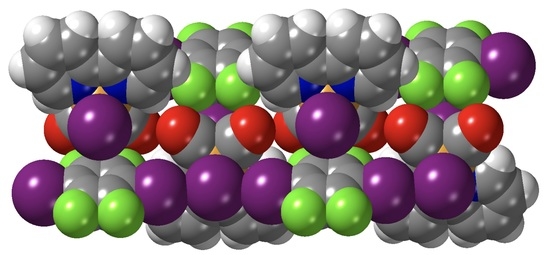
Extended Assemblies of Ru(bpy)(CO)2X2 (X = Cl, Br, I) Molecules Linked by 1,4-Diiodotetrafluoro-Benzene (DITFB) Halogen Bond Donors
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Syntheses of co-crystals 1–3
2.3. X-ray Structure Determination
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Strength of the Halogen Bonds
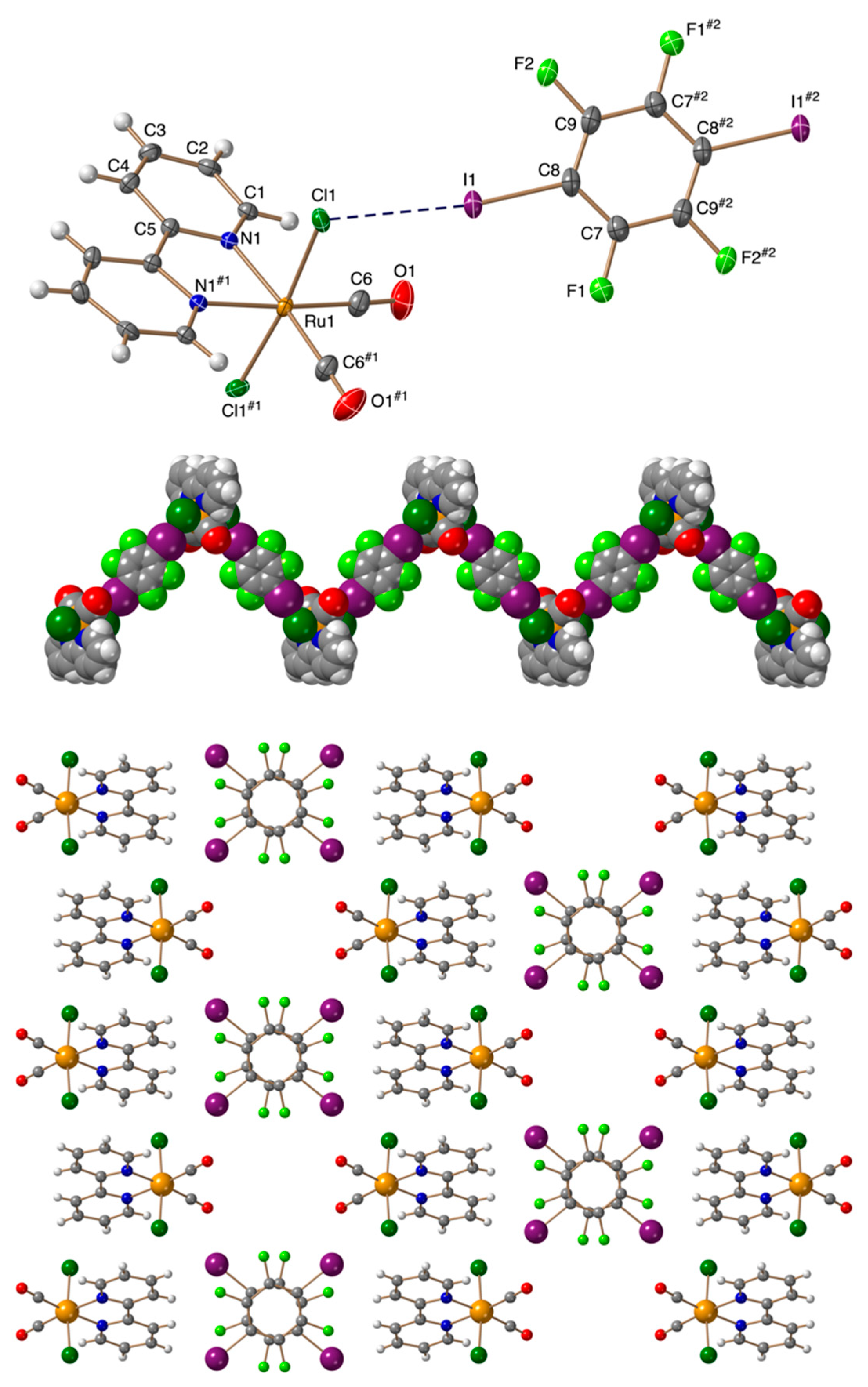
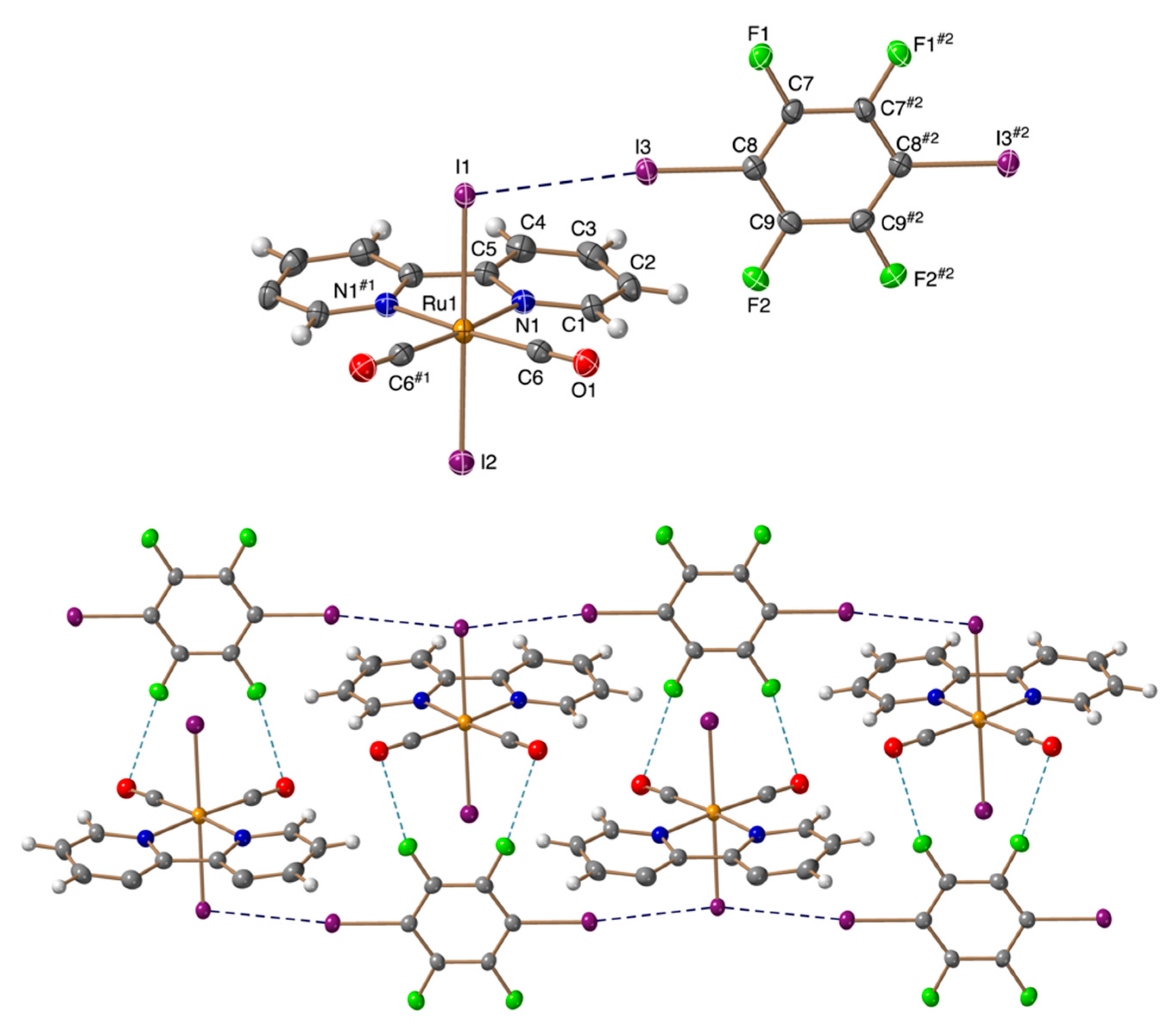
3.2. Crystal Structures
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Metrangolo, P.; Resnati, G.; Pilati, T.; Liantonio, R.; Meyer, F. Engineering functional materials by halogen bonding. J. Polym. Sci. Part A Polym. Chem. 2007, 45, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cinčić, D.; Friščić, T.; Jones, W. Isostructural Materials Achieved by Using Structurally Equivalent Donors and Acceptors in Halogen-Bonded Cocrystals. Chem. A Eur. J. 2008, 14, 747–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nemec, V.; Fotović, L.; Friščić, T.; Cinčić, D. A large family of halogen-bonded cocrystals involving metal-organic building blocks with open coordination sites. Cryst. Growth Des. 2017, 17, 6169–6173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ovens, J.S.; Geisheimer, A.R.; Bokov, A.A.; Ye, Z.G.; Leznoff, D.B. The Use of Polarizable [AuX2(CN)2]− (X = Br, I) Building Blocks Toward the Formation of Birefringent Coordination Polymers. Inorg. Chem. 2010, 49, 9609–9616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosokha, S.V.; Vinakos, M.K. Hybrid Network Formation via Halogen Bonding of the Neutral Bromo-Substituted Organic Molecules with Anionic Metal–Bromide Complexes. Cryst. Growth Des. 2012, 12, 4149–4156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertani, R.; Sgarbossa, P.; Venzo, A.; Lelj, F.; Amati, M.; Resnati, G.; Pilati, T.; Metrangolo, P.; Terraneo, G. Halogen bonding in metal-organic-supramolecular networks. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2010, 254, 677–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desiraju, G.R.; Ho, P.S.; Kloo, L.; Legon, A.C.; Marquardt, R.; Metrangolo, P.; Politzer, P.; Resnati, G.; Rissanen, K. Definition of the halogen bond (IUPAC Recommendations 2013). Pure Appl. Chem. 2013, 85, 1711–1713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, T.; Hennemann, M.; Murray, J.S.; Politzer, P. Halogen bonding: The σ-hole. J. Mol. Model. 2007, 13, 291–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Politzer, P.; Murray, J.S. σ-Holes and π-holes: Similarities and Differences. J. Comput. Chem. 2018, 39, 464–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Politzer, P.; Murray, J.; Clark, T.; Resnati, G. The σ-Hole revisited. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2017, 19, 32166–32178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esrafili, M.D.; Mousavian, P. The strengthening effect of a halogen, chalcogen or pnicogen bonding on halogen–π interaction: A comparative ab initio study. Mol. Phys. 2017, 116, 526–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavallo, G.; Metrangolo, P.; Milani, R.; Pilati, T.; Priimagi, A.; Resnati, G.; Terraneo, G. The Halogen Bond. Chem. Rev. 2016, 116, 2478–2601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cheng, N.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, C.; Liu, C. A theoretical study on the halogen bonding interactions of C6F5I with a series of group 10 metal monohalides. J. Mol. Model. 2013, 19, 3821–3829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, M.T.; Džolić, Z.; Cetina, M.; Wendt, O.F.; Öhrström, L.; Rissanen, K. Neutral Organometallic Halogen Bond Acceptors: Halogen Bonding in Complexes of PCPPdX (X = Cl, Br, I) with Iodine (I2), 1,4-Diiodotetrafluorobenzene (F4DIBz), and 1,4-Diiodooctafluorobutane (F8DIBu). Cryst. Growth Des. 2012, 12, 362–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsuzuki, S.; Wakisaka, A.; Ono, T.; Sonoda, T. Magnitude and origin of the attraction and directionality of the halogen bonds of the complexes of C6F5X and C6H5X (X = I, Br, Cl and F) with pyridine. Chem. Eur. J. 2012, 18, 951–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Politzer, P.; Murray, J.S.; Clark, T. Halogen bonding: An electrostatically-driven highly directional noncovalent interaction. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2010, 12, 7748–7757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Legon, A.C. The halogen bond: An interim perspective. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2010, 12, 7736–7747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Politzer, P.; Lane, P.; Concha, M.C.; Ma, Y.; Murray, J.S. An overview of halogen bonding. J. Mol. Model. 2007, 13, 305–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkorta, I.; Sanchez-Sanz, G.; Elguero, J.; Del Bene, J.E. FCl:PCX complexes: Old and new types of halogen bonds. J. Phys. Chem. A 2012, 116, 2300–2308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murray, J.S.; Macaveiu, L.; Politzer, P. Factors affecting the strengths of σ-hole electrostatic potentials. J. Comput. Sci. 2014, 5, 590–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zbačnik, M.; Pajski, M.; Stilinović, V.; Vitković, M.; Cinčić, D. The halogen bonding proclivity of the ortho-methoxy–hydroxy group in cocrystals of o-vanillin imines and diiodotetrafluoro-benzenes. CrystEngComm 2017, 19, 5576–5582. [Google Scholar]
- Jeske, J.; du Mont, W.-W.; Jones, P.G. Iodophosphane Selenides: Building Blocks for Supramolecular Soft ± Soft. Chem. Eur. J. 1999, 5, 385–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madzhidov, T.I.; Chmutova, G.A.; Martín Pendás, Á. The nature of the interaction of organoselenium molecules with diiodine. J. Phys. Chem. A 2011, 115, 10069–10077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Politzer, P.; Murray, J.S. Halogen bonding and beyond: Factors influencing the nature of CN-R and SiN-R complexes with F-Cl and Cl2. Theor. Chem. Acc. 2012, 131, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivanov, D.M.; Novikov, A.S.; Ananyev, I.V.; Kirina, Y.V.; Kukushkin, V.Y. Halogen bonding between metal centers and halocarbons. Chem. Commun. 2016, 52, 5565–5568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Groenewald, F.; Dillen, J.; Esterhuysen, C. Ligand-driven formation of halogen bonds involving Au(I) complexes. New J. Chem. 2018, 42, 10529–10538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novikov, A.S. Theoretical confirmation of existence of X···Au non-covalent contacts. Inorg. Chim. Acta 2018, 471, 126–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brammer, L.; Mínguez Espallargas, G.; Libri, S. Combining metals with halogen bonds. CrystEngComm 2008, 10, 1712–1727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sivchik, V.V.; Solomatina, A.I.; Chen, Y.T.; Karttunen, A.J.; Tunik, S.P.; Chou, P.T.; Koshevoy, I.O. Halogen Bonding to Amplify Luminescence: A Case Study Using a Platinum Cyclometalated Complex. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2015, 54, 14057–14060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuikka, M.; Niskanen, M.; Hirva, P.; Rissanen, K.; Valkonen, A.; Haukka, M. Concerted halogen and hydrogen bonding in [RuI2(H2dcbpy)(CO)2]···I2···(CH3OH)···I2···[RuI2(H2dcbpy)(CO)2]. ChemComm 2011, 47, 3427–3429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, X.; Tuikka, M.J.; Hirva, P.; Kukushkin, V.Y.; Novikov, A.S.; Haukka, M. Fine-tuning halogen bonding properties of diiodine through halogen–halogen charge transfer—Extended [Ru(2,2′-bipyridine)(CO)2X2]·I2 systems (X = Cl, Br, I). CrystEngComm 2016, 18, 1987–1995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, X.; Tuikka, M.; Hirva, P.; Haukka, M. Halogen bond preferences of thiocyanate ligand coordinated to Ru(II)via sulphur atom. Solid State Sci. 2017, 71, 8–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lisac, K.; Cinčić, D. Simple design for metal-based halogen-bonded cocrystals utilizing the M–Cl⋯I motif. CrystEngComm 2018, 20, 5955–5963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kia, R.; Mahmoudi, S.; Raithby, P.R. New rhenium-tricarbonyl complexes bearinghalogen-substituted bidentate ligands: Structural, computational and Hirshfeld surfaces studies. CrystEngComm 2019, 21, 77–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torubaev, Y.V.; Skabitskiy, I.V.; Rusina, P.; Pasynskii, A.A.; Raic, D.K.; Singhd, A. Organometallic halogen bond acceptors: Directionality, hybrid cocrystal precipitation, and blueshifted CO ligand vibrational band. CrystEngComm 2018, 20, 2258–2266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheiner, S. On the capability of metal–halogen groups to participate in halogen bonds. CrystEngComm 2019, 21, 2875–2883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mills, A.M.; Van Beek, J.A.M.; Van Koten, G.; Spek, A.L. {2, 6-bis[(dimethylamino-κN)methyl]phenyl-κc}iodopalladium(ii) bis(diiodine). Acta Cryst. Sect. C Cryst. Struct. Commun. 2002, 58, m304–m306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slugovc, C.; Kirchner, K.; Mereiter, K. (Hydridotripyrazolylborato)iodo{(1,2,5,6-η)-1-[(Z)-1-iodo-2-phenylethenyl]cycloocta-1,5-diene} ruthenium(II)–diiodine (2/1). Acta Cryst. Sect. E Struct. Rep. Online 2005, E61, m1646–m1648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmer, S.M.; Stanton, J.L.; Jaggi, N.K.; Hoffman, B.M.; Ibers, J.A.; Schwartz, L.H. Preparation, Structures, and Physical Properties of Two Products from the Iodination of (Phthalocyaninato)iron(II). Inorg. Chem. 1985, 24, 2040–2046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enders, M.; Ludwig, G.; Pritzkow, H. Nitrogen-functionalized cyclopentadienyl ligands with a rigid framework: Complexation behavior and properties of Cobalt(I), -(II), and -(III) half-sandwich complexes. Organometallics 2001, 20, 827–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.-B.; Wang, R.-Y.; Wang, S. Reactivity of SiMe3-and SnR3-Functionalized Bis (7-azaindol-1-yl) methane with [PtR2(µ-SMe2)]n (R)=Me, Ph) and the Resulting Pt(II) and Pt(IV) Complexes. Organometallics 2009, 28, 2572–2582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buse, K.D.; Keller, H.J.; Pritzkow, H. Reaction of Molecular Iodine with cis-Dihalo (2,2′-bipyridyl) platinum(II) and cis-Dihalo (1,lQ-phenanthroline) platinum(II). Oxidative Addition and Inclusion Compounds. Inorg. Chem. 1977, 16, 1072–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fanizzi, F.P.; Natile, G.; Lanfranchi, M.; Tiripicchio, A.; Laschi, F.; Zanello, P. Steric Crowding and Redox Reactivity in Platinum(II) and Platinum(IV) Complexes Containing Substituted 1,10-Phenanthrolines. Inorg. Chem. 1996, 35, 3173–3182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safa, M.; Puddephatt, R.J. Organoplatinum complexes with an ester substituted bipyridine ligand: Oxidative addition and supramolecular chemistry. J. Organomet. Chem. 2013, 724, 7–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosquera, M.E.G.; Egido, I.; Hortelano, C.; López-López, M.; Gómez-Sal, P. Comparison of Halogen Bonding networks with Ru(II) complexes and analysis of the influence of the XB interaction on their reactivity. Faraday Discuss. 2017, 203, 257–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hewison, L.; Crook, S.H.; Mann, B.E.; Meijer, A.J.H.M.; Adams, H.; Sawle, P.; Motterlini, R.A. New types of CO-releasing molecules (CO-RMs), based on iron dithiocarbamate complexes and [Fe(CO)3I(S2COEt)]. Organometallics 2012, 31, 5823–5834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosquera, M.E.G.; Gomez-Sal, P.; Diaz, I.; Aguirre, L.M.; Ienco, A.; Manca, G.; Mealli, C. Intriguing I2 Reduction in the Iodide for Chloride Ligand Substitution at a Ru(II) Complex: Role of Mixed Trihalides in the Redox Mechanism. Inorg. Chem. 2016, 55, 283–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coronado, E.; Day, P. Magnetic Molecular Conductors. Chem. Rev. 2004, 104, 5419–5448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haukka, M.; Kiviaho, J.; Ahlgrén, M.; Pakkanen, T.A. Studies on Catalytically Active Ruthenium Carbonyl Bipyridine Systems. Synthesis and Structural Characterization of [Ru(bpy)(CO)2Cl2], [Ru(bpy)(CO)2Cl(C(O)OCH3)], [Ru(bpy)(CO)2Cl]2, and [Ru(bpy)(CO)2ClH] (bpy = 2,2′-Bipyridine). Organometallics 1995, 14, 825–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haukka, M.; Ahlgrén, M.; Pakkanen, T.A. Reactions of [Ru(bipy)(CO)2Cl2] in aqueous HX and HX–HNO3 solutions (X = F, Br or I; bipy = 2,2′-bipyridine). J. Chem. Soc. Dalton Trans. 1996, 1927–1933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rikagu Oxford Diffraction. CrysAlisPro V. 1.171.37.35; Rikagu Oxford Diffraction: Yarnton, Oxfordshire, UK, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Bruker AXS. APEX2-Software Suite for Crystallographic Programs; Bruker AXS, Inc.: Madison, WI, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Palatinus, L.; Chapuis, G. Superflip—A computer program for the solution of crystal structures by charge flipping in arbitrary dimensions. J. Appl. Cryst. 2007, 40, 786–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheldrick, G.M. Crystal structure refinement with SHELXL. Acta Cryst. 2015, C71, 3–8. [Google Scholar]
- Spek, A.L. Structure validation in chemical crystallography. Acta Cryst. 2009, D65, 148–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lommerse, P.M.; Stone, A.J.; Taylor, R.; Allen, F.H. The nature and geometry of intermolecular interactions between halogens and oxygen or nitrogen. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1996, 118, 3108–3116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brammer, L.; Bruton, E.A.; Sherwood, P. Understanding the Behavior of Halogens as Hydrogen Bond Acceptors. Cryst. Growth Des. 2001, 1, 277–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zordan, F.; Brammer, L.; Sherwood, P. Supramolecular Chemistry of Halogens: Complementary Features of Inorganic (M−X) and Organic (C−X′) Halogens Applied to M−X···X′−C Halogen Bond Formation. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2005, 127, 5979–5989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bondi, A. van der Waals Volumes and Radii. J. Phys. Chem. 1964, 68, 441–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, B.N.; Lahtinen, M.; Kalenius, E.; Mal, P.; Rissanen, K. 2,2′:6′,2″-Terpyridine trimethylplatinum(IV) iodide complexes as bifunctional halogen bond acceptors. Cryst. Growth Des. 2016, 16, 2527–2534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| 1 | 2 | 3 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Formulas | C18H8Cl2F4I2N2O2Ru [+ solvent] [+ solvent] | C18H8Br2F4I2N2O2Ru [+ solvent] | C18H8F4I4N2O2Ru |
| Fw | 786.03 * | 874.95 * | 968.93 |
| temp (K) | 120(2) | 120(2) | 120(2) |
| λ(Å) | 0.71073 | 0.71073 | 0.71073 |
| Crystal system | Monoclinic | Monoclinic | Orthorhombic |
| space group | C2/c | C2/c | Pnma |
| a (Å) | 11.9736(7) | 12.2824(4) | 8.3320(3) |
| b (Å) | 29.8725(13) | 30.3634(11) | 14.0070(5) |
| c (Å) | 6.7654(3) | 6.8630(2) | 20.6378(7) |
| β (°) | 96.925(5) | 100.444(2) | 90 |
| V (Å3) | 2402.2(2) | 2517.05(14) | 2408.56(15) |
| Z | 4 | 4 | 4 |
| ρcalc (Mg/m3) | 2.173 | 2.309 | 2.672 |
| μ(Kα) (mm−1) | 3.493 | 6.297 | 5.826 |
| No. reflns. | 18821 | 12583 | 26750 |
| θ Range (°) | 3.326–32.783 | 2.626–29.145 | 2.636–29.258 |
| Unique reflns. | 4175 | 3387 | 3384 |
| GOOF (F2) | 1.064 | 1.147 | 1.152 |
| Rint | 0.0498 | 0.0292 | 0.0505 |
| R1 a (I ≥ 2σ) | 0.0359 | 0.0281 | 0.0360 |
| wR2 b (I ≥ 2σ) | 0.0761 | 0.0586 | 0.0795 |
| Compound | Ru-X⋅⋅⋅I (Å) | C-I⋅⋅⋅X (°) | M-X⋅⋅⋅I (°) | RXB |
| 1 | 3.1790(8) | 170.60(9) | 114.94(3) | 0.85 |
| 2 | 3.3191(4) | 171.34(10) | 112.108(14) | 0.87 |
| 3 | 3.5301(3) | 177.66(13) | 96.672(9) | 0.89 |
| Ref. [31] | Ru-X⋅⋅⋅I (Å) | I-I⋅⋅⋅X (°) | M-X⋅⋅⋅I (°) | RXB |
| Cl⋅⋅⋅I2 | 3.0421(3) | 174.566(8) | 115.76(1) | 0.82 |
| Br⋅⋅⋅I2 | 3.2938(4) | 170.28(1) | 101.3(1) | 0.86 |
| Br⋅⋅⋅I2 | 3.3627(3) | 173.80(1) | 102.27(1) | 0.88 |
| Br⋅⋅⋅I2 | 3.2381(3) | 175.405(9) | 101.66(1) | 0.85 |
| Br⋅⋅⋅I2 | 3.3001(3) | 174.164(9) | 102.57(1) | 0.86 |
| I⋅⋅⋅I2 | 3.1984(2) | 177.941(7) | 97.91(1) | 0.81 |
| I⋅⋅⋅I2 | 3.7984(3) | 152.083(6) | 104.26(1) | 0.96 |
| I⋅⋅⋅I2 | 3.2553(13) | 172.75(2) | 97.81(2) | 0.82 |
| I⋅⋅⋅I2 | 3.4108(15) | 166.50(2) | 98.90(2) | 0.86 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ding, X.; Tuikka, M.; Rissanen, K.; Haukka, M. Extended Assemblies of Ru(bpy)(CO)2X2 (X = Cl, Br, I) Molecules Linked by 1,4-Diiodotetrafluoro-Benzene (DITFB) Halogen Bond Donors. Crystals 2019, 9, 319. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst9060319
Ding X, Tuikka M, Rissanen K, Haukka M. Extended Assemblies of Ru(bpy)(CO)2X2 (X = Cl, Br, I) Molecules Linked by 1,4-Diiodotetrafluoro-Benzene (DITFB) Halogen Bond Donors. Crystals. 2019; 9(6):319. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst9060319
Chicago/Turabian StyleDing, Xin, Matti Tuikka, Kari Rissanen, and Matti Haukka. 2019. "Extended Assemblies of Ru(bpy)(CO)2X2 (X = Cl, Br, I) Molecules Linked by 1,4-Diiodotetrafluoro-Benzene (DITFB) Halogen Bond Donors" Crystals 9, no. 6: 319. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst9060319
APA StyleDing, X., Tuikka, M., Rissanen, K., & Haukka, M. (2019). Extended Assemblies of Ru(bpy)(CO)2X2 (X = Cl, Br, I) Molecules Linked by 1,4-Diiodotetrafluoro-Benzene (DITFB) Halogen Bond Donors. Crystals, 9(6), 319. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst9060319