Generating a High Valency Biotin Binder by Selecting Uniform Protein Assemblies via Crystallization
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Identification, Expression and Purification of P61C Hoefavidin
2.2. Crystallization, Data Collection and Structure Solution
2.3. Size Exclusion Chromatography and Anion Exchange
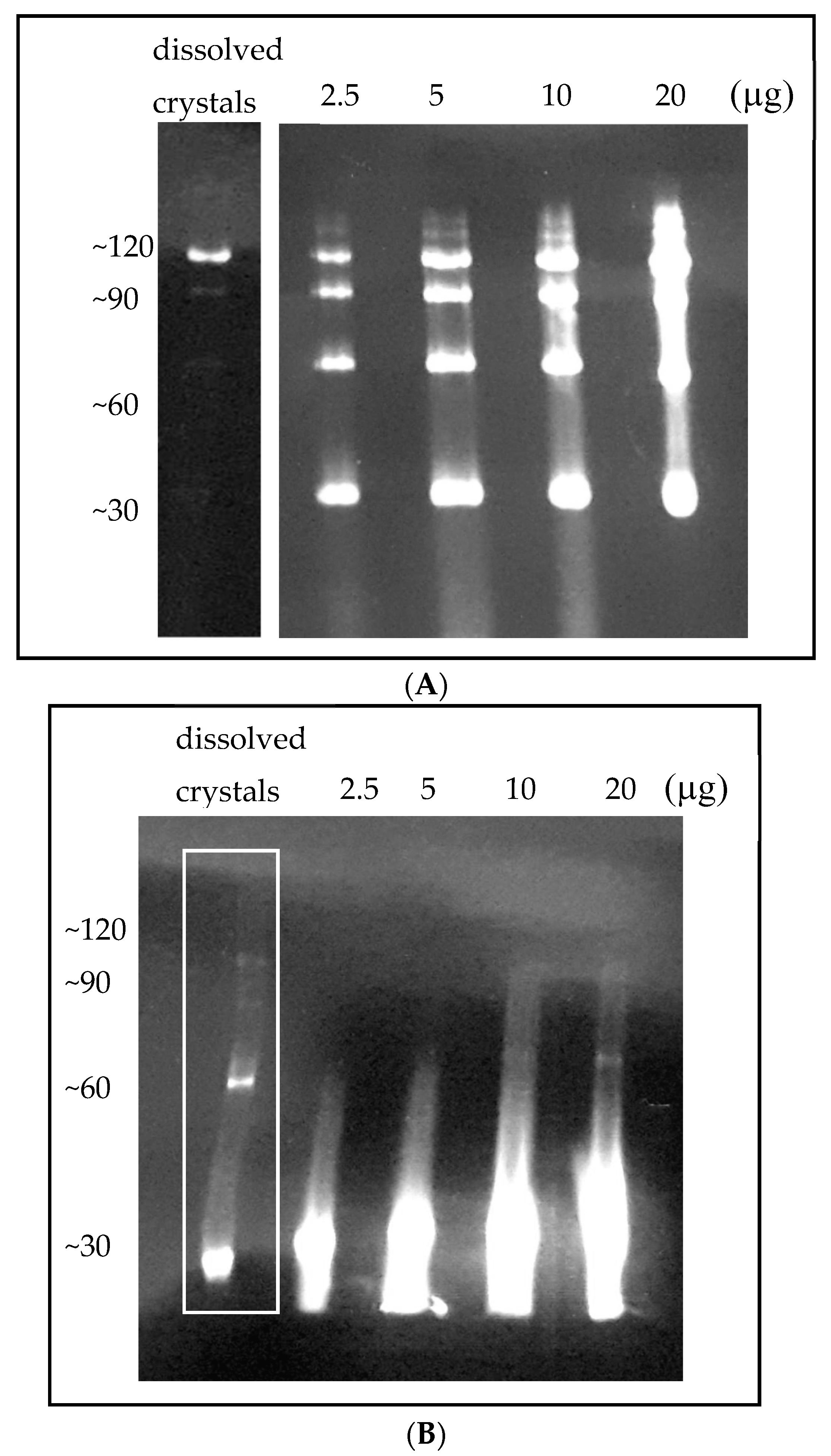
2.4. Analysis of Dissolved Crystals
2.5. Thermostability and Affinity Measurements
2.6. TEM Analysis of P61C Hoefavidin
3. Results
3.1. Generating the Covalently Linked Octamer
3.2. Structure and Assembly of the P61C Hoefavidin
3.3. Obtaining a Homogeneous Octameric Sample
3.4. Thermostability Properties and Affinity Towards 2-Iminobiotin
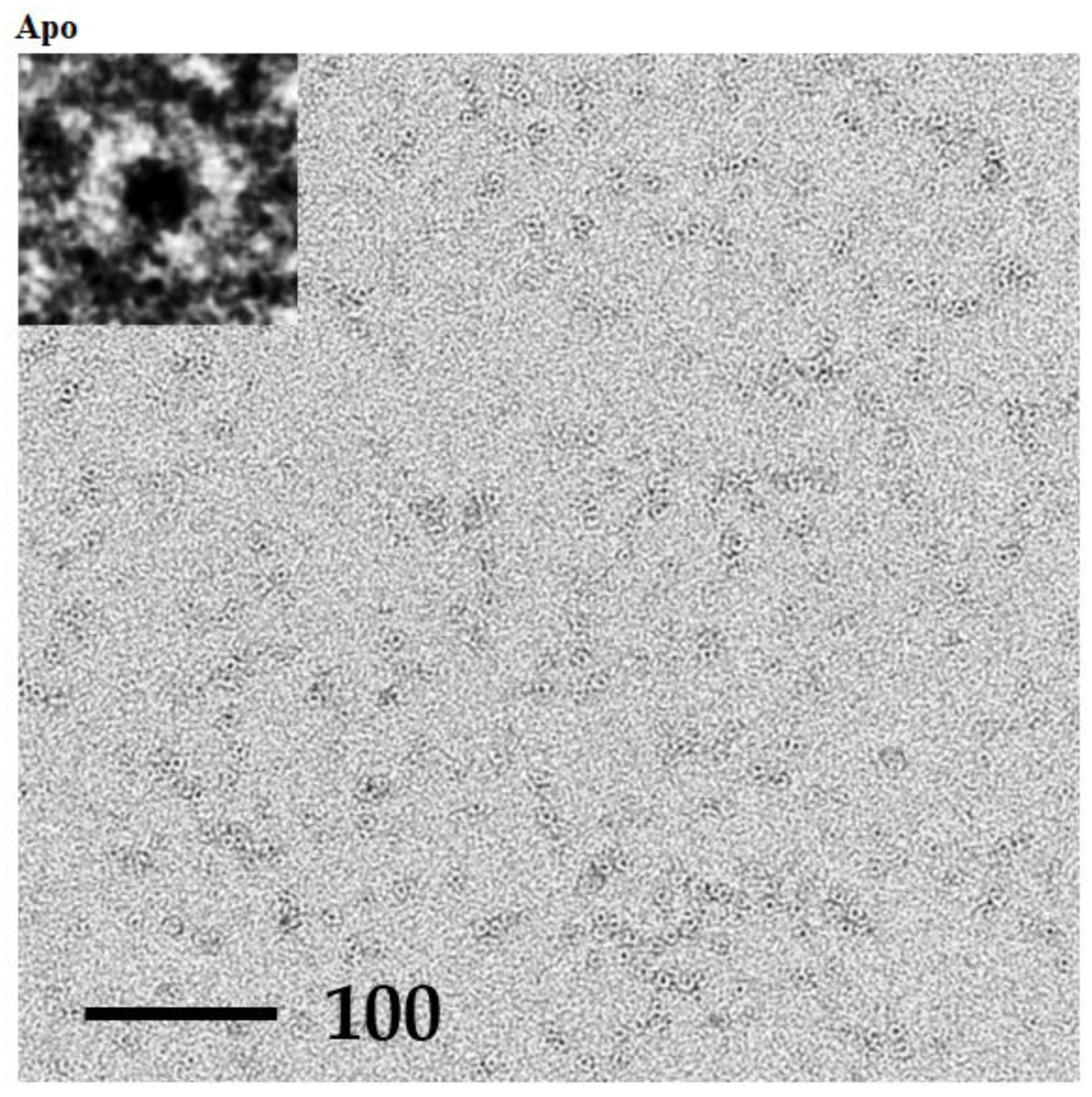
3.5. TEM Analysis of P61C Hoefavidin
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lesch, H.P.; Kaikkonen, M.U.; Pikkarainen, J.T.; Yla-Herttuala, S. Avidin-biotin technology in targeted therapy. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2010, 7, 551–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laitinen, O.H.; Nordlund, H.R.; Hytonen, V.P.; Kulomaa, M.S. Brave new (strept)avidins in biotechnology. Trends Biotechnol. 2007, 25, 269–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yeates, T.O. Geometric Principles for Designing Highly Symmetric Self-Assembling Protein Nanomaterials. Annu. Rev. Biophys. 2017, 46, 23–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Green, N.M. Avidin. Adv. Protein Chem. 1975, 29, 85–133. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Green, N.M. Avidin and streptavidin. Methods Enzymol. 1990, 184, 51–67. [Google Scholar]
- Chaiet, L.; Wolf, F.J. The Properties of Streptavidin, a Biotin-Binding Protein Produced by Streptomycetes. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 1964, 106, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takakura, Y.; Tsunashima, M.; Suzuki, J.; Usami, S.; Kakuta, Y.; Okino, N.; Ito, M.; Yamamoto, T. Tamavidins—Novel avidin-like biotin-binding proteins from the Tamogitake mushroom. FEBS J. 2009, 276, 1383–1397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maatta, J.A.; Helppolainen, S.H.; Hytonen, V.P.; Johnson, M.S.; Kulomaa, M.S.; Airenne, T.T.; Nordlund, H.R. Structural and functional characteristics of xenavidin, the first frog avidin from Xenopus tropicalis. BMC Struct. Biol. 2009, 9, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taskinen, B.; Zmurko, J.; Ojanen, M.; Kukkurainen, S.; Parthiban, M.; Maatta, J.A.; Leppiniemi, J.; Janis, J.; Parikka, M.; Turpeinen, H.; et al. Zebavidin—An avidin-like protein from zebrafish. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e77207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahlroth, M.K.; Kola, E.H.; Ewald, D.; Masabanda, J.; Sazanov, A.; Fries, R.; Kulomaa, M.S. Characterization and chromosomal localization of the chicken avidin gene family. Anim. Genet. 2000, 31, 367–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laitinen, O.H.; Hytonen, V.P.; Ahlroth, M.K.; Pentikainen, O.T.; Gallagher, C.; Nordlund, H.R.; Ovod, V.; Marttila, A.T.; Porkka, E.; Heino, S.; et al. Chicken avidin-related proteins show altered biotin-binding and physico-chemical properties as compared with avidin. Biochem. J. 2002, 363, 609–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sardo, A.; Wohlschlager, T.; Lo, C.; Zoller, H.; Ward, T.R.; Creus, M. Burkavidin: A novel secreted biotin-binding protein from the human pathogen Burkholderia pseudomallei. Protein Expr. Purif. 2011, 77, 131–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Green, N.M.; Joynson, M.A. A preliminary crystallographic investigation of avidin. Biochem. J. 1970, 118, 71–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hendrickson, W.A.; Pahler, A.; Smith, J.L.; Satow, Y.; Merritt, E.A.; Phizackerley, R.P. Crystal structure of core streptavidin determined from multiwavelength anomalous diffraction of synchrotron radiation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1989, 86, 2190–2194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Livnah, O.; Bayer, E.A.; Wilchek, M.; Sussman, J.L. Three-dimensional structures of avidin and the avidin-biotin complex. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1993, 90, 5076–5080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meir, A.; Helppolainen, S.H.; Podoly, E.; Nordlund, H.R.; Hytonen, V.P.; Maatta, J.A.; Wilchek, M.; Bayer, E.A.; Kulomaa, M.S.; Livnah, O. Crystal structure of rhizavidin: Insights into the enigmatic high-affinity interaction of an innate biotin-binding protein dimer. J. Mol. Biol. 2009, 386, 379–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laitinen, O.H.; Hytonen, V.P.; Nordlund, H.R.; Kulomaa, M.S. Genetically engineered avidins and streptavidins. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2006, 63, 2992–3017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Howarth, M.; Chinnapen, D.J.; Gerrow, K.; Dorrestein, P.C.; Grandy, M.R.; Kelleher, N.L.; El-Husseini, A.; Ting, A.Y. A monovalent streptavidin with a single femtomolar biotin binding site. Nat. Methods 2006, 3, 267–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hytonen, V.P.; Nordlund, H.R.; Horha, J.; Nyholm, T.K.; Hyre, D.E.; Kulomaa, T.; Porkka, E.J.; Marttila, A.T.; Stayton, P.S.; Laitinen, O.H.; et al. Dual-affinity avidin molecules. Proteins 2005, 61, 597–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nordlund, H.R.; Hytonen, V.P.; Horha, J.; Maatta, J.A.; White, D.J.; Halling, K.; Porkka, E.J.; Slotte, J.P.; Laitinen, O.H.; Kulomaa, M.S. Tetravalent single-chain avidin: From subunits to protein domains via circularly permuted avidins. Biochem. J. 2005, 392, 485–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, K.H.; Huang, H.; Pralle, A.; Park, S. Stable, high-affinity streptavidin monomer for protein labeling and monovalent biotin detection. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2013, 110, 57–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Demonte, D.; Drake, E.J.; Lim, K.H.; Gulick, A.M.; Park, S. Structure-based engineering of streptavidin monomer with a reduced biotin dissociation rate. Proteins 2013, 81, 1621–1633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goodsell, D.S.; Olson, A.J. Structural symmetry and protein function. Annu. Rev. Biophys. Biomol. Struct. 2000, 29, 105–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Avraham, O.; Meir, A.; Fish, A.; Bayer, E.A.; Livnah, O. Hoefavidin: A dimeric bacterial avidin with a C-terminal binding tail. J. Struct. Biol. 2015, 191, 139–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meir, A.; Bayer, E.A.; Livnah, O. Structural adaptation of a thermostable biotin-binding protein in a psychrophilic environment. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 17951–17962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Avraham, O.; Bayer, E.A.; Livnah, O. Crystal structure of afifavidin reveals common features of molecular assemblage in the bacterial dimeric avidins. FEBS J. 2018, 285, 4617–4630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Helppolainen, S.H.; Nurminen, K.P.; Maatta, J.A.; Halling, K.K.; Slotte, J.P.; Huhtala, T.; Liimatainen, T.; Yla-Herttuala, S.; Airenne, K.J.; Narvanen, A.; et al. Rhizavidin from Rhizobium etli: The first natural dimer in the avidin protein family. Biochem. J. 2007, 405, 397–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meir, A.; Livnah, O. Challenging semi-bootstrapping molecular-replacement strategy reveals intriguing crystal packing of rhizavidin. Acta Cryst. Sect. F Struct. Biol. Cryst. Commun. 2010, F66, 373–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Humbert, N.; Zocchi, A.; Ward, T.R. Electrophoretic behavior of streptavidin complexed to a biotinylated probe: A functional screening assay for biotin-binding proteins. Electrophoresis 2005, 26, 47–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kada, G.; Falk, H.; Gruber, H.J. Accurate measurement of avidin and streptavidin in crude biofluids with a new, optimized biotin-fluorescein conjugate. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1999, 1427, 33–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hofmann, K.; Wood, S.W.; Brinton, C.C.; Montibeller, J.A.; Finn, F.M. Iminobiotin affinity columns and their application to retrieval of streptavidin. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1980, 77, 4666–4668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bergfors, T. Seeds to crystals. J. Struct. Biol. 2003, 142, 66–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stura, E.A.; Wilson, I.A. Applications of the Streak Seeding Technique in Protein Crystallization. J. Cryst. Growth 1991, 110, 270–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Incardona, M.F.; Bourenkov, G.P.; Levik, K.; Pieritz, R.A.; Popov, A.N.; Svensson, O. EDNA: A framework for plugin-based applications applied to X-ray experiment online data analysis. J. Synchrotron Radiat. 2009, 16, 872–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vagin, A.; Teplyakov, A. Molecular replacement with MOLREP. Acta Cryst. Sect. D Biol. Cryst. 2010, 66, 22–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Winn, M.D.; Ballard, C.C.; Cowtan, K.D.; Dodson, E.J.; Emsley, P.; Evans, P.R.; Keegan, R.M.; Krissinel, E.B.; Leslie, A.G.; McCoy, A.; et al. Overview of the CCP4 suite and current developments. Acta Cryst. Sect. D Biol. Cryst. 2011, 67, 235–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vagin, A.A.; Steiner, R.A.; Lebedev, A.A.; Potterton, L.; McNicholas, S.; Long, F.; Murshudov, G.N. REFMAC5 dictionary: Organization of prior chemical knowledge and guidelines for its use. Acta Cryst. Sect. D Biol. Cryst. 2004, 60, 2184–2195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Emsley, P.; Lohkamp, B.; Scott, W.G.; Cowtan, K. Features and development of Coot. Acta Cryst. Sect. D Biol. Cryst. 2010, 66, 486–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richardson, J.S. The anatomy and taxonomy of protein structure. Adv. Protein Chem. 1981, 34, 167–339. [Google Scholar]
- Amartely, H.; Avraham, O.; Friedler, A.; Livnah, O.; Lebendiker, M. Coupling Multi Angle Light Scattering to Ion Exchange chromatography (IEX-MALS) for protein characterization. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 6907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, C.H.; Lai, Y.H.; Chen, Y.W.; Yao, C.H.; Chen, K.Y. Immobilization of bone morphogenetic protein-2 to gelatin/avidin-modified hydroxyapatite composite scaffolds for bone regeneration. J. Biomater. Appl. 2019, 33, 1147–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Q.; Dunbrack, R.L.J. Principles and characteristics of biological assemblies in experimentally determined protein structures. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 2019, 55, 34–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giffard, M.; Ferte, N.; Ragot, F.; El Hajji, M.; Castro, B.; Bonnete, F. Urate oxidase purification by salting-in crystallization: Towards an alternative to chromatography. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e19013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hekmat, D. Large-scale crystallization of proteins for purification and formulation. Bioprocess Biosyst. Eng. 2015, 38, 1209–1231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]






| PDB Entry | 6RTQ |
|---|---|
| ESRF Beamline | D23-1 |
| Wavelength (Å) | 0.978 |
| Space Group | P 62 22 |
| Unit Cell Parameters (Å) | a = 81.4, c = 130.4 |
| Resolution Range (Å) | 43.48–2.00 |
| (Outer shell) | (2.05–2.00) |
| Mosaicity (°) | 0.23 |
| Unique Reflections | 18,089 (1313) |
| Redundancy | 6.1 |
| Rsym(I) a | 4.0 (78.4) |
| Rmeas | 4.4 (89.6) |
| Rpim | 2.4 (61.9) |
| Completeness | 99.7 (99.1) |
| I/σ | 17.8 (1.6) |
| CC (1/2) | 99.9 (62.8) |
| Number of protein atoms | 1996 |
| Number of solvent atoms | 77 |
| R-factor | 22.7 (39.4) |
| R-free b | 28.3 (38.0) |
| Average B factor (Å2) | |
| Protein | 62.2 |
| Solvent | 59.7 |
| rmsd from ideality | |
| Bond Length | 0.014 |
| Bond Angle | 2.1 |
| Ramachandran plot (Ramapage) | |
| Favored | 93.9% |
| Generously Allowed | 6.1% |
| Disallowed | 0.0% |
| Protein | Tm apo (°C) | Tm Biotin Complex (°C) | Affinity towards 2-Iminobiotin (*10−7 M) |
|---|---|---|---|
| P61C hoefavidin | 69.1 ± 0.06, 80.9 ± 0.05 | 88.8 ± 0.78 | 22 ± 5.9 |
| P61C hoefavidin dissolved crystals | 81.5 ± 0.08 | 89.5 ± 0.10 | -- |
| WT Intact hoefavidin | 73.0 ± 0.16, 81.9 ± 0.06 | >95 | 2.0 [24] |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Avraham, O.; Levi-Kalisman, Y.; Livnah, O. Generating a High Valency Biotin Binder by Selecting Uniform Protein Assemblies via Crystallization. Crystals 2019, 9, 353. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst9070353
Avraham O, Levi-Kalisman Y, Livnah O. Generating a High Valency Biotin Binder by Selecting Uniform Protein Assemblies via Crystallization. Crystals. 2019; 9(7):353. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst9070353
Chicago/Turabian StyleAvraham, Orly, Yael Levi-Kalisman, and Oded Livnah. 2019. "Generating a High Valency Biotin Binder by Selecting Uniform Protein Assemblies via Crystallization" Crystals 9, no. 7: 353. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst9070353
APA StyleAvraham, O., Levi-Kalisman, Y., & Livnah, O. (2019). Generating a High Valency Biotin Binder by Selecting Uniform Protein Assemblies via Crystallization. Crystals, 9(7), 353. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst9070353





