Carbochlorination Reduction Process of Waelz ZnO: Characterization of Resulting ZnO-Based Oxides
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Obtention of the Samples
2.2. Characterization of the Samples
3. Results and Discussion
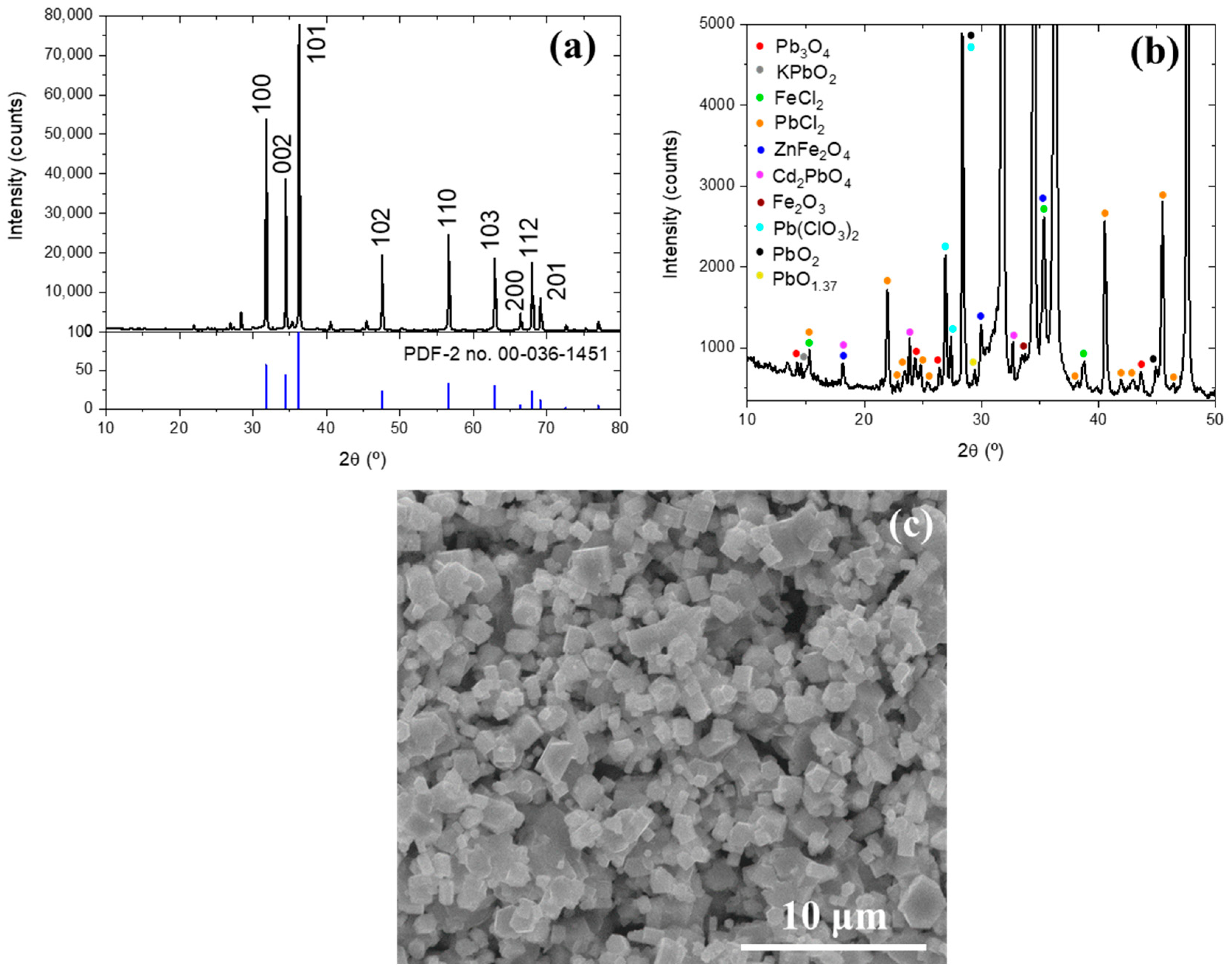
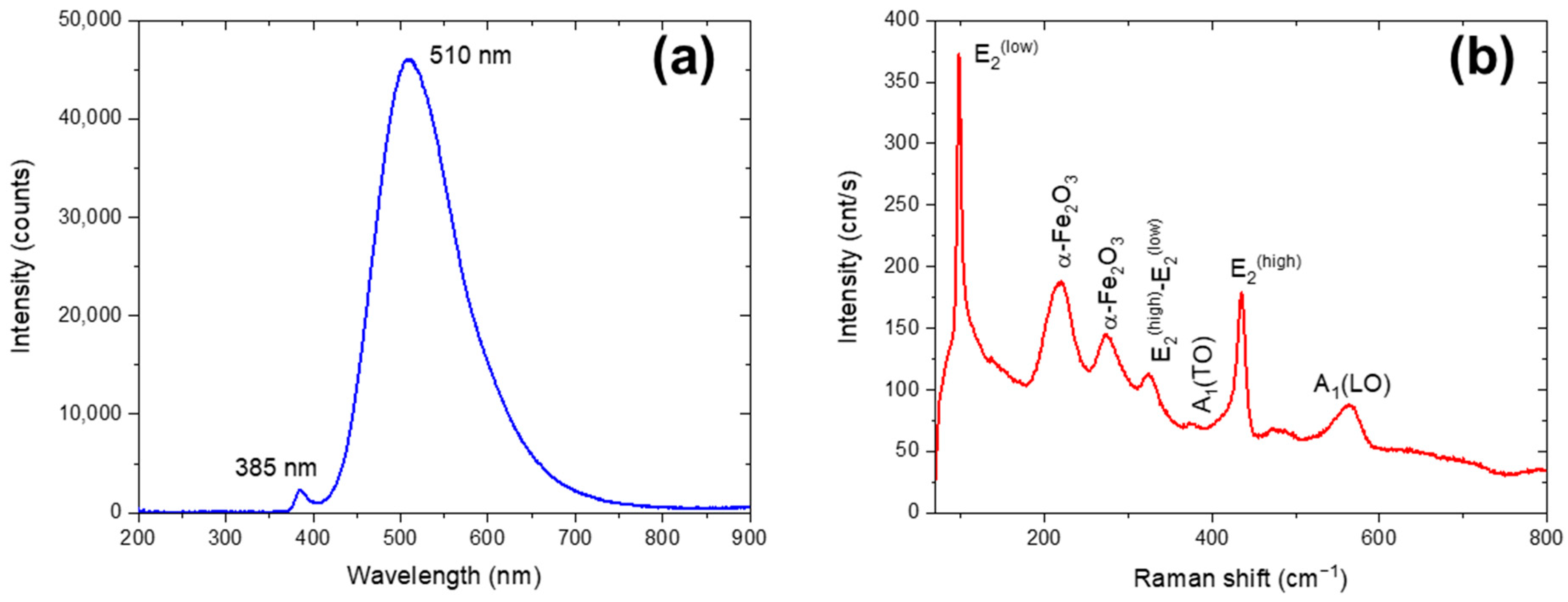
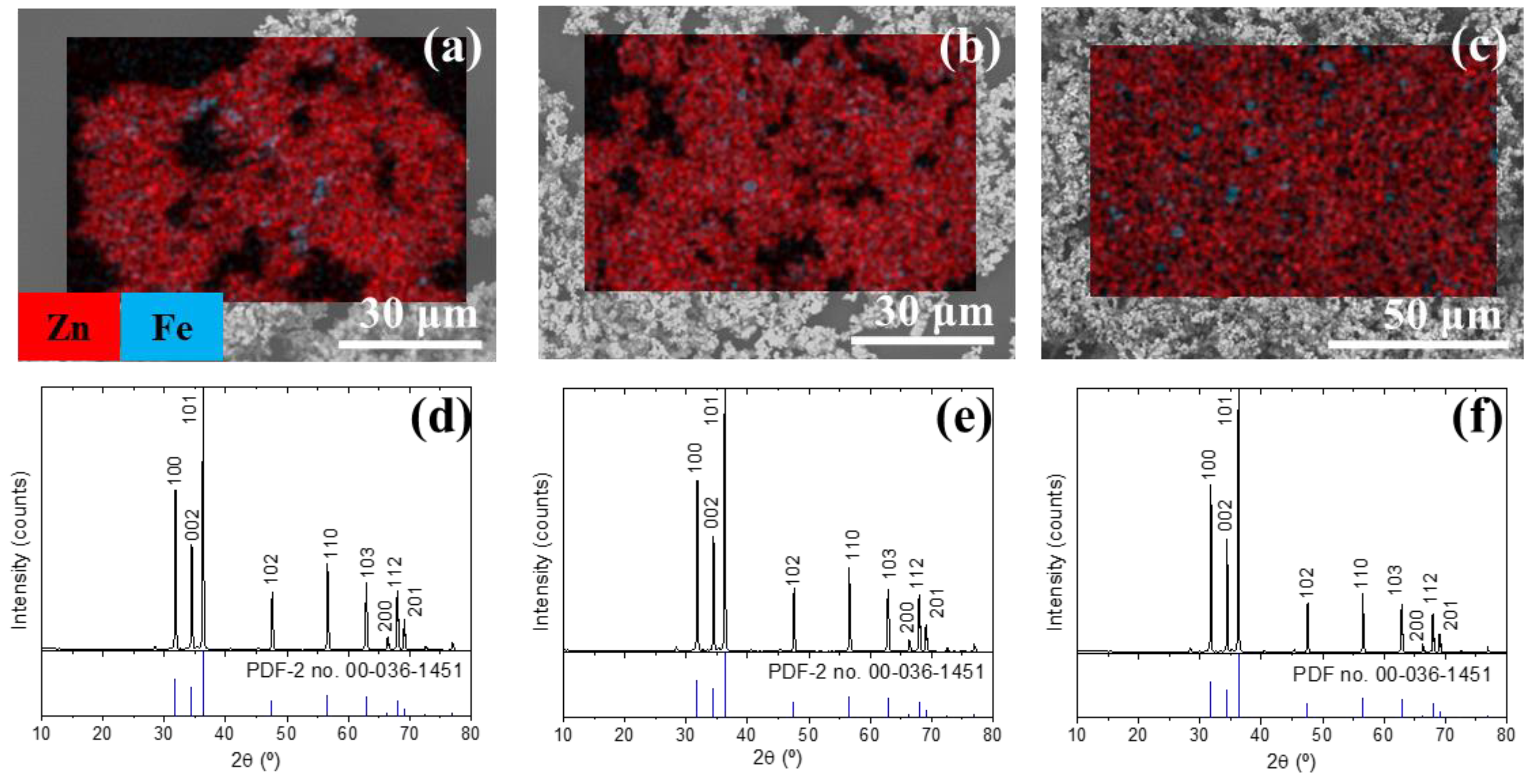
3.1. Characterization of the Initial Waelz Oxide Sample
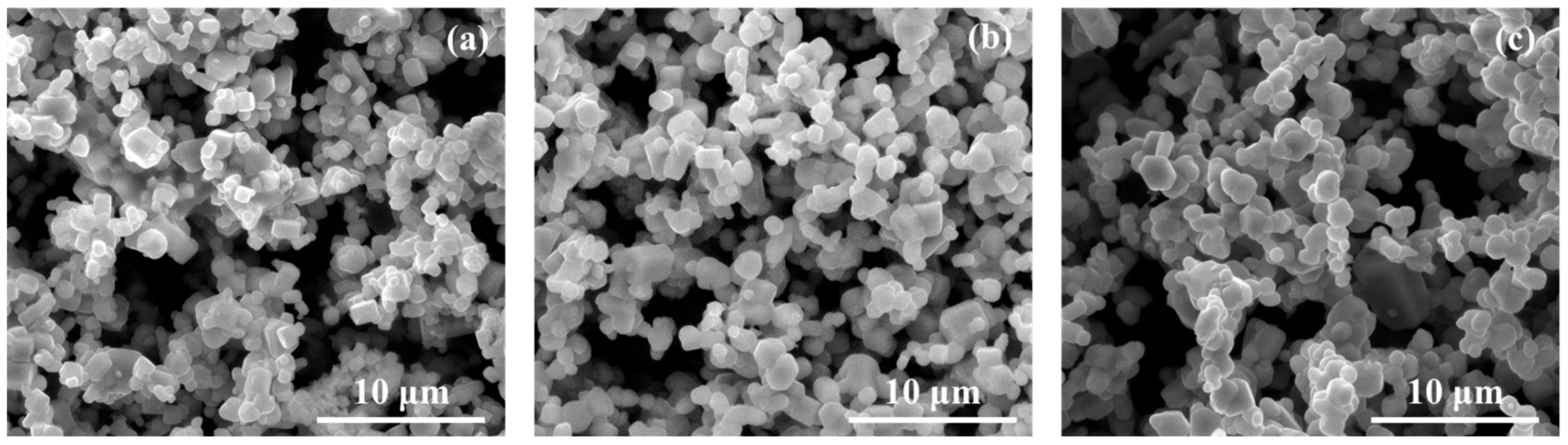
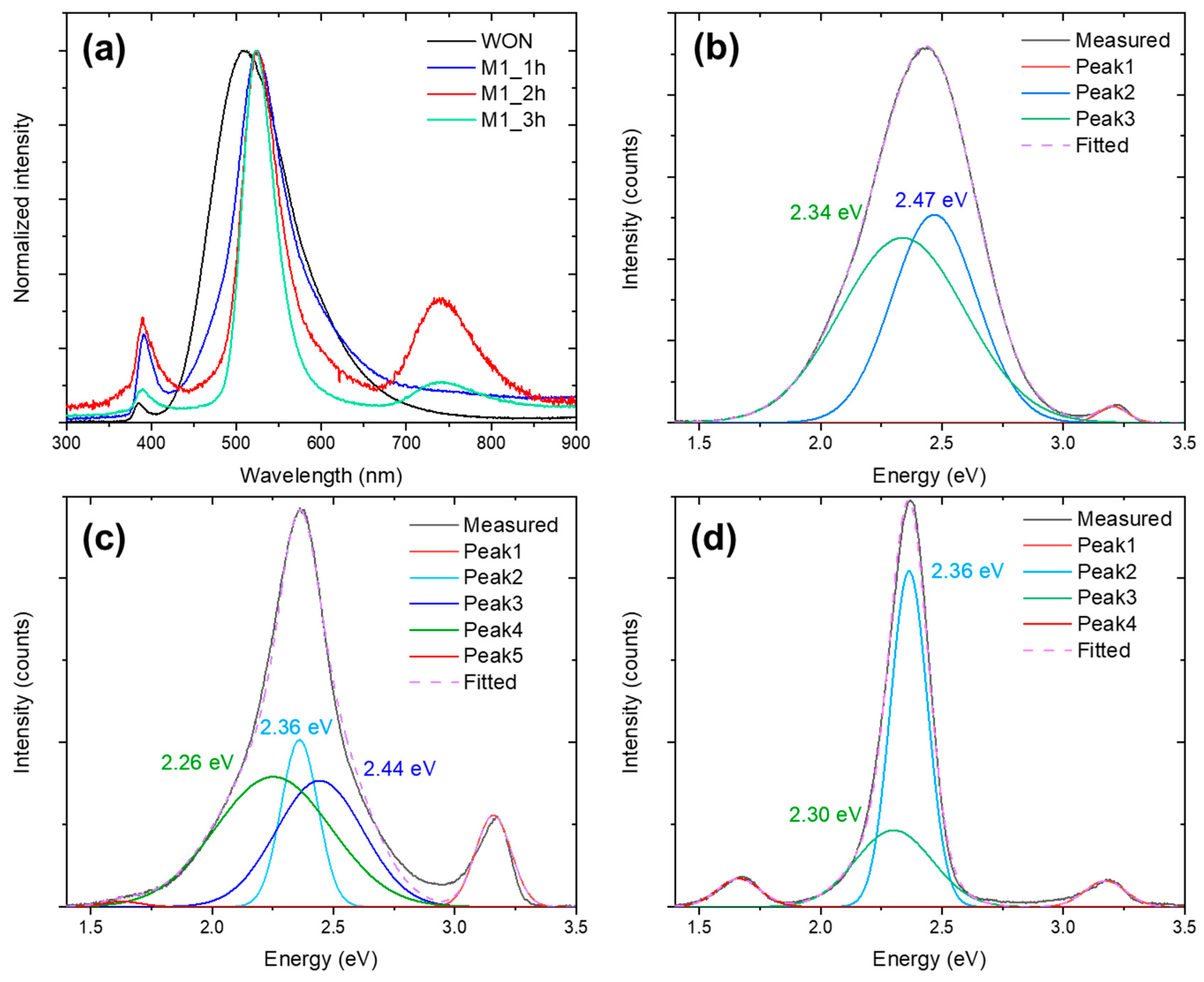
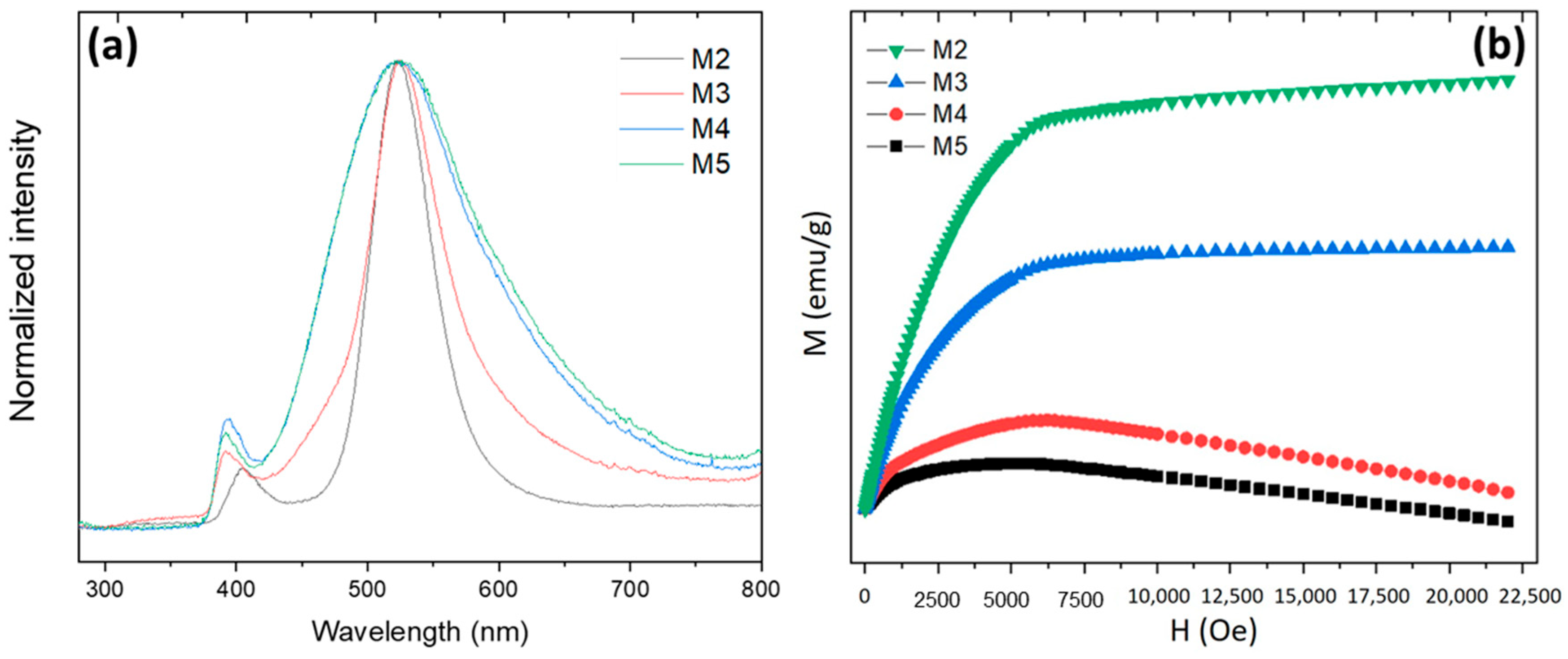
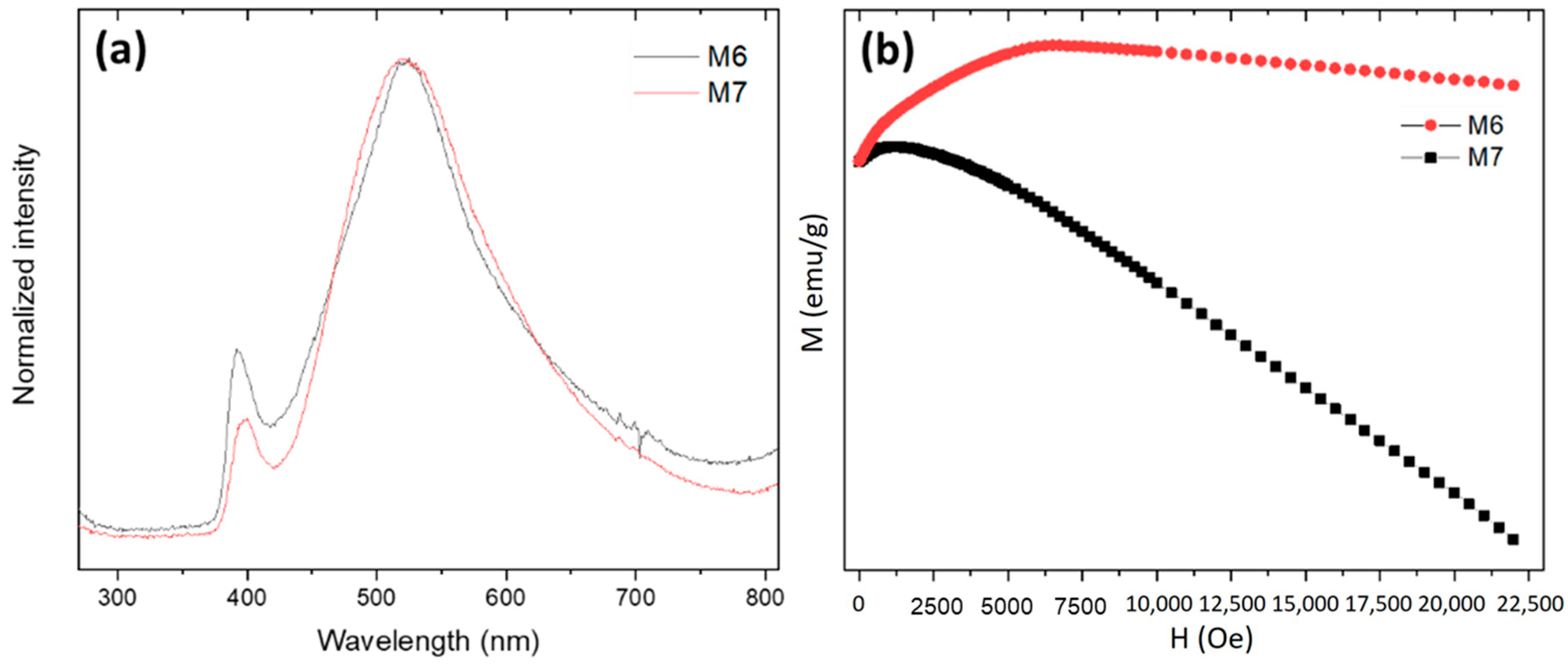
3.2. Effect of the Reaction Time
3.3. Carbochlorination Reduction Tests from Waelz Oxide
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sinha, S.; Choudhari, R.; Mishra, D.; Shekhar, S.; Agrawal, A.; Sahu, K.K. Valorisation of Waste Galvanizing Dross: Emphasis on Recovery of Zinc with Zero Effluent Strategy. J. Environ. Manag. 2020, 256, 109985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sar, S.; Sundqvist Ökvist, L.; Sparrman, T.; Engström, F.; Samuelsson, C. Characterization of Double Leached Waelz Oxide for Identification of Fluoride Mineral. Metals 2019, 9, 361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antuñano, N.; Cambra, J.F.; Arias, P.L. Hydrometallurgical Processes for Waelz Oxide Valorisation—An Overview. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2019, 129, 308–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zoraga, M.; Yucel, T.; Ilhan, S.; Kalpakli, A. Investigation of Selective Leaching Conditions of ZnO, ZnFe2O4 and Fe2O3 in Electric Arc Furnace Dust in HNO3. J. Serbian Chem. Soc. 2022, 87, 377–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, A.; Mishra, B. Investigation of the Carbochlorination Process for Conversion of Cerium and Neodymium Oxides into Their Chlorides. J. Sustain. Metall. 2015, 1, 189–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buitrago, L.J.H.; Prada, I.D.; Amaral-Labat, G.; Beneduce Neto, F.; e Silva, G.F.B.L. Microstructural, Thermochemistry and Mechanical Evaluation of Self-Reducing Pellets Using Electric Arc Furnace (EAF) Dust Containing Zinc for Waelz Process. Matéria 2018, 23, e12006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Available online: https://www.icdd.com/Pdf-Product-Summary/ (accessed on 15 March 2025).
- Ariza, R.; Dael, M.; Sotillo, B.; Urbieta, A.; Solis, J.; Fernández, P. Vapor-Solid Growth ZnO:ZrO2 Micro and Nanocomposites. J. Alloys Compd. 2021, 877, 160219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Röder, R.; Geburt, S.; Zapf, M.; Franke, D.; Lorke, M.; Frauenheim, T.; da Rosa, A.L.; Ronning, C. Transition Metal and Rare Earth Element Doped Zinc Oxide Nanowires for Optoelectronics. Phys. Status Solidi 2019, 256, 1800604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuscó, R.; Alarcón-Lladó, E.; Ibáñez, J.; Artús, L.; Jiménez, J.; Wang, B.; Callahan, M.J. Temperature Dependence of Raman Scattering in ZnO. Phys. Rev. B 2007, 75, 165202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Lu, X.; Han, C.; Lu, R.; Yang, S.; Song, X. Electrospun Hollow Cage-like α-Fe2O3 Microspheres: Synthesis, Formation Mechanism, and Morphology-Preserved Conversion to Fe Nanostructures. CrystEngComm 2014, 16, 10618–10623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansour, H.; Letifi, H.; Bargougui, R.; De Almeida-Didry, S.; Negulescu, B.; Autret-Lambert, C.; Gadri, A.; Ammar, S. Structural, Optical, Magnetic and Electrical Properties of Hematite (α-Fe2O3) Nanoparticles Synthesized by Two Methods: Polyol and Precipitation. Appl. Phys. A 2017, 123, 787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, R.S.; Kuřitka, I.; Vilcakova, J.; Urbánek, P.; Machovsky, M.; Masař, M.; Holek, M. Structural, Magnetic, Optical, Dielectric, Electrical and Modulus Spectroscopic Characteristics of ZnFe2O4 Spinel Ferrite Nanoparticles Synthesized via Honey-Mediated Sol-Gel Combustion Method. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 2017, 110, 87–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alcaraz, L.; Urbieta, A.; Rabanal, M.E.; Fernández, P.; López, F.A. Photocatalytic Activity of Electric-Arc Furnace Flue Dusts. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2020, 9, 1261–1272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, H.; Pan, N.; Li, M.; Wu, Y.; Wang, X.; Hou, J.G. Probing the Strain Effect on near Band Edge Emission of a Curved ZnO Nanowire via Spatially Resolved Cathodoluminescence. Nanotechnology 2010, 21, 215701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mselmi, F.; Neffati, A.; Kammoun, S. Theoretical Investigation of the Cathodoluminescence Spectra of Co-Doped ZnO Nanowires. J. Lumin. 2018, 198, 124–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, S.; Zhou, M.; Li, Q.; Ronning, C. Intra-Shell Luminescence of Transition-Metal-Implanted Zinc Oxide Nanowires. Nanotechnology 2009, 20, 135704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogugua, S.N.; Ntwaeaborwa, O.M.; Swart, H.C. Luminescence, Structure and Insight on the Inversion Degree from Normal to Inverse Spinel in a ZnAl(2-x)Fex3+O4system. Bol. Soc. Esp. Ceram. Vidr. 2021, 60, 147–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kjeldby, S.B.; Nguyen, P.D.; García-Fernández, J.; Haug, K.; Galeckas, A.; Jensen, I.J.T.; Thøgersen, A.; Vines, L. Prytz Optical Properties of ZnFe2O4 Nanoparticles and Fe-Decorated Inversion Domain Boundaries in ZnO. Nanoscale Adv. 2023, 5, 2102–2110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Granone, L.I.; Nikitin, K.; Emeline, A.; Dillert, R.; Bahnemann, D.W. Effect of the Degree of Inversion on the Photoelectrochemical Activity of Spinel ZnFe2O4. Catalysts 2019, 9, 434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bououdina, M.; Azzaza, S.; Ghomri, R.; Shaikh, M.N.; Dai, J.H.; Song, Y.; Song, W.; Cai, W.; Ghers, M. Structural and Magnetic Properties and DFT Analysis of ZnO:(Al,Er) Nanoparticles. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 32931–32941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dasari, M.; Godavarti, U.; Mote, V. Structural, Morphological, Magnetic and Electrical Properties of Ni-Doped ZnO Nanoparticles Synthesized by Co-Precipitation Method. Process. Appl. Ceram. 2018, 12, 100–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, C.; Zeng, Q.; Goya, G.F.; Torres, T.; Liu, J.; Wu, H.; Ge, M.; Zeng, Y.; Wang, Y.; Jiang, J.Z. ZnFe2O4 Nanocrystals: Synthesis and Magnetic Properties. J. Phys. Chem. C 2007, 111, 12274–12278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| ZnCl2 (wt%) | Reducing Agent | C (wt%) | Time (h) | Sample Notation |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3.5 | Fluid PET | 5 | 1 | M1_1h |
| 2 | M1_2h | |||
| 3 | M1_3h | |||
| 2 | Fluid PET | 3 | 1 | M2 |
| 5 | M3 | |||
| Anthracite | 3 | M4 | ||
| 5 | M5 | |||
| 3.5 | Anthracite | 3 | M6 | |
| 5 | M7 |
| Element | Zn | Fe | Pb | Cd | Mn | Cl |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| wt% | 72.4 | 0.45 | 2.64 | 0.17 | 0.01 | 5.8 |
| Element/C wt% | M2 | M3 | M4 | M5 | M6 | M7 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Zn | 73.74 | 74.23 | 78.29 | 71.67 | 70.71 | 67.21 |
| Fe | 0.61 | 0.77 | 0.57 | 0.52 | 0.51 | 0.52 |
| Pb | 0.01 | 0.57 | 0.10 | 0.54 | 0.03 | 0.67 |
| Cd | 0.01 | - | 0,01 | - | - | - |
| Mn | 0.06 | 0.08 | 0.06 | 0.06 | 0.06 | 0.06 |
| Cl | 0.07 | 0.08 | 0.07 | 0.09 | 0.86 | 0.88 |
| Σ Impurities | 0.76 | 1.5 | 0.8 | 1.21 | 1.46 | 2.13 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Alcaraz, L.; Sotillo, B.; Fernández, P.; López, F.A. Carbochlorination Reduction Process of Waelz ZnO: Characterization of Resulting ZnO-Based Oxides. Crystals 2025, 15, 326. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst15040326
Alcaraz L, Sotillo B, Fernández P, López FA. Carbochlorination Reduction Process of Waelz ZnO: Characterization of Resulting ZnO-Based Oxides. Crystals. 2025; 15(4):326. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst15040326
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlcaraz, Lorena, Belén Sotillo, Paloma Fernández, and Félix A. López. 2025. "Carbochlorination Reduction Process of Waelz ZnO: Characterization of Resulting ZnO-Based Oxides" Crystals 15, no. 4: 326. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst15040326
APA StyleAlcaraz, L., Sotillo, B., Fernández, P., & López, F. A. (2025). Carbochlorination Reduction Process of Waelz ZnO: Characterization of Resulting ZnO-Based Oxides. Crystals, 15(4), 326. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst15040326








