Fabrication of Microcrystalline Silicon Thin Film by Ionized Physical Vapor Deposition Process
Abstract
1. Introduction
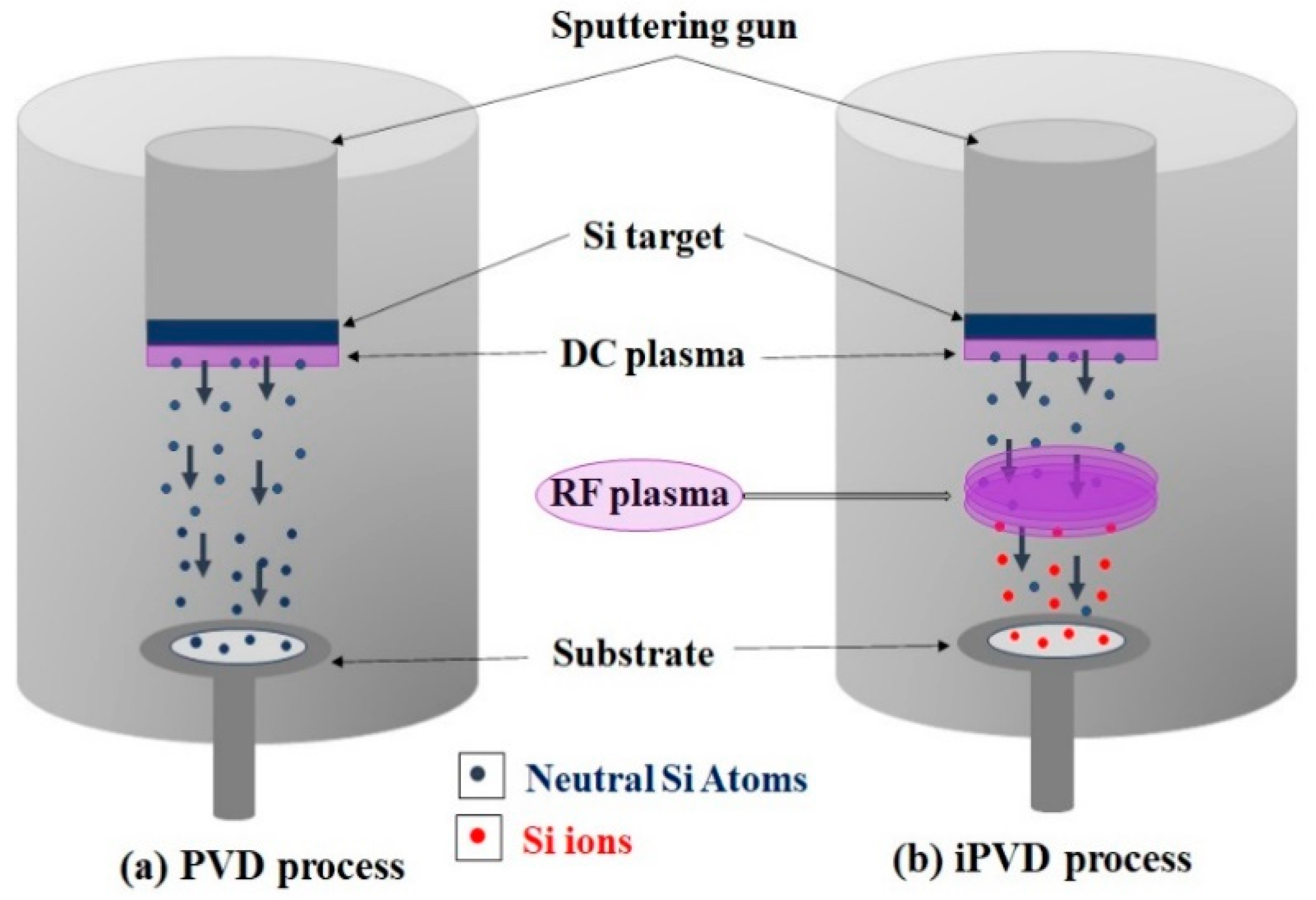
2. Experimental Set-Up
3. Results and Discussion
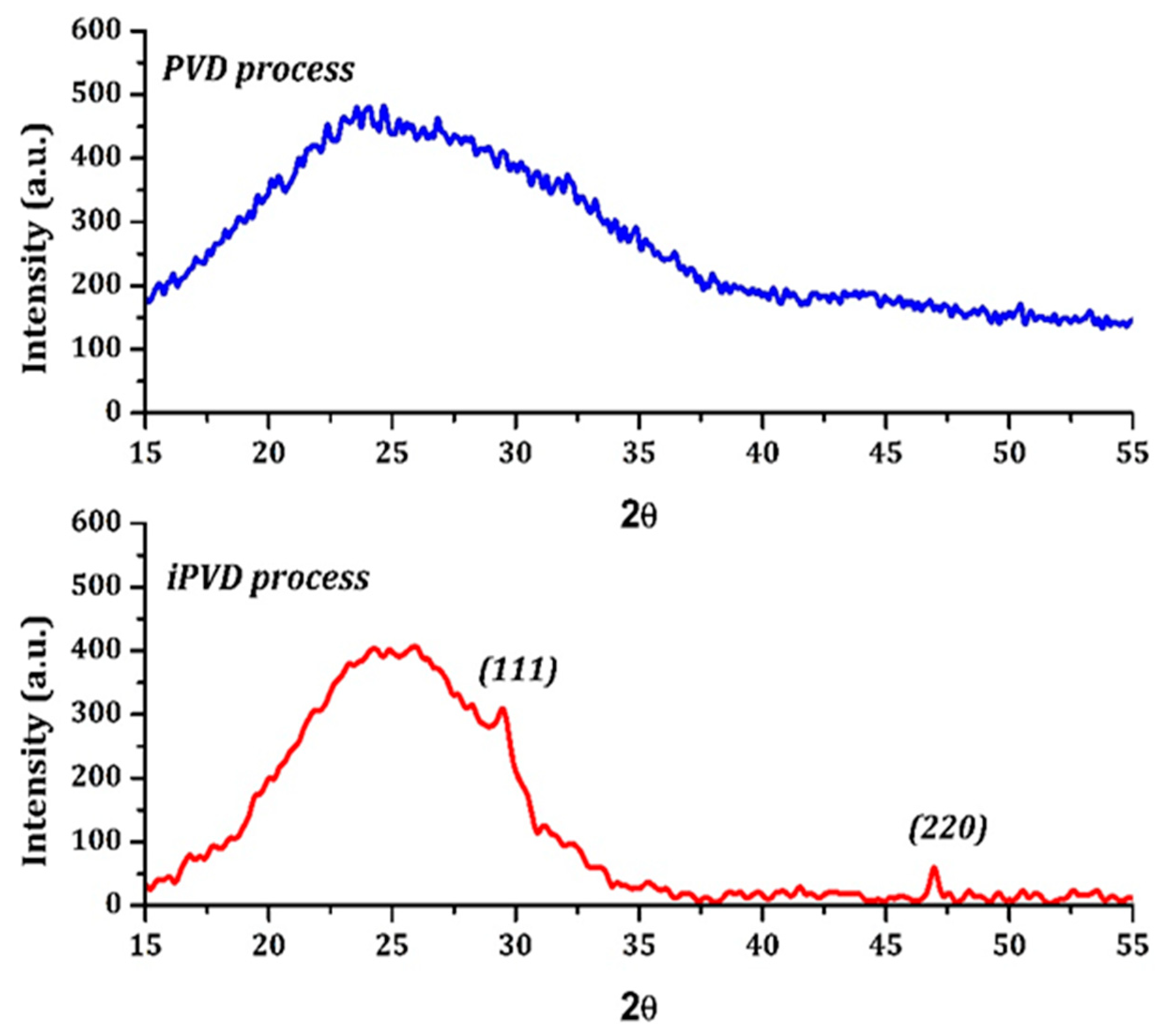
3.1. Structural Analysis
- (a)
- The deposition flux during the iPVD process consists of more ions than neutrals or ΓM+ > ΓM
- (b)
- The ions are deposited with higher energy in the iPVD process due to the acceleration by the sheath electric field than the neutrals in the PVD process.
- (c)
- The ions are collimated by the sheath electric field before the deposition in the iPVD process.
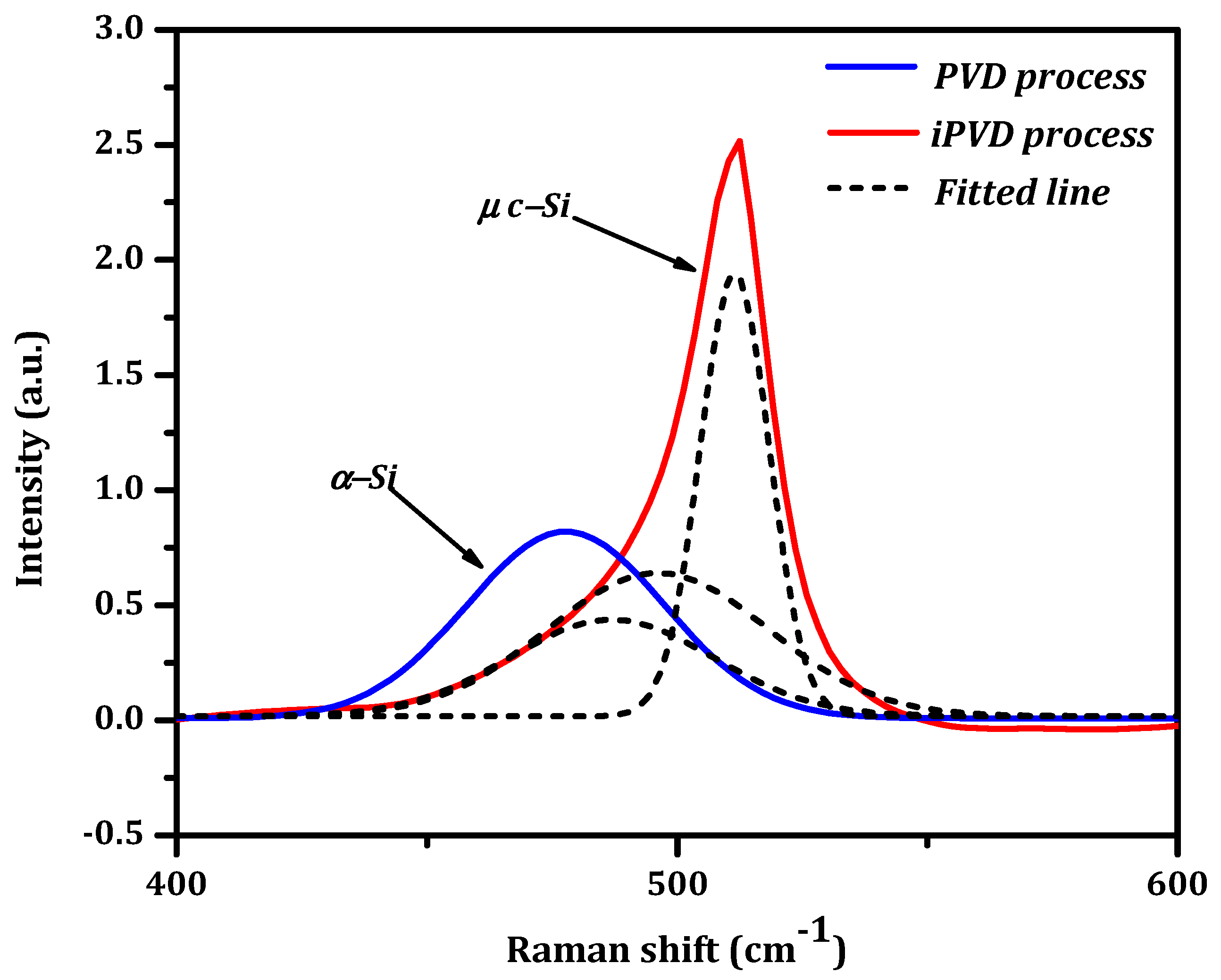
3.2. Raman Spectroscopy
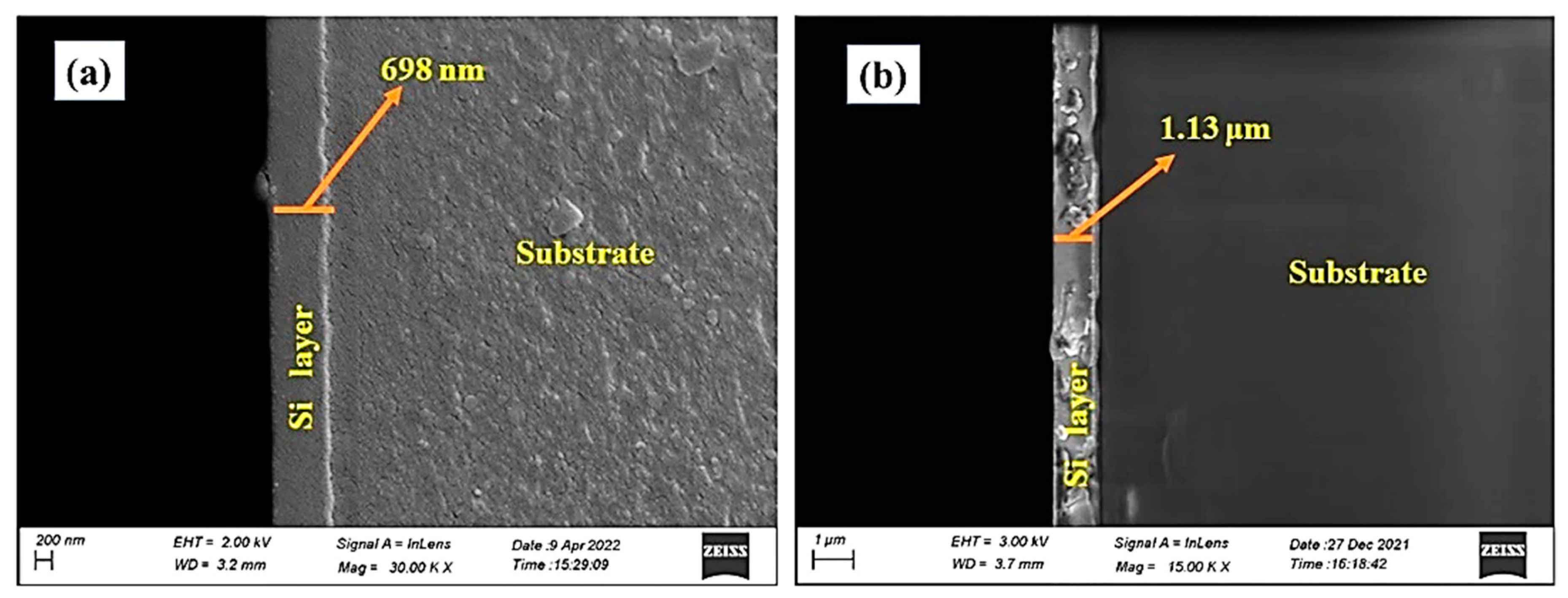
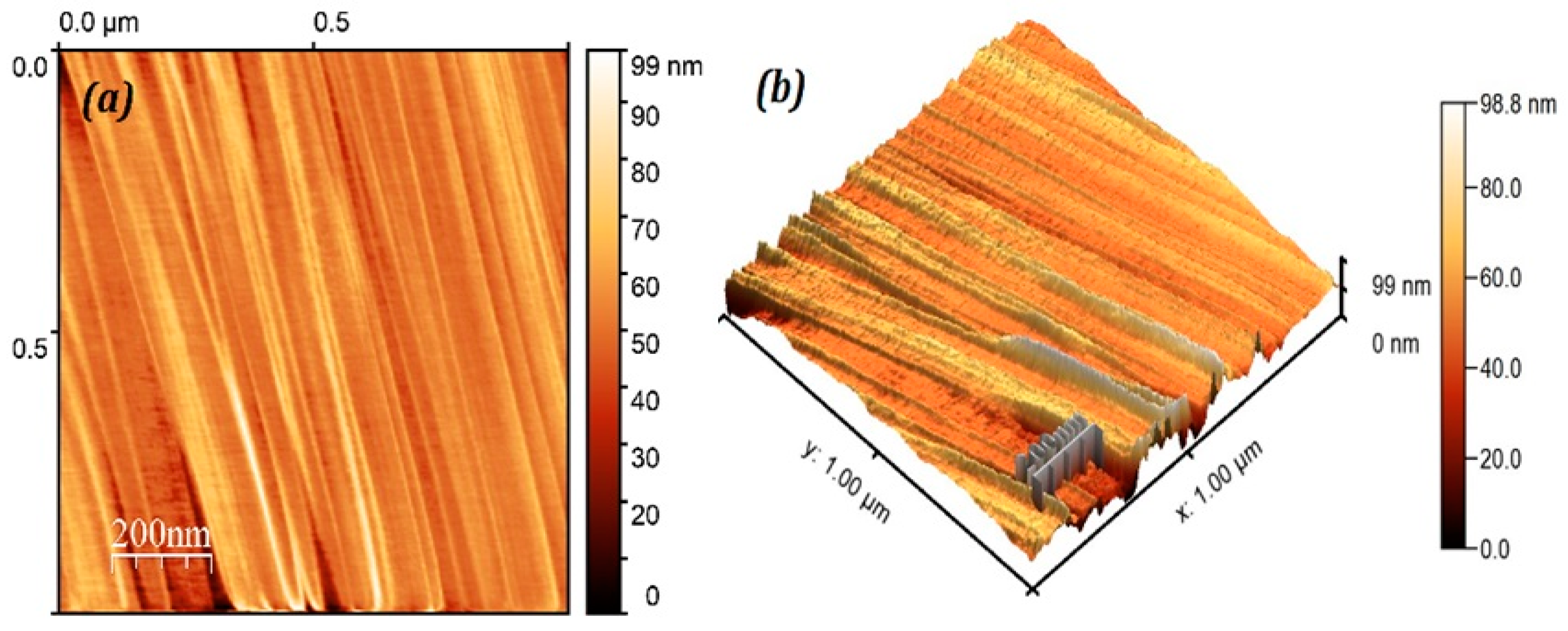
3.3. Morphological Studies
3.4. Surface Roughness
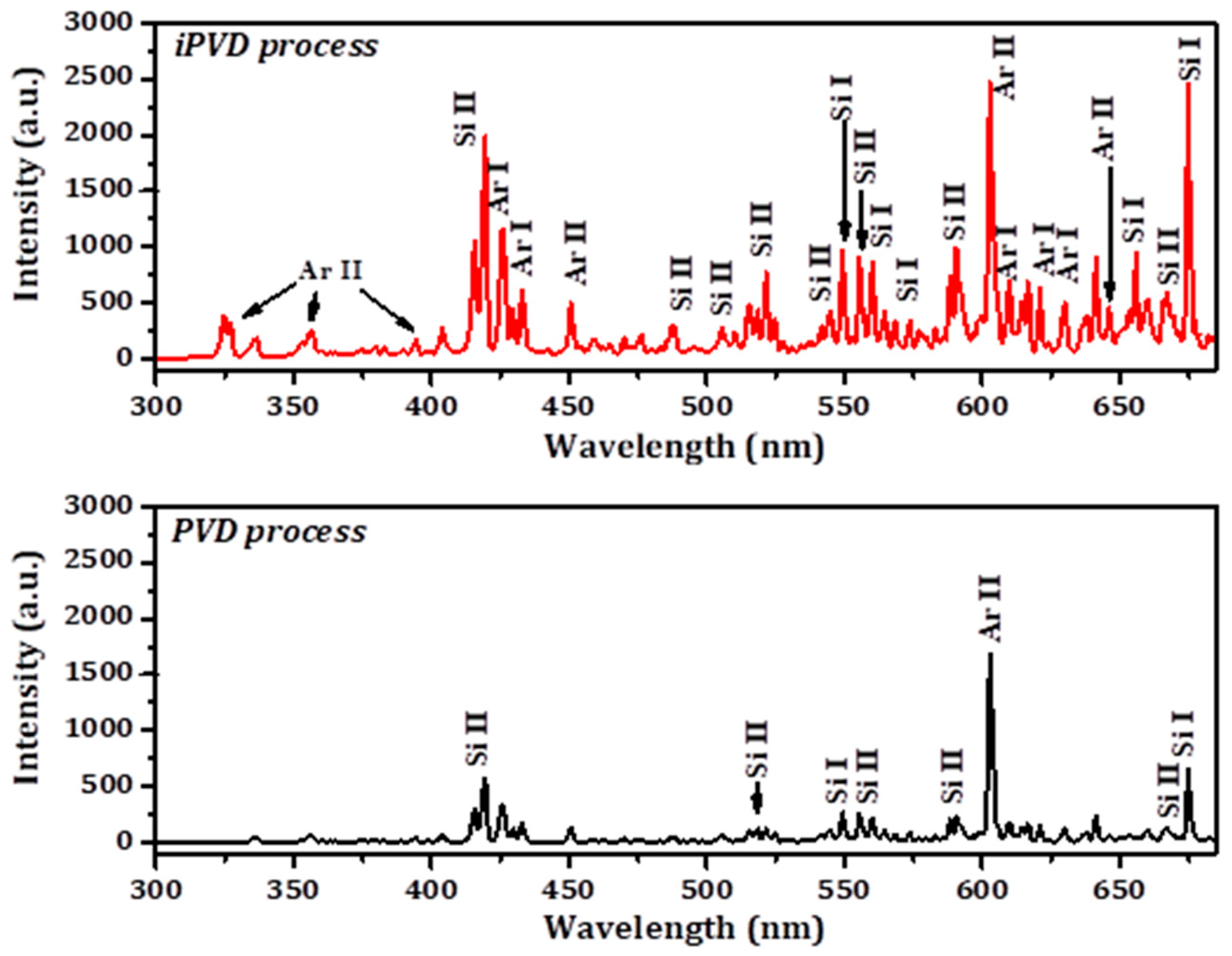
3.5. Optical Emission Spectroscopy (OES) Analysis
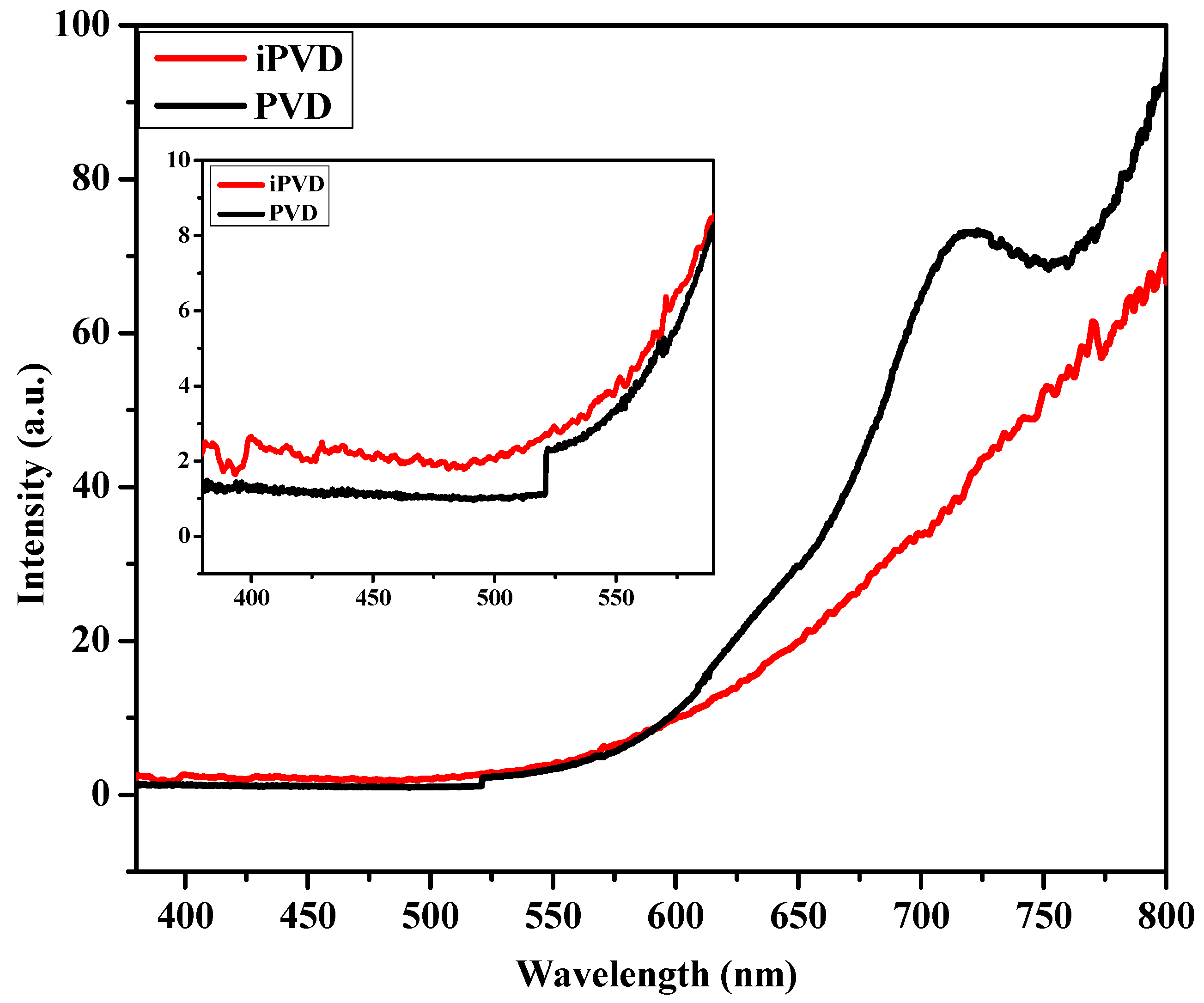
3.6. UV-Visible Spectroscopy
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Takenaka, K.; Setsuhara, Y.; Han, J.G.; Uchida, G.; Ebe, A. Plasma-enhanced reactive linear sputtering source for formation of silicon-based thin films. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 2018, 89, 083902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kunii, T.; Mori, K.; Kiriyama, T.; Kitao, J.; Yoshida, N.; Nonomura, S. Resonant photothermal bending spectroscopy at variable temperature 25–150 °C and its application to hydrogenated microcrystalline silicon films. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 2003, 74, 881–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, K.Y.; Hashem, E.; Gordijn, A.; Stiebig, H.; Knipp, D. Modelling of contact effects in microcrystalline silicon thin-film transistors. Appl. Phys. A 2009, 96, 751–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schropp, R.E.I. Amorphous (Protocrystalline) and Microcrystalline Thin Film Silicon Solar Cells. In Nanostructured Materials for Solar Energy Conversion; Soga, T., Ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2006; pp. 131–166. [Google Scholar]
- Shah, A.; Vallat-Sauvain, E.; Torres, P.; Meier, J.; Kroll, U.; Hof, C.; Droz, C.; Goerlitzer, M.; Wyrsch, N.; Vanecek, M. Intrinsic microcrystalline silicon (μc-Si:H) deposited by VHF-GD (very high frequency-glow discharge): A new material for photovoltaics and optoelectronics. Mater. Sci. Eng. B 2000, 69–70, 219–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Zhang, X.; Bai, L.; Yan, B. Hydrogenated Amorphous Silicon Thin Film. In Handbook of Photovoltaic Silicon; Yang, D., Ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2019; pp. 693–756. [Google Scholar]
- Cashmore, J.S.; Apolloni, M.; Braga, A.; Caglar, O.; Cervetto, V.; Fenner, Y.; Goldbach-Aschemann, S.; Goury, C.; Hötzel, J.E.; Iwahashi, T.; et al. Improved conversion efficiencies of thin-film silicon tandem (MICROMORPH™) photovoltaic modules. Sol. Energy Mater Sol. Cells 2016, 144, 84–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, M.; Chen, G.; Chen, P. Green/blue light emission and chemical feature of nanocrystalline silicon embedded in silicon-oxide thin film. Appl. Phys. A 1997, 65, 195–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Xia, D.; Wang, H.; Zhao, X.J. Hydrogenated nanocrystalline silicon thin film prepared by RF-PECVD at high pressure. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 2010, 356, 2552–2556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schropp, R.E.I. Industrialization of Hot Wire Chemical Vapor Deposition for thin film applications. Thin Solid Film. 2015, 595, 272–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, S.; Wang, D.; Yang, F.; Wang, Z.; Ma, F.J. Grown low-temperature microcrystalline silicon thin film by VHF PECVD for thin films solar cell. J. Nanomater. 2015, 327596, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukhopadhyay, S.; Das, C.; Ray, S.J. Structural analysis of undoped microcrystalline silicon thin films deposited by PECVD technique. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2004, 37, 1736–1741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sher, M.J.; Hammond, K.; Christakis, L.; Mazur, E. The photovoltaic potential of femtosecond-laser textured amorphous silicon. In Laser-Based Micro- and Nanopackaging and Assembly VI; Klotzbach, U., Lu, Y., Washio, K., Eds.; SPIE: St. Bellingham, WA, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Adhikari, D.; Junda, M.M.; Sylvain, X.; Collins, R.W.; Podraza, N.J. Nanostructure evolution of magnetron sputtered hydrogenated silicon thin films. J. Appl. Phys. 2017, 122, 075302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shekoofa, O.; Wang, J.; Li, D.; Luo, Y. Investigation of Microcrystalline Silicon Thin Film Fabricated by Magnetron Sputtering and Copper-Induced Crystallization for Photovoltaic Applications. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 6320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuda, A.J. Microcrystalline silicon.: Growth and device application. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 2004, 338–340, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimizu, S.; Matsuda, A.; Kondo, M. Stability of thin film solar cells having less-hydrogenated amorphous silicon i-layers. Sol. Energ. Mater. Sol. Cells 2008, 92, 1241–1244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.; Wu, Z.L.; Zhang, X.H.; Mishra, B.; Moore, J.J.; Sproul, W.D. A comparative study of CrNx coatings Synthesized by dc and pulsed dc magnetron sputtering. Thin Solid Film. 2009, 517, 1887–1894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.C. Metal-AlN cermet solar selective coatings deposited by direct current magnetron sputtering technology. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 1998, 31, 355–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sproul, W.D.; Graham, M.E.; Wong, M.S.; Lopez, S.; Li, D.J. Reactive direct current magnetron sputtering of aluminum oxide coatings. Vac. Sci. Technol. A 1995, 13, 1188–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelesoglu, E.; Mitterer, C. Structure and properties of TiB2 based coatings prepared by unbalanced DC magnetron sputtering. Surf. Coat. Technol. 1988, 98, 1483–1489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swann, S. Magnetron sputtering. Phys. Technol. 1988, 19, 67–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tohsophon, T.; Hüpkes, J.; Siekmann, H.; Rech, B.; Schultheis, M.; Sirikulrat, N. High rate direct current magnetron sputtered and texture-etched zinc oxide films for silicon thin film solar cells. Thin Solid Film. 2008, 516, 4628–4632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kluth, O.; Rech, B.; Houben, L.; Wieder, S.; Schöpe, G.; Beneking, C.; Wagner, H.; Löffl, A.; Schock, H.W. Texture etched ZnO:Al coated glass substrates for silicon based thin film solar cells. Thin Solid Film. 1999, 351, 247–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ou, Y.X.; Ouyang, X.P.; Liao, B.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, S. Hard yet tough CrN/Si3N4 multilayer coatings deposited by the combined deep oscillation magnetron sputtering and pulsed dc magnetron sputtering. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2020, 502, 144168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batan, A.; Franquet, A.; Vereecken, J.; Reniers, F. Characterisation of the silicon nitride thin films deposited by plasma magnetron. Surf. Interface Anal. 2008, 40, 754–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fthenakis, V.M.; Moskovitz, P.D. An assessment of silane hazards. Solid State Technol. 1990, 33, 81–85. [Google Scholar]
- Van Ommeren, J. Silane gas venting/treatment lessons learned and best practices. Process. Saf. Prog. 2011, 30, 104–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khelifati, N.; Tata, S.; Rahal, A.; Cherfi, R.; Fedala, A.; Kechouane, M.; Mohammed-Brahim, T. The annealing temperature effecton the electrical properties of boron-doped hydrogenated amorphous silicon a-Si:H(B). Phys. Status Solidi 2010, C7, 679–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Whibi, S.; Derbali, L.; Tristant, P.; Jaoul, C.; Colas, M.; Mayet, R.; Cornette, J.; Ezzaouia, H. Optimized nc-Si:H thin films with enhanced optoelectronic properties prepared by micro-waves PECVD used as an effective silicon surface passivation layer. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2019, 30, 2351–2359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, H.; Wu, A.; Zhang, X.; Li, T. New two-step growth of microcrystalline silicon thin films without incubation layer. J. Cryst. Growth. 2011, 322, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Layadi, N.; Cabarrocas, P.R.I.; Drevillon, B. Real-time spectroscopic ellipsometry study of the growth of amorphous and microcrystalline silicon thin films prepared by alternating silicon deposition and hydrogen plasma treatment. Phys. Rev. B 1995, 52, 5136–5143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, P.; Tripathi, N.; Gupta, N. Nanocrystalline silicon thin film prepared by e-beam evaporation for display application. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2017, 28, 3891–3896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.-Q.; Wang, W.-Y.; Huang, J.-H.; Tan, R.-Q.; Song, W.J.; Chen, J.-M. Growth and properties of hydrogenated microcrystalline silicon thin films prepared by magnetron sputtering with different substrate temperatures. Rare Met. 2022, 41, 1037–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konstantinidis, S.; Nouvellon, C.; Dauchot, J.P.; Wautelet, M.; Hecq, M. RF amplified magnetron source for efficient titanium nitride deposition. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2003, 174–175, 100–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alami, J.; Persson, P.O.; Music, D.; Gudmundsson, J.T.; Bohlmark, J.; Helmersson, U. Ion-assisted physical vapor deposition for enhanced film properties on nonflat surfaces. J. Vac. Sci. Technol. A 2005, 23, 278–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Allain, J.P.; Ruzic, D.N. Enhancement of aluminum oxide physical vapor deposition with a secondary plasma. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2002, 149, 161–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuda, Y.; Koyama, Y.; Tashiro, K.; Fujiyama, H. MgO deposition using reactive ionized sputtering. Thin Solid Film. 2003, 435, 154–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuda, Y.; Iwaya, M.; Koyama, Y.; Shinohara, M.; Fujiyama, H. Effect of inductively-coupled plasma assist on the crystal orientation of magnesium oxide thin films produced by reactive sputtering. Thin Solid Film. 2004, 457, 64–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, J.M.; Sproul, W.D.; Voevodin, A.A.; Matthews, A. Crystalline alumina deposited at low temperatures by ionized magnetron sputtering. J. Vac. Sci. Technol. A 1997, 15, 1084–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helmersson, U.; Lattemann, M.; Bohlmark, J.; Ehiasarian, A.P.; Gudmundsson, J.T. Ionized physical vapor deposition (IPVD): A review of technology and applications. Thin Solid Film. 2006, 513, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bohlmark, J.; Östbye, M.; Lattemann, M.; Ljungcrantz, H.; Rosell, T.; Helmersson, U. Guiding the deposition flux in an ionized magnetron discharge. Thin Solid Film. 2006, 515, 1928–1931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, K.S.; Sahu, B.B.; Kumar, M.; Leksakul, K.; Han, J.G. Tailoring of microstructure in hydrogenated nanocrystalline Si thin films by ICP-assisted RF magnetron sputtering. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2015, 48, 475303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasques, A.L.Q.; Torchynska, T.V.; Polupan, G.; Matsumoto-Kuwabara, Y.; Khomenkova, L.; Shcherbyna, L.V. Size Dependent Photoluminescence of Si Nano-Crystals Embedded in Amorphous Silicon. Solid State Phenom. 2008, 131–133, 71–76. [Google Scholar]
- Hsin-Ying, L.; Ting-Chun, W.; Chun-Yen, T. Performance Improvement of Microcrystalline p-SiC/i-Si/n-Si Thin Film Solar Cells by Using Laser-Assisted Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition. Int. J. Photoenergy 2014, 2014, 795152. [Google Scholar]
- Moreno, M.; Boubekri, R.; Cabarrocas, P.R.I. Study of the effects of different fractions of large grains of μc-Si: H: F films on the infrared absorption on thin film solar cells. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 2012, 100, 16–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elsholz, F.; Schöll, E.; Rosenfeld, A. Control of surface roughness in amorphous thin-film growth. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2004, 84, 4167–4169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klossek, A.; Mankovics, D.; Arguirov, T.; Ratzke, M.; Kirner, S.; Friedrich, F.; Gabriel, O.; Stannowski, B.; Schlatmann, R.; Kittler, M. Growth process of microcrystalline silicon studied by combined photoluminescence and Raman investigations. J. Appl. Phys. 2013, 114, 223511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kakati, B.; Kausik, S.S.; Bandyopadhyay, M.; Saikia, B.K.; Kaw, P.K. Development of a novel surface assisted volume negative hydrogen ion source. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 11078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kakati, B.; Kausik, S.S.; Bandyopadhyay, M.; Saikia, B.K.; Saxena, Y.C. Effect of argon addition on plasma parameters and dust charging in hydrogen plasma. J. Appl. Phys. 2014, 116, 163302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nisha, N.; Sahu, B.B. Overall aspect for designing magnetron sputtering plasma sources and their applications in the deposition of ITO films. AIP Adv. 2024, 14, 050702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahne, N.; Čekada, M.; Panjan, M. Total and differential sputtering yields explored by SRIM simulations. Coatings 2022, 12, 1541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, F.; Serra, R.; Oliveira, J.C.; Cavaleiro, A. Effect of peak target power on the properties of Cr thin films sputtered by HiPIMS in deep oscillation magnetron sputtering (DOMS) mode. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2014, 258, 249–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, W.; Peng, J.; Xu, Z.; Shen, Q.; Wang, C. Effect of power on structural and mechanical properties of DC magnetron sputtered Cr coatings. Metals 2023, 13, 691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, H.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, X.D.; Ge, H.; Wang, Z.P. Microcrystalline silicon thin films and triple-junction solar cells. Adv. Mater. Res. 2012, 468–471, 1912–1915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.-H.; Shin, M.; Lim, M.-H.; Seo, J.-Y.; Lee, J.-E.; Lee, H.-Y.; Kim, B.-J.; Choi, D. Material properties of microcrystalline silicon for solar cell application. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 2011, 95, 207–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, B.; Yue, G.; Yang, J.; Banerjee, A.; Guha, S. Hydrogenated microcrystalline silicon single-junction and multi-junction solar cells. Mater. Res. Soc. Symp. Proc. 2003, 762, A4.1.1–A4.1.12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müllerova, J.; Šutta, P.; Holá, M. Optical absorption in Si: H thin films: Revisiting the role of the refractive index and the absorption coefficient. Coatings 2021, 11, 1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Sl. No. | Deposition Technique | Substrate Temperature (°C) | Post Annealing (°C) | Silane Gas Used | Hydrogen Gas Used | Crystallization Fraction (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Microwave plasma-enhanced chemical vapor deposition (MW-PECVD) [30] | 250 | No | Yes | Yes | ~91 |
| 2 | Electron cyclotron resonance plasma-enhanced chemical vapor deposition (ECR-PECVD) [31] | 250 | No | Yes | Yes | 22.9 to 50.6 |
| 3 | Capacitively coupled rf (13.56 MHz) glow discharge system [32] | 250 | No | Yes | Yes | 64 |
| 4 | E-beam evaporation technique [33] | 90 | 300 | No | - | Crystalline |
| 5 | RF (13.56 MHz) magnetron sputtering [34] | 100–300 | No | No | Yes | ~49.2% to ~61.0%. |
| 6 | Ionized physical vapor deposition (Present work) | Room temperature | No | No | No | ~70% |
| Si Deposition | Sputtering Process | Substrate Temperature | Operating Pressure (MBAR) | Ar flow Rate (SCCM) | DC Discharge Voltage/Discharge Current | RF Power (W) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sample 1 | PVD (DC) | Room temperature | 35 | 500 volt/250 mA | 0 | |
| Sample 2 | iPVD (RF-DC) | Room temperature | 35 | 500 volt/300 mA | 250 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Saikia, R.; Kakati, B.; Hazarika, T.; Sharma, S.; Rajbongshi, T.; Das, M.; Biswas, S.; Kundu, S.; Mahanta, M.K. Fabrication of Microcrystalline Silicon Thin Film by Ionized Physical Vapor Deposition Process. Crystals 2025, 15, 106. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst15020106
Saikia R, Kakati B, Hazarika T, Sharma S, Rajbongshi T, Das M, Biswas S, Kundu S, Mahanta MK. Fabrication of Microcrystalline Silicon Thin Film by Ionized Physical Vapor Deposition Process. Crystals. 2025; 15(2):106. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst15020106
Chicago/Turabian StyleSaikia, Rimlee, Bharat Kakati, Tonmoi Hazarika, Shivam Sharma, Tapan Rajbongshi, Mausumi Das, Subir Biswas, Sarathi Kundu, and Manoj Kumar Mahanta. 2025. "Fabrication of Microcrystalline Silicon Thin Film by Ionized Physical Vapor Deposition Process" Crystals 15, no. 2: 106. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst15020106
APA StyleSaikia, R., Kakati, B., Hazarika, T., Sharma, S., Rajbongshi, T., Das, M., Biswas, S., Kundu, S., & Mahanta, M. K. (2025). Fabrication of Microcrystalline Silicon Thin Film by Ionized Physical Vapor Deposition Process. Crystals, 15(2), 106. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst15020106






