Morphology Transition of ZnO Nanorod Arrays Synthesized by a Two-Step Aqueous Solution Method
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Substrate Preparation
2.2. Seed Layer Deposition
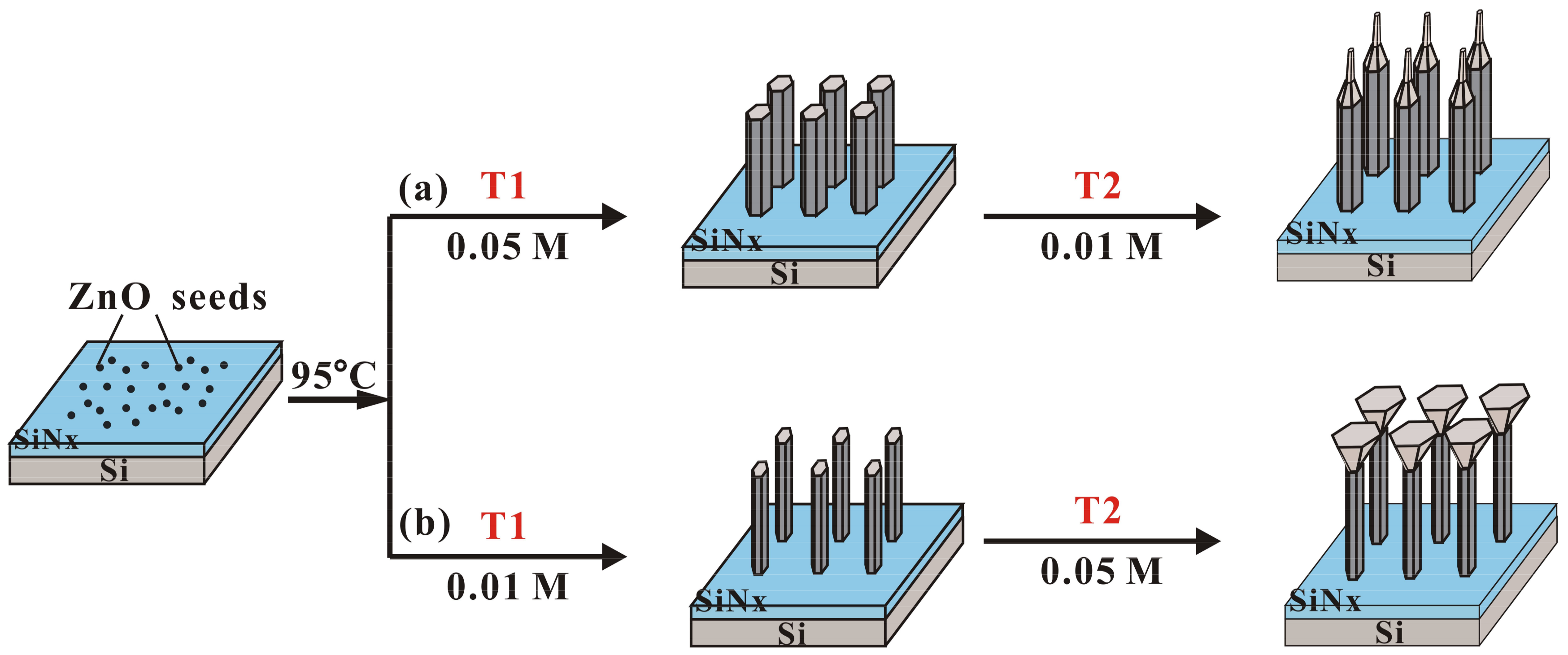
2.3. ZNAs Fabrication
2.4. Characterization
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Choi, S.; Bonyani, B.; Sun, G.J.; Lee, J.K.; Hyun, S.K.; Lee, C. Cr2O3 nanoparticle-functionalized WO3 nanorods for ethanol gas sensors. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2018, 432, 241–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, H.W.; Li, Y.Q.; Zeng, W. Substrate-free synthesis of WO3 nanorod arrays and their superb NH3-sensing performance. Mater. Lett. 2017, 209, 342–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Z.Z.; Cheng, S.W.; Xu, L.B.; Liu, H.Y.; Huang, K.; Li, L.; Zhai, Y.Y.; Zeng, Y.B.; Liu, H.Q.; Shao, Y.; et al. Highly sensitive and selective sensor for sunset yellow based on molecularly imprinted polydopmine-coated multi-walled carbon nanotubes. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2018, 100, 565–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.H.; Yang, C.C.; Yu, H.C.; Yeh, H.T.; Peng, Y.M.; Su, Y.K. Electron field emission enhancement based on Al-doped ZnO nanorod arrays with UV exposure. IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 2018, 65, 251–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, J.W.; Wang, B.B.; Ding, Z.J.; Dai, R.C.; Wang, Z.P.; Zhang, Z.M.; Zhang, J.W. Facile fabrication of infrared photodetector using metastable vanadium dioxide VO2 (B) nanorod networks. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2017, 111, 072107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Lee, W.Y.; Jang, B.; Kim, T.; Bae, J.H.; Cho, K.; Kim, S.; Jang, J. Sol-gel processed p-type CuO phototransistor for a near-infrared sensor. IEEE Electron Device Lett. 2018, 39, 47–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.M.; Zhang, Q.S.; Niu, L.Y.; Liu, J.; Zhou, X.F. TiO2 nanorod arrays modified with SnO2-Sb2O3 nanoparticles and application in perovskite solar cell. Thin Solid Films 2017, 621, 6–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Momeni, M.M.; Ghayeb, Y.; Menati, M. Facile and green synthesis of CuO nanoneedles with high photo catalytic activity. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2016, 27, 9454–9460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Özgür, Ü.; Alivov, Y.I.; Liu, C.; Teke, A.; Reshchikov, M.A.; Doğan, S.; Avrutin, V.; Cho, S.-J.; Morkoç, H. A comprehensive review of ZnO materials and devices. J. Appl. Phys. 2005, 98, 041301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montenegro, D.N.; Souissi, A.; Martinez-Tomas, C.; Munoz-Sanjose, V.; Sallet, V. Morphology transtions in ZnO nanorods grown by MOCVD. J. Cryst. Growth 2012, 359, 122–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, S.N.; Qi, J.J.; Wang, Z.Z.; Lin, P.; Liu, S.; Zhang, Y. Size effect in a cantilevered ZnO micro/nanowire and its potential as a performance tunable force sensor. RSC Adv. 2013, 3, 19375–19379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Z.L.; Yao, J.C. Growth of well-aligned ZnO nanorod arrays and their application for photovoltaic devices. J. Electron. Mater. 2017, 46, 6461–6465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lung, C.M.; Wang, W.C.; Chen, C.H.; Chen, L.Y.; Chen, M.J. ZnO/Al2O3 core/shell nanorods array as excellent anti-reflection layers on silicon solar cells. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2016, 180, 195–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujiwara, H.; Suzuki, T.; Niyuki, R.; Sasaki, K. ZnO nanorod array random lasers fabricated by a laser-induced hydrothermal synthesis. New J. Phys. 2016, 18, 103046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harale, N.S.; Kamble, A.S.; Tarwal, N.L.; Mulla, I.S.; Rao, V.K.; Kim, J.H.; Patil, P.S. Hydrothermally grown ZnO nanorods arrays for selective NO2 gas sensing: Effect of anion generating agents. Ceram. Int. 2016, 42, 12807–12814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.; Kim, W.; Jeon, S.; Yong, K. Highly efficient UV-sensing properties of Sb-doped ZnO nanorod arrays synthesized by a facile, singlestep hydrothermal reaction. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 40539–40548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Husham, M.; Hamidon, N.M.; Paiman, S.; Abuelsamen, A.A.; Farhat, O.F.; Al-Dulaimi, A.A. Synthesis of ZnO nanorods by microwave-assisted chemical-bath deposition for highly sensitive self-powered UV detection application. Sens. Actuators A-Phys. 2017, 263, 166–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, C.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, N.; Colmenares, J.C.; Xu, Y.J. Hierarchically CdS decorated 1D ZnO nanorods-2D graphene hybrids: Low temperature synthesis and enhanced photocatalytic performance. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2015, 25, 221–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, N.; Xie, S.J.; Wenig, B.; Xu, Y.J. Vertically aligned ZnO-Au@CdS core-shell nanorod arrays as an all-solid-state vectorial Z-scheme system for photocatalytic application. J. Mater. Chem. A 2016, 4, 18804–18814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.Q.; Tang, Z.R.; Sun, Y.G.; Colmenares, J.C.; Xu, Y.J. One-dimension-based spatially ordered architectures for solar energy conversion. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2015, 44, 5053–5075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, C.C.; Wuu, D.S.; Lin, P.R.; Chen, T.N.; Horng, R.H. Realization and manipulation of ZnO nanorod arrays on sapphire substrates using a catalyst-free metalorganic chemical vapor deposition technique. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2010, 10, 3001–3011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, C.C.; Wuu, D.S.; Lin, P.R.; Chen, T.N.; Horng, R.H. Three-step growth of well-aligned ZnO nanotube arrays by self-catalyzed metalorganic chemical vapor deposition method. Cryst. Growth Des. 2009, 9, 4555–4561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawakami, M.; Hartanto, A.B.; Nakata, Y.; Okada, T. Synthesis of ZnO nanorods by nanoparticle assisted pulsed-laser deposition. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 2003, 42, L33–L35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.S.; Nam, G.; Leem, J.Y. Photoluminescence studies of ZnO nanorods grown by plasma-assisted molecular beam epitaxy. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2013, 13, 3582–3585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Z.T.; Gao, L. A facile route to ZnO nanorod arrays using wet chemical method. J. Cryst. Growth 2006, 293, 522–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sardana, S.K.; Chandrasekhar, P.S.; Kumar, R.; Komarala, V.K. Efficiency enhancement of silicon solar cells with vertically aligned ZnO nanorod arrays as an antireflective layer. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 2017, 56, 040305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahsanylhaq, Q.; Umar, A.; Hahn, Y.B. Growth of aligned ZnO nanorods and nanopencils on ZnO/Si in aqueous solution: Growth mechanism and structural and optical properties. Nanotechnology 2007, 18, 115603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.; Lao, C.S.; Weintraub, B.; Wang, Z.L. Density-controlled growth of aligned ZnO nanowire arrays by seedless chemical approach on smooth surfaces. J. Mater. Res. 2008, 23, 2072–2077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Qian, X.F.; Yin, J.; Zhu, Z.K. Aqueous solution fabrication of large-scale arrayed obelisk-like zinc oxide nanorods with high efficiency. J. Solid State Chem. 2004, 177, 2144–2149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prabhu, M.; Mayandi, J.; Mariammal, R.N.; Vishnukanthan, V.; Pearce, J.M.; Soundararajan, N.; Ramachandran, K. Peanut shaped ZnO microstructures: Controlled synthesis and nucleation growth toward low-cost dye sensitized solar cells. Mater. Res. Express 2015, 2, 066202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, J.M.; Kim, S.D.; Kim, S.D.; Choi, H.M.; Kim, J.Y.; Jung, W.G. Morphology change of self-assembled ZnO 3D nanostructures with different pH in the simple hydrothermal process. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2009, 113, 389–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, S.J.; Hutley, M.C. The optical properties of ‘moth eye’ antireflection surfaces. Opt. Acta 1982, 29, 993–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.B.; Wang, S.J.; Cheng, K.; Dai, S.X.; Hu, B.B.; Han, X.; Shi, Q.; Du, Z.L. Controllable fabrication of patterned ZnO nanorod arrays: Investigations into the impacts on their morphology. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2012, 4, 2969–2977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yue, S.S.; Lu, J.J.; Zhang, J.Y. Controlled growth of well-aligned hierarchical ZnO arrays by a wet chemical method. Mater. Lett. 2009, 63, 2149–2152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, S.L.; Guo, T.; Zhao, Y.B.; Luo, R.X.; Li, D.Q.; Chen, A.F.; Liu, C.C. Mechanism enhancing gas sensing and first-principle calculations of Al-doped ZnO nanostructures. J. Mater. Chem. A 2013, 1, 11335–11342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.J.; Shen, Z.R.; Chen, Y.L.; Zhang, Y.; Ji, H.M. Atomic structure-dominated enhancement of acetone sensing for a ZnO nanoplate with highly exposed (0001) facet. CrystEngComm 2017, 19, 6711–6718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.P.; Shi, S.B.; Wang, C.; Zhang, Y.Z.; Liu, Z.M.; Zhang, X.G.; Li, L. Effect of surface-to-volume ratio on the optical and magnetic properties of ZnO nanorods by hydrothermal method. J. Alloys Compd. 2015, 648, 521–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Sample | Growth Temperature (°C) | T1 | T2 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Precursor Concentration (M) | Growth Time (h) | Precursor Concentration (M) | Growth Time (h) | ||
| H-0 | 95 | 0.05 | 2 | ---- | ---- |
| H-1 | 0.01 | 1 | |||
| H-2 | 2 | ||||
| H-4 | 4 | ||||
| H-10 | 10 | ||||
| L-0 | 0.01 | ---- | ---- | ||
| L-2 | 0.05 | 2 | |||
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
He, G.; Huang, B.; Lin, Z.; Yang, W.; He, Q.; Li, L. Morphology Transition of ZnO Nanorod Arrays Synthesized by a Two-Step Aqueous Solution Method. Crystals 2018, 8, 152. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst8040152
He G, Huang B, Lin Z, Yang W, He Q, Li L. Morphology Transition of ZnO Nanorod Arrays Synthesized by a Two-Step Aqueous Solution Method. Crystals. 2018; 8(4):152. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst8040152
Chicago/Turabian StyleHe, Guannan, Bo Huang, Zhenxuan Lin, Weifeng Yang, Qinyu He, and Lunxiong Li. 2018. "Morphology Transition of ZnO Nanorod Arrays Synthesized by a Two-Step Aqueous Solution Method" Crystals 8, no. 4: 152. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst8040152
APA StyleHe, G., Huang, B., Lin, Z., Yang, W., He, Q., & Li, L. (2018). Morphology Transition of ZnO Nanorod Arrays Synthesized by a Two-Step Aqueous Solution Method. Crystals, 8(4), 152. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst8040152





