Computer Simulations of a Twist Bend Nematic (NTB): A Coarse-Grained Simulation of the Phase Behaviour of the Liquid Crystal Dimer CB7CB
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Computational
2.1. Choice of Methodology and CG Mapping
2.2. Coarse-Grained Methods Used: IBI, FM, Martini 3
2.3. Cost of Computational Models
2.4. Bonded Potentials
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. CG Potentials
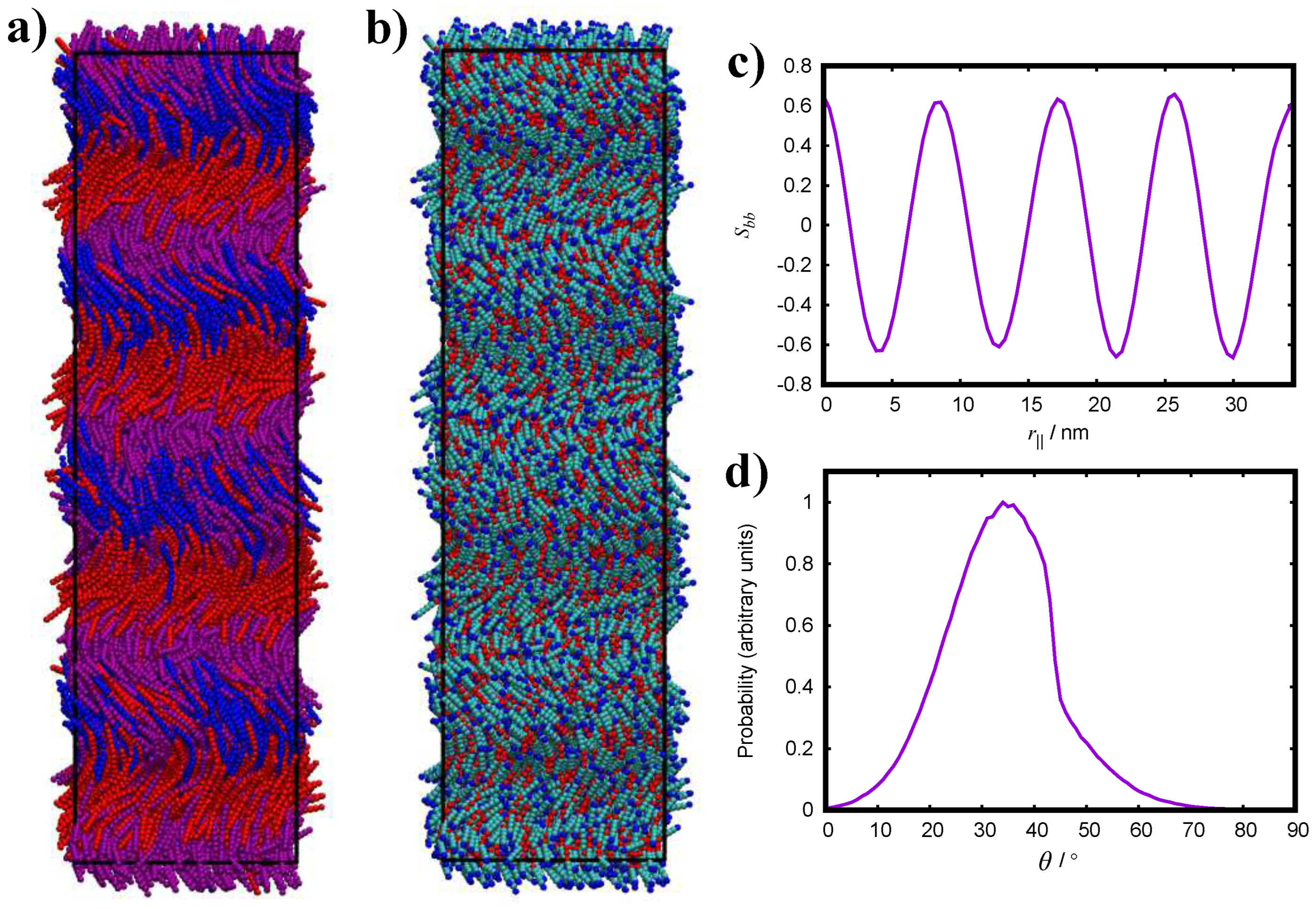
3.2. Phase Behaviour of the Coarse-Grained Models at 370 K
3.3. Further Simulation of the FM Model
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zannoni, C. Liquid Crystals and Their Computer Simulations; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Freiser, M. Ordered states of a nematic liquid. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1970, 24, 1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brochard, F.; De Gennes, P. Theory of magnetic suspensions in liquid crystals. J. Phys. 1970, 31, 691–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dozov, I. On the spontaneous symmetry breaking in the mesophases of achiral banana-shaped molecules. Europhys. Lett. 2001, 56, 247–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandle, R.J.; Cowling, S.J.; Goodby, J.W. A nematic to nematic transformation exhibited by a rod-like liquid crystal. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2017, 19, 11429–11435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nishikawa, H.; Shiroshita, K.; Higuchi, H.; Okumura, Y.; Haseba, Y.; Yamamoto, S.i.; Sago, K.; Kikuchi, H. A fluid liquid-crystal material with highly polar order. Adv. Mater. 2017, 29, 1702354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mertelj, A.; Cmok, L.; Sebastián, N.; Mandle, R.J.; Parker, R.R.; Whitwood, A.C.; Goodby, J.W.; Čopič, M. Splay nematic phase. Phys. Rev. X 2018, 8, 041025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Borshch, V.; Kim, Y.K.; Xiang, J.; Gao, M.; Jákli, A.; Panov, V.P.; Vij, J.K.; Imrie, C.T.; Tamba, M.G.; Mehl, G.H.; et al. Nematic twist-bend phase with nanoscale modulation of molecular orientation. Nat. Comuun. 2013, 4, 2635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Walker, R.; Pociecha, D.; Martinez-Felipe, A.; Storey, J.M.D.; Gorecka, E.; Imrie, C.T. Twist-Bend Nematogenic Supramolecular Dimers and Trimers Formed by Hydrogen Bonding. Crystals 2020, 10, 175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Severing, K.; Saalwächter, K. Biaxial nematic phase in a thermotropic liquid-crystalline side-chain polymer. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2004, 92, 125501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.; Saupe, A. Observation of a biaxial nematic phase in potassium laurate-1-decanol-water mixtures. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1980, 45, 1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mertelj, A.; Lisjak, D.; Drofenik, M.; Čopič, M. Ferromagnetism in suspensions of magnetic platelets in liquid crystal. Nature 2013, 504, 237–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotni, R.; Grau-Carbonell, A.; Chiappini, M.; Dijkstra, M.; van Blaaderen, A. Splay-bend nematic phases of bent colloidal silica rods induced by polydispersity. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 7264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernández-Rico, C.; Chiappini, M.; Yanagishima, T.; de Sousa, H.; Aarts, D.G.; Dijkstra, M.; Dullens, R.P. Shaping colloidal bananas to reveal biaxial, splay-bend nematic, and smectic phases. Science 2020, 369, 950–955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cestari, M.; Diez-Berart, S.; Dunmur, D.; Ferrarini, A.; de La Fuente, M.; Jackson, D.; Lopez, D.; Luckhurst, G.; Perez-Jubindo, M.; Richardson, R.; et al. Phase behavior and properties of the liquid-crystal dimer 1″, 7″-bis (4-cyanobiphenyl-4′-yl) heptane: A twist-bend nematic liquid crystal. Phys. Rev. E 2011, 84, 031704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Meyer, R.B. Les Houches Summer School in Theoretical Physics; Gordon and Breach: New York, NY, USA, 1976; pp. 273–373. [Google Scholar]
- Meyer, C.; Luckhurst, G.R.; Dozov, I. Flexoelectrically Driven Electroclinic Effect in the Twist-Bend Nematic Phase of Achiral Molecules with Bent Shapes. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2013, 111, 067801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Porada, J.H.; Hooper, J.B.; Klittnick, A.; Shen, Y.; Tuchband, M.R.; Korblova, E.; Bedrov, D.; Walba, D.M.; Glaser, M.A.; et al. Chiral heliconical ground state of nanoscale pitch in a nematic liquid crystal of achiral molecular dimers. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 15931–15936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sepelj, M.; Lesac, A.; Baumeister, U.; Diele, S.; Nguyen, H.L.; Bruce, D.W. Intercalated liquid-crystalline phases formed by symmetric dimers with an α,ω-diiminoalkylene spacer. J. Mater. Chem. 2007, 17, 1154–1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panov, V.P.; Nagaraj, M.; Vij, J.K.; Panarin, Y.P.; Kohlmeier, A.; Tamba, M.G.; Lewis, R.A.; Mehl, G.H. Spontaneous Periodic Deformations in Nonchiral Planar-Aligned Bimesogens with a Nematic-Nematic Transition and a Negative Elastic Constant. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2010, 105, 167801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Henderson, P.A.; Imrie, C.T. Methylene-linked liquid crystal dimers and the twist-bend nematic phase. Liq. Cryst. 2011, 38, 1407–1414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adlem, K.; Čopič, M.; Luckhurst, G.R.; Mertelj, A.; Parri, O.; Richardson, R.M.; Snow, B.D.; Timimi, B.A.; Tuffin, R.P.; Wilkes, D. Chemically induced twist-bend nematic liquid crystals, liquid crystal dimers, and negative elastic constants. Phys. Rev. E 2013, 88, 022503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandle, R.J.; Davis, E.J.; Lobato, S.A.; Vol, C.C.A.; Cowling, S.J.; Goodby, J.W. Synthesis and characterisation of an unsymmetrical, ether-linked, fluorinated bimesogen exhibiting a new polymorphism containing the NTB or ‘twist-bend’ phase. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2014, 16, 6907–6915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mandle, R.J.; Davis, E.J.; Archbold, C.T.; Cowling, S.J.; Goodby, J.W. Microscopy studies of the nematic NTB phase of 1,11-di-(1″-cyanobiphenyl-4-yl)undecane. J. Mater. Chem. C 2014, 2, 556–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandle, R.J.; Davis, E.J.; Archbold, C.T.; Voll, C.C.A.; Andrews, J.L.; Cowling, S.J.; Goodby, J.W. Apolar Bimesogens and the Incidence of the Twist–Bend Nematic Phase. Chem.—Eur. J. 2015, 21, 8158–8167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorecka, E.; Vaupotic, N.; Zep, A.; Pociecha, D.; Yoshioka, J.; Yamamoto, J.; Takezoe, H. A Twist-Bend Nematic (NTB) Phase of Chiral Materials. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2015, 54, 10155–10159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paterson, D.A.; Gao, M.; Kim, Y.K.; Jamali, A.; Finley, K.L.; Robles-Hernández, B.; Diez-Berart, S.; Salud, J.; de la Fuente, M.R.; Timimi, B.A.; et al. Understanding the twist-bend nematic phase: The characterisation of 1-(4-cyanobiphenyl-4′-yloxy)-6-(4-cyanobiphenyl-4′-yl)hexane (CB6OCB) and comparison with CB7CB. Soft Matter 2016, 12, 6827–6840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Paterson, D.A.; Abberley, J.P.; Harrison, W.T.A.; Storey, J.M.D.; Imrie, C.T. Cyanobiphenyl-based liquid crystal dimers and the twist-bend nematic phase. Liq. Cryst. 2017, 44, 127–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Nakata, M.; Shao, R.; Tuchband, M.R.; Shuai, M.; Baumeister, U.; Weissflog, W.; Walba, D.M.; Glaser, M.A.; Maclennan, J.E.; et al. Twist-bend heliconical chiral nematic liquid crystal phase of an achiral rigid bent-core mesogen. Phys. Rev. E 2014, 89, 022506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sreenilayam, S.P.; Panov, V.P.; Vij, J.K.; Shanker, G. The NTB phase in an achiral asymmetrical bent-core liquid crystal terminated with symmetric alkyl chains. Liq. Cryst. 2017, 44, 244–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jansze, S.M.; Martínez-Felipe, A.; Storey, J.M.D.; Marcelis, A.T.M.; Imrie, C.T. A Twist-Bend Nematic Phase Driven by Hydrogen Bonding. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2015, 54, 643–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, R.; Pociecha, D.; Abberley, J.P.; Martinez-Felipe, A.; Paterson, D.A.; Forsyth, E.; Lawrence, G.B.; Henderson, P.A.; Storey, J.M.D.; Gorecka, E.; et al. Spontaneous chirality through mixing achiral components: A twist-bend nematic phase driven by hydrogen-bonding between unlike components. Chem. Commun. 2018, 54, 3383–3386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, R.; Pociecha, D.; Salamończyk, M.; Storey, J.M.D.; Gorecka, E.; Imrie, C.T. Supramolecular liquid crystals exhibiting a chiral twist-bend nematic phase. Mater. Adv. 2020, 1, 1622–1630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, J.; Li, Y.; Li, Q.; Paterson, D.A.; Storey, J.M.D.; Imrie, C.T.; Lavrentovich, O.D. Electrically Tunable Selective Reflection of Light from Ultraviolet to Visible and Infrared by Heliconical Cholesterics. Adv. Mater. 2015, 27, 3014–3018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Xiang, J.; Varanytsia, A.; Minkowski, F.; Paterson, D.A.; Storey, J.M.D.; Imrie, C.T.; Lavrentovich, O.D.; Palffy-Muhoray, P. Electrically tunable laser based on oblique heliconical cholesteric liquid crystal. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 12925–12928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mrukiewicz, M.; Iadlovska, O.S.; Babakhanova, G.; Siemianowski, S.; Shiyanovskii, S.V.; Lavrentovich, O.D. Wide temperature range of an electrically tunable selective reflection of light by oblique helicoidal cholesteric. Liq. Cryst. 2019, 46, 1544–1550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasad, S.K.; Madhuri, P.L.; Satapathy, P.; Yelamaggad, C.V. A soft-bent dimer composite exhibiting twist-bend nematic phase: Photo-driven effects and an optical memory device. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2018, 112, 253701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sridurai, V.; Kanakala, M.B.; Yelamaggad, C.V.; Nair, G.G. Effect of gelation on the Frank elastic constants in a liquid crystalline mixture exhibiting a twist bend nematic phase. Soft Matter 2019, 15, 9982–9990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aya, S.; Salamon, P.; Paterson, D.A.; Storey, J.M.; Imrie, C.T.; Araoka, F.; Jákli, A.; Buka, Á. Fast-and-giant photorheological effect in a liquid crystal dimer. Adv. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 6, 1802032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Feng, C.; Feng, J.; Saha, R.; Arakawa, Y.; Gleeson, J.; Sprunt, S.; Zhu, C.; Jákli, A. Manipulation of the nanoscale heliconical structure of a twist-bend nematic material with polarized light. Phys. Rev. Res. 2020, 2, 032004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, M.R.; Yu, G.; Potter, T.D.; Walker, M.; Gray, S.J.; Li, J.; Boyd, N.J. Molecular Simulation Approaches to the Study of Thermotropic and Lyotropic Liquid Crystals. Crystals 2022, 12, 685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, M.P. Molecular simulation of liquid crystals. Mol. Phys. 2019, 117, 2391–2417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wilson, M.R. Progress in computer simulations of liquid crystals. Int. Rev. Phys. Chem. 2005, 24, 421–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, M.R. Molecular simulation of liquid crystals: Progress towards a better understanding of bulk structure and the prediction of material properties. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2007, 36, 1881–1888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Peláez, J.; Wilson, M.R. Atomistic Simulations of a Thermotropic Biaxial Liquid Crystal. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2006, 97, 267801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chami, F.; Wilson, M.R. Molecular order in a chromonic liquid crystal: A molecular simulation study of the anionic azo dye sunset yellow. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132, 7794–7802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boyd, N.J.; Wilson, M.R. Optimization of the GAFF force field to describe liquid crystal molecules: The path to a dramatic improvement in transition temperature predictions. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2015, 17, 24851–24865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Boyd, N.J.; Wilson, M.R. Validating an optimized GAFF force field for liquid crystals: TNI predictions for bent-core mesogens and the first atomistic predictions of a dark conglomerate phase. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2018, 20, 1485–1496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yu, G.; Walker, M.; Wilson, M.R. Atomistic simulation studies of ionic cyanine dyes: Self-assembly and aggregate formation in aqueous solution. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2021, 23, 6408–6421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chami, F.; Wilson, M.; Oganesyan, V. Molecular dynamics and EPR spectroscopic studies of 8CB liquid crystal. Soft Matter 2012, 8, 6823–6833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zannoni, C. From idealised to predictive models of liquid crystals. Liq. Cryst. 2018, 45, 1880–1893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGrother, S.C.; Williamson, D.C.; Jackson, G. A re-examination of the phase diagram of hard spherocylinders. J. Chem. Phys. 1996, 104, 6755–6771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, M.P.; Warren, M.A.; Wilson, M.R. Molecular-dynamics simulation of the smectic-A* twist grain-boundary phase. Phys. Rev. E 1998, 57, 5585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Duncan, P.D.; Dennison, M.; Masters, A.J.; Wilson, M.R. Theory and computer simulation for the cubatic phase of cut spheres. Phys. Rev. E 2009, 79, 031702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wilson, M.R.; Duncan, P.D.; Dennison, M.; Masters, A.J. Molecular dynamics simulation studies of platelets with square cross-sectional area: Formation of a stable cubatic phase. Soft Matter 2012, 8, 3348–3356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, M.; Allen, M. Computer simulation study of liquid crystal formation in a semi-flexible system of linked hard spheres. Mol. Phys. 1993, 80, 277–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lintuvuori, J.S.; Yu, G.; Walker, M.; Wilson, M.R. Emergent chirality in achiral liquid crystals: Insights from molecular simulation models of the behaviour of bent-core mesogens. Liq. Cryst. 2018, 45, 1996–2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cook, M.J.; Wilson, M.R. Simulation studies of dipole correlation in the isotropic liquid phase. Liq. Cryst. 2000, 27, 1573–1583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cook, M.J.; Wilson, M.R. The First Thousand-Molecule Simulation of a Mesogen at the Fully Atomistic Level. Mol. Cryst. Liq. Cryst. 2001, 363, 181–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fegan, S.K.; Kirsch, P.; Müller-Plathe, F. The alignment of dichroic dyes in a nematic liquid crystal: A molecular dynamics investigation. Liq. Cryst. 2018, 45, 1377–1384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sims, M.T.; Mandle, R.J.; Goodby, J.W.; Moore, J.N. Guest–host systems containing anthraquinone dyes with multiple visible transitions giving positive and negative dichroic order parameters: An assessment of principal molecular axes and computational methods. Liq. Cryst. 2017, 44, 2029–2045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Humpert, A.; Allen, M.P. Elastic constants and dynamics in nematic liquid crystals. Mol. Phys. 2015, 113, 2680–2692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stelzer, J.; Berardi, R.; Zannoni, C. Flexoelectric coefficients for model pear shaped molecules from monte carlo simulations. Mol. Cryst. Liq. Cryst. 2000, 352, 187–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheung, D.L.; Clark, S.J.; Wilson, M.R. Calculation of flexoelectric coefficients for a nematic liquid crystal by atomistic simulation. J. Chem. Phys. 2004, 121, 9131–9139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Allen, M.P. Diffusion coefficient increases with density in hard ellipsoid liquid crystals. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1990, 65, 2881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheung, D.L.; Clark, S.J.; Wilson, M.R. Calculation of the rotational viscosity of a nematic liquid crystal. Chem. Phys. Lett. 2002, 356, 140–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greco, C.; Ferrarini, A. Entropy-Driven Chiral Order in a System of Achiral Bent Particles. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2015, 115, 147801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, G.; Wilson, M.R. All-atom simulations of bent liquid crystal dimers: The twist-bend nematic phase and insights into conformational chirality. Soft Matter 2022, 18, 3087–3096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandle, R.J. A Ten-Year Perspective on Twist-Bend Nematic Materials. Molecules 2022, 27, 2689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandle, R.J.; Archbold, C.T.; Sarju, J.P.; Andrews, J.L.; Goodby, J.W. The dependency of nematic and twist-bend mesophase formation on bend angle. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 36682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Panov, V.P.; Vij, J.K.; Mehl, G.H. Twist-bend nematic phase in cyanobiphenyls and difluoroterphenyls bimesogens. Liq. Cryst. 2017, 44, 147–159. [Google Scholar]
- Shadpour, S.; Nemati, A.; Boyd, N.J.; Li, L.; Prévôt, M.E.; Wakerlin, S.L.; Vanegas, J.P.; Salamończyk, M.; Hegmann, E.; Zhu, C.; et al. Heliconical-layered nanocylinders (HLNCs)—Hierarchical self-assembly in a unique B4 phase liquid crystal morphology. Mater. Horiz. 2019, 6, 959–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shadpour, S.; Nemati, A.; Salamończyk, M.; Prévôt, M.E.; Liu, J.; Boyd, N.J.; Wilson, M.R.; Zhu, C.; Hegmann, E.; Jákli, A.I.; et al. Missing Link between Helical Nano- and Microfilaments in B4 Phase Bent-Core Liquid Crystals, and Deciphering which Chiral Center Controls the Filament Handedness. Small 2020, 16, 1905591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruhle, V.; Junghans, C.; Lukyanov, A.; Kremer, K.; Andrienko, D. Versatile object-oriented toolkit for coarse-graining applications. J. Chem. Theory Comput. 2009, 5, 3211–3223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rühle, V.; Junghans, C. Hybrid Approaches to Coarse-Graining using the VOTCA Package: Liquid Hexane. Macromol. Theory Simul. 2011, 20, 472–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mashayak, S.; Jochum, M.N.; Koschke, K.; Aluru, N.; Rühle, V.; Junghans, C. Relative entropy and optimization-driven coarse-graining methods in VOTCA. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0131754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Izvekov, S.; Voth, G.A. Multiscale coarse-graining of monosaccharides. J. Phys. Chem. B 2007, 111, 11566–11575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dunn, N.J.; Lebold, K.M.; DeLyser, M.R.; Rudzinski, J.F.; Noid, W. BOCS: Bottom-up open-source coarse-graining software. J. Phys. Chem. B 2017, 122, 3363–3377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Potter, T.D.; Tasche, J.; Wilson, M.R. Assessing the transferability of common top-down and bottom-up coarse-grained molecular models for molecular mixtures. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2019, 21, 1912–1927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yu, G.; Wilson, M.R. Molecular simulation studies of self-assembly for a chromonic perylene dye: All-atom studies and new approaches to coarse-graining. J. Mol. Liq. 2022, 345, 118210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potter, T.D.; Walker, M.; Wilson, M.R. Self-assembly and mesophase formation in a non-ionic chromonic liquid crystal: Insights from bottom-up and top-down coarse-grained simulation models. Soft Matter 2020, 16, 9488–9498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Souza, P.C.; Alessandri, R.; Barnoud, J.; Thallmair, S.; Faustino, I.; Grünewald, F.; Patmanidis, I.; Abdizadeh, H.; Bruininks, B.M.; Wassenaar, T.A.; et al. Martini 3: A general purpose force field for coarse-grained molecular dynamics. Nat. Methods 2021, 18, 382–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martini Open Beta. Available online: http://cgmartini.nl/index.php/martini3beta (accessed on 13 February 2023).
- De Jong, D.H.; Baoukina, S.; Ingólfsson, H.I.; Marrink, S.J. Martini straight: Boosting performance using a shorter cutoff and GPUs. Comput. Phys. Commun. 2016, 199, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheung, D.; Clark, S.; Wilson, M.R. Parametrization and validation of a force field for liquid-crystal forming molecules. Phys. Rev. E 2002, 65, 051709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bennett, C.H. Efficient estimation of free energy differences from Monte Carlo data. J. Comput. Phys. 1976, 22, 245–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, G. Multiscale Modelling of Self-Assembly in Soft Matter. Ph.D. Thesis, Durham University, Durham, UK, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.P.; Martinez, T.J.; Pande, V.S. Building force fields: An automatic, systematic, and reproducible approach. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2014, 5, 1885–1891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Avendaño, C.; Lafitte, T.; Galindo, A.; Adjiman, C.S.; Jackson, G.; Müller, E.A. SAFT-γ Force Field for the Simulation of Molecular Fluids. 1. A Single-Site Coarse Grained Model of Carbon Dioxide. J. Phys. Chem. B 2011, 115, 11154–11169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lafitte, T.; Avendaño, C.; Papaioannou, V.; Galindo, A.; Adjiman, C.S.; Jackson, G.; Müller, E.A. SAFT-γ force field for the simulation of molecular fluids: 3. Coarse-grained models of benzene and hetero-group models of n-decylbenzene. Mol. Phys. 2012, 110, 1189–1203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avendaño, C.; Lafitte, T.; Adjiman, C.S.; Galindo, A.; Müller, E.A.; Jackson, G. SAFT-γ Force Field for the Simulation of Molecular Fluids: 2. Coarse-Grained Models of Greenhouse Gases, Refrigerants, and Long Alkanes. J. Phys. Chem. B 2013, 117, 2717–2733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tasche, J.; Sabattié, E.F.; Thompson, R.L.; Campana, M.; Wilson, M.R. Oligomer/polymer blend phase diagram and surface concentration profiles for squalane/polybutadiene: Experimental measurements and predictions from SAFT-γ Mie and molecular dynamics simulations. Macromolecules 2020, 53, 2299–2309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potter, T.D.; Tasche, J.; Barrett, E.L.; Walker, M.; Wilson, M.R. Development of new coarse-grained models for chromonic liquid crystals: Insights from top-down approaches. Liq. Cryst. 2017, 44, 1979–1989. [Google Scholar]
- Evans, F.; Skinner, H. The heats of combustion of organic compounds of nitrogen. Part 2.—n-Propyl, iso propyl and phenyl cyanides. Trans. Faraday Soc. 1959, 55, 255–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Ness, H.C.; Soczek, C.; Peloquin, G.; Machado, R. Thermodynamic excess properties of three alcohol-hydrocarbon systems. J. Chem. Eng. Data 1967, 12, 217–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Stillinger, F.H.; Torquato, S. Sensitivity of pair statistics on pair potentials in many-body systems. J. Chem. Phys. 2020, 153, 124106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, C.; Luckhurst, G.R.; Dozov, I. The temperature dependence of the heliconical tilt angle in the twist-bend nematic phase of the odd dimer CB7CB. J. Mater. Chem. C 2015, 3, 318–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, G.; Fu, J.; Agra-Kooijman, D.M.; Song, J.K.; Vengatesan, M.R.; Srinivasarao, M.; Fisch, M.R.; Kumar, S. X-ray and Raman scattering study of orientational order in nematic and heliconical nematic liquid crystals. Phys. Rev. E 2016, 94, 060701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chiappini, M.; Drwenski, T.; van Roij, R.; Dijkstra, M. Biaxial, Twist-bend, and Splay-bend Nematic Phases of Banana-shaped Particles Revealed by Lifting the “Smectic Blanket”. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2019, 123, 068001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reddy, R.A.; Zhu, C.; Shao, R.; Korblova, E.; Gong, T.; Shen, Y.; Garcia, E.; Glaser, M.A.; Maclennan, J.E.; Walba, D.M.; et al. Spontaneous ferroelectric order in a bent-core smectic liquid crystal of fluid orthorhombic layers. Science 2011, 332, 72–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osipov, M.A.; Pajak, G. Molecular theory of proper ferroelectricity in bent-core liquid crystals. Eur. Phys. J. E 2014, 37, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lavrentovich, O.D. Ferroelectric nematic liquid crystal, a century in waiting. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 14629–14631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandle, R.J.; Sebastián, N.; Martinez-Perdiguero, J.; Mertelj, A. On the molecular origins of the ferroelectric splay nematic phase. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 4962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abberley, J.P.; Killah, R.; Walker, R.; Storey, J.M.D.; Imrie, C.T.; Salamończyk, M.; Zhu, C.; Gorecka, E.; Pociecha, D. Heliconical smectic phases formed by achiral molecules. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Walker, R.; Pociecha, D.; Strachan, G.J.; Storey, J.M.D.; Gorecka, E.; Imrie, C.T. Molecular curvature, specific intermolecular interactions and the twist-bend nematic phase: The synthesis and characterisation of the 1-(4-cyanobiphenyl-4′-yl)-6-(4-alkylanilinebenzylidene-4′-oxy)hexanes (CB6O.m). Soft Matter 2019, 15, 3188–3197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Salamończyk, M.; Vaupotič, N.; Pociecha, D.; Walker, R.; Storey, J.M.D.; Imrie, C.T.; Wang, C.; Zhu, C.; Gorecka, E. Multi-level chirality in liquid crystals formed by achiral molecules. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 1922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Stone, A.J. The description of bimolecular potentials, forces and torques: The S and V function expansions. Mol. Phys. 1978, 36, 241–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanakaras, A.G.; Photinos, D.J. Molecular dynamics simulations of nematic phases formed by cyano-biphenyl dimers. Liq. Cryst. 2018, 45, 2184–2196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
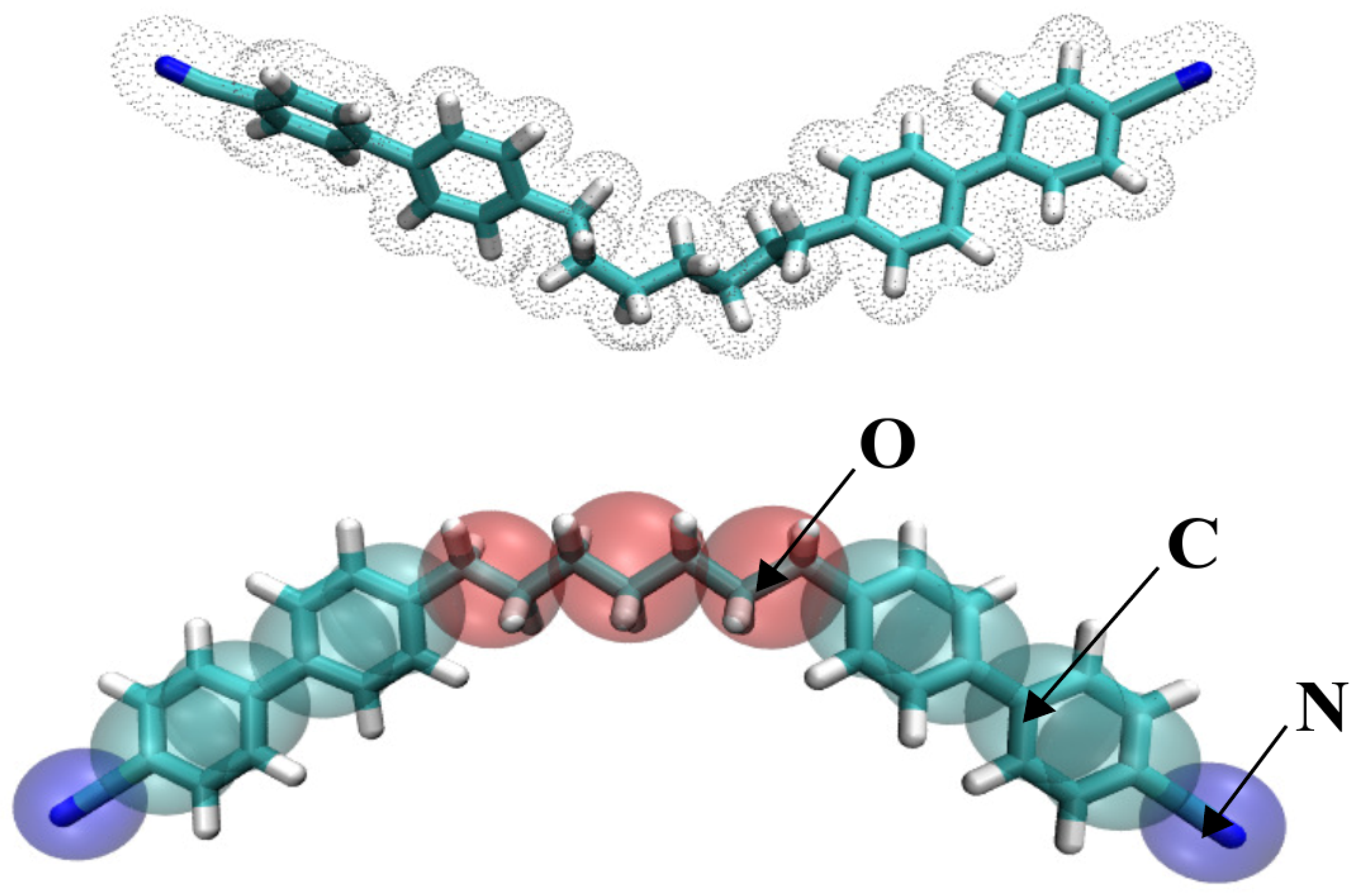
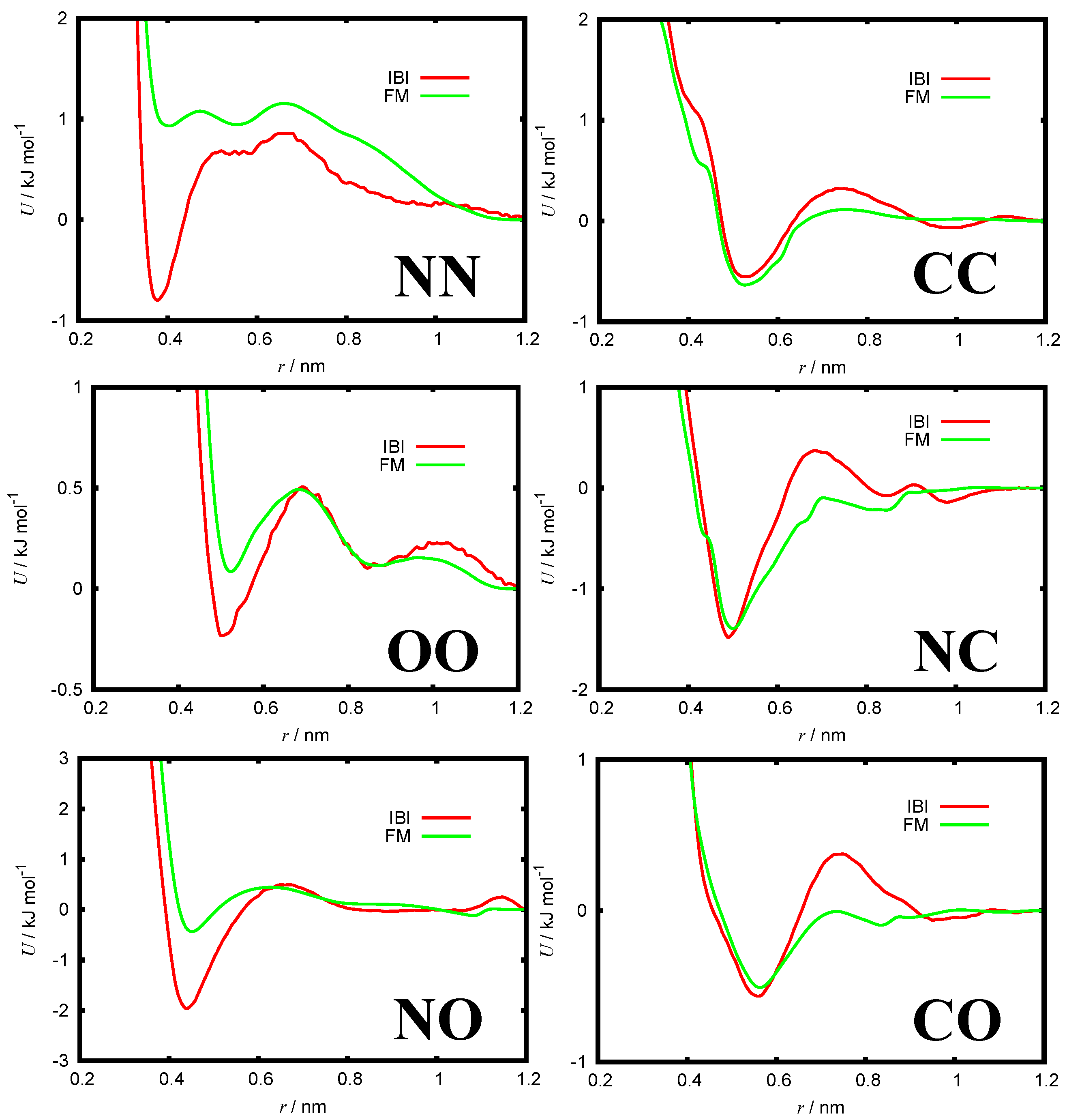
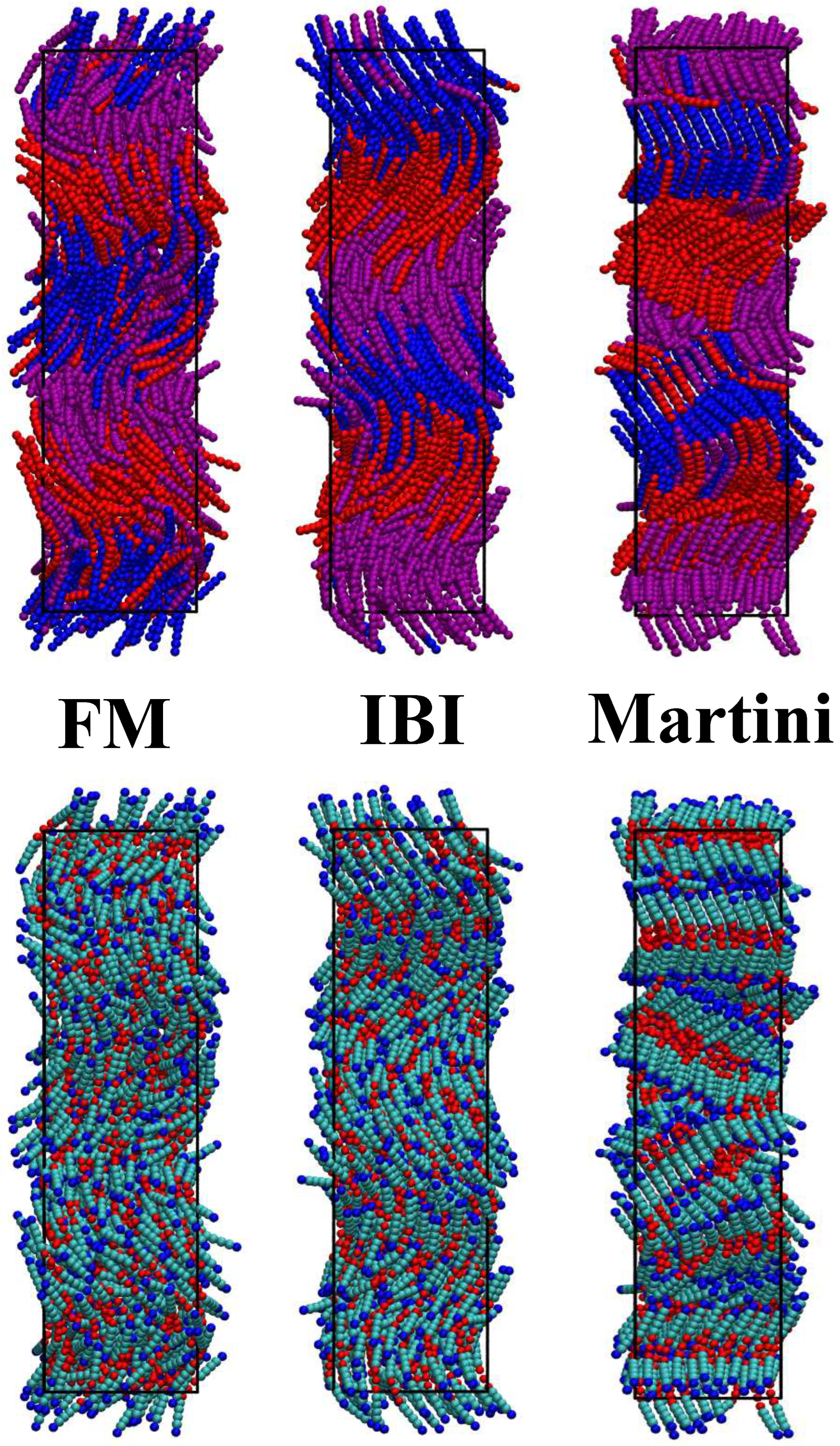
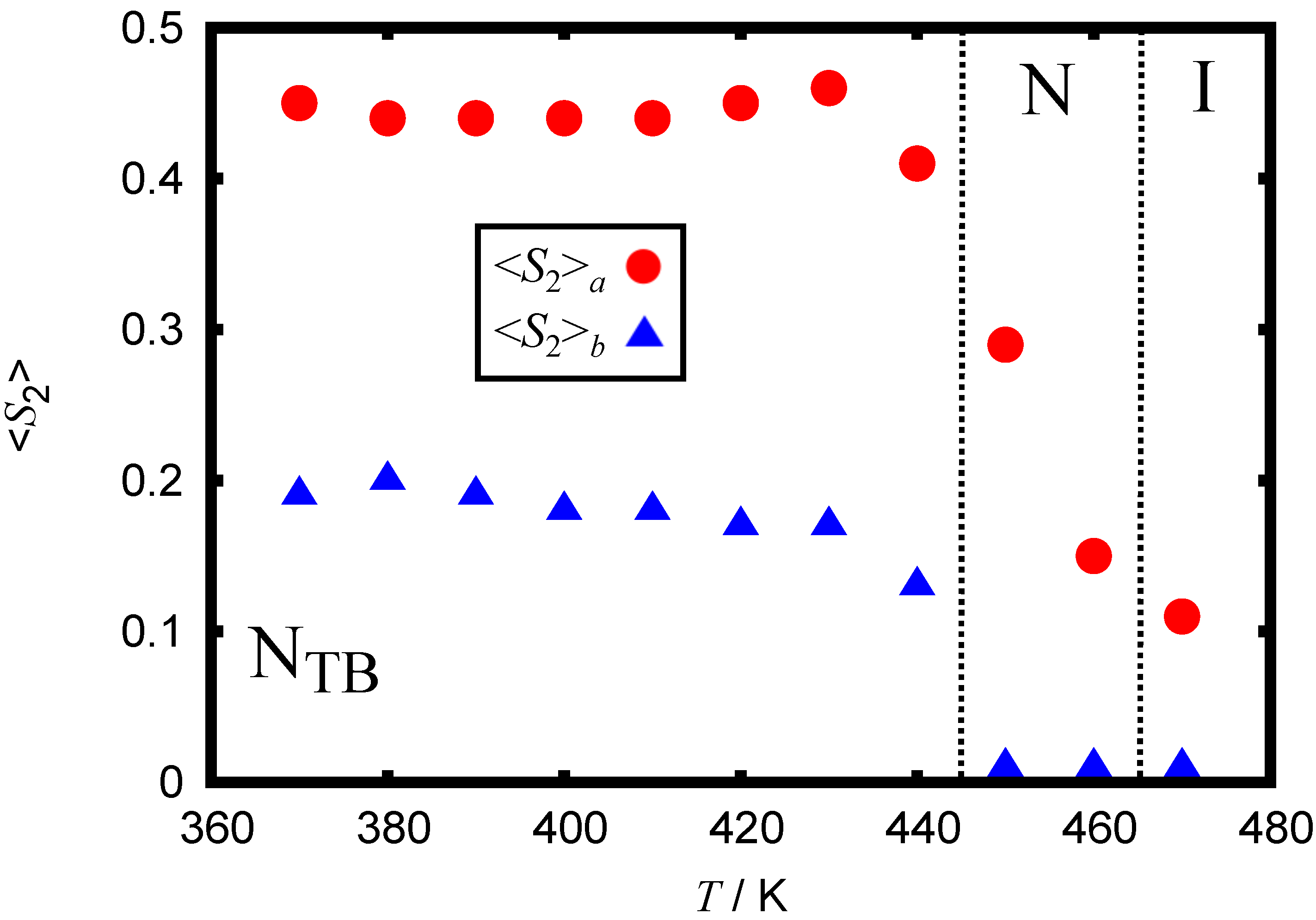
| Property | Experiment | AA Model | Martini 3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| (cyanobiphenyl) | 55.5 [94] | ||
| (heptane) | 36.4 [95] | ||
| (cyanobiphenyl, ) | – | ||
| (heptane, | – | ||
| (cyanobiphenyl, ) | – | ||
| (heptane, ) | – |
| Atoms | Length/nm | /kJ mol nm |
|---|---|---|
| N–O | 0.25 | 15,000 |
| C–C | 0.22 | 15,000 |
| C–O | 0.24 | 10,000 |
| O–O | 0.32 | 10,000 |
| Atoms | Angle/deg | /kJ mol deg |
|---|---|---|
| N–C–C | 180 | 5000 |
| C–C–C | 180 | 5000 |
| C–C–O | 170 | 750 |
| C–O–O | 170 | 750 |
| O–O–O | 170 | 750 |
| Atoms | Dihedral/deg | /kJ mol |
|---|---|---|
| C–C–O–O | 180 | 25 |
| C–O–O–O | 180 | 25 |
| Model | p/nm | θ/° | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| AA | 0.36 | 0.16 | 8.35 | 29 |
| FM | 0.44 | 0.18 | 8.35 | 32 |
| IBI | 0.51 | 0.28 | 8.42 | 31 |
| Martini 3 | 0.49 | 0.30 | 8.5 | 32 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wilson, M.R.; Yu, G. Computer Simulations of a Twist Bend Nematic (NTB): A Coarse-Grained Simulation of the Phase Behaviour of the Liquid Crystal Dimer CB7CB. Crystals 2023, 13, 502. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst13030502
Wilson MR, Yu G. Computer Simulations of a Twist Bend Nematic (NTB): A Coarse-Grained Simulation of the Phase Behaviour of the Liquid Crystal Dimer CB7CB. Crystals. 2023; 13(3):502. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst13030502
Chicago/Turabian StyleWilson, Mark R., and Gary Yu. 2023. "Computer Simulations of a Twist Bend Nematic (NTB): A Coarse-Grained Simulation of the Phase Behaviour of the Liquid Crystal Dimer CB7CB" Crystals 13, no. 3: 502. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst13030502
APA StyleWilson, M. R., & Yu, G. (2023). Computer Simulations of a Twist Bend Nematic (NTB): A Coarse-Grained Simulation of the Phase Behaviour of the Liquid Crystal Dimer CB7CB. Crystals, 13(3), 502. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst13030502







