Comparison of the Mesomorphic Behaviour of 1:1 and 1:2 Mixtures of Charged Gay-Berne GB(4.4,20.0,1,1) and Lennard-Jones Particles
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
3.1. Comparison of 1:1 and 1:2 Stoichiometry for a Packing Fraction 0.371
3.2. Comparison of 1:1 and 1:2 Stoichiometry for a Packing Fraction 0.428
3.3. Comparison of 1:1 and 1:2 Stoichiometry for a Packing Fraction 0.514
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Goossens, K.; Lava, K.; Bielawski, C.W.; Binnemans, K. Ionic liquid crystals: Versatile materials. Chem. Rev. 2016, 116, 4643–4807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bowlas, C.J.; Bruce, D.W.; Seddon, K.R. Liquid-crystalline ionic liquids. Chem. Commun. 1996, 14, 1625–1626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nusselder, J.J.H.; Engberts, J.B.F.N.; VanDoren, H.A. Liquid-crystalline and thermochromic behavior of 4-substituted 1-methylpyridinium iodide surfactants. Liq. Cryst. 1993, 13, 213–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ujiie, S.; Mori, A. Cubic mesophase formed by thermotropic liquid crystalline ionic systems-effects of polymeric counterion. Mol. Cryst. Liq. Cryst. 2005, 437, 1269–1275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Causin, V.; Saielli, G. Effect of asymmetric substitution on the mesomorphic behaviour of low-melting viologen salts of bis(trifluoromethanesulfonyl)amide. J. Mater. Chem. 2009, 19, 9153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casella, G.; Causin, V.; Rastrelli, F.; Saielli, G. Viologen-based ionic liquid crystals: Induction of a smectic A phase by dimerisation. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2014, 16, 5048–5051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casella, G.; Causin, V.; Rastrelli, F.; Saielli, G. Ionic liquid crystals based on viologen dimers: Tuning the mesomorphism by varying the conformational freedom of the ionic layer. Liq. Cryst. 2016, 43, 1161–1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Asaftei, S.; Ciobanu, M.; Lepadatu, A.M.; Enfeng, S.; Beginn, U. Thermotropic ionic liquid crystals by molecular-assembly and ion pairing of 4,4’-bipyridinium derivatives and tris(dodecyloxy)benzenesulfonats in a non-polar solvent. J. Mater. Chem. 2012, 22, 14426–14437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butschies, M.; Sauer, S.; Kessler, E.; Siehl, H.-U.; Claasen, B.; Fischer, P.; Frey, W.; Laschat, S. Influence of N-Alkyl Substituents and Counterions on the Structural and Mesomorphic Properties of Guanidinium Salts: Experiment and Quantum Chemical Calculations. Chemphyschem 2010, 11, 3752–3765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sauer, S.; Saliba, S.; Tussetschlager, S.; Baro, A.; Frey, W.; Giesselmann, F.; Laschat, S.; Kantlehner, W. p-Alkoxybiphenyls with guanidinium head groups displaying smectic mesophases. Liq. Cryst. 2009, 36, 275–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sauer, S.; Steinke, N.; Baro, A.; Laschat, S.; Giesselmann, F.; Kantlehner, W. Guanidinium chlorides with triphenylene moieties displaying columnar mesophases. Chem. Mater. 2008, 20, 1909–1915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butschies, M.; Frey, W.; Laschat, S. Designer ionic liquid crystals based on congruently shaped guanidinium sulfonates. Chem. Eur. J. 2012, 18, 3014–3022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tao, J.; Zhong, J.; Liu, P.; Daniels, S.; Zeng, Z. Pyridinium-based ionic liquid crystals with terminal fluorinated pyrrolidine. J. Fluor. Chem. 2012, 144, 73–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goossens, K.; Nockemann, P.; Driesen, K.; Goderis, B.; Goerller-Walrand, C.; Hecke, K.; Van Meervelt, L.; Van Pouzet, E.; Binnemans, K.; Cardinaels, T. Imidazolium ionic liquid crystals with pendant mesogenic groups. Chem. Mater. 2008, 20, 157–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, W.; Zhang, J.; Li, B.; Zhang, M.; Wu, L. Branched quaternary ammonium amphiphiles: Nematic ionic liquid crystals near room temperature. Chem. Commun. 2009, 35, 5269–5271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ringstrand, B.; Jankowiak, A.; Johnson, L.E.; Kaszynski, P.; Pociecha, D.; Gorecka, E. Anion-driven mesogenicity: A comparative study of ionic liquid crystals based on the [closo-1-CB9H10](-) and [closo-1-CB11H12](-) clusters. J. Mater. Chem. 2012, 22, 4874–4880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, R.; Wang, Y. Dual ionic and organic nature of ionic liquids. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 19612–19644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Urahata, S.M.; Ribeiro, M.C.C. Structure of ionic liquids of 1-alkyl-3-methylimidazolium cations: A systematic computer simulation study. J. Chem. Phys. 2004, 120, 1855–1863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Voth, G.A. Unique Spatial Heterogeneity in Ionic Liquids. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2005, 127, 12192–12193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Canongia Lopes, J.N.A.; Pàdua, A.A.H. Nanostructural Organization in Ionic Liquids. J. Phys. Chem. B 2006, 110, 3330–3335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Triolo, A.; Russina, O.; Bleif, H.-J.; Di Cola, E. Nanoscale Segregation in Room Temperature Ionic Liquids. J. Phys. Chem. B 2007, 111, 4641–4644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayes, R.; Warr, G.G.; Atkin, R. Structure and Nanostructure in Ionic Liquids. Chem. Rev. 2015, 115, 6357–6426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kondrat, S.; Bier, M.; Harnau, L. Phase behavior of ionic liquid crystals. J. Chem. Phys. 2010, 132, 184901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Saielli, G.; Bagno, A.; Wang, Y. Insights on the isotropic-to-Smectic a transition in ionic liquid crystals from coarse-grained molecular dynamics simulations: The role of microphase segregation. J. Phys. Chem. B 2015, 119, 3829–3836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saielli, G.; Wang, Y. Role of the electrostatic interactions in the stabilization of ionic liquid crystals: Insights from coarse-grained MD simulations of an imidazolium model. J. Phys. Chem. B 2016, 120, 9152–9160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kofu, M.; Tyagi, M.; Inamura, Y.; Miyazaki, K.; Yamamuro, O. Quasielastic neutron scattering studies on glass-forming ionic liquids with imidazolium cations. J. Chem. Phys. 2015, 143, 234502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nemoto, F.; Kofu, M.; Yamamuro, O. Thermal and structural studies of imidazolium-based ionic liquids with and without liquid-crystalline phases: The origin of nanostructure. J. Phys. Chem. B 2015, 119, 5028–5034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nemoto, F.; Kofu, M.; Nagao, M.; Ohishi, K.; Takata, S.; Suzuki, J.; Yamada, T.; Shibata, K.; Ueki, T.; Kitazawa, Y.; Watanabe, M.; Yamamuro, O. Neutron scattering studies on short- and long-range layer structures and related dynamics in imidazolium-based ionic liquids. J. Chem. Phys. 2018, 149, 54502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nelyubina, Y.V.; Shaplov, A.S.; Lozinskaya, E.I.; Buzin, M.I.; Vygodskii, Y.S. A New volume-based approach for predicting thermophysical behavior of ionic liquids and ionic liquid crystals. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2016, 138, 10076–10079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quevillon, M.J.; Whitmer, J.K. Charge transport and phase behavior of imidazolium-based ionic liquid crystals from fully atomistic simulations. Materials 2018, 11, 64. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, H.; Kubo, M.; Shiba, H. Molecular dynamics study of mesophase transitions upon annealing of imidazolium-based ionic liquids with long-alkyl chains. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2018, 20, 9796–9805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bates, M.A.; Luckhurst, G.R. Computer simulation studies of anisotropic systems. XXX. The phase behavior and structure of a Gay-Berne mesogen. J. Chem. Phys. 1999, 110, 7087–7108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Margola, T.; Saielli, G.; Satoh, K. MD simulations of mixtures of charged Gay-Berne and Lennard-Jones particles as models of ionic liquid crystals. Mol. Cryst. Liq. Cryst. 2017, 649, 50–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saielli, G.; Margola, T.; Satoh, K. Tuning Coulombic interactions to stabilize nematic and smectic ionic liquid crystal phases in mixtures of charged soft ellipsoids and spheres. Soft Matter 2017, 13, 5204–5213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plimpton, S. Fast parallel algorithms for short-range molecular dynamics. J. Comput. Phys. 1995, 117, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Sternberg, M.; Kohler, F.T.U.; Melcher, B.U.; Wasserscheid, P.; Meyer, K. Long-alkyl-chain-derivatized imidazolium salts and ionic liquid crystals with tailor-made properties. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 12476–12481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rohini, R.; Lee, C.-K.; Lu, J.-T.; Lin, I.J.B. Symmetrical 1, 3-dialkylimidazolium based ionic liquid crystals. J. Chin. Chem. Soc. 2013, 60, 745–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhowmik, P.K.; Han, H.S.; Akhter, S.; Han, H.S. Lyotropic liquid-crystalline main-chain viologen polymers. J. Polym. Sci. Part A-Polymer Chem. 1995, 33, 1745–1749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhowmik, P.K.; Han, H.S.; Cebe, J.J.; Burchett, R.A.; Acharya, B.; Kumar, S. Ambient temperature thermotropic liquid crystalline viologen bis(triflimide) salts. Liq. Cryst. 2003, 30, 1433–1440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Causin, V.; Saielli, G. Effect of a structural modification of the bipyridinium core on the phase behaviour of viologen-based bistriflimide salts. J. Mol. Liq. 2009, 145, 41–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berardi, R.; Emerson, A.P.J.; Zannoni, C. Monte Carlo investigations of a Gay-Berne liquid crystal. J. Chem. Soc. Faraday Trans. 1993, 89, 4069–4078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gay, J.G.; Berne, B.J. Modification of the overlap potential to mimic a linear site-site potential. J. Chem. Phys. 1981, 74, 3316–3319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berardi, R.; Fava, C.; Zannoni, C. A Gay–Berne potential for dissimilar biaxial particles. Chem. Phys. Lett. 1998, 297, 8–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, W.M.; Petersen, M.K.; Plimpton, S.J.; Grest, G.S. Liquid crystal nanodroplets in solution. J. Chem. Phys. 2009, 130, 44901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hockney, R.; Eastwood, J. Computer Simulation Using Particles; Adam Hilger; CRC Press: New York, NY, USA, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Shinoda, W.; Shiga, M.; Mikami, M. Rapid estimation of elastic constants by molecular dynamics simulation under constant stress. Phys. Rev. B 2004, 69, 134103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabriel, A.T.; Meyer, T.; Germano, G. Molecular graphics of convex body fluids. J. Chem. Theory Comput. 2008, 4, 468–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frenkel, D.; Louis, A.A. Phase separation in binary hard-core mixtures: An exact result. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1992, 68, 3363–3365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Antypov, D.; Cleaver, D.J. The role of attractive interactions in rod–sphere mixtures. J. Chem. Phys. 2004, 120, 10307–10316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wysocki, A.; Löwen, H. Oscillatory driven colloidal binary mixtures: Axial segregation versus laning. Phys. Rev. E 2009, 79, 41408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vissers, T.; Van Blaaderen, A.; Imhof, A. Band formation in mixtures of oppositely charged colloids driven by an ac electric field. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2011, 106, 228303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, F.; Chen, B.; Glettner, B.; Prehm, M.; Das, M.K.; Baumeister, U.; Zeng, X.; Ungar, G.; Tschierske, C. The trapezoidal cylinder phase: A new mode of self-assembly in liquid-crystalline soft matter. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2008, 130, 9666–9667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, B.; Zeng, X.; Baumeister, U.; Ungar, G.; Tschierske, C. liquid crystalline networks composed of pentagonal, square, and triangular cylinders. Science 2005, 307, 96–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bader, K.; Neidhardt, M.M.; Wöhrle, T.; Forschner, R.; Baro, A.; Giesselmann, F.; Laschat, S. Amino acid/crown ether hybrid materials: How charge affects liquid crystalline self-assembly. Soft Matter 2017, 13, 8379–8391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kirchner, B.; Malberg, F.; Firaha, D.S.; Holl, O. Ion pairing in ionic liquids. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 2015, 27, 463002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
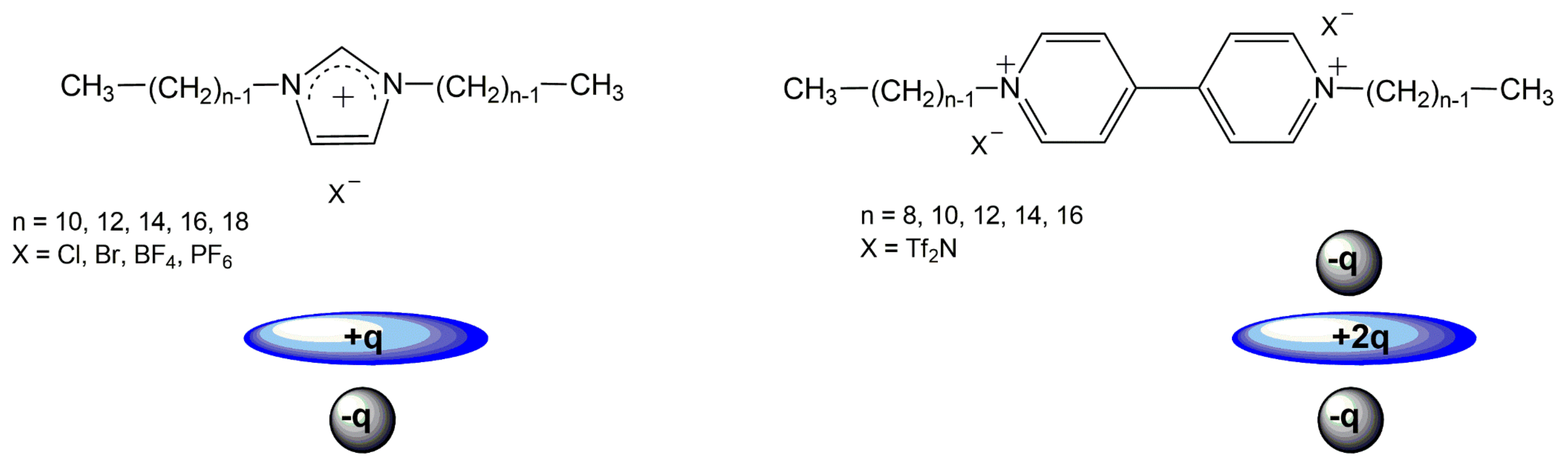









| ρ*(1:1) | ρ*(1:2) | η* | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Case #1 | 0.261 | 0.332 | 0.371 |
| Case #2 | 0.303 a | 0.383 | 0.428 |
| Case #3 | 0.363 a | 0.460 | 0.514 |
| GB:LJ = 1:1 | GB:LJ = 1:2 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| |q*| | Phases | q* | Phases | η* |
| 0.0 a | Sm–1.05–N–1.15–Iso | 0.0/0.0 a | Sm–1.10–Iso | 0.371 |
| 0.5 | Sm–0.70–N–0.75–Iso | 0.50/−0.25 | Sm–0.70–Iso | |
| 2.0 | Cr–0.50–Iso | 1.00/−0.50 | Iso | |
| 0.0 a | Sm–1.35–N–1.84–Iso | 0.0/0.0 a | Sm–1.5–N–2.0–Iso | 0.428 |
| 0.5 | Sm−0.90–N–1.25–Iso | 0.50/−0.25 | Sm–1.0–N–1.10–Iso | |
| 2.0 | Cr–0.65–Iso | 1.00/−0.50 | Cr–0.65–Iso | |
| 2.00/−1.00 | Cr–0.55–Iso | |||
| 0.0 a | Sm–1.9–N–5.7–Iso | 0.0/0.0 a | Sm–2.05–N–4.30–Iso | 0.514 |
| 0.5 | Sm–1.4–N–4.9–Iso | 0.50/−0.25 | Sm–1.0–N–3.1–Iso | |
| 2.0 | Sm–0.75–N–2.25–Iso | 1.00/−0.50 | Sm–0.75–N–2.2–Iso | |
| 2.00/−1.00 | Cr–1.0–Iso | |||
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Margola, T.; Satoh, K.; Saielli, G. Comparison of the Mesomorphic Behaviour of 1:1 and 1:2 Mixtures of Charged Gay-Berne GB(4.4,20.0,1,1) and Lennard-Jones Particles. Crystals 2018, 8, 371. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst8100371
Margola T, Satoh K, Saielli G. Comparison of the Mesomorphic Behaviour of 1:1 and 1:2 Mixtures of Charged Gay-Berne GB(4.4,20.0,1,1) and Lennard-Jones Particles. Crystals. 2018; 8(10):371. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst8100371
Chicago/Turabian StyleMargola, Tommaso, Katsuhiko Satoh, and Giacomo Saielli. 2018. "Comparison of the Mesomorphic Behaviour of 1:1 and 1:2 Mixtures of Charged Gay-Berne GB(4.4,20.0,1,1) and Lennard-Jones Particles" Crystals 8, no. 10: 371. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst8100371
APA StyleMargola, T., Satoh, K., & Saielli, G. (2018). Comparison of the Mesomorphic Behaviour of 1:1 and 1:2 Mixtures of Charged Gay-Berne GB(4.4,20.0,1,1) and Lennard-Jones Particles. Crystals, 8(10), 371. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst8100371






