Tetramer Compound of Manganese Ions with Mixed Valence [MnII MnIII MnIV] and Its Spatial, Electronic, Magnetic, and Theoretical Studies
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Methods
2.1. Equipment and Measurements Conditions
2.2. Computational Details
2.3. Synthesis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Synthesis
3.2. Structural Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Baibich, M.N.; Broto, J.M.; Fert, A.; Nguyen van Dau, F.; Petroff, F.; Etienne, P.; Creuzert, G.; Friedrich, A.; Chazelas, J. Giant magnetoresistance of (001)Fe/(001)Cr magnetic superlattices. J. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1988, 61, 2472–2475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hellman, F.; Tran, M.Q.; Gebala, A.E.; Wilcox, E.M.; Dynes, R.C. Metal-insulator transition and giant negative magnetoresistance in amorphous magnetic rare earth silicon alloys. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1996, 77, 4652–4655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rao, C.N.R.; Cheetham, A.K. Giant magnetoresistance in transition metal oxides. Science 1996, 272, 369–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subramanian, M.A.; Toby, B.H.; Ramirez, A.P.; Marshall, W.J.; Sleight, A.W.; Kwei, G.H. Colossal magnetoresistance without Mn3+/Mn4+ double exchange in the stoichiometric pyrochlore Tl2Mn2O7. Science 1996, 273, 81–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramirez, A.P.; Cava, R.J.; Krajewski, J. Colossal magnetoresistance in Cr-based chalcogenide spinels. Nature 1997, 386, 156–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, J.Y.; Kauzlarich, S.M.; Klavins, P.; Shelton, R.N.; Webb, D.J. Colossal negative magnetoresistance in an antiferromagnet. Phys. Rev. 1998, 57, R8103–R8106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Klavins, P.; Kauzlarich, S.M. Structure, magnetism, and magnetoresistance of the rare-earth transition metal compounds Eu(13)AMnSb(11) (A = Ca, Sr, Ba, and Yb). Chem. Mater. 2002, 14, 2308–2316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sivanesan, D.; Son, K.; Lee, H.-J.; Park, K.T.; Jang, Z.; Suh, B.J.; Yoon, S. Synthesis and magnetic characterization of a cubane-type Mn4 cluster, housed in a sterically hindered carboxylate ligand pocket. Polyhedron 2013, 50, 339–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gatteschi, D.; Sessoli, R. Quantum tunneling of magnetization and related phenomena in molecular materials. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2003, 42, 268–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ritter, S.K. Single-molecule magnets evolve. Chem. Eng. News 2004, 82, 29–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aubin, S.M.J.; Dilley, N.R.; Wemple, M.W.; Maple, M.B.; Christou, G.; Hendrickson, D.N. Half-integer-spin small molecule magnet exhibiting resonant magnetization tunneling. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1998, 120, 839–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.-W.; Zhou, Y.-L.; Chen, Q.; Zeng, M.-H. A unique tridecanuclear Co(II) cluster with derivatised salicylaldoxime ligands: Structure, electrospray ionization mass spectrometry analysis and preliminary magnetic studies. Polyhedron 2010, 29, 148–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Payne, A.C.; Olmstead, M.M.; Kauzlarich, S.M.; Webb, D.J. Structure, magnetism, and magnetoresistance of the compounds Eu14MnAs11 and Eu14MnP11. Chem. Mater. 2001, 13, 1398–1406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Olmstead, M.M.; Klavins, P.; Webb, D.J.; Kauzlarich, S.M. Structure, magnetism, and colossal magnetoresistance (CMR) of the ternary transition metal solid solution Ca14-xEuxMnSb11 (0 < x < 14). Chem. Mater. 2002, 14, 3382–3390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.; Olmstead, M.M.; Kauzlarich, S.M.; Lee, H.O.; Klavins, P.; Fisk, Z. Negative magnetoresistance in a magnetic semiconducting Zintl phase: Eu3In2P4. Inorg. Chem. 2005, 44, 5322–5327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pecoraro, V.L.; Hsieh, W.-Y. The use of model complexes to elucidate the structure and function of manganese redox enzymes. In Metals in Biological Systems; Astrid, S., Helmut, S., Eds.; Marcel-Dekker, Inc.: Basel, Switzerland, 2000; pp. 429–504. [Google Scholar]
- Carrell, T.G.; Tyryshkin, A.M.; Dismukes, G.C. An evaluation of structural models for the photosynthetic water-oxidizing complex derived from spectroscopic and X-ray diffraction signatures. J. Biol. Inorg. Chem. 2002, 7, 2–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kok, B.; Forbush, B.; McGloid, M. Cooperation of charges in photosynthetic O2 evolution-I. A linear four step mechanism. Photochem. Photobiol. 1970, 11, 457–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yachandra, V.K.; Guiles, R.D.; McDermott, A.E.; Britt, R.D.; Cole, J.; Dexheimer, S.L.; Sauer, K.; Klein, M.P.J. The state of manganese in the photosynthetic apparatus determined by X-ray absorption spectroscopy. Phys. Colloq. (Paris) 1986, 47, C8/1121–C8/1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, M.K.; Armstrong, W.H. Tetranuclear manganese-Oxo complex with a 2.7-Å Mn∙∙∙Mn separation and intramolecular H2O∙∙∙(µ-O) hydrogen-bonded contacts: [Mn4O2(TPHPN)2(H2O)2(CF3SO3)2](CF3SO3)3—Possible mode for binding of water at the active site of the oxygen-evolving complex in photosystem-II. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1990, 112, 4985–4986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Zhou, Q.; Chen, Y.; Yang, F.; Yu, Y.; Shi, Z.; Feng, S. Constructing octa- and hexadecanuclear manganese clusters from tetrahedral (Mn3MnII) cores bridged by quinquedentate Schiff base and versatile azide groups. Dalton Trans. 2010, 39, 5504–5508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stoe & Cie. X-AREA and X-RED32; Stoe & Cie: Darmstadt, Germany, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Sheldrick, G.M. A short history of SHELX. Acta Cryst. 2008, A64, 112–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheldrick, G.M. Crystal structure refinement with SHELXL. Acta Cryst. 2015, A71, 3–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frisch, M.J.; Trucks, G.W.; Schlegel, H.B.; Scuseria, G.E.; Robb, M.A.; Cheeseman, J.R.; Scalmani, G.; Barone, V.; Petersson, G.A.; Nakatsuji, H.; et al. Gaussian 09, Revision A.02; Gaussian, Inc.: Wallingford, CT, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Perdew, J.P.; Burke, K.; Ernzerhof, M. Generalized gradient approximation made simple. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1996, 77, 3865–3868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perdew, J.P.; Burke, K.; Ernzerhof, M. Generalized gradient approximation made simple. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1997, 78, 1396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hehre, W.J.; Ditchfield, R.; Pople, J.A. Self-consistent molecular orbital methods. XII. Further extensions of gaussian—type basis sets for use in molecular orbital studies of organic molecules. J. Chem. Phys. 1972, 56, 2257–2261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rassolov, V.A.; Ratner, M.A.; Pople, J.A.; Redfern, P.C.; Curtiss, L.A. 6-31G*basis set for third-row atoms. J. Comput. Chem. 2001, 22, 976–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becke, A.D. Density-functional thermochemistry. III. The role of exact exchange. J. Chem. Phys. 1993, 98, 5648–5652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hay, P.J.; Wadt, W.R. Ab initio effective core potentials for molecular calculations. Potentials for the transition metal atoms Sc to Hg. J. Chem. Phys. 1985, 82, 270–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shriver, D.F.; Atkins, P.W. Inorganic Chemistry, 3rd ed.; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Cungen, Z.; Peizi, Z.; Dan, W.; Kaibei, Y. Evidence of proton transfer from the hydroxyl O atom to the imine N atom, crystal structure of N-salicylideneamine-1-tris(hydroxymethyl)methane. J. Chem. Res. (S) 2000, 8, 402–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagotsky, V.S. Fundamentals of Electrochemistr, 2nd ed.; John Wiley and Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Q; Shi, Q.; Li, Y.-G.; Wang, E.-B. Synthesis, crystal structure and magnetic properties of new MnIII–CuII heterometallic aggregates based on multidentate Schiff-base ligands. J. Coord. Chem. 2008, 61, 3080–3091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Thorp, H.H. Bond valence sum analysis of metal-ligand bond lengths in metalloenzymes and model complexes. 2. Refined distances and other enzymes. Inorg. Chem. 1993, 32, 4102–4105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altermatt, D.; Brown, I.D. The automatic searching for chemical bonds in inorganic crystal structures. Acta Cryst. 1985, B41, 240–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taguchi, T.; Stone, L.K.; Gupta, R.; Kaiser-Lassalle, B.; Yano, J.; Hendrich, P.M.; Borovik, A.S. Preparation and properties of an MnIV-hydroxide complex: Proton and electron transfer at a mononuclear manganese site and its relationship to the oxygen evolving complex within photosystem II. Chem. Sci. 2014, 5, 3064–3071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alvarez, S.; Avnir, D.; Llunell, M.; Pinsky, M. Continuous symmetry maps and shape classification. The case of six-coordinated metal compounds. New J. Chem. 2002, 26, 996–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunitz, J.D.; Orgel, L.E. Electronic properties of transition-metal oxides-I Distortions from cubic symmetry. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 1957, 3, 20–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Origin 2017 Feature Highlights; OriginLab Corporation: Northampton, MA, USA, 2017.
- Robinson, M.B.; Day, P. Mixed-valence chemistry: A survey and classification. Advances. In Inorganic Chemistry and Radiochemistry; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1968; pp. 247–422. [Google Scholar]
- Ross, C.R.; Rubie, D.C.; Paris, E. Rietveld refinement of the high-pressure polymorph of Mn3O4. Am. Mineral. 1990, 75, 1249–1252. [Google Scholar]
- Oku, M. X-ray photoelectron spectra of KMnO4 and K2MnO4 fractured in situ. J. Electron. Spectrosc. Relat. Phenom. 1995, 74, 135–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biesinger, M.C.; Laua, L.W.M.; Gersonb, A.R.; Smart, R.S.C. Resolving surface chemical states in XPS analysis of first row transition metals, oxides and hydroxides: Sc, Ti, V, Cu and Zn. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2010, 257, 2717–2730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nesbitt, H.W.; Banerjee, D. Interpretation of XPS Mn(2p) spectra of Mn oxyhydroxides and constraints on the mechanism of MnO2 precipitation. Am. Mineral. 1998, 83, 305–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iltona, E.S.; Post, J.E.; Heaney, P.J.; Ling, F.T.; Kerisit, S.N. XPS determination of Mn oxidation states in Mn (hydr)oxides. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2016, 366, 475–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Connor, J.A.; Derrick, L.M.R.; Hillier, I.H. H. High energy photoelectron spectroscopy of transition metal complexes. J. Chem. Soc. Faraday Trans. 2 1974, 70, 941–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van De Vondel, D.F.; Wuyts, L.F.; Van Der Kelen, G.P.; Bevernage, L.J. X-ray pes of some manganese carbonyl compounds. J. Electron. Spectrosc. Relat. Phenom. 1977, 10, 389–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, B.J.; Klabunde, K.J.; Sherwood, P.M.A. XPS studies of solvated metal atom dispersed (SMAD) catalysts. Evidence for layered cobalt-manganese particles on alumina and silica. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1991, 113, 855–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, G.C.; Harris, S.J.; Jutson, J.A.; Dyke, J.M. A study of a number of mixed transition metal oxide spinels using X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy. Appl. Surf. Sci. 1989, 37, 111–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Escard, J.; Mavel, G.; Guerchais, J.E.; Kergoat, R. X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy study of some metal(II) halide and pseudohalide complexes. Inorg. Chem. 1974, 13, 695–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, S.-L.; Anderegg, J.W.; Thiel, P.A. Surface oxidation of an A1-Pd-Mn quasicrystal, characterized by X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy. J. Non-cryst. Solids 1996, 195, 95–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenks, C.J.; Chang, S.-L.; Anderegg, J.W.; Thiel, P.A.; Lynch, D.W. Photoelectron spectra of an Al70Pd21Mn9 quasicrystal and the cubic alloy Al60Pd25Mn15. Phys. Rev. B 1996, 54, 6301–6306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stranick, M.A. Mn2O3 by XPS. Surf. Sci. Spectra 1999, 6, 39–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myers, C.E.; Franzen, H.F.; Anderegg, J.W. X-ray photoelectron spectra and bonding in transition-metal phosphides. Inorg. Chem. 1985, 24, 1822–1824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brabers, A.M.; Van Setten, F.M.; Knapen, P.S.A. X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy study of the cation valencies in nickel manganite. J. Solid State Chem. 1983, 49, 93–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nefedov, V.I.; Gati, D.; Dzhurinskii, B.F.; Sergushin, N.P.; Salyn, Y.V. The x-ray electronic studies of oxides of certain elements. Zh. Neorg. Khimii. 1975, 20, 2307. [Google Scholar]
- Calabrese, I.; Merli, M.; Liveri, M.L.T. Deconvolution procedure of the UV–vis spectra. A powerful tool for the estimation of the binding of a model drug to specific solubilisation loci of bio-compatible aqueous surfactant-forming micelle. Spectrochim. Acta Part A: Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2015, 142, 150–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cotton, F.A.; Wilkinson, G. Advanced in Inorganic Chemistry: A Comprehensive Text, 4th ed.; John Wiley and Sons: New York, NY, USA, 1980. [Google Scholar]
- Orgel, L.E. Spectra of transition-metal complexes. J. Chem. Phys. 1955, 23, 1004–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romero, I.; Collomb, M.-N.; Deronzier, A.; Llobet, A.; Perret, E.; Pécaut, J.; Le Pape, L.; Latour, J.-M. A novel dimanganese(II) complex with two chloride bridges—A two-electron oxidation system. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2001, 69–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferguson, J.; Guggenheim, H.J.; Tanabe, Y. The effects of exchange interactions in the spectra of octahedral manganese. II. Compounds. J. Phys. Soc. Jpn. 1966, 21, 692–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muñoz, A.; Casáis, M.T.; Alonso, J.A.; Martínez-Lope, M.J.; Martínez, J.L.; Fernández-Díaz, M.T. Complex magnetism and magnetic structures of the metastable HoMnO3 perovskite. Inorg. Chem. 2001, 40, 1020–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukhopadhyay, S.; Staples, R.J.; Armstrong, W.H. Toward synthetic models for high oxidation state forms of the photosystem II active site metal cluster: The first tetranuclear manganese cluster containing a [Mn4(μ-O)5]6+ core. Chem. Commun. 2002, 864–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bloembergen, N.; Purcell, E.M.; Pound, R.V. Relaxation effects in nuclear magnetic resonance absorption PY. Phys. Rev. 1948, 73, 679–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- La Mar, G.N.; Walker, F.A. Proton nuclear magnetic resonance line widths and spin relaxatin in paramagnetic metalloporphyrins of chomium(III), manganese(III), and iron(III). J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1973, 95, 6950–6956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mabbs, F.E.; Collison, D. Electron Paramagnetic Resonance of d Transition Metal Compounds; Elsevier: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Drago, R.S. Physical Methods in Chemistry, 2nd ed.; Saunders College: Rochester, NY, USA, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Feher, G. Electron Paramagnetic Resonance with Applications to Selected Problems in Biology; Gordon and Breach, Science Publishers: New York, NY, USA, 1970. [Google Scholar]
- Azamat, D.V.; Dejneka, A.; Lancok, J.; Trepakov, V.A.; Jastrabik, L.; Badalyan, A.G. Electron paramagnetic resonance studies of manganese centers in SrTiO3: Non-Kramers Mn3+ ions and spin-spin coupled Mn4+ dimers. J. Appl. Phys. 2012, 111, 104119-1–104119-6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramírez, D.R.; Zamorano, R.U.; Pérez, O.M. Electron spin resonance study of the conversion of Mn4+ to Mn2+ in the Pb1−x EuxTi1−y MnyO3 ceramic system. Solid State Commun. 2001, 118, 371–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syiemlieh, I.; Kumar, A.; Kurbah, S.D.; De, A.K.; Lal, R.A. Low-spin manganese(II) and high-spin manganese(III) complexes derived from disalicylaldehyde oxaloyldihydrazone: Synthesis, spectral characterization and electrochemical studies. J. Mol. Struct. 2018, 1151, 343–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gross, R.; Wolfang, K. Electron spin resonance and electronic spectroscopy of low-spin manganese(II) complexes (C5R5)(CO)2(L)Mn with L = hydrazido(1-), arylamido, anionic nitrile and purine-type ligands. J. Chem. Soc. Faraday Trans. 1 1987, 83, 3549–3564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dexheimer, S.L.; Gohdes, J.W.; Chan, M.K.; Hagen, K.S.; Armstrong, W.H.; Klein, M.P. Detection of EPR spectra in S = 2 states of trivalent manganese complexes. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1989, 11, 8923–8925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abragam, A.; Bleany, B. Electron Paramangnetic Resonance of Transitions Metals Ions; Clarendon Press: Oxford, UK, 1970; pp. 209–211. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, M.K.; Kar, N.K.; Lal, R.A. Synthesis and structural characterization of manganese(III, IV) and ruthenium(III) complexes derived from 2-hydroxy-1-naphthaldehydebenzoylhydrazone. J. Coord. Chem. 2009, 62, 1677–1689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pal, S.; Ghosh, P.; Chakravorty, A. Manganese(IV) in discrete O3S3 coordination. Inorg. Chem. 1985, 24, 3704–3706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bukovec, P.; Hoppe, R. Zur kenntnis von hexagonalem K2[MnF6] [1]. J. Fluor. Chem. 1983, 23, 579–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedersen, E.; Toftlund, H. Electron spin resonance spectra of tetragonal chromium(III) complexes. I. trans-[Cr(NH3)4XY]n+ and trans-Cr(py)4XY]n+ in frozen solutions and powders. Correlation between zero-field splittings and ligand field parameters via complete d-electron calculations. Inorg. Chem. 1974, 13, 1603–1612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krivokapic, I.; Noble, C.; Klitgaard, S.; Tregenna-Piggott, P.; Weihe, H.; Barra, A.-L. Anisotropic hyperfine interaction in the manganese(III) hexaaqua ion. Angew. Chem. 2005, 117, 3679–3682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rotlevi, E.; Eaton, D.R. Magnetic interactions in the Mn(II)/cyanide system. Canadian J. Chem. 1970, 48, 1073–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sheats, J.E.; Czernuszewics, R.S.; Dismikes, G.C.; Rehingold, A.L.; Petrouleas, V.; Stubbe, J.A.; Armstrong, W.H.; Beer, R.H.; Lippard, S.J. Binuclear manganese(III) complexes of potential biological significance. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1987, 109, 1435–1444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milios, J.C.; Piligkos, S.; Bell, R.A.; Laye, H.R.; Teat, J.S.; Vicente, R.; McInnes, E.; Escuer, A.; Perlepes, P.S.; Winpenny, P.E.R. A rare mixed-valence state manganese(II/IV) tetranuclear cage formed using phenyl 2-pyridyl ketone oxime and azide as ligands. Inorg. Chem. Commun. 2006, 9, 638–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, J.; Brechin, E.; Yamaguchi, A.; Nakano, M.; Huffman, C.J.; Maniero, L.A.; Brunel, L.C.; Awaga, K.; Ishimoto, H.; Christou, G.; et al. Single-molecule magnets: A new class of tetranuclear manganese magnets. Inorg. Chem. 2000, 39, 3615–3623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bleaney, B.; Bowers, D.K. Anomalous paramagnetism of copper acetate. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. A 1952, 214, 451–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willet, R.D.; Gateschi, D.; Khan, O. Magnetostructural Correlations in Exchange Coupled Systems; Riedel: Hingham, MA, USA, 1985. [Google Scholar]
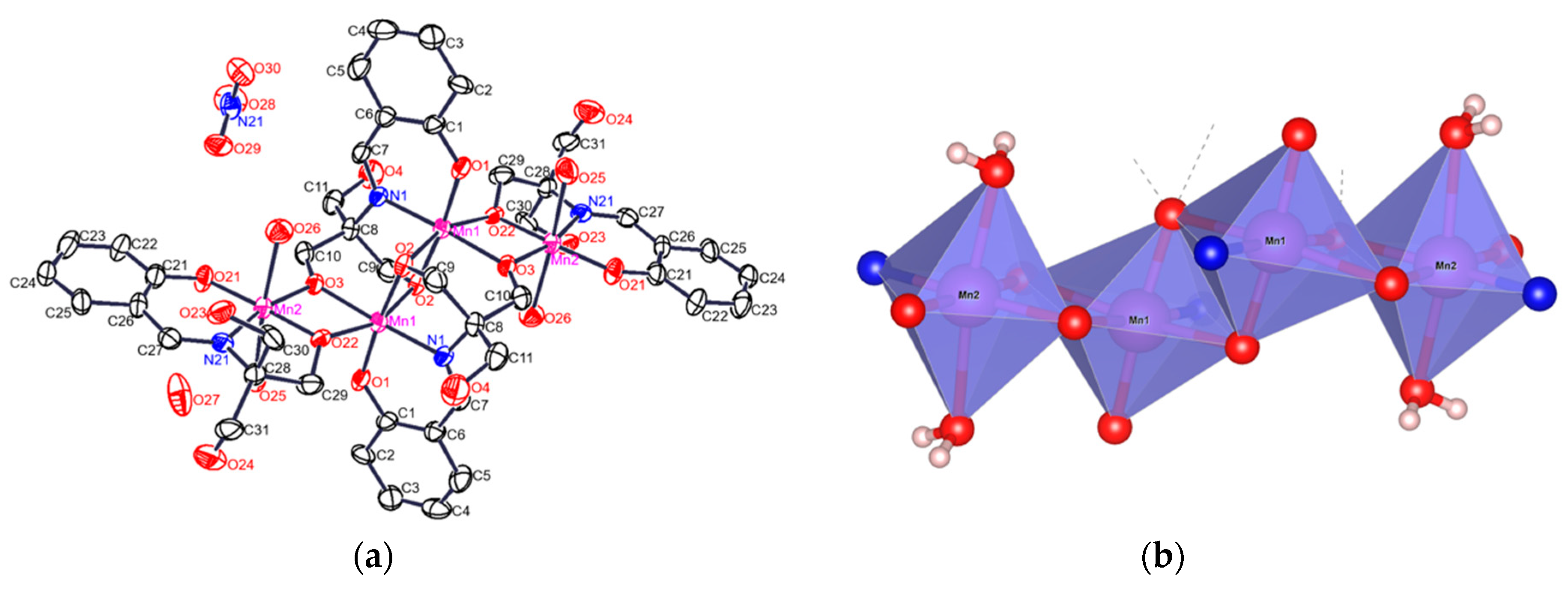




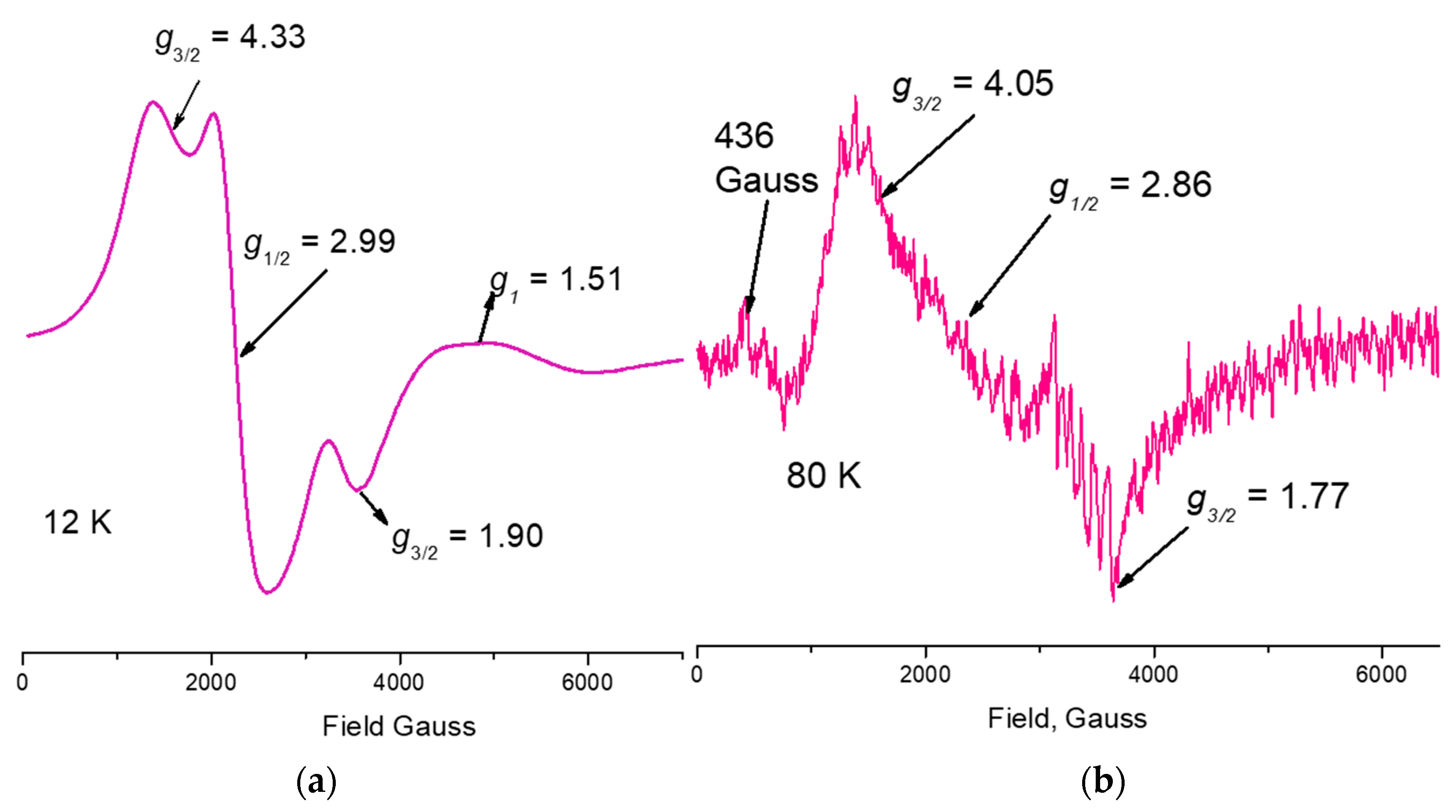



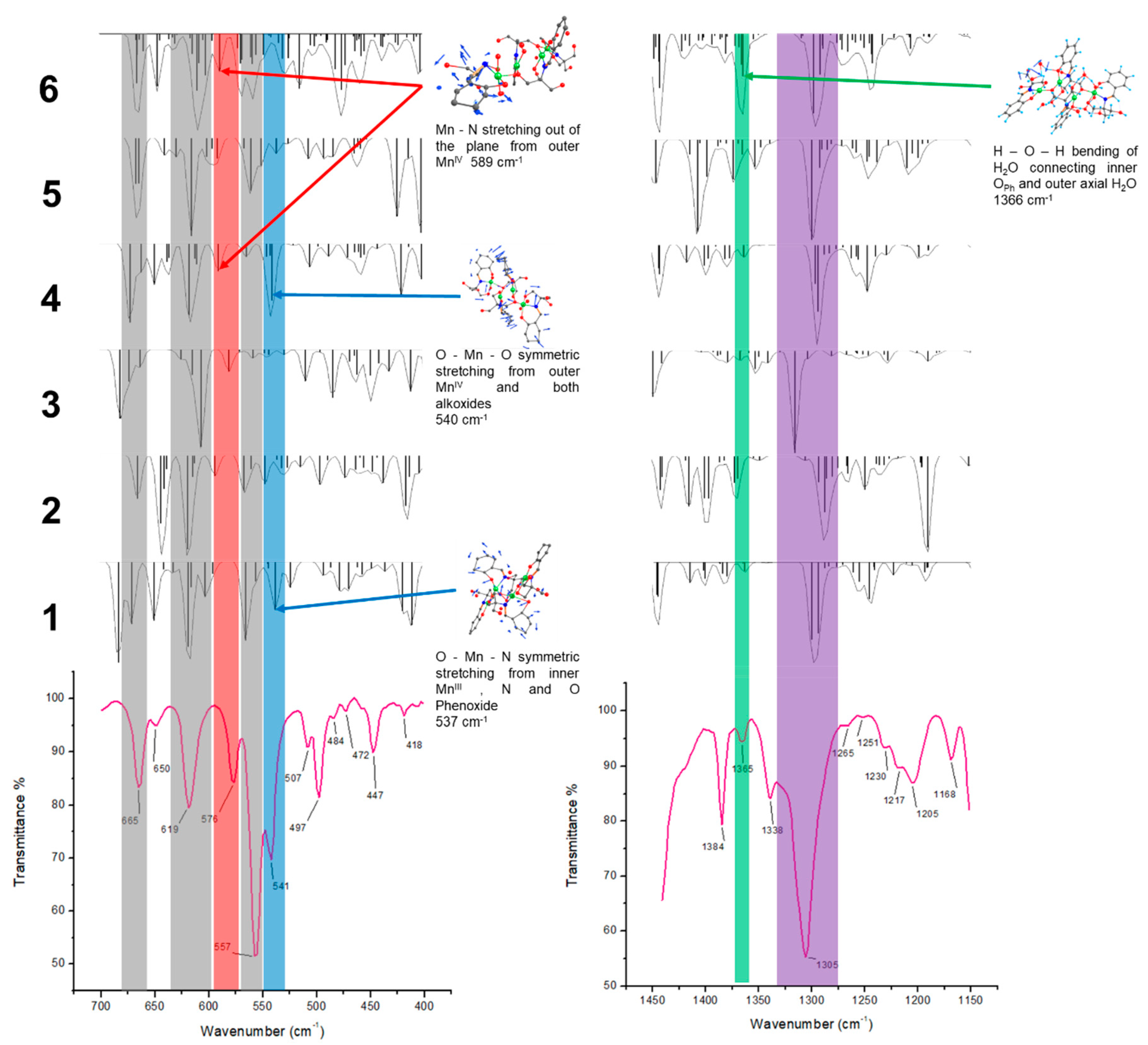
| Empirical Formula | C44 H60 Mn4 N6 O27 |
|---|---|
| Formula weight | 1324.74 |
| Crystalline system | Triclinic |
| Space group | P-1 |
| a = 10.757(3) Å | α = 98.72(2)° |
| b = 11.687(3) Å | β = 110.37(2)° |
| c = 13.328(4) Å | γ = 108.08(2)° |
| Volume | 1428.4(7) Å3 |
| R-Factor (%) | R = 12.43 |
| Bond Length | (Å) | Angles | (°) | Angles | (°) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mn1–O1 | 1.875(10) | O1–Mn1–O2 | 174.3(4) | O22–Mn2–O21 | 176.5(4) |
| Mn1–O2 | 1.880(10) | O1–Mn1–N1 | 92.1(4) | O22–Mn2–O3 | 83.6(4) |
| Mn1–N1 | 1.997(11) | O2–Mn1–N1 | 82.6(4) | O21–Mn2–O3 | 99.8(4) |
| Mn1–O3#1 | 2.023(9) | O1–Mn1–O3#1 | 92.5(4) | O22–Mn2–N21 | 83.1(5) |
| Mn1–O2#1 | 2.161(10) | O2–Mn1–O3#1 | 92.8(4) | O21–Mn2–N21 | 93.5(5) |
| Mn1–O22#1 | 2.152(9) | N1–Mn1–O3#1 | 175.3(5) | O3–Mn2–N21 | 166.6(4) |
| O1–Mn1–O22#1 | 93.8(4) | O22–Mn2–O26 | 89.9(4) | ||
| Mn2–O3 | 1.852(9) | O2–Mn1–O22#1 | 89.6(4) | O21–Mn2–O26 | 90.0(5) |
| Mn2–O21 | 1.868(10) | N1–Mn1–O22#1 | 103.7(4) | O3–Mn2–O26 | 85.5(4) |
| Mn2–O22 | 1.960(9) | O3#1–Mn1–O22#1 | 75.0(4) | N21–Mn2–O26 | 96.5(5) |
| Mn2–N21 | 1.976(12) | O1–Mn1–O2#1 | 95.4(4) | O22–Mn2–O25 | 90.0(4) |
| Mn2–O25 | 2.305(12) | O2–Mn1–O2#1 | 82.9(4) | O21–Mn2–O25 | 90.6(5) |
| Mn2–O26 | 2.240(11) | N1–Mn1–O2#1 | 93.4(4) | O3–Mn2–O25 | 85.9(4) |
| O3#1–Mn1–O2#1 | 87.2(4) | N21–Mn2–O25 | 92.1(5) | ||
| O22#1–Mn1–O2#1 | 160.3(3) | O26–Mn2–O25 | 171.3(4) |
| Transition | λmax (nm)/ε (M−1·cm−1) | Energy cm−1 | f M−1·cm−1 |
|---|---|---|---|
| π→π* | 211/6143 | 47,396 | 0.086 |
| π→π* | 237/5086 | 42,196 | 0.059 |
| n→π* | 269/2561 | 37,177 | 0.015 |
| LCT→M | 388/2317 | 25,841 | 0.0123 |
| d-d | 500/778 | 20,965 | 0.00139 |
| d-d | 579/441 | 19,158 | 0.00045 |
| Compound | C–O Mn(II)i | C–O Mn(IV)e | C–O Mn(III)i | C–O Mn(III)e |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Exp | 1305 | 1308 | ||
| 1 | 1295 | 1301 | ||
| 2 | 1287 | 1289 | ||
| 3 | 1304 | 1316 | ||
| 4 | 1297 | 1294 | ||
| 5 | 1293 | 1300 | ||
| 6 | 1295 | 1291 | 1294 | 1300 |
| Protons | Widthline (ppm) | T2 (sec) | Average Distance to Mnn+, (Å) |
|---|---|---|---|
| H4L O–―H | 0.4 | 1.35 × 10−2 | n/a |
| H4L aromatic | 0.3 | 1.35 × 10−2 | n/a |
| H4L C=N and C–H | 0.1 | 2.25 × 10−2 | n/a |
| 1, H+ aromatic | 1.5 | 4.16 × 10−4 | 5.50 |
| 1, H+ of the C=N | 1.2 | 3.35 × 10−4 | 3.78 |
| 1, aliphatic C–H | 3 | 1.21 × 10−5 | 3.06 |
| M–X Bond | Crystal | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6a* | 6b* | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mne,e’ | Mn–N | 1.976(12) | 1.960 | 1.936 | 2.000 | 1.948 | 1.973 | 1.990 | 1.974 |
| Mn–OPh | 1.868(10) | 1.838 | 1.816 | 1.880 | 1.823 | 1.835 | 1.843 | 1.858 | |
| Mn–OCH2 A | 1.960(9) | 1.899 | 1.847 | 1.886 | 1.893 | 1.873 | 1.877 | 1.895 | |
| Mn–OCH2 C1 | 1.976(12) | 1.972 | 1.917 | 1.869 | 1.928 | 2.011 | 1.891 | 1.963 | |
| Mn–OH2O A | 2.240(11) | 2.348 | 1.977 | 2.452 | 2.147 | 3.750 | 1.938 | 2.273 | |
| Mn–OH2O B | 2.305(12) | 2.301 | 2.016 | 2.334 | 1.779 | 2.077 | 1.877 | 2.317 | |
| Mni,i’ | Mn–N | 1.997(11) | 2.000 | 1.964 | 2.174 | 1.985 | 2.226 | 2.225 | 2.006 |
| Mn–OPh | 1.875(10) | 1.869 | 1.843 | 2.096 | 1.857 | 2.214 | 2.095 | 1.850 | |
| Mn–OCH2 B | 1.880(10) | 1.929 | 1.944 | 2.218 | 1.931 | 2.169 | 2.271 | 1.926 | |
| Mn–OCH2 C1 | 2.023(9) | 1.991 | 2.048 | 2.174 | 2.042 | 2.201 | 2.226 | 1.995 | |
| Mn–OCH2 A | 2.152(9) | 2.205 | 2.241 | 2.181 | 2.198 | 2.200 | 2.161 | 2.188 | |
| Mn–OCH2 C2 | 2.161(10) | 2.299 | 2.250 | 2.088 | 2.279 | 2.108 | 2.184 | 2.378 | |
| DFT Method/Basis Set | Mn type | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6* |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PBE/631g | Inner | 3.837 | 3.804 | 4.390 | 3.830 | 4.533 | 4.624(3.884) |
| Outer | 3.844 | 2.743 | 4.063 | 2.817 | 3.995 | 3.041(3.860) | |
| B3LYP/631g(d) | Inner | 3.850 | 3.848 | 4.745 | 3.856 | 4.781 | 4.797(3.858) |
| Outer | 3.832 | 2.546 | 3.840 | 2.850 | 3.785 | 2.906(3.871) | |
| B3LYP/631g+(d) | Inner | 4.663 | 4.709 | 5.283 | 4.637 | 5.366 | 5.327(4.509) |
| Outer | 4.270 | 2.735 | 4.245 | 3.096 | 4.042 | 3.132(4.280) |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pastor-Ramírez, C.; Zamorano-Ulloa, R.; Ramírez-Rosales, D.; Vázquez-Lima, H.; Hernández-Anzaldo, S.; Reyes-Ortega, Y. Tetramer Compound of Manganese Ions with Mixed Valence [MnII MnIII MnIV] and Its Spatial, Electronic, Magnetic, and Theoretical Studies. Crystals 2018, 8, 447. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst8120447
Pastor-Ramírez C, Zamorano-Ulloa R, Ramírez-Rosales D, Vázquez-Lima H, Hernández-Anzaldo S, Reyes-Ortega Y. Tetramer Compound of Manganese Ions with Mixed Valence [MnII MnIII MnIV] and Its Spatial, Electronic, Magnetic, and Theoretical Studies. Crystals. 2018; 8(12):447. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst8120447
Chicago/Turabian StylePastor-Ramírez, Cándida, Rafael Zamorano-Ulloa, Daniel Ramírez-Rosales, Hugo Vázquez-Lima, Samuel Hernández-Anzaldo, and Yasmi Reyes-Ortega. 2018. "Tetramer Compound of Manganese Ions with Mixed Valence [MnII MnIII MnIV] and Its Spatial, Electronic, Magnetic, and Theoretical Studies" Crystals 8, no. 12: 447. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst8120447
APA StylePastor-Ramírez, C., Zamorano-Ulloa, R., Ramírez-Rosales, D., Vázquez-Lima, H., Hernández-Anzaldo, S., & Reyes-Ortega, Y. (2018). Tetramer Compound of Manganese Ions with Mixed Valence [MnII MnIII MnIV] and Its Spatial, Electronic, Magnetic, and Theoretical Studies. Crystals, 8(12), 447. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst8120447





