Magnetron Sputtering for ZnO:Ga Scintillation Film Production and Its Application Research Status in Nuclear Detection
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Magnetron Sputtering
2.1. Magnetron Sputtering Principle
2.2. Comparison with Other Depositing Technologies
- a.
- High deposition rate
- b.
- High power efficiency
- c.
- Low energy sputtering
- d.
- Low substrate temperature
- a.
- The equipment is complicated due to the requirements of high vacuum and inert gas [50].
- b.
- High-energy particles easily damage the surface of the film which has grown, resulting in an increment of defect concentration in films [50].
- c.
- In the commonly used magnetron sputtering system, the inhomogeneous magnetic field acting on the target inevitably leads to the inhomogeneous plasma convergence effect, which makes the etching rate of plasma aggregation area extremely large and further inevitably produces such uneven etching on the target, so the utilization rate of the target is generally only 30% [51].
- d.
- High-speed sputtering for strong magnetic materials at low temperature cannot be realized because a strong magnetic field cannot be introduced near the target surface [52].
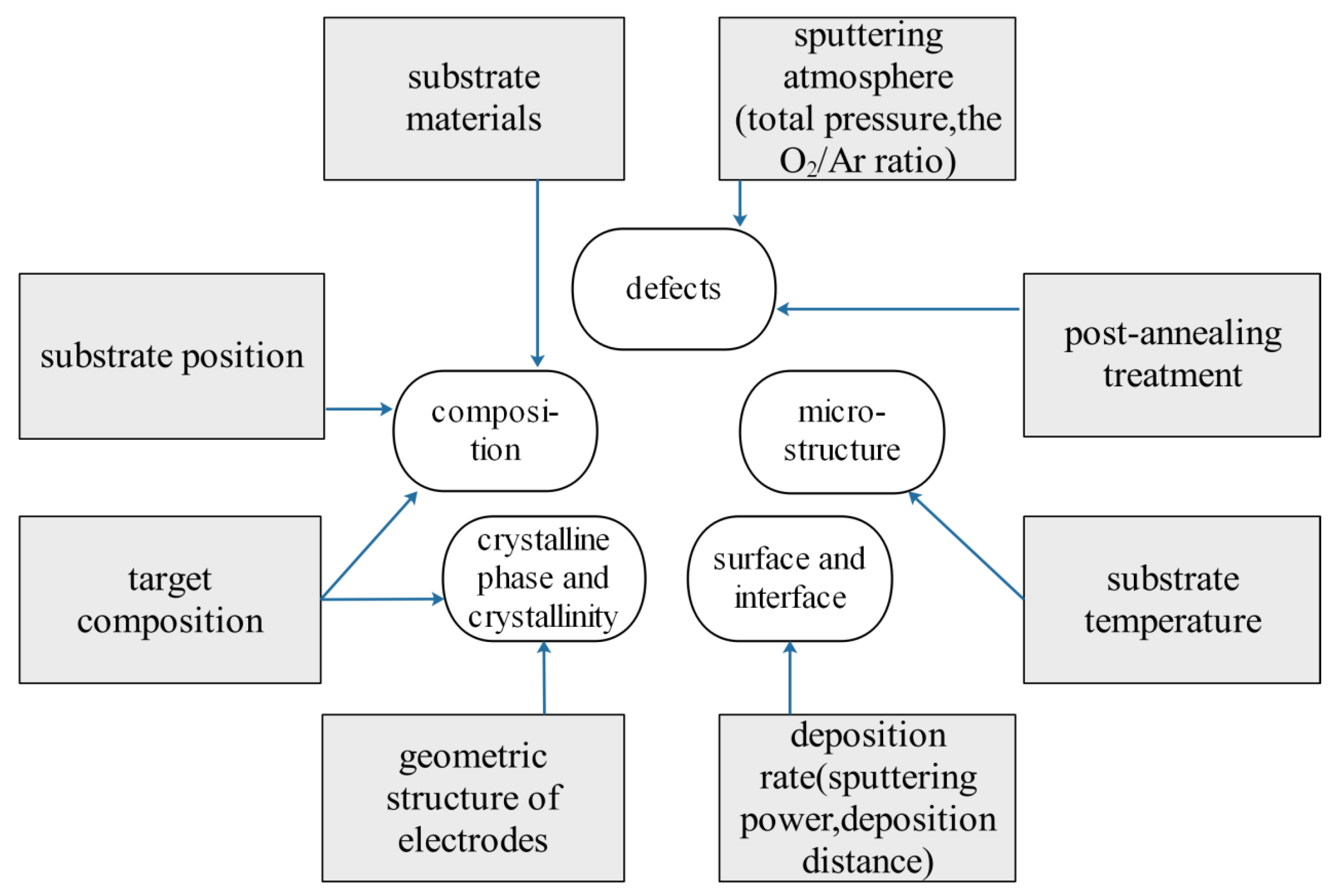
3. ZnO:Ga Performance’s Dependence on Technical Conditions of Magnetron Sputtering
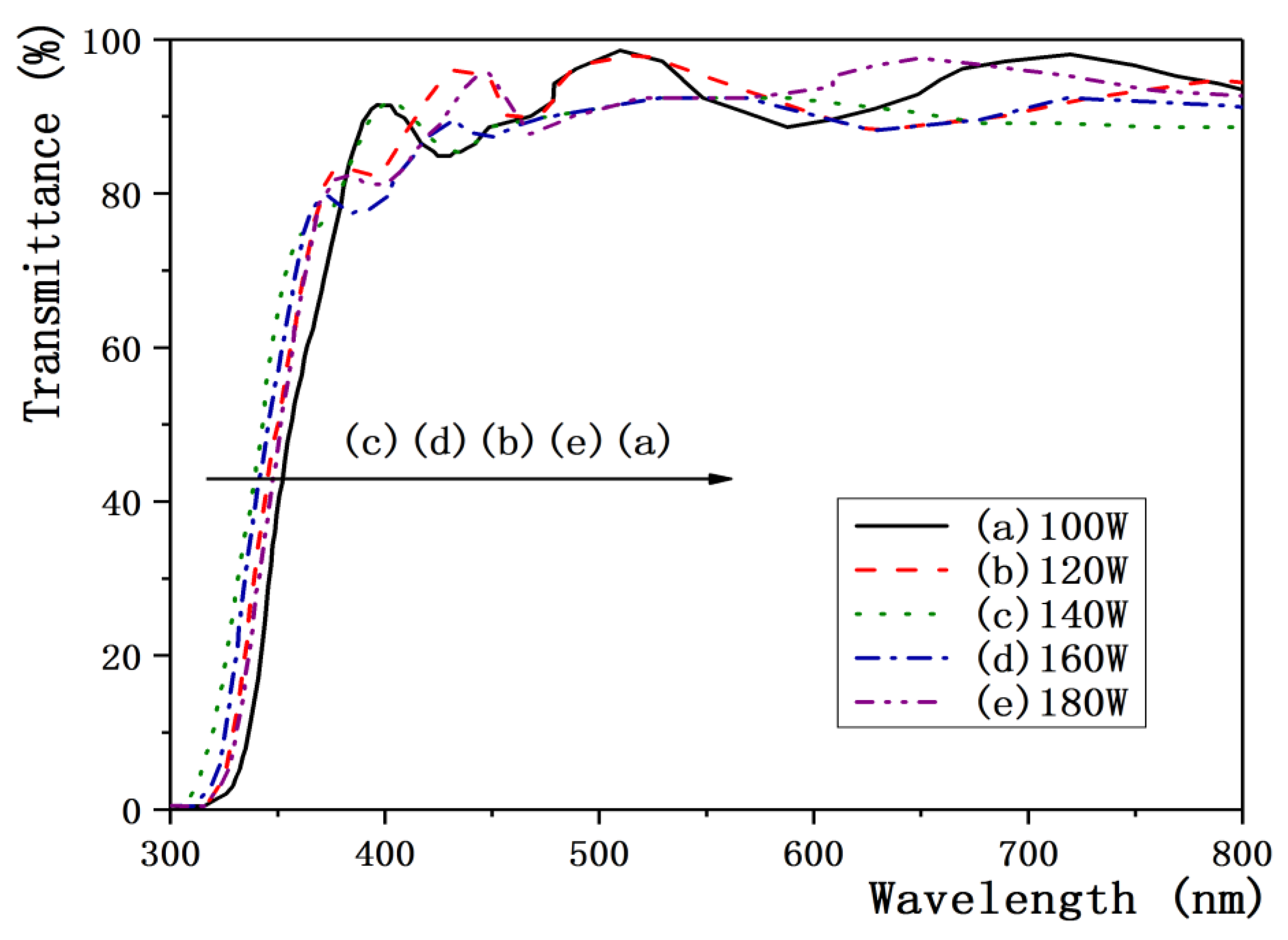
3.1. Effect of Sputtering Power on Properties of ZnO:Ga Films
3.2. Effect of Substrate Temperature on Properties of ZnO:Ga Films
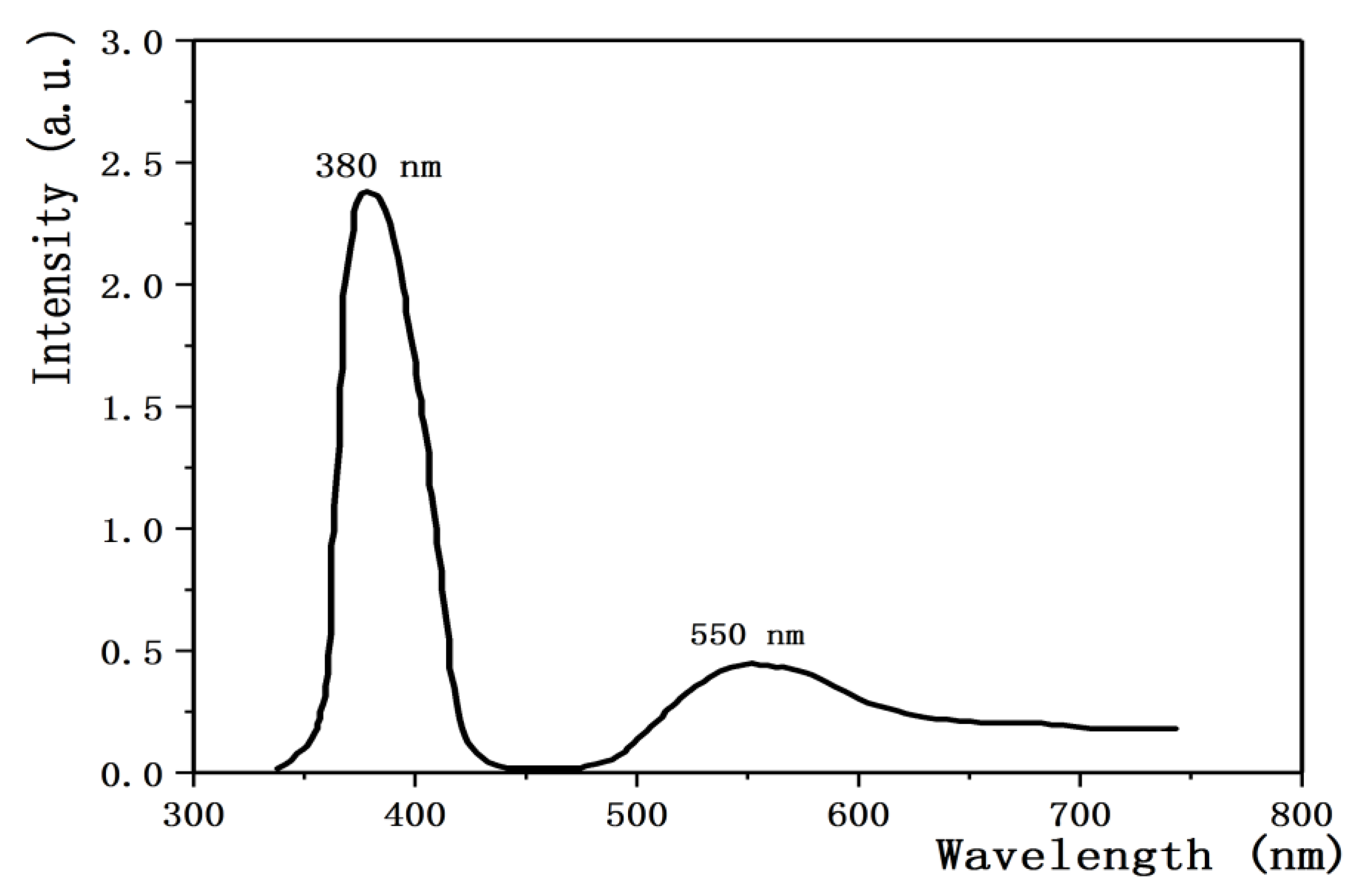
3.3. Effect of Sputtering Atmosphere on Properties of ZnO:Ga Films
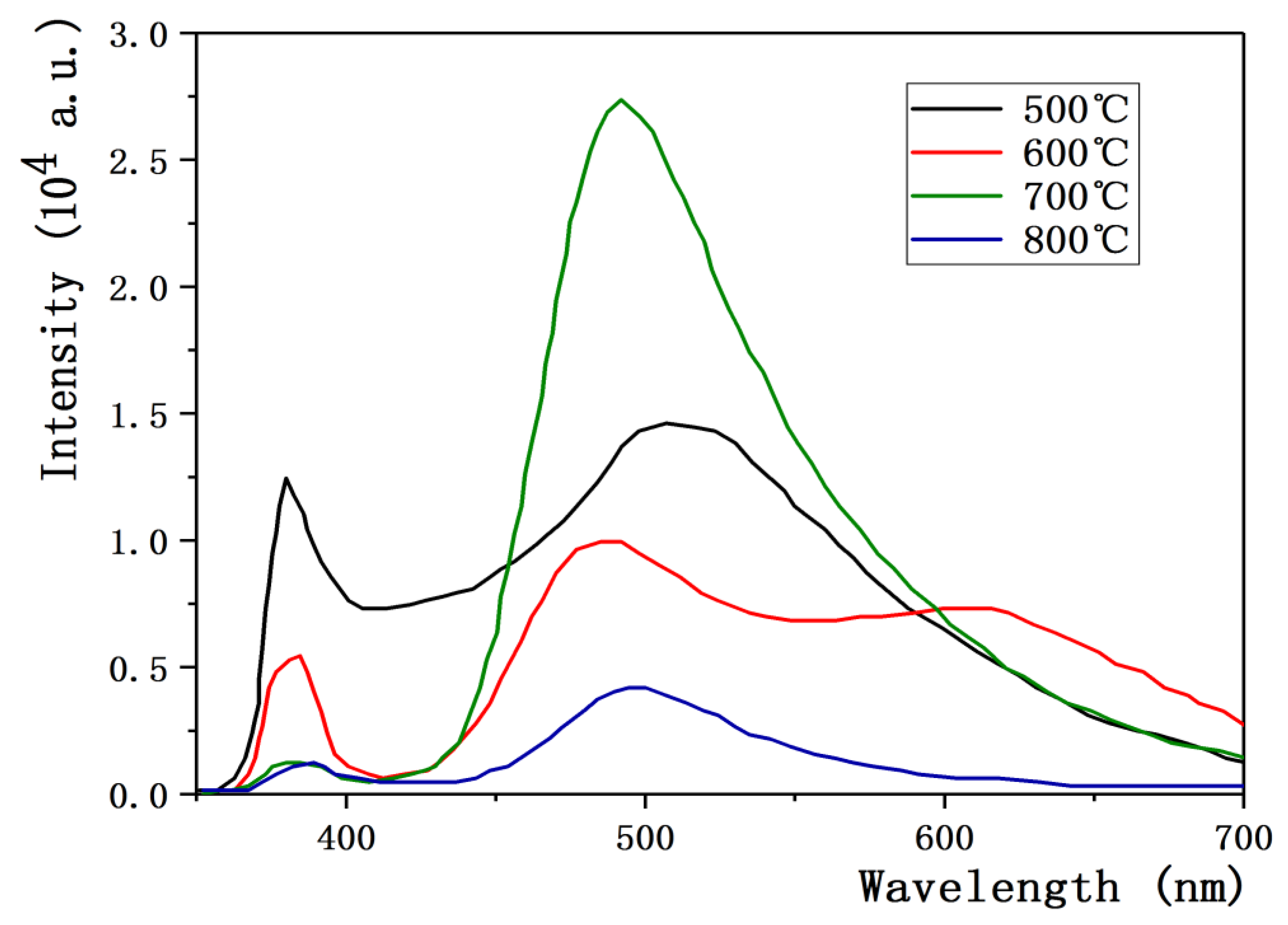
3.4. Effect of Annealing Temperature on Properties of ZnO:Ga Films
3.5. Summary
4. The Application Research Status of ZnO:Ga in Nuclear Detection
5. Summary
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ozgur, U.; Alivov, Y.I.; Liu, C.; Teke, A.; Reshchikov, M.A.; Dogan, S.; Avrutin, V.; Cho, S.J.; Morkoc, H. A comprehensive review of ZnO materials and devices. J. Appl. Phys. 2005, 98, 041301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Z.Z.; Lv, J.G.; Zhang, Y.Z.; He, H.P. ZnO: Doping and Application; Zhejiang University Press: Hangzhou, China, 2009. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Koike, K.; Aoki, T.; Fujimoto, R.; Sasa, S.; Yano, M.; Gonda, S.; Ishigami, R.; Kume, K. Radiation hardness of single-crystalline zinc oxide films. Phys. Status Solid(c) 2012, 9, 1577–1579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hausladen, P.A.; Neal, J.S.; Mihalczo, J.T. An alpha particle detector for a portable neutron generator for the Nuclear Materials Identification System (NMIS). Nucl. Instrum. Meth. Phys. Res. B 2005, 241, 835–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klimm, D.; Ganschow, S.; Schulz, D.; Fornari, R. The growth of ZnO crystals from the melt. J. Cryst. Growth 2008, 310, 3009–3013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simpson, P.J.; Tjpssem, R.; Hunt, A.W.; Lynn, K.G.; Munne, V. Superfast timing performance from ZnO scintillators. Nucl. Instrum. Method Phys. Res. A 2003, 505, 82–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayo, D.C.; Nolen, J.R.; Cook, A.; Mu, R.R.; Haglund, R.F. Zinc oxide nanowire gamma ray detector with high spatiotemporal resolution. Proc. SPIE Synth. Photonics Nanoscale Mater. 2016, 9737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobsson, J.; Viarbitskaya, S.; Mukhtar, E.; Edvinsson, T. A size dependent discontinuous decay rate for the exciton emission in ZnO quantum dots. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2014, 16, 13849–13857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sinha, S.; Kwong, J.; Langeveld, W.; Ryge, P. Characterization of ZnO, BaF2 and PbWO4 scintillator detectors for cargo inspection using transmitted X-ray spectroscopy. IEEE Trans. Nucl. Sci. 2013, 60, 1016–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujimoto, Y.; Yanagida, T.; Miyamoto, M.; Chani, V.I. Scintillation and dosimetric properties of Cu-doped zinc oxide thin films. e-J. Surf. Sci. Nanotechnol. 2014, 12, 275–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melcher, C.L. Perspectives on the future development of new scintillators. Nucl. Instrum. Method Phys. Res. A 2005, 537, 6–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.L.; Liu, X.L.; Hu, Y.H.; Li, F.R.; Liu, S.; Wu, Q.; Sun, Z.X.; Zhang, J.N.; Huang, S.M.; Zhang, Z.J.; et al. Development of ZnO-based nanorod arrays as scintillator layer for ultrafast and high-spatial-resolution X-ray imaging system. Opt. Express 2018, 26, 31290–31298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hormozan, Y.; Sychugov, I.; Linnros, J. High-resolution X-ray imaging using a structured scintillator. Med. Phys. 2016, 43, 696–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clementi, C.; Rosi, F.; Romani, A.; Vivani, R.; Brunetti, B.G.; Miliani, C. Photoluminescence properties of zinc oxide in paints: A study of the effect of self-absorption and passivation. Appl. Spectrosc. 2012, 66, 1233–1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahn, C.H.; Kim, Y.Y.; Kim, D.C.; Mohanta, S.K.; Cho, H.K. A comparative analysis of deep level emission in ZnO layers deposited by various methods. J. Appl. Phys. 2009, 105, 013502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vempati, S.; Mitra, J.; Dawson, P. One-step synthesis of ZnO nanosheets:a blue-white fluorophore. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2012, 7, 470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derenzo, S.E.; Weber, M.J.; Courchesne, E.B.; Klintenberg, M.K. The quest for the ideal inorganic scintillator. Nucl. Instrum. Method Phys. Res. A 2003, 505, 111–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, J.; Gu, S.L.; Zhu, S.M. Fermi-level band filling and band-gap renormalization in Ga-doped ZnO. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2005, 86, 192111–192113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshioka, S.; Oba, F.; Huang, R.; Tanaka, I.; Mizoguchi, T.; Yamamoto, T. Atomic structures of supersaturated ZnO-Al2O3 solid solutions. J. Appl. Phys. 2008, 103, 140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, D.; Tan, C.L.; Tian, X.H.; Huang, Y.W. Comparative study on ZnO monolayer doped with Al, Ga and in atoms as transparent electrodes. Materials 2017, 10, 703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ungula, J.; Dejene, F.B.; Swart, H.C. Effects of different Ga doping concentration on structural and optical properties of Ga-doped ZnO nanoparticles by precipitation reflux method. In Proceedings of the 61st Annual Conference of the South African Institute of Physics, Johannesburg, South Africa, 4–8 July 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Ryan, M.T.; Poston, J.W. A half Century of Health Physics: 50th Anniversary of the Health Physics Society; Lippincott Williams & Wilkins: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Wilkinson, F. Emission Tomography: The fundamentals of PET and SPECT; Chapter 13; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2004; pp. 229–254. [Google Scholar]
- Batischev, A.G.; Aleksandrin, S.Y.; Gurov, Y.B.; Koldashov, S.V.; Lapushkin, S.V.; Mayorov, A.G. Multilayer scintillation detector for nuclear physics monitoring of space weather. Phys. Procedia 2015, 74, 132–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Nikl, M.; Yoshikawa, A.; Vedda, A.; Fukuda, T. Development of novel scintillator crystals. J. Cryst. Growth 2006, 292, 416–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Eijk, C.W.E. Inorganic-scintillator development. Nucl. Instrum. Method Phys. Res. A 2001, 460, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehmann, W. Edge emission of n-type conducting ZnO and CdS. Solid Stat. Electron. 1966, 9, 1107–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luckey, D. A fast inorganic Scintillator. Nucl. Instrum. Method 1968, 62, 119–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourrent-Courchesne, E.D.; Derenzo, S.E.; Weber, M.J. Development of ZnO:Ga as an ultra-fast scintillator. Nucl. Instrum. Method Phys. Res. A 2009, 601, 358–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neal, J.S.; Giles, N.C.; Yang, X.; Wall, R.A.; Ucer, K.B.; Williams, R.T.; Wisniewski, D.J.; Boatner, L.A.; Rengarajan, V.; Nause, J.; Nemeth, B. Evaluation of melt-grown, ZnO single crystals for use as alpha-particle detectors. IEEE Trans. Nucl. Sci. 2008, 55, 1397–1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moses, W.W. Current trends in scintillator detectors and materials. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. Sect. A 2002, 487, 123–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neal, J.S.; Boatner, L.A.; Giles, N.C.; Halliburton, L.E.; Derenzo, S.E.; Bourret-Courchesne, E.D. Comparative investigation of the performance of ZnO-based scintillators for use as α-particle detectors. Nucl. Instrum. Method Phys. Res. A 2006, 568, 803–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Look, D.C.; Reynolds, D.C.; Hemsky, J.W.; Jones, R.L.; Sizelove, J.R. Production and annealing of electron irradiation damage in ZnO. Appl. Phys. Lett. 1999, 75, 811–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergman, L.; McHale, J.L. Handbook of Luminescent Semiconductor Materials; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Bagnall, D.M.; Chen, Y.F.; Zhu, Z.; Yao, T.; Koyama, S.; Shen, M.Y.; Goto, T. Optically pumped lasing of ZnO at room temperature. Appl. Phys. Lett. 1997, 70, 2230–2232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, Z.R.; Khan, M.S.; Zulfequar, M.; Khan, M.S. Optical and structural properties of ZnO thin films fabricated by Sol-Gel method. Mater. Sci. Appl. 2011, 2, 340–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsieh, P.T.; Chen, Y.C.; Kao, K.S.; Wang, C.M. Luminescence mechanism of ZnO thin film investigated by XPS measurement. Appl. Phys. A 2008, 90, 317–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manzano, C.V.; Alegre, D.; Caballero-Calero, O.; Alen, B.; Martin-Gonzalez, M.S. Synthesis and luminescence properties of electrodeposited ZnO films. J. Appl. Phys. 2011, 110, 043538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, B.M.; Chang, S.; Kim, S.Y. Chopping effect on the crystallinity of ZnO films prepared by a r.f. planar magnetron sputtering method. Thin Solid Films 1999, 338, 265–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Constantin, D.G.; Apreutesei, M.; Arvinte, R.; Marin, A.; Andrei, O.C.; Munteanu, D. Magnetron sputtering technique used for coatings deposition; technologies and applications. In Proceedings of the Conference on Materials Science and Engineering-BRAMAT, Brasov, Romania, 24–26 February 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Mejia, M.I.; Restrepo, G.; Marin, J.M.; Sanjines, R.; Pulgarin, R.; Mielczarski, E.; Mielczarski, J.; Kiwi, J. Magnetron sputtered Ag surfaces. New evidence of the nature of the Ag ions intervening in bacterial inactivation. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2010, 2, 230–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pflug, A.; Siemers, M.; Schwanke, C.; Kurnia, B.F.; Sittinger, V.; Szyszka, B. Simulation of plasma potential and ion energies in magnetron sputtering. Mater. Technol. 2011, 26, 10–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Wei, W.; Zhang, B.; Liu, W.; Tang, K.; Fan, L.; Pei, X.; Hong, Y.; Xu, Y.; Wang, Y.S. Simulation of the trajectory of electrons in a magnetron sputtering system of TIN with CST particle studio. In Proceedings of the Conference: IPAC14, Dresden, Germany, 15–20 June 2014; pp. 2341–2343. [Google Scholar]
- Aijaz, A. Design and Characterization of a Synchronous Co-Axial Double Magnetron Sputtering System; Linkoping University: Linkoping, Sweden, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Jilani, A.; Abdel-wahab, M.S.; Hammad, A.H. Advance deposition techniques for thin film and coating. In Modern Technologies for Creating the Thin-Film Systems and Coatings; InTech: London, UK, 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alami, J.; Sarakinos, K.; Mark, G.; Wutting, M. On the deposition rate in a high power pulsed magnetron sputtering discharge. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2006, 89, 154104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anders, A.; Andersson, J.; Ehiasarian, A. High power impulse magnetron sputtering: Current-voltage-time characteristics indicate the onset of sustained self-sputtering. J. Appl. Phys. 2007, 102, 113303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mattox, D.M. Handbook of Physical Vapor Deposition(PVD) Processing: Film Formation, Adhesion, Surface Preparation and Contamination Control. Available online: https://www.sciencedirect.com/book/9780815514220/handbook-of-physical-vapor-deposition-pvd-processing (accessed on 20 April 2019).
- Guttler, D. An Investigation of Target Poisoning during Reactive Magnetron Sputtering; Technichen Universitat Dresden: Saxony, Germany, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Silva-Bermudez, P.; Ramirez, G.; Rodil, S.E. Corrosion Resistant Coatings for Dental Implants. Bio-Tribocorrosion in Biomaterials and Medical Implants; Woodhead Publishing: Sawston, Cambridge, UK, 2013; pp. 250–308. [Google Scholar]
- Feist, C.; Plankensteiner, A.; Winkler, J. Studying target erosion in planar sputtering magnetrons using a discrete model for energetic electrons. In Proceedings of the Conference: COMSOL 2013, Rotterdam, The Netherlands, 23–25 October 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Nakano, T. Study of Particle Transport in High Pressure Sputter Deposition Process; Seikei University: Musashino, Japan, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Vaha-Nissi, M.; Hirvikorpi, T.; Mustonen, T.; Karppinen, M.; Harlin, A. Thin film deposition techniques—Steps towards more sustainable packages. In Proceedings of the 2010 TAPPI International Conference on Nanotechnology for the Forest Product Industry, Espoo, Finland, 27–29 September 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Douglass, D. Thin-Film Coatings: Thin-Film Manufacturing Considerations for Semiconductor Lasers; Laser Focus World: Nashua, NH, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Ohshima, E.; Ogino, H.; Niikura, I.; Maeda, K.; Sato, M.; Ito, M.; Fukuda, T. Growth of the 2-in-size bulk ZnO single crystals by the hydrothermal method. J. Cryst. Growth 2004, 260, 166–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sekiguchi, T.; Miyashita, S.; Obara, K.; Shishido, T. Hydrothermal growth of ZnO single crystal and their optical characterization. J. Cryst. Growth 2000, 214, 72–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Horwitz, J.S.; Pique, A.; Gilmore, C. Electrical and optical properties of indium tin oxide thin films grown by pulsed laser deposition. Appl. Phys. A 1999, 69, 447–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabas, M.; Diaz-Carrasco, P.; Agullo-Rueda, F.; Fernandez, P.H. High quality ZnO and Ga:ZnO thin films grown onto crystalline Si(1 0 0)by RF magnetron sputtering. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 2011, 95, 2327–2334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, H.C.; Chiu, M.C.; Wu, W.T.; Shieu, F.S. Influence of radio frequency bias on the characteristics of TiO2 thin films prepared by DC sputtering. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2006, 153, 237–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thorsen, A.C.; Manasevit, H.M. Heteroepitaxial GaAs on aluminum oxide: Electrical properties of undoped films. J. Appl. Phys. 1971, 42, 2519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wasa, K.; Kitabatake, M.; Adachi, H. Thin Film Materials Technology: Sputtering of Compound Materials; Willian Andrew Publishing: Norwich, UK, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Chan, K.Y.; Teo, B.S. Sputtering power and deposition pressure effects on the electrical and structural properties of copper thin films. J. Mater. Sci. 2005, 40, 5971–5981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.W.; Diao, X.G.; Wang, Z.; Yang, M.L. Preparation and characterization of high-performance direct current magnetron sputtered ZnO:Al films. Thin Solid Films 2005, 491, 54–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Q.B.; Ye, Z.S.; He, H.P.; Wang, J.R. Preparation and characterization of transparent conductive ZnO:Ga films by DC reactive magnetron sputtering. Mater. Charact. 2008, 59, 124–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drude, P. Zur Elektronentheorie der Metalle. Annalen der physik 1900, 306, 566–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drude, P. Zur Elektronentheorie der Metalle:II.Teil.Galvanomagnetische und thermomagnetische Effecte. Annalen der physik 1900, 308, 369–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purcell, E.M.; Morin, D.J. Electricity and Magnatism; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 1965; pp. 117–122. [Google Scholar]
- Frank, G.; Kauer, E.; Kostlin, H. Transparent heat-reflecting coatings based on highly doped semiconductors. Thin Solid Films 1981, 77, 107–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.F.; Chiou, B.S. Deposition of indium tin oxide films on polycarbonate substrate by radio-frequency magnetron sputtering. Thin Solid Films 1997, 298, 221–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, Z.H.; Agashe, C.; Mergel, D. Dielectric modeling of transmittance spectra of thin ZnO:Al films. Thin Solid Films 2006, 496, 520–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujiwara, H.; Kondo, M. Effects of carrier concentration on the dielectric function of ZnO:Ga and In2O3:Sn studied by spectroscopic ellipsometry: Analysis of free-carrier and band-edge absorption. Phys. Rev. B 2005, 71, 075109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sernelius, B.E.; Berggren, K.F.; Jin, Z.C.; Hamberg, I.I.; Grangvist, C.G. Band-gap tailoring of ZnO by means of heavy Al doping. Phys. Rev. B 1988, 37, 10244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Z.C.; Hamberg, I.; Granqvist, C.G. Optical properties of sputter-deposited ZnO:Al thin films. J. Appl. Phys. 1988, 64, 5117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peter, K.; Willeke, G.; Prasad, K.; Shah, A. Free-carrier absorption in microcrystalline silicon thin films prepared by very-high frequency glow discharge. Philos. Mag. B 1994, 69, 197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Q.B. Preparation and Characterization of Transparent High Conductivity Near Infrared Reflective ZnO:Ga Thin Films; Zhejiang University: Hangzhou, China, 2007. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Cullity, B.D. Elements of X-ray Diffraction, 2nd ed.; Addison Wesley: Reading, MA, USA, 1978. [Google Scholar]
- Gomez, H.; Maldonado, A.; Olvera, M.L.; Acosta, D. Gallium-doped ZnO thin films deposited by chemical spray. Acosta Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 2005, 87, 107–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, J.F.; Hon, M.H. The effect of deposition temperature on the properties of Al-doped zinc oxide thin films. Thin Solid Films 2001, 386, 79–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salameh, B.; Alsmadi, A.M.; Akkad, F.E. Physicochemistry of point defects in fluorine doped zinc tin oxide thin films. Thin Solid Films 2017, 626, 76–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tauc, J. Optical properties and electronic structure of amorphous Ge and Si. Mater. Res. Bull. 1968, 3, 37–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amala, R.A.; Ernest, S. Structural, morphological, optical and compositional characterization of spray deposited Ga doped ZnO thin film for Dye-Sensitized Solar Cell application. Super Micro 2014, 75, 398–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, P.C.; Huang, C.H.; Lin, M.Y.; Chou, C.Y. The effect of sputtering parameters on the film properties of molybdenum back contact for CIGS solar cells. Int. J. Photoenergy 2013, 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobs, C.B.; Maksov, A.B.; Muckley, E.S.; Collins, L. UV-activated ZnO films on a flexible substrate for room temperature O2 and H2O sensing. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 6053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.H.; Cheon, D.H.; Kim, W.J.; Ham, M.H. Ga-doped ZnO films deposited with varying sputtering powers and substrate temperatures by pulsed DC magnetron sputtering and their property improvement potentials. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2012, 258, 6537–6544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyake, A.; Yamada, T.; Makino, H. Structural, electrical and optical properties of Ga-doped ZnO films on cyclo-olefin polymer substrates. Thin Solid Films 2009, 517, 3130–3133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, E.G.; Zhuang, D.M.; Zhang, G.; Yang, W.F.; Zhao, M. Substrate temperature dependence of the properties of ZAO thin films deposited by magnetron sputtering. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2003, 217, 88–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.H.; Park, K.C.; Ma, D.Y. Structural, electrical and optical properties of aluminum doped zinc oxide films prepared by radio frequency magnetron sputtering. J. Appl. Phys. 1997, 81, 7764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, R.J.; Jiang, X.; Szyszka, B.; Sittinger, V.; Pflug, A. Studies on ZnO:Al thin films deposited by in-line reactive mid-frequency magnetron sputtering. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2003, 207, 341–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.L.; Ma, S.Y.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, G.H. Structure and luminescence properties of ZnO films prepared by RF magnetron sputtering. Spectrosc. Spectr. Anal. 2008, 28, 2028–2032. [Google Scholar]
- Tongay, S.; Suh, J.; Ataca, C.; Fan, W. Defects activated photoluminescence in two-dimensional semiconductors: Interplay between bound, charged, and free excitons. Sci. Rep. 2013, 3, 2657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myhajlenko, S. Luminescence of Solids; Springer Science+Business Media: New York, NY, USA, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Carozo, V.; Wang, Y.X.; Fujisawa, K.; Carvalho, B.R. Optical identification of sulfur vacancies: Bound excitons at the edges of monolayer tungsten disulfide. Sci. Adv. 2017, 3, 1602813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramamoorthy, K.; Sanjeeviraja, C.; Jayachandran, M.; Sankaranarayanan, K.; Misra, P.; Kukreja, L.M. Development of a novel high optical quality ZnO thin films by PLD for III–V opto-electronic devices. Curr. Appl. Phys. 2006, 6, 103–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanheusden, K.; Warren, W.L.; Seager, C.H.; Tallant, D.R. Mechanisms behind green photoluminescence in ZnO phosphor powders. J. Appl. Phys. 1996, 79, 7983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, D.; Das, A.K.; Ajimsha, R.S.; Misra, P. Effect of disorder on carrier transport in ZnO thin films grown by atomic layer deposition at different temperatures. J. Appl. Phys. 2013, 114, 043703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, B.X.; Fu, Z.X.; Jia, Y.B. Green luminescent center in undoped zinc oxide films deposited on silicon substrates. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2001, 79, 943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fabbri, F.; Vilani, M.; Catellani, A.; Calzolari, A. Zn vacancy induced green luminescence on non-polar surfaces in ZnO nanostructures. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 5158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuste, M.; Galindo, R.E.; Caretti, I.; Torres, R. Influence of the oxygen partial pressure and post-deposition annealing on the structure and optical properties of ZnO films grown by dc magnetron sputtering at room temperature. J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys. 2012, 45, 025303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Igasaki, Y.; Kanma, H. Argon gas pressure dependence of the properties of transparent conducting ZnO:Al films deposited on glass substrates. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2001, 169–170, 508–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assunção, V.; Fortunato, E.; Marques, A.; Aguas, H. Influence of the deposition pressure on the properties of transparent and conductive ZnO:Ga thin-film produced by r.f. sputtering at room temperature. Thin Solid Films 2003, 427, 401–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sam, Z. Organic Nanostructured Thin Film Devices and Coatings for Clean Energy; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Fairose, S.; Ernest, S.; Daniel, S. Effect of oxygen sputter pressure on the structural, morphological and optical properties of ZnO thin films for gas sensing application. Sens. Imaging 2018, 19, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Q.B.; Zhu, L.P.; Ye, Z.S.; He, H.P.; Wang, J.R.; Hu, S.H.; Zhao, B.H. Influence of sputtering pressure on the properties of ZnO:Ga films prepared by DC reactive magnetron sputtering. China J. Semicond. 2007, 28, 285–288. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Song, D.Y.; Aberle, A.G.; Xia, J. Optimisation of ZnO:Al films by change of sputter gas pressure for solar cell application. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2002, 195, 291–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro, M.V.; Tavares, C.J. Dependence of Ga-doped ZnO thin film properties on different sputtering process parameters: Substrate temperature, sputtering pressure and bias voltage. Thin Solid Films 2015, 586, 13–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gies, A.; Pecquenard, B.; Benayad, A.; Martinez, H. Effect of total gas and oxygen partial pressure during deposition on the properties of sputtered V2O5 thin films. Solid State Ion. 2005, 176, 1627–1634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, S.; Khan, Y.; Khranovskyy, V.; Muhammad, R. Effect of oxygen content on the structural and optical properties of ZnO films grown by atmospheric pressure MOCVD. Proc. Natl. Sci. Mater. Int. USA 2013, 23, 44–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Ahn, C.H.; Kim, Y.Y.; Kang, S.W.; Kong, B.H. Dependency of oxygen partial pressure on the characteristics of ZnO films grown by radio frequency magnetron sputtering. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2008, 19, 744–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.L.; Lau, S.P.; Chen, J.S.; Chen, G.Y. Polycrystalline ZnO thin films on Si(1 0 0) deposited by filtered cathodic vacuum arc. J. Cryst. Growth 2001, 223, 201–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.G.; Lau, S.P.; Lee, H.W.; Yu, S.F. Comprehensive study of ZnO films prepared by filtered cathodic vacuum arc at room temperature. J. Appl. Phys. 2003, 94, 1597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Lee, S.; Vilmercati, P.; Lee, H.N. Atomically flat reconstructed rutile TiO2(0 0 1) surfaces for oxide film growth. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2016, 108, 091604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.P.; Shi, S.B.; Li, L.; Song, Z.X. Effects of annealing temperature on structural and optical properties of ZnO thin films. Chin. Phys. Lett. 2010, 27, 047803. [Google Scholar]
- Ahn, B.D.; Oh, S.H.; Lee, C.H.; Kim, G.H. Influence of thermal annealing ambient on Ga-doped ZnO thin films. J. Cryst. Growth 2007, 309, 128–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsieh, P.T.; Chen, Y.C.; Kao, K.S.; Wang, C.M. Structural and luminescent characteristics of non-stoichiometric ZnO films by various sputtering and annealing temperatures. Phys. B 2008, 403, 178–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Q.B.; Ye, Z.Z.; He, H.P.; Zhu, L.P. Influence of annealing temperature on the properties of transparent conductive and near-infrared reflective ZnO:Ga films. Scr. Mater. 2008, 58, 21–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heo, S.B.; Jeon, J.H.; Gong, T.K.; Moon, H.J. Influence of a Ni interlayer on the optical and electrical properties of trilayer GZO/Ni/GZO films. Ceram. Int. 2015, 48, 157–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahdhi, H.; Ayadi, Z.B.; Gauffier, J.L.; Djessas, K. Influence of sputtering power on the properties of thin layers of GZO for photovoltaic applications. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2015, 26, 3336–3343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gotz, W.; Kern, R.S.; Chen, C.H.; Liu, H. Hall-effect characterization of III—V nitride semiconductors for high efficiency light emitting diodes. Mater. Sci. Eng. B 1999, 59, 211–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, G.Z.; Yao, B.; Cong, C.X.; Yang, T. Effect of annealing on conductivity behavior of undoped zinc oxide prepared by RF magnetron sputtering. J. Alloys Compd. 2008, 457, 36–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsieh, P.T.; Chen, Y.C.; Wang, C.M.; Tsai, Y.Z. Structural and photoluminescence characteristics of ZnO films by room temperature sputtering and rapid thermal annealing process. Appl. Phys. A 2006, 84, 345–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ungula, J.; Dejene, B.F.; Swart, H.C. Effect of annealing on the structural, morphological and optical properties of Ga-doped ZnO nanoparticles by reflux precipitation method. Results Phys. 2017, 7, 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.G.; Lau, S.P.; Lee, H.W.; Yu, S.F. Photoluminescence study of ZnO films prepared by thermal oxidation of Zn metallic films in air. J. Appl. Phys. 2003, 94, 354–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiller, D.; Lopez-Vidrier, J.; Gutsch, S.; Zacharias, M. Defect-induced luminescence quenching vs. charge carrier generation of phosphorus incorporated in silicon nanocrystals as function of size. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.T.; Du, G.T.; Liu, D.L.; Wang, X.Q. Crystal growth of undoped ZnO films on Si substrates under different sputtering conditions. J. Cryst. Growth 2002, 243, 439–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohan, A.F.; Ceder, G.; Morgan, D. First-principles study of native point defects in ZnO. Phys. Rev. B 2000, 61, 15019–15027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Q.B.; Ye, Z.Z.; He, H.P.; Hu, S.H. Structural, electrical, and optical properties of transparent conductive ZnO:Ga films prepared by DC reactive magnetron sputtering. J. Cryst. Growth 2007, 304, 64–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Negi, S.; Rana, M.P.S.; Gautam, S.K.; Singh, R.G. Structural and optical modification of Ga-doped zinc oxide thin films induced by thermal annealing. Indian J. Pure Appl. Phys. 2016, 54, 236–240. [Google Scholar]
- John, W.; Ucer, K.B.; Williams, R.T. Picosecond excitonic luminescence in ZnO and other wide-gap semiconductors. Radiat. Meas. 2004, 38, 501–505. [Google Scholar]
- Wahl, M. Time-Correlated Single Photon Counting. Available online: https://www.picoquant.com/images/uploads/page/files/7253/technote_tcspc.pdf (accessed on 20 April 2019).
- Lakowicz, J.R. Principles of Fluorescence Spectroscopy, 3rd ed.; Springer Science+Business Media: New York, NY, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Conner, O.D.V.O.; Phillips, D. Time-Correlated Single Photon Counting; Academic Press: London, UK, 1984. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.S.; Zheng, G.X. 500 fs UV laser system and its application to fluorescence test of thin film scintillators. Opt. Precis. Eng. 2011, 19, 475–481. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.L.; Ouyang, X.P.; Zhang, J.W.; Zhang, Z.B. Properties study of ZnO:Ga crystal on pulsed radiation detections. Chin. Phys. C 2010, 34, 354–358. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, Y.L.; Ouyang, X.P.; Zhang, Z.B.; Zhang, J.W. Response of ZnO:Ga crystal to proton beam. Atomic Energy Sci&Tech 2009, 43, 848–850. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Ma, Y.L.; Ouyang, X.P.; Chen, L.; Zhang, Z.B.; Zhang, J.W.; Quan, L.; Luo, J.H.; Zhou, H.S.; Guo, Y.J. Time and energy response of ZnO:Ga crystal to hard X-ray. High Power Laser Part. Beams 2008, 20, 2088–2090. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Ma, Y.L.; Ouyang, X.P.; Zhang, Z.B.; Zhang, J.W. Study on Response of ZnO:Ga Crystal to Single Heavy Charged Particle. Atom. Energy Sci. Technol. 2009, 43, 170–173. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Q.M.; Yan, J.; Deng, B.J.; Zhang, J.W.; Lv, J.G.; Wen, X.; Gao, K.Q. An ultrafast X-ray scintillating detector made of ZnO(Ga). J. Instrum. 2017, 12, 12033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koyama, S.; Nanto, H.; Kinoshita, A.; Fujiwara, A. Neutron scintillator using Ga-doped ZnO phosphor with high detection efficiency. In Proceedings of the 2008 IEEE Nuclear Science Symposium Conference, Dresden, Germany, 19–25 October 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Cates, J.W.; Hayward, J.P.; Zhang, X. Measurement of achievable timing resolution with ZnO:Ga films. IEEE Trans. Nucl. Sci. 2013, 60, 3127–3133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.X.; Chen, L.; Yao, Z.M.; Ren, S.Q. Transient radiation imaging based on a ZnO:Ga single-crystal image converter. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 4178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.Q.; Wang, J.L.; Ren, M.D. Study of Hydrothermal Growth Process and Properties of ZnO:Ga Crystal. Superhard Mater. Eng. 2016, 28, 57–62. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Cheong, K.Y.; Muti, N.; Ramanan, S.R. Electrical and optical studies of ZnO:Ga thin films fabricated via the sol-gel technique. Thin Solid Films 2002, 410, 142–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, S.W.; Sim, K.U.; Moon, J.H.; Kim, J.H. The effect of processing parameters on properties of Ga-doped ZnO thin films by RF magnetron sputtering. Curr. Appl. Phys. 2010, 11, 274–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








| Depositing Methods | Vacuum Thermal Evaporation | Ion Plating Evaporation | Magnetron Sputtering | Chemical Vapor Deposition | Sol-Gel Method | Atomic Layer Deposition |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Materials | metals or low melting point materials | metals and dielectrics | metals and dielectrics | dielectric materials | materials with melting point above 500 °C | metals, dielectrics and polymer |
| Uniformity | poor | excellent | good | excellent | good | very good |
| Grain Size (nm) | 10–100 | 10–100 | –10 | 1–100 | 0.5–500 | <1 nm |
| Deposition Rate (nm/s) | 1.67–1167 | 1.67–833.5 | 0.167–8.335 | 1–10 | very slow | 0.1 |
| Deposition Quality | poor | excellent | good | excellent | poor | good |
| Porosity | high | no porosity, but many defects | lower, but more gaseous impurities | lower | higher | low |
| Substrate Temperature (°C) | 50–100 | 50–200 | –200 | 150–2000 | 300–800 | 50–500 |
| Adhesion | poor | excellent | good | good | good | good |
| Sputtering Power(W) | 100 | 120 | 140 | 160 | 180 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FWHM (°) | 0.41 | 0.37 | 0.35 | 0.42 | 0.47 |
| Grain size (nm) | 23.9 | 26.4 | 27.4 | 22.9 | 20 |
| Resistivity (× 10−4Ω·cm) | 8.0 | 4.52 | 3.0 | 4.42 | 6.8 |
| Mobility (cm2/V·s) | 6.82 | 7.85 | 8.32 | 6.77 | 5.98 |
| Carrier concentration (× 1021cm−3) | 1.16 | 1.78 | 2.53 | 2.12 | 1.56 |
| Optical band-gap (eV) | 3.595 | 3.65 | 3.76 | 3.71 | 3.62 |
| Substrate Temperature (°C) | 200 | 250 | 300 | 350 | 400 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FWHM (°) | 0.43 | 0.38 | 0.36 | 0.37 | 0.426 |
| Grain size (nm) | 22.6 | 25.5 | 27.0 | 26.1 | 22.8 |
| Resistivity (× 10−4Ω·cm) | 13.0 | 6.34 | 3.0 | 4.0 | 8.1 |
| Mobility (cm2/V·s) | 3.8 | 5.48 | 8.32 | 6.95 | 4.38 |
| Carrier concentration (× 1021/cm3) | 1.28 | 1.82 | 2.5 | 2.22 | 1.78 |
| Sputtering Pressure (Pa) | 0.5 | 0.7 | 1.0 | 1.5 | 2.0 | 2.5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FWHM (°) | 0.415 | 0.393 | 0.35 | 0.363 | 0.374 | 0.418 |
| Grain size (nm) | 23.4 | 24.7 | 27.4 | 26.7 | 25.9 | 23.2 |
| Resistivity (× 10−4Ω·cm) | 16.33 | 9.08 | 3.0 | 4.17 | 8.1 | 23.45 |
| Mobility (cm2/V·s) | 4.55 | 4.7 | 8.31 | 8.02 | 7.4 | 4.18 |
| Carrier concentration (× 1021 cm−3) | 0.85 | 1.46 | 2.5 | 1.875 | 1.06 | 0.28 |
| Oxygen Partial Pressure (Pa) | 0.2 | 0.25 | 0.3 | 0.35 | 0.4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FWHM (°) | 0.485 | 0.362 | 0.35 | 0.371 | 0.49 |
| Grain size (nm) | 17.23 | 22.32 | 27.42 | 22.45 | 17.03 |
| Resistivity (× 10−4Ω·cm) | 9.45 | 6.46 | 3.01 | 8.33 | 12.14 |
| Mobility (cm2/V·s) | 5.01 | 6.12 | 8.33 | 5.57 | 4.85 |
| Carrier concentration (× 1021 cm−3) | 1.32 | 1.59 | 2.5 | 1.36 | 1.06 |
| Annealing Temperature (°C) | 300 | 350 | 400 | 450 | 500 | 550 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Resistivity (× 10-4Ω·cm) | 2.94 | 2.88 | 2.85 | 2.6 | 2.8 | 4.39 |
| Mobility (cm2/V·s) | 8.98 | 9.73 | 10.56 | 11.83 | 13.28 | 14.77 |
| Carrier concentration (× 1021 cm−3) | 2.41 | 2.28 | 2.13 | 2.09 | 1.74 | 1.0 |
| Optical band-gap (eV) | 3.74 | 3.74 | 3.726 | 3.72 | 3.66 | 3.59 |
| Crystal Size | Measurement | Performances | Application | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. [133] | diameter: 50 mm thickness: 50 µm | time response to femtosecond laser | rise time: 104.9 ps FWHM: 153.5 ps decay time: 0.097 nm | fast time response in femtosecond level detection |
| 2. [134] | thickness: 300 µm | pulsed proton | well reflected intensity characteristics of pulsed proton source | as a recoil proton detector to detect pulsed neutron |
| 3. [135] | diameter: 50 mm thickness: 50 µm | the time response and energy response to the pulsed hard X-ray | FWHM: 440 ps rise time: 315 ps energy response above 40 KeV was very flat | a new type of hard X-ray energy spectrum measuring material |
| 4. [136] | Φ50 µm × 50 µm | time response to single α-particle | rise time: 342 ps FWHM: 686 ps | the monitoring of α-particles |
| 5. [137] | thickness: ~ µm | X-ray | fluorescence lifetime: 173 ps, FWHM: 355.1 ps light yield: 14,740 photons/MeV | Ultra-fast X-ray scintillating detector |
| Reference [140] | Reference [141] | |
|---|---|---|
| Crystal size | Φ40 mm × 1 mm | 32.36 mm × 27.46 mm × 5.52 mm |
| Measurement | the spatial distribution of cathode electron emission in intense current diode | crystal growth rate and crystal quality |
| Performances | 63.94 arcsec FWHM, fast response speed, 5.5% Bi4E3O12 (BGO) luminescence intensity, 8% luminous non-uniformity | excellent crystalline quality, 11arcsec FWHM of +c[002] crystal plane, the transmittance began to decrease at 750 nm, |
| Application | high time resolution diagnosis of pulsed radiation field | in the visible and infrared regions at wavelength greater than 750 nm |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wen, X.; Zhang, Q.; Shao, Z. Magnetron Sputtering for ZnO:Ga Scintillation Film Production and Its Application Research Status in Nuclear Detection. Crystals 2019, 9, 263. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst9050263
Wen X, Zhang Q, Shao Z. Magnetron Sputtering for ZnO:Ga Scintillation Film Production and Its Application Research Status in Nuclear Detection. Crystals. 2019; 9(5):263. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst9050263
Chicago/Turabian StyleWen, Xin, Qingmin Zhang, and Zhuang Shao. 2019. "Magnetron Sputtering for ZnO:Ga Scintillation Film Production and Its Application Research Status in Nuclear Detection" Crystals 9, no. 5: 263. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst9050263
APA StyleWen, X., Zhang, Q., & Shao, Z. (2019). Magnetron Sputtering for ZnO:Ga Scintillation Film Production and Its Application Research Status in Nuclear Detection. Crystals, 9(5), 263. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst9050263