Dissimilar Infrared Brazing of CoCrFe(Mn)Ni Equiatomic High Entropy Alloys and 316 Stainless Steel
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Wetting Behavior
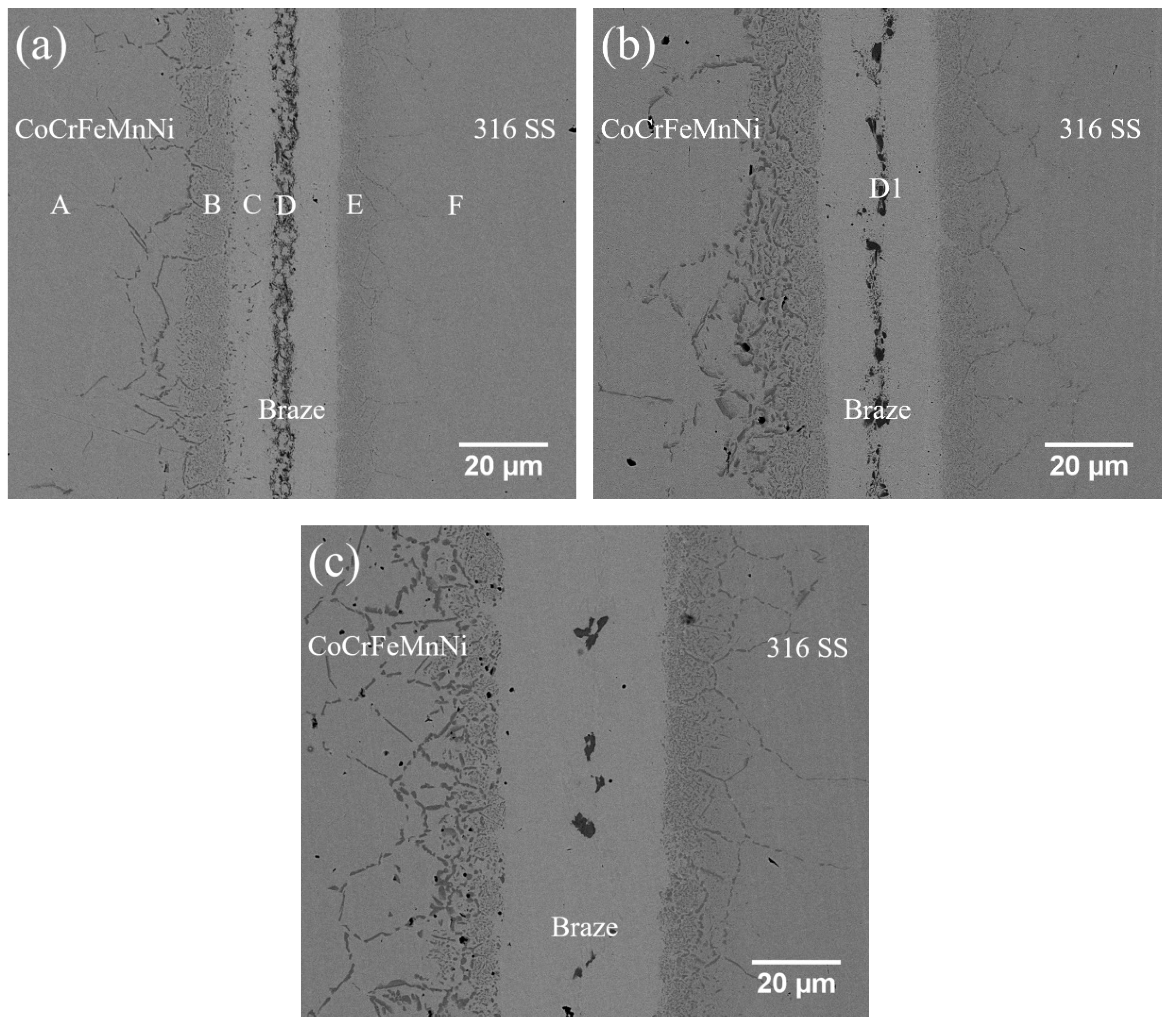
3.2. CoCrFeMnNi/BNi-2/316 Infrared Joints
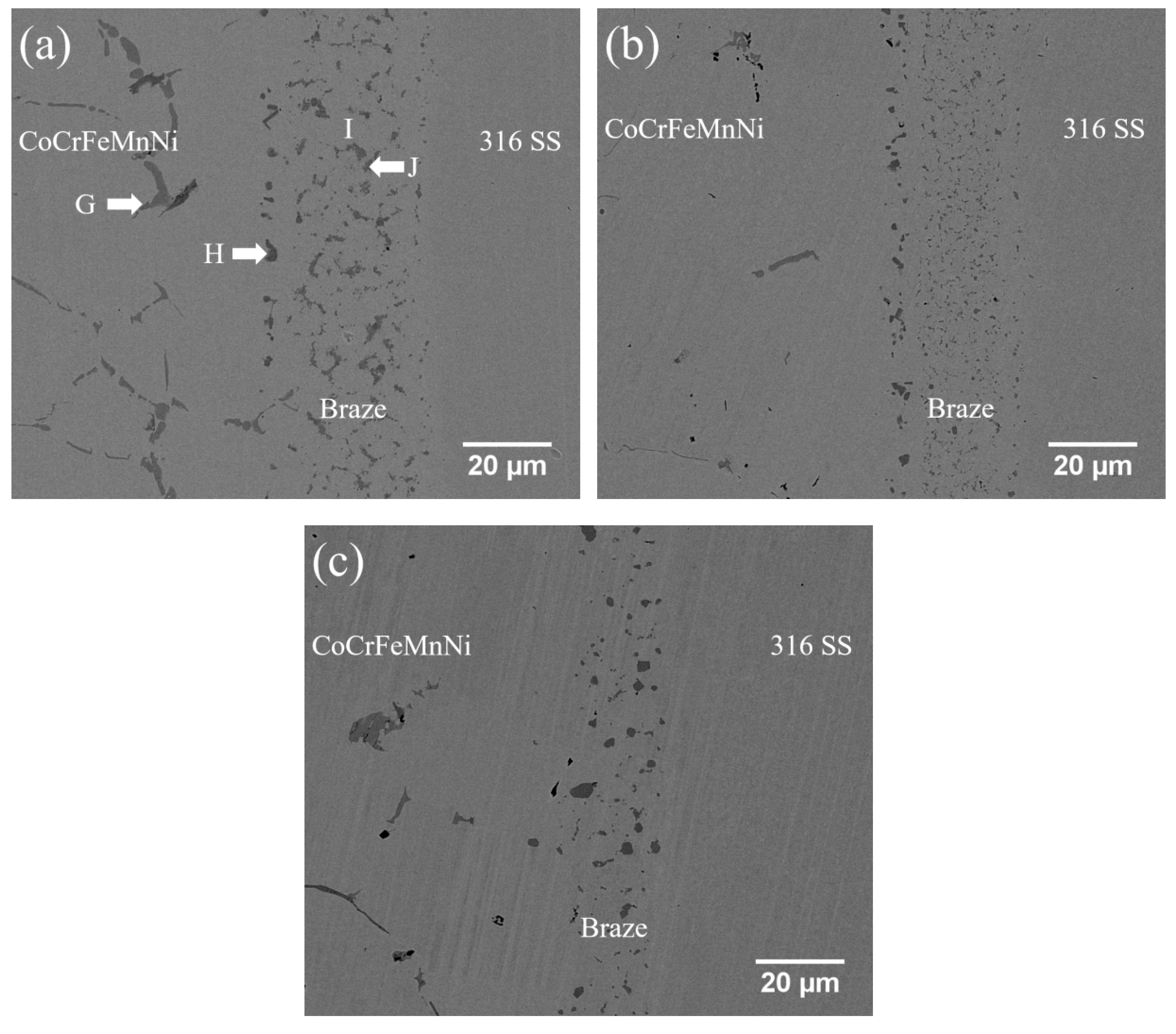
3.3. CoCrFeMnNi/MBF601/316 Infrared Joints
3.4. CoCrFeNi/BNi-2/316 Infrared Joints
3.5. CoCrFeNi/MBF601/316 Infrared Joints
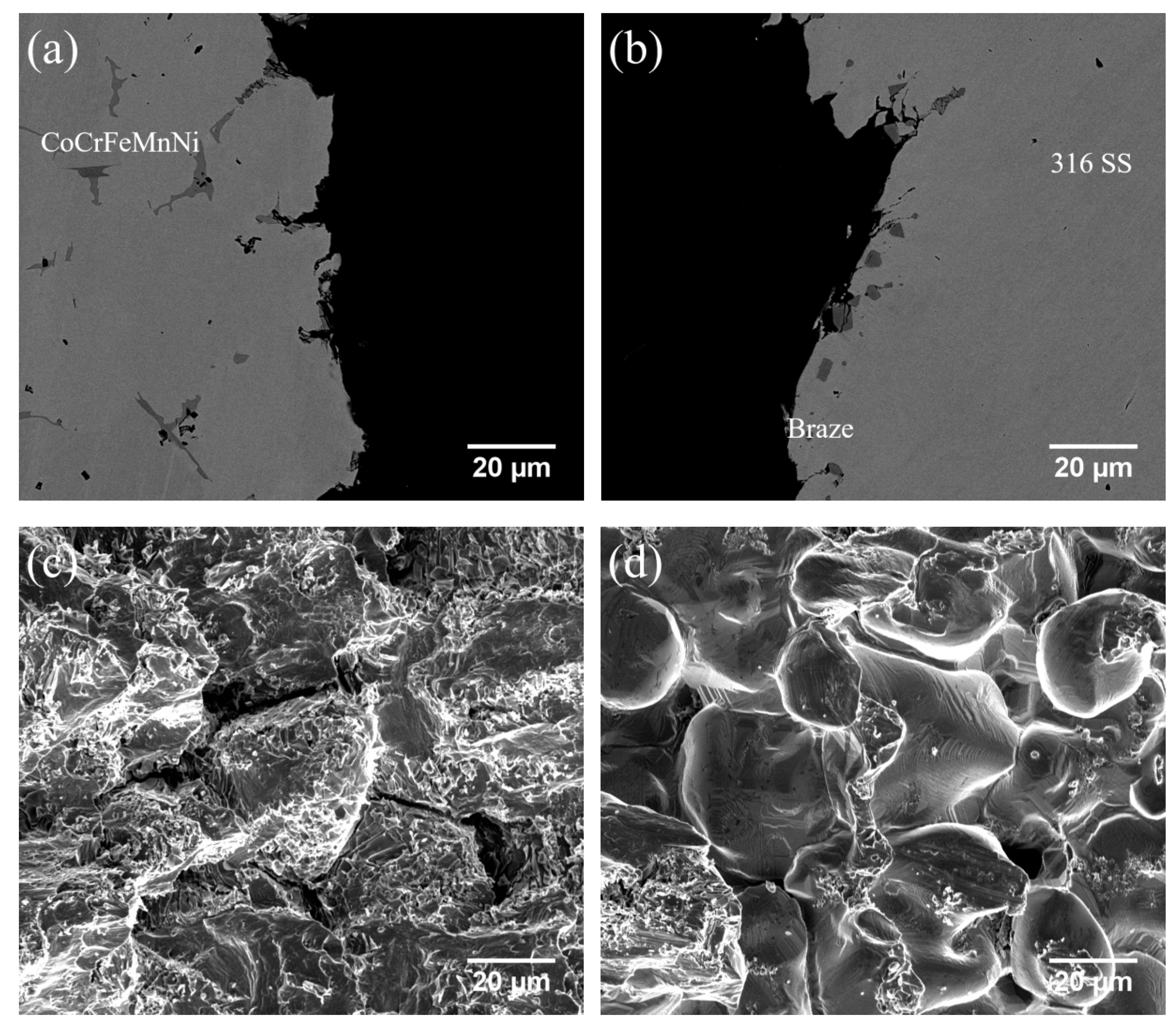
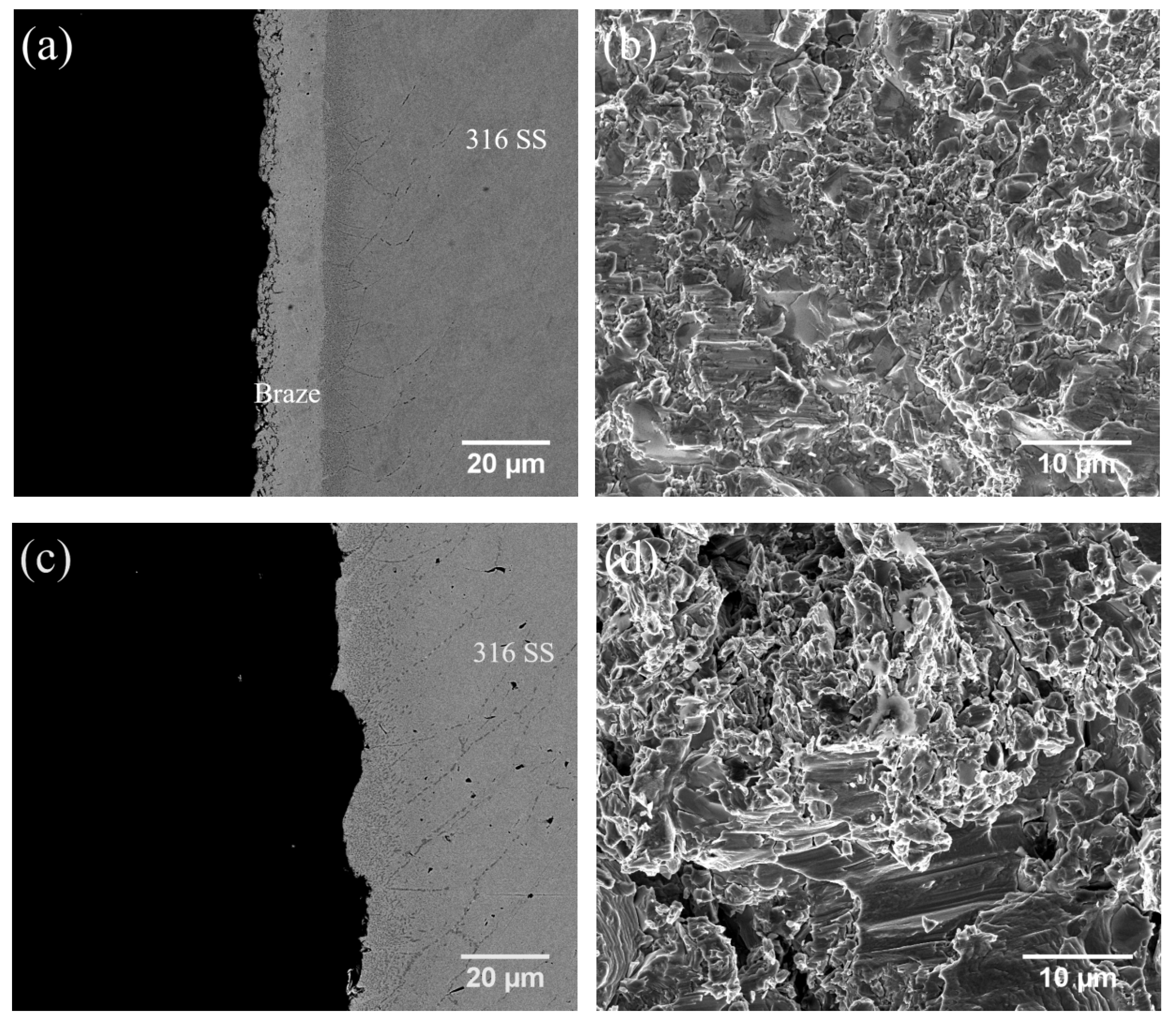
3.6. Shear Strength and Failure Analyses
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cantor, B.; Chang, I.T.H.; Knight, P.; Vincent, A.J.B. Microstructural development in equiatomic multicomponent alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2004, 375–377, 213–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, C.Y.; Yeh, J.W.; Chen, S.K.; Shun, T.T. Wear resistance and high-temperature compression strength of FCC CuCoNiCrAl0.5Fe alloy with boron addition. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2004, 35, 1465–1469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeh, J.W.; Chen, S.K.; Lin, S.J.; Gan, J.Y.; Chin, T.S.; Shun, T.T.; Tsau, C.H.; Chang, S.Y. Nanostructured High-Entropy Alloys with Multiple Principal Elements: Novel Alloy Design Concepts and Outcomes. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2004, 6, 299–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeh, J.W.; Lin, S.J.; Chin, T.S.; Gan, J.Y.; Chen, S.K.; Shun, T.T.; Tsau, C.H.; Chou, S.Y. Formation of simple crystal structures in Cu-Co-Ni-Cr-Al-Fe-Ti-V alloys with multiprincipal metallic elements. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2004, 35, 2533–2536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeh, J.W. Recent progress in high-entropy alloys. Ann. Chim. Sci. Mat. 2006, 31, 633–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, M.C. Progress in High-Entropy Alloys. JOM 2013, 65, 1749–1750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tsai, M.-H. Physical Properties of High Entropy Alloys. Entropy 2013, 15, 5338–5345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gao, M.C. Progress in High-Entropy Alloys. JOM 2014, 66, 1964–1965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tsai, M.H.; Yeh, J.W. High-Entropy Alloys: A Critical Review. Mater. Res. Lett. 2014, 2, 107–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zuo, T.T.; Tang, Z.; Gao, M.C.; Dahmen, K.A.; Liaw, P.K.; Lu, Z.P. Microstructures and properties of high-entropy alloys. Prog. Mater Sci. 2014, 61, 1–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhadeshia, H.K.D.H. High entropy alloys. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2015, 31, 1139–1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gao, M.C.; Yeh, J.W.; Liaw, P.K.; Zhang, Y. High-Entropy Alloys: Fundamentals and Applications; Springer International Publishing: New York, NY, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Pickering, E.J.; Jones, N.G. High-entropy alloys: A critical assessment of their founding principles and future prospects. Int. Mater. Rev. 2016, 61, 183–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miracle, D.B.; Senkov, O.N. A critical review of high entropy alloys and related concepts. Acta Mater. 2017, 122, 448–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shi, Y.; Yang, B.; Liaw, P.K. Corrosion-Resistant High-Entropy Alloys: A Review. Metals 2017, 7, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Zhou, X.; Wang, W.; Liu, B.; Lv, Y.; Yang, W.; Xu, D.; Liu, Y. A review on fundamental of high entropy alloys with promising high–temperature properties. J. Alloys Compd. 2018, 760, 15–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senkov, O.N.; Miracle, D.B.; Chaput, K.J.; Couzinie, J.-P. Development and exploration of refractory high entropy alloys—A review. J. Mater. Res. 2018, 33, 3092–3128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murty, B.S.; Yeh, J.W.; Ranganathan, S.; Bhattacharjee, P.P. High-Entropy Alloys; Elsevier Science: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Otto, F.; Yang, Y.; Bei, H.; George, E.P. Relative effects of enthalpy and entropy on the phase stability of equiatomic high-entropy alloys. Acta Mater. 2013, 61, 2628–2638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gludovatz, B.; Hohenwarter, A.; Catoor, D.; Chang, E.H.; George, E.P.; Ritchie, R.O. A fracture-resistant high-entropy alloy for cryogenic applications. Science 2014, 345, 1153–1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Otto, F.; Dlouhý, A.; Somsen, C.; Bei, H.; Eggeler, G.; George, E.P. The influences of temperature and microstructure on the tensile properties of a CoCrFeMnNi high-entropy alloy. Acta Mater. 2013, 61, 5743–5755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gludovatz, B.; George, E.P.; Ritchie, R.O. Processing, Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of the CrMnFeCoNi High-Entropy Alloy. JOM 2015, 67, 2262–2270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laplanche, G.; Horst, O.; Otto, F.; Eggeler, G.; George, E.P. Microstructural evolution of a CoCrFeMnNi high-entropy alloy after swaging and annealing. J. Alloys Compd. 2015, 647, 548–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Bei, H.; Otto, F.; Pharr, G.M.; George, E.P. Recovery, recrystallization, grain growth and phase stability of a family of FCC-structured multi-component equiatomic solid solution alloys. Intermetallics 2014, 46, 131–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.; Fu, L.M.; Liu, P.; Xu, X.D.; Chen, B.; Zhu, G.Z.; Wang, X.D.; Shan, A.D.; Chen, M.W. Deformation stimulated precipitation of a single-phase CoCrFeMnNi high entropy alloy. Intermetallics 2017, 85, 90–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuh, B.; Mendez-Martin, F.; Völker, B.; George, E.P.; Clemens, H.; Pippan, R.; Hohenwarter, A. Mechanical properties, microstructure and thermal stability of a nanocrystalline CoCrFeMnNi high-entropy alloy after severe plastic deformation. Acta Mater. 2015, 96, 258–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- He, J.Y.; Zhu, C.; Zhou, D.Q.; Liu, W.H.; Nieh, T.G.; Lu, Z.P. Steady state flow of the FeCoNiCrMn high entropy alloy at elevated temperatures. Intermetallics 2014, 55, 9–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pickering, E.J.; Muñoz-Moreno, R.; Stone, H.J.; Jones, N.G. Precipitation in the equiatomic high-entropy alloy CrMnFeCoNi. Scr. Mater. 2016, 113, 106–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.-C.; Tsao, C.-S.; Wu, S.-K.; Lin, C.; Chen, C.-H. Nano-precipitates in severely deformed and low-temperature aged CoCrFeMnNi high-entropy alloy studied by synchrotron small-angle X-ray scattering. Intermetallics 2019, 105, 146–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otto, F.; Dlouhý, A.; Pradeep, K.G.; Kuběnová, M.; Raabe, D.; Eggeler, G.; George, E.P. Decomposition of the single-phase high-entropy alloy CrMnFeCoNi after prolonged anneals at intermediate temperatures. Acta Mater. 2016, 112, 40–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, Z.; Bei, H.; Pharr, G.M.; George, E.P. Temperature dependence of the mechanical properties of equiatomic solid solution alloys with face-centered cubic crystal structures. Acta Mater. 2014, 81, 428–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huo, W.; Zhou, H.; Fang, F.; Hu, X.; Xie, Z.; Jiang, J. Strain-rate effect upon the tensile behavior of CoCrFeNi high-entropy alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2017, 689, 366–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gali, A.; George, E.P. Tensile properties of high- and medium-entropy alloys. Intermetallics 2013, 39, 74–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huo, W.; Fang, F.; Zhou, H.; Xie, Z.; Shang, J.; Jiang, J. Remarkable strength of CoCrFeNi high-entropy alloy wires at cryogenic and elevated temperatures. Scr. Mater. 2017, 141, 125–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kashaev, N.; Ventzke, V.; Stepanov, N.; Shaysultanov, D.; Sanin, V.; Zherebtsov, S. Laser beam welding of a CoCrFeNiMn-type high entropy alloy produced by self-propagating high-temperature synthesis. Intermetallics 2018, 96, 63–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.G.; Sun, Y.F.; Ng, F.L.; Goh, M.H.; Liaw, P.K.; Fujii, H.; Nguyen, Q.B.; Xu, Y.; Shek, C.H.; Nai, S.M.L.; et al. Friction-stir welding of a ductile high entropy alloy: Microstructural evolution and weld strength. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2018, 711, 524–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Tang, C.; Rothwell, G.; Li, L.; Wang, Y.-C.; Yang, Q.; Ren, X. Welding of high entropy alloys—A review. Entropy 2019, 21, 431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; David, S.A.; Feng, Z.; Bei, H. Weldability of a high entropy CrMnFeCoNi alloy. Scr. Mater. 2016, 124, 81–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, Z.; David, S.A.; Leonard, D.N.; Feng, Z.; Bei, H. Microstructures and mechanical properties of a welded CoCrFeMnNi high-entropy alloy. Sci. Technol. Weld. Joining 2018, 23, 585–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jo, M.-G.; Kim, H.-J.; Kang, M.; Madakashira, P.P.; Park, E.S.; Suh, J.-Y.; Kim, D.-I.; Hong, S.-T.; Han, H.N. Microstructure and mechanical properties of friction stir welded and laser welded high entropy alloy CrMnFeCoNi. Met. Mater. Int. 2018, 24, 73–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.; Shiue, R.K.; Wu, S.K.; Huang, H.L. Infrared brazing Of CoCrFeMnNi equiatomic high entropy alloy using nickel-based braze alloys. Entropy 2019, 21, 283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.J.; Wu, S.K.; Lin, R.Y. Infrared joining of TiAl intermetallics using Ti—15Cu—15Ni foil—I. The microstructure morphologies of joint interfaces. Acta Mater. 1998, 46, 1283–1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiue, R.K.; Wu, S.K.; Chen, S.Y. Infrared brazing of TiAl intermetallic using BAg-8 braze alloy. Acta Mater. 2003, 51, 1991–2004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Humpston, G.; Jacobson, D.M. Principles of Soldering and Brazing; ASM International: Materials Park, OH, USA, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Rabinkin, A. Brazing with (NiCoCr)–B–Si amorphous brazing filler metals: Alloys, processing, joint structure, properties, applications. Sci. Technol. Weld. Joining 2004, 9, 181–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaidya, M.; Trubel, S.; Murty, B.S.; Wilde, G.; Divinski, S.V. Ni tracer diffusion in CoCrFeNi and CoCrFeMnNi high entropy alloys. J. Alloys Compd. 2016, 688, 994–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiue, R.K.; Wu, S.K.; Chan, C.H. Infrared brazing Cu and Ti using a 95Ag-5Al braze alloy. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2004, 35, 3177–3186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiue, R.-K.; Wu, S.K.; Yang, S.-H. Infrared brazing of Ti50Ni50 shape memory alloy and inconel 600 alloy with two ag-cu-ti active braze alloys. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2017, 48, 735–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okamoto, H.; Schlesinger, M.E.; Mueller, E.M. ASM Handbook. Volume 3, Alloy Phase Diagrams; ASM International: Materials Park, OH, USA, 1992. [Google Scholar]










| Filler | Base Metal | Time | Temperature | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1020 °C | 1050 °C | 1080 °C | |||
| BNi-2 | CoCrFeMnNi/316 SS CoCrFeNi/316 SS | 180 s | M/S | ||
| 600 s | M/S | M/S | |||
| MBF601 | CoCrFeMnNi/316 SS CoCrFeNi/316 SS | 180 s | M/S | ||
| 600 s | M/S | M/S | |||
| at.% | A | B | C | D | D1 | E | F |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Co | 20.4 | 16.3 | 1.0 | 0.5 | 0.1 | 0.2 | 0.2 |
| Cr | 20.6 | 17.2 | 8.4 | 47.6 | 52.4 | 14.9 | 18.6 |
| Fe | 19.9 | 16.0 | 7.3 | 2.7 | 0.6 | 52.3 | 68.9 |
| Mn | 18.7 | 13.3 | 1.2 | 1.0 | 0.3 | 0.6 | 0.9 |
| Ni | 20.4 | 17.1 | 73.4 | 4.6 | 2.4 | 10.7 | 9.3 |
| B | 0.0 | 19.8 | 0.6 | 40.3 | 44.0 | 19.6 | 0.0 |
| Mo | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.1 | 0.9 | 1.1 |
| Si | 0.0 | 0.3 | 8.1 | 3.3 | 0.1 | 0.8 | 1.0 |
| phase | CoCrFeMnNi | boride | Ni-rich | CrB | CrB | boride | 316 SS |
| at.% | G | H | I | J |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Co | 12.4 | 7.3 | 13.7 | 12.4 |
| Cr | 21.4 | 33.9 | 18.5 | 21.5 |
| Fe | 11.2 | 11.9 | 25.1 | 11.2 |
| Mn | 15.4 | 9.7 | 14.0 | 15.2 |
| Ni | 17.7 | 13.1 | 26.7 | 17.7 |
| B | 0.9 | 11.7 | 0.0 | 0.8 |
| Mo | 0.3 | 0.9 | 0.2 | 0.3 |
| P | 20.4 | 11.2 | 0.8 | 20.6 |
| Si | 0.3 | 0.3 | 1.0 | 0.3 |
| phase | phosphide | B/Co/Cr/Fe/Mn/Ni/P compound | CoCrFeMnNi-based | phosphide |
| at.% | K | L | M | N | O | P |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Co | 25.6 | 23.6 | 0.8 | 0.5 | 0.2 | 0.2 |
| Cr | 25.1 | 21.2 | 7.9 | 47.0 | 17.0 | 18.7 |
| Fe | 25.0 | 22.6 | 7.3 | 2.8 | 61.0 | 69.6 |
| Ni | 24.3 | 23.3 | 74.9 | 4.7 | 9.2 | 9.3 |
| B | 0.0 | 9.2 | 0.0 | 41.5 | 10.8 | 0.0 |
| Mo | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.1 | 0.9 | 1.1 |
| Si | 0.0 | 0.1 | 9.1 | 3.4 | 0.9 | 1.1 |
| phase | CoCrFeNi | boride | Ni-rich | CrB | boride | 316 SS |
| at.% | Q | R | S |
|---|---|---|---|
| Co | 2.0 | 7.1 | 0.5 |
| Cr | 14.6 | 29.2 | 54.9 |
| Fe | 39.2 | 13.8 | 7.8 |
| Ni | 39.8 | 16.6 | 1.5 |
| B | 0.0 | 0.2 | 21.6 |
| Mo | 0.1 | 1.5 | 2.7 |
| P | 1.1 | 31.4 | 11.0 |
| Si | 3.2 | 0.2 | 0.0 |
| phase | (Fe,Ni)-rich | phosphide | B/Cr/Fe/P compound |
| Substrate | Filler | Temperature | Time | Average Shear Strength | Thickness of Brazed Zone |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CoCrFeMnNi/316 SS | BNi-2 | 1020 °C | 180 s | 361 ± 27 MPa | 42 μm |
| 600 s | 294 ± 20 MPa | 44 μm | |||
| 1050 °C | 600 s | 328 ± 45 MPa | 56 μm | ||
| MBF601 | 1050 °C | 180 s | 216 ± 36 MPa | 37 μm | |
| 600 s | 276 ± 43 MPa | 31 μm | |||
| 1080 °C | 600 s | 248 ± 44 MPa | 30 μm | ||
| CoCrFeNi/316 SS | BNi-2 | 1020 °C | 180 s | 349 ± 14 MPa | 40 μm |
| 600 s | 374 ± 10 MPa | 46 μm | |||
| 1050 °C | 600 s | 329 ± 11 MPa | 60 μm | ||
| MBF601 | 1050 °C | 180 s | 293 ± 13 MPa | 15 μm | |
| 600 s | 284 ± 14 MPa | 11 μm | |||
| 1080 °C | 600 s | 324 ± 6 MPa | 7 μm |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lin, C.; Shiue, R.-K.; Wu, S.-K.; Lin, Y.-S. Dissimilar Infrared Brazing of CoCrFe(Mn)Ni Equiatomic High Entropy Alloys and 316 Stainless Steel. Crystals 2019, 9, 518. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst9100518
Lin C, Shiue R-K, Wu S-K, Lin Y-S. Dissimilar Infrared Brazing of CoCrFe(Mn)Ni Equiatomic High Entropy Alloys and 316 Stainless Steel. Crystals. 2019; 9(10):518. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst9100518
Chicago/Turabian StyleLin, Chieh, Ren-Kae Shiue, Shyi-Kaan Wu, and Yu-Sy Lin. 2019. "Dissimilar Infrared Brazing of CoCrFe(Mn)Ni Equiatomic High Entropy Alloys and 316 Stainless Steel" Crystals 9, no. 10: 518. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst9100518
APA StyleLin, C., Shiue, R.-K., Wu, S.-K., & Lin, Y.-S. (2019). Dissimilar Infrared Brazing of CoCrFe(Mn)Ni Equiatomic High Entropy Alloys and 316 Stainless Steel. Crystals, 9(10), 518. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst9100518






