conference, Beijing, China, 24–27 July 2007; Volume 2. [Google Scholar]
- Murthy, J.; Mathur, S.; Choudhary, D. CFD Simulation of Flows in Stirred Tank Reactors Using a Sliding Mesh Technique. In Proceedings of the 8th European Conference of Mixing, Cambridge, UK, 21–23 September 1994; Volume 136, pp. 155–162. [Google Scholar]
- Vikash; Kumar, V. Turbulent Statistics of Flow Fields Using Large Eddy Simulations in Batch High Shear Mixers. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2019, 147, 561–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padron, G.A. Measurement and Comparison of Power Draw in Batch Rotor-Stator Mixers. Master’s Thesis, University of Maryland, College Park, MD, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Murthy, S.; Jayanti, S. CFD Study of Power and Mixing Time for Paddle Mixing in Unbaffled Vessels. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2002, 80, 482–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

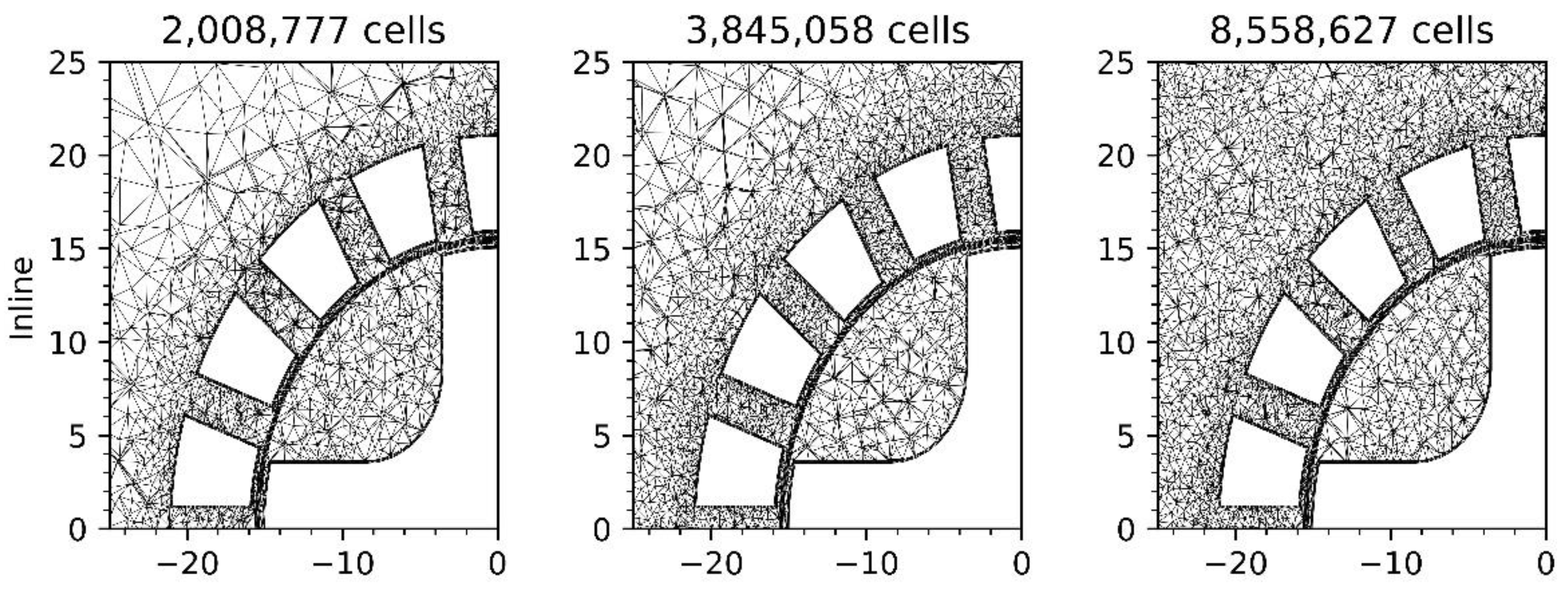

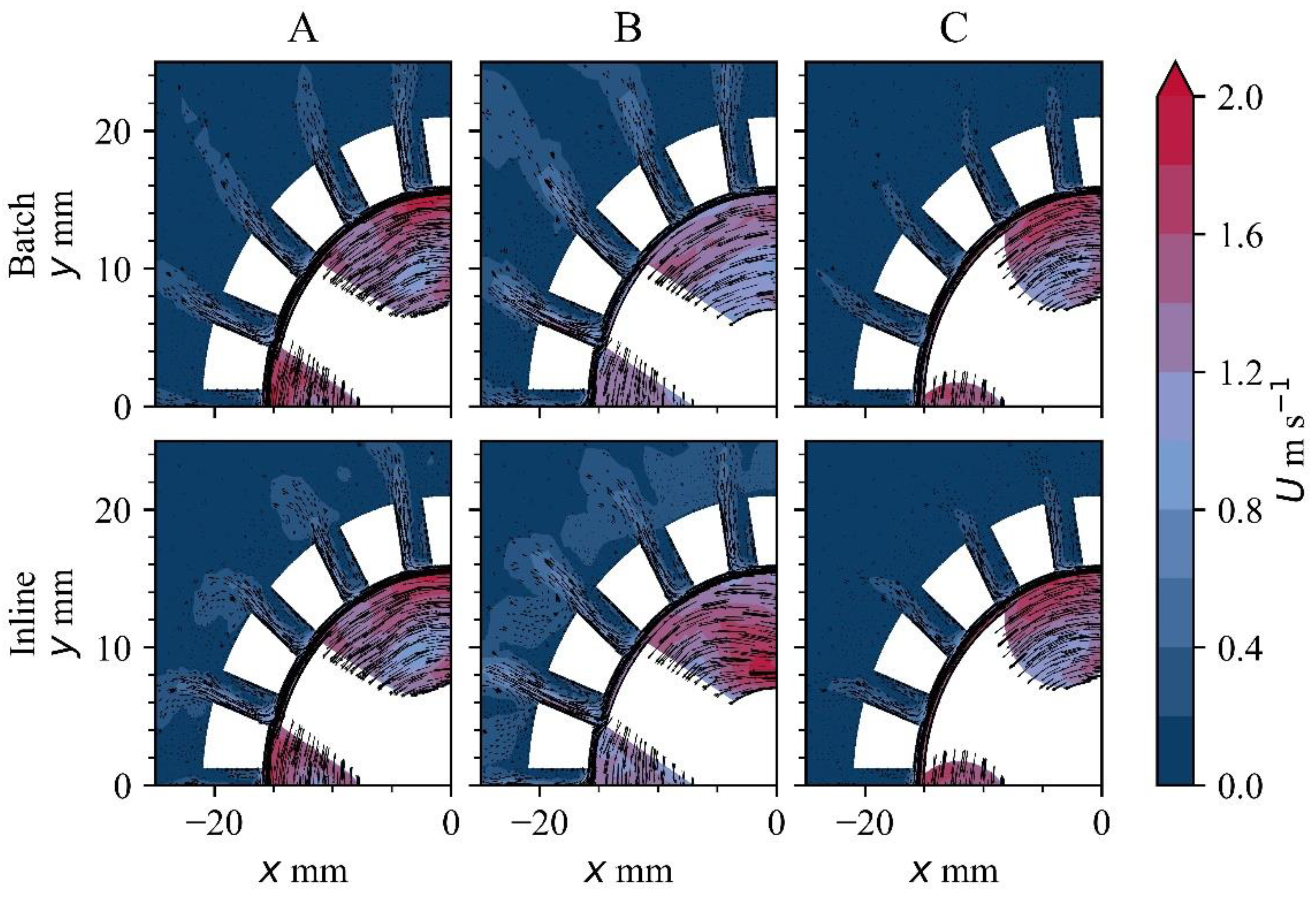

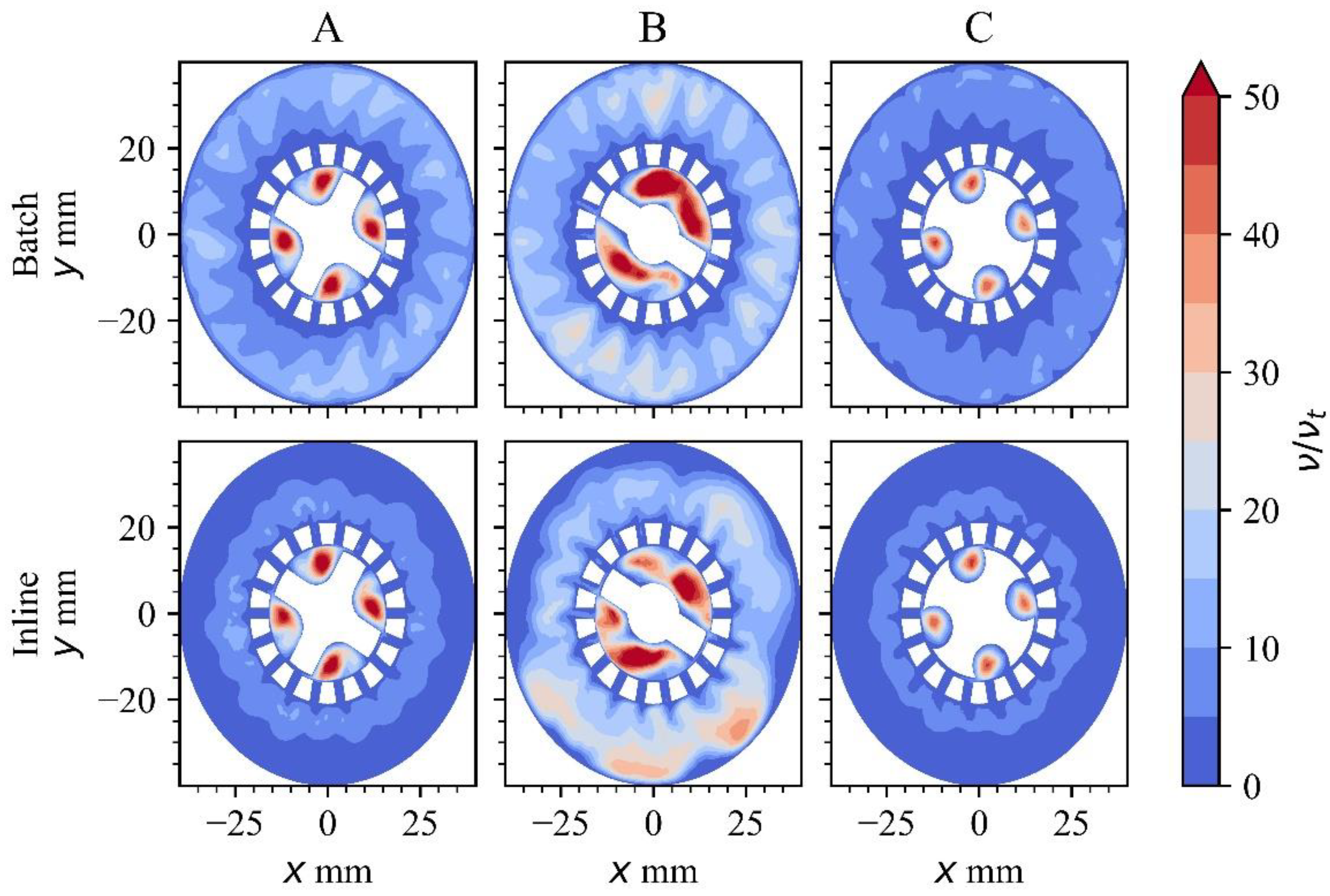
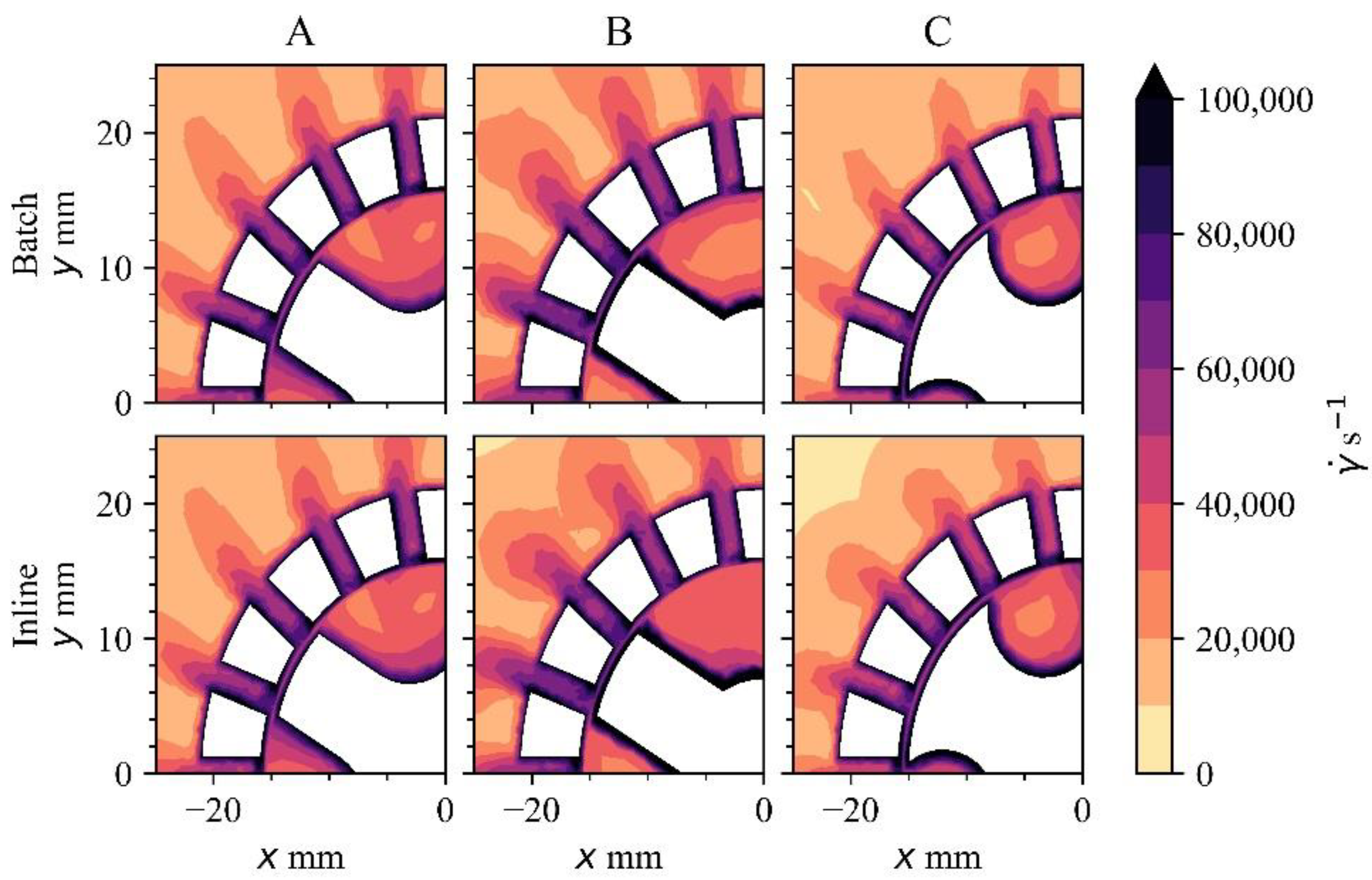
| Variable | Inlet | Outlet | Walls and Stator | Rotor Blades |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Velocity | Dirichlet boundary condition with a fixed value of Batch mode: (0, 0, 0) m s−1 Inline mode: (0, 0, 0.1) m s−1 | Neumann boundary condition (zero normal gradient | No slip boundary m s−1 | Moving wall velocity set to 0 m s−1 relative to the rotating frame of reference |
| Pressure | Neumann boundary condition | Dirichlet boundary condition with a fixed value of 0 Pa | Neumann boundary condition | Neumann boundary condition |
| Turbulent kinetic energy | Turbulent intensity % | Neumann boundary condition | Neumann boundary condition | Neumann boundary condition |
| Turbulent dissipation rate | Mixing length m | Neumann boundary condition | wall function [29] | wall function |
| Turbulent viscosity ratio | Calculated (not prescribed) | Calculated (not prescribed) | wall function [28] | wall function [28] |
| Mesh Size (Number of Cells) | Power Number (Po) | Power Number Standard Deviation | Melt Flow Rate Through Mixer (kg s−1) | Melt Flow Rate Standard Deviation |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2,008,777 | 0.394 | 6 × 10−3 | 0.336 | 0.006 |
| 3,845,058 | 0.386 | 4 × 10−3 | 0.386 | 0.004 |
| 8,558,627 | 0.387 | 0.03 | 0.386 | 0.006 |
| Case | Power Number (Po) | Mass Flow Rate through Mixer (kg s−1) |
|---|---|---|
| Experimental work [37] | 2.3 | Not available |
| k- model [24] | 2.05 | 0.389 |
| LES model [36] | 2.2 | 0.418 |
| Present methodology | 2.1 ± 0.1 | 0.35 ± 0.01 |
| Operating Mode | Rotor | Melt Flow Rate through Mixer (kg s−1) | Melt Flow Rate Standard Deviation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Batch | A | 0.382 | 0.004 |
| Inline | A | 0.386 | 0.004 |
| Batch | B | 0.434 | 0.04 |
| Inline | B | 0.488 | 0.02 |
| Batch | C | 0.238 | 0.002 |
| Inline | C | 0.254 | 0.002 |
| Operating Mode | Rotor | Power Number (Po) | Power Number Standard Deviation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Batch | A | 0.374 | 4 × 10−3 |
| Inline | A | 0.386 | 4 × 10−3 |
| Batch | B | 0.47 | 4 × 10−2 |
| Inline | B | 0.52 | 3 × 10−2 |
| Batch | C | 0.28 | 2 × 10−3 |
| Inline | C | 0.29 | 2 × 10−3 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lebon, G.S.B.; Patel, J.B.; Fan, Z. Numerical Studies of Batch and Inline High Shear Melt Conditioning Technology Using Different Rotors. Crystals 2022, 12, 1299. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst12091299
Lebon GSB, Patel JB, Fan Z. Numerical Studies of Batch and Inline High Shear Melt Conditioning Technology Using Different Rotors. Crystals. 2022; 12(9):1299. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst12091299
Chicago/Turabian StyleLebon, Gerard Serge Bruno, Jayesh B. Patel, and Zhongyun Fan. 2022. "Numerical Studies of Batch and Inline High Shear Melt Conditioning Technology Using Different Rotors" Crystals 12, no. 9: 1299. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst12091299
APA StyleLebon, G. S. B., Patel, J. B., & Fan, Z. (2022). Numerical Studies of Batch and Inline High Shear Melt Conditioning Technology Using Different Rotors. Crystals, 12(9), 1299. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst12091299











