Effect of Ultrasonic Vibration and Average Grain Size on the Deformability of T2 Copper in T-Shaped Micro-Upsetting
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental
2.1. Experimental Setup
2.2. Experimental Material
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Effect of Grain Size
3.2. Effect of Die Opening Angle
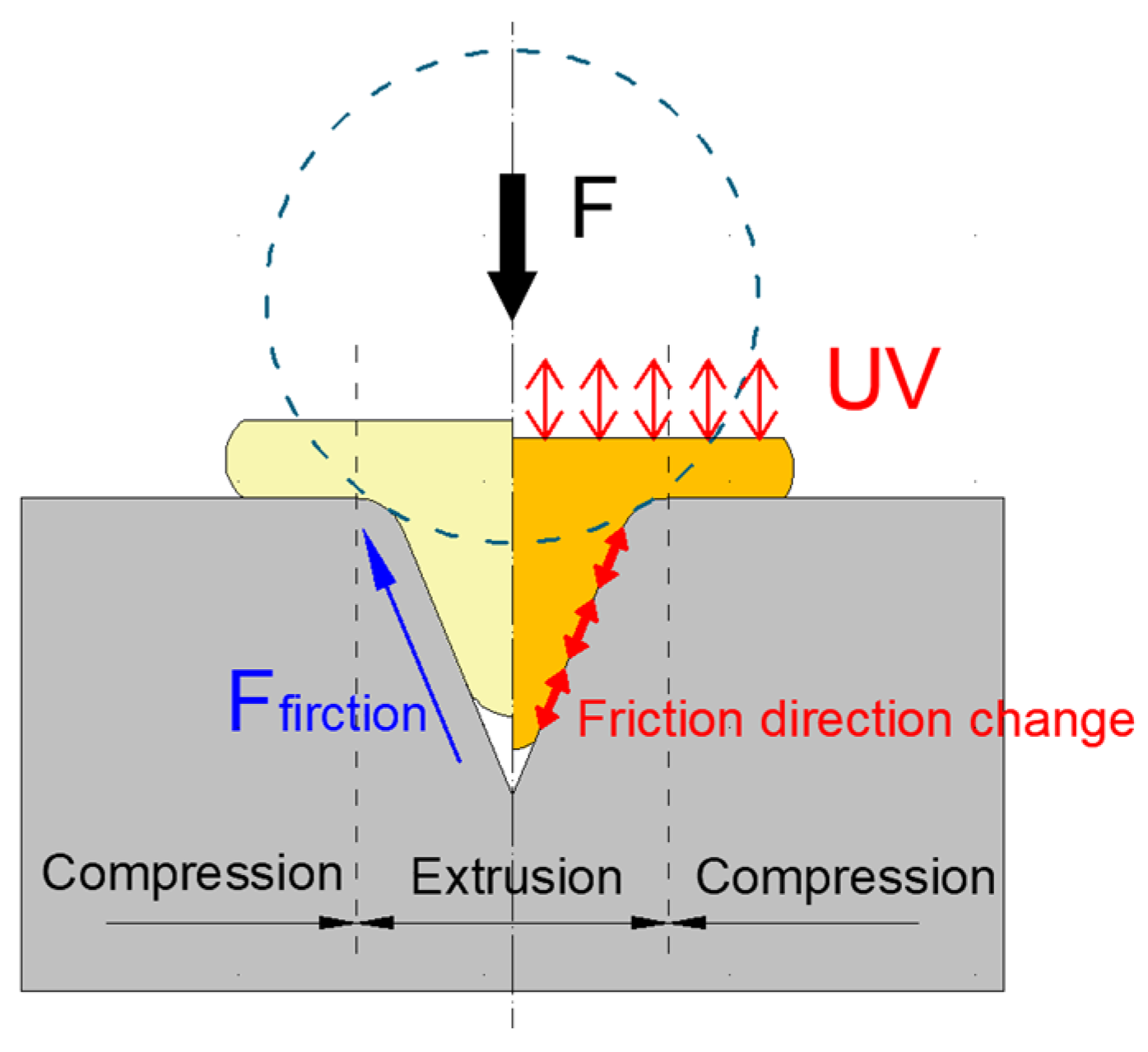
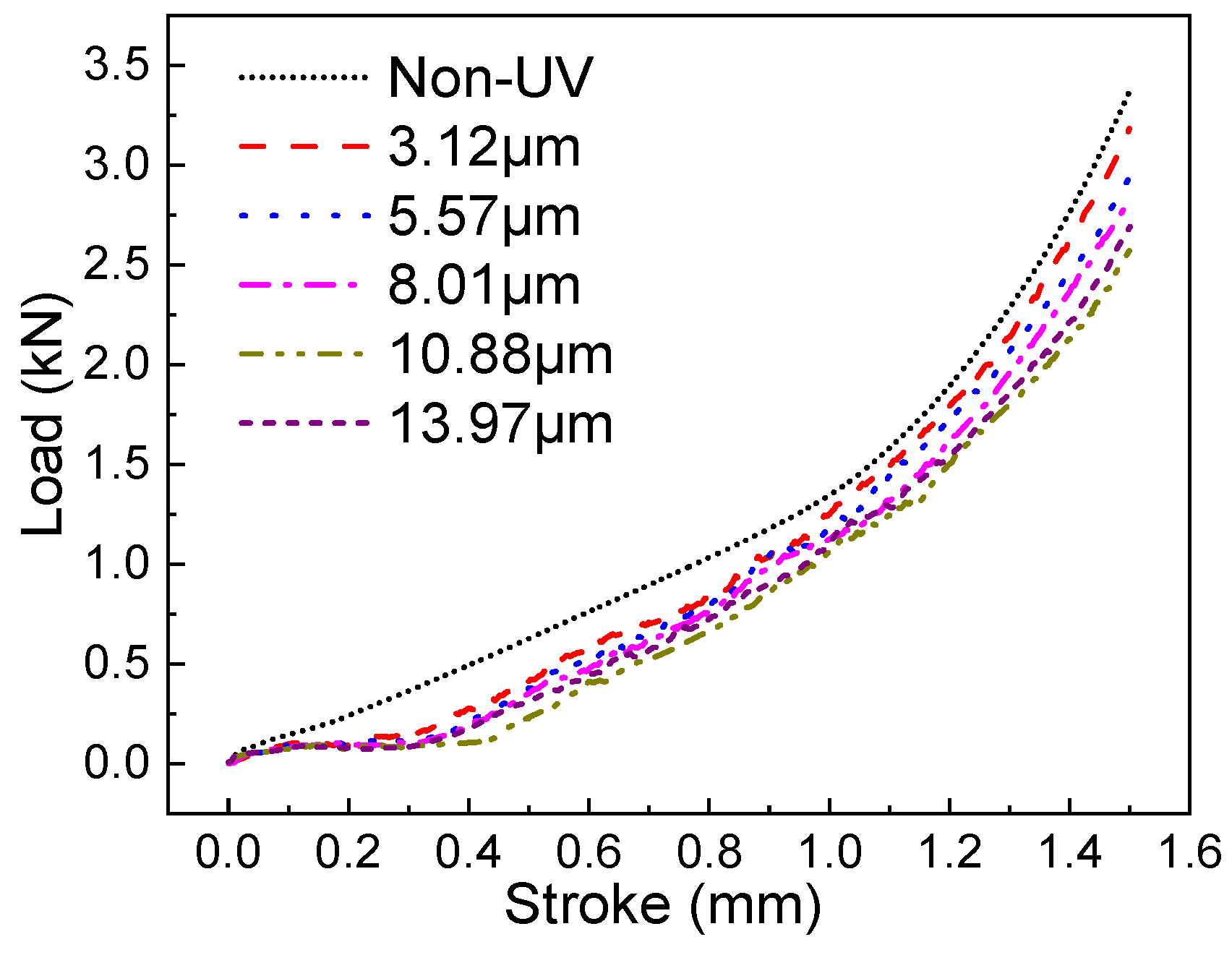
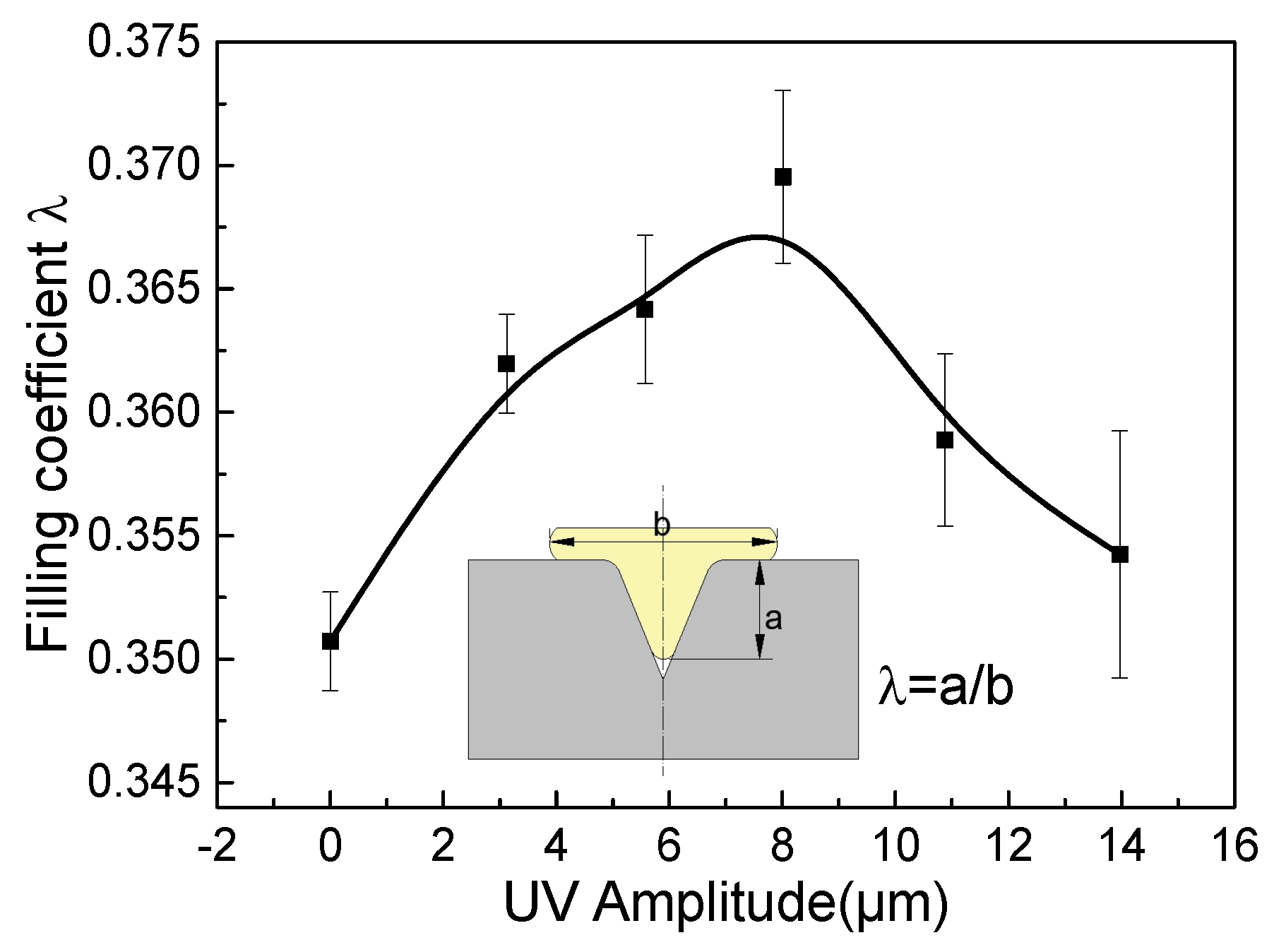
3.3. Effect of Ultrasonic Amplitude
4. Conclusions
- UV can effectively reduce the influence of grain size effects on material plastic forming. The smaller the grain size, the more obvious the softening effect of UV, and the better the V-groove filling performance of the material.
- The forming load in T-shaped micro-upsetting increases with the die opening angle, primarily due to the continuous change in the direction of friction at the specimen/die interface under UV, which reduces the load required for material plastic deformation.
- As the ultrasonic amplitude increases, the forming load monotonically decreases, while the V-groove filling coefficient λ initially increases and then decreases. The material exhibits optimal V-groove filling performance when the ultrasonic amplitude is 8.01 μm.
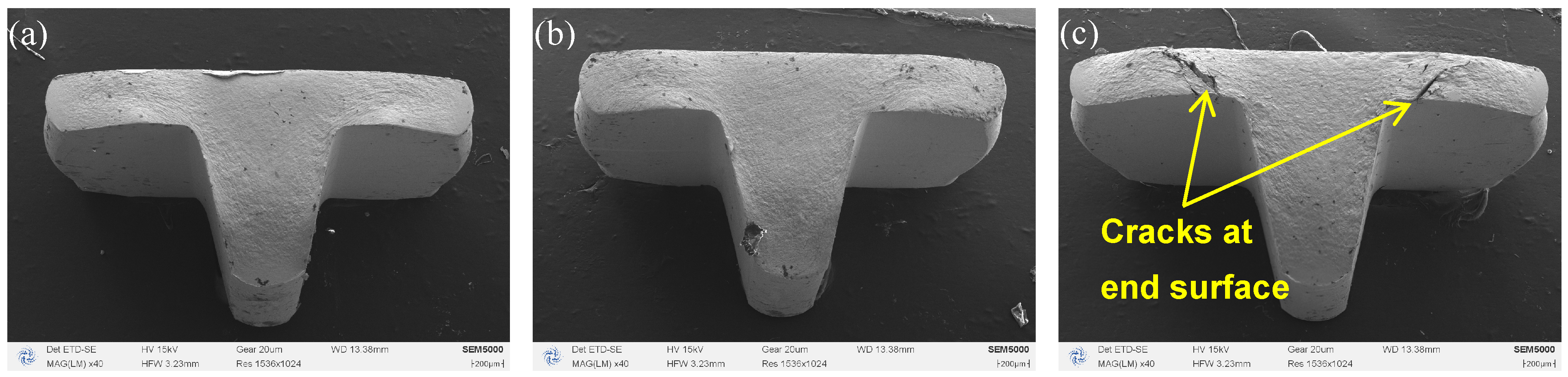
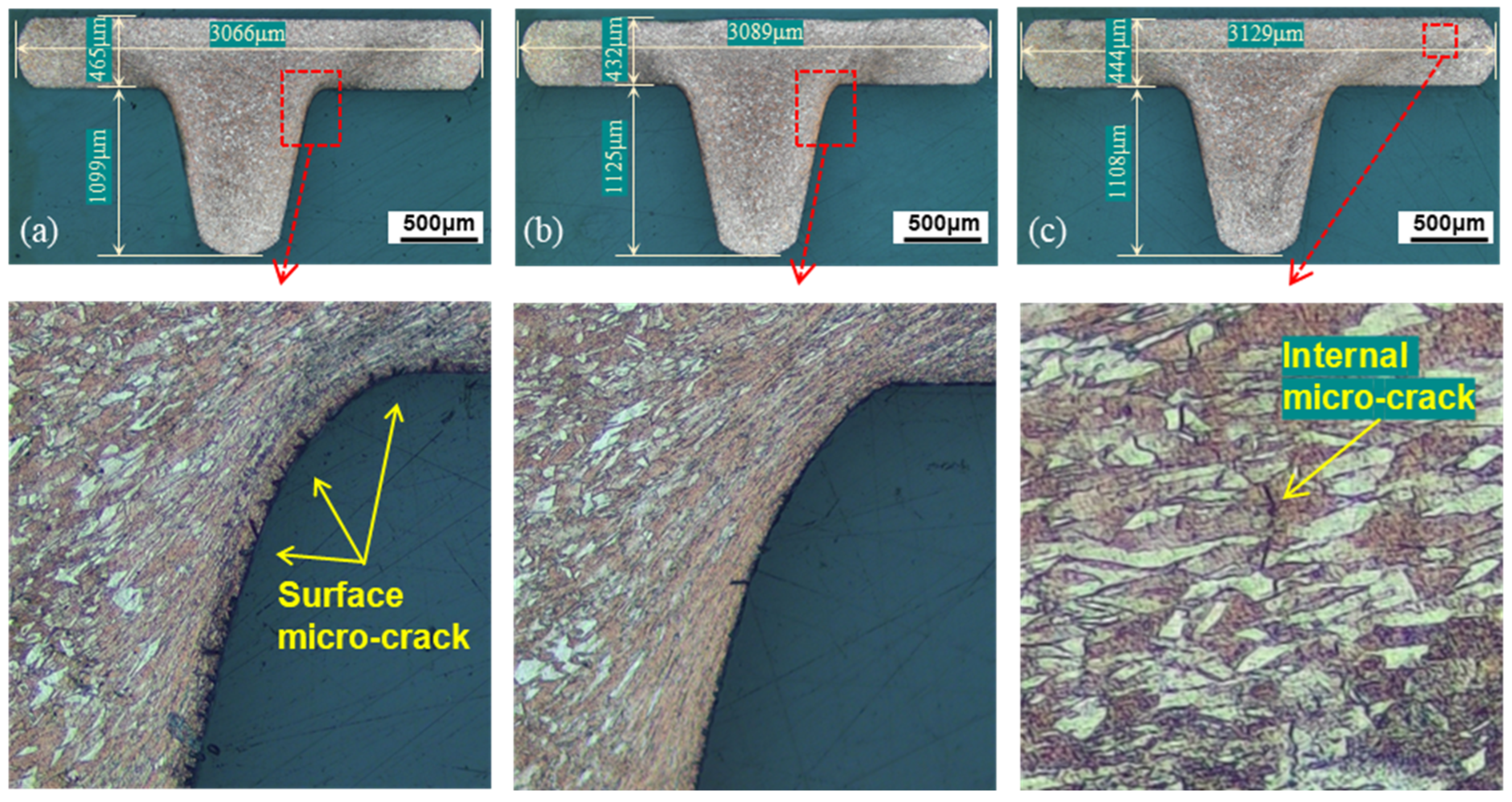
- An appropriate ultrasonic amplitude improves material flowability and reduces surface cracks. However, excessive ultrasonic amplitude can lead to stress concentration within the material, resulting in micro-cracks and premature fracture failure.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shan, D.B.; Li, H.S.; Chen, Y.X.; Ding, C.G.; Xu, Z.H.; Guo, B. Research progress on energy field assisted micro-forming of complex micro parts. J. Netshape Form. Eng. 2024, 16, 23–47. [Google Scholar]
- Rafael, S. Calculating the grain size effect during strain hardening through a probabilistic analysis of the mean slip distance in polycrystals. Int. J. Plast. 2024, 178, 104012. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.D.; Pan, Y.Z.; Wang, H.; Zhang, Z.W.; Fu, X.L.; Men, X.H. Dislocation density evolution and hardening mechanism of AA7050-T7451 surface layer based on anisotropy. Mach. Sci. Technol. 2023, 27, 107–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.J.; Wang, C.J.; Cheng, L.D.; Guo, B.; Shan, D.B. Surface topograph and microstructure analysis in micro forward extrusion parts of T2 copper. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2013, 21, 139–142. [Google Scholar]
- Sui, C.; Liu, Z.; Ai, X.; Liu, C.; Zou, Z. Effect of Ultrasonic Vibration on Grain Size and Precipitated Phase Distribution of 6061 Aluminum Alloy Welded Joint. Crystals 2022, 12, 240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, F.; Hu, Z.; Qin, X.; Ni, M.; Xiong, X.; Liu, G. Improving microstructure and mechanical properties of thin-wall part fabricated by wire arc additive manufacturing assisted with high-intensity ultrasound. J. Mater. Sci. 2023, 58, 2381–2395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, N.; Zhang, C.; Hui, W.J.; Che, H.L.; Yang, Z.G. Study of an economical and effective heat treatment method to improve the performance of gear steels. Steel Res. Int. 2023, 94, 2300030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.X.; Liu, H.W.; Ren, Y.C.; Zhu, L.X. Effect of two-dimensional ultrasonic rolling on grain size and micro-hardness of 7075 aluminum alloy. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2020, 106, 503–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, P.; Yuan, G.; Zhu, X.; Xing, Y.; Wang, Y. Grain size effect of pure Ti foils by micro blanking-deep-drawing compound process. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2022, 123, 1799–1810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alipour, M.; Keshavamurthy, R.; Koppad, P.G.; Shakiba, A.; Reddy, N.C. Investigation of microstructure and mechanical properties of cast Al–10Zn–3.5Mg–2.5Cu nanocomposite reinforced with graphene nano sheets produced by ultrasonic assisted stir casting. Int. J. Met. 2022, 17, 935–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.H.; He, X.C.; Liu, C.C.; Wei, C.G.; Yang, R.; Dong, X.G. Study on the effects of ultrasonic assistance and external heat dissipation on friction stir welded 7075 aluminum alloy joints. J. Manuf. Process. 2023, 107, 280–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bie, W.B.; Zhao, B.; Chen, F.; Wang, X.B.; Zhao, C.Y.; Niu, Y. Progress of ultrasonic vibration-assisted machining surface micro-texture and serviceability. Diam. Abras. Eng. 2023, 43, 401–416. [Google Scholar]
- Deshpande, A.; Hsu, K. Acoustic energy enabled dynamic recovery in aluminium and its effects on stress evolution and post-deformation microstructure. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2018, 711, 62–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Z.D.; Guan, Y.J.; Zhu, L.H.; Zhai, J.Q.; Lin, J.; Yu, X.H. Investigations on the surface effect of ultrasonic vibration-assisted 6063 aluminum alloy ring upsetting. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2018, 96, 4407–4421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bunget, C.; Ngaile, G. Influence of Ultrasonic Vibration on Micro-extrusion. Ultrasonic 2011, 51, 606–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiou, F.J.; Pan, J.N.; Ding, Z.L.; Lin, S.P. Ultrasonic-assisted surface finishing of STAVAX mold steel using lab-made polishing balls on a 5-Axis CNC machining center. Materials 2023, 16, 5888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimizu, T.; Kosuge, S.; Yang, M. Grain size effecton transferability in micro-coining process assisted by ultrasonic vibration. Manuf. Rev. 2015, 2, 5. [Google Scholar]
- Zhai, J.Q.; Guan, Y.J.; Chen, F.J.; Lin, J.; Chu, H.Q. Ultrasonic vibration assisted micro-coining and its mechanism. J. Plast. Eng. 2023, 30, 187–193. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, C.J.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, Z.Q.; Cheng, L.D.; Shan, D.B.; Guo, B. Soft die micro bulging assisted by ultrasonic vibration using T2 copper foil. J. Netshape Form. Eng. 2023, 15, 156–163. [Google Scholar]
- Pang, S.Q.; Ma, C.F.; Zhou, T.F.; Li, G.; Liang, Z.Q.; Wang, X.B. Simulation and experiment study on ultrasonic vibration assisted micro upsetting. J. Harbin Inst. Technol. 2021, 53, 70–77. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.W.; Wang, C.J.; Liu, Y.; Liu, C.; Wang, Z.L.; Guo, B.; Shan, D.B. An energy based modeling for the acoustic softening effect on the Hall-Petch behavior of pure titanium in ultrasonic vibration assisted micro-tension. Int. J. Plast. 2021, 136, 102879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bata, V.; Pereloma, E.V. An alternative physical explanation of the Hall-Petch relation. Acta Mater. 2004, 52, 657–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Zhu, X.C.; Shi, L.; Shan, D.B.; Guo, B.; Terence, G.L. Micro-forming using ultrafine-grained aluminum processed by equal-channel angular pressing. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2015, 17, 1022–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Felder, E.; Bruschi, S. Evaluation of friction condition in cold forging by using T-shape compression test. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2009, 209, 5720–5729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngaile, G.; Bunget, C. Influence of ultrasonic vibration on microforming. Trans. NAMRI/SME 2008, 36, 137–144. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, Z.D.; Guan, Y.J.; Yu, X.H.; Zhu, L.H.; Lin, J. Effects of ultrasonic vibration on performance and microstructure of AZ31 magnesium alloy under tensile deformation. J. Cent. South Univ. 2018, 25, 1545–1559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
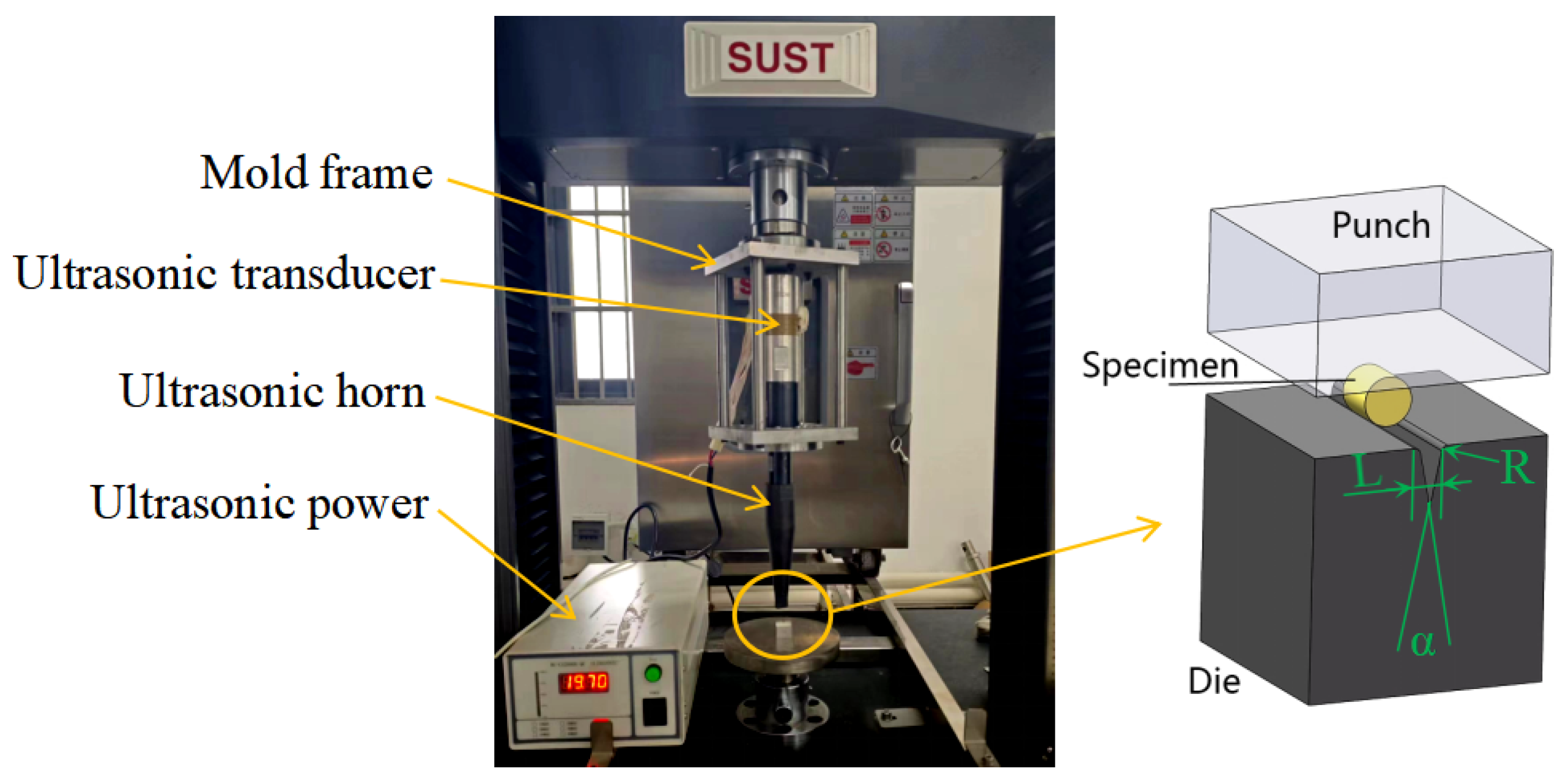
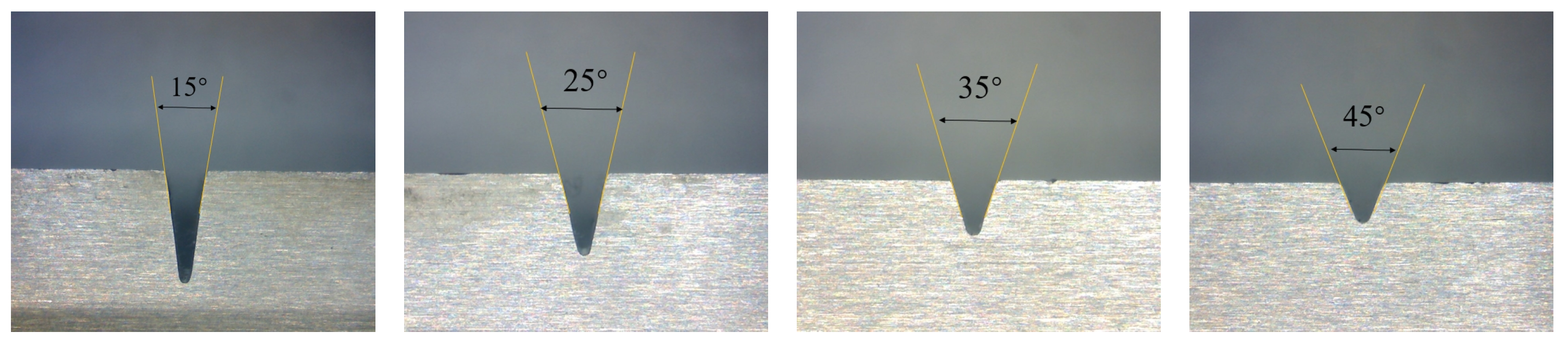



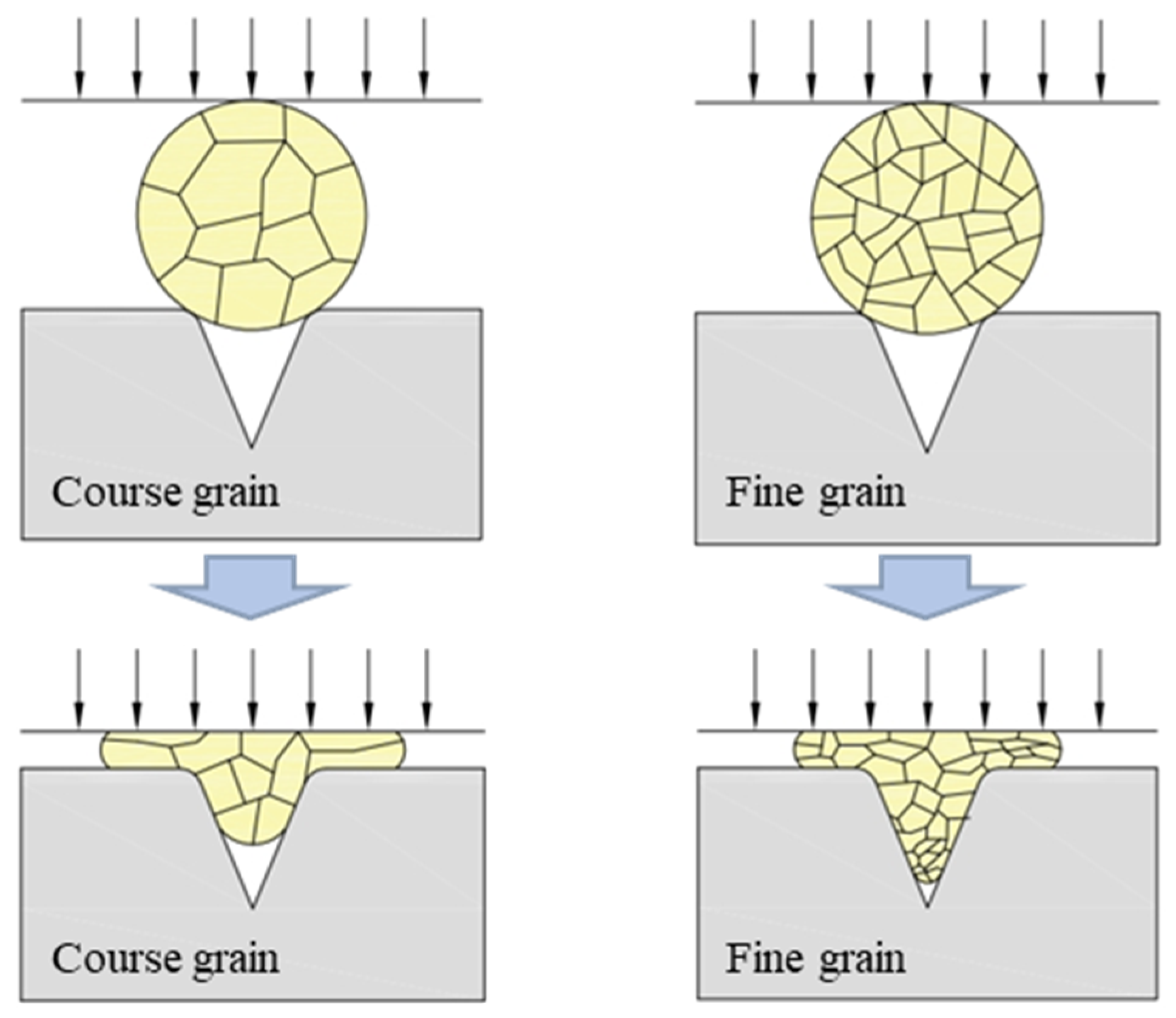
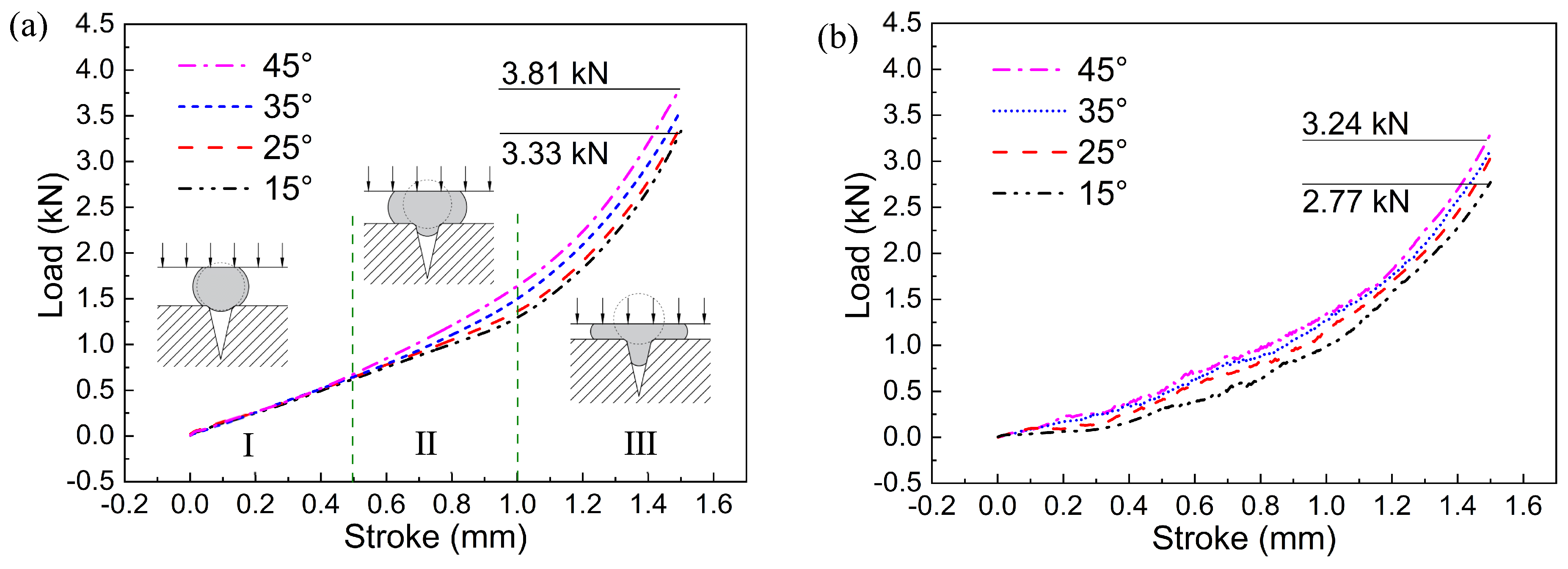
| C | Si | Mn | P | S | Cr | Ni | Cu |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.42–0.50 | 0.17–0.37 | 0.50–0.80 | ≤0.035 | ≤0.035 | ≤0.25 | ≤0.25 | ≤0.25 |
| Cu | Sn | Zn | Bi | Sb | Pb | Fe | As | S | O |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ≥99.90 | ≤0.002 | ≤0.005 | ≤0.002 | ≤0.002 | ≤0.005 | ≤0.005 | ≤0.002 | ≤0.005 | ≤0.006 |
| Heat Treatment | 400 °C for 3 h | 600 °C for 5 h | 700 °C for 12 h |
|---|---|---|---|
| Average grain size | 8.8 μm | 43.5 μm | 84.6 μm |
| Microstructure | 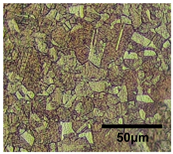 | 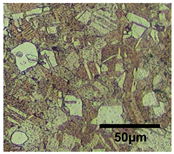 | 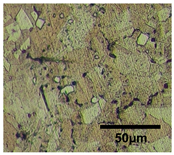 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jia, L.; Liu, Y.; Bi, R.; Li, J. Effect of Ultrasonic Vibration and Average Grain Size on the Deformability of T2 Copper in T-Shaped Micro-Upsetting. Crystals 2025, 15, 307. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst15040307
Jia L, Liu Y, Bi R, Li J. Effect of Ultrasonic Vibration and Average Grain Size on the Deformability of T2 Copper in T-Shaped Micro-Upsetting. Crystals. 2025; 15(4):307. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst15040307
Chicago/Turabian StyleJia, Liangsong, Yang Liu, Rengui Bi, and Jian Li. 2025. "Effect of Ultrasonic Vibration and Average Grain Size on the Deformability of T2 Copper in T-Shaped Micro-Upsetting" Crystals 15, no. 4: 307. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst15040307
APA StyleJia, L., Liu, Y., Bi, R., & Li, J. (2025). Effect of Ultrasonic Vibration and Average Grain Size on the Deformability of T2 Copper in T-Shaped Micro-Upsetting. Crystals, 15(4), 307. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst15040307






